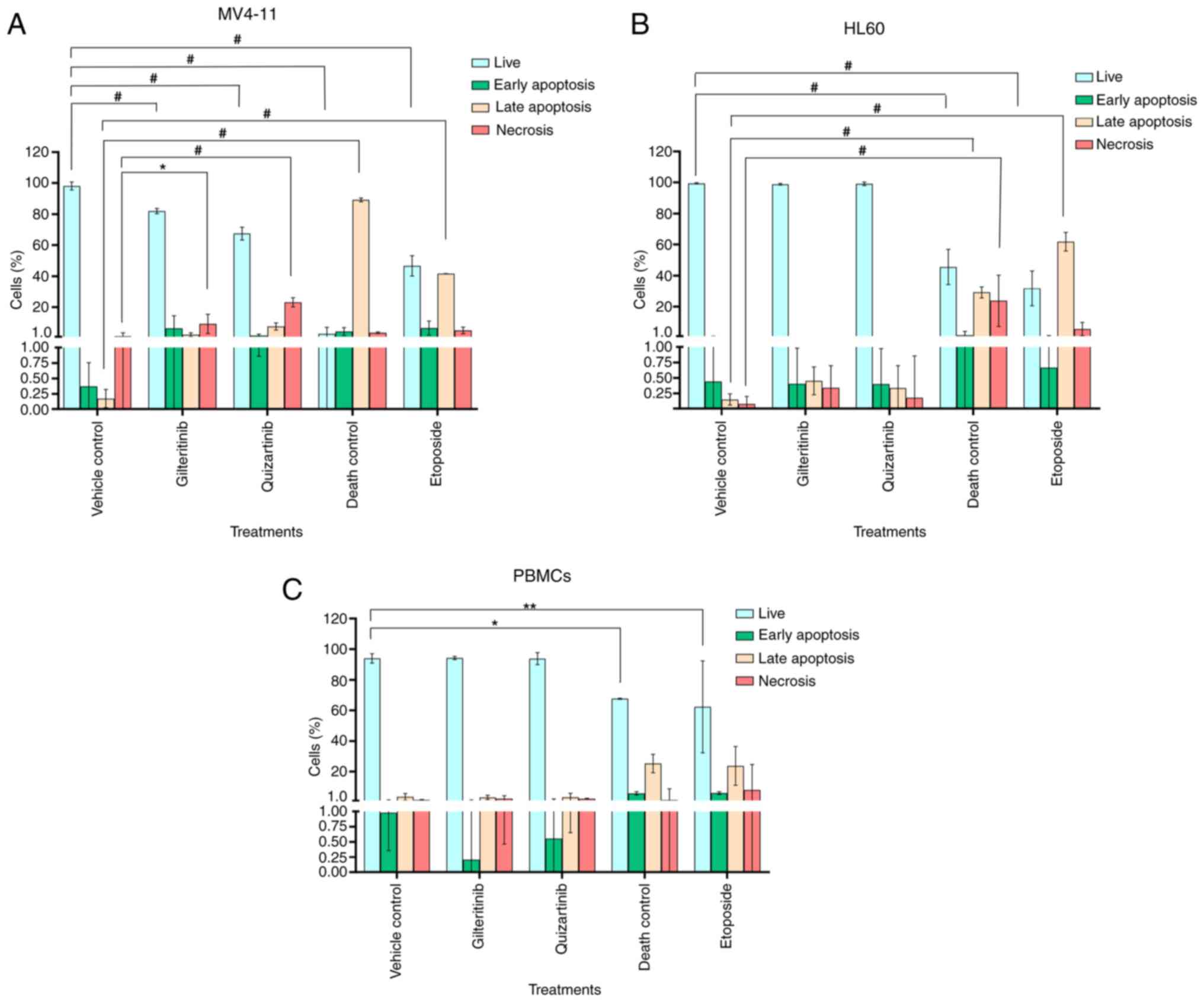
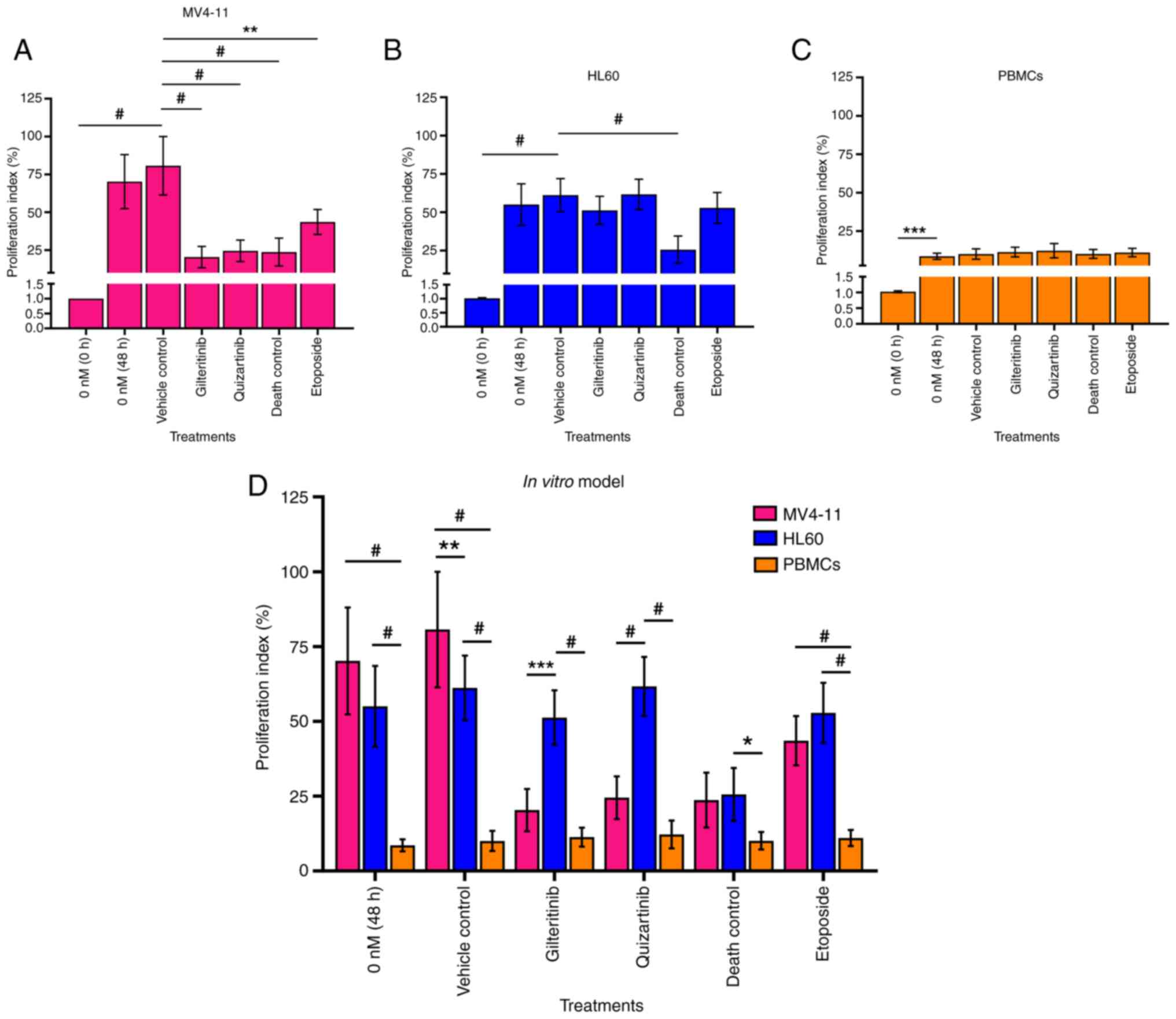
|
1
|
Shimony S, Stahl M and Stone RM: Acute
myeloid leukemia: 2023 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification,
and management. Am J Hematol. 98:502–526. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Laversanne M,
Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I and Bray F:
Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. International agency for
research on cancer; Lyon: 2024, Available from:. https://gco.iarc.who.int/today06–May. 2024
|
|
3
|
Gokhale P, Chauhan APS, Arora A, Khandekar
N, Nayarisseri A and Singh SK: FLT3 inhibitor design using
molecular docking based virtual screening for acute myeloid
leukemia. Bioinformation. 15:104–115. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Azizidoost S, Babashah S, Rahim F,
Shahjahani M and Saki N: Bone marrow neoplastic niche in leukemia.
Hematology. 19:232–238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ding L, Ley T, Larson D, Miller C, Koboldt
D, Welch J, Ritchey J, Young M, Lamprecht T, McLellan M, et al:
Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by
whole-genome sequencing. Nature. 481:506–510. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Santoyo-Sánchez A, Ramos-Peñafiel CO,
Saavedra-González A, González-Almanza L, Martínez-Tovar A,
Olarte-Carrillo I and Collazo-Jaloma J: The age and sex frequencies
of patients with leukemia seen in two reference centers in the
metropolitan area of Mexico City. Gac Med Mex. 152:186–189.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gilliland D and Griffin J: The roles of
FLT3 in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Blood. 100:1532–1542. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lagunas-Rangel FA and Chávez-Valencia V:
FLT3-ITD and its current role in acute myeloid leukaemia. Med
Oncol. 34:1142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Arber D, Orazi A, Hasserjia R, Thiele J,
Borowitz M, Beau M, Bloomfield C, Cazzola M and Vardiman J: The
2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of
myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 127:2391–2405. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kazi J and Rönnstrand L: FMS-like tyrosine
kinase 3/FLT3: From basic science to clinical implications. Physiol
Rev. 99:1433–1466. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fernández S, Desplat V, Villacreces A,
Guitart A, Milpied N, Rigneux A, Vigo I, Pasquet J and Dumas P:
Targeting tyrosine kinases in acute myeloid leukemia: Why, who and
how? Int J Mol Sci. 20:34292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Marensi V, Keeshan KR and MacEwan DJ:
Pharmacological impact of FLT3 mutations on receptor activity and
responsiveness to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol.
183:1143482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ke YY, Singh VK, Coumar MS, Hsu YC, Wang
WC, Song JS, Chen CH, Lin WH, Wu SH, Hsu JT, et al: Homology
modeling if DFG-in FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) and
structure-based virtual screening for inhibitor identification. Sci
Rep. 5:117022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peng YH, Shiao HY, Tu CH, Liu PM, Hsu JT,
Amancha PK, Wu JS, Coumar MS, Chen CH, Wang SY, et al: Protein
kinase inhibitor design by targeting the Asp-Phe-Gly (DFG) motif:
The role of the DFG motif in the design of epidermal growth factor
receptor inhibitors. J Med Chem. 56:3889–3903. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mashkani B, Tanipour MH, Saadatmandzadeh
M, Ashman LK and Griffith R: FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3)
inhibitors: Molecular docking and experimental studies. Eur J
Pharmacol. 776:156–166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fabbro D, Cowan-Jacob SW and Moebitz H:
Ten things you should know about protein kinases: IUPHAR review 14.
Br J Pharmacol. 172:2675–2700. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ung PM and Schlessinger A: DFGmodel:
Predicting protein kinase structures in inactive states for
structure-based discovery of type-II inhibitors. ACS Chem Biol.
10:269–278. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vijayan RS, He P, Modi V, Duong-Ly KC, Ma
H, Peterson JR, Dunbrack RL and Levy RM: Conformational analysis of
the DFG-out kinase motif and biochemical profiling of structurally
validated type II inhibitors. Med Chem. 58:466–479. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Uras I, Maurer B, Nebenfuehr S, Zujer M,
Valent P and Sexl V: Therapeutic vulnerabilities in FLT3-mutant AML
unmasked by Palbociclib. Int J Mol Sci. 19:39872018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rücker FG, Du L, Luck TJ, Benner A,
Krzykalla J, Gathmann I, Voso MT, Amadori S, Prior TW, Brandwein
JM, et al: Molecular landscape and prognostic impact of FLT3-ITD
insertion site in acute myeloid leukemia: RATIFY study results.
Leukemia. 36:90–99. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bohl SR, Bullinger L and Rücker FG: New
targeted agents in acute myeloid leukemia: New hope on the rise.
Int J Mol Sci. 20:19832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kayser S, Schlenk RF, Londono MC,
Breitenbuecher F, Wittke K, Du J, Groner S, Späth D, Krauter J,
Ganser A, et al: Insertion of FLT3 internal tandem duplication in
the tyrosine kinase domain-1 is associated with resistance to
chemotherapy and inferior outcome. Blood. 114:2386–2392. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sexauer A and Tasian S: Targeting FLT3
signaling in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Front pediatr.
5:2482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Daver N, Schlenk RF, Russell NH and Levis
MJ: Targeting FLT3 mutations in AML: review of current knowledge
and evidence. Leukemia. 33:299–312. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mori M, Kaneko N, Ueno Y, Yamada M, Tanaka
R, Saito R, Shimada I, Mori K and Kuromitsu S: Gilteritinib, a
FLT3/AXL inhibitor, shows antileukemic activity in mouse models of
FLT3 mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Invest New Drugs. 35:556–565.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Loschi M, Sammut R, Chiche E and Cluzeau
T: FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of fit and
unfit patients with FLT3-mutated AML: A systematic review. Int J
Mol Sci. 11:58732021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sun J, Hu R, Han M, Tan Y, Xie M, Gao S
and Hu JF: Mechanisms underlying therapeutic resistance of tyrosine
kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Int J Biol Sci.
1:175–181. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Barton GJ: Protein sequence alignment
techniques. Acta Crystallogr D Biol. 54:1139–1146. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Contreras-Moreira B, Fitzjohn P and Bates
P: Comparative modelling: And essential methodology for protein
structure prediction in the post-genomic era. Appl Bioinformatics.
1:177–190. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saxena A, Sangwan RS and Mishra S:
Fundamentals of homology modeling steps and comparison among
important bioinformatics tools: An overview. Sci Int. 1:237–252.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Meng XY, Zhang HX, Mezei M and Cui M:
Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug
discovery. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 7:146–157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Quentmeier H, Reinhardt J, Zaborski M and
Drexler HG: FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines.
Leukemia. 17:120–124. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu B, Zhao Y, Wang X, Gong P and Ge W:
MZH29 is a novel potent inhibitor that overcomes drug resistance
FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 31:913–921.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kawase T, Nakazawa T, Eguchi T, Tsuzuki H,
Ueno Y, Amano Y, Suzuki T, Mori M and Yoshida T: Effect of Fms-like
tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) ligand (FL) on antitumor activity of
gilteritinib, a FLT3 inhibitor, in mice xenografted with
FL-overexpressing cells. Oncotarget. 101:6111–6123. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Akwata D, Kempen AL and Sintim HO:
Identification of a selective FLT3 inhibitor with low activity
against VEGFR, FGFR, PDGFR, c-KIT, and RET anti-targets.
ChemMedChem. 19:e2023004422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zorn JA, Wang Q, Fujimura E, Barros T and
Kuriyan J: Crystal structure of the FLT3 kinase domain bound to the
inhibitor Quizartinib (AC220). PLoS One. 10:e01211772015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Todde G and Friedman R: Conformational
modifications induced by internal tandem duplication on the FLT3
kinase and juxtamembrane domains. Phys Chem Chem Phys.
21:18467–18476. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Griffith J, Black J, Faerman C, Swenson L,
Wynn M, Lu F, Lippke J and Kumkum Saxena K: The structural basis
for autoinhibition of FLT3 by the juxtamembrane domain. Mol Cell.
13:169–178. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Thomas C: Crystal structure of the FLT3
kinase bound to a small molecule inhibitor. 2018.Available from:.
https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb6il3/pdb
|
|
40
|
Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer
G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, de Beer TAP, Rempfer C,
Bordoli L, et al: SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein
structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:W296–W303. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW
and Lipman DJ: Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol.
215:403–410. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mol CD, Lim KB, Sridhar V, Zou H, Chien
EY, Sang BC, Nowakowski J, Kassel DB, Cronin CN and McRee DE:
Structure of a c-kit product complex reveals the basis for kinase
transactivation. JBC. 278:31461–31464. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Thompson JD, Higgins DG and Gibson TJ:
CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple
sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific
gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res.
22:4673–4680. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Reiter K, Polzer H, Krupka C, Maiser A,
Vick B, Rothenberg-Thurley M, Metzeler KH, Dörfel D, Salih HR, Jung
G, et al: Tyrosine kinase inhibition increases the cell surface
localization of FLT3-ITD and enhances FLT3-directed immunotherapy
of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 32:313–322. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Webb B and Sali A: Comparative protein
structure modeling using modeller. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics.
54:5.6.1–5.6.37. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pettersen E, Goddard T, Huang C, Couch G,
Greenblatt D, Meng E and Ferriny T: UCSF chimera visualization
system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem.
25:1605–1612. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shen MY and Sali A: Statistical potential
for assessment and prediction of protein structures. Protein Sci.
15:2507–2524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bhattacharya D, Nowotny J, Cao R and Cheng
J: 3Drefine: An interactive web server for efficient protein
structure refinement. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:W406–W409. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Colvos C and Yeates T: Verification of
protein structures: Patterns of nonbonded atomic interactions.
Protein Sci. 2:1511–1519. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Eisenberg D, Luthy R and Bowie J:
VERIFY3D: Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional
profiles. Methods Enzymol. 277:396–404. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Laskowski R, Moss D and Thornton J:
Main-chain bond length and bond angles in protein structures. J Mol
Biol. 231:1049–1067. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Benkert P, Biasini M and Schwede T: Toward
the estimation of the absolute quality of individual protein
structure models. Bioinformatics. 27:343–350. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Williams CJ, Headd JJ, Moriarty NW,
Prisant MG, Videau LL, Deis LN, Verma V, Keedy DA, Hintze BJ, Chen
VB, et al: MolProbity: More and better reference data for improved
all-atom structure validation. Protein Sci. 27:293–315. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wiederstein M and Sippl M: ProSA-web:
Interactive web service for the recognition of errors in
three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res.
35:W407–W410. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cristobal S, Zemla A, Fischer D,
Rychlewski L and Elofsson A: A study of quality measures for
protein threading models. BMC Bioinformatics. 2:52001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Morris G, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner M,
Belew R, Goodsell D and Olson A: AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4:
Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput
Chem. 30:2785–2791. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Irwin J and Shoichet B: ZINC-A Free
database of commercially available compounds for virtual screening.
J Chem Inf Model. 45:177–182. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Goodsell D, Morris G and Olson A:
Automated docking of flexible ligands: Applications of autodock.
JMR. 9:1–5. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Trott O and Olson A: AutoDock Vina:
Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring
function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput
Chem. 31:455–461. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Schrödinger L and DeLano W: PyMOL.
2020.Available from:. http://www.pymol.org/pymol
|
|
61
|
Den Dunnen JT, Dalgleish R, Maglott DR,
Hart RK, Greenblatt MS, McGowan-Jordan J, Roux AF, Smith T,
Antonarakis SE and Taschner PEM: HGVS recommendations for the
description of sequence variants: 2016 update. Hum Mutat.
37:564–569. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Schiffer CA and Stone RM: Morphologic
Classification and Clinical and Laboratory Correlates. Holland-Frei
Cancer Medicine. Kufe DW, Pollock RE, Weichselbaum RR, et al: 6th
edition. BC Decker; Hamilton, ON: 2003, Available from:. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK13452/
|
|
63
|
Skopek R, Palusińsk M, Kaczor-Keller K,
Pingwara R, Papierniak-Wyglądała A, Schenk T, Lewicki S, Zelent A
and Szymański Ł: Choosing the right cell line for acute myeloid
leukemia (AML) research. Int J Mol Sci. 24:53772023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sambrook J and Russell DW: Molecular
Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 1. 3rd edition. Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory Press; New York, NY: 2001
|
|
65
|
Huang Y, Hu J, Lu T, Luo Y, Shi J, Wu W,
Han X, Zheng W, He J, Cai Z, et al: Acute myeloid leukemia patient
with FLT3-ITD and NPM1 double mutation should undergo allogeneic
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in CR1 for better
prognosis. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 11:4129–4142. 2019.
|
|
66
|
FlowJo™ Software (Windows) [software
application] Version 10.6.2. Becton-Dickinson and Company; Ashland,
OR: 2023
|
|
67
|
Pulte ED, Norsworthy KJ, Wang Y, Xu Q,
Qosa H, Gudi R, Przepiorka D, Fu W, Okusanya OO, Goldberg KB, et
al: FDA approval summary: Gilteritinib for relapsed or refractory
acute myeloid leukemia with a FLT3 mutation. Clin Cancer Re.
27:3515–3521. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Erba HP, Montesinos P, Kim HJ, Patkowska
E, Vrhovac R, Žák P, Wang PN, Mitov T, Hanyok J, Kamel YM, et al:
Quizartinib plus chemotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with
FLT3-internal-tandem-duplication-positive acute myeloid leukaemia
(QuANTUM-First): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
phase 3 trial. Lancet Glob Health. 401:1571–1583. 2023.
|
|
69
|
Hu X, Cai J, Zhu J, Lang W, Zhong J, Zhong
H and Chen F: Arsenic trioxide potentiates Gilteritinib-induced
apoptosis in FLT3-ITD positive leukemic cells via
IRE1a-JNK-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer Cell Int.
20:2502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
James AJ, Smith CC, Litzow M, Perl AE,
Altman JK, Shepard D, Kadokura T, Souda K, Patton M, Lu Z, et al:
Pharmacokinetic profile of Gilteritinib: A novel FLT-3 tyrosine
kinase inhibitor. Clin Pharmacokinet. 59:1273–1290. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Li J, Trone D, Mendell J, O'Donnel P and
Cook N: A drug-drug interaction study to assess the potential
effect of acid-reducing agent, lansoprazole, on quizartinib
pharmacokinetics. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 84:799–807. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Motulsky H and Christopoulos A: Fitting
models to biological data using linear and nonlinear regression.
Oxford Press; Oxford, UK: in press; pp. 211–316. 2004
|
|
73
|
RStudio Team: RStudio: Integrated
Development for R. RStudio. PBC; Boston, MA: 2020, Available from:.
http://www.rstudio.com/
|
|
74
|
Jilani I, Estey E, Manshuri T, Caligiuri
M, Keating M, Giles F, Thomas D, Kantarjian H and Albitar M: Better
detection of FLT3 internal tandem duplication using peripheral
blood plasma DNA. Leukemia. 17:114–119. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Razumovskaya E, Masson K, Khan R,
Bengtsson S and Rönnstrand L: Oncogenic Flt3 receptors display
different specificity and kinetics of autophosphorylation. Exp
Hematol. 37:979–989. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Friedman R: The molecular mechanisms
behind activation of FLT3 in acute myeloid leukemia and resistance
to therapy by selective inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev
Cancer. 1877:1886662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Patnaik MM: The importance of FLT3
mutational analysis in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma.
59:2273–2286. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Castaño-Bonilla T, Alonso-Dominguez JM,
Barragán E, Rodríguez-Veiga R, Sargas C, Gil C, Chillón C,
Vidriales MB, García R, Martínez-López J, et al: Prognostic
significance of FLT3-ITD length in AML patients treated with
intensive regimens. Sci Rep. 11:207452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Xie T, Saleh T, Rossi P and Kalodimos CG:
Conformational states dynamically populated by a kinase determine
its function. Science. 370:eabc27542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lee CC, Chuang YC, Liu YL and Yang CN: A
molecular dynamics simulation study for variant drug responses due
to FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 G697R mutation. RSC Adv.
7:29871–29881. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Todde G and Friedman R: Pattern and
dynamics of FLT3 duplications. J Chem Inf Model. 60:4005–4020.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhao J, Song Y and Liu D: Gilteritinib: A
novel FLT3 inhibitor for acute myeloid leukemia. Biomark Res.
7:192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Iyer R, Fetterly G, Lugade A and Thanavala
Y: Sorafenib: A clinical and pharmacologic review. Expert Opin
Pharmacother. 11:1943–1955. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kawano T, Inokuchi J, Eto M, Murata M and
Kang JH: Activators and inhibitors of protein kinase C (PKC): Their
applications in clinical trials. Pharmaceutics. 13:17482021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Assi R and Ravandi F: FLT3 inhibitors in
acute myeloid leukemia: Choosing the best when the optimal does not
exist. Am J Hematol. 93:553–563. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Tarver TC, Hill JE, Rahmat L, Perl AE,
Bahceci E, Mori K and Smith CC: Gilteritinib is a clinically active
FLT3 inhibitor with broad activity against FLT3 kinase domain
mutations. Blood Adv. 4:514–524. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhou F, Ge Z and Chen B: Quizartinib
(AC220) a promising option for acute myeloid leukemia. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 13:1117–1125. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kennedy VE and Smith CC: FLT3 mutations in
acute myeloid leukemia: Key concepts and emerging controversies.
Front Oncol. 10:6128802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Pandurang S, Keretsu S and Joo S: Design
of new therapeutic agents targeting FLT3 receptor tyrosine kinase
using molecular docking and 3D-QSAR approach. Lett Drug Des Discov.
17:585–596. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Perl AE, Martinelli G, Cortes JE, Neubauer
A, Berman E, Paolini S, Montesinos P, Baer MR, Larson RA, Ustun C,
et al: Gilteritinib or chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory
FLT3-mutated AML. N Engl J Med. 381:1728–1740. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Smith CC, Levis MJ, Perl AE, Hill JE,
Rosales M and Bahceci E: Molecular profile of FLT3-mutated
relapsed/refractory patients with AML in the phase 3 ADMIRAL study
of gilteritinib. Blood Adv. 6:2144–2155. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Larrosa-Garcia M and Baer MR: FLT3
inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia: Current status and future
directions. Mol Cancer Ther. 16:991–1001. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Egbuna C, Patrick-Iwuanyanwu KC, Onyeike
EN, Khan J and Alshehri B: FMS-like tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3)
inhibitors with better binding affinity and ADMET properties than
sorafenib and gilteritinib against acute myeloid leukemia: In
silico studies. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 40:12248–12259. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Bultum LE, Tolossa GB and Lee D: Combining
empirical knowledge, in silico molecular docking and ADMET
profiling to identify therapeutic phytochemicals from Brucea
antidysentrica for acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS One.
17:e02700502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Mirza Z, Al-Saedi DA, Alganmi N and Karim
S: Landscape of FLT3 variations associated with structural and
functional impact on acute myeloid leukemia: A computational study.
Int J Mol Sci. 25:34192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Ezelarab HAA, Ali TFS, Abbas SH, Hassan HA
and Beshr EAM: Indole-based FLT3 inhibitors and related scaffolds
as potential therapeutic agents for acute myeloid leukemia. BMC
Chem. 17:732023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Chen D, Oezguen N, Urvil P, Ferguson C,
Dann SM and Savidge TC: Regulation of protein-ligand binding
affinity by hydrogen bond pairing. Sci Adv. 2:e15012402016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Madushanka A, Moura Jr RT, Verma N and
Kraka E: Quantum mechanical assessment of protein-ligand hydrogen
bond strength patterns: Insights from semiempirical tight-binding
and local vibrational mode theory. Int J Mol Med Sci. 24:63112023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Wodicka LM, Ciceri P, Davis MI, Hunt JP,
Floyd M, Salerno S, Hua XH, Ford JM, Armstrong RC, Zarrinkar PP and
Treiber DK: Activation state-dependent binding of small molecule
kinase inhibitors: structural insights from biochemistry. Chem
Biol. 17:1241–1249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Stirewalt DL, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL,
Tsuchiya K, Joaquin J and Meshinchi S: Copy-neutral loss of
heterozygosity is prevalent and a late event in the pathogenesis of
FLT3/ITD AML. Blood Cancer J. 4:e2082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Daver N, Venugopal S and Ravandi F: FLT3
mutated acute myeloid leukemia: 2021 treatment algorithm. Blood
Cancer J. 11:1042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Kim ES: Midostaurin: First global
approval. Drugs. 77:1251–1259. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Wang ES and Baron J: Management of
toxicities associated with targeted therapies for acute myeloid
leukemia: When to push through and when to stop. Hematology Am Soc
Hematol Educ Program. 1:57–66. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Scholl S, Fleischmann M, Schnetzke U and
Heidel FH: Molecular mechanisms of resistance to FLT3 inhibitors in
acute myeloid leukemia: Ongoing challenges and future treatments.
Cells. 9:24932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Levis M: Quizartinib for the treatment of
FLT3/ITD acute myeloid leukemia. Future Oncol. 10:1571–1579. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Perl AE, Hosono N, Montesinos P, Podoltsev
N, Martinelli G, Panoskaltsis N, Recher C, Smith CC, Levis MJ,
Strickland S, et al: Clinical outcomes in patients with
relapsed/refractory FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia treated
with gilteritinib who received prior midostaurin or sorafenib.
Blood Cancer J. 12:842022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Ueno Y, Mori M, Kamiyama Y, Saito R,
Kaneko N, Isshiki E, Kuromitsu S and Takeuchi M: Evaluation of
gilteritinib in combination with chemotherapy in preclinical models
of FLT3-ITD+ acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget. 10:2530–2545.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Qiao X, Ma J, Knight T, Su Y, Edwards H,
Polin L, Li J, Kushner J, Dzinic SH, White K, et al: The
combination of CUDC-907 and gilteritinib shows promising in
vitro and in vivo antileukemic activity against FLT3-ITD
AML. Blood Cancer J. 11:1112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Qiu Y, Li Y, Chai M, Hua H, Wang R, Waxman
S and Jing Y: The GSK3β/Mcl-1 axis is regulated by both FLT3-ITD
and Axl and determines the apoptosis induction abilities of
FLT3-ITD inhibitors. Cell Death Discov. 9:442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Darici S, Jørgensen HG, Huang X, Serafin
V, Antolini L, Barozzi P, Luppi M, Forghieri F, Marmiroli S and
Zavatti M: Improved efficacy of quizartinib in combination therapy
with PI3K inhibition in primary FLT3-ITD AML cells. Adv Biol Regul.
89:1009742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wang Y, Zhang L, Tang X, Luo J, Tu Z,
Jiang K, Ren X, Xu F, Chan S, Li Y, et al: GZD824 as a FLT3, FGFR1
and PDGFRα inhibitor against leukemia in vitro and in
vivo. Transl Oncol. 13:100766. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Zhu R, Li L, Nguyen B, Seo J, Min Wu M,
Seale T, Levis M, Duffield A, Hu Y and Small D: FLT3 tyrosine
kinase inhibitors synergize with BCL-2 inhibition to eliminate
FLT3/ITD acute leukemia cells through BIM activation. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 6:1862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|