Infectious diseases remain one of the top ten causes
of human morbidity and mortality worldwide (1). Pathogen identification from clinical
samples is key to guide treatment and management strategies for
patients with infections. Currently, a number of traditional
diagnostic techniques are used for etiological diagnosis, including
microbial culture, antigen and antibody testing and PCR of
microbial DNA or RNA (2). However,
in ~50% of infected patients there are difficulties in pathogen
identification due to the wide variety of pathogens, low throughput
of traditional clinical methods and time-consuming nature of
microbial culture (3).
Assays using next-generation sequencing (NGS)
technology have potential to improve diagnosis of infectious
diseases. NGS allows for sequencing of multiple individual DNA or
RNA molecules in parallel, generating millions to billions of reads
per run. The common applications of NGS in diagnostic microbiology
laboratories include metagenomics NGS (mNGS) and targeted NGS
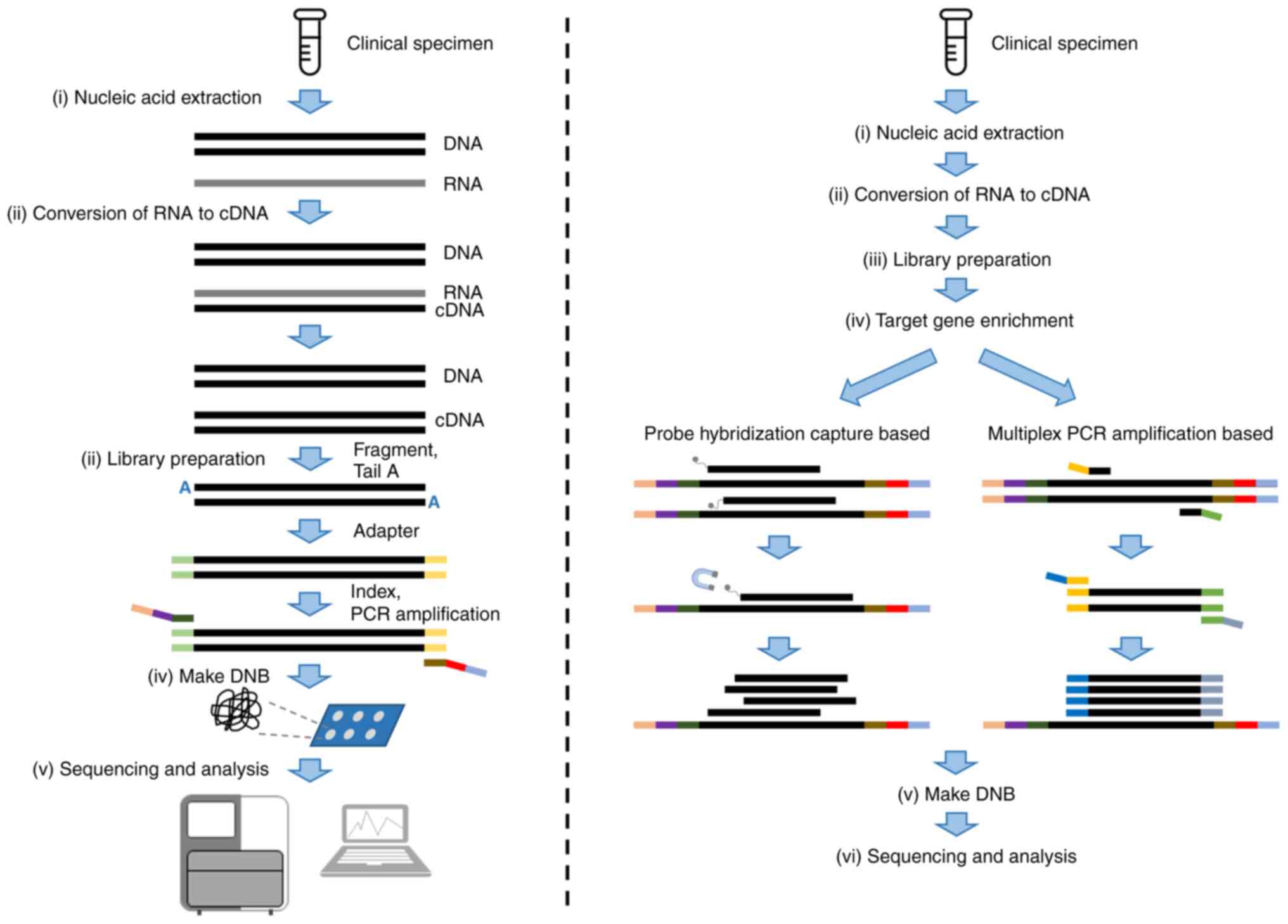
(tNGS; Fig. 1). mNGS approaches
characterize all DNA or RNA in a sample to enable analysis of the
entire microbiome, whereas tNGS approaches enrich specific genetic
targets to identify specific pathogens or genes of interest. Given
the success of the clinical exploration of mNGS, attention has been
focused on making NGS more widely and economically available in the
clinical setting. The use of tNGS as a solution for this is also
being assessed. The present review aimed to elucidate the
diagnostic value of tNGS in clinical application.
As a successful example of the clinical application
of NGS methods, previous studies have reported the promise of mNGS
in clinical application (4–14).
mNGS successfully diagnosed neuroleptospirosis in a 14-year-old,
which put the application of mNGS in the diagnosis of infectious
diseases into the public light (4). In 2019, Blauwkamp et al
(5) described the commercial mNGS
sequencing Karius test (Karius, Inc.) in a cohort of 350 patients
with suspected sepsis. It presented sensitivity of 92.9% and a
specificity of 62.7% compared with the composite reference standard
including culture, serology and nucleic acid testing and clinical
adjudication when testing the plasma specimens from this cohort
(5). Studies have confirmed the
diagnostic value of mNGS in a number of patient cohorts assessing
complex and atypical pathogen infection, including meningitis and
pneumonia (3,6–9).
mNGS is a potential method for identifying emerging or rare
pathogens. For example, RNA-based mNGS identified the novel
coronavirus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
(SARS-CoV-2) as the cause of severe pneumonia (10). mNGS could provide clues for
identifying rare pathogens including Chlamydia psittaci,
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), anaerobe and fungus (11–13).
Moreover, sensitivity of mNGS is relatively less affected by prior
antibiotics therapy compared to methods such as clinical cultures
and immunologic assays. A previous study reported the sensitivity
of mNGS is significantly higher than that of culture (52.7 vs.
34.4%) when patients had received prior antibiotic therapy
(12). This conclusion was
supported by Zhang et al (14), who found a higher sensitivity rate
(66.67%) of mNGS in empirically-treated patients.
However, with widespread clinical use, shortcomings
of mNGS have also received attention. The first problem is
over-representation of human DNA in sequence data. As samples
contain large amounts of human nucleic acid and the human genome is
notably larger than the microbial genome, 80–99% of raw NGS reads
are derived from human DNA (7,15),
which decreases sensitivity of assays for microbial detection,
especially when these are present in low abundance. Techniques for
depleting host nucleic acid include physical methods such as
centrifugation and filtration (16,17),
chemical methods, including differential cleavage with chemical
reagents (18), and selective
hybridization removal using clustered regularly interspaced short
palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated systems 9 (19) (Table
I). However, these methods introduce new problems. Partial
pathogens will be lost by these methods (20) and the risk of exogenous background
contamination increases due to the addition of reagents. The
complexity of these issues increases the difficulty of host nucleic
acid depletion. At present, there is no relatively achievable
method (20).
The detection performance of mNGS can be affected by
the characteristics of pathogens. Small-genome, low-abundance
pathogens such as viruses have limited coverage. A study assessing
mNGS virus detection reported that median viral genome coverage is
~2% (21,22). In addition, antimicrobial
resistance genes and virulence genes are also short in length,
again a challenge for mNGS detection (23). Furthermore, the application of mNGS
in fungal detection is limited. Pathogens with cell walls including
fungi and intracellular bacteria affect nucleic acid extraction
efficiency, which reduces the microbial nucleic acid abundance in
sample (6,9,15,24–27).
Besides, the high cost of mNGS limits its broader adoption in
clinical settings. In China, the average cost per mNGS test is
¥3,000 (~US$400), which is significantly more expensive than
individual traditional pathogen tests. For instance, culture tests
cost around ¥600-700, the Cryptococcus antigen test is ¥320,
and both the Aspergillus serological test and T-cell
immunospot test T.SPOT are priced at ~¥600 (12).
tNGS is an NGS method that detects a predetermined
range of target genes. tNGS has been widely applied in disease
identification including tumor detection, whereas studies assessing
its use in pathogen detection are limited. Compared with mNGS, tNGS
extracts predefined genes through enrichment, which allows
pathogens to be targeted for sequencing. Targeted approaches are
used to enrich known pathogens, especially low-concentration
pathogens and their virulence and/or antimicrobial resistance genes
in a single sample. This can increase the detection sensitivity for
microorganisms being targeted, although it limits the breadth of
potential pathogens that can be identified. Target enrichment is
key to ensure sufficient sequencing depth and coverage in the
regions of interest in tNGS workflow for accurate pathogen
identification. Compared with mNGS, tNGS can enrich microbial
nucleic acid content by several 10-fold to several 1,000-fold
(28).
Multiplex PCR amplicon-based and hybrid
capture-based methodologies are used for target enrichment in tNGS.
The multiplex PCR amplicon-based method amplifies and enriches
target fragments through multiple primers designed for target
region fragments. Multiple target fragments are amplified at the
same time for library construction and sequencing. Hybrid-capture
targeted method uses probes which hybridize with target fragments
to capture and enrich target regions. Hybrid capture-based assays
use magnetic beads to purify captured fragments to remove
non-specific hybridization and constructs a DNA library for
sequencing. The main differences between the approaches are shown
in Table II.
The advantages of the amplicon-based method are low
cost and quick and simple operation. The amplicon-based method can
detect pathogens with low concentration. A study assessing the
corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) detection ability of these
methods reported that amplicon- and hybrid probe-based methods
generally have the same enrichment effect on target gene fragments,
but the amplicon-based method has a better enrichment effect for
lower concentration viruses <1×104 copies/ml or
Ct>28.7 (29). Moreover, the
specificity of the amplicon-based method is better according to the
stringency of the primer binding to the target region. Therefore,
this method more efficiently detects single nucleotide variations.
However, the fact that it has undergone PCR amplification makes it
difficult to quantify, which may result in poor performance in
detecting copy number and structural variation (29).
There are limitations for amplicon-based assay in
applications. Firstly, the amplicon-based method has limitations
for the detection spectrum. To avoid dimerization between primers,
only ~20,000 primers can be designed. Considering the specificity
of pathogens, the melting temperature value and the secondary
structure of primers, this number will be greatly reduced. This
upper limit of the number of primers increases the difficulty of
adjusting design of primers, which affects the flexibility of
pathogen detection in the face of novel pathogens and different
environments. Secondly, the amplicon-based method has a low
tolerance for primer mismatch. This method requires almost 100%
match between the primers and target sequence, rendering the
amplification ineffective if mutations are present in the primer
binding region. Thirdly, the amplicon-based method, used for
sequencing SARS-CoV-2 genomes directly from clinical samples, has
limitations in detecting minor alleles. Specifically, this method
introduces biases that affect the accuracy of detecting the
frequency of these minor alleles. Additionally, it has a
significantly higher false-positive rate compared to the hybrid
capture-based method (0.74 vs. 0.02%). This means that the
amplicon-based method is less reliable and more prone to errors
when identifying less prevalent genetic variations within the viral
genome (29).
The hybrid capture-based method is able to detect a
wider range of pathogens with more comprehensive genome coverage
and more flexible pathogen detection design. The number of species
detected by hybrid capture can be several 1,000. In the context of
pandemics including COVID-19 and influenza A that require analysis
of genome variation and virus monitoring and traceability, the
whole genome can be covered by the hybrid capture-based method. The
hybrid capture-based method can combine new pathogen-specific
probes without affecting performance. Furthermore, hybrid
capture-based method has high tolerance for primer mismatch making
it more suitable for use in samples with a high occurrence of
mutations. Unlike the amplicon-based method, the hybrid
capture-based method is able to amplify the target region with a
matching accuracy of 70–80% (30).
A genome sequencing study of hepatitis C virus (HCV) reported that
the hybrid capture-based method can achieve the maximum capture
efficiency of HCV at 80% probe matching (31). Furthermore, the hybrid
capture-based method is less likely to capture identical nucleic
acid fragments due to technical principles and therefore has a
better uniformity. A previous study reported that the hybrid
capture-based method has better uniformity and less bias than the
amplicon-based method and may reflect the true content of pathogens
in samples more objectively (29).
According to our experience, the hybrid
capture-based method requires a higher initial concentration of
pathogens and extracted DNA and cDNA need to be fragmented prior to
probe hybridization capture. During fragmentation, loss of DNA and
cDNA is possible. Furthermore, the probes may partially hybridize
and capture non-specific fragments. IN addition, poor design of
capture probes, suboptimal capture conditions, insufficient
blocking of repetitive sequences in genomic DNA and improper ratio
of genomic DNA to capture probe can affect capture specificity.
Compared with the amplicon-based method, the hybrid capture-based
method is more complicated, has a higher cost and longer workflow
time. The time required for a typical probe hybridization capture
process is ~12 h, which limits clinical application of this method.
Rapid hybrid capture-based method can reduce the hybridization time
to 2 h; however, time for the whole process of the hybrid
capture-based tNGS is still longer than that of amplicon-based
method at ~16 vs. ~12 h, respectively.
Enriching pathogen nucleic acid sequences being
targeted can increase detection sensitivity (2). The virus identification ability
between host depletion methods and target enrichment have been
compared. Targeted capture-based approaches increase the nucleic
acid of 90% viruses assessed, but host nucleic acid load was at
times not reduced successfully (32). Zhao et al (22) used tNGS to enrich ribosomal RNA
(rRNA) and reported that the quantity of microbial nucleic acid
increases seven-fold. The detection results are consistent with the
clinical findings for the identification of virus, fungus and
antimicrobial resistance, demonstrating the accuracy of the
detection method. Through enrichment, tNGS increases abundance and
coverage of fastidious or low-abundance pathogens to improve
reliability of detection results. In a study assessing fever in
children using hybrid capture-based tNGS, the median increase in
the reads of viruses as a percentage of all reads post-capture was
674-fold and the median genome coverage increased from 2.1 to 83.2%
post-capture. This can also be applied for the analysis of an
anrovirus, even if its sequences have up to 58% variation from the
reference sequences used to select the capture probes (21).
The chemistry and software used in mNGS and
capture-based tNGS and amplification-based tNGS vary notably. mNGS
commonly uses reagents such as nucleotides and enzymes, including
DNA polymerases (33). In addition
to these, amplification-based tNGS requires primers specific to the
targeted pathogens (34).
Conversely, capture-based tNGS uses biotinylated oligonucleotide
probes and streptavidin-coated magnetic beads instead of primers
(35). Regarding bioinformatics
analysis, sequence-based ultra-rapid+ pipeline is frequently used
in mNGS for processing data, including the filtration of host
sequences and identification of microbial sequences (36). The open-source platform IDseq is
also widely applied in mNGS (37).
Amplification-based tNGS often uses Primer3 for designing PCR
primers and quantitative insights into microbial ecology for
sequence analysis and microbial community profiling (38,39).
Since capture-based tNGS is relatively new, researchers often
develop custom pipelines in-house, combining steps for alignment,
variant calling and annotation tailored to the captured targets
(40). These techniques, along
with associated costs, vary in terms of reagent and computational
resource requirement. Amplification-based methods generally incur
higher costs due to the necessity of specific primers and enzymes.
By contrast, capture-based methods, while having high initial costs
for probe design, benefit from lower ongoing operational costs.
Notably, when considering the number of reads per workflow, the
cost of capture-based tNGS is comparable to that of mNGS, at
US$150–160 per sample. Although capture-based tNGS requires notably
less time for bioinformatics analysis compared with mNGS at 5 min
vs. 1.5 h, it requires an additional 12 h for target enrichment
(41).
A notable variant of preliminary tNGS integrates 16S
rRNA gene PCR amplification with Sanger sequencing. A study using
this method in clinical pathogen identification for infective
endocarditis reported that sensitivity, specificity and positive
predictive value and negative predictive value of tNGS were 92, 78,
78 and 92% respectively, compared with the culture methods, which
reported values of 44, 100, 39 and 100%, respectively,
demonstrating a significantly higher sensitivity (56). Further research on patients with
infective endocarditis reported a similarly high positive ratio
associated with this form of tNGS (50,57).
Moreover, tNGS is used for pathogen identification in synovial
fluid from patients with periprosthetic joint infections, where the
sensitivity and specificity of tNGS are 69 and 100% respectively,
which are lower compared with the culture method which had
sensitivity and specificity values of 72 and 100%, respectively
(58). Furthermore, a comparative
study between these two forms of preliminary tNGS report that 16S
rRNA gene PCR amplification followed by NGS exhibits higher
accuracy compared with Sanger sequencing (59). Another study highlighted that after
the sequencing method was changed from NGS to Sanger, based on 16S
rRNA gene PCR amplification, notably increased the test positivity
rate by 87% (60).
Amidst the challenges posed by the COVID-19
pandemic, tNGS has been used for infectious disease surveillance
and genotyping (61,62). A comprehensive study including the
surveillance data from six hospitals in Guangzhou (China) in
2022–2023 used a number of methodologies, including tNGS, to
elucidate dynamics of the pandemic (61). The aforementioned study reported
the Οmicron BA.5.2 variant as the predominant strain in the region.
Furthermore, ~49.8% of SARS-CoV-2 infections are concomitant with
other pathogenic infections, underscoring the complexity of
clinical management scenarios during the pandemic (61). Danilenko et al (63) applied tNGS for mutation analysis of
the A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses, reporting an association between the
hemagglutinin D222G/N mutation and mortality, thereby
offering insight for effective disease prevention strategies.
Moreover, Chao et al (64)
reported the use of tNGS in pathogen identification in patients
with acute lower respiratory tract infection. Benchmarked against
the gold standard sputum culture, tNGS has a notable positive rate
of 95.6% (64). tNGS can also be
used in pediatric populations, with numerous studies reporting its
clinical applicability (65–68).
Lin et al (65) used
respiratory pathogen identity/antimicrobial resistance enrichment
sequencing (RPIP), a type of tNGS predicated on probe hybridization
capture, for analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF)
samples from children with respiratory infections. RPIP
demonstrated sensitivities and specificities of 84.4 and 97.7%,
respectively, compared with culture-based gold standards (65). Moreover, another study reported the
use of tNGS in identification of pneumonia in children through
testing upper respiratory tract samples (66). Recent studies have reported the use
of tNGS in identifying rare pathogens, including Legionella
pneumophila, Chlamydia psittaci, Tropheryma whipplei, Aspergillus
fumigatus and Cryptococcus neoformans (69–72).
A number of studies have reported the feasibility of
tNGS in clinical application by comparing mNGS with tNGS (41,73).
A study compared the performance of mNGS and tNGS in the detection
of BALF specimens from patients with respiratory pathogen
infection. tNGS demonstrated a similar performance to mNGS but the
sequencing data were 1/3 of mNGS. The overall accuracy of tNGS
workflow was 65.6%, which is similar to mNGS workflow at 67.1%
(41). In another study of
patients with lung infection, tNGS comprised 153 species and had a
comparable detection rate to mNGS (82.17 vs. 86.51%, respectively).
Detection rate of tNGS in bacteria, fungi and viruses was
consistent with mNGS (73). These
findings underscore the significance and practicality of tNGS in
the clinical landscape, particularly in respiratory infectious
disease.
tNGS has been used to diagnose and manage
bloodstream infection in hospitalized patients, owing to its high
sensitivity, specificity and broad-spectrum pathogen detection
capabilities. Studies (74,75)
have reported the ability of tNGS to detect P. falciparum, a
malaria-causing parasite (74). In
Ghana, a tNGS approach using probes, has been used in the
surveillance of malaria in pediatric populations (75). Furthermore, Deng et al
(76) reported a metagenomic
sequencing method using primer enrichment that enriches targeted
RNA viral genomes. This methodology has improved viral diagnostics
in blood, reporting a median ten-fold enrichment and a notable
increase in genome coverage, which is particularly effective for
hard-to-detect viruses such as Zika and Ebola (76). In a comprehensive study (77), a tNGS termed ultrasensitive
single-genome sequencing (uSGS) was assessed. The aforementioned
study used uSGS for the diagnosis of patients infected with HIV-1,
reporting a >100-fold greater depth in HIV-1 RNA sequencing.
This approach not only decreases PCR errors but also offers
improved variant detection (77).
Moreover, targeted amplification sequencing technologies including
ampliseq detection system have demonstrated promising results in
rapidly identifying pathogens directly from blood samples, with a
detection accuracy >92.81% in both spiked samples and clinical
specimens (78). These results
underscore the role of tNGS in improving diagnostic precision and
guiding effective treatment strategies in clinical bloodstream
infections.
In a broader clinical context, a study of patients
with meningitis reported that tNGS exhibits improved sensitivity
compared with mNGS at 70.8 vs. 41.7%, respectively. tNGS has
improved diagnostic speed and cost-effectiveness. However, mNGS has
specificity at 78.6 vs. 64.3%, respectively. These findings suggest
that tNGS could be more suitable in certain clinical settings, such
as when pathogens cannot be detected by conventional methods
(82).
tNGS identifies antimicrobial resistance genes by
enriching target regions. In a study using RPIP for detection of
pathogens and antimicrobial resistance genes in 201 respiratory
tract samples, 53.8% of antimicrobial resistance genes reported by
RPIP were consistent with clinical drug susceptibility testing
(41). Nevertheless, the
antimicrobial resistance effect of the same gene in different
microorganisms is unequal. In the aforementioned study, the
blaOXA genes encoding carbapenemases were
detected in multiple Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates;
however, these were demonstrated to be susceptible to carbapenems.
Therefore, considering the complexity of drug resistance genes and
current databases requiring supplementation, it is necessary to
analyze resistance genes in combination with pathogenic strains in
single test. Lin et al (65) evaluated the efficacy of RPIP in
pediatric patients with respiratory infections. The aforementioned
study included 25 patients with confirmed Streptococcus
pneumoniae infection who were tested for a spectrum of
antimicrobial resistance genes. A total of 58 antimicrobial
resistance genes associated with resistance to tetracycline,
macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin, β-lactams, sulfonamides and
aminoglycosides, were identified in 19 patients. Compared with the
results from clinical drug susceptibility testing, the concordance
rates for erythromycin, tetracycline, penicillin and sulfonamides
resistance are 89.5, 79.0, 36.8 and 42.1%, respectively (65). Application of tNGS for
antimicrobial resistance gene detection has been extensively
documented in an array of infectious diseases, including
bloodstream infections, localized infection, infective
endocarditis, urinary tract infections, malaria and leprosy
(57,74,75,77,78,85–88).
In TB infections, the main challenge lies in the
accessibility of efficient pathogen identification and
comprehensive drug susceptibility testing. The World Health
Organization recommended the Deeplex Myc-TB assay, a tNGS using
multiplex PCR amplification (89–94).
This assay has efficacy in prediction of resistance profiles
against anti-tuberculous drugs (89–94).
A study reported the high predictive accuracy of Deeplex Myc-TB
with sensitivity of 95.3% and specificity of 97.4% in determining
resistance to both first and second-line anti-TB medications. When
used in the analysis of sputum samples, Deeplex Myc-TB parallels,
and in some cases exceeds, performance of other advanced
whole-genome sequencing methodologies (89). Sibandze et al (93) reported on the use of Deeplex Myc-TB
with stool samples; this is an advancement for patient populations
that are unable to provide sputum samples.
A number of other tNGS platforms have been used in
the clinical application of TB testing. Predominantly, these
platforms are used in the assessment of respiratory tract specimens
(Table IV). For example, Wu et
al (95) reported the efficacy
of a multiplex PCR-based tNGS approach in the detection of MTB and
its resistance to first-line drugs directly from BALF,
demonstrating commensurate performance with traditional diagnostic
methodologies, while assessing a broader range of resistance genes.
Likewise, Colman et al (96) reported rapid and efficient
characterization of drug resistant TB directly from sputum samples
using amplicon sequencing. This method demonstrates a high
concordance with phenotypic drug susceptibility testing and detects
low abundance resistant variants (96). The effectiveness of tNGS in sputum
samples detection has been validated by numerous subsequent studies
(97–99). Extending beyond respiratory
samples, tNGS has applicability in other types of clinical
specimen. A study used tNGS for the detection of MTB in spinal
tissues, demonstrating higher sensitivity compared with traditional
culture methods at 100.00 vs. 18.75%, respectively. This approach
successfully identifies antimicrobial resistance genes and
mutations associated with drug resistance and suggests potential
use in guiding personalized treatment strategies (100). A study assessing lung tissue
samples from patients with TB reported the effectiveness of tNGS in
detecting antimicrobial resistance (101). Furthermore, Song et al
(102) reported the application
of amplicon-based tNGS for diagnosing drug resistant TB using
formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues. The
aforementioned study reported that the detection sensitivity of
tNGS for first-line drugs like rifampicin and isoniazid is high at
96 and 94%, respectively. The aforementioned study demonstrated the
feasibility of using tNGS for FFPE samples, which can be
challenging due to DNA degradation and reported advantages in terms
of cost-efficiency, customizable for specific pathogen detection
and reduced testing durations (102).
It has been reported that results obtained by tNGS
are more concise than those reported by mNGS (41). In a comparative study of mNGS and
tNGS, the number of analytes for mNGS workflow was 4–24 per sample,
while one or two analytes were identified by tNGS (41). These results were compared with a
comprehensive mNGS database, which covers tens of thousands of
microorganisms, the tNGS database includes information on dozens to
hundreds of target pathogens, with more in-depth and nuanced
differentiation of subspecies and subtypes. In bioinformatics
analysis workflows, 96.8% of microorganisms detected by mNGS are
interpreted as non-pathogenic microorganism, while 75.2%
microorganisms detected by tNGS are interpreted as non-pathogenic
microorganisms (41). Moreover,
refining the design of a database for tNGS is complex but
necessary. A good design of the database can ensure accurate
identification of pathogens. In a comparative study of tNGS and
mNGS, Pneumocystis carinii was detected by both methods, but
not reported, as it was considered a non-pathogenic microorganism
for humans, and Cryptococcus neoformans was incorrectly
reported as Cryptococcus gattii by tNGS (103).
Where mNGS sequences all nucleic acids present in a
sample, tNGS only detects pathogens within the designed panel,
resulting in a more stable performance and lower cost of sequencing
at 1/3-1/2 of the cost of mNGS. Considering of the simplified
interpretation and low cost, tNGS testing may be suitable for use
in hospital microbiology laboratories. Overall, tNGS is more
economical and may be more suitable for clinical application.
tNGS represents an advancement in infectious disease
diagnostics, particularly in its capacity to identify a range of
common pathogens via meticulously designed panels. This technology
increases the reliability of detection results through its targeted
amplification approach. tNGS may bridge the diagnostic gap between
conventional tests and mNGS. tNGS has attracted attention of the
clinical testing community. However, operational efficiency and
applicability of tNGS are dependent on a number of factors,
including the need to define the sample type, target pathogen
range, positive judgment value and supporting database.
tNGS may not operate in isolation but in conjunction
with conventional testing methods. This approach may contribute to
effective and precise clinical diagnosis. By combining the
universality of conventional tests with high specificity and
sensitivity of tNGS, clinicians may be better equipped to make more
accurate diagnoses. This integrated diagnostic strategy may improve
patient outcomes by enabling timely and appropriate therapeutic
interventions.
In summary, tNGS may serve a role in infectious
disease diagnostics. By addressing limitations of current testing
methodologies, tNGS may provide a more refined, accurate and
comprehensive approach to pathogen detection. Its continued
development and integration into clinical practice may impact
infectious disease diagnosis and management.
Not applicable.
The present study was supported by National High Level Hospital
Clinical Research Funding (grant no. 2022-PUMCH-A-139).
Not applicable.
QYC and JY supervised the study and wrote the
manuscript. YWL, YL, CLY, YJS and JD analyzed data. DJG and HL
wrote the manuscript. YC and YCX reviewed the manuscript. All
authors have read and approved the manuscript. Data authentication
is not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
|
1
|
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S,
Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, et
al: Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20
age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the global
burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 380:2095–2128. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chiu CY and Miller SA: Clinical
metagenomics. Nat Rev Genet. 20:341–355. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li N, Cai Q, Miao Q, Song Z, Fang Y and Hu
B: High-throughput metagenomics for identification of pathogens in
the clinical settings. Small Methods. 5:20007922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wilson MR, Naccache SN, Samayoa E, Biagtan
M, Bashir H, Yu G, Salamat SM, Somasekar S, Federman S, Miller S,
et al: Actionable diagnosis of neuroleptospirosis by
next-generation sequencing. N Engl J Med. 370:2408–2417. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blauwkamp TA, Thair S, Rosen MJ, Blair L,
Lindner MS, Vilfan ID, Kawli T, Christians FC, Venkatasubrahmanyam
S, Wall GD, et al: Analytical and clinical validation of a
microbial cell-free DNA sequencing test for infectious disease. Nat
Microbiol. 4:663–674. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wilson MR, Sample HA, Zorn KC, Arevalo S,
Yu G, Neuhaus J, Federman S, Stryke D, Briggs B, Langelier C, et
al: Clinical metagenomic sequencing for diagnosis of meningitis and
encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 380:2327–2340. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ramachandran PS and Wilson MR:
Metagenomics for neurological infections-expanding our imagination.
Nat Rev Neurol. 16:547–556. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han D, Li R, Shi J, Tan P, Zhang R and Li
J: Liquid biopsy for infectious diseases: A focus on microbial
cell-free DNA sequencing. Theranostics. 10:5501–5513. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng Y, Qiu X, Wang T and Zhang J: The
Diagnostic value of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in lower
respiratory tract infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
11:6947562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song
J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, et al: A novel coronavirus from
patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 382:727–733.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu L, Liu W, Ru M, Lin J, Yu G, Ye J, Zhu
ZA, Liu Y, Chen J, Lai G and Wen W: The application of metagenomic
next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Chlamydia psittaci
pneumonia: A report of five cases. BMC Pulm Med. 20:652020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miao Q, Ma Y, Wang Q, Pan J, Zhang Y, Jin
W, Yao Y, Su Y, Huang Y, Wang M, et al: Microbiological diagnostic
performance of metagenomic next-generation sequencing when applied
to clinical practice. Clin Infect Dis. 67 (Suppl 2):S231–S240.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi CL, Han P, Tang PJ, Chen MM, Ye ZJ, Wu
MY, Shen J, Wu HY, Tan ZQ, Yu X, et al: Clinical metagenomic
sequencing for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. J Infect.
81:567–574. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Cui P, Zhang HC, Wu HL, Ye MZ,
Zhu YM, Ai JW and Zhang WH: Clinical application and evaluation of
metagenomic next-generation sequencing in suspected adult central
nervous system infection. J Transl Med. 18:1992020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou Y, Xu Y, Gong Y, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Wang
C, Yao R, Li P, Guan Y, Wang J, et al: Clinical factors associated
with circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in primary breast cancer. Mol
Oncol. 13:1033–1046. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ji XC, Zhou LF, Li CY, Shi YJ, Wu ML,
Zhang Y, Fei XF and Zhao G: Reduction of human DNA contamination in
clinical cerebrospinal fluid specimens improves the sensitivity of
metagenomic next-generation sequencing. J Mol Neurosci. 70:659–666.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bal A, Pichon M, Picard C, Casalegno JS,
Valette M, Schuffenecker I, Billard L, Vallet S, Vilchez G, Cheynet
V, et al: Quality control implementation for universal
characterization of DNA and RNA viruses in clinical respiratory
samples using single metagenomic next-generation sequencing
workflow. BMC Infect Dis. 18:5372018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bowden R, Davies RW, Heger A, Pagnamenta
AT, de Cesare M, Oikkonen LE, Parkes D, Freeman C, Dhalla F, Patel
SY, et al: Sequencing of human genomes with nanopore technology.
Nat Commun. 10:18692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gu W, Crawford ED, O'Donovan BD, Wilson
MR, Chow ED, Retallack H and DeRisi JL: Depletion of abundant
sequences by hybridization (DASH): Using Cas9 to remove unwanted
high-abundance species in sequencing libraries and molecular
counting applications. Genome Biol. 17:412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gu W, Miller S and Chiu CY: clinical
metagenomic next-generation sequencing for pathogen detection. Annu
Rev Pathol. 14:319–338. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wylie TN, Wylie KM, Herter BN and Storch
GA: Enhanced virome sequencing using targeted sequence capture.
Genome Res. 25:1910–1920. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao N, Cao J, Xu J, Liu B, Liu B, Chen D,
Xia B, Chen L, Zhang W, Zhang Y, et al: Targeting RNA with next-
and third-generation sequencing improves pathogen identification in
clinical samples. Adv Sci (Weinh). 8:e21025932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Medicine CSoL: Expert consensus on the
standardized management of bioinformatics analysis for the
detection of pathogenic microorganisms in mNGS. Chin J Lab Med.
44:799–807. 2021.
|
|
24
|
Wang Q, Wu B, Yang D, Yang C, Jin Z, Cao J
and Feng J: Optimal specimen type for accurate diagnosis of
infectious peripheral pulmonary lesions by mNGS. BMC Pulm Med.
20:2682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fang X, Mei Q, Fan X, Zhu C, Yang T, Zhang
L, Geng S and Pan A: Diagnostic value of metagenomic
next-generation sequencing for the detection of pathogens in
bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in ventilator-associated pneumonia
patients. Front Microbiol. 11:5997562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mongkolrattanothai K, Naccache SN, Bender
JM, Samayoa E, Pham E, Yu G, Dien Bard J, Miller S, Aldrovandi G
and Chiu CY: Neurobrucellosis: Unexpected answer from metagenomic
next-generation sequencing. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 6:393–398.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mason A, Foster D, Bradley P, Golubchik T,
Doumith M, Gordon NC, Pichon B, Iqbal Z, Staves P, Crook D, et al:
Accuracy of different bioinformatics methods in detecting
antibiotic resistance and virulence factors from staphylococcus
aureus whole-genome sequences. J Clin Microbiol. 56:e01815–17.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Singh RR: Target enrichment approaches for
next-generation sequencing applications in oncology. Diagnostics
(Basel). 12:15392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiao M, Liu X, Ji J, Li M, Li J, Yang L,
Sun W, Ren P, Yang G, Zhao J, et al: Multiple approaches for
massively parallel sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 genomes directly from
clinical samples. Genome Med. 12:572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Briese T, Kapoor A, Mishra N, Jain K,
Kumar A, Jabado OJ and Lipkin WI: Virome capture sequencing enables
sensitive viral diagnosis and comprehensive virome analysis. mBio.
6:e01491–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bonsall D, Ansari MA, Ip C, Trebes A,
Brown A, Klenerman P, Buck D; STOP-HCV Consortium, ; Piazza P,
Barnes E and Bowden R: ve-SEQ: Robust, unbiased enrichment for
streamlined detection and whole-genome sequencing of HCV and other
highly diverse pathogens. F1000Res. 4:10622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Piantadosi A, Mukerji SS, Ye S, Leone MJ,
Freimark LM, Park D, Adams G, Lemieux J, Kanjilal S, Solomon IH, et
al: Enhanced virus detection and metagenomic sequencing in patients
with meningitis and encephalitis. mBio. 12:e01143212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang ZY, Li LL, Cao XL, Li P, Du J, Zou MJ
and Wang LL: Clinical application of amplification-based versus
amplification-free metagenomic next-generation sequencing test in
infectious diseases. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 13:11381742023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang D, Zhang J, Du J, Zhou Y, Wu P, Liu
Z, Sun Z, Wang J, Ding W, Chen J, et al: Optimized sequencing
adaptors enable rapid and real-time metagenomic identification of
pathogens during runtime of sequencing. Clin Chem. 68:826–836.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Deng X, Achari A, Federman S, Yu G,
Somasekar S, Bártolo I, Yagi S, Mbala-Kingebeni P, Kapetshi J,
Ahuka-Mundeke S, et al: Metagenomic sequencing with spiked primer
enrichment for viral diagnostics and genomic surveillance. Nat
Microbiol. 5:443–454. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miller S, Naccache SN, Samayoa E, Messacar
K, Arevalo S, Federman S, Stryke D, Pham E, Fung B, Bolosky WJ, et
al: Laboratory validation of a clinical metagenomic sequencing
assay for pathogen detection in cerebrospinal fluid. Genome Res.
29:831–842. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kalantar KL, Carvalho T, de Bourcy CFA,
Dimitrov B, Dingle G, Egger R, Han J, Holmes OB, Juan YF, King R,
et al: IDseq-An open source cloud-based pipeline and analysis
service for metagenomic pathogen detection and monitoring.
Gigascience. 9:giaa1112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nugen SR, Leonard B and Baeumner AJ:
Application of a unique server-based oligonucleotide probe
selection tool toward a novel biosensor for the detection of
Streptococcus pyogenes. Biosens Bioelectron. 22:2442–2448. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Siegwald L, Touzet H, Lemoine Y, Hot D,
Audebert C and Caboche S: Assessment of common and emerging
bioinformatics pipelines for targeted metagenomics. PLoS One.
12:e01695632017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Simner PJ, Miller HB, Breitwieser FP,
Pinilla Monsalve G, Pardo CA, Salzberg SL, Sears CL, Thomas DL,
Eberhart CG and Carroll KC: Development and optimization of
metagenomic next-generation sequencing methods for cerebrospinal
fluid diagnostics. J Clin Microbiol. 56:e00472–18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gaston DC, Miller HB, Fissel JA, Jacobs E,
Gough E, Wu J, Klein EY, Carroll KC and Simner PJ: Evaluation of
metagenomic and targeted next-generation sequencing workflows for
detection of respiratory pathogens from bronchoalveolar lavage
fluid specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 60:e00526222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gauduchon V, Chalabreysse L, Etienne J,
Célard M, Benito Y, Lepidi H, Thivolet-Béjui F and Vandenesch F:
Molecular diagnosis of infective endocarditis by PCR amplification
and direct sequencing of DNA from valve tissue. J Clin Microbiol.
41:763–766. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Marín M, Muñoz P, Sánchez M, Del Rosal M,
Alcalá L, Rodríguez-Créixems M and Bouza E; Group for the
Management of Infective Endocarditis of the Gregorio Marañón
Hospital (GAME), : Molecular diagnosis of infective endocarditis by
real-time broad-range polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and
sequencing directly from heart valve tissue. Medicine (Baltimore).
86:195–202. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vondracek M, Sartipy U, Aufwerber E,
Julander I, Lindblom D and Westling K: 16S rDNA sequencing of valve
tissue improves microbiological diagnosis in surgically treated
patients with infective endocarditis. J Infect. 62:472–478. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Maneg D, Sponsel J, Müller I, Lohr B,
Penders J, Madlener K and Hunfeld KP: Advantages and limitations of
direct PCR amplification of bacterial 16S-rDNA from resected heart
tissue or swabs followed by direct sequencing for diagnosing
infective endocarditis: A retrospective analysis in the routine
clinical setting. Biomed Res Int. 2016:79238742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Peeters B, Herijgers P, Beuselinck K,
Verhaegen J, Peetermans WE, Herregods MC, Desmet S and Lagrou K:
Added diagnostic value and impact on antimicrobial therapy of 16S
rRNA PCR and amplicon sequencing on resected heart valves in
infective endocarditis: A prospective cohort study. Clin Microbiol
Infect. 23:888.e1–888.e5. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim MS, Chang J, Kim MN, Choi SH, Jung SH,
Lee JW and Sung H: Utility of a direct 16S rDNA PCR and sequencing
for etiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Ann Lab Med.
37:505–510. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Santibáñez P, García-García C, Portillo A,
Santibáñez S, García-Álvarez L, de Toro M and Oteo JA: What does
16S rRNA gene-targeted next generation sequencing contribute to the
study of infective endocarditis in heart-valve tissue? Pathogens.
11:342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Flurin L, Wolf MJ, Fisher CR, Cano
Cevallos EJ, Vaillant JJ, Pritt BS, DeSimone DC and Patel R:
Pathogen detection in infective endocarditis using targeted
metagenomics on whole blood and plasma: A prospective pilot study.
J Clin Microbiol. 60:e00621222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hong HL, Flurin L, Greenwood-Quaintance
KE, Wolf MJ, Pritt BS, Norgan AP and Patel R: 16S rRNA gene
PCR/sequencing of heart valves for diagnosis of infective
endocarditis in routine clinical practice. J Clin Microbiol.
61:e00341232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Poulsen SH, Søgaard KK, Fuursted K and
Nielsen HL: Evaluating the diagnostic accuracy and clinical utility
of 16S and 18S rRNA gene targeted next-generation sequencing based
on five years of clinical experience. Infect Dis (Lond).
55:767–775. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hong HL, Flurin L, Thoendel MJ, Wolf MJ,
Abdel MP, Greenwood-Quaintance KE and Patel R: Targeted versus
shotgun metagenomic sequencing-based detection of microorganisms in
sonicate fluid for periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis. Clin
Infect Dis. 76:e1456–e1462. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fida M, Wolf MJ, Hamdi A, Vijayvargiya P,
Esquer Garrigos Z, Khalil S, Greenwood-Quaintance KE, Thoendel MJ
and Patel R: Detection of pathogenic bacteria from septic patients
using 16s ribosomal RNA gene-targeted metagenomic sequencing. Clin
Infect Dis. 73:1165–1172. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Okuda KI, Yoshii Y, Yamada S, Chiba A,
Hironaka I, Hori S, Yanaga K and Mizunoe Y: Detection of bacterial
DNA from central venous catheter removed from patients by next
generation sequencing: A preliminary clinical study. Ann Clin
Microbiol Antimicrob. 17:442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Flurin L, Wolf MJ, Greenwood-Quaintance
KE, Sanchez-Sotelo J and Patel R: Targeted next generation
sequencing for elbow periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis.
Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 101:1154482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Miller RJ, Chow B, Pillai D and Church D:
Development and evaluation of a novel fast broad-range 16S
ribosomal DNA PCR and sequencing assay for diagnosis of bacterial
infective endocarditis: Multi-year experience in a large Canadian
healthcare zone and a literature review. BMC Infect Dis.
16:1462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mularoni A, Mikulska M, Barbera F,
Graziano E, Medaglia AA, Di Carlo D, Monaco F, Bellavia D, Cascio
A, Raffa G, et al: Molecular analysis with 16S rRNA PCR/sanger
sequencing and molecular antibiogram performed on DNA extracted
from valve improve diagnosis and targeted therapy of infective
endocarditis: A prospective study. Clin Infect Dis. 76:e1484–e1491.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Flurin L, Hemenway JJ, Fisher CR, Vaillant
JJ, Azad M, Wolf MJ, Greenwood-Quaintance KE, Abdel MP and Patel R:
Clinical use of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene-based sanger and/or next
generation sequencing assay to test preoperative synovial fluid for
periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis. mBio. 13:e01322222022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sabat AJ, van Zanten E, Akkerboom V,
Wisselink G, van Slochteren K, de Boer RF, Hendrix R, Friedrich AW,
Rossen JWA and Kooistra-Smid AMDM: Targeted next-generation
sequencing of the 16S-23S rRNA region for culture-independent
bacterial identification-increased discrimination of closely
related species. Sci Rep. 7:34342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Flurin L, Wolf MJ, Mutchler MM, Daniels
ML, Wengenack NL and Patel R: Targeted metagenomic sequencing-based
approach applied to 2146 tissue and body fluid samples in routine
clinical practice. Clin Infect Dis. 75:1800–1808. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cheng LL, Li SY and Zhong NS: New
characteristics of COVID-19 caused by the Omicron variant in
Guangzhou. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 46:441–443. 2023.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ramos N, Panzera Y, Frabasile S, Tomás G,
Calleros L, Marandino A, Goñi N, Techera C, Grecco S, Fuques E, et
al: A multiplex-NGS approach to identifying respiratory RNA viruses
during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch Virol. 168:872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Danilenko AV, Kolosova NP, Shvalov AN,
Ilyicheva TN, Svyatchenko SV, Durymanov AG, Bulanovich JA,
Goncharova NI, Susloparov IM, Marchenko VY, et al: Evaluation of
HA-D222G/N polymorphism using targeted NGS analysis in A(H1N1)pdm09
influenza virus in Russia in 2018–2019. PLoS One. 16:e02510192021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chao L, Li J, Zhang Y, Pu H and Yan X:
Application of next generation sequencing-based rapid detection
platform for microbiological diagnosis and drug resistance
prediction in acute lower respiratory infection. Ann Transl Med.
8:16442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lin R, Xing Z, Liu X, Chai Q, Xin Z, Huang
M, Zhu C, Luan C, Gao H, Du Y, et al: Performance of targeted
next-generation sequencing in the detection of respiratory
pathogens and antimicrobial resistance genes for children. J Med
Microbiol. 72:2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ip M, Liyanapathirana V, Ang I, Fung KS,
Ng TK, Zhou H and Tsang DN: Direct detection and prediction of all
pneumococcal serogroups by target enrichment-based next-generation
sequencing. J Clin Microbiol. 52:4244–4252. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li F, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Shi P, Cao L, Su L,
Zhu Q, Wang L, Lu R, Tan W and Shen J: Etiology of severe pneumonia
in children in alveolar lavage fluid using a high-throughput gene
targeted amplicon sequencing assay. Front Pediatr. 9:6591642021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Dai Y, Sheng K and Hu L: Diagnostic
efficacy of targeted high-throughput sequencing for lower
respiratory infection in preterm infants. Am J Transl Res.
14:8204–8214. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Li S, Tong J, Li H, Mao C, Shen W, Lei Y
and Hu P: L. pneumophila infection diagnosed by tNGS in a
lady with lymphadenopathy. Infect Drug Resist. 16:4435–4442. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhang Y, Jiang X, Ye W and Sun J: Clinical
features and outcome of eight patients with Chlamydia
psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by targeted next generation
sequencing. Clin Respir J. 17:915–930. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Du ZM and Chen P: Co-infection of
Chlamydia psittaci and Tropheryma whipplei: A case
report. World J Clin Cases. 11:7144–7149. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ren HQ, Zhao Q, Jiang J, Yang W, Fu AS and
Ge YL: Acute heart failure due to pulmonary Aspergillus
fumigatus and Cryptococcus neoformans infection
associated with COVID-19. Clin Lab; 69. 2023
|
|
73
|
Li S, Tong J, Liu Y, Shen W and Hu P:
Targeted next generation sequencing is comparable with metagenomic
next generation sequencing in adults with pneumonia for pathogenic
microorganism detection. J Infect. 85:e127–e129. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kunasol C, Dondorp AM, Batty EM, Nakhonsri
V, Sinjanakhom P, Day NPJ and Imwong M: Comparative analysis of
targeted next-generation sequencing for Plasmodium falciparum drug
resistance markers. Sci Rep. 12:55632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Mensah BA, Aydemir O, Myers-Hansen JL,
Opoku M, Hathaway NJ, Marsh PW, Anto F, Bailey J, Abuaku B and
Ghansah A: Antimalarial drug resistance profiling of plasmodium
falciparum infections in ghana using molecular inversion probes and
next-generation sequencing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
64:e01423–19. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Deng X, Achari A, Federman S, Yu G,
Somasekar S, Bártolo I, Yagi S, Mbala-Kingebeni P, Kapetshi J,
Ahuka-Mundeke S, et al: Author correction: Metagenomic sequencing
with spiked primer enrichment for viral diagnostics and genomic
surveillance. Nat Microbiol. 5:5252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Boltz VF, Rausch J, Shao W, Hattori J,
Luke B, Maldarelli F, Mellors JW, Kearney MF and Coffin JM:
Ultrasensitive single-genome sequencing: accurate, targeted, next
generation sequencing of HIV-1 RNA. Retrovirology. 13:872016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Li Q, Huang W, Zhang S, Zheng Y, Lv Q,
Kong D, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Zhao Z, Wang M, et al: Target-enriched
sequencing enables accurate identification of bloodstream
infections in whole blood. J Microbiol Methods. 192:1063912022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Jiang J, Lv M, Yang K, Zhao G and Fu Y: A
case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria
monocytogenes meningitis with NGS. Open Life Sci.
18:202207382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen W, Wu Y and Zhang Y: Next-generation
sequencing technology combined with multiplex polymerase chain
reaction as a powerful detection and semiquantitative method for
herpes simplex virus type 1 in adult encephalitis: A case report.
Front Med (Lausanne). 9:9053502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yang HH, He XJ, Nie JM, Guan SS, Chen YK
and Liu M: Central nervous system aspergillosis misdiagnosed as
Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis in a patient with AIDS: A
case report. AIDS Res Ther. 19:402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gao D, Hu Y, Jiang X, Pu H, Guo Z and
Zhang Y: Applying the pathogen-targeted next-generation sequencing
method to pathogen identification in cerebrospinal fluid. Ann
Transl Med. 9:16752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
McGill F, Tokarz R, Thomson EC, Filipe A,
Sameroff S, Jain K, Bhuva N, Ashraf S, Lipkin WI, Corless C, et al:
Viral capture sequencing detects unexpected viruses in the
cerebrospinal fluid of adults with meningitis. J Infect.
84:499–510. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Li J, Zhang L, Yang X, Wang P, Feng L, Guo
E and Chen Y: Diagnostic significance of targeted next-generation
sequencing in central nervous system infections in neurosurgery of
pediatrics. Infect Drug Resist. 16:2227–2236. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Huang C, Huang Y, Wang Z, Lin Y, Li Y,
Chen Y, Chen X, Zhang C, Li W, Zhang W, et al: Multiplex PCR-based
next generation sequencing as a novel, targeted and accurate
molecular approach for periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis.
Front Microbiol. 14:11813482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hulten KG, Genta RM, Kalfus IN, Zhou Y,
Zhang H and Graham DY: Comparison of culture with antibiogram to
next-generation sequencing using bacterial isolates and
formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded gastric biopsies.
Gastroenterology. 161:1433–1442.e2. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ferreira I, Lepuschitz S, Beisken S, Fiume
G, Mrazek K, Frank BJH, Huber S, Knoll MA, von Haeseler A, Materna
A, et al: Culture-free detection of antibiotic resistance markers
from native patient samples by hybridization capture sequencing.
Microorganisms. 9:16722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Jouet A, Braet SM, Gaudin C, Bisch G,
Vasconcellos S, Epaminondas Nicacio de Oliveira do Livramento RE,
Prado Palacios YY, Fontes AB, Lucena N, Rosa P, et al: Hi-plex deep
amplicon sequencing for identification, high-resolution genotyping
and multidrug resistance prediction of Mycobacterium leprae
directly from patient biopsies by using deeplex Myc-Lep.
EBioMedicine. 93:1046492023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Jouet A, Gaudin C, Badalato N,
Allix-Béguec C, Duthoy S, Ferré A, Diels M, Laurent Y, Contreras S,
Feuerriegel S, et al: Deep amplicon sequencing for culture-free
prediction of susceptibility or resistance to 13 anti-tuberculous
drugs. Eur Respir J. 57:20023382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Cabibbe AM, Spitaleri A, Battaglia S,
Colman RE, Suresh A, Uplekar S, Rodwell TC and Cirillo DM:
Application of targeted next-generation sequencing assay on a
portable sequencing platform for culture-free detection of
drug-resistant tuberculosis from clinical samples. J Clin
Microbiol. 58:e00632–20. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Mesfin AB, Araia ZZ, Beyene HN, Mebrahtu
AH, Suud NN, Berhane YM, Hailu DT, Kassahun AZ, Auguet OT, Dean AS,
et al: First molecular-based anti-TB drug resistance survey in
Eritrea. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 25:43–51. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Mansoor H, Hirani N, Chavan V, Das M,
Sharma J, Bharati M, Oswal V, Iyer A, Morales M, Joshi A, et al:
Clinical utility of target-based next-generation sequencing for
drug-resistant TB. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 27:41–48. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Sibandze DB, Kay A, Dreyer V, Sikhondze W,
Dlamini Q, DiNardo A, Mtetwa G, Lukhele B, Vambe D, Lange C, et al:
Rapid molecular diagnostics of tuberculosis resistance by targeted
stool sequencing. Genome Med. 14:522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Kambli P, Ajbani K, Kazi M, Sadani M, Naik
S, Shetty A, Tornheim JA, Singh H and Rodrigues C: Targeted next
generation sequencing directly from sputum for comprehensive
genetic information on drug resistant Mycobacterium
tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 127:1020512021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wu X, Liang R, Xiao Y, Liu H, Zhang Y,
Jiang Y, Liu M, Tang J, Wang W, Li W, et al: Application of
targeted next generation sequencing technology in the diagnosis of
Mycobacterium tuberculosis and first line drugs resistance
directly from cell-free DNA of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J
Infect. 86:399–401. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Colman RE, Anderson J, Lemmer D, Lehmkuhl
E, Georghiou SB, Heaton H, Wiggins K, Gillece JD, Schupp JM,
Catanzaro DG, et al: Rapid drug susceptibility testing of
drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates directly
from clinical samples by use of amplicon sequencing: A
proof-of-concept study. J Clin Microbiol. 54:2058–2067. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Iyer A, Ndlovu Z, Sharma J, Mansoor H,
Bharati M, Kolan S, Morales M, Das M, Issakidis P, Ferlazzo G, et
al: Operationa-lising targeted next-generation sequencing for
routine diagnosis of drug-resistant TB. Public Health Action.
13:43–49. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Leung KS, Tam KK, Ng TT, Lao HY, Shek RC,
Ma OCK, Yu SH, Chen JX, Han Q, Siu GK and Yam WC: Clinical utility
of target amplicon sequencing test for rapid diagnosis of
drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis from respiratory
specimens. Front Microbiol. 13:9744282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Comín J, Viñuelas J, Lafoz C, Cebollada A,
Ibarz D, Iglesias MJ and Samper S: Rapid identification of lineage
and drug resistance in clinical samples of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis. Microorganisms. 11:14672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Zhang G, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Hu X, Tang M
and Gao Q: Targeted next-generation sequencing technology showed
great potential in identifying spinal tuberculosis and predicting
the drug resistance. J Infect. 87:e110–e112. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Murphy SG, Smith C, Lapierre P, Shea J,
Patel K, Halse TA, Dickinson M, Escuyer V, Rowlinson MC and Musser
KA: Direct detection of drug-resistant Mycobacterium
tuberculosis using targeted next generation sequencing. Front
Public Health. 11:12060562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Song J, Du W, Liu Z, Che J, Li K and Che
N: Application of amplicon-based targeted NGS technology for
diagnosis of drug-resistant tuberculosis using FFPE specimens.
Microbiol Spectr. 10:e01358212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Wilson MR, O'Donovan BD, Gelfand JM,
Sample HA, Chow FC, Betjemann JP, Shah MP, Richie MB, Gorman MP,
Hajj-Ali RA, et al: Chronic meningitis investigated via metagenomic
next-generation sequencing. JAMA Neurol. 75:947–955. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|