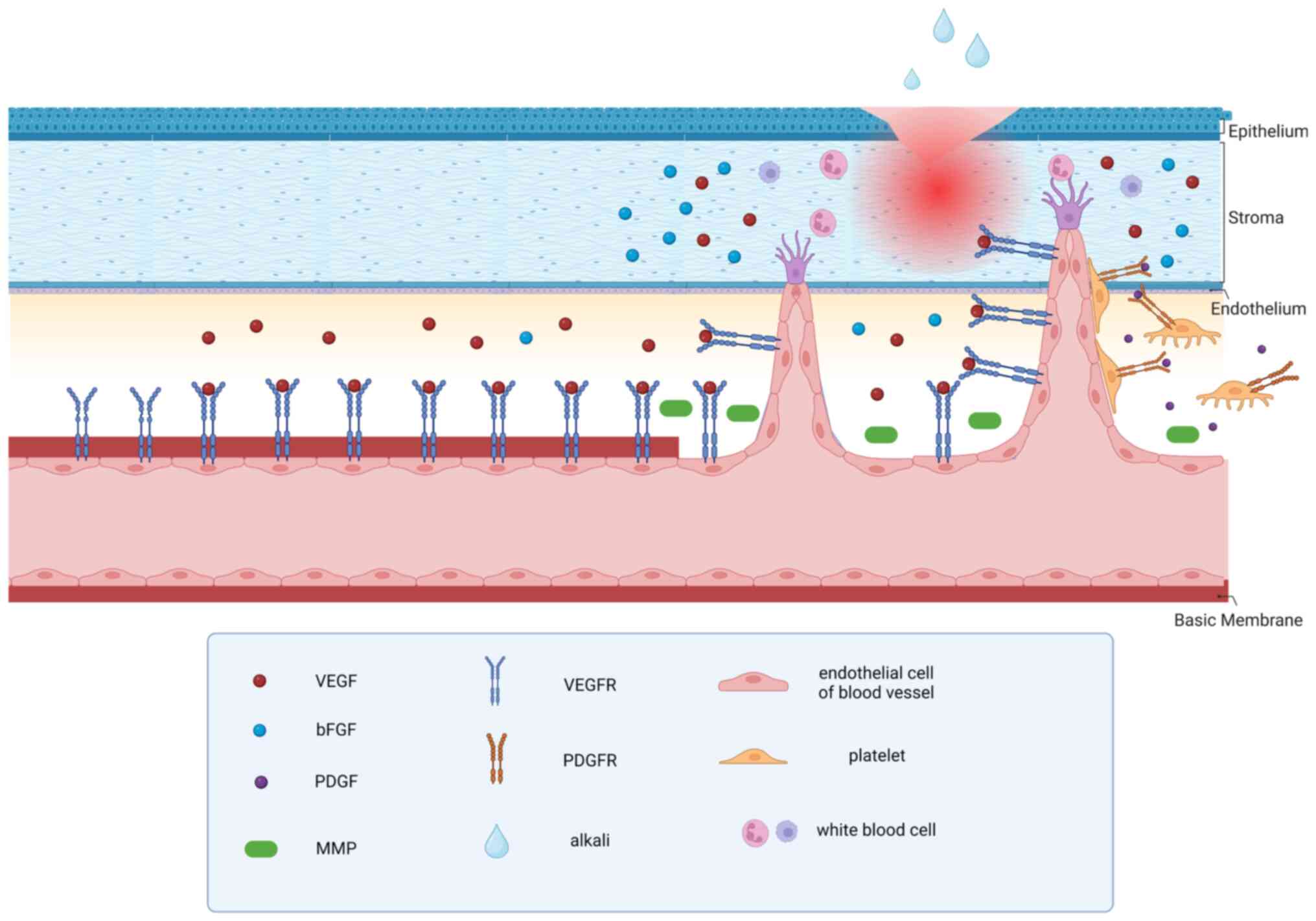
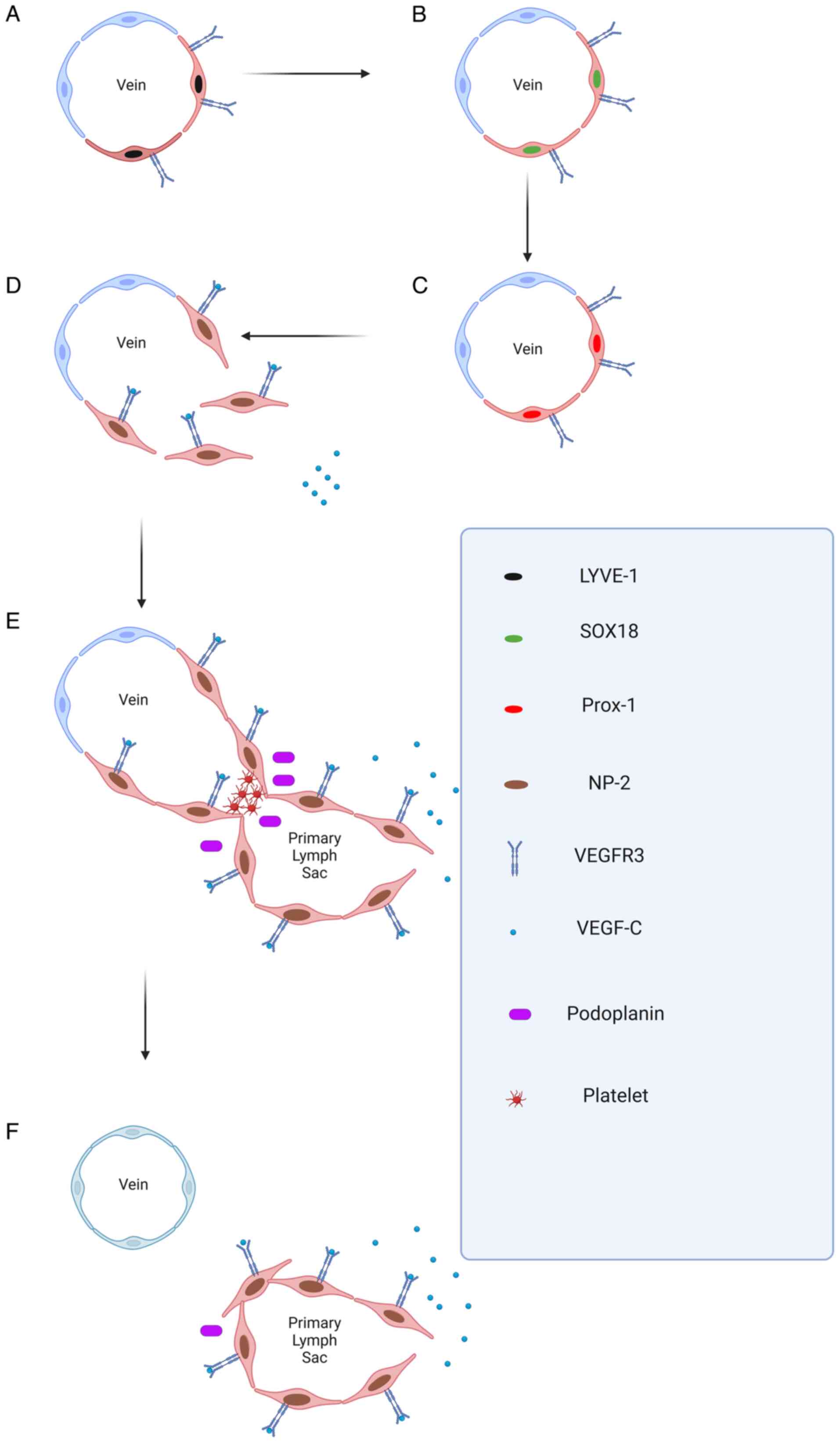
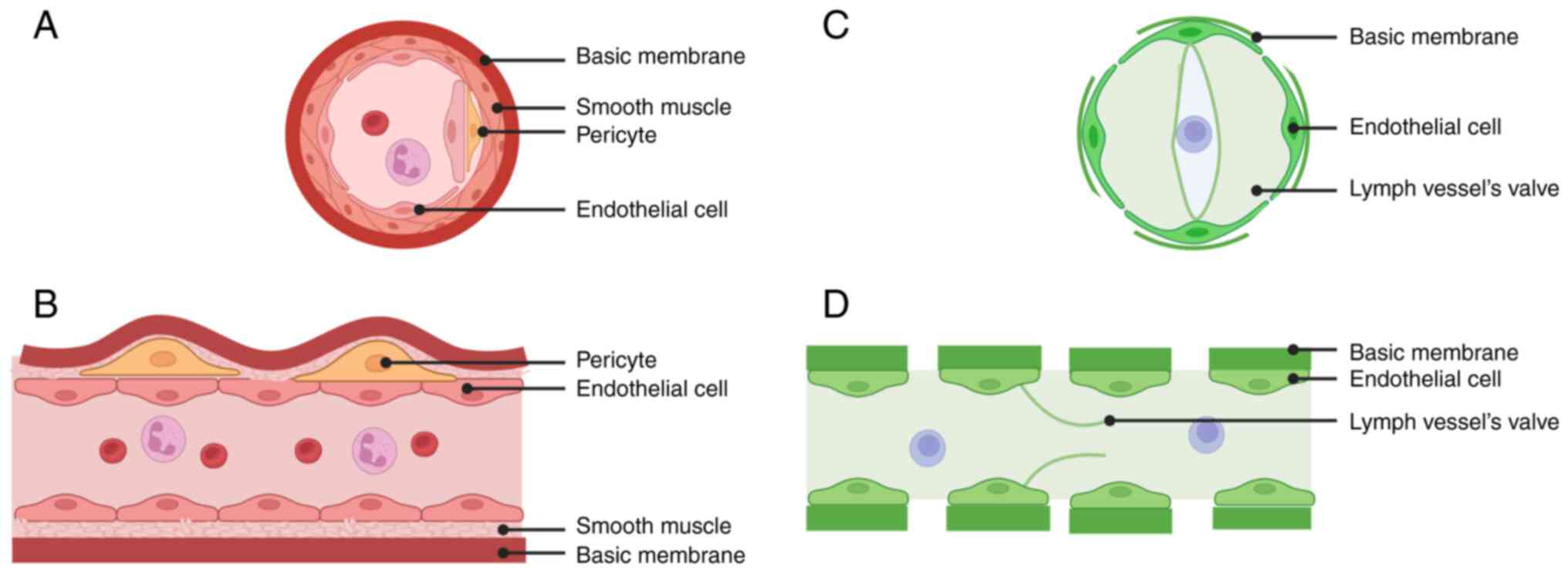
|
1
|
Zhong W, Montana M, Santosa SM, Isjwara
ID, Huang YH, Han KY, O'Neil C, Wang A, Cortina MS, de la Cruz J,
et al: Angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in corneal
transplantation-A review. Surv Ophthalmol. 63:453–479. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Narimatsu A, Hattori T, Koike N, Tajima K,
Nakagawa H, Yamakawa N, Usui Y, Kumakura S, Matsumoto T and Goto H:
Corneal lymphangiogenesis ameliorates corneal inflammation and
edema in late stage of bacterial keratitis. Sci Rep. 9:29842019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang LK, Garcia-Cardeña G, Farnebo F,
Fannon M, Chen EJ, Butterfield C, Moses MA, Mulligan RC, Folkman J
and Kaipainen A: Dose-dependent response of FGF-2 for
lymphangiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:11658–11663. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dietrich T, Bock F, Yuen D, Hos D,
Bachmann BO, Zahn G, Wiegand S, Chen L and Cursiefen C: Cutting
edge: Lymphatic vessels, not blood vessels, primarily mediate
immune rejections after transplantation. J Immunol. 184:535–539.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meshko B, Volatier TLA, Hadrian K, Deng S,
Hou Y, Kluth MA, Ganss C, Frank MH, Frank NY, Ksander B, et al:
ABCB5+ limbal epithelial stem cells inhibit developmental but
promote inflammatory (Lymph) angiogenesis while preventing corneal
inflammation. Cells. 12:17312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dana MR: Angiogenesis and
lymphangiogenesis-implications for corneal immunity. Semin
Ophthalmol. 21:19–22. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cursiefen C, Chen L, Dana MR and Streilein
JW: Corneal lymphangiogenesis: Evidence, mechanisms, and
implications for corneal transplant immunology. Cornea. 22:273–281.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Di Zazzo A, Gaudenzi D, Yin J, Coassin M,
Fernandes M, Dana R and Bonini S: Corneal angiogenic privilege and
its failure. Exp Eye Res. 204:1084572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Benayoun Y, Casse G, Forte R, Dallaudière
B, Adenis JP and Robert PY: Corneal neovascularization:
epidemiological, physiopathological, and clinical features. J Fr
Ophtalmol. 36:627–639. 2013.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hadrian K and Cursiefen C: The role of
lymphatic vessels in corneal fluid homeostasis and wound healing. J
Ophthalmic Inflamm Infect. 14:42024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kimyon Comert G, Basaran D, Ergin Akkoz H,
Celik B, Sinaci S, Turkmen O, Karalok A, Kandemir O and Turan T:
Blood Vessel Invasion in Endometrial Cancer Is One of the
Mechanisms of Spread to the Cervix. Pathol Oncol Res. 25:1431–1436.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jackson DG, Prevo R, Clasper S and Banerji
S: LYVE-1, the lymphatic system and tumor lymphangiogenesis. Trends
Immunol. 22:317–321. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi W, Liu J, Li M, Gao H and Wang T:
Expression of MMP, HPSE, and FAP in stroma promoted corneal
neovascularization induced by different etiological factors. Curr
Eye Res. 35:967–977. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cogan DG: Vascularization of the cornea;
ats experimental induction by small lesions and a new theory of its
pathogenesis. Arch Ophthal. 41:406–416. 1949. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cursiefen C, Chen L, Borges LP, Jackson D,
Cao J, Radziejewski C, D'Amore PA, Dana MR, Wiegand SJ and
Streilein JW: VEGF-A stimulates lymphangiogenesis and
hemangiogenesis in inflammatory neovascularization via macrophage
recruitment. J Clin Invest. 113:1040–1050. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gothard TW, Hardten DR, Lane SS, Doughman
DJ, Krachmer JH and Holland EJ: Clinical findings in Brown-McLean
syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 115:729–737. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kenyon BM, Voest EE, Chen CC, Flynn E,
Folkman J and D'Amato RJ: A model of angiogenesis in the mouse
cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 37:1625–1632. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Simons M, Gordon E and Claesson-Welsh L:
Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:611–625. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Viallard C and Larrivée B: Tumor
angiogenesis and vascular normalization: Alternative therapeutic
targets. Angiogenesis. 20:409–426. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nicholas MP and Mysore N: Corneal
neovascularization. Exp Eye Res. 202:1083632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roshandel D, Eslani M, Baradaran-Rafii A,
Cheung AY, Kurji K, Jabbehdari S, Maiz A, Jalali S, Djalilian AR
and Holland EJ: Current and emerging therapies for corneal
neovascularization. Ocul Surf. 16:398–414. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wigle JT, Harvey N, Detmar M, Lagutina I,
Grosveld G, Gunn MD, Jackson DG and Oliver G: An essential role for
Prox1 in the induction of the lymphatic endothelial cell phenotype.
EMBO J. 21:1505–1513. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu Y, Yuan L, Mak J, Pardanaud L, Caunt M,
Kasman I, Larrivée B, Del Toro R, Suchting S, Medvinsky A, et al:
Neuropilin-2 mediates VEGF-C-induced lymphatic sprouting together
with VEGFR3. J Cell Biol. 188:115–130. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abdelfattah NS, Amgad M, Zayed AA, Hussein
H and Abd El-Baky N: Molecular underpinnings of corneal
angiogenesis: Advances over the past decade. Int J Ophthalmol.
9:768–779. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mäkinen T, Veikkola T, Mustjoki S,
Karpanen T, Catimel B, Nice EC, Wise L, Mercer A, Kowalski H,
Kerjaschki D, et al: Isolated lymphatic endothelial cells transduce
growth, survival and migratory signals via the VEGF-C/D receptor
VEGFR-3. EMBO J. 20:4762–4773. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Goyal S, Chauhan SK, El Annan J, Nallasamy
N, Zhang Q and Dana R: Evidence of corneal lymphangiogenesis in dry
eye disease: A potential link to adaptive immunity? Arch
Ophthalmol. 128:819–824. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chauhan SK, Jin Y, Goyal S, Lee HS,
Fuchsluger TA, Lee HK and Dana R: A novel pro-lymphangiogenic
function for Th17/IL-17. Blood. 118:4630–4634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee SJ, Im ST, Wu J, Cho CS, Jo DH, Chen
Y, Dana R, Kim JH and Lee SM: Corneal lymphangiogenesis in dry eye
disease is regulated by substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor system
through controlling expression of vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor 3. Ocul Surf. 22:72–79. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wilting J, Neeff H and Christ B: Embryonic
lymphangiogenesis. Cell Tissue Res. 297:1–11. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee HK, Lee SM and Lee DI: Corneal
Lymphangiogenesis: Current pathophysiological understandings and
its functional role in ocular surface disease. Int J Mol Sci.
22:116282021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sáinz-Jaspeado M and Claesson-Welsh L:
Cytokines regulating lymphangiogenesis. Curr Opin Immunol.
53:58–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Patnam M, Dommaraju SR, Masood F, Herbst
P, Chang JH, Hu WY, Rosenblatt MI and Azar DT: Lymphangiogenesis
guidance mechanisms and therapeutic implications in pathological
states of the cornea. Cells. 12:3192023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cao R, Ji H, Feng N, Zhang Y, Yang X,
Andersson P, Sun Y, Tritsaris K, Hansen AJ, Dissing S and Cao Y:
Collaborative interplay between FGF-2 and VEGF-C promotes
lymphangiogenesis and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:15894–15899. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cursiefen C, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U,
Küchle M, Sorokin L, Breiteneder-Geleff S, Alitalo K and Jackson D:
Lymphatic vessels in vascularized human corneas:
Immunohistochemical investigation using LYVE-1 and podoplanin.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 43:2127–2135. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cursiefen C, Maruyama K, Jackson DG,
Streilein JW and Kruse FE: Time course of angiogenesis and
lymphangiogenesis after brief corneal inflammation. Cornea.
25:443–447. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shi W, Ming C, Liu J, Wang T and Gao H:
Features of corneal neovascularization and lymphangiogenesis
induced by different etiological factors in mice. Graefes Arch Clin
Exp Ophthalmol. 249:55–67. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Giacomini C, Ferrari G, Bignami F and Rama
P: Alkali burn versus suture-induced corneal neovascularization in
C57BL/6 mice: An overview of two common animal models of corneal
neovascularization. Exp Eye Res. 121:1–4. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Song S, Cheng J, Yu BJ, Zhou L, Xu HF and
Yang LL: LRG1 promotes corneal angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis
in a corneal alkali burn mouse model. Int J Ophthalmol. 13:365–373.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ammassam Veettil R, Li W, Pflugfelder SC
and Koch DD: A Mouse Model for Corneal Neovascularization by Alkali
Burn. J Vis Exp. 2023. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Park JH, Joo CK and Chung SK: Comparative
study of tacrolimus and bevacizumab on corneal neovascularization
in rabbits. Cornea. 34:449–455. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Maier AK, Reichhart N, Gonnermann J,
Kociok N, Riechardt AI, Gundlach E, Strauß O and Joussen AM:
Effects of TNFα receptor TNF-Rp55- or TNF-Rp75- deficiency on
corneal neovascularization and lymphangiogenesis in the mouse. PLoS
One. 16:e02451432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ung L and Chodosh J: Foundational concepts
in the biology of bacterial keratitis. Exp Eye Res. 209:1086472021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Koganti R, Yadavalli T, Naqvi RA, Shukla D
and Naqvi AR: Pathobiology and treatment of viral keratitis. Exp
Eye Res. 205:1084832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gurung HR, Carr MM, Bryant K,
Chucair-Elliott AJ and Carr DJ: Fibroblast growth factor-2 drives
and maintains progressive corneal neovascularization following
HSV-1 infection. Mucosal Immunol. 11:172–185. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xie F, Zhang X, Luo W, Ge H, Sun D and Liu
P: Notch signaling pathway is involved in bFGF-induced corneal
lymphangiogenesis and hemangiogenesis. J Ophthalmol.
2019:96139232019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li S, Li L, Zhou Q, Gao H, Liu M and Shi
W: Blood vessels and lymphatic vessels in the cornea and iris after
penetrating keratoplasty. Cornea. 38:742–747. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hos D, Bukowiecki A, Horstmann J, Bock F,
Bucher F, Heindl LM, Siebelmann S, Steven P, Dana R, Eming SA and
Cursiefen C: Transient ingrowth of lymphatic vessels into the
physiologically avascular cornea regulates corneal edema and
transparency. Sci Rep. 7:72272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gao X, Guo K, Santosa SM, Montana M,
Yamakawa M, Hallak JA, Han KY, Doh SJ, Rosenblatt MI, Chang JH and
Azar DT: Application of corneal injury models in dual fluorescent
reporter transgenic mice to understand the roles of the cornea and
limbus in angiogenic and lymphangiogenic privilege. Sci Rep.
9:123312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Goyal S, Chauhan SK and Dana R: Blockade
of prolymphangiogenic vascular endothelial growth factor C in dry
eye disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 130:84–89. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wuest TR and Carr DJ: VEGF-A expression by
HSV-1-infected cells drives corneal lymphangiogenesis. J Exp Med.
207:101–115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wuest T, Zheng M, Efstathiou S, Halford WP
and Carr DJ: The herpes simplex virus-1 transactivator infected
cell protein-4 drives VEGF-A dependent neovascularization. PLoS
Pathog. 7:e10022782011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Thangamathesvaran L, Kong J, Bressler SB,
Singh M, Wenick AS, Scott AW, Arévalo JF and Bressler NM: Severe
intraocular inflammation following intravitreal faricimab. JAMA
Ophthalmol. 142:365–370. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jaggi D, Nagamany T, Wolf S, Zinkernagel
MS and Heussen FM: Aflibercept for central retinal vein occlusions:
Long-term outcomes of a ‘Treat-and-Extend’ regimen. BMJ Open
Ophthalmol. 9:e0016592024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Limon DU, Kaplan FB, Saygın I, Önder Tokuç
E, Kutlutürk Karagöz I, Kanar HS, Sevik MO, Yayla U, Çelik E,
Sönmez A, et al: One-Year functional and morphological prognosis
after intravitreal injection treatments according to different
morphological patterns of diabetic macular edema in real-life:
MARMASIA Study Group Report No.13. Semin Ophthalmol. 39:460–467.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yang XM, Li QP, Wang ZH and Zhang MN:
Comparison of ranibizumab and conbercept treatment in type 1
prethreshold retinopathy of prematurity in zone II. BMC Pediatr.
24:5562024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hong SH and Kim HD: Central retinal artery
occlusion after intravitreal brolucizumab injection for
treatment-naïve neovascular age-related macular degeneration; a
case report. BMC Ophthalmol. 24:2002024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
HARMONi-A Study Investigators, . Fang W,
Zhao Y, Luo Y, Yang R, Huang Y, He Z, Zhao H, Li M, Li K, et al:
Ivonescimab Plus Chemotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer With
EGFR Variant: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 332:561–570. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cho W, Mittal SK, Elbasiony E and Chauhan
SK: Ocular surface mast cells promote inflammatory
lymphangiogenesis. Microvasc Res. 141:1043202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ferrari G, Bignami F, Giacomini C,
Franchini S and Rama P: Safety and efficacy of topical infliximab
in a mouse model of ocular surface scarring. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 54:1680–1688. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang Q, Lu Y, Proulx ST, Guo R, Yao Z,
Schwarz EM, Boyce BF and Xing L: Increased lymphangiogenesis in
joints of mice with inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
9:R1182007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ji RC: Macrophages are important mediators
of either tumor- or inflammation-induced lymphangiogenesis. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 69:897–914. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ji RC: Lymphatic endothelial cells,
inflammatory lymphangiogenesis, and prospective players. Curr Med
Chem. 14:2359–2368. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hos D, Bucher F, Regenfuss B, Dreisow ML,
Bock F, Heindl LM, Eming SA and Cursiefen C: IL-10 indirectly
regulates corneal lymphangiogenesis and resolution of inflammation
via macrophages. Am J Pathol. 186:159–171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Nakao S, Kuwano T, Tsutsumi-Miyahara C,
Ueda S, Kimura YN, Hamano S, Sonoda KH, Saijo Y, Nukiwa T, Strieter
RM, et al: Infiltration of COX-2-expressing macrophages is a
prerequisite for IL-1 beta-induced neovascularization and tumor
growth. J Clin Invest. 115:2979–2991. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lu P, Li L, Liu G, Zhang X and Mukaida N:
Enhanced experimental corneal neovascularization along with
aberrant angiogenic factor expression in the absence of IL-1
receptor antagonist. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:4761–4768. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Doz E, Noulin N, Boichot E, Guénon I, Fick
L, Le Bert M, Lagente V, Ryffel B, Schnyder B, Quesniaux VF and
Couillin I: Cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary inflammation is
TLR4/MyD88 and IL-1R1/MyD88 signaling dependent. J Immunol.
180:1169–1178. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Reuer T, Schneider AC, Cakir B, Bühler AD,
Walz JM, Lapp T, Lange C, Agostini H, Schlunck G, Cursiefen C, et
al: Semaphorin 3F Modulates Corneal Lymphangiogenesis and Promotes
Corneal Graft Survival. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 59:5277–5284.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang X, Abraham S, McKenzie JAG, Jeffs N,
Swire M, Tripathi VB, Luhmann UFO, Lange CAK, Zhai Z, Arthur HM, et
al: LRG1 promotes angiogenesis by modulating endothelial TGF-β
signalling. Nature. 499:306–311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang J, Zhu L, Fang J, Ge Z and Li X:
LRG1 modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis
in colorectal cancer via HIF-1α activation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35:292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Hu H, Wang S, He Y, Shen S, Yao B, Xu D,
Liu X and Zhang Y: The role of bone morphogenetic protein 4 in
corneal injury repair. Exp Eye Res. 212:1087692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Rezzola S, Di Somma M, Corsini M, Leali D,
Ravelli C, Polli VAB, Grillo E, Presta M and Mitola S: VEGFR2
activation mediates the pro-angiogenic activity of BMP4.
Angiogenesis. 22:521–533. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Shokirova H, Inomata T, Saitoh T, Zhu J,
Fujio K, Okumura Y, Yanagawa A, Fujimoto K, Sung J, Eguchi A, et
al: Topical administration of the kappa opioid receptor agonist
nalfurafine suppresses corneal neovascularization and inflammation.
Sci Rep. 11:86472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Liu Y, Shu Y, Yin L, Xie T, Zou J, Zhan P,
Wang Y, Wei T, Zhu L, Yang X, et al: Protective roles of the
TIR/BB-loop mimetic AS-1 in alkali-induced corneal
neovascularization by inhibiting ERK phosphorylation. Exp Eye Res.
207:1085682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Song HB, Park SY, Ko JH, Park JW, Yoon CH,
Kim DH, Kim JH, Kim MK, Lee RH, Prockop DJ and Oh JY: Mesenchymal
Stromal Cells Inhibit Inflammatory Lymphangiogenesis in the Cornea
by Suppressing Macrophage in a TSG-6-Dependent Manner. Mol Ther.
26:162–172. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bai Y, Jiao X, Hu J, Xue W, Zhou Z and
Wang W: WTAP promotes macrophage recruitment and increases VEGF
secretion via N6-methyladenosine modification in corneal
neovascularization. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1869:1667082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhang W, Schönberg A, Bock F and Cursiefen
C: Posttransplant VEGFR1R2 Trap Eye Drops Inhibit Corneal
(Lymph)angiogenesis and Improve Corneal Allograft Survival in Eyes
at High Risk of Rejection. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 11:62022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhang W, Schönberg A, Hamdorf M, Georgiev
T, Cursiefen C and Bock F: Preincubation of donor tissue with a
VEGF cytokine trap promotes subsequent high-risk corneal transplant
survival. Br J Ophthalmol. 106:1617–1626. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Le VNH, Hos D, Hou Y, Witt M, Barkovskiy
M, Bock F and Cursiefen C: VEGF TrapR1R2 Suspended in the
Semifluorinated Alkane F6H8 Inhibits Inflammatory Corneal Hem- and
Lymphangiogenesis. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 9:152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Salabarria AC, Koch M, Schönberg A, Zinser
E, Hos D, Hamdorf M, Imhof T, Braun G, Cursiefen C and Bock F:
Topical VEGF-C/D Inhibition Prevents Lymphatic Vessel Ingrowth into
Cornea but Does Not Improve Corneal Graft Survival. J Clin Med.
9:12702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Han Y, Sengupta S, Lee BJ, Cho H, Kim J,
Choi HG, Dash U, Kim JH, Kim ND, Kim JH and Sim T: Identification
of a Unique Resorcylic Acid Lactone Derivative That Targets Both
Lymphangiogenesis and Angiogenesis. J Med Chem. 62:9141–9160. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Cho YK, Shin EY, Uehara H and Ambati B:
The Effect of 0.5% Timolol Maleate on Corneal(Lymph)Angiogenesis in
a Murine Suture Model. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 34:403–409. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Cho YK, Shin EY, Uehara H and Ambati B:
Antiangiogenesis Effect of Albendazole on the Cornea. J Ocul
Pharmacol Ther. 35:254–261. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ellenberg D, Azar DT, Hallak JA, Tobaigy
F, Han KY, Jain S, Zhou Z and Chang JH: Novel aspects of corneal
angiogenic and lymphangiogenic privilege. Prog Retin Eye Res.
29:208–248. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tzeng HE, Chang AC, Tsai CH, Wang SW and
Tang CH: Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes VEGF-C-dependent
lymphangiogenesis via inhibition of miR-381 in human chondrosarcoma
cells. Oncotarget. 7:38566–38578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Shin JW, Min M, Larrieu-Lahargue F, Canron
X, Kunstfeld R, Nguyen L, Henderson JE, Bikfalvi A, Detmar M and
Hong YK: Prox1 promotes lineage-specific expression of fibroblast
growth factor (FGF) receptor-3 in lymphatic endothelium: A role for
FGF signaling in lymphangiogenesis. Mol Biol Cell. 17:576–584.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hellström M, Phng LK and Gerhardt H: VEGF
and Notch signaling: the yin and yang of angiogenic sprouting. Cell
Adh Migr. 1:133–136. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kofler NM, Shawber CJ, Kangsamaksin T,
Reed HO, Galatioto J and Kitajewski J: Notch signaling in
developmental and tumor angiogenesis. Genes Cancer. 2:1106–1116.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Food and Drug Administration, . Drug
Approvals and Databases. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/development-approval-process-drugs/drug-approvals-and-databasesOctober
20–2024
|
|
89
|
Imamura K, Yoshida W, Seshima F, Aoki H,
Yamashita K, Kitamura Y, Murakami T, Ambiru M, Bizenjima T,
Katayama A, et al: Periodontal regenerative therapy using
recombinant human fibroblast growth factor (rhFGF)-2 in combination
with carbonate apatite granules or rhFGF-2 alone: 12-month
randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Investig. 28:5742024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Clark AJ, Mullooly N, Safitri D, Harris M,
de Vries T, MaassenVanDenBrink A, Poyner DR, Gianni D, Wigglesworth
M and Ladds G: CGRP, adrenomedullin and adrenomedullin 2 display
endogenous GPCR agonist bias in primary human cardiovascular cells.
Commun Biol. 4:7762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhu S, Zidan A, Pang K, Musayeva A, Kang Q
and Yin J: Promotion of corneal angiogenesis by sensory
neuron-derived calcitonin gene-related peptide. Exp Eye Res.
220:1091252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Majima M, Ito Y, Hosono K and Amano H:
CGRP/CGRP Receptor Antibodies: Potential adverse effects due to
blockade of neovascularization? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 40:11–21.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Li S, Shi S, Xia F, Ha Y, Luisi J, Gupta
PK, Merkley KH, Motamedi M, Liu H and Zhang W: CXCR3 deletion
aggravates corneal neovascularization in a corneal alkali-burn
model. Exp Eye Res. 225:1092652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Nibbs RJ and Graham GJ: Immune regulation
by atypical chemokine receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:815–829. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Chevigné A, Janji B, Meyrath M, Reynders
N, D'Uonnolo G, Uchański T, Xiao M, Berchem G, Ollert M, Kwon YJ,
et al: CXCL10 Is an Agonist of the CC Family Chemokine Scavenger
Receptor ACKR2/D6. Cancers (Basel). 13:10542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Muramatsu M, Osawa T, Miyamura Y, Nakagawa
S, Tanaka T, Kodama T, Aburatani H, Sakai J, Ryeom S and Minami T:
Loss of Down syndrome critical region-1 leads to cholesterol
metabolic dysfunction that exaggerates hypercholesterolemia in
ApoE-null background. J Biol Chem. 296:1006972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ren Y, Dong X, Zhao H, Feng J, Chen B,
Zhou Y, Peng Y, Zhang L, Zhou Q, Li Y, et al: Myeloid-derived
suppressor cells improve corneal graft survival through suppressing
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Am J Transplant. 21:552–566.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ren Y, Dong X, Liu Y, Kang H, Guan L,
Huang Y, Zhu X, Tian J, Chen B, Jiang B and He Y: Rapamycin
antagonizes angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis through
myeloid-derived suppressor cells in corneal transplantation. Am J
Transplant. 23:1359–1374. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Wei C, Mi Y, Sun L, Luo J, Zhang J, Gao Y,
Yu X, Ge H and Liu P: Cannabidiol alleviates suture-induced corneal
pathological angiogenesis and inflammation by inducing
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
137:1124292024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Kang H, Feng J, Peng Y, Liu Y, Yang Y, Wu
Y, Huang J, Jie Y, Chen B and He Y: Human mesenchymal stem cells
derived from adipose tissue showed a more robust effect than those
from the umbilical cord in promoting corneal graft survival by
suppressing lymphangiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 14:3282023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Yu F, Gong D, Yan D, Wang H, Witman N, Lu
Y, Fu W and Fu Y: Enhanced adipose-derived stem cells with
IGF-1-modified mRNA promote wound healing following corneal injury.
Mol Ther. 31:2454–2471. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zhu J, Inomata T, Fujimoto K, Uchida K,
Fujio K, Nagino K, Miura M, Negishi N, Okumura Y, Akasaki Y, et al:
Ex Vivo-Induced bone marrow-derived myeloid suppressor cells
prevent corneal allograft rejection in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 62:32021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zhu Y, Reinach PS, Ge C, Li Y, Wu B, Xie
Q, Tong L and Chen W: Corneal collagen cross-linking pretreatment
mitigates injury-induced inflammation, hemangiogenesis and
lymphangiogenesis in vivo. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 10:112021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Hou Y, Le VNH, Tóth G, Siebelmann S,
Horstmann J, Gabriel T, Bock F and Cursiefen C: UV light
crosslinking regresses mature corneal blood and lymphatic vessels
and promotes subsequent high-risk corneal transplant survival. Am J
Transplant. 18:2873–2884. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Dietrich-Ntoukas T, Bock F, Onderka J, Hos
D, Bachmann BO, Zahn G and Cursiefen C: Selective, Temporary
Postoperative Inhibition of Lymphangiogenesis by Integrin α5β1
blockade improves allograft survival in a murine model of high-risk
corneal transplantation. J Clin Med. 13:44182024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Farooq AV and Shukla D: Herpes simplex
epithelial and stromal keratitis: An epidemiologic update. Surv
Ophthalmol. 57:448–462. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Park PJ, Chang M, Garg N, Zhu J, Chang JH
and Shukla D: Corneal lymphangiogenesis in herpetic stromal
keratitis. Surv Ophthalmol. 60:60–71. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Yu T, Schuette F, Christofi M, Forrester
JV, Graham GJ and Kuffova L: The atypical chemokine receptor-2
fine-tunes the immune response in herpes stromal keratitis. Front
Immunol. 13:10542602022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Anderson C, Zhou Q and Wang S: An
alkali-burn injury model of corneal neovascularization in the
mouse. J Vis Exp. 86:511592014.
|
|
110
|
Oh S, Seo M, Choi JS, Joo CK and Lee SK:
MiR-199a/b-5p Inhibits Lymphangiogenesis by Targeting Discoidin
Domain Receptor 1 in Corneal Injury. Mol Cells. 41:93–102.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Li Y, Chen A, Hong A, Xiong S, Chen X and
Xie Q: Shark Cartilage-Derived Anti-Angiogenic Peptide Inhibits
Corneal Neovascularization. Bioengineering (Basel). 11:6932024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Adams RH and Alitalo K: Molecular
regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 8:464–478. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|