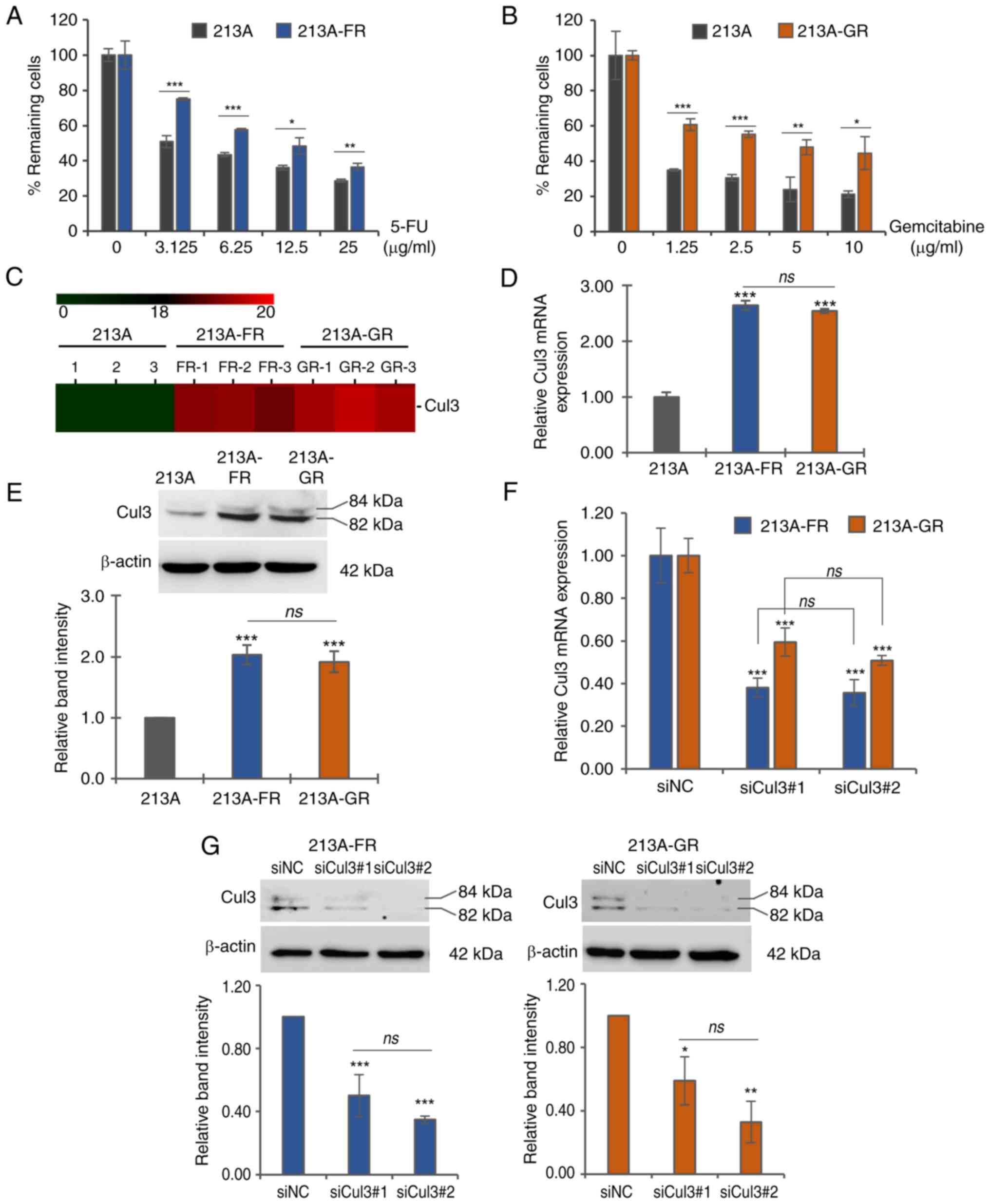
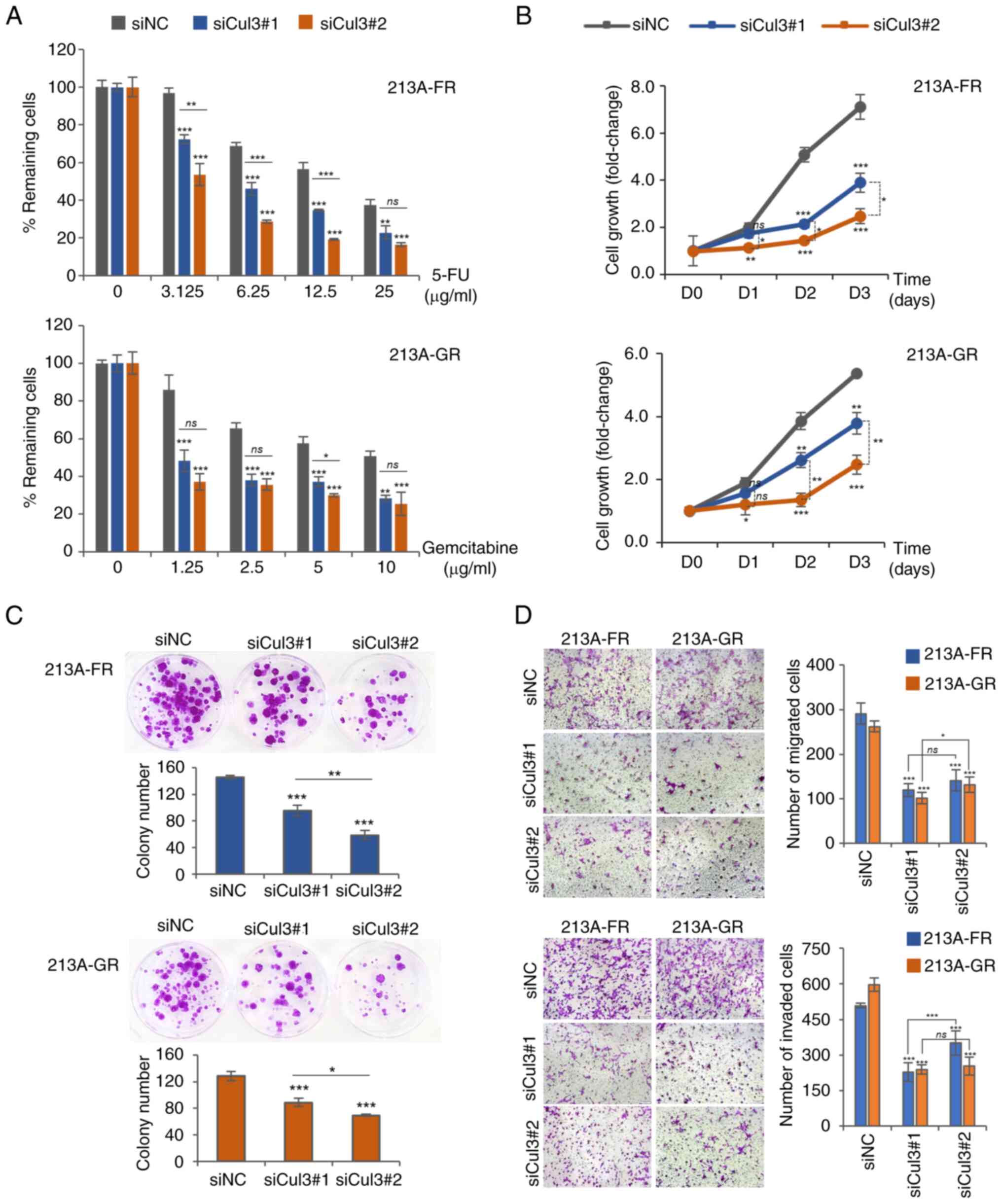
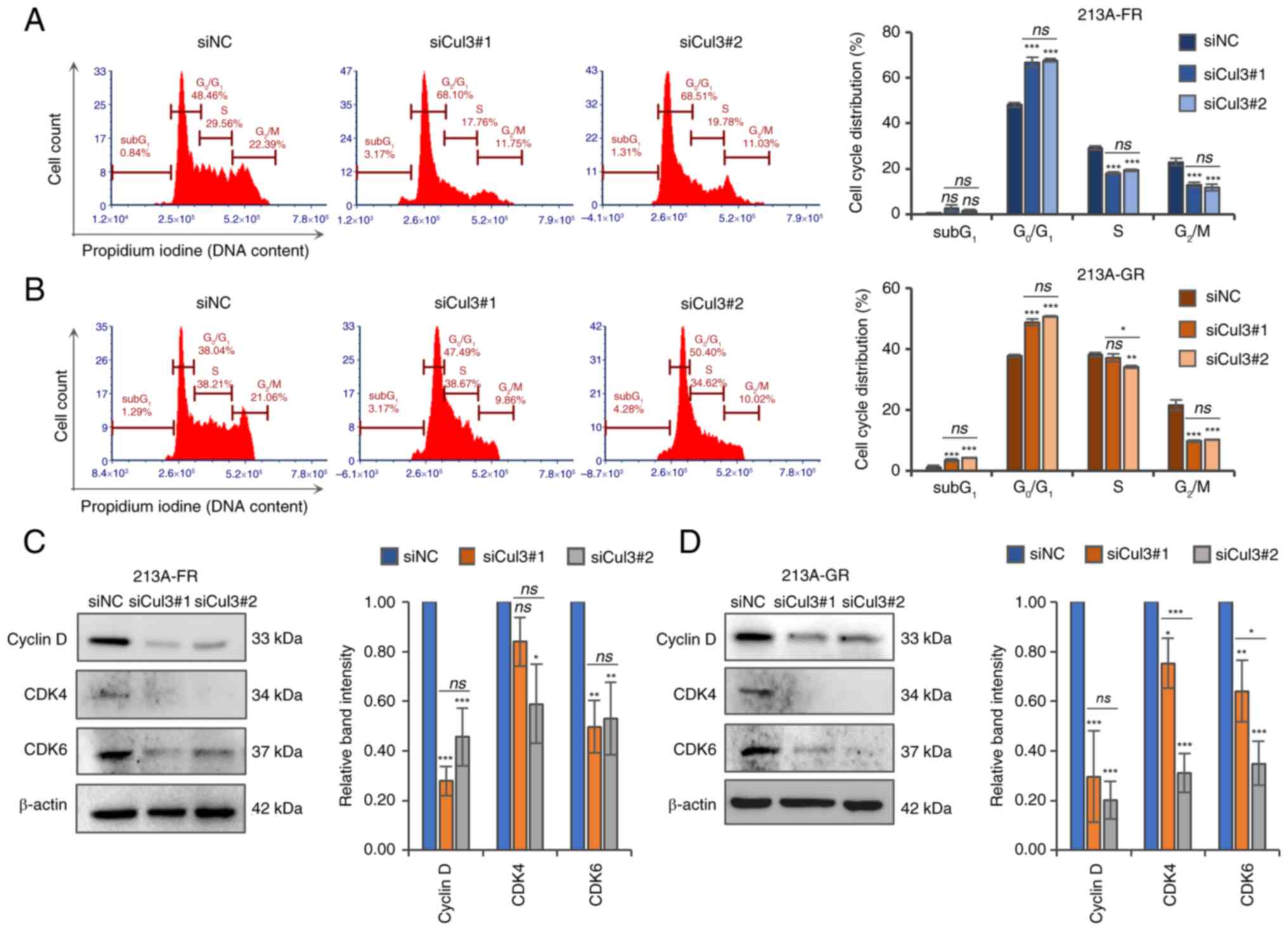
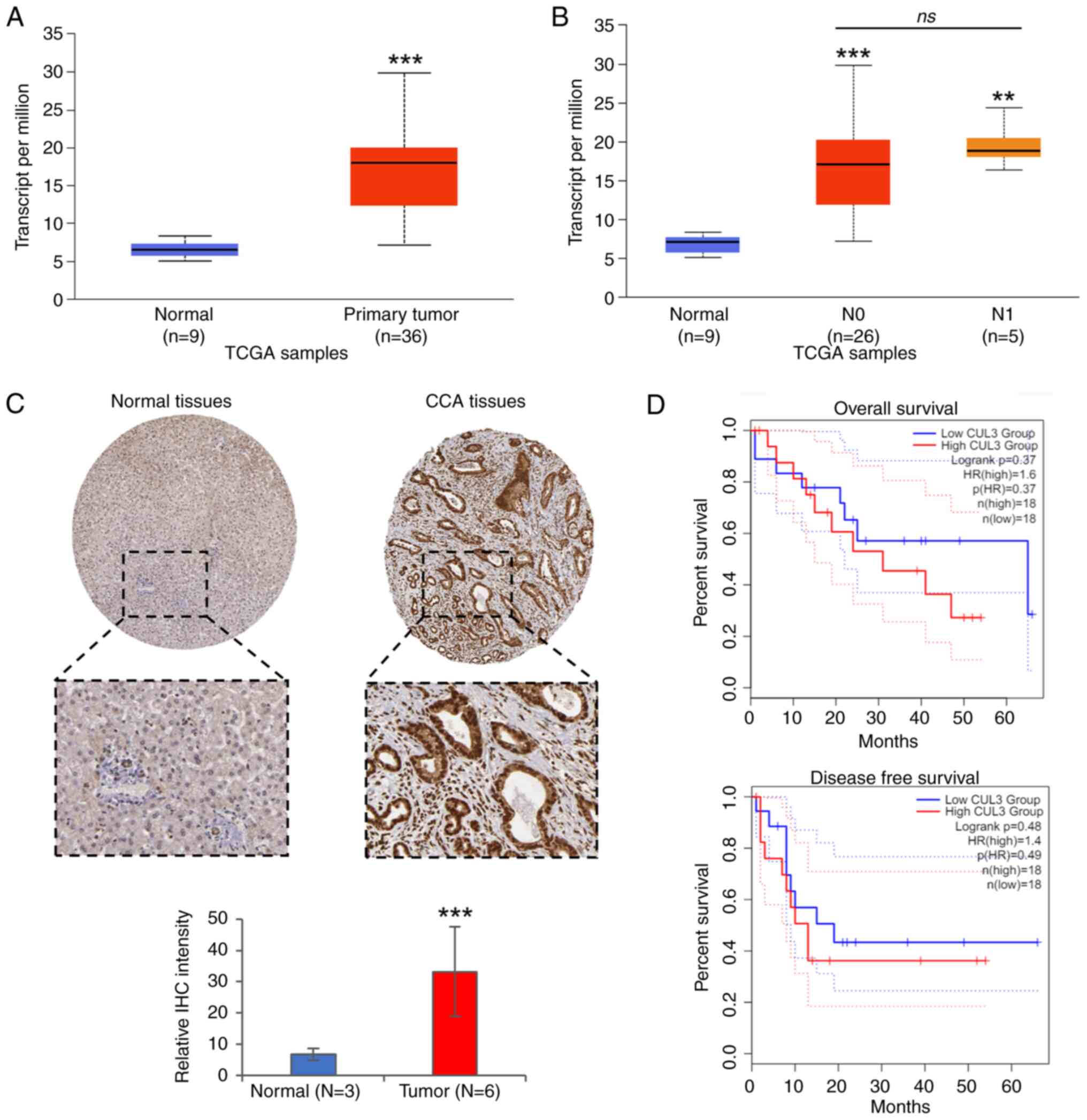
|
1
|
Kirstein MM and Vogel A: Epidemiology and
risk factors of cholangiocarcinoma. Visc Med. 32:395–400. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blechacz B: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current
knowledge and new developments. Gut Liver. 11:13–26. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kodali S, Connor AA, Brombosz EW and
Ghobrial RM: Update on the screening, diagnosis, and management of
cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 20:151–158.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bertuccio P, Malvezzi M, Carioli G, Hashim
D, Boffetta P, El-Serag HB, La Vecchia C and Negri E: Global trends
in mortality from intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
J Hepatol. 71:104–114. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Adeva J, Sangro B, Salati M, Edeline J, La
Casta A, Bittoni A, Berardi R, Bruix J and Valle JW: Medical
treatment for cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. 39 (Suppl
1):S123–S142. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rizvi S and Gores GJ: Pathogenesis,
diagnosis and management of cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology.
145:1215–1229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Neoptolemos JP, Moore MJ, Cox TF, Valle
JW, Palmer DH, McDonald AC, Carter R, Tebbutt NC, Dervenis C, Smith
D, et al: Effect of adjuvant chemotherapy with fluorouracil plus
folinic acid or gemcitabine vs observation on survival in patients
with resected periampullary adenocarcinoma: The ESPAC-3
periampullary cancer randomized trial. JAMA. 308:147–156. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okusaka T, Nakachi K, Fukutomi A, Mizuno
N, Ohkawa S, Funakoshi A, Nagino M, Kondo S, Nagaoka S, Funai J, et
al: Gemcitabine alone or in combination with cisplatin in patients
with biliary tract cancer: A comparative multicentre study in
Japan. Br J Cancer. 103:469–474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Valle J, Wasan H, Palmer DH, Cunningham D,
Anthoney A, Maraveyas A, Madhusudan S, Iveson T, Hughes S, Pereira
SP, et al: Cisplatin plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine for
biliary tract cancer. N Engl J Med. 362:1273–1281. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fouassier L, Marzioni M, Afonso MB, Dooley
S, Gaston K, Giannelli G, Rodrigues CMP, Lozano E, Mancarella S,
Segatto O, et al: Signalling networks in cholangiocarcinoma:
Molecular pathogenesis, targeted therapies and drug resistance.
Liver Int. 39:43–62. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sarikas A, Hartmann T and Pan ZQ: The
cullin protein family. Genome Biol. 12:2202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kamitani T, Kito K, Nguyen HP and Yeh ET:
Characterization of NEDD8, a developmentally down-regulated
ubiquitin-like protein. J Biol Chem. 272:28557–28562. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang S, Yu Q, Li Z, Zhao Y and Sun Y:
Protein neddylation and its role in health and diseases. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 9:852024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang P, Song J and Ye D: CRL3s: The
BTB-CUL3-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1217:211–223.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng J, Guo J, Wang Z, North BJ, Tao K,
Dai X and Wei W: Functional analysis of Cullin 3 E3 ligases in
tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1869:11–28. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim B, Nam HJ, Pyo KE, Jang MJ, Kim IS,
Kim D, Boo K, Lee SH, Yoon JB, Baek SH and Kim JH: Breast cancer
metastasis suppressor 1 (BRMS1) is destabilized by the Cul3-SPOP E3
ubiquitin ligase complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 415:720–726.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Grau L, Luque-Garcia JL, González-Peramato
P, Theodorescu D, Palou J, Fernandez-Gomez JM and Sánchez-Carbayo
M: A quantitative proteomic analysis uncovers the relevance of CUL3
in bladder cancer aggressiveness. PLoS One. 8:e533282013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yuan WC, Lee YR, Huang SF, Lin YM, Chen
TY, Chung HC, Tsai CH, Chen HY, Chiang CT, Lai CK, et al: A
Cullin3-KLHL20 ubiquitin ligase-dependent pathway targets PML to
potentiate HIF-1 signaling and prostate cancer progression. Cancer
Cell. 20:214–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou J, Zhang S, Xu Y, Ye W, Li Z, Chen Z
and He Z: Cullin 3 overexpression inhibits lung cancer metastasis
and is associated with survival of lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 37:115–124. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kerdkumthong K, Roytrakul S, Songsurin K,
Pratummanee K, Runsaeng P and Obchoei S: Proteomics and
bioinformatics identify drug-resistant-related genes with
prognostic potential in cholangiocarcinoma. Biomolecules.
14:9692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wattanawongdon W, Hahnvajanawong C, Namwat
N, Kanchanawat S, Boonmars T, Jearanaikoon P, Leelayuwat C,
Techasen A and Seubwai W: Establishment and characterization of
gemcitabine-resistant human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines with
multidrug resistance and enhanced invasiveness. Int J Oncol.
47:398–410. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kerdkumthong K, Chanket W, Runsaeng P,
Nanarong S, Songsurin K, Tantimetta P, Angsuthanasombat C,
Aroonkesorn A and Obchoei S: Two recombinant bacteriocins,
rhamnosin and lysostaphin, show synergistic anticancer activity
against gemcitabine-resistant cholangiocarcinoma cell lines.
Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 16:713–725. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Johansson C, Samskog J, Sundström L,
Wadensten H, Björkesten L and Flensburg J: Differential expression
analysis of Escherichia coli proteins using a novel software
for relative quantitation of LC-MS/MS data. Proteomics.
6:4475–4485. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thorsell A, Portelius E, Blennow K and
Westman-Brinkmalm A: Evaluation of sample fractionation using
micro-scale liquid-phase isoelectric focusing on mass spectrometric
identification and quantitation of proteins in a SILAC experiment.
Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 21:771–778. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chandrashekar DS, Karthikeyan SK, Korla
PK, Patel H, Shovon AR, Athar M, Netto GJ, Qin ZS, Kumar S, Manne
U, et al: UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis
platform. Neoplasia. 25:18–27. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang Z, Kang B, Li C, Chen T and Zhang Z:
GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling
and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:W556–W560. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pontén F, Jirström K and Uhlen M: The
Human Protein Atlas-a tool for pathology. J Pathol. 216:387–393.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC, Lyon D,
Kirsch R, Pyysalo S, Doncheva NT, Legeay M, Fang T, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks
and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement
sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 49:D605–D612. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mi H, Muruganujan A, Ebert D, Huang X and
Thomas PD: PANTHER version 14: More genomes, a new PANTHER GO-slim
and improvements in enrichment analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res.
47:D419–D426. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ge SX, Jung D and Yao R: ShinyGO: A
graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants.
Bioinform. 36:2628–2629. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bulatov E and Ciulli A: Targeting
Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases for drug discovery: Structure,
assembly and small-molecule modulation. Biochem J. 467:365–386.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen RH: Cullin 3 and its role in
tumorigenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1217:187–210. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Genschik P, Sumara I and Lechner E: The
emerging family of CULLIN3-RING ubiquitin ligases (CRL3s): Cellular
functions and disease implications. EMBO J. 32:2307–2320. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen HY and Chen RH: Cullin 3 ubiquitin
ligases in cancer biology: Functions and therapeutic implications.
Front Oncol. 6:1132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Haagenson KK, Tait L, Wang J, Shekhar MP,
Polin L, Chen W and Wu GS: Cullin-3 protein expression levels
correlate with breast cancer progression. Cancer Biol Ther.
13:1042–1046. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dong M, Qian M and Ruan Z: CUL3/SPOP
complex prevents immune escape and enhances chemotherapy
sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells through degradation of PD-L1
protein. J Immunother Cancer. 10:e0052702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dorr C, Janik C, Weg M, Been RA, Bader J,
Kang R, Ng B, Foran L, Landman SR, O'Sullivan MG, et al: Transposon
mutagenesis screen identifies potential lung cancer drivers and
CUL3 as a tumor suppressor. Mol Cancer Res. 13:1238–1247. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Feng Y, Zhao M, Wang L, Li L, Lei JH, Zhou
J, Chen J, Wu Y, Miao K and Deng CX: The heterogeneity of signaling
pathways and drug responses in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with
distinct genetic mutations. Cell Death Dis. 15:342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao M, Quan Y, Zeng J, Lyu X, Wang H, Lei
JH, Feng Y, Xu J, Chen Q, Sun H, et al: Cullin3 deficiency shapes
tumor microenvironment and promotes cholangiocarcinoma in
liver-specific Smad4/Pten mutant mice. Int J Biol Sci.
17:4176–4191. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li X, Yang KB, Chen W, Mai J, Wu XQ, Sun
T, Wu RY, Jiao L, Li DD, Ji J, et al: CUL3 (cullin 3)-mediated
ubiquitination and degradation of BECN1 (beclin 1) inhibit
autophagy and promote tumor progression. Autophagy. 17:4323–4340.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zeng R, Tan G, Li W and Ma Y: Increased
expression of cullin 3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and knockdown
inhibits proliferation and invasion. Oncol Res. 26:111–122. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Howley BV, Mohanty B, Dalton A, Grelet S,
Karam J, Dincman T and Howe PH: The ubiquitin E3 ligase ARIH1
regulates hnRNP E1 protein stability, EMT and breast cancer
progression. Oncogene. 41:1679–1690. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mao X, Gluck N, Chen B, Starokadomskyy P,
Li H, Maine GN and Burstein E: COMMD1 (copper metabolism MURR1
domain-containing protein 1) regulates Cullin RING ligases by
preventing CAND1 (Cullin-associated Nedd8-dissociated protein 1)
binding. J Biol Chem. 286:32355–32365. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu T, Peng X, Cheng Z, Gong X, Xing D,
Cheng W and Zhang M: COMMD3 expression affects angiogenesis through
the HIF1α/VEGF/NF-κB signaling pathway in
hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2022:16555022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huang W, Mei J, Liu YJ, Li JP, Zou X, Qian
XP and Zhang Y: An analysis regarding the association between
proteasome (PSM) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J Hepatocell
Carcinoma. 10:497–515. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sun L, Wu C, Ming J, Guo E, Zhang W, Li L
and Hu G: EGLN1 induces tumorigenesis and radioresistance in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma by promoting ubiquitination of p53 in a
hydroxylase-dependent manner. J Cancer. 13:2061–2073. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gulliver C, Hoffmann R and Baillie G: The
enigmatic helicase DHX9 and its association with the hallmarks of
cancer. Future Sci OA. 7:FSO6502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bielli P, Pagliarini V, Pieraccioli M,
Caggiano C and Sette C: Splicing dysregulation as oncogenic driver
and passenger factor in brain tumors. Cells. 9:102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mi H, Muruganujan A, Casagrande JT and
Thomas PD: Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER
classification system. Nat Protoc. 8:1551–1566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Thomas PD: The Gene Ontology and the
meaning of biological function. Methods Mol Biol. 1446:15–24. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Esteve-Puig R, Bueno-Costa A and Esteller
M: Writers, readers and erasers of RNA modifications in cancer.
Cancer lett. 474:127–137. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hu H, Hu W, Guo AD, Zhai L, Ma S, Nie HJ,
Zhou BS, Liu T, Jia X, Liu X, et al: Spatiotemporal and direct
capturing global substrates of lysine-modifying enzymes in living
cells. Nat Commun. 15:14652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wilkinson E, Cui YH and He YY:
Context-dependent roles of RNA modifications in stress responses
and diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 22:19492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|