|
1
|
Hargreaves M and Spriet LL: Skeletal
muscle energy metabolism during exercise. Nat Metab. 2:817–828.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thyfault JP and Bergouignan A: Exercise
and metabolic health: Beyond skeletal muscle. Diabetologia.
63:1464–1474. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Newman AB, Kupelian V, Visser M, Simonsick
EM, Goodpaster BH, Kritchevsky SB, Tylavsky FA, Rubin SM and Harris
TB: Strength, but not muscle mass, is associated with mortality in
the health, aging and body composition study cohort. J Gerontol A
Biol Sci Med Sci. 61:72–77. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Landi F, Liperoti R, Russo A, Giovannini
S, Tosato M, Capoluongo E, Bernabei R and Onder G: Sarcopenia as a
risk factor for falls in elderly individuals: Results from the
ilSIRENTE study. Clin Nutr. 31:652–658. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peng P, Hyder O, Firoozmand A, Kneuertz P,
Schulick RD, Huang D, Makary M, Hirose K, Edil B, Choti MA, et al:
Impact of sarcopenia on outcomes following resection of pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 16:1478–1486. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
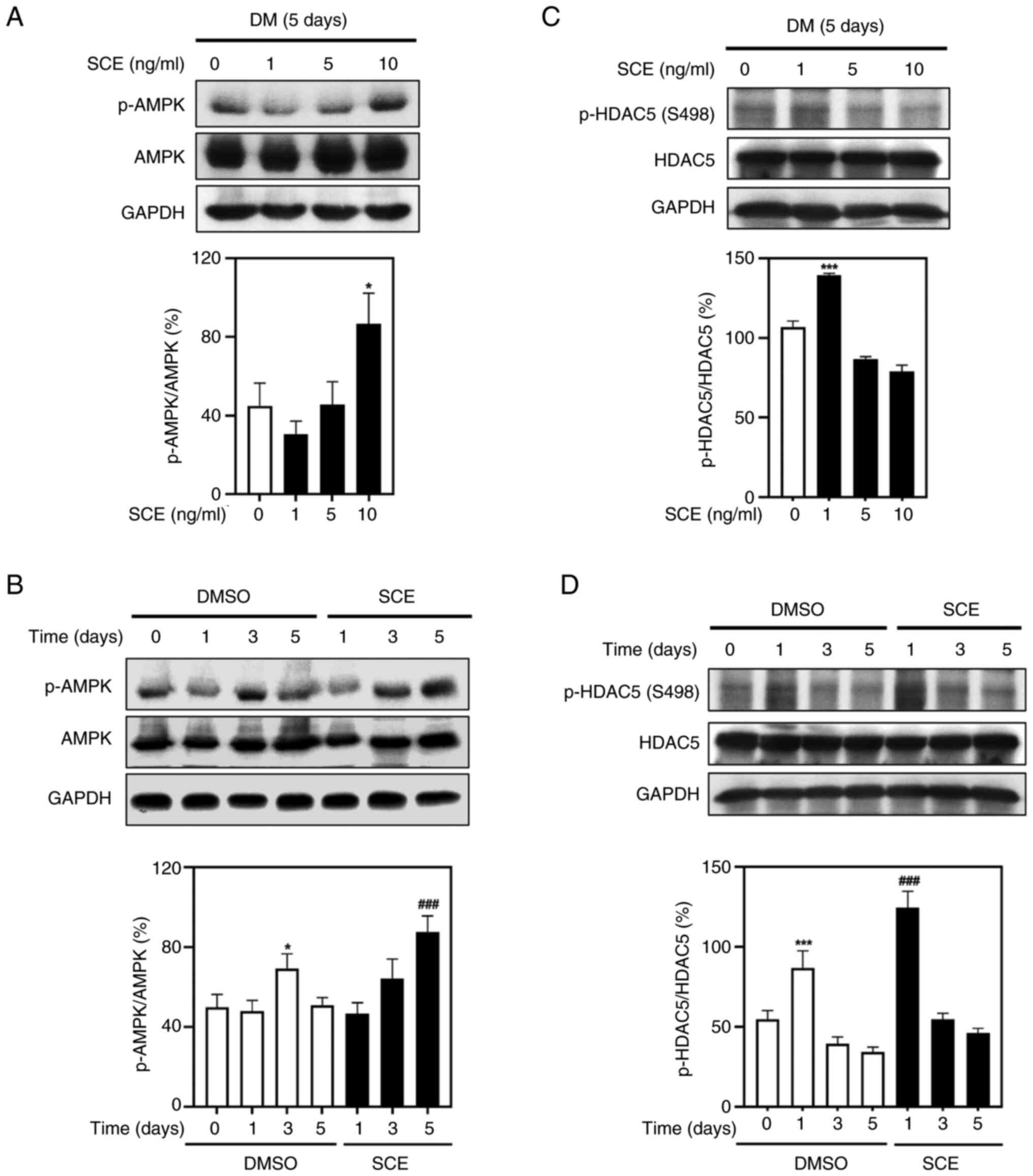
6
|
Fielding RA, Vellas B, Evans WJ, Bhasin S,
Morley JE, Newman AB, Abellan van Kan G, Andrieu S, Bauer J,
Breuille D, et al: Sarcopenia: An undiagnosed condition in older
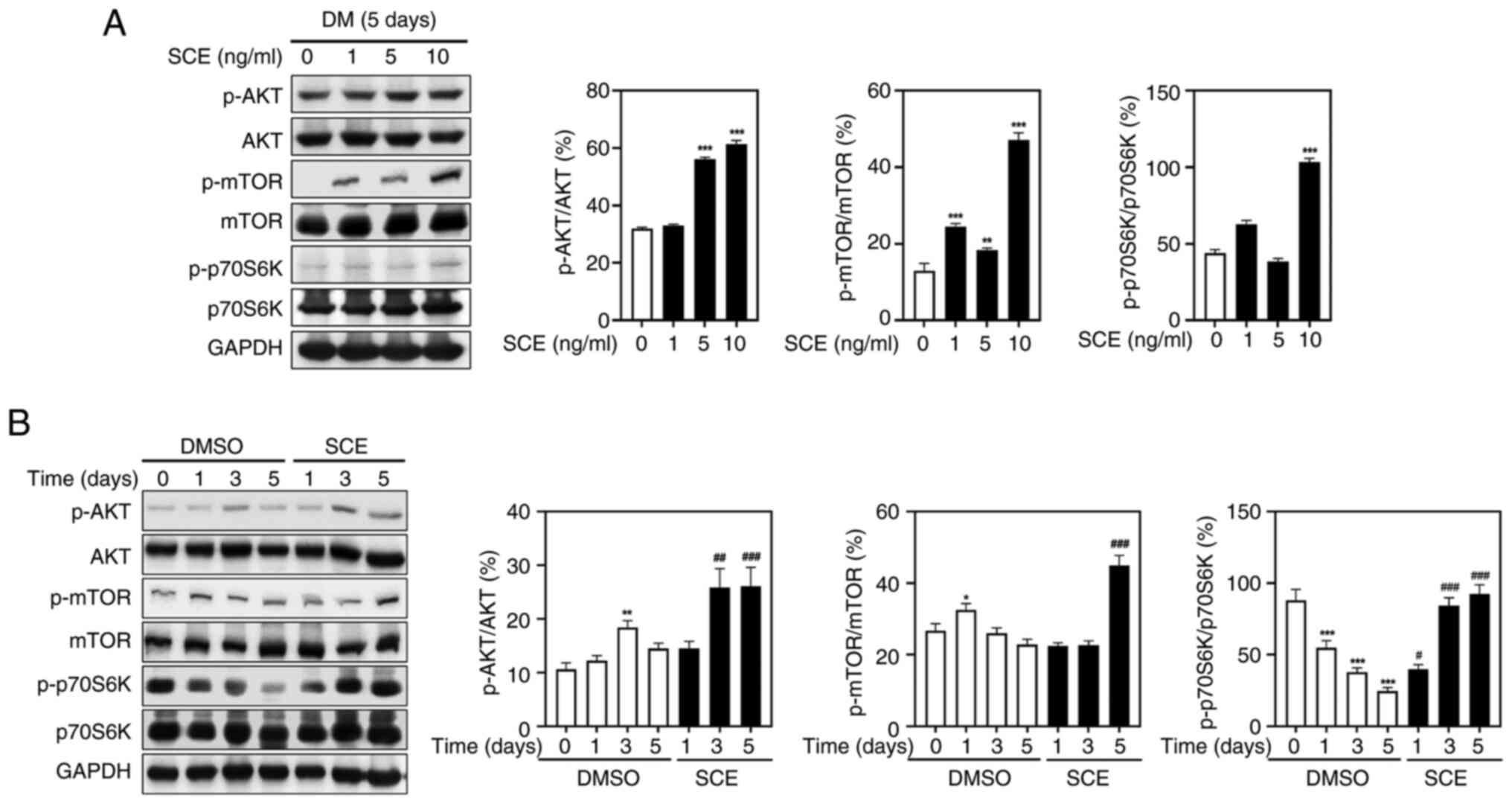
adults. Current consensus definition: Prevalence, etiology, and
consequences. International working group on sarcopenia. J Am Med
Dir Assoc. 12:249–256. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mankhong S, Kim S, Moon S, Kwak HB, Park
DH and Kang JH: Experimental models of sarcopenia: Bridging
molecular mechanism and therapeutic strategy. Cell. 9:13852020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ma J, Meng X, Kang SY, Zhang J, Jung HW
and Park YK: Regulatory effects of the fruit extract of Lycium
chinense and its active compound, betaine, on muscle
differentiation and mitochondrial biogenesis in C2C12 cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118:1092972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shin EJ, Jo S, Choi S, Cho CW, Lim WC,
Hong HD, Lim TG, Jang YJ, Jang M, Byun S and Rhee Y: Red ginseng
improves exercise endurance by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis
and myoblast differentiation. Molecules. 25:8652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim YH, Jung JI, Jeon YE, Kim SM, Oh TK,
Lee J, Moon JM, Kim TY and Kim EJ: Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract
and Gypenoside L enhance skeletal muscle differentiation and
mitochondrial metabolism by activating the PGC-1α pathway in C2C12
myotubes. Nutr Res Pract. 16:14–32. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
National Institute of Biological
Resources, . Korean Red List of Threatened Species. 2nd edition.
National Institute of Biological Resources 2014; 2nd edition. Suh
MH, Lee BY, Kim ST, Park CH, Oh HK, Kim HY, Lee JH and Lee SY:
National Institute of Biological Resources; Incheon: 2014
|
|
12
|
Chang CS, Lee JS, Park TY and Kim H:
Reconsideration of rare and endangered plant species in Korea based
on the IUCN red list categories. Korean J Pl Taxon. 31:107–142.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ryu SY, Oh KS, Kim YS and Lee BH:
Antihypertensive, vasorelaxant and inotropic effects of an
ethanolic extract of the roots of Saururus chinensis. J
Ethnopharmacol. 118:284–289. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yoo HJ, Kang HJ, Jung HJ, Kim K, Lim CJ
and Park EH: Anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic and
anti-nociceptive activities of Saururus chinensis extract. J
Ethnopharmacol. 120:282–286. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nho JH, Lee HJ, Jung HK, Jang JH, Lee KH,
Kim AH, Sung TK and Cho HW: Effect of Saururus chinensis
leaves extract on type II collagen-induced arthritis mouse model.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 19:22019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheng Y, Yin Z, Jiang F, Xu J, Chen H and
Gu Q: Two new lignans from the aerial parts of Saururus
chinensis with cytotoxicity toward nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Fitoterapia. 141:1043442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sung SH, Lee EJ, Cho JH, Kim HS and Kim
YC: Sauchinone, a lignan from Saururus chinensis, attenuates
CCl4-induced toxicity in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Biol
Pharm Bull. 23:666–668. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hwang BY, Lee JH, Nam JB, Hong YS and Lee
JJ: Lignans from Saururus chinensis inhibiting the
transcription factor NF-kappaB. Phytochemistry. 64:765–771. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Quan Z, Lee YJ, Yang JH, Lu Y, Li Y, Lee
YK, Jin M, Kim JY, Choi JH, Son JK and Chang HW: Ethanol extracts
of Saururus chinensis suppress ovalbumin-sensitization
airway inflammation. J Ethnopharmacol. 132:143–149. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alaklabi A, Arif IA, Ahamed A, Surendra
Kumar R and Idhayadhulla A: Evaluation of antioxidant and
anticancer activities of chemical constituents of the Saururus
chinensis root extracts. Saudi J Biol Sci. 25:1387–1392. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang J, Rho Y, Kim MY and Cho JY: TAK1 in
the AP-1 pathway is a critical target of Saururus chinensis
(Lour.) Baill in its anti-inflammatory action. J Ethnopharmacol.
279:1144002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoo SR, Ha H, Shin HK and Seo CS:
Anti-inflamatory activity of neolignan compound isolated from the
roots of Saururus chinensis. Plants (Basel). 9:9322020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jung YW, Lee BM, Ha MT, Tran MH, Kim JA,
Lee S, Lee JH, Woo MH and Min BS: Lignans from Saururus
chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory activity by influencing the
Nrf2/HO-1 activation pathway. Arch Pharm Res. 42:332–343. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Choi MS, Kim EC, Lee HS, Kim SK, Choi HM,
Park JH, Han JB, An HJ, Um JY, Kim HM, et al: Inhibitory effects of
Saururus chinensis (LOUR.) BAILL on the development of
atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Biol Pharm
Bull. 31:51–56. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jeong HJ, Koo BS, Kang TH, Shin HM, Jung S
and Jeon S: Inhibitory effects of Saururus chinensis and its
components on stomach cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 22:256–261.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang L, Cheng D, Wang H, Di L, Zhou X, Xu
T, Yang X and Liu Y: The hepatoprotective and antifibrotic effects
of Saururus chinensis against carbon tetrachloride induced
hepatic fibrosis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 126:487–491. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jung MH, Song MC, Bae K, Kim HS, Kim SH,
Sung SH, Ye SK, Lee KH, Yun YP and Kim TJ: Sauchinone attenuates
oxidative stress-induced skeletal muscle myoblast damage through
the down-regulation of ceramide. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:575–579. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu H, Lee SM and Joung H: 2-D08 treatment
regulates C2C12 myoblast proliferation and differentiation via the
Erk1/2 and proteasome signaling pathways. J Muscle Res Cell Motil.
42:193–202. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim JY, Cheon YH, Ahn SJ, Kwak SC, Chung
CH, Lee CH and Lee MS: Harpagoside attenuates local bone Erosion
and systemic osteoporosis in collagen-induced arthritis in mice.
BMC Complement Med Ther. 22:2142022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sayer AA, Robinson SM, Patel HP,
Shavlakadze T, Cooper C and Grounds MD: New horizons in the
pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of sarcopenia. Age Ageing.
42:145–150. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oh KS, Choi YH, Ryu SY, Oh BK, Seo HW, Yon
GH, Kim YS and Lee BH: Cardiovascular effects of lignans isolated
from Saururus chinensis. Planta Med. 74:233–238. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dumont NA, Bentzinger CF, Sincennes MC and
Rudnicki MA: Satellite cells and skeletal muscle regeneration.
Compr Physiol. 5:1027–1059. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Langley B, Thomas M, Bishop A, Sharma M,
Gilmour S and Kambadur R: Myostatin inhibits myoblast
differentiation by down-regulating MyoD expression. J Biol Chem.
277:49831–49840. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tanaka S, Terada K and Nohno T: Canonical
Wnt signaling is involved in switching from cell proliferation to
myogenic differentiation of mouse myoblast cells. J Mol Signal.
6:122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kang C and Li Ji L: Role of PGC-1α
signaling in skeletal muscle health and disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1271:110–117. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Taherzadeh-FardE SC, Akkad DA, Wieczorek
S, Haghikia A, Chan A, Epplen JT and Arning L: PGC-1alpha
downstream transcription factors NRF-1 and TFAM are genetic
modifiers of Huntington disease. Mol Neurodegener. 6:322011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hardie DG, Ross FA and Hawley SA: AMPK: A
nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:251–262. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gasparrini M, Giampieri F, Alvarez Suarez
J, Mazzoni L, Y Forbes Hernandez T, Quiles JL, Bullon P and Battino
M: AMPK as a new attractive therapeutic target for disease
prevention: The role of dietary compounds AMPK and disease
prevention. Curr Drug Targets. 17:865–889. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fu X, Zhao JX, Liang J, Zhu MJ, Foretz M,
Viollet B and Du M: AMP-activated protein kinase mediates myogenin
expression and myogenesis via histone deacetylase 5. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 305:C887–C895. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tao R, Gong J, Luo X, Zang M, Guo W, Wen R
and Luo Z: AMPK exerts dual regulatory effects on the PI3K pathway.
J Mol Signal. 5:12010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Simone C, Forcales SV, Hill DA, Imbalzano
AN, Latella L and Puri PL: p38 pathway targets SWI-SNF
chromatin-remodeling complex to muscle-specific loci. Nat Genet.
36:738–743. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bae GU, Lee JR, Kim BG, Han JW, Leem YE,
Lee HJ, Ho SM, Hahn MJ and Kang JS: Cdo interacts with APPL1 and
activates Akt in myoblast differentiation. Mol Biol Cell.
21:2399–2411. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Glass DJ: Signalling pathways that mediate
skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy. Nat Cell Biol. 5:87–90.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bodine SC, Stitt TN, Gonalez M, Kline WO,
Stover GL, Bauerlein R, Zlotchenko E, Scrimgeour A, Lawrence JC,
Glass DJ and Yancopoulos GD: Akt/mTOR pathway is a crucial
regulator of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and can prevent muscle
atrophy in vivo. Nat Cell Biol. 3:1014–1019. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lipina C, Kendall H, McPherron AC, Taylor
PM and Hundal HS: Mechanisms involved in the enhancement of
mammalian target of rapamycin signalling and hypertrophy in
skeletal muscle of myostatin-deficient mice. FEBS Lett.
584:2403–2408. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|