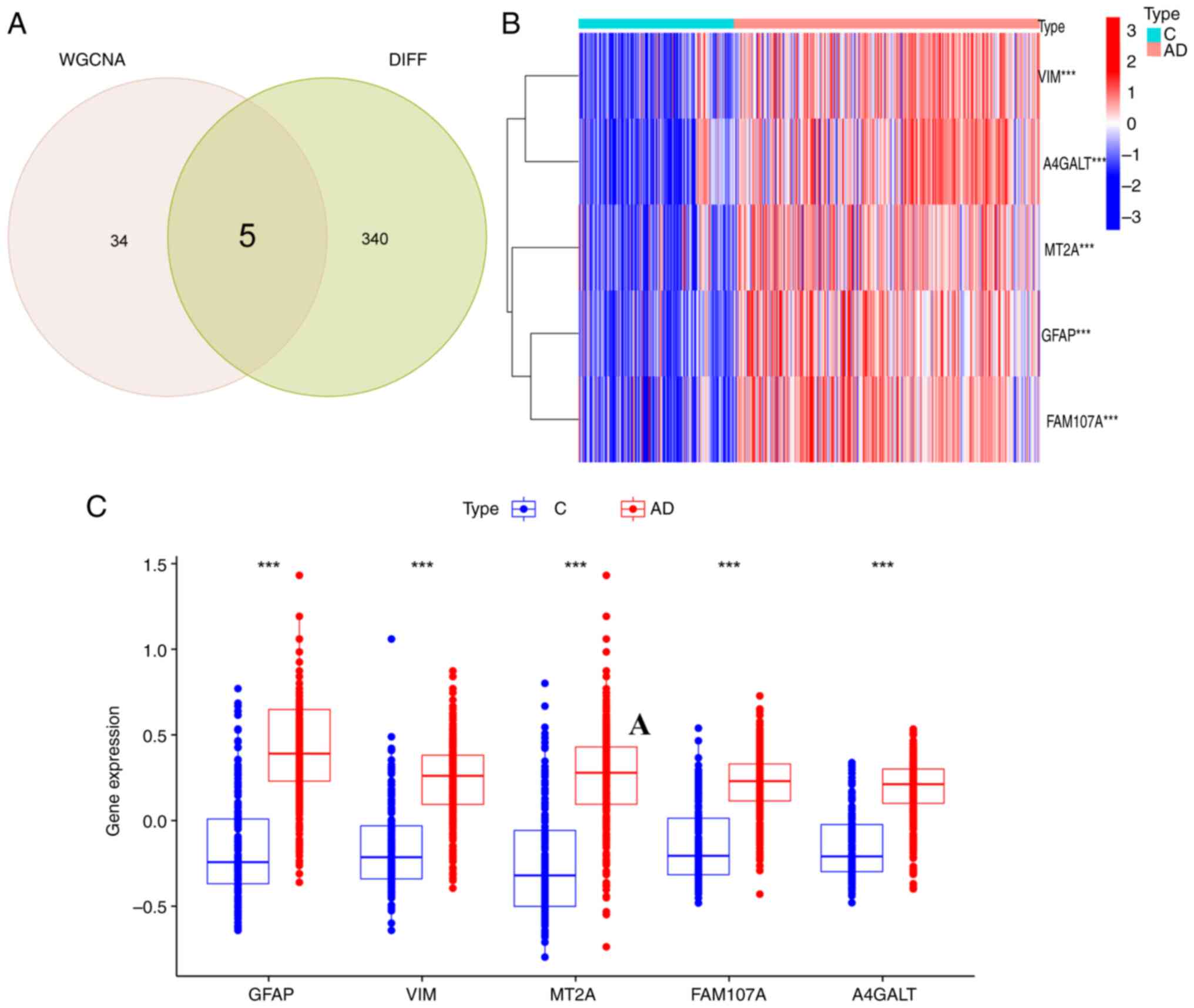
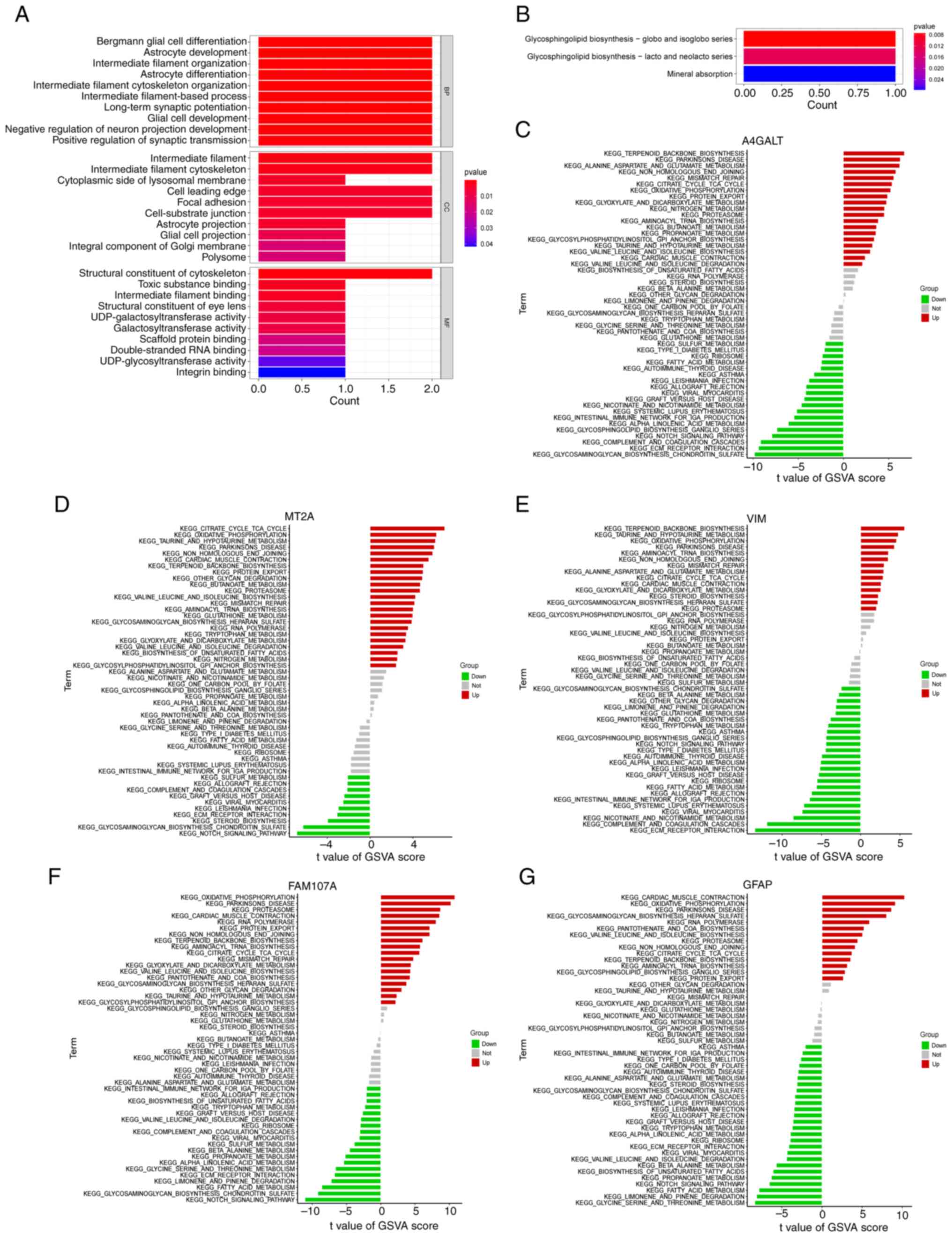
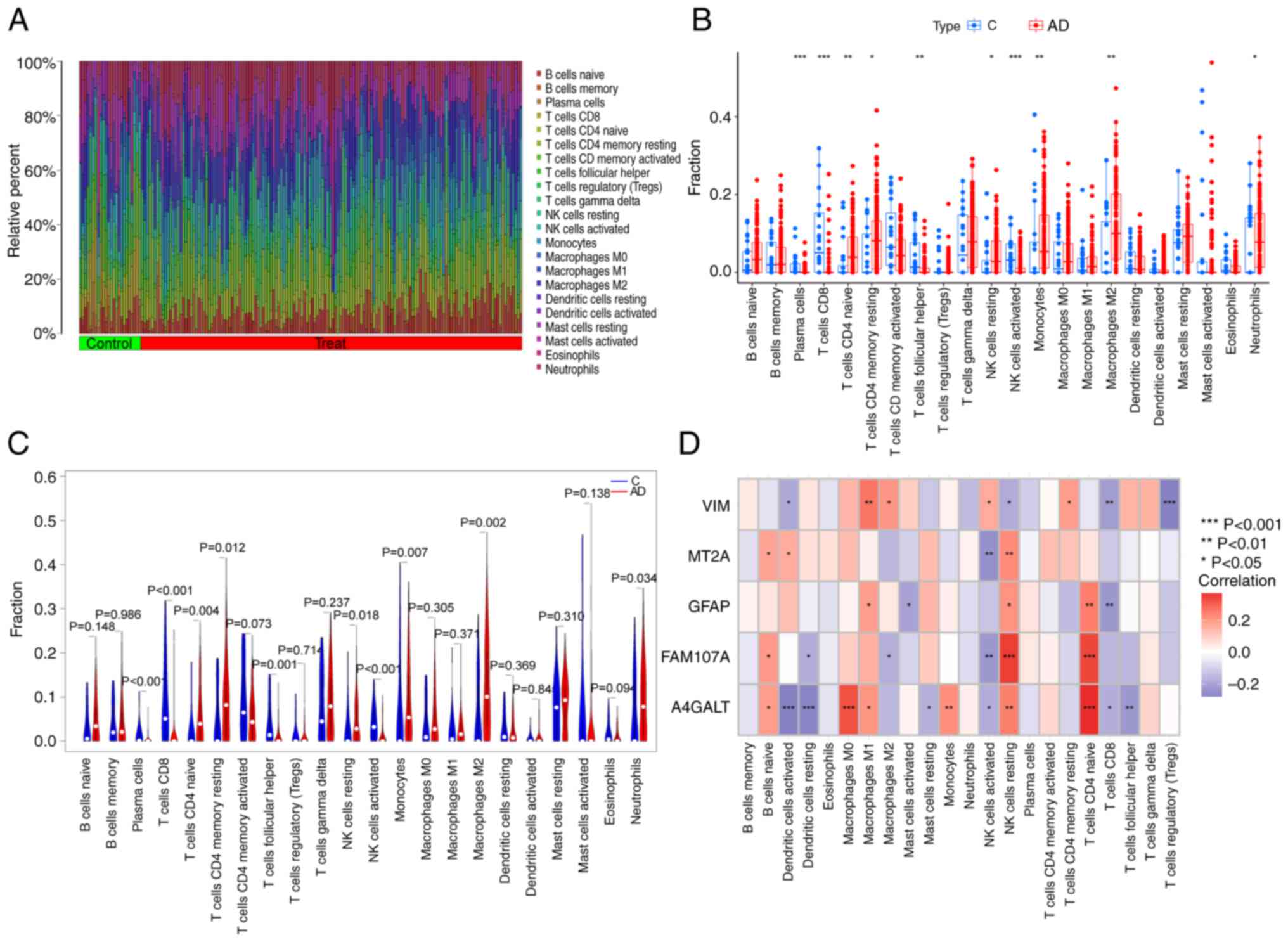
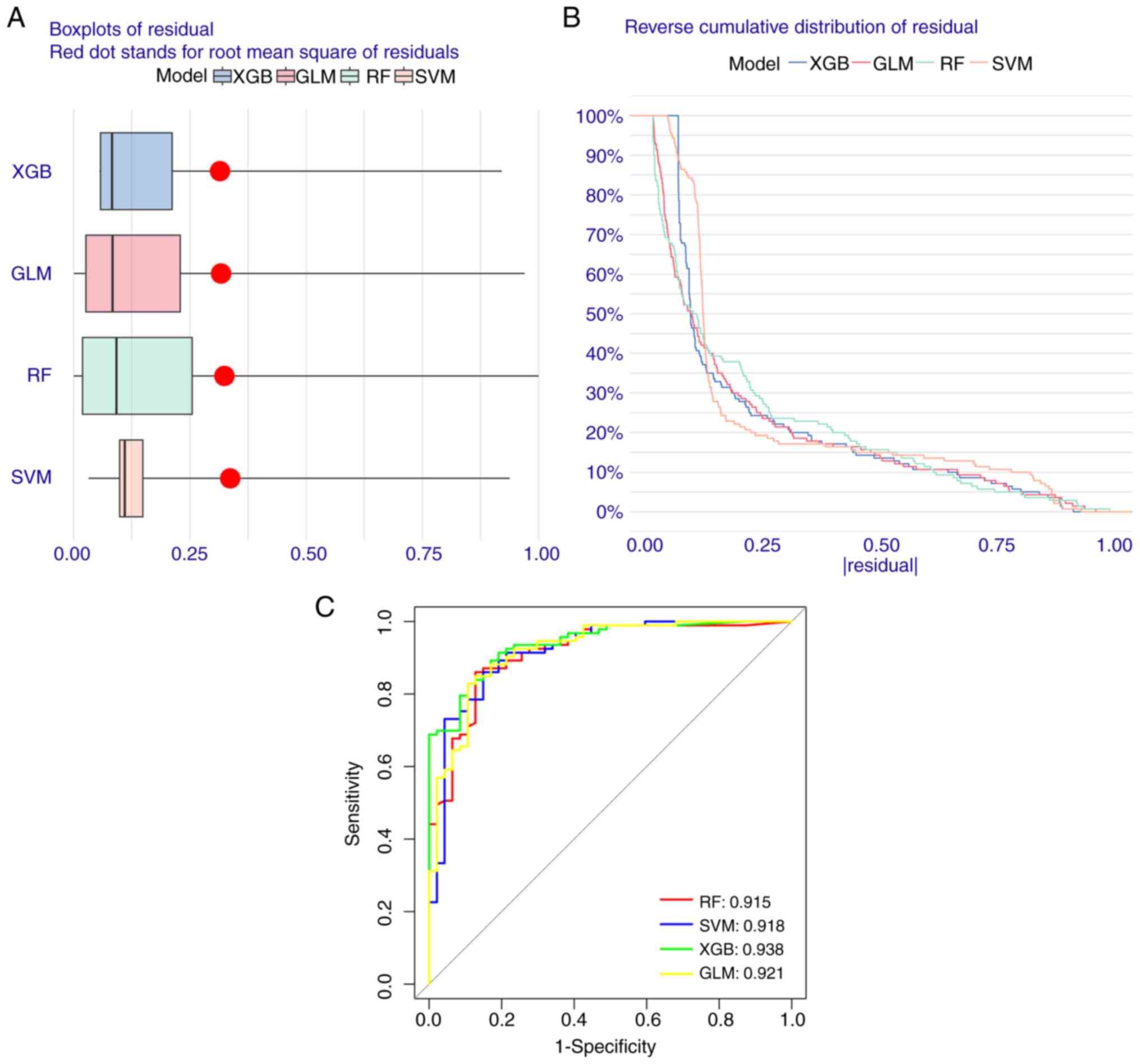
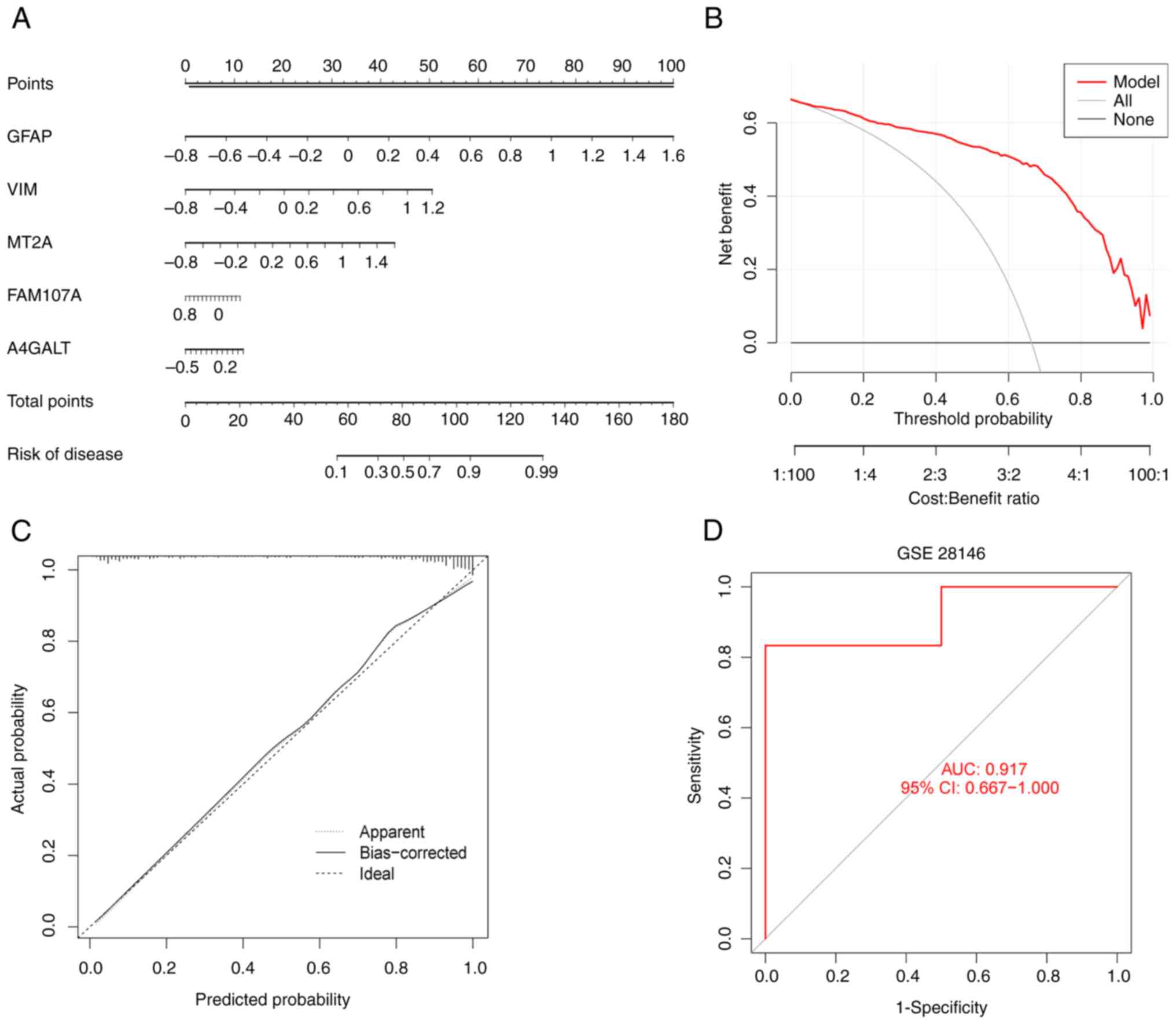
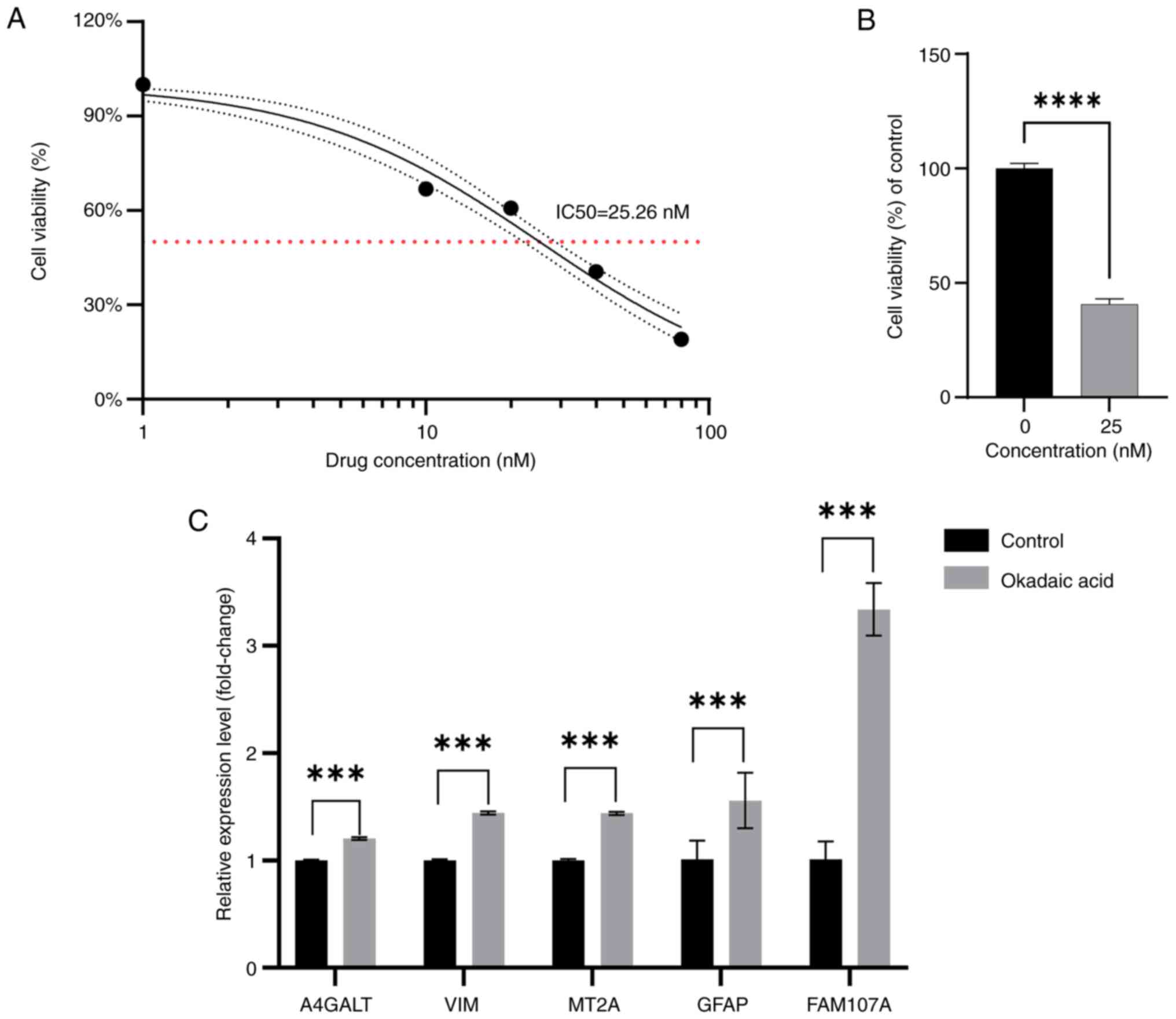
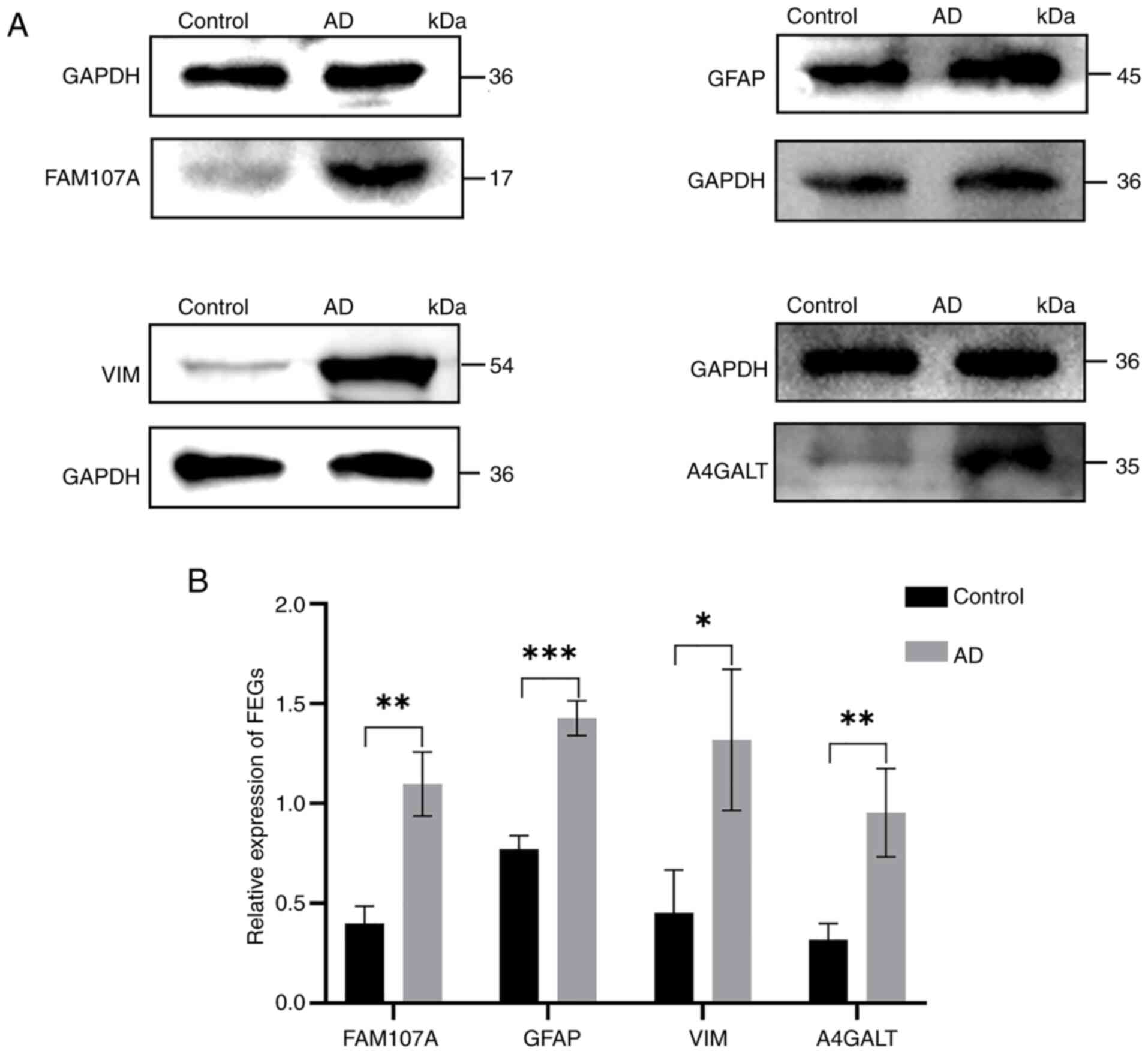
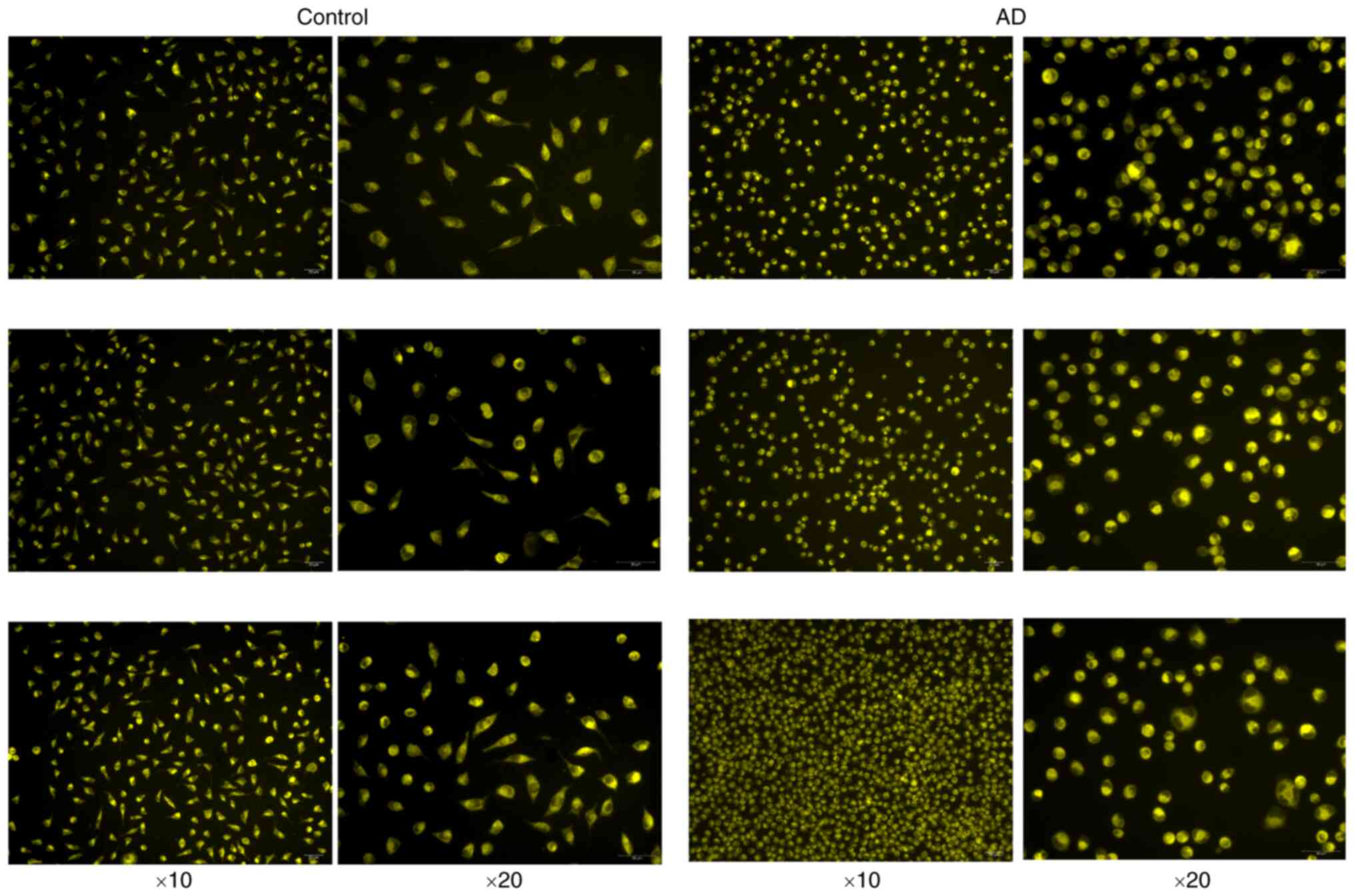
|
1
|
Yu Q and Zhong C: Membrane aging as the
real culprit of Alzheimer's disease: Modification of a hypothesis.
Neurosci Bull. 34:369–381. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Scheltens P, De Strooper B, Kivipelto M,
Holstege H, Chételat G, Teunissen CE, Cummings J and van der Flier
WM: Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 397:1577–1590. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lane CA, Hardy J and Schott JM:
Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurol. 25:59–70. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schneider AR and Sari Y: Therapeutic
perspectives of drugs targeting toll-like receptors based on immune
physiopathology theory of Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurol Disord
Drug Targets. 13:909–920. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Simard AR, Soulet D, Gowing G, Julien JP
and Rivest S: Bone marrow-derived microglia play a critical role in
restricting senile plaque formation in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron.
49:489–502. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman
BT, Jack CR Jr, Kawas CH, Klunk WE, Koroshetz WJ, Manly JJ, Mayeux
R, et al: The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease:
Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's
Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's
disease. Alzheimers Dement. 7:263–269. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fernández-Mendívil C, Arreola MA,
Hohsfield LA, Green KN and Lopez MG: Aging and progression of
beta-amyloid pathology in Alzheimer's disease correlates with
microglial heme-oxygenase-1 overexpression. Antioxidants (Basel).
9:6442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang XD, Liu ZY, Wang MS, Guo YX, Wang
XK, Luo K, Huang S and Li RF: Ferroptosis, iron metabolism, lipid
metabolism, Alzheimer ferroptosis. Front Immunol. 14:12694512023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir
H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK,
Kagan VE, et al: Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking
metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 171:273–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma H, Dong Y, Chu Y, Guo Y and Li L: The
mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in alzheimer's disease.
Front Mol Biosci. 9:9650642022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Smith MA, Zhu X, Tabaton M, Liu G, McKeel
DW Jr, Cohen ML, Wang X, Siedlak SL, Dwyer BE, Hayashi T, et al:
Increased iron and free radical generation in preclinical Alzheimer
disease and mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis.
19:363–372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shimohama S: Apoptosis in Alzheimer's
disease-an update. Apoptosis. 5:9–16. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nixon RA and Yang DS: Autophagy failure in
Alzheimer's disease-locating the primary defect. Neurobiol Dis.
43:38–45. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Caccamo A, Branca C, Piras IS, Ferreira E,
Huentelman MJ, Liang WS, Readhead B, Dudley JT, Spangenberg EE,
Green KN, et al: Necroptosis activation in Alzheimer's disease. Nat
Neurosci. 20:1236–1246. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tan MS, Tan L, Jiang T, Zhu XC, Wang HF,
Jia CD and Yu JT: Amyloid-β induces NLRP1-dependent neuronal
pyroptosis in models of Alzheimer's disease. Cell Death Dis.
5:e13822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang L and Nao J: Ferroptosis: A potential
therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. Rev Neurosci.
34:573–598. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Narayanan M, Huynh JL, Wang K, Yang X, Yoo
S, McElwee J, Zhang B, Zhang C, Lamb JR, Xie T, et al: Common
dysregulation network in the human prefrontal cortex underlies two
neurodegenerative diseases. ol Syst Biol. 10:7432014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Blalock EM, Buechel HM, Popovic J, Geddes
JW and Landfield PW: Microarray analyses of laser-captured
hippocampus reveal distinct gray and white matter signatures
associated with incipient Alzheimer's disease. J Chem Neuroanat.
42:118–126. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
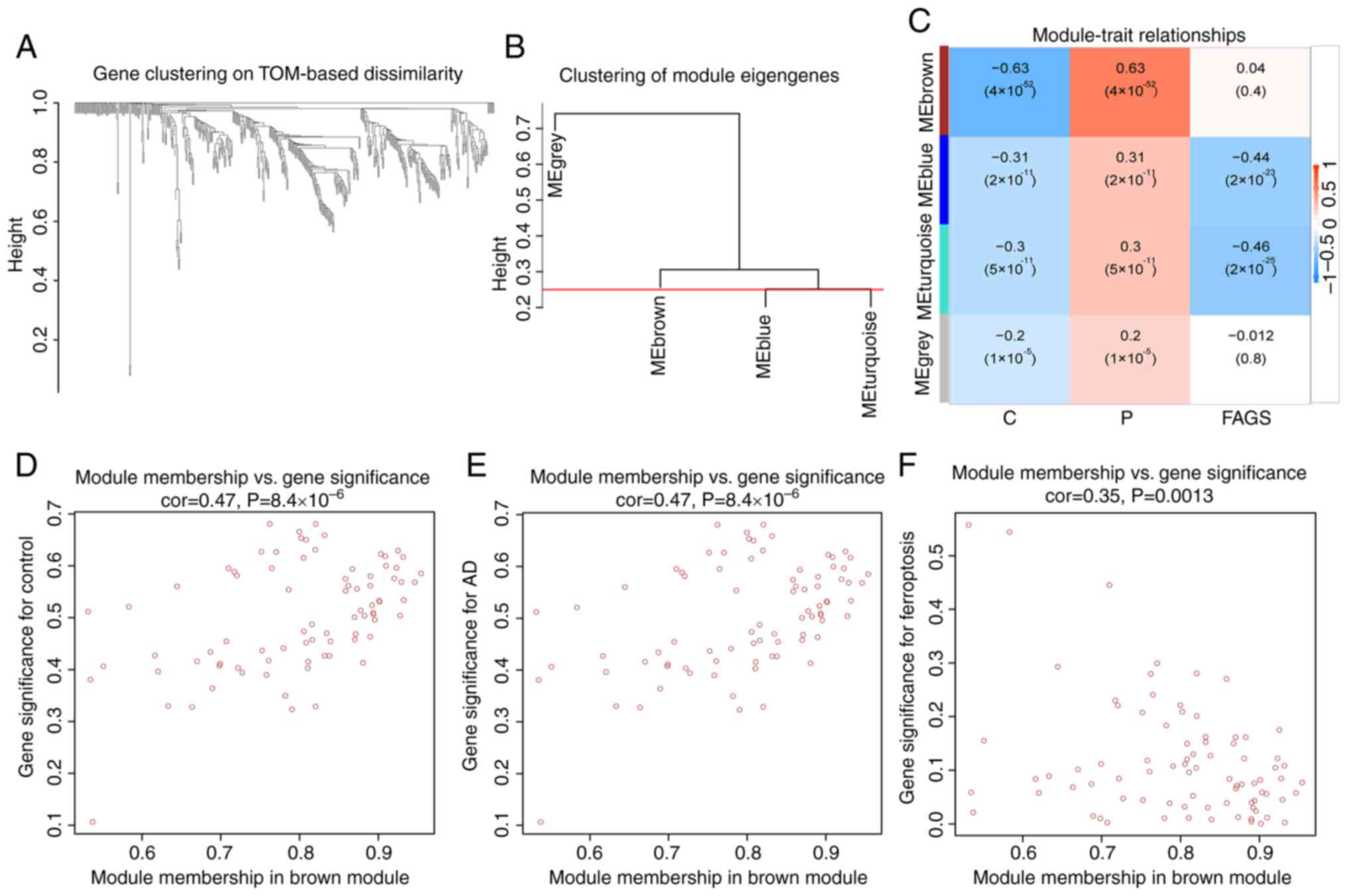
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ,
Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M and Alizadeh AA: Robust enumeration
of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods.
12:453–457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Amonruttanapun P, Chongthammakun S and
Chamniansawat S: The effects of okadaic acid-treated SH-SY5Y cells
on microglia activation and phagocytosis. Cell Biol Int.
46:234–242. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Medeiros LM, De Bastiani MA, Rico EP,
Schonhofen P, Pfaffenseller B, Wollenhaupt-Aguiar B, Grun L,
Barbé-Tuana F, Zimmer ER, Castro MAA, et al: Cholinergic
differentiation of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line and its
potential use as an in vitro model for Alzheimer's disease studies.
Mol Neurobiol. 56:7355–7367. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang F, Jia Y, Liu J, Zhai J, Cao N, Yue
W, He H and Pei X: Dental pulp stem cells promote regeneration of
damaged neuron cells on the cellular model of Alzheimer's disease.
Cell Biol Int. 41:639–650. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kamat PK, Rai S, Swarnkar S, Shukla R and
Nath C: Molecular and cellular mechanism of okadaic acid
(OKA)-induced neurotoxicity: A novel tool for Alzheimer's disease
therapeutic application. Mol Neurobiol. 50:852–865. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Maltsev DI, Aniol VA, Golden MA, Petrina
AD, Belousov VV, Gulyaeva NV and Podgorny OV: Aging modulates the
ability of quiescent radial glia-like stem cells in the hippocampal
dentate gyrus to be recruited into division by pro-neurogenic
stimuli. Mol Neurobiol. 61:3461–3476. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Singh D: Astrocytic and microglial cells
as the modulators of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. J
Neuroinflammation. 19:2062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Good PF, Perl DP, Bierer LM and Schmeidler
J: Selective accumulation of aluminum and iron in the
neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease: A laser microprobe
(LAMMA) study. Ann Neurol. 31:286–292. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ayton S, Wang Y, Diouf I, Schneider JA,
Brockman J, Morris MC and Bush AI: Brain iron is associated with
accelerated cognitive decline in people with Alzheimer pathology.
Mol Psychiatry. 25:2932–2941. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Derry PJ, Hegde ML, Jackson GR, Kayed R,
Tour JM, Tsai AL and Kent TA: Revisiting the intersection of
amyloid, pathologically modified tau and iron in Alzheimer's
disease from a ferroptosis perspective. Prog Neurobiol.
184:1017162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsatsanis A, McCorkindale AN, Wong BX,
Patrick E, Ryan TM, Evans RW, Bush AI, Sutherland GT,
Sivaprasadarao A, Guennewig B and Duce JA: The acute phase protein
lactoferrin is a key feature of Alzheimer's disease and predictor
of Aβ burden through induction of APP amyloidogenic processing. Mol
Psychiatry. 26:5516–5531. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mi Y, Gao X, Xu H, Cui Y, Zhang Y and Gou
X: The emerging roles of ferroptosis in Huntington's disease.
Neuromolecular Med. 21:110–119. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu J, Yang JJ, Cao Y, Li H, Zhao H, Yang S
and Li K: Iron overload contributes to general anaesthesia-induced
neurotoxicity and cognitive deficits. J Neuroinflammation.
17:1102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu Y, Liang S, Zhu H and Zhu Y: Analysis
of immune-related key genes in Alzheimer's disease. Bioengineered.
12:9610–9624. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chai JF, Raichur S, Khor IW, Torta F, Chew
WS, Herr DR, Ching J, Kovalik JP, Khoo CM, Wenk MR, et al:
Associations with metabolites in Chinese suggest new metabolic
roles in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Hum Mol Genet.
29:189–201. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Z and Tan L, Zong Y, Ma YH, Wang ZB;
Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, ; Wang HF and Tan L:
sTREM2 and GFAP mediated the association of IGF-1 signaling
biomarkers with Alzheimer's disease pathology. J Alzheimers Dis.
92:791–797. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun T, Zeng L, Cai Z, Liu Q, Li Z and Liu
R: Comprehensive analysis of dysregulated circular RNAs and
construction of a ceRNA network involved in the pathology of
Alzheimer's disease in a 5 × FAD mouse model. Front Aging Neurosci.
14:10206992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|