Introduction
Neuroinflammation is an important pathological
feature of epilepsy and other brain diseases, such as Alzheimer's
disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and
stroke (1). It involves two key
cell types called microglia and astrocytes in the central nervous
system (CNS), which can undergo a myriad of molecular and
functional reactive changes contingent upon the pathological
context, ultimately contributing to the escalation of the disease
(2–4). Inhibition of neuroinflammation is a
promising therapeutic strategy for inflammation-related brain
diseases, and the exploration of action targets is particularly
critical.
Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) is primarily
expressed in astrocytes in the CNS and Schwann cells in the
peripheral nervous system (5). In
both in vivo and in vitro co-culture, the interaction
of normal neurons and astrocytes greatly inhibited the expression
of CNTF in astrocytes (6). In
addition, evidence from animal models of epilepsy has indicated
that after an epileptic seizure, the expression level of CNTF in
brain tissue is increased, implying its potential role in
pathogenesis (7). Moreover,
elevated CNTF levels in the serum and tears are also considered a
biomarker of focal epilepsy (8).
Nevertheless, the specific pathological effect of CNTF changes in
epilepsy remains obscure. It is hypothesized that as a glia-derived
neurotrophic factor, CNTF plays a neuroprotective role (9), but it may promote chronic diseases as
it belongs to the IL-6 family of cytokines (10). Each IL-6 family member elicits
responses essential to the physiological control of immune
homeostasis, haematopoiesis, inflammation, development and
metabolism. Accordingly, distortion of these cytokine activities
often promotes chronic disease, such as inflammatory arthritis,
multiple sclerosis, renal injury and scarring (10).
In addition to contributing to epilepsy onset,
neuroinflammation can also trigger the tangible release of
inflammatory mediators that worsen seizures, creating a vicious
cycle (11). Therefore, the role
of neuroinflammation in the development of epilepsy has been
actively discussed (12,13). Acute inflammation induced by CNTF
activates astrocytes and microglia (14). These two neuroglial cells have both
pro- and anti-inflammatory effects (15), therefore, the mechanism by which
these cells exhibit beneficial effects is a focus for further
exploration. It has been shown that persistent overproduction of
CNTF by striatal neurons induces the upregulation of the 18kDa
transporter protein (TSPO) (a marker of neuroinflammation) in
astrocytes (16), which also
confirms the critical role of astrocytes in the process of
neuroinflammation affected by CNTF.
IL-6, one of the major pro-inflammatory cytokines,
is produced within the CNS primarily by activated astrocytes and
microglia and has environmentally dependent pro-inflammatory and
anti-inflammatory properties, making it now recognized as a crucial
target for clinical intervention (17). Elevated IL-6 expression in
cerebrospinal fluid and plasma is strongly associated with seizure
severity (18). In addition,
numerous studies have shown that during the process of
epileptogenesis (19,20), IL-6 evaluates and activates
different signaling pathways, while also altering the levels of two
major neurotransmitters, glutamate and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
This results in increased neuronal excitability, as both
neurotransmitters are closely related to epileptic seizures
(21). Inflammatory communication
between neurons and neuroglial cells is closely associated with
promoting epileptogenesis and seizure maintenance (22). However, the specific molecular
mechanisms involved warrant further investigation.
In the present study, astrocytes and neurons from
the cerebral cortex of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were isolated and
cultured to determine the effects of CNTF-induced inflammatory
activation of astrocytes. In addition, IL-6, IL-6Ra and IL-6a were
used to explore the effects of activated astrocytes on neuronal
activity and excitability to understand the possible mediating
mechanism of IL-6 in this process.
Materials and methods
Primary astrocyte culture
Cerebral cortices from SD rats (within 24 h of being
born) were finely minced and trypsinized in 0.125% trypsin-EDTA
(Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The cell suspension was
prepared with DMEM/F12 (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.)
containing 10% fetal bovine serum (TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd.), 10%
calf serum (TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd.), and L-glutamine (2 mmol/l;
Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology). The cells were then seeded in
poly-L-lysine-coated culture flasks (MilliporeSigma) and incubated
at 37°C in 5% CO2. The culture medium was changed every
3 days. After confluence at 7–10 days in vitro, the cells
were cultivated at 37°C and 250 rpm on a shaking incubator with a
rotational radius of 10 cm for 16–18 h to facilitate the separation
of oligodendrocytes and microglia. After astrocytes were
sub-cultured for 2–4 generations, immunofluorescence staining for
GFAP (PeproTech, Inc.) was performed and an astrocyte yield of
>95% was achieved (23) (S1).
The specific methods for immunofluorescence were as follows: The
cell slides were washed with PBS twice, fixed at room temperature
with 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 min, and then permeated with 0.1%
TritonX-100 at 4°C. The cells were blocked with 10% rabbit serum
(cat. no. C-0006; BIOSS) for 30 min at room temperature and
incubated overnight at 4°C in rabbit anti-rat GFAP antibody (cat.
no. 16825-1-AP; 1:200; PeproTech, Inc.). After washing with PBS,
the FITC-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG fluorescent secondary
antibody (cat. no. A0562; 1:200; Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology) was added, incubated at room temperature for 2 h.
Nuclei were stained with DAPI (cat. no. C1006; Beyotime Institute
of Biotechnology) at room temperature for 5 min and washed with PBS
three times for 5 min each. The slides were examined under a ZEISS
Axio observation microscope (Carl Zeiss AG) and images were
captured. All animal studies was approved by The Animal Ethics
Committee of Bengbu Medical University (Bengbu, China; approval no.
2020-094).
Primary neuron culture
SD rats were obtained within 24 h of birth and
placed on ice and frozen to a state of shock. After which, 75%
ethanol was applied to the head and neck for 5 min. The rats were
promptly decapitated and immersed in ice-cold PBS buffer containing
2% penicillin-streptomycin. The skulls were sliced open, the brains
were removed and transferred to a new culture dish. The cerebral
cortex was stripped and immersed in ice-cold HANKS solution
containing 2% penicillin-streptomycin. Cerebral cortices from SD
rats were harvested, cut into small pieces (~1 mm3),
treated with a 0.125% trypsin-EDTA and dissociated into single
cells by gentle suspension. The cell suspension was centrifuged at
4°C and 200 × g for 3 min and resuspended in DMEM/F12 with
penicillin (100 U/ml), streptomycin (100 µg/ml; Beyotime Institute
of Biotechnology) and 10% FBS (Hyclone; Cytiva). Suspended primary
neurons were seeded in poly-L-lysine-coated culture plate and
incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 6 h. After which, the
medium was replaced with a neurobasal medium supplemented with B27
(Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), 2 mM GlutaMAX (Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology), 12.5 µM L-glutamic acid (Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology) and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic (Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology) and incubated at 37°C in 5%
CO2. After the neurons were seeded in plates for 48 h,
cytarabine (5 µmol/l; MedChemExpress) was added to inhibit the
proliferation of glial cells for 24 h at 37°C in 5% CO2,
and then the culture medium was replaced with full volume of
neurobasal medium containing B27 incubated at 37°C in 5%
CO2. After which, the medium was replaced by half volume
every 3 days. The cells were cultured until the 7th-10th day, after
which immunofluorescence staining for microtubule-associated
protein-2 antibody (PeproTech, Inc.) was performed (the
identification method is similar to that of astrocytes); the yield
of neurons was >95% (24)
(Fig. S1).
Bioinformatics analysis
The publicly available gene expression datasets were
obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). The human
dataset GSE32534 (epileptic patients, n=5; controls, n=5) was
originally reported by Niesen et al (25). The mouse dataset GSE157689
(epileptic, n=5; controls, n=4) was originally reported by Joseph
et al (26). Differential
expression analysis was conducted using the limma package in R
(version 4.2.1). This analysis aimed to identify key factors
potentially playing significant roles in epileptic conditions. The
significance thresholds were set at log fold change (logFC)
>|0.5| and adjusted P-value (adj-P) <0.05. The results of the
differential expression analysis were visualized using the ggplot2
package in R (version 4.2.1).
ELISA and collection of conditioned
culture medium
The cultured astrocytes were randomly divided into
the control group (astrocytes were cultured with DMEM/F12 medium
containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 10% calf serum) and the CNTF
treatment group (50 ng/ml; PeproTech, Inc.) at 37°C in 5%
CO2 for 12, 24 and 48 h. The levels of IL-6, TNF-α and
IL-1β in the culture supernatants of the corresponding groups were
detected in accordance with the instructions of the ELISA kits
(IL-6, cat. no. EK0412; TNF-α, cat. no. EK0526; IL-1β, cat. no.
EK0393; Wuhan Boster Biological Technology, Ltd.). Subsequent to
rinsing with PBS thrice, the cells were incubated in fresh,
serum-free DMEM for 48 h. Following this, the CNTF-astrocyte
culture medium (ACM) was collected, centrifuged at 4°C and 1,200 ×
g for 10 min and filtered through a 0.2 µm filter. The untreated
ACM served as the control. Finally, the samples were stored at
−80°C until further analyses.
The cultured neurons were randomly divided into the
following groups: i) Normal control group (neurobasal medium
containing B27); ii) CNTF-treated group (CNTF, 50 ng); iii)
CNTF-ACM-treated group (astrocytes were treated with 50 ng/ml CNTF
for 48 h, and then replaced with fresh serum-free medium and
continued to culture for 48 h to obtain the culture supernatant,
and the neuronal cells were cultured with this supernatant); iv)
CNTF-ACM combined with IL-6a (BIOSS) treated group (CNTF-ACM +
IL-6a, 60 ng/ml) (27); and v)
IL-6a-treated group (neurobasal medium containing B27 + IL-6a, 60
ng/ml). All groups were incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 for
48 h, the levels of GABA in the culture supernatants corresponding
to each group were detected according to the instructions of the
Rat GABA ELISA kit (cat. no. JN352241; Jining Biotech).
Cell counting kit 8 (CCK-8) assay
To test the effect of CNTF-ACM on neuronal activity
and the mediating role of IL-6 in this process, neurons were
inoculated in 96-well plates at 15,000 cells/well, and neurons were
treated according to the same groupings used to detect GABA on the
7th day of culture. The previous culture medium of each well was
replaced by the neurobasal medium containing B27 (100 µl) and CCK-8
(Biosharp Life Sciences) solution (10 µl) was added and cultured at
37°C for 2 h on the 9th day of culture. Subsequently, the optical
density at 450 nm was detected by a microplate reader.
Microwell plate methods for glutamate
content in cell culture supernatants of each group
The cultured astrocytes were randomly divided into
the following groups: i) control group (normal culture medium); ii)
IL-6-treated group (IL-6, 30 ng/ml; 24 h); and iii) IL-6-combined
with IL-6Ra-treated group (IL-6Ra pre-treatment, 60 ng/ml, 1 h;
followed by IL-6, 30 ng/ml, 24 h). The Glutamate Content Assay Kit
(cat. no. JN365241; 4°C) was purchased from Jining Biotech.
The cultured neurons were grouped according to the
same groupings used to detect GABA. The culture supernatants of the
aforementioned groups were collected into 1.5 ml microfuge tube and
centrifuged at 8,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C. After which, the
supernatant samples were aspirated. The enzyme counter was warmed
up for 30 min and the wavelength was adjusted to 340 nm. Briefly,
50 µl of the sample, 120 µl reagent I and 20 µl reagent II were
added to each well of a 96-well plate and incubated for 2 min,
after which the A1 value was read at 340 nm. After which, 10 µl
reagent III was added to each well and the 96-well plate was
allowed to stand for 20–30 min, and the A2 value was read at 340
nm. The glutamate content was calculated as follows: Glutamate
content (µg/ml)=[ΔA ÷ (ε × d) × V2 × Mr × 106] ÷ V1=186.84 × ΔA,
ΔA=A2-A1.
Detection of [Ca2+]i and
ROS by flow cytometry
Fluo-3 AM (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) was
diluted in DMEM/F12 medium to a final concentration of 5 µM.
Neurons were incubated with diluted Fluo-3 AM for 1 h at 37°C and
then washed twice with PBS. Subsequently, neurons were again
incubated with DMEM/f12 solution for 0.5 h at 37°C and washed with
PBS. After which, the cells were digested with 0.25% trypsin
without EDTA for 30 s. After digestion was terminated, cells were
gently blown until they were suspended in solution. The cell
suspension was centrifuged at 200 × g for 5 min at 4°C, and the
supernatant was discarded. The collected cells were washed with PBS
and resuspended in 300 µl PBS, followed by flow cytometric analysis
(FlowJo V10; BD Biosciences) using the LSRFortessa Cell Analyzer
(BD Biosciences). Fluo-3 AM, as a fluorescent probe, can penetrate
the cell membrane and enter the cell, where it is cleaved by
esterases to form Fluo-3. After binding with Ca2+, its
fluorescence intensity significantly increases, making it suitable
for flow cytometry to detect changes in intracellular
Ca2+ concentration.
Neurons were incubated with the
2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (fluorescent probe of reactive
oxygen species; 10 µmol/l; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) for
1 h at 37°C in the dark. The cells were washed twice with PBS and
then were incubated with DMEM/f12 solution for 30 min at 37°C.
Subsequently, the cells were washed thrice with PBS and digested
with trypsin for 30 s, followed by rewashing and resuspension in
PBS. Flow cytometric analysis was carried out using LSRFortessa
Cell Analyzer (Cytek Biosciences).
RT-qPCR assay
Total RNA (cultured astrocytes treated with IL-6 in
combination with IL-6Ra or alone, and cultured neurons treated with
CNTF-ACM in combination with IL-6a or alone, and control groups)
was extracted by TRIzol® (Ambion; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) reagent, and cDNA was synthesized by reverse
transcription using the Revertaid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit
(cat. no. K1622; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at 25°C for 5 min,
42°C for 1 h, and 70°C for 5 min. The cDNA chain was amplified by
Fast SYBR Green Master Mix kit (TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd.), and
quantitative PCR was performed. The composition of the PCR reaction
system is as shown: cDNA 2 µl, 2X PerfectStart Green qPCR SuperMix
(including SYBR Green I fluorescent dye, Taq enzyme, dTNP mixture)
10 µl, with 0.4 µl each of the upstream primer (10 µM) and
downstream primer (10 µM) and 7.2 µl ddH2O. The
thermocycling program (45 cycles) was set at 94°C pre-denaturation
for 30 s; denaturation at 94°C for 5 s; annealing at 55–60°C for 15
s and a final extension at 72°C for 10 s. RQ=2−∆∆Cq
formula (28) was used to
calculate the relative expression of the target gene with GAPDH
used as the reference gene. Each experiment was repeated at least
thrice and the sequences of each gene primer are shown in Table I.
 | Table I.Primers sequences. |
Table I.
Primers sequences.
| Gene | Forward primer
5′-3′ | Reverse primer
5′-3′ |
|---|
| Cx43 |
CCACTCTCGCCTATGTCTCC |
TAGTTCGCCCAGTTTTGCTC |
| GLT-1 |
ATTGGTGCAGCCAGTATTCC |
CCAAAAGAATCGCCCACTAC |
| BKCa |
CCGTCCACAGCAAATCGGCCA |
CCATGTGGGTACTCATGGGCTTGG |
| Bcl-2 |
GACTGAGTACCTGAACCGGCATC |
CTAGACAGCGTCTTCAGAGACA |
| BAX |
TGTTTGCTGATGGCAACTTC |
GATCAGCTCGGGCACTTTAG |
| GAPDH |
GGGTGTGAACCACGAGAAAT |
ACTGTGGTCATGAGCCCTTC |
Western blotting detection of the
expression of Cx43, GLT-1, KCa1.1, Bcl-2 and Bax
Cells collected from different groups (cultured
astrocytes treated with IL-6 in combination with IL-6Ra or alone,
and cultured neurons treated with CNTF-ACM in combination with
IL-6a or alone, and control groups) were lysed on ice with RIPA
lysate (Biosharp Life Sciences; cat. no. BL504A) to extract total
proteins and protein quantification was performed with a BCA
Protein Assay Kit (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology). SDS-PAGE
Protein Sampling Buffer (5X) was mixed in a 4:1 ratio, and protein
was denatured in a 100°C incubator for 5 min. Proteins (30 µg/well)
were separated by gel electrophoresis (80 V for 0.5 h; and 120 V
for 1 h) using 10% (w/v) SDS-PAGE gels, followed by transfer to a
PVDF membrane (MilliporeSigma; constant pressure of 100 V for 1 h).
The PVDF membranes were then incubated with 5% skim milk for 2 h at
room temperature. After which, the following antibodies were added:
Rabbit anti-rat antibody KCa1.1 (Abbexa, Ltd.; cat. no.
APC-151;1:200), connexin 43 (Cx43; cat. no. 26980-1-AP; 1:4,000;
PeproTech, Inc.), glutamate transporter-1 (GLT-1; cat. no.
21829-1-AP; 1:4,000; PeproTech, Inc.), Bax (cat. no. 50599-2-Ig;
1:8,000; PeproTech, Inc.), Bcl-2 (cat. no. 26593-1-AP; 1:1,500;
PeproTech, Inc.) and GAPDH (Biosharp Life Sciences; cat. no.
BL006B; 1:2,000) and incubated at 4°C for ~12 h. The samples were
washed with TBST three times for 10 min. After which, the
HRP-labelled goat anti-rabbit IgG antibody (Biosharp Life Sciences;
cat. no. BL003A; 1:15,000) was added and incubated at 25°C for 2 h.
The samples were rinsed with TBST (0.05% Tween-20) three times for
10 min for the final ECL (BeyoECL Plus; Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology; cat. no. P0018S) chemiluminescence reaction.
Blotting signaling was detected with ChemiDoc XRS+ gel imaging
system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.).
Statistical Analysis
Experiments were performed in triplicate, data are
expressed as means ± SD and were analyzed using SPSS software (v16;
SPSS, Inc.). The differences between groups were tested using
one-way analysis of variance, followed Tukey's post hoc test.
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
CNTF induces astrocytes to release
pro-inflammatory factors IL-6, TNF-αand IL-1β
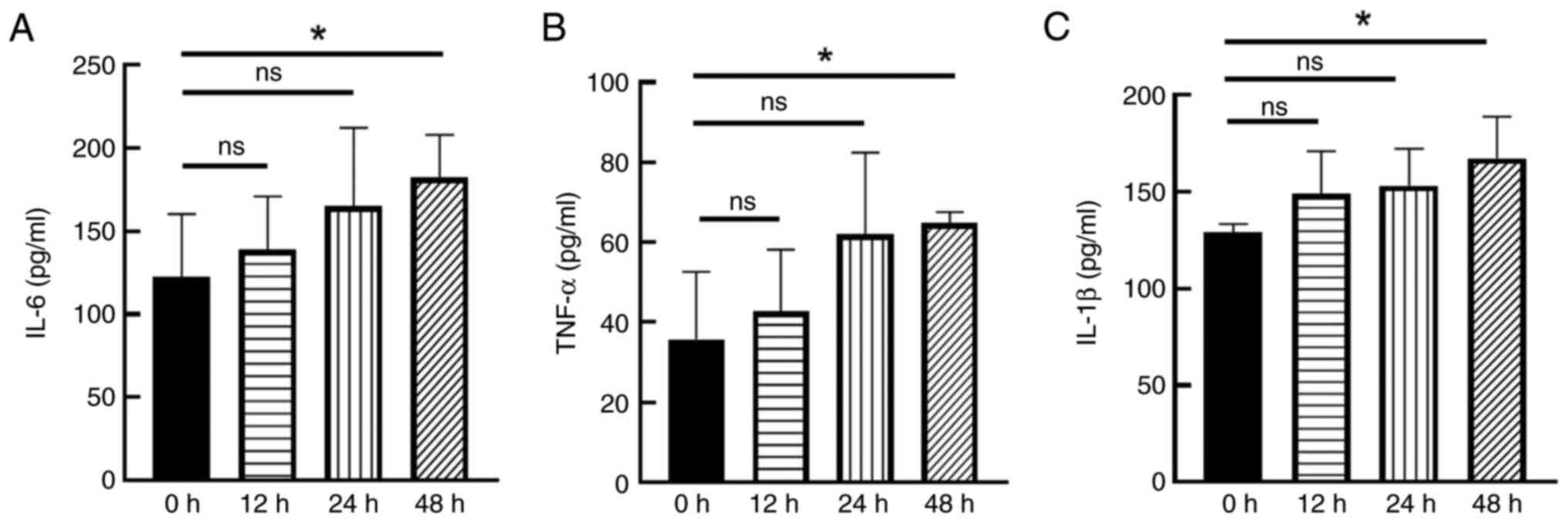
ELISA results showed that the levels of IL-6, TNF-α
and IL-1β in cell culture supernatants were time-dependently
increased after CNTF (50 ng/ml) treatment of astrocytes at
different time points (12, 24 and 48 h). A significant increase in
IL-6 (Fig. 1A), TNF-α (Fig. 1B) and IL-1β (Fig. 1C) between the 48 h group and the
control group was noted (P<0.05; Fig. 1). The results of the differential
analysis presented the data, highlighting IL-6 as the most
significantly upregulated gene in both the human (GSE32534) and
mouse (GSE157689) datasets. (Fig.
S2). Therefore, it was decided to focus on IL-6 in the present
study.
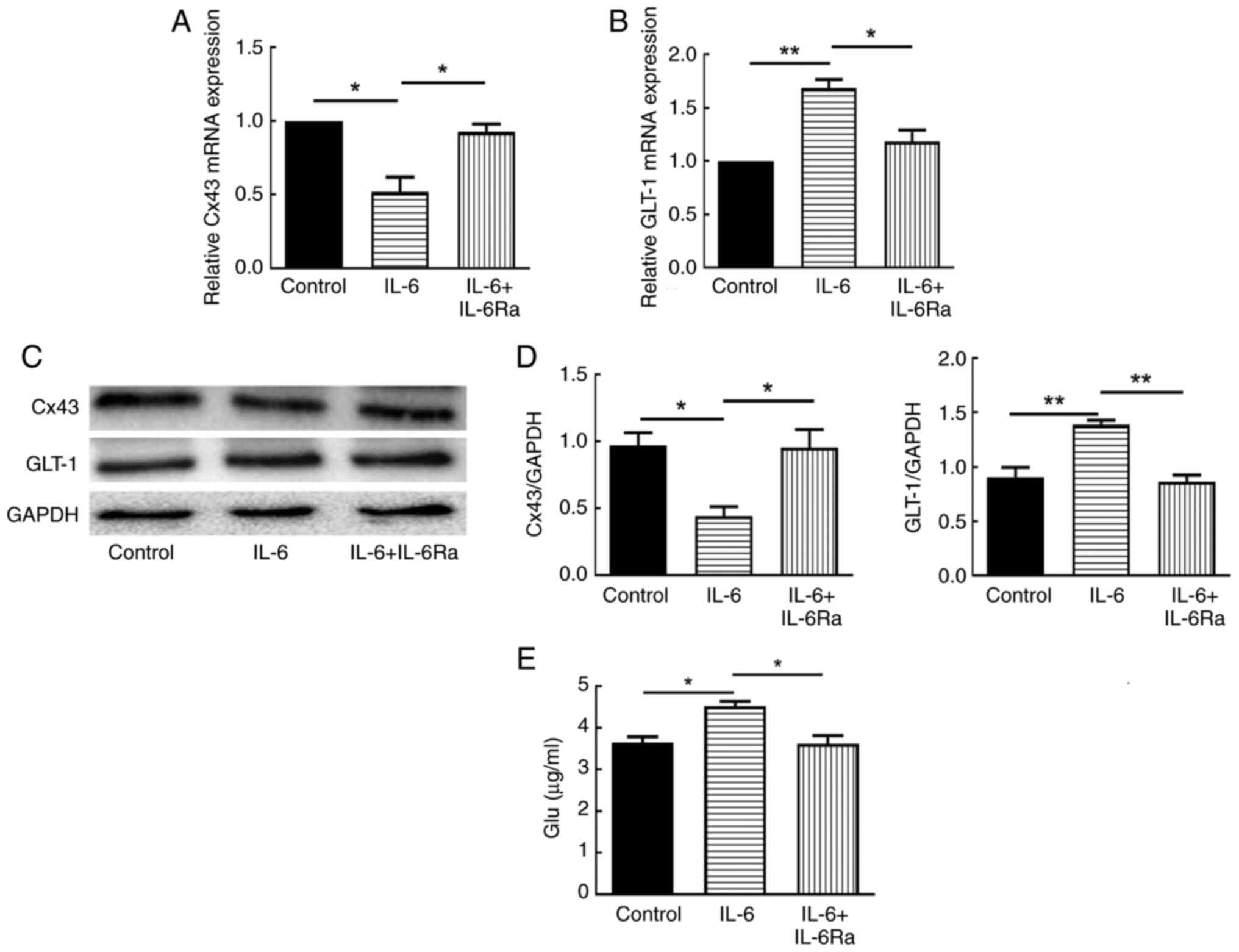
IL-6 downregulates Cx43 expression and
upregulates GLT-1 expression and glutamate release in
astrocytes
To clarify the potential mechanism of CNTF-induced
astrocyte activation in neuroinflammation, the effects of IL-6 on
the expression of Cx43 and GLT-1 in astrocytes were first examined
by RT-qPCR and western blotting. The results showed that 30 ng/ml
IL-6 significantly decreased the mRNA and protein expression of
Cx43 in astrocytes (P<0.05; Fig.
2A, C and D) and significantly increased the mRNA and protein
expression of GLT-1 in astrocytes (P<0.01; Fig. 2B-D). After pretreatment with
IL-6Ra, the mRNA and protein expression of Cx43 and GLT-1 showed
significant reversal (P<0.05; Fig.
2). The effect of IL-6 on glutamate levels in astrocyte culture
supernatants was also examined using the microplate assay, and the
results showed that IL-6 significantly promoted the release of
glutamate from astrocytes (P<0.05; Fig. 2E), whereas IL-6Ra pretreatment
significantly down-regulated the level of glutamate release
(P<0.05; Fig. 2E).
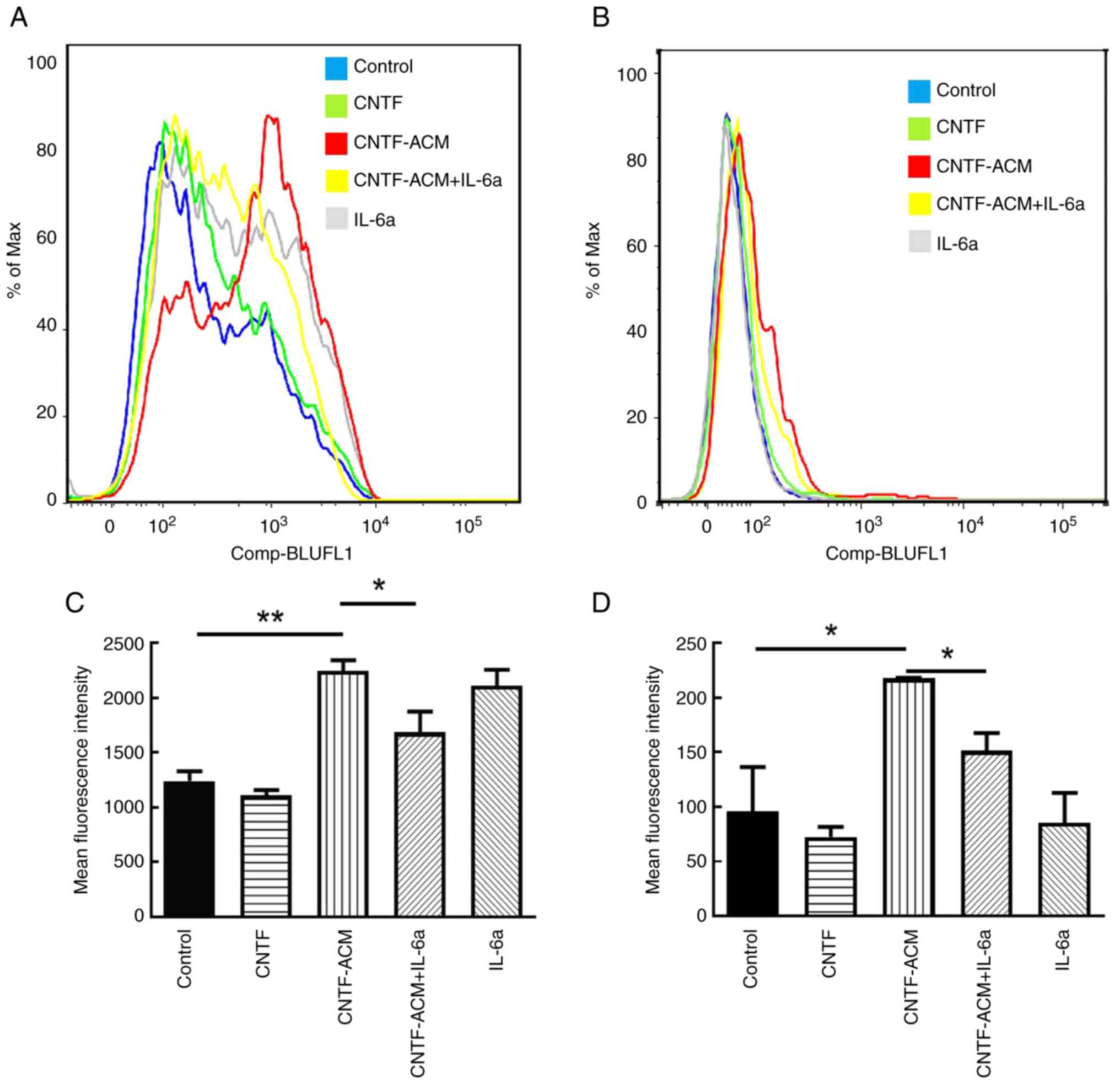
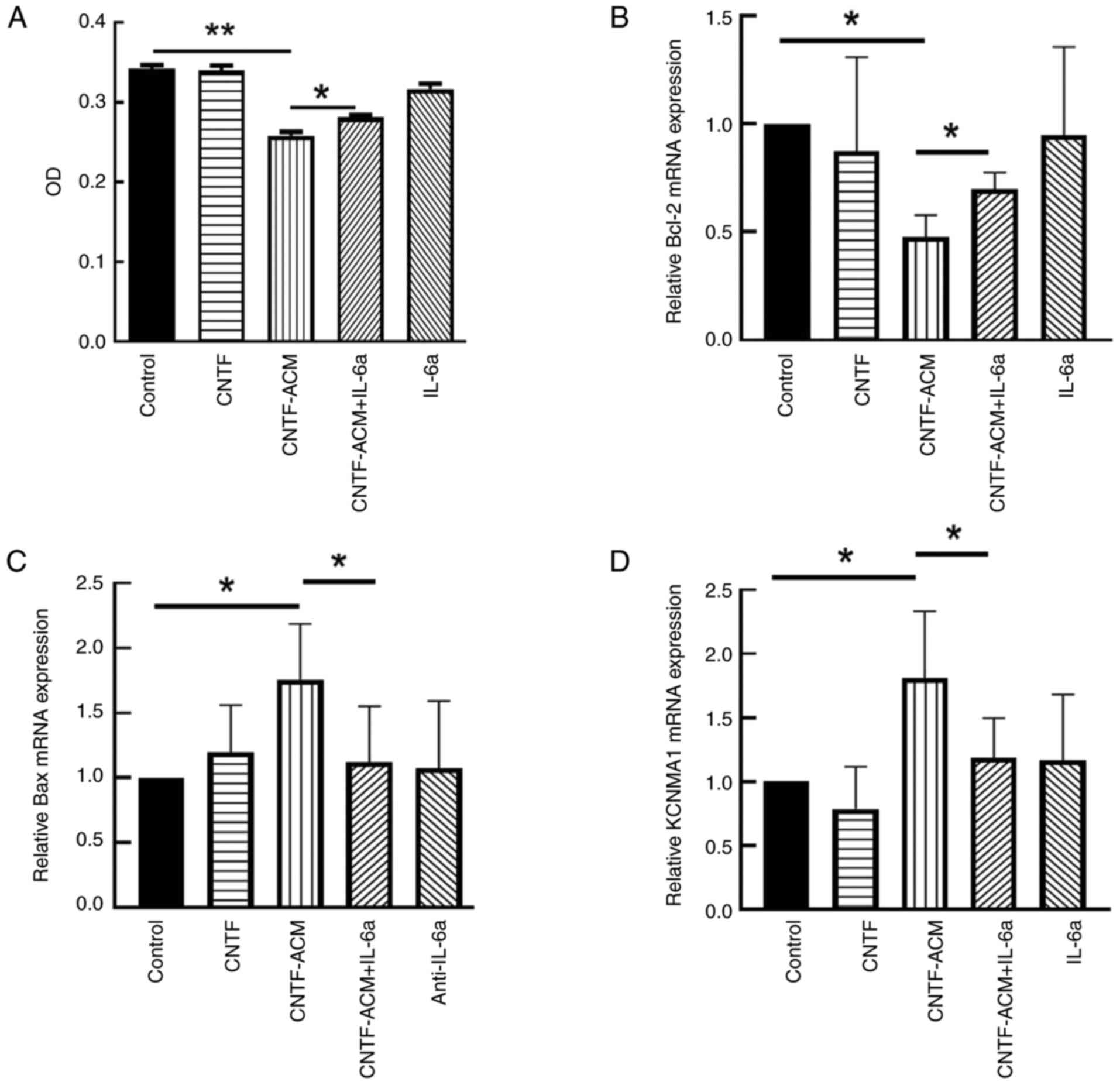
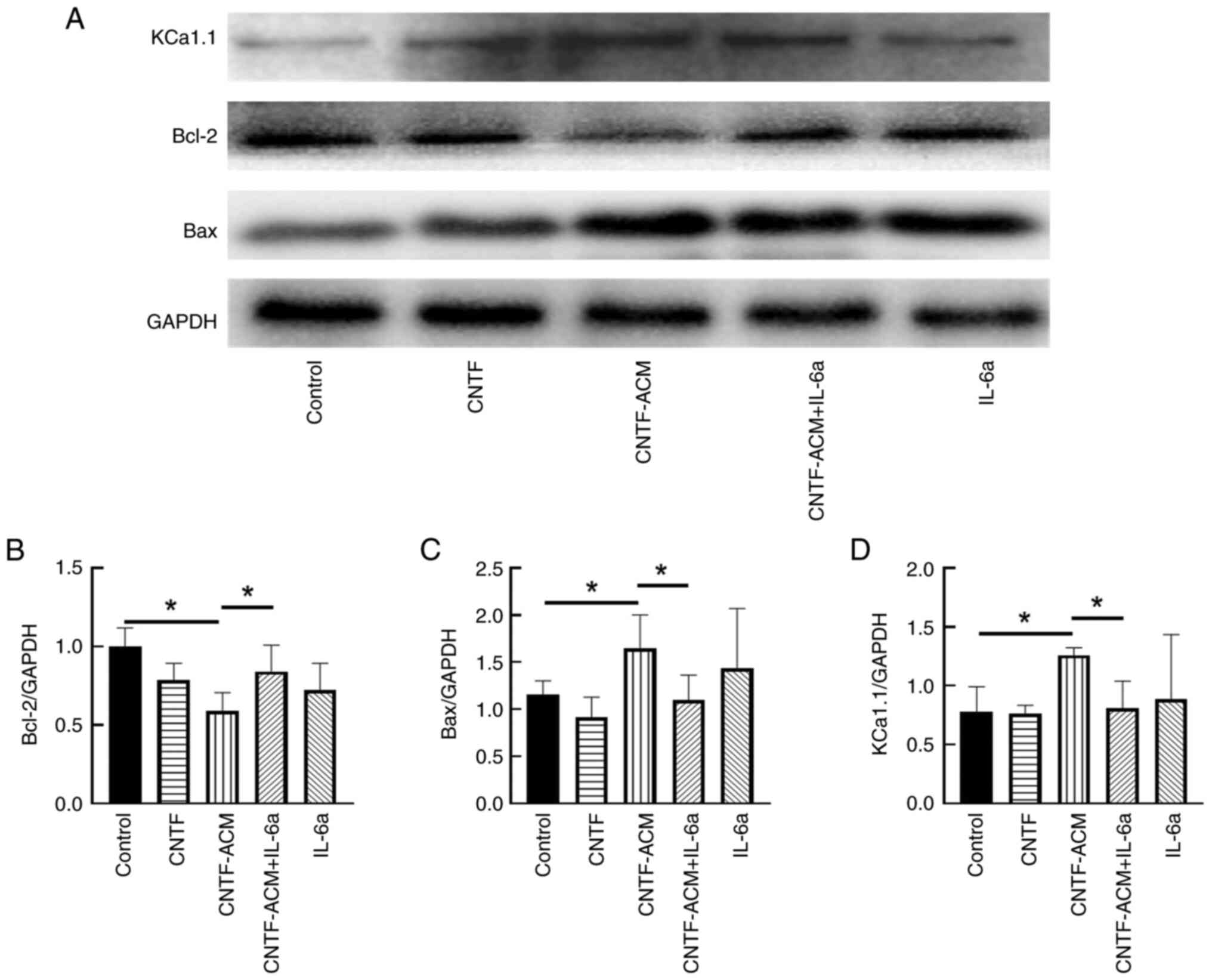
CNTF-ACM enhances oxidative stress,
activates BKCa channels, increases neuronal excitability, decreases
neuronal activity and promotes neuronal apoptosis via the
IL-6/IL-6R pathway
To illustrate the potential mechanism of
CNTF-induced astrocyte activation in neuroinflammation, the
cultured neurons were treated with CNTF-ACM, and the results of
flow cytometry showed that CNTF-ACM significantly elevated neuronal
[Ca2+]i (P<0.01; Fig. 3A
and B) and ROS levels (P<0.05; Fig. 3C and D). The results of the CCK8
assay showed that CNTF-ACM significantly decreased neuronal
viability (P<0.01; Fig. 4A);
RT-qPCR and western blotting assays showed that CNTF-ACM
significantly upregulated the expression of KCa1.1 (P<0.05;
Figs. 4D and 5D), promoted the expression of
apoptosis-related factor Bax (P<0.05; Figs. 4C and 5C) and decreased the expression of Bcl-2
(P<0.05; Figs. 4B, 5A and B). The results of the microplate
assay showed that CNTF-ACM significantly increased the level of
glutamate in the supernatants of neuronal cultures (P<0.05;
Fig. 6A). The ELISA results showed
that CNTF-ACM significantly decreased the level of GABA in the
supernatants of neuronal cultures (P<0.05; Fig. 6B). However, pretreatment of
CNTF-ACM with IL-6a for 1 h significantly reversed all the
aforementioned changes (P<0.05, Fig. 3, Fig.
4, Fig. 5, Fig. 6).
Discussion
There is a positive feedback loop between
neuroinflammation and epileptogenesis; hence, neuroinflammation is
closely related to the pathogenic process associated with seizures,
especially in refractory epilepsy (29). The results of the present study
showed that CNTF-induced astrocyte-mediated inflammation leads to
glutamate excitotoxicity and oxidative stress, followed by neuronal
damage, and the IL-6/IL-6R pathway plays an important regulatory
role in this process, which reveals its significance as a
therapeutic target in epilepsy.
It has been shown that astrocytes are the main cell
type in which CNTF affects neuroinflammatory processes (16), while immunoinflammatory dysfunction
of neuroglia is a major factor that induces or promotes seizures
(30,31). Therefore, to delve into the
possible role of CNTF-induced neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis
of epilepsy, the pro-inflammatory effects of CNTF on astrocytes
were first explored, and the results showed that 50 ng/ml CNTF
promoted the release of several pro-inflammatory cytokines, namely
IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α, from astrocytes in a time-dependent manner.
The 48 h time groups with significant differences compared with the
control group were selected to obtain the CNTF-activated astrocyte
conditioned cultures (24,32,33)
(in vitro model of CNTF-mediated astrocytes activation).
Based on the differential expression of the publicly available gene
expression datasets, GSE32534 and GSE157689, to identify key
factors that may play an important role in epileptic conditions,
IL-6 showed the most significant upregulation in both datasets.
Therefore, it was decided to focus on IL-6 in the present
study.
IL-6 is an important pro-inflammatory cytokine in
the IL-6 family and is elevated in a variety of neurological
disorders including epilepsy (19,20).
In CNS, IL-6 is mainly produced by activated astrocytes and
microglia, and excess IL-6 continues to activate astrocytes in an
autocrine manner, leading to a vicious cycle (23), which not only contributes to
epilepsy onset but also increases the susceptibility (34). The role of astrocyte gap junction
dysfunction as well as impaired extracellular potassium ion and
glutamate buffering in the pathogenesis of epilepsy has been widely
validated (35–37). Astrocytes take up excess
extracellular potassium ions via Kir4.1 and then transfer them from
high to low concentrations via gap junctions coupled between
themselves, termed spatial buffering, which subsequently maintains
or influences neuronal excitability (38). The expression of Kir4.1 may be
affected by inflammatory environments (39), and recent studies have shown that
IL-1β and IL-6 promote astrocyte activation and downregulate Kir4.1
expression (23,40,41).
It is also hypothesized that IL-1β and TNF-α may play important
roles in the pathological process of epilepsy and deserve further
exploration. In future studies, the research scope will be further
expanded based on the results of the present study, including an
in-depth exploration of the role of these two cytokines.
Excitotoxicity due to extracellular glutamate is a
pathogenic mechanism in numerous CNS disorders including epilepsy
(42). Regulation of extracellular
glutamate is primarily through clearance by appropriate
transporters, and GLT-1, predominantly found in astrocytes, is
responsible for ~90% clearance (43). However, dysfunction of GLT-1 in
astrocytes is common in both patients with epilepsy (44) and animal models of epilepsy
(45,46). In addition to extracellular
glutamate uptake, astrocytes could also regulate glutamate
homeostasis by releasing glutamate into the synaptic gap, which is
involved in the step to excitotoxicity in neurological disorders
(47,48). Under these circumstances, impaired
uptake and excessive release of glutamate can lead to elevated
glutamate concentrations in the synaptic gap, which subsequently
brings about neuronal hyperexcitability and excitotoxicity
(49,50). To further explore the possible
effects of the inflammatory environment on the glutamate buffering
function of astrocytes, astrocytes were treated with 30 ng/ml IL-6
for 24 h. The results showed that the expression of GLT-1 and the
level of glutamate in the culture supernatant were significantly
elevated, suggesting that IL-6 promotes the release of glutamate
from astrocytes, which may be a pathway for astrocytes to
participate in the modulation of neuronal excitability in the local
inflammatory environment. While the majority of previous studies
have shown decreased GLT-1 expression in epilepsy models (51,52),
the results of the present study found markedly elevated GLT-1
expression in activated astrocytes in the inflammatory environment,
suggesting that the ability of astrocytes to uptake extracellular
glutamate may be enhanced. Recently conducted research has reported
that in a pentylenetetrazole-induced epilepsy model, the level of
extracellular glutamate was noticeably increased, and the
expression of GLT-1 was significantly upregulated, but the time for
reuptake of glutamate was prolonged (53). This was consistent with the
findings of the present study, and may confirm an adaptive
mechanism for high levels of glutamate under certain conditions;
specifically that high levels of glutamate increase the expression
of glutamate transporter proteins, but it is not sufficient to
remove excess glutamate.
Astrocytes can redistribute elevated K+
and neurotransmitters from the sites of increased neuronal activity
through a large number of gap junction couplings (54), or they can release gliotransmitters
through hemichannels, which affect neuronal excitability (55,56).
Cx43 is a prime connectivity protein expressed in astrocytes and
acts as a major component in the construction of astrocyte gap
junctions and hemichannels (57,58).
However, the expression of Cx43 in both excised human epileptic
tissues and animal models of epilepsy showed different observations
of decreased levels (59,60), increased levels (61) or unchanged levels (62). Epilepsy of different etiologies or
refractory epilepsy may have different effects on protein
expression in tissue samples (58–62).
However, in vivo and in vitro studies have shown that
the pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and TNFα, released by
microglia, inhibit gap junction coupling between astrocytes
(59,63,64),
but activate hemichannels (65).
The results of the present study showed that IL-6 downregulated
Cx43 expression, indicating that IL-6 may cause decreased buffering
capacity of astrocytes for extracellular K+ and
neurotransmitters through the reduction of gap junction coupling
and aberrant opening of hemichannels, which ultimately leads to
excitotoxicity of neurons. This hypothesis needs further
experimental verification.
Taken together, IL-6 may continuously activate
astrocytes through autocrine secretion and subsequently
downregulate the expression of Kir4.1 and Cx43 as well as promote
glutamate release, which subsequently affects neuronal
excitability. It is worth noting in the present study that all the
aforementioned processes were reversed by pretreatment with IL-6a.
These results suggest that IL-6/IL-6R may be a non-neuronal
anti-epileptic target, and provide the experimental basis for
clinical treatment with IL-6 receptor blockers.
Activated astrocytes can be involved in the process
of epileptic activity and release a variety of neuroactive factors
that can act on neurons not only indirectly by autocrine activation
of astrocytes but also directly by affecting the structure and
function of neurons by paracrine secretion (66,67).
A previous study treated primary cultured neurons with CNTF-ACM and
showed that fibroblast growth factor-2 contained in CNTF-ACM was
involved in the upregulation of [Ca2+]i, as well as in
the enhanced activity of large conductance calcium-activated
potassium channels that affect neuronal excitability (24). Based on previous studies and to
further investigate the direct effects of astrocyte-mediated
neuroinflammation on neuronal structure and function, cultured
neurons in the present study were treated with a combination of
CNTF-ACM and IL-6a. The results showed that CNTF-ACM significantly
elevated [Ca2+]i and the levels of ROS, decreased
neuronal viability and promoted neuronal apoptosis; whereas, IL-6a
partially reversed the aforementioned changes, suggesting that IL-6
secreted by CNTF-activated astrocytes is involved in the neuronal
damage process previously described.
Abnormalities in intracellular Ca2+
homeostasis in neurons may be associated with epilepsy (31). Ca2+, a second messenger
in cellular signaling, is predominantly stored in the endoplasmic
reticulum and mitochondria in neurons and is involved in virtually
all neurophysiological functions including the regulation of
membrane excitability and mitochondrial function, synaptic
transmission, intracellular and paracellular signaling in neurons,
the formation of ROS and apoptosis/necrosis (68,69).
Mitochondria are responsible for maintaining intracellular
Ca2+ homeostasis through Ca2+ uptake and
release (70), and are also the
main site of ROS production (71).
However, mitochondrial dysfunction can lead to oxidative stress
triggered by excessive ROS production, leading to neuronal death
(72). Sustained high levels of
[Ca2+]i have been shown to cause mitochondrial calcium
overload (73,74) and increased ROS production
(75). During epileptogenesis,
oxidative stress can induce neuronal death via pro-inflammatory and
pro-apoptotic factors released from activated glial cells (30,76).
Therefore, mitochondria play a key role in epilepsy-induced
cellular damage. In addition, ROS can cause mitochondrial
dysfunction by initiating toxic signaling cascades against
mitochondria or by damaging mitochondrial DNA (77). In the present study, it was
demonstrated that CNTF-ACM significantly elevated the levels of
[Ca2+]i and ROS, as well as upregulated the mRNA and
protein expression of Bax, downregulated the mRNA and protein
expression of Bcl-2 and decreased neuronal viability. It is
suggested that neuronal apoptosis and reduced neuronal activity
resulting from astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation may be
associated with intracellular calcium overload and oxidative
stress.
The large conductance calcium-activated potassium
channel is a potassium channel whose activity is dependent on
intracellular calcium ions (78).
It is not only involved in the maintenance of neuronal resting
potential and the onset and development of action potentials, but
is also coupled to intracellular calcium ions (78), regulating the synthesis and
secretion of a variety of neurotransmitters, such as Glu and GABA,
that in turn modulate the excitability of neurons (79). Numerous studies have confirmed that
hyperactivity of large conductance calcium-activated potassium
channels (BKCa) increases neuronal excitability (80–82),
and it has also been demonstrated that epileptic seizures promote
BKCa function (83), suggesting
that activation of BKCa may be the cause of epilepsy or the result
of epileptic development. In addition, loss of function due to
mutations in the BKCa gene can cause seizures (84). This suggests that the functional
abnormalities of BKCa are closely related to epileptogenesis and
have a complex pathologic role. It has been shown that LPS enhances
the expression and function of BKCa channels in mesenchymal stem
cells (MSCs), and the use of blockers of BKCa channels
significantly reduces the level of IL-6 secreted by LPS-stimulated
MSCs (85). However, IL-6 at a
concentration of 10 ng/ml inhibited BKCa channel activity in smooth
muscle cells (86). At present,
little is known about the association between neuroinflammation and
BKCa activity. The results of the present study showed that
CNTF-ACM upregulated neuronal BKCa expression, promoted neuronal
glutamate release and inhibited neuronal GABA release, while IL-6a
partially reversed these changes. The results of the present
experiment suggest that CNTF-induced astrocyte-derived IL-6
upregulates neuronal BKCa expression and increases neuronal
excitability. Although the association between BKCa expression and
glutamate release was not investigated in the present experiment, a
possible inflammatory pathway in the development of epilepsy was
elucidated.
In summary, CNTF-induced astrocyte-mediated
neuroinflammation further leads to neuronal intracellular calcium
overload through the released pro-inflammatory factor IL-6.
Subsequently, the overloaded intracellular calcium ions may promote
the overproduction of ROS, leading to oxidative damage in neurons.
They may also promote the expression of BKCa and the release of
glutamate, leading to excitotoxic damage in neurons.
In conclusion, neuroinflammation is a crucial
mechanism in numerous neurological disorders. In the present study,
the possible mechanisms by which CNTF induces astrocyte-mediated
inflammatory responses that are involved in neuronal damage through
autocrine and paracrine modes were explored, and the significance
of IL-6 as a target for the treatment of inflammatory
evidence-associated neurological diseases was elucidated. It was
found that CNTF mediates the neuroinflammatory response by inducing
astrocytes to secrete IL-6. The role of CNTF in triggering neuronal
immune signaling was demonstrated and evidence that the
CNTF-IL-6/IL-6R axis mediated the immune cascade across the
AST-Neuron-glutamate/GABA network was shown. These findings
revealed an as yet unknown pathway in the inflammation of the
nervous system, with implications for the mechanisms behind
epileptic seizures. However, the causal relationship between
inflammation-induced intracellular calcium overload and ROS
overproduction, as well as the direct relationship between BKCa and
the release of glutamate need to be further investigated.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from The Natural Science
Foundation of the Education Department of Anhui Province (grant no.
KJ2019ZD26) and Open Project of Anhui Key Laboratory of Basic and
Clinical Immunology of Chronic Diseases (grant no.
KLICD-2022-Z4).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
HTW wrote the original draft, conceptualized the
study, curated the data, and was involved in the formal analysis,
investigation and methodology, software visualization and
validation. STL curated the data, and performed the formal
analysis, investigation and methodology. ZHX curated the data and
performed the study methodology. TX curated, analyzed and
interpreted the data, and wrote the original draft. WYZ performed
the study methodology, obtained the resources, performed study
supervision and validation, and reviewed and edited the manuscript.
MQS conceptualized the study, acquired the funding, performed the
investigation and methodology, obtained the resources, performed
study supervision, and reviewed and edited the manuscript. HTW and
MQS confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors read
and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The animal studies were approved by The Animal
Ethics Committee of Bengbu Medical University (Bengbu, China;
approval No. 2020-094).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Vezzani A, French J, Bartfai T and Baram
TZ: The role of inflammation in epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol. 7:31–40.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Herrera G, Silvero CMJ, Becerra MC, Lasaga
M and Scimonelli T: Modulatory role of α-MSH in
hippocampal-dependent memory impairment, synaptic plasticity
changes, oxidative stress, and astrocyte reactivity induced by
short-term high-fat diet intake. Neuropharmacology. 239:1096882023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang T, Liang W, Ou W, Zhang M, Cui S and
Zhang S: Daphnetin alleviates neuropathic pain in chronic
constrictive injury rats via regulating the NF-κB dependent
CXCL1/CXCR2 signaling pathway. Pharm Biol. 61:746–754. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lovotti M, Mangan MSJ, McManus RM,
Shkarina K, Vasconcelos MB and Latz E: Monitoring of inflammasome
activation of macrophages and microglia in vitro, part 2: Assessing
inflammasome activation. Methods Mol Biol. 2713:431–451. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Richardson PM: Ciliary neurotrophic
factor: A review. Pharmacol Ther. 63:187–198. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kang SS, Keasey MP, Cai J and Hagg T: Loss
of neuron-astroglial interaction rapidly induces protective CNTF
expression after stroke in mice. J Neurosci. 32:9277–9287. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moradi P, Ganjkhani M, Anarkooli IJ and
Abdanipour A: Neuroprotective effects of lovastatin in the
pilocarpine rat model of epilepsy according to the expression of
neurotrophic factors. Metab Brain Dis. 34:1061–1069. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shpak A, Guekht A, Druzhkova T, Rider F,
Gudkova A and Gulyaeva N: Increased ciliary neurotrophic factor in
blood serum and lacrimal fluid as a potential biomarkers of focal
epilepsy. Neurol Sci. 43:493–498. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bechstein M, Häussler U, Neef M, Hofmann
HD, Kirsch M and Haas CA: CNTF-mediated preactivation of astrocytes
attenuates neuronal damage and epileptiform activity in
experimental epilepsy. Exp Neurol. 236:141–150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jones SA and Jenkins BJ: Recent insights
into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases
and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 18:773–789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liang W, Wang J, Sui J, Yun F, Shen Y,
Zhou J, Wu Y, Shen D and Zhang Q: Inflammation as a target for the
treatment of fever-associated epilepsy in zebrafish larvae. Int
Immunopharmacol. 116:1098022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hou X, Xiao S and Xu X, Qin M, Cheng X and
Xu X: Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein B (GPNMB)
protects against neuroinflammation and neuronal loss in
pilocarpine-induced epilepsy via the regulation of microglial
polarization. Neuroscience. 551:166–176. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ahmad SR, Zeyaullah M, AlShahrani AM,
Dawria A, Ali H, Mohieldin A, Altijani AA, Razi U, Mehdi M, Akram S
and Hussain ER: Deciphering the enigma of neuron-glial interactions
in neurological disorders. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 29:1422024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kahn MA, Ellison JA, Speight GJ and de
Vellis J: CNTF regulation of astrogliosis and the activation of
microglia in the developing rat central nervous system. Brain Res.
685:55–67. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liddelow SA, Guttenplan KA, Clarke LE,
Bennett FC, Bohlen CJ, Schirmer L, Bennett ML, Münch AE, Chung WS,
Peterson TC, et al: Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by
activated microglia. Nature. 541:481–487. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ceyzériat K, Nicolaides A, Amossé Q,
Fossey C, Cailly T, Fabis F, Garibotto V, Escartin C, Tournier BB
and Millet P: Reactive astrocytes mediate TSPO overexpression in
response to sustained CNTF exposure in the rat striatum. Mol Brain.
16:572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rohani R, Aliaghaei A, Abdollahifar MA,
Sadeghi Y, Zare L, Dehghan S and Heidari MH: Long-Term effects of
hippocampal low-frequency stimulation on pro-inflammatory factors
and astrocytes activity in kindled rats. Cell J. 23:85–92.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Leo A, Nesci V, Tallarico M, Amodio N,
Gallo Cantafio EM, De Sarro G, Constanti A, Russo E and Citraro R:
IL-6 Receptor Blockade by Tocilizumab Has Anti-absence and
Anti-epileptogenic Effects in the WAG/Rij Rat Model of Absence
Epilepsy. Neurotherapeutics. 17:2004–2014. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Uludag IF, Duksal T, Tiftikcioglu BI,
Zorlu Y, Ozkaya F and Kirkali G: IL-1β, IL-6 and IL1Ra levels in
temporal lobe epilepsy. Seizure. 26:22–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Uludag IF, Bilgin S, Zorlu Y, Tuna G and
Kirkali G: Interleukin-6, interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-1
receptor antagonist levels in epileptic seizures. Seizure.
22:457–461. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiaoqin Z, Zhengli L, Changgeng Z,
Xiaojing W and Li L: Changes in behavior and amino acid
neurotransmitters in the brain of rats with seizure induced by
IL-1beta or IL-6. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
25:236–239. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vezzani A, Balosso S and Ravizza T: The
role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of epilepsy. Brain Behav
Immun. 22:797–803. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu S, Wang J, Sun T, Yan H, Zou W, Li H,
Qi Q and Sun M: IL-6 promotes the activation of rat astrocytes and
down-regulation of the expression of Kir4.1 channel. Xi Bao Yu Fen
Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 38:316–320. 2022.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun M, Liu H, Xu H, Wang H and Wang X:
CNTF-Treated astrocyte conditioned medium enhances
large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity in
rat cortical neurons. Neurochem Res. 41:1982–1992. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Niesen CE, Xu J, Fan X, Li X, Wheeler CJ,
Mamelak AN and Wang C: Transcriptomic profiling of human
peritumoral neocortex tissues revealed genes possibly involved in
tumor-induced epilepsy. PLoS One. 8:e560772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Joseph DJ, Von Deimling M, Hasegawa Y,
Cristancho AG, Ahrens-Nicklas RC, Rogers SL, Risbud R, McCoy AJ and
Marsh ED: Postnatal Arx transcriptional activity regulates
functional properties of PV interneurons. iScience. 24:1019992020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo Y, Nemeth J, O'Brien C, Susa M, Liu X,
Zhang Z, Choy E, Mankin H, Hornicek F and Duan Z: Effects of
siltuximab on the IL-6-induced signaling pathway in ovarian cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 16:5759–5769. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zabrodskaya Y, Paramonova N, Litovchenko
A, Bazhanova E, Gerasimov A, Sitovskaya D, Nezdorovina V, Kravtsova
S, Malyshev S, Skiteva E and Samochernykh K: Neuroinflammatory
dysfunction of the blood-brain barrier and basement membrane
dysplasia play a role in the development of drug-resistant
epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci. 24:126892023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tan TH, Perucca P, O'Brien TJ, Kwan P and
Monif M: Inflammation, ictogenesis, and epileptogenesis: An
exploration through human disease. Epilepsia. 62:303–324. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Purnell BS, Alves M and Boison D:
Astrocyte-neuron circuits in epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis.
179:1060582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sun M, Liu H, Xu H, Wang H and Wang X:
CNTF-ACM promotes mitochondrial respiration and oxidative stress in
cortical neurons through upregulating L-type calcium channel
activity. Mol Cell Biochem. 420:195–206. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Escartin C, Brouillet E, Gubellini P,
Trioulier Y, Jacquard C, Smadja C, Knott GW, Kerkerian-Le Goff L,
Déglon N, Hantraye P and Bonvento G: Ciliary neurotrophic factor
activates astrocytes, redistributes their glutamate transporters
GLAST and GLT-1 to raft microdomains, and improves glutamate
handling in vivo. J Neurosci. 26:5978–5989. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Foiadelli T, Santangelo A, Costagliola G,
Costa E, Scacciati M, Riva A, Volpedo G, Smaldone M, Bonuccelli A,
Clemente AM, et al: Neuroinflammation and status epilepticus: A
narrative review unraveling a complex interplay. Front Pediatr.
11:12519142023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Andrioli A, Fabene PF, Mudò G, Barresi V,
Di Liberto V, Frinchi M, Bentivoglio M and Condorelli DF:
Downregulation of the astroglial connexin expression and
neurodegeneration after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Int
J Mol Sci. 24:232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Çarçak N, Onat F and Sitnikova E:
Astrocytes as a target for therapeutic strategies in epilepsy:
current insights. Front Mol Neurosci. 16:11837752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hotz AL, Jamali A, Rieser NN, Niklaus S,
Aydin E, Myren-Svelstad S, Lalla L, Jurisch-Yaksi N, Yaksi E and
Neuhauss S: Loss of glutamate transporter eaat2a leads to aberrant
neuronal excitability, recurrent epileptic seizures, and basal
hypoactivity. Glia. 70:196–214. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bellot-Saez A, Kékesi O, Morley JW and
Buskila Y: Astrocytic modulation of neuronal excitability through
K(+) spatial buffering. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 77:87–97. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zurolo E, de Groot M, Iyer A, Anink J, van
Vliet EA, Heimans JJ, Reijneveld JC, Gorter JA and Aronica E:
Regulation of Kir4.1 expression in astrocytes and astrocytic
tumors: A role for interleukin-1 β. J Neuroinflammation. 9:2802012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun M, Wang H, Qi Q, Yan H, Zou W, Dong X,
Wang Z, Wang J and Wang X: IL-1β promotes the proliferation of
astrocytes and downregulates the expression of Kir4.1. Xi Bao Yu
Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 33:446–449. 2017.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sun M, Yan H, Zou W, Wang Y, Li H and Wang
X: Lipopolysaccharide induces astrocyte activation and
downregulates the expression of Kir4.1 channel. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi
Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 32:196–200. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ma L, Wu Q, You Y, Zhang P, Tan D, Liang
M, Huang Y, Gao Y, Ban Y, Chen Y and Yuan J: Neuronal small
extracellular vesicles carrying miR-181c-5p contribute to the
pathogenesis of epilepsy by regulating the protein kinase
C-δ/glutamate transporter-1 axis in astrocytes. Glia. 72:1082–1095.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hazell AS, Rao KV, Danbolt NC, Pow DV and
Butterworth RF: Selective down-regulation of the astrocyte
glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST within the medial thalamus
in experimental Wernicke's encephalopathy. J Neurochem. 78:560–568.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rakhade SN and Loeb JA: Focal reduction of
neuronal glutamate transporters in human neocortical epilepsy.
Epilepsia. 49:226–236. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Peterson AR, Garcia TA, Cullion K,
Tiwari-Woodruff SK, Pedapati EV and Binder DK: Targeted
overexpression of glutamate transporter-1 reduces seizures and
attenuates pathological changes in a mouse model of epilepsy.
Neurobiol Dis. 157:1054432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Muñoz-Ballester C, Berthier A, Viana R and
Sanz P: Homeostasis of the astrocytic glutamate transporter GLT-1
is altered in mouse models of Lafora disease. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1862:1074–1083. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mahmoud S, Gharagozloo M, Simard C and
Gris D: Astrocytes maintain glutamate homeostasis in the CNS by
controlling the balance between glutamate uptake and release.
Cells. 8:1842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang J, Vitery M, Chen J, Osei-Owusu J,
Chu J and Qiu Z: Glutamate-Releasing SWELL1 channel in astrocytes
modulates synaptic transmission and promotes brain damage in
stroke. Neuron. 102:813–827.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cao W, Xiong S, Ji W, Wei H, Ma F and Mao
L: Neuroprotection Role of Vitamin C by Upregulating Glutamate
Transporter-1 in Auditory Cortex of Noise-Induced Tinnitus Animal
Model. ACS Chem Neurosci. 15:1197–1205. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Skórkowska A, Krzyżanowska W, Bystrowska
B, Torregrossa R, Whiteman M, Pomierny B and Budziszewska B: The
Hydrogen Sulfide Donor AP39 reduces glutamate-mediated
excitotoxicity in a rat model of brain ischemia. Neuroscience.
539:86–102. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hameed MQ, Hui B, Lin R, MacMullin PC,
Pascual-Leone A, Vermudez SAD and Rotenberg A: Depressed glutamate
transporter 1 expression in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome. Ann
Clin Transl Neurol. 10:1695–1699. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mohamed AM, Ali DA, Kolieb E and Abdelaziz
EZ: Ceftriaxone and selenium mitigate seizures and neuronal injury
in pentylenetetrazole-kindled rats: Oxidative stress and
inflammatory pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 120:1103042023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Taspinar N, Hacimuftuoglu A, Butuner S,
Togar B, Arslan G, Taghizadehghalehjoughi A, Okkay U, Agar E,
Stephens R Jr, Turkez H and Abd El-Aty AM: Differential effects of
inhibitors of PTZ-induced kindling on glutamate transporters and
enzyme expression. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 48:1662–1673. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wallraff A, Köhling R, Heinemann U, Theis
M, Willecke K and Steinhäuser C: The impact of astrocytic gap
junctional coupling on potassium buffering in the hippocampus. J
Neurosci. 26:5438–5447. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Moraga-Amaro R, Jerez-Baraona JM, Simon F
and Stehberg J: Role of astrocytes in memory and psychiatric
disorders. J Physiol Paris. 108:240–251. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Orellana JA and Stehberg J: Hemichannels:
New roles in astroglial function. Front Physiol. 5:1932014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bruzzone S, Guida L, Zocchi E, Franco L
and De Flora A: Connexin 43 hemi channels mediate Ca2+-regulated
transmembrane NAD+ fluxes in intact cells. FASEB J. 15:10–12. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
De Bock M, Wang N, Decrock E, Bultynck G
and Leybaert L: Intracellular Cleavage of the Cx43 C-Terminal
Domain by Matrix-Metalloproteases: A novel contributor to
inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2015:2574712015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bedner P and Steinhäuser C: Role of
impaired astrocyte gap junction coupling in epileptogenesis. Cells.
12:16692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Vizuete AFK, Leal MB, Moreira AP, Seady M,
Taday J and Gonçalves CA: Arundic acid (ONO-2506) downregulates
neuroinflammation and astrocyte dysfunction after status
epilepticus in young rats induced by Li-pilocarpine. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 123:1107042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu B, Ran X, Yi Y, Zhang X, Chen H and Hu
Y: Anticonvulsant effect of carbenoxolone on chronic epileptic rats
and its mechanism related to connexin and high-frequency
oscillations. Front Mol Neurosci. 15:8709472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Elisevich K, Rempel SA, Smith BJ and
Edvardsen K: Hippocampal connexin 43 expression in human complex
partial seizure disorder. Exp Neurol. 145:154–164. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bedner P, Dupper A, Hüttmann K, Müller J,
Herde MK, Dublin P, Deshpande T, Schramm J, Häussler U, Haas CA, et
al: Astrocyte uncoupling as a cause of human temporal lobe
epilepsy. Brain 138(Pt 5). 1208–1222. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Haghikia A, Ladage K, Hinkerohe D, Vollmar
P, Heupel K, Dermietzel R and Faustmann PM: Implications of
antiinflammatory properties of the anticonvulsant drug
levetiracetam in astrocytes. J Neurosci Res. 86:1781–1788. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Retamal MA, Froger N, Palacios-Prado N,
Ezan P, Sáez PJ, Sáez JC and Giaume C: Cx43 hemichannels and gap
junction channels in astrocytes are regulated oppositely by
proinflammatory cytokines released from activated microglia. J
Neurosci. 27:13781–13792. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sano F, Shigetomi E, Shinozaki Y,
Tsuzukiyama H, Saito K, Mikoshiba K, Horiuchi H, Cheung DL,
Nabekura J, Sugita K, et al: Reactive astrocyte-driven
epileptogenesis is induced by microglia initially activated
following status epilepticus. JCI Insight. 6:e1353912021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li T, Lan JQ and Boison D: Uncoupling of
astrogliosis from epileptogenesis in adenosine kinase (ADK)
transgenic mice. Neuron Glia Biol. 4:91–99. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Griffioen G: Calcium dyshomeostasis drives
pathophysiology and neuronal demise in age-related
neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 24:132432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gola L, Bierhansl L, Csatári J, Schroeter
CB, Korn L, Narayanan V, Cerina M, Abdolahi S, Speicher A, Hermann
AM, et al: NOX4-derived ROS are neuroprotective by balancing
intracellular calcium stores. Cell Mol Life Sci. 80:1272023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Cai Q and Jeong YY: Mitophagy in
Alzheimer's disease and other age-related neurodegenerative
diseases. Cells. 9:1502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Petrosillo G, Ruggiero FM and Paradies G:
Role of reactive oxygen species and cardiolipin in the release of
cytochrome c from mitochondria. FASEB J. 17:2202–2208. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Esteras N, Kopach O, Maiolino M, Lariccia
V, Amoroso S, Qamar S, Wray S, Rusakov DA, Jaganjac M and Abramov
AY: Mitochondrial ROS control neuronal excitability and cell fate
in frontotemporal dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 18:318–338. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Jung S, Chung Y, Lee Y, Lee Y, Cho JW,
Shin EJ, Kim HC and Oh YJ: Buffering of cytosolic calcium plays a
neuroprotective role by preserving the autophagy-lysosome pathway
during MPP(+)-induced neuronal death. Cell Death Discov. 5:1302019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Park J, Jang KM and Park KK: Effects of
Apamin on MPP(+)-Induced Calcium Overload and Neurotoxicity by
Targeting CaMKII/ERK/p65/STAT3 signaling pathways in dopaminergic
neuronal cells. Int J Mol Sci. 23:152552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Stutzmann GE: The pathogenesis of
Alzheimers disease is it a lifelong ‘calciumopathy’.
Neuroscientist. 13:546–559. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hwang Y, Kim HC and Shin EJ: Enhanced
neurogenesis is involved in neuroprotection provided by rottlerin
against trimethyltin-induced delayed apoptotic neuronal damage.
Life Sci. 262:1184942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Schulien AJ, Justice JA, Di Maio R, Wills
ZP, Shah NH and Aizenman E: Zn(2+)-induced Ca(2+) release via
ryanodine receptors triggers calcineurin-dependent redistribution
of cortical neuronal Kv2.1 K(+) channels. J Physiol. 594:2647–2659.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Shah KR, Guan X and Yan J: Structural and
functional coupling of calcium-activated BK channels and
calcium-permeable channels within nanodomain signaling complexes.
Front Physiol. 12:7965402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Griguoli M, Sgritta M and Cherubini E:
Presynaptic BK channels control transmitter release: Physiological
relevance and potential therapeutic implications. J Physiol.
594:3489–3500. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sun AX, Yuan Q, Fukuda M, Yu W, Yan H, Lim
G, Nai MH, D'Agostino GA, Tran HD, Itahana Y, et al: Potassium
channel dysfunction in human neuronal models of Angelman syndrome.
Science. 366:1486–1492. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Du W, Bautista JF, Yang H, Diez-Sampedro
A, You SA, Wang L, Kotagal P, Lüders HO, Shi J, Cui J, et al:
Calcium-sensitive potassium channelopathy in human epilepsy and
paroxysmal movement disorder. Nat Genet. 37:733–738. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Brenner R, Chen QH, Vilaythong A, Toney
GM, Noebels JL and Aldrich RW: BK channel beta4 subunit reduces
dentate gyrus excitability and protects against temporal lobe
seizures. Nat Neurosci. 8:1752–1759. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Shruti S, Clem RL and Barth AL: A
seizure-induced gain-of-function in BK channels is associated with
elevated firing activity in neocortical pyramidal neurons.
Neurobiol Dis. 30:323–330. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Benton MD, Lewis AH, Bant JS and Raman IM:
Iberiotoxin-sensitive and -insensitive BK currents in Purkinje
neuron somata. J Neurophysiol. 109:2528–2541. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Song A, Wang J, Tong Y, Fang J, Zhang Y,
Zhang H, Ruan H, Wang K and Liu Y: BKCa channels regulate the
immunomodulatory properties of WJ-MSCs by affecting the exosome
protein profiles during the inflammatory response. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 11:4402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Zhang X, Wang L, Xu L and Zou L: Effects
of Atractylodes macrocephala on the cytomembrane Ca2+-activated K+
currents in cells of human pregnant myometrial smooth muscles. J
Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 28:200–203. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|