Introduction
Artificial hip replacement surgery is one of the
most effective surgical methods in orthopedic treatment of
end-stage hip joint disease. Number of total hip arthroplasties
(THAs) in the United States is expected to increase from 49,8000 in
2020 to 1,429,000 in 2040 (1).
Despite notable improvements in surgical methods and prosthesis
design, aseptic loosening (AL) caused by periprosthetic bone
resorption remains a notable cause of hip implant failure and
reoperation. Revision surgery can cause physical and mental damage
to patients and increase economic pressure on families, society and
healthcare systems (2–4). As the life expectancy of patients
undergoing joint replacement surgery increases, service life of
artificial joints becomes increasingly important. Therefore,
prevention and treatment of AL are key to improve the success rate
of patients with THA and their quality of life. At present, there
are no effective drugs for prevention and treatment of AL in
clinical practice.
Metabolites participate in enzymatic chemical
reactions which are crucial for cellular function. The metabolome
can serve as an important indicator of physiological or
pathological status to understand the occurrence and progression of
diseases (5–8). Non-targeted metabolomics analysis of
intracellular metabolites present during osteoblast differentiation
demonstrates glycolysis, nucleotides and lipid metabolism are
markedly regulated during osteoblast differentiation (9). Moreover, metabolites associated with
oxidative stress are significantly enriched (10). Transcriptomics studies found that
pathways related to congenital inflammatory response are the main
driving factors for osteolysis in rat models, revealing the
mechanism by which mechanical factors lead to implant loosening
(11,12). In the present study, metabolomics
was used to measure aggregation of all small molecular components
of metabolism in AL. A comprehensive multi-omics analysis was
conducted on biological samples, changes in metabolites were
studied, metabolic properties of AL were determined and metabolic
micro-molecular characteristics or biomarkers for AL diagnosis and
pathogenesis were investigated.
Materials and methods
Patients and samples
Patients diagnosed with AL after THA (n=8) who
underwent revision surgery at the Department of Orthopedics of
Henan Provincial People's Hospital (Zhengzhou, China) from May to
October 2023 were selected as AL group and patients (n=8) diagnosed
with avascular necrosis of femoral head (ANFH) or femoral neck
fracture who underwent primary THA in the same time period were
selected as control group. Inclusion criteria for AL were as
follows: i) History of THA surgery; ii) persistent hip pain,
limited activity and other symptoms (such as muscle atrophy) after
THA; iii) radiological examination (such as X-ray, CT or MRI) shows
a radiolucent line or other signs of loosening around the
prosthesis and iv) clinical and laboratory examination rule out
infection, trauma or other causes of prosthesis loosening (13). Exclusion criteria were as follows:
i) Prosthesis loosening caused by postoperative infection, trauma
or other diseases (such as bone tumors, systemic lupus
erythematosus); ii) postoperative time <6 months (before stable
evaluation period) and iii) severe systemic disease that prevents
further treatment. Inclusion criteria for controls were as follows:
i) Radiological examination (such as X-ray or MRI) shows typical
signs of ANFH or femoral neck fracture and ii) clinical examination
reveals typical symptoms (ANFH, pain in the groin, limited internal
rotation and abduction activities, positive patrick sign; femoral
neck fracture: hip pain, limitation of movement, deformity of lower
limb, and shortening of affected limb). Exclusion criteria were as
follows: i) Hip pain and functional impairment caused by other
disease (such as hip infection or tumor); ii) severe systemic
inflammatory disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic
lupus erythematosus; iii) severe neurological disease; iv) severe
systemic diseases that prevent further treatment and v) mental
health issues that prevent treatment and assessment. The samples
from patients with AL were collected within 3 months of the onset
of loosening symptoms upon completion of diagnosis and revision
surgery. The samples of the control group were taken during primary
THA surgery. Both AL and control group samples were derived from
the surrounding tissue of the liner/head/stem junction of the
prosthesis, ensuring consistency in tissue sampling.
The present study was conducted according to the
principles of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the
Medical Ethics Committee of the Henan Provincial People's Hospital
(approval no. 2022-68). All participants provided written informed
consent to participate.
Preparation and analysis of
metabolomic samples
A total of eight pairs of tissue samples were
collected for metabolomics analysis and a 4:1 solution of methanol
to water was added to the tissue sample. The samples were ground
using a grinder for 6 min (−10°C; 50 Hz), followed by
low-temperature ultrasound extraction for 30 min (5°C; 40 kHz). The
samples were stored at −20°C for 30 min and centrifuged for 15 min
(4°C, 13,000 × g); supernatant was transferred to an injection vial
with an internal tube for analysis. The instrument used for liquid
chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis was UHPLC-Q
Active system, with an HSST3 chromatographic column (100.0×2.1 mm;
internal diameter, 1.8 µm; flow rate of 0.5 ml/min). The sample MS
signal was collected in positive and negative ion scanning modes
with the following settings: Mass scanning range, 70–1,050 m/z;
positive ion voltage 3,500; negative ion voltage 2,800 V; sheath
gas, 40 psi; auxiliary heating gas, 10 psi; ion source heating
temperature, 400°C; cycle collision energy, 20–60 V; MS1
resolution, 70,000 and MS2 resolution, 17,500 full width at half
maxima.
Metabolomic data processing
Raw LC-MS data were imported into Progenesis QI
metabolomics processing software (version 2.0, Waters Corporation)
for analysis, while MS and MS/MS information was integrated with
human metabolome database public metabolic database (hmdb.ca/) and
Metlin (metlin.scripps.edu/) and matched with Majorbio database
(majorbio.com/). The response intensity of sample MS peaks was
normalized using the sum normalization method to obtain the
normalized data matrix (14).
Variables with relative standard deviation >30% were removed
from the quality control samples and log10 logarithmization was
performed to obtain the final data matrix for analysis using the R
package ropls (version 1.6.2) for principal component analysis
(PCA) and orthogonal least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA)
(15). Metabolites with variable
importance (VIP)>1 and P<0.05 (assessed by unpaired student's
t test) obtained from the OPLS-DA model were considered
differential metabolites. MetaboAnalyst (Version 5.0) was used for
metabolic pathway analysis based on the KEGG and The Small Molecule
Pathway Database (SMPDB) databases (16).
Transcriptomic sample processing and
analysis
Following tissue grinding as aforementioned, TRIzol
(cat. no. 15596018CN, Invitrogen) was added to extract RNA, Oligo
dT (cat. no. 18418012, Invitrogen) was used to enrich mRNA,
fragmentation buffer was added; mRNA was randomly broken into small
fragments of ~300 bp and reverse-transcribed using Hieff NGS
ds-cDNA Synthesis Kit (cat. no. 13488ES96, Yeasen); EndRepairMix
(cat. no. N203-01/02, Vazyme) was added to supplement the flat end.
Next, A base was added at the 3′ end to connect the Y-shaped
junction. cDNA purification and fragment sorting that utilize beads
to selectively bind and isolate the 200–300 bp of DNA fragments
were done using sorting kits (cat. no. 12601ES56, Hieff
NGS® DNA Selection Beads, Yeasen). The sorted products
were used for amplification by PCR using Phusion Hot Start II
High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (cat. no. F565L, Thermo Fisher
Scientific). Forward primer:
5′-AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCT-3′,
reverse:
5′-CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCGGTCTCGGCATTCCTGCTGAACCGCTCTTCCGATCT-3′.
Thermo cycling conditions were as follows: Initial denaturation:
98°C for 30 sec to denature the double-stranded DNA, denaturation:
98°C for 15 sec to separate the DNA strands, annealing: 55°C for 30
seconds, elongation: 72°C for 30 sec, 30 cycles, and final
extension: 72°C for 5 min. Prepared libraries were performed by
VAHTS Universal Plus DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (cat. no.
ND617-01/02, Vazyme) according to the manual. Qubit 2.0
(Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) was used to detect the
concentration of the library, and the loading concentration of the
library were pooled at 10 nM concentration, we performed the 2×150
bp paired-end sequencing (PE150) and an average read depth of 15
million read pairs/library on Illumina NovaSeq X Plus platform
(Illumina, Inc.) following the vendor's recom-mended protocol.
Illumina BaseSpace (Version: V5.2.0,
illumina.com/software/basespace.html) for base calling and
demultiplexing. Trimmomatic (Version: V0.39,
usadellab.org/cms/?page=trimmomatic) for quality trimming of
sequence reads. STAR (Version: V2.7.3a, URL: http://github.com/alexdobin/STAR) for aligning reads
to a reference genome.
Transcriptomic data processing
DESeq2 (Version 1.24.0;
bioconductor.org/packages/stats/bioc/DESeq2/) with a screening
threshold of |log2FC|≥1 and Padj<0.05 was used to
identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Functional
enrichment analyses included Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and
Genomes (KEGG; Version 2022.10; genome.jp/kegg/), Gene Ontology
(GO; goatools; Version 0.6.5;
files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bb/7b/0c76e3), Reactome (Version
82; reactome.org) and Disease Ontology (DO; disease-ontology.org)
enrichment analyses. The screening threshold for determining
significant differences in transcript expression between samples
was determined by DESeq2, with Padj<0.05. P-value was
corrected using the Benjamini-Hochberg method.
Padj<0.05 was considered to indicate significant
enrichment.
Proteomic sample processing and
analysis
The tissue samples were ground as aforementioned to
extract protein and concentration was measured using the BCA
method. Enzymatic alkylation was performed by adding iodoacetamide
(10 mM, room temperature for 30 min) to protein. Adding
DL-Dithiothreitol (DTT, 50 mM, room temperature for 15 min) to
quenching the reaction to generate stable and specific peptides for
mass spectrometry analysis. Enzymatic alkylation was performed on
100 µg samples; the next day, samples were subjected to tandem mass
tag labeling and mixing, mixed with an equal amount of labeled
products in a tube, dried with a vacuum concentrator (30°C, 20 min)
and the peptide samples were dissolved in Ultra Performance Liquid
Chromatography buffer (Waters Corporation). Next, high-pH
liquid-phase separation was performed using a reverse-phase C18
column and the two-dimensional Easy-nLC1200 result was analyzed by
using a QExactive (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) mass
spectrometer. The peptide segments were dissolved in MS loading
buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and subjected to separation
in a C18 chromatography column (35°C, 5 µl, 75 µMx25 cm; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.) for 120 min at a flow rate of 300 µl/min.
The process was based on EASY-nLC liquid-phase gradient elution
[phase A, 2% acetonitrile (with 0.1% formic acid) and B, 80%
acetonitrile (with 0.1% formic acid)] with the following settings:
0–1 min, 0–5% B; 1–63 min, 5–23% B; 63–88 min, 23–48% B; 88–89 min,
48–100% B and 89–95 min, 100% B. MS and MS/MS modes were switched
automatically for collection, with MS resolutions of 70 and 35 K,
respectively. With each MS full scan (m/z, 350–1,300), the top 20
parent ions were selected for secondary fragmentation, with dynamic
exclusion time of 18 sec.
Proteomic data processing
The original files were analyzed by using
ProteomeDiscoverer™ (version 2.2; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
The false discovery rate for peptide identification during the
search process was ≤0.01. The t test function in R software
(search.r-project.org/CRAN/refmans/DACF/html/lw.t.test.html;
version 1.6.2) was used to calculate the significance of the
inter-sample differences, as well as the fold-change (FC) of the
inter-group differences. The screening criteria for significantly
differentially expressed proteins were P<0.05 and FC >1.2 for
up- and FC <0.83 for downregulated proteins. Functional
annotation and metabolic pathway analysis were performed on all
differentially expressed proteins. GO enrichment analysis was
performed using Goatools (Version no. 1.4.4;
pypi.org/project/goatools/) and Fisher's exact test. Based on
Meiji's independently developed process, KEGG pathway enrichment
analysis was performed (17).
Padj<0.05 was considered to indicate significant
enrichment.
Comprehensive analysis
Using Cytoscape (version 3.9.1; js.cytoscape.org/),
a network of genes, proteins and metabolic compounds was
constructed to identify pathways significantly enriched according
to DEGs and reveal potential regulatory mechanisms between genes
and metabolites. Differential metabolites and DEG expression data
between the AL and control group were imported into Cytoscape to
assess genetic and metabolic changes in AL, as well as the
potential mechanisms of metabolism.
Bioinformatics analyses
DESeq2 (Version 1.24.0;
bioconductor.org/packages/stats/bioc/DESeq2/) was used for
differential gene analysis. KEGG (Version 2022.10;
genome.jp/kegg/), GO (goatools; Version 0.6.5;
files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bb/7b/0c76e3) and Reactome
databases (Version 82; reactome.org/) were used to determine signal
transduction pathways related to the DEGs. DO database (https://disease-ontology.org) was used to determine
human diseases associated with DEGs, while the GO and KEGG
databases were used for protein functional annotation and
functional enrichment. R software (Version1.6.2) was used for
differential protein analysis in sample tissues. MultiLoc2 (Version
2.0) was used for subcellular localization analysis (18). Differential metabolite analysis was
performed with ropls
(master.bioconductor.org/packages/stats/bioc/ropls/; R package;
Version1.6.2) and multivariate statistics with scipy (https://www.scipy.org/; Python; Version1.0.0) based on
KEGG pathway enrichment results of the human metabolism, metabolic
disease and metabolite signaling pathways associated with
differential metabolite enrichment.
Reverse transcription-quantitative
(RT-q)PCR
Total RNA from AL samples and controls was isolated
using TRIzol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). RNA was subjected to
phenol-chloroform extraction for purification. The quantity and
quality of the purified RNA were assessed by measuring the
absorbance at 260/280 nm (acceptable ratio ≤1.8 and ≥2.2) using
Microplate Reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). cDNA was
synthesized using HiScript II RT SuperMix (Vazyme Biotech Co.,
Ltd.) at 37°C for 15 min and 85°C for 5 sec and maintained at 4°C.
RT-qPCR was conducted with AceTaq DNA Polymerase (Vazyme Biotech
Co., Ltd.) as follows: Initial denaturation at 95°C for 1 min,
followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 10 sec and 60°C for 30 sec. Each
transcript concentration was normalized to the level of GAPDH using
the 2−ΔΔCq method (19). The primer sequences were as
follows: GAPDH forward, 5′GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT-3′ and reverse,
5′-GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG-3′; cytokine receptor-like factor-1
(CRLF1) forward, 5′-CTCTCCCGTGTACTCAACGC-3′ and reverse,
5′-GGGCAGGCCAACATAGAGG-3′ and glutathione-S transferase µ1 (GSTM1)
forward, 5′-GCCCATGATACTGGGGTACTG-3′ and reverse,
5′-GGGCAGATTGGGAAAGTCCA-3′.
Western blotting
Samples from patients with AL and controls were
collected and lysed in RIPA buffer (Merck KGaA) on ice for 30 min.
Protein concentration was determined using the BCA method. A total
of 20 µg/lane protein samples were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and
transferred onto PVDF membranes (MilliporeSigma). The membrane was
blocked with 5% skimmed milk at room temperature for 2 h.
Subsequently, the membrane was incubated overnight at 4°C with
primary antibodies targeting CRLF1 (1:1,000; 43 kDa; cat. no.
bs-8663R; Beijing Biosynthesis Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), GSTM1
(1:2,000; 27 kDa; cat. no. 12412-1-AP; Wuhan Sanying Biotechnology)
and GAPDH (1:10,000; 36 kDa; cat. no. HRP-60004; Wuhan Sanying
Biotechnology). Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary
antibodies (1:5,000; cat. no. I1904-65C; Shanghai Univ
Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) were incubated at room temperature for 2
h. Signal analysis was performed using enhanced chemiluminescence
reagent (cat. no. BL520A, Biosharp) and an image analyzer (Bio-Rad
Laboratories) to detect protein expression levels, and Image Lab
software (Bio-Rad Laboratories; Version 6.1). The intensity of each
band was quantified using AlphaEaseFC software.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism (version
6.01; Dotmatics). Continuous variables that conform to normal
distribution are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of ≥3
independent experimental repeats and were tested using unpaired
Student's t-test. Categorical variables were tested using
χ2 test. Pearson correlation analysis was performed
between CRLF1, GSTM1 and differential metabolites. P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Clinical characteristics of
patients
All patients presented with unilateral onset of AL
and had undergone unilateral surgery. Of patients with AL who had
undergone revision surgery, reasons for the initial total hip
replacement included ANFH in six cases and femoral neck fracture in
two cases. The friction interface of the initial replacement
surgery in the AL group was ceramic on polyethylene in six cases
and metal on polyethylene in two cases. The initial prosthesis
fixation types in the AL group were cementless in seven cases and
cemented in one case; in the latter, the femoral stem was cemented
and the acetabular cup cementless, the acetabular cup did not
loosen, but the femoral stem prosthesis did. In all cases in the AL
group, prosthesis failure due to infection was excluded. AL group
consisted of six females and two males, with a mean age of
60.75±3.62 years. The average duration from the initial replacement
surgery to the revision surgery in the AL group was 109.5±62.99
months. In the AL group, there were three cases of isolated
acetabular cup loosening, one case with isolated femoral stem
loosening and four cases with the loosening of both the acetabular
cup and femoral stem.
In the control group, reasons for surgery included
ANFH in five cases and femoral neck fracture in three cases. The
control group consisted of six females and two males, with an
average age of 61.88±2.29 years. There were no significant
differences in sex ratio or the average age between the two groups
(Table I).
 | Table I.Patient and control demographics. |
Table I.
Patient and control demographics.
| Characteristic | Control | AL | P-value |
|---|
| Sex,
male/female | 2/6 | 2/6 | >0.999 |
| Mean age,
years | 61.88±2.29 | 60.75±3.62 | 0.797 |
| Mean BMI | 25.29±1.05 | 23.77±1.35 | 0.388 |
| Operative site,
left/right | 5/3 | 5/3 | >0.999 |
| Type of
surgery | Primary total hip
arthroplasty | Revision total hip
arthroplasty |
|
| Drinking history,
yes/no | 2/6 | 1/7 | 0.521 |
| Smoking history,
yes/no | 2/6 | 1/7 | 0.521 |
| Preoperative
diagnosis, avascular necrosis of femoral head/fracture of neck of
femur | 5/3 | 6/2 | 0.589 |
Transcriptomics
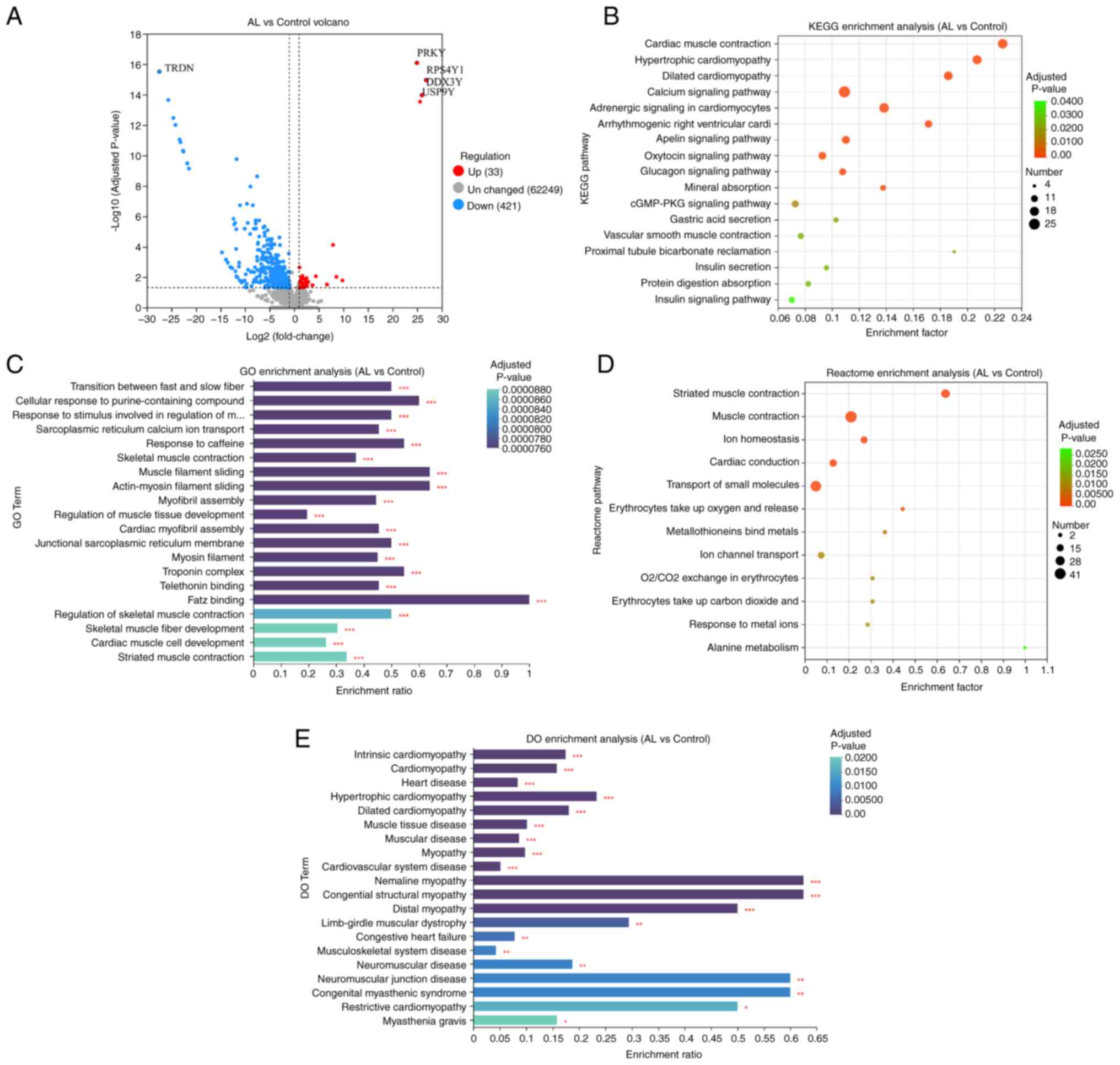
There were 454 DEGs in the AL vs. control groups
(Table SI), 33 of which were up-
and 421 were downregulated. Triadin, which is associated with
muscle contraction (20), was the
most significantly downregulated gene in patients with AL. PRKY
gene was significantly upregulated in the AL group (Fig. 1A). To determine molecular functions
(MFs) affected by differential gene expression, the KEGG database
was used. A total of 17 enriched KEGG pathways were identified,
including ‘cardiac muscle contraction’, ‘hypertrophic cardiopathy’
and ‘dilated cardiopathy’ (Fig.
1B). By mapping DEGs to GO database for analysis, it was
revealed that there may be an association between AL and genes
involved in the regulation of the ‘troponin complex’, ‘transition
between fast and slow fiber’, ‘cellular response to
purine-containing compound’, ‘response to stimulus involved in
regulation of muscle adaptation’, ‘telethonin binding’ and ‘FATZ
binding’ (Fig. 1C). Reactome
database revealed significant changes in reactions and biological
pathways such as ‘muscle contraction’, ‘transport of small
molecules’ (Fig. 1D). DO showed
enrichment of genes associated with diseases such as ‘intrinsic
cardiopathy’, ‘cardiomyopathy’ and ‘heart disease’ (Fig. 1E).
Proteomics
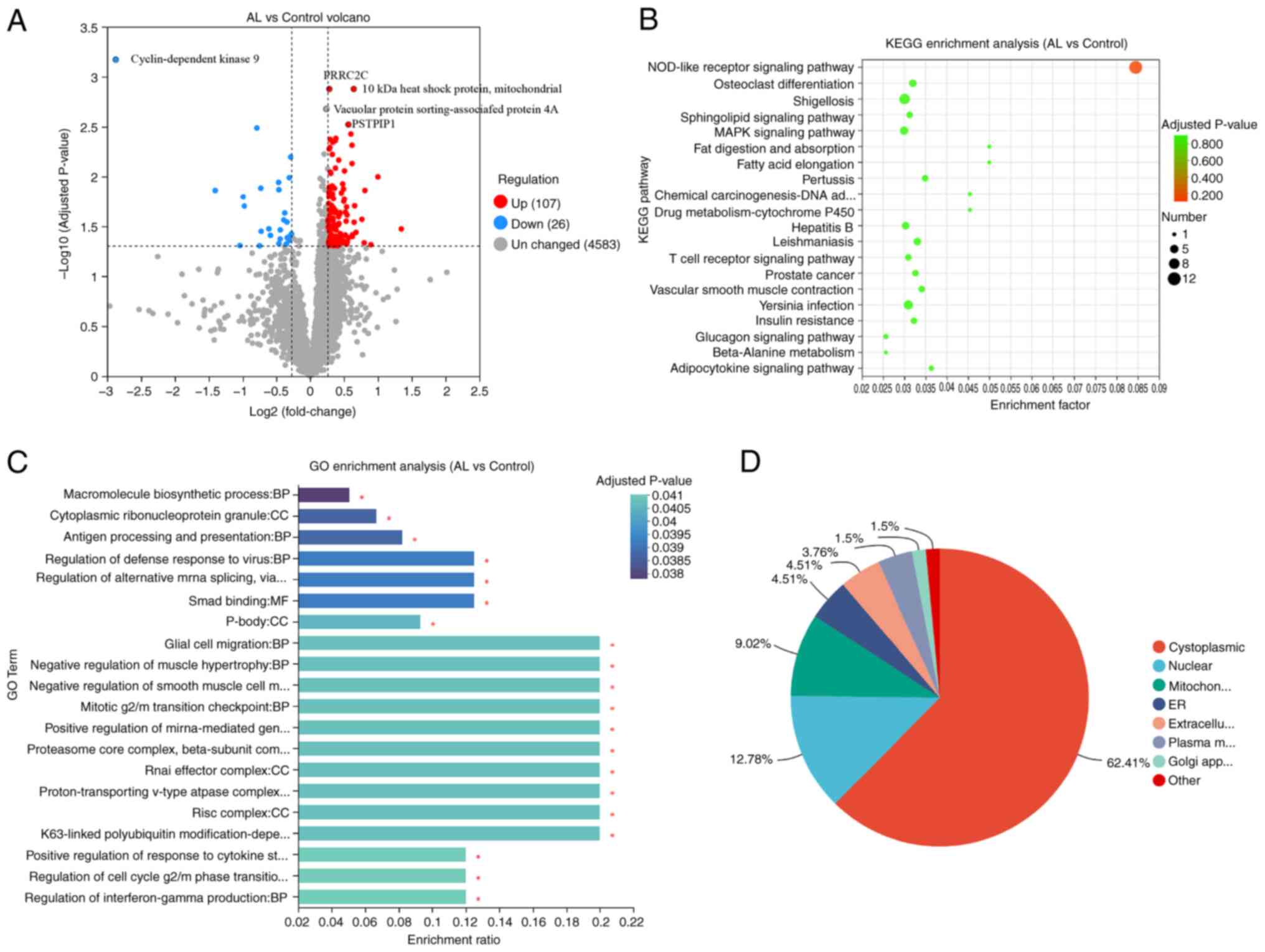
Between AL and control, there were 133
differentially expressed proteins, 107 of which were up- and 26
were downregulated (Fig. 2A). The
most significant downregulation in the AL group was
cyclin-dependent kinase 9 protein, which is associated with
osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption activity (21). The expression of proline rich
coiled-coil 2C protein was significantly upregulated (Fig. 2A). KEGG enrichment analysis
indicated nine significantly enriched KEGG pathways, including
‘NOD-like receptor signaling pathway’, ‘osteoclast
differentiation’, and ‘Shigellosis’. (Fig. 2B). In GO, ‘macromolecule
biosynthetic process’, ‘cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule’, and
‘antigen processing and presentation’ were enriched (Fig. 2C). Subcellular localization
analysis elucidates the specific cellular localization of
differential proteins, which is closely related to protein function
(22). The differentially
expressed proteins were primarily located in the cytoplasmic,
nuclear and mitochondrial regions (Fig. 2D).
Metabolomics
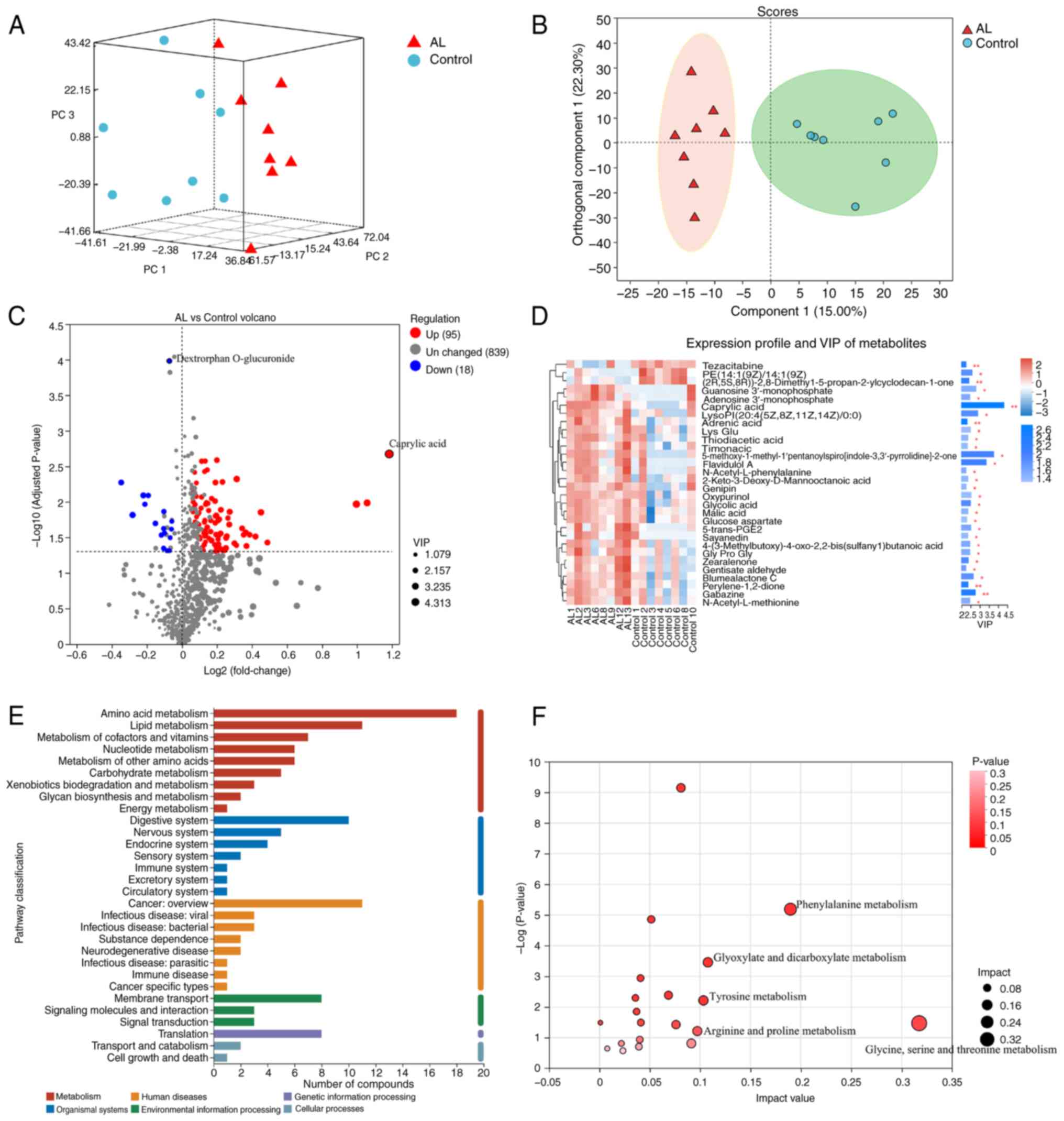
PCA (Fig. 3A) and
OPLS-DA (Fig. 3B) showed
significant separation and metabolic changes. According to VIP
>1.5, 113 significant differential metabolites were screened,
including 95 up- and 18 downregulated. Dextrophan O-glucuronide was
significantly downregulated and caprylic acid was significantly
upregulated, with the highest VIP value of 4.32 (Fig. 3C and D). KEGG annotation showed
differential compounds were primarily associated with metabolism
(Fig. 3E), with significant
enrichment of ‘glycine, serine and threonine metabolism’,
‘phenylalanine metabolism’, ‘glyoxylate and dicarboxylate
metabolism’, ‘tyrosine metabolism’ and ‘arginine and proline
metabolism’ (Fig. 3F).
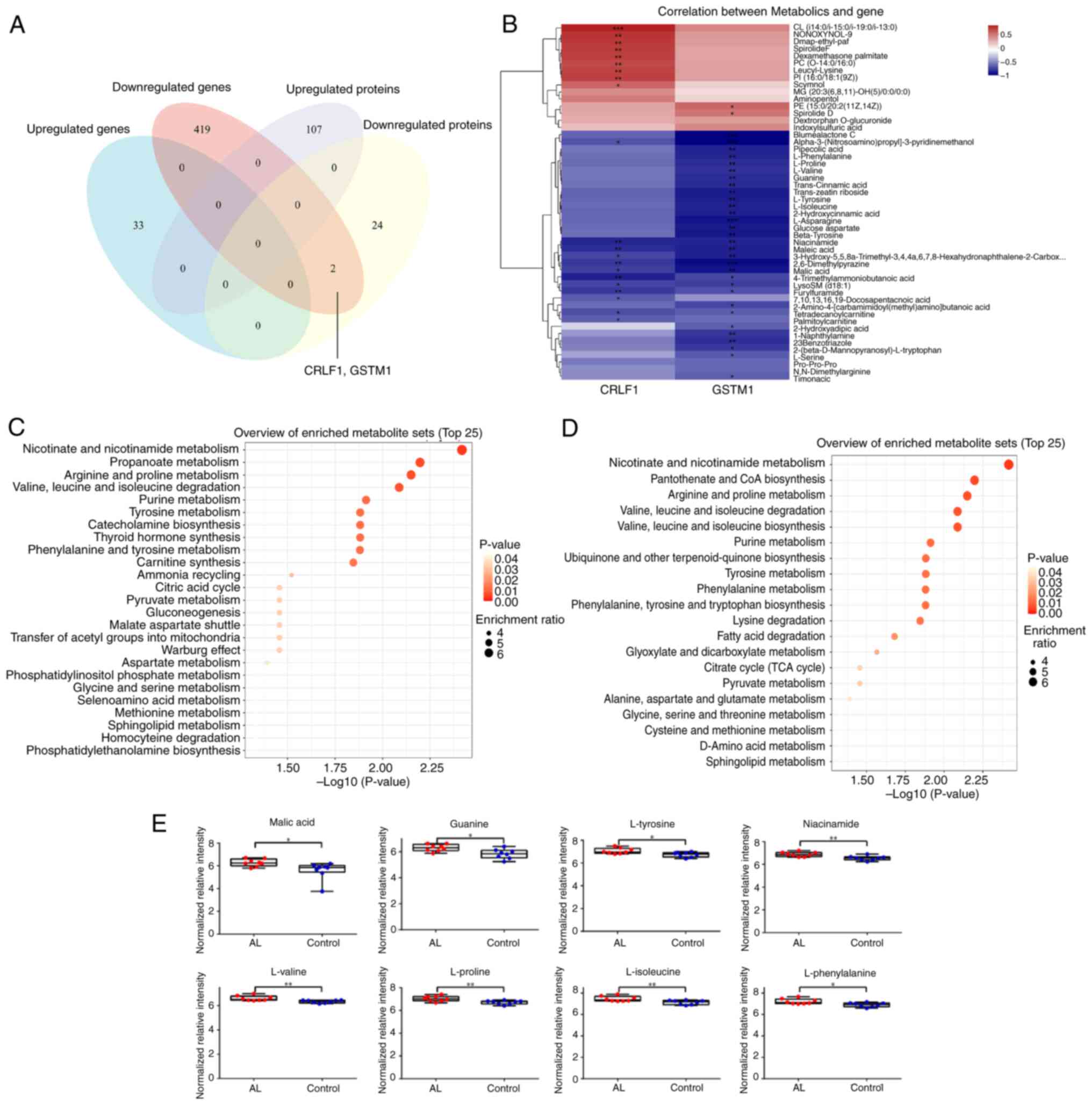
Differential expression of GSTM1 and CRLF1 was consistent at the
mRNA and protein levels (Fig. 4A).
Pearson correlation analysis between CRLF1 and GSTM1 genes and
differential metabolites showed that these genes were associated
with changes in 44 metabolites (Fig.
4B). SMPDB (Fig. 4C) and KEGG
enrichment analysis (Fig. 4D)
showed that CRLF1 and GSTM1 affected ‘pyruvate metabolism’,
‘citrate cycle (TCA cycle)’, ‘tyrosine metabolism’, ‘purine
metabolism’, ‘valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation’,
‘arginine and proline metabolism’, ‘phenylalanine, tyrosine and
tryptophan biosynthesis’. Corresponding metabolites of associated
pathways, such as malic acid, guanine, L-tyrosine, niacinamide,
L-valine, L-proline, L-isoleucine and L-phenylalanine were
increased (Fig. 4E).
Integration of transcriptomics,
proteomics and metabolomics
Pathway analysis was conducted at the
transcriptional, protein and metabolite levels and KEGG enrichment
revealed common pathways regulated at transcriptional, protein and
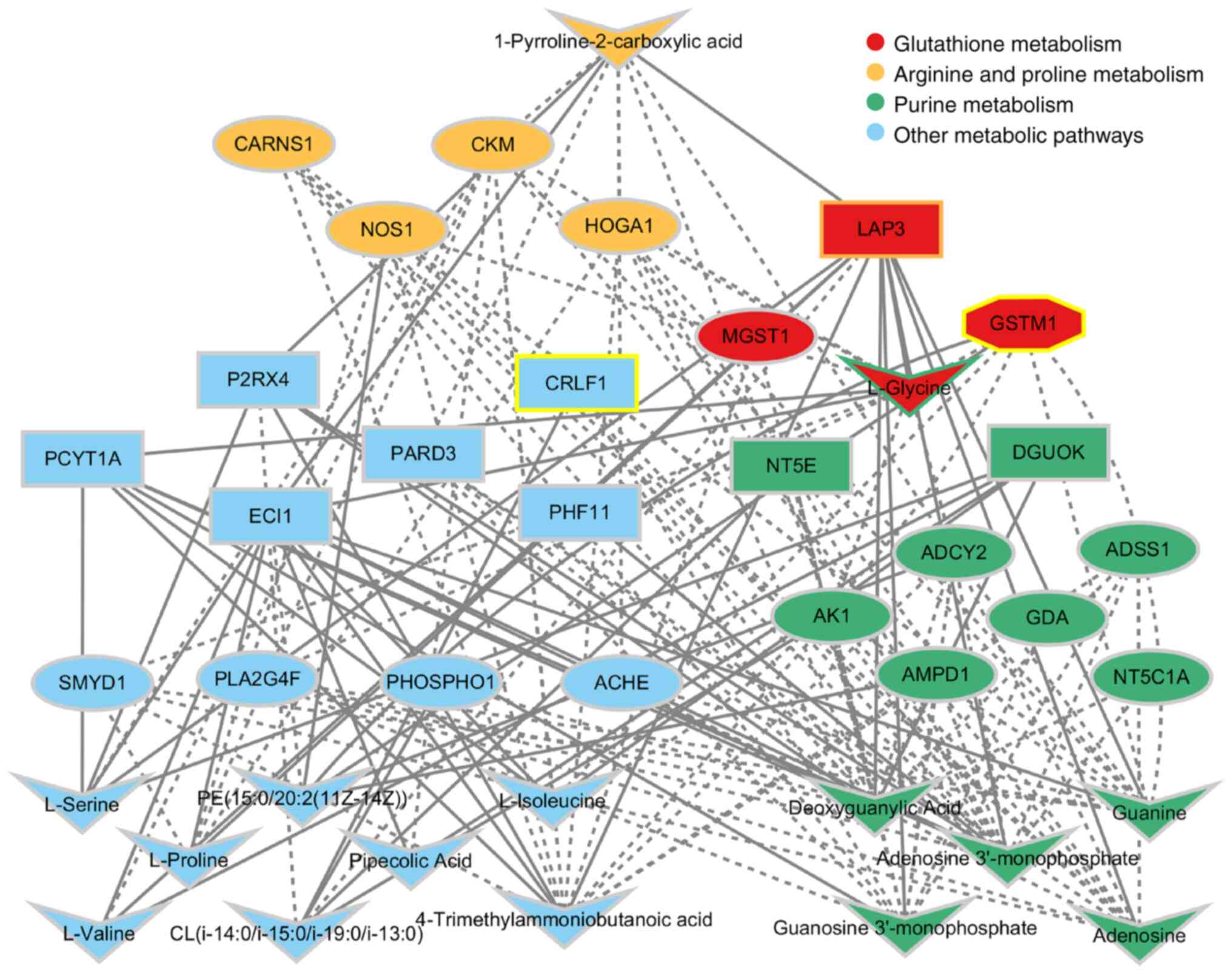
metabolite levels, with 24 pathways in the AL group (Fig. 5). The ‘arginine and proline
metabolism’, ‘purine metabolism’ and ‘glutathione metabolic
pathways’ were regulated at the transcriptional, protein and
metabolite levels in AL. The metabolites guanosine
3′-monophosphate, deoxyguanylic acid, adenosine 3′-monophosphate,
guanine, L-glycine and adenosine were significantly overexpressed
in the AL group, participating in the ‘purine metabolic pathway’
and affecting expression levels of the guanine deaminase (GDA),
Adenylosuccinate Synthase 1 (ADSS1), Adenosine Monophosphate
Deaminase 1 (AMPD1), Adenylate Kinase 1 (AK1), Adenylate Cyclase 2
(ADCY2) and 5′-Nucleotidase, Cytosolic IA (NT5C1A) genes and the
5′-Nucleotidase Ecto (NT5E) and Deoxyguanosine Kinase (DGUOK)
proteins. The ‘arginine and proline metabolic pathway’ is a key
pathway in AL, in which the metabolic levels of
1-pyroline-2-carboxylic acid and protein expression of Leucine
Aminopeptidase 3 (LAP3) was increased, and gene expression of the
nitric oxide synthase 1 (NOS1), Creatine Kinase M-Type (CKM),
4-Hydroxy-2-Oxoglutarate Aldolase 1 (HOGA1), Carnosine Synthase 1
(CARNS1) and Creatine Kinase, Mitochondrial 2 (CKMT2) genes were
downregulated. The ‘glutathione metabolic pathway’ is also one of
the important pathways in AL, in which the expression level of the
L-glycine metabolite was significantly increased, the gene and
protein expression levels of GSTM1 were significantly reduced, the
LAP3 protein expression level was significantly increased, and the
gene expression level of MGST1 was significantly reduced (Fig. 5).
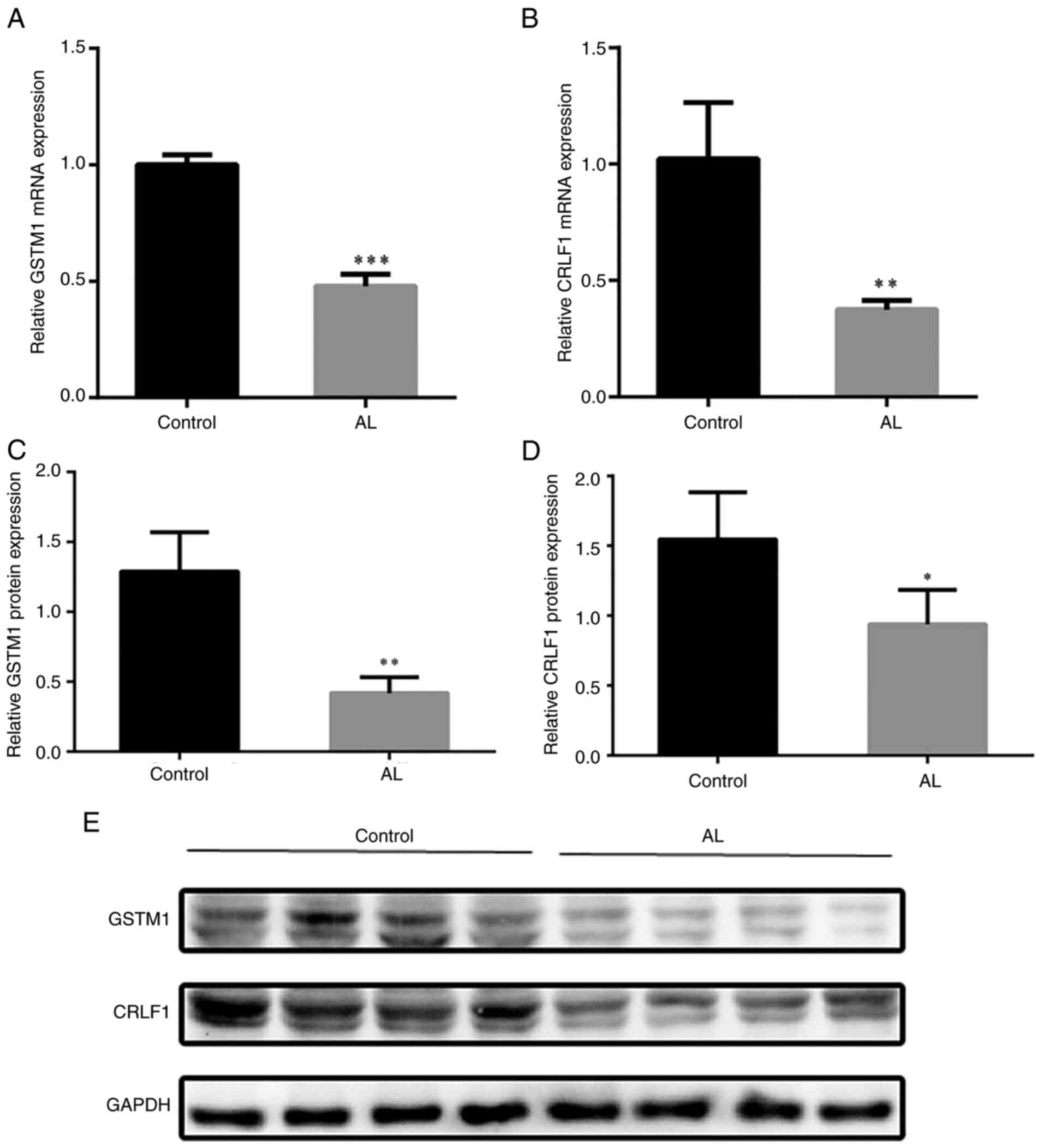
DEG verification
DEG verification was conducted using RT-qPCR and
western blotting to measure mRNA and protein expression levels of
CRLF1 and GSTM1 in tissue samples. The results showed that,
compared with the control group, the mRNA expression of CRLF1 and
GSTM1 in AL (Fig. 6A and B), as
well as protein expression (Fig.
6C-E), was significantly decreased.
Discussion
AL of prostheses is the primary cause of revision
surgery, and its occurrence and development are associated with
metabolic disorders of bone formation and dissolution around joint
prostheses, as well as aseptic inflammation induced by prosthesis
wear particles (such as metal and polyethylene particles) (23). In the present study, transcriptome,
proteomic and non-targeted metabolomic data were analyzed in
synovial tissue and a combined multi-omics analysis was conducted
to reveal changes in metabolites and potential pathogenesis in AL,
providing a novel perspective for the pathogenesis and potential
diagnosis.
Driven by advances in high-throughput technology,
transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics have clinical
application and biomarkers can be used to improve accuracy, enhance
diagnosis and decrease errors (24). Functionally, the transcriptome
encompasses all RNA present in cells; although a large portion of
it is not translated into proteins, it serves a role in determining
cell phenotype and has clinical value in clinical diagnosis
(25). Proteomics can complement
other ‘omics’ techniques, such as genomics and transcriptomics, to
identify the structure and function of specific proteins (26). By contrast, metabolomics is
primarily used to determine small-molecule fingerprints of cellular
processes (27). Metabolites are
the final downstream products of protein translation, gene
transcription or cellular disturbances in the proteome, genome, or
transcriptome. As the final product of cell regulatory processes,
they are considered the ultimate response of biological systems to
metabolic disorders and pathophysiological changes (28). However, the proteome and metabolome
are connected. The protein expression affects the metabolic profile
and concentration of metabolites in turn affects protein expression
(29). Therefore, integrated omics
may provide insights into biological systems and mechanisms.
The present study identified CRLF1 and GSTM1 as
potential biomarkers for AL. CRLF1 is a soluble type I cytokine
receptor that serves an important role in the immune system and
fetal development (30). It is
upregulated by proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6 and
IFN-γ, indicating that human CRLF1 may participate in immune system
regulation during the inflammatory response (31). As this protein is expressed at high
levels in damaged human knee osteoarthritis cartilage and
participates in TGF-β downregulation, it may serve as a biomarker
for osteoarthritis (32,33). The transcription and protein levels
of CRLF1 were significantly decreased in AL synovial tissue,
suggesting that CRLF1 may be involved in wear particle-induced
aseptic inflammation in AL. GSTM1, belonging to the glutathione
S-transferase superfamily, is involved in the metabolism and
detoxification of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and carcinogens
(34). It serves a key role in
determining disease susceptibility, with research showing that
ineffective variants of GSTM1 are associated with increased risk of
ovarian cancer (35). Cytochrome
P450 family 1 subfamily a member 1 and GSTM1 polymorphisms are
genetic risk factors in patients with bone tumors and allele
variations in these genes increase risk of bone tumor occurrence
(36). Given the association
between GSTM1 and glutathione S-transferase θ1 genes and bone
mineral density, these genes may be used as candidates for studying
the genetics of osteoporosis (37). Glutathione metabolism and
ferroptosis serve important roles in normal differentiation of
osteoblasts and senile osteoporosis. GSTM1 and transferrin receptor
(TFRC) are key genes in this process, involved in decreasing ROS
levels in senile osteoporotic osteoblasts (38). GSTM1 is a phase II enzyme of the
glutathione-S-transferase family that protects cells by catalyzing
conjugation of hazardous chemicals to reduced glutathione (GSH)
(39). TFRC encodes transferrin
receptor protein 1 (TFR1) in humans, which controls the levels of
intracellular iron levels (40).
TFR1 imports iron from the extracellular environment into cells,
contributing to the cellular iron pool, and serves a key role in
ferroptosis (40). Kinov et
al (41) demonstrated that the
occurrence of AL is associated with high oxidative stress,
GSH/oxidized glutathione ratio of loose hip prostheses is lower
than that of stable hip prostheses, suggesting that high oxidative
stress may serve a key role in AL. Dong et al (42) showed that DNA methylation-mediated
glutathione peroxidase 4 transcriptional suppression and osteoblast
ferroptosis can promote osteolysis induced by titanium particles.
Xu et al (43) confirmed
that regulating osteoblast ferroptosis via NF-E2-related factor 2
(Nrf2)/antioxidant response element signaling induces peri-implant
osteolysis (43). Here, GSTM1 was
significantly downregulated at both transcriptional and protein
levels in the AL group and was involved in the glutathione
metabolic pathway. Studies have found that glutathione accelerates
osteoclast differentiation and inflammatory bone destruction,
indicating that glutathione is a key molecule in the mechanisms of
osteoclast and inflammatory bone destruction (44,45).
Purine metabolism serves a key role in bone
metabolism and remodeling through coordination of purine receptor
networks (46). Adenosine
derivatives are locally released in bone by osteoblasts or
osteoclasts that form bone tissue, acting directly through
mechanical loading and indirectly through systemic hormones
(47). Under physiological
conditions, intracellular concentration of adenosine is low, while
under pathological conditions such as hypoxia, stress or
inflammation, it increases (46).
Locally released adenosine mediates physiological processes through
its interaction with G protein-coupled receptors (46). Bone marrow cells from adenosine A1
receptors (A1Rs)-knockout mice produce fewer osteoclasts than those
from wild-type mice and A1R antagonists inhibit formation of
osteoclasts with reduced bone resorption capacity, indicating that
adenosine serves a crucial role in bone homeostasis through its
interaction with adenosine (48).
N6 methyladenosine is a methylated adenosine nucleotide and its
methylation promotes proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis
of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, osteoblasts and osteoclasts
by regulating expression of alkaline phosphatase, Runx2, osterix
and VEGF (49). Nitric oxide,
bicarbonate, atrial, brain and C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP),
guanosine, uridine and guanylate cyclase-activating protein
activate guanosine, guanylate or guanylate cyclase (GC) to catalyze
the conversion of guanosine triphosphate into cyclic (c)GMP and
pyrophosphate (50). 8-Nitro-cGMP
is a downstream molecule of nitric oxide and ROS that can promote
RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation (51). CNP activates GC-B to catalyze the
synthesis of cGMP in chondrocytes and osteoblasts. Elevated cGMP
stimulates long-bone growth and GC-B-dependent bone formation in
mice is associated with early juvenile process, which require an
increase in osteoblasts and a decrease in osteoclasts (52). These data collectively indicate
that adenosine, guanine and associated enzymes are all associated
with biological activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone
metabolism. In the AL group, guanosine 3′-monophosphate,
deoxyguanylic acid, adenosine 3′-monophosphate, guanine, L-glycine
and adenosine were significantly upregulated, suggesting they may
affect the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts and participate
in occurrence and development of AL.
Arginine and proline are functional amino acids that
exert anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in treatment of
inflammation-associated diseases such as osteoarthritis (53). Proline/arginine-rich end
leucine-rich repeat protein is a peptide corresponding to the
N-terminal heparin-binding domain of the matrix protein
proline/arginine-rich terminal leucine repeat protein, which
inhibits osteoclast generation and entry into pre-fusion
osteoclasts via chondroitin sulfate-dependent and
membrane-associated protein 2-dependent mechanisms, decreasing
nuclear factor-κB transcription factor activity, which counteracts
bone loss induced by increased osteoclast activity in various bone
disease models in vivo (54). In bone loss, the G protein-coupled
receptor Gpr54 recruits active Src and dual specificity phosphatase
18 (Dusp18) at its C-terminus, which is rich in proline/arginine.
Kisspeptin-10 (Kp-10)/Gpr54 inhibits bone resorption via
Dusp18-mediated Src dephosphorylation (55). In the AL group, the metabolite
1-pyroline-2-carboxylic acid associated with the arginine and
proline metabolic pathway was significantly elevated, indicating
that abnormal metabolism of this metabolite may affect the arginine
and proline metabolic pathway.
Due to the limitations of clinical sample
collection, the present study did not obtain paired hip joint
samples or pre- and postoperative tissues. Mouse calvarial
osteolysis induced by titanium particles is a classic model to
simulate the loosening of artificial prostheses (56). Due to the ability to test the host
response in an orthotopic bone site, speed of developing
osteolysis, availability of quantified images of bone loss and
relatively low cost, the cranial model is the most widely used for
the study of particle-induced osteolysis (57,58).
Therefore, future studies should construct mouse cranial osteolysis
models.
In summary, CRLF1 and GSTM1 were identified as
potential biomarkers of AL based on transcriptomics and proteomics
analysis of samples from AL and control subjects. The
transcriptomic, proteomic and metabolomic data were integrated to
describe key immune metabolic pathways associated with AL. Amino
acid metabolism, including arginine and proline metabolism, and
lipid metabolism, such as adenosine and guanine and L-glycine
metabolism, were involved in AL and altered metabolites may provide
useful diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by Henan Province Science and
Technology Research Project (grant no. 232102310076) and Henan
Province Medical Science and Technology Research Project (grant no.
LHGJ20210004).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be found
in the National Center for Biotechnology Information, iproX and
OMIX database under accession numbers PRJNA1160056, PXD058886 and
PRJCA030476, respectively, or at the following URLs: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/?term=SRP533942,
https://proteomecentral.proteomexchange.org/cgi/GetDataset?ID=PXD058886
and ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/omix/release/OMIX007477.
Authors' contributions
YKL and JZ conceived and designed the study. YHD,
XML, SQ, MEL and ZS analyzed and interpretation of data, YHD, XML,
SQ and MEL wrote the manuscript. YKL and ZS edited the manuscript.
XZ and ZHY analyzed data. All authors have read and approved the
final manuscript. YKL and JZ confirm the authenticity of all the
raw data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was conducted according to the
principles of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by
the Medical Ethics Committee of Henan Provincial People's Hospital
(Zhengzhou, China; approval no. 2022-68). Written informed consent
was secured from all participants for involvement and use of their
tissue samples.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Singh JA, Yu S, Chen L and Cleveland JD:
Rates of total joint replacement in the United States: Future
projections to 2020–2040 using the national inpatient sample. J
Rheumatol. 46:1134–1140. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Apostu D, Lucaciu O, Berce C, Lucaciu D
and Cosma D: Current methods of preventing aseptic loosening and
improving osseointegration of titanium implants in cementless total
hip arthroplasty: A review. J Int Med Res. 46:2104–2119. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bozic KJ, Kamath AF, Ong K, Lau E, Kurtz
S, Chan V, Vail TP, Rubash H and Berry DJ: Comparative epidemiology
of revision arthroplasty: Failed THA poses greater clinical and
economic burdens than failed TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
473:2131–2138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kurtz SM, Lau EC, Ong KL, Adler EM,
Kolisek FR and Manley MT: Which clinical and patient factors
influence the national economic burden of hospital readmissions
after total joint arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res.
475:2926–2937. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Di Minno A, Gelzo M, Stornaiuolo M,
Ruoppolo M and Castaldo G: The evolving landscape of untargeted
metabolomics. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 31:1645–1652. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schrimpe-Rutledge AC, Codreanu SG, Sherrod
SD and McLean JA: Untargeted metabolomics strategies-challenges and
emerging directions. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 27:1897–1905. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cui L, Lu H and Lee YH: Challenges and
emergent solutions for LC-MS/MS based untargeted metabolomics in
diseases. Mass Spectrom Rev. 37:772–792. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Muthubharathi BC, Gowripriya T and
Balamurugan K: Metabolomics: Small molecules that matter more. Mol
Omics. 17:210–229. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu D, Ma L, Zheng J, Zhang Z, Zhang N,
Han Z, Wang X, Zhao J, Lv S and Cui H: Isopsoralen improves
glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by regulating purine metabolism
and promoting cGMP/PKG pathway-mediated osteoblast differentiation.
Curr Drug Metab. 25:288–297. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Misra BB, Jayapalan S, Richards AK,
Helderman RCM and Rendina-Ruedy E: Untargeted metabolomics in
primary murine bone marrow stromal cells reveals distinct profile
throughout osteoblast differentiation. Metabolomics. 17:862021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Amirhosseini M, Andersson G, Aspenberg P
and Fahlgren A: Mechanical instability and titanium particles
induce similar transcriptomic changes in a rat model for
periprosthetic osteolysis and aseptic loosening. Bone Rep. 7:17–25.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pioletti DP, Leoni L, Genini D, Takei H,
Du P and Corbeil J: Gene expression analysis of osteoblastic cells
contacted by orthopedic implant particles. J Biomed Mater Res.
61:408–420. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Abele JT, Swami VG, Russell G, Masson EC
and Flemming JP: The accuracy of single photon emission computed
tomography/computed tomography arthrography in evaluating aseptic
loosening of hip and knee prostheses. J Arthroplasty. 30:1647–1651.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hou Y, He D, Ye L, Wang G, Zheng Q and Hao
H: An improved detection and identification strategy for untargeted
metabolomics based on UPLC-MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 191:1135312020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y and Huang J: Untargeted metabolomic
analysis of metabolites related to body dysmorphic disorder (BDD).
Funct Integr Genomics. 23:702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Z, Yin Y, Chen T, You J, Zhang W,
Zhao Y, Ren Y, Wang H, Chen X and Zuo X: Investigating the impact
of human blood metabolites on the Sepsis development and
progression: A study utilizing two-sample Mendelian randomization.
Front Med (Lausanne). 10:13103912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamamoto N, Suzuki T, Kobayashi M, Dohra
H, Sasaki Y, Hirai H, Yokoyama K, Kawagishi H and Yano K: A-WINGS:
An integrated genome database for Pleurocybella porrigens (Angel's
wing oyster mushroom, Sugihiratake). BMC Res Notes. 7:8662014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Blum T, Briesemeister S and Kohlbacher O:
MultiLoc2: Integrating phylogeny and gene ontology terms improves
subcellular protein localization prediction. BMC Bioinformatics.
10:2742009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chopra N and Knollmann BC: Triadin
regulates cardiac muscle couplon structure and microdomain Ca(2+)
signalling: A path towards ventricular arrhythmias. Cardiovasc Res.
98:187–191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xue S, Shao Q, Zhu LB, Jiang YF, Wang C,
Xue B, Lu HM, Sang WL and Ma JZ: LDC000067 suppresses RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis in vitro and prevents LPS-induced osteolysis in
vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 75:1058262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gillani M and Pollastri G: Protein
subcellular localization prediction tools. Comput Struct Biotechnol
J. 23:1796–1807. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Abu-Amer Y, Darwech I and Clohisy JC:
Aseptic loosening of total joint replacements: Mechanisms
underlying osteolysis and potential therapies. Arthritis Res Ther.
9 (Suppl 1):S62007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee JD, Kim HY, Kang K, Jeong HG, Song MK,
Tae IH, Lee SH, Kim HR, Lee K, Chae S, et al: Integration of
transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics identifies biomarkers
for pulmonary injury by polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate
(PHMG-p), a humidifier disinfectant, in rats. Arch Toxicol.
94:887–909. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koks G, Pfaff AL, Bubb VJ, Quinn JP and
Koks S: At the dawn of the transcriptomic medicine. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 246:286–292. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aslam B, Basit M, Nisar MA, Khurshid M and
Rasool MH: Proteomics: Technologies and their applications. J
Chromatogr Sci. 55:182–196. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Newgard CB: Metabolomics and metabolic
diseases: Where do we stand? Cell Metab. 25:43–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qiu S, Cai Y, Yao H, Lin C, Xie Y, Tang S
and Zhang A: Small molecule metabolites: Discovery of biomarkers
and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:1322023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wishart DS: Metabolomics for investigating
physiological and pathophysiological processes. Physiol Rev.
99:1819–1875. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Paquette AG, MacDonald J, Bammler T, Day
DB, Loftus CT, Buth E, Mason WA, Bush NR, Lewinn KZ, Marsit C, et
al: Placental transcriptomic signatures of spontaneous preterm
birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 228:73.e1–73.e18. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Elson GC, Graber P, Losberger C, Herren S,
Gretener D, Menoud LN, Wells TN, Kosco-Vilbois MH and Gauchat JF:
Cytokine-like factor-1, a novel soluble protein, shares homology
with members of the cytokine type I receptor family. J Immunol.
161:1371–1379. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tsuritani K, Takeda J, Sakagami J, Ishii
A, Eriksson T, Hara T, Ishibashi H, Koshihara Y, Yamada K and
Yoneda Y: Cytokine receptor-like factor 1 is highly expressed in
damaged human knee osteoarthritic cartilage and involved in
osteoarthritis downstream of TGF-beta. Calcif Tissue Int. 86:47–57.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu H, Ding C, Guo C, Xiang S, Wang Y, Luo
B and Xiang H: Suppression of CRLF1 promotes the chondrogenic
differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem and
protects cartilage tissue from damage in osteoarthritis via
activation of miR-320. Mol Med. 27:1162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li P, Li D, Lu Y, Pan S, Cheng F, Li S,
Zhang X, Huo J, Liu D and Liu Z: GSTT1/GSTM1 deficiency aggravated
cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via ROS-triggered
ferroptosis. Front Immunol. 15:14572302024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ye J, Mu YY, Wang J and He XF: Individual
effects of GSTM1 and GSTT1 polymorphisms on cervical or ovarian
cancer risk: An updated meta-analysis. Front Genet. 13:10745702023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li L, Li JG, Liu CY and Ding YJ: Effect of
CYP1A1 and GSTM1 genetic polymorphisms on bone tumor
susceptibility. Genet Mol Res. 14:16600–16607. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mlakar SJ, Osredkar J, Prezelj J and Marc
J: Opposite effects of GSTM1-and GSTT1: Gene deletion variants on
bone mineral density. Dis Markers. 31:279–287. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang Y, Jia Y, Xu Y, Liu X, Wang Z, Liu Y,
Li B and Liu J: Exploring the association between glutathione
metabolism and ferroptosis in osteoblasts with disuse osteoporosis
and the key genes connecting them. Comput Math Methods Med.
12:49147272022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li P, Liu Z, Wang J, Bi X, Xiao Y, Qiao R,
Zhou X, Guo S, Wan P, Chang M, et al: Gstm1/Gstt1 is essential for
reducing cisplatin ototoxicity in CBA/CaJ mice. FASEB J.
36:e223732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Feng H, Schorpp K, Jin J, Yozwiak CE,
Hoffstrom BG, Decker AM, Rajbhandari P, Stokes ME, Bender HG, Csuka
JM, et al: Transferrin receptor is a specific ferroptosis marker.
Cell Rep. 30:3411–3423. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kinov P, Leithner A, Radl R, Bodo K,
Khoschsorur GA, Schauenstein K and Windhager R: Role of free
radicals in aseptic loosening of hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Res.
24:55–62. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dong J, Ruan B, Zhang L, Wei A, Li C, Tang
N, Zhu L, Jiang Q and Cao W: DNA methylation-mediated GPX4
transcriptional repression and osteoblast ferroptosis promote
titanium particle-induced osteolysis. Research (Wash D C).
7:04572024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xu Y, Sang W, Zhong Y, Xue S, Yang M, Wang
C, Lu H, Huan R, Mao X, Zhu L, et al: CoCrMo-Nanoparticles induced
peri-implant osteolysis by promoting osteoblast ferroptosis via
regulating Nrf2-ARE signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 54:e131422021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fujita H, Ochi M, Ono M, Aoyama E, Ogino
T, Kondo Y and Ohuchi H: Glutathione accelerates osteoclast
differentiation and inflammatory bone destruction. Free Radic Res.
53:226–236. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hyeon S, Lee H, Yang Y and Jeong W: Nrf2
deficiency induces oxidative stress and promotes RANKL-induced
osteoclast differentiation. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:789–799. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mediero A and Cronstein BN: Adenosine and
bone metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 24:290–300. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Agrawal A and Jørgensen NR: Extracellular
purines and bone homeostasis. Biochem Pharmacol. 187:1144252021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kara FM, Chitu V, Sloane J, Axelrod M,
Fredholm BB, Stanley ER and Cronstein BN: Adenosine A1 receptors
(A1Rs) play a critical role in osteoclast formation and function.
FASEB J. 24:2325–2333. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Huang M, Xu S, Liu L, Zhang M, Guo J, Yuan
Y, Xu J, Chen X and Zou J: m6A methylation regulates osteoblastic
differentiation and bone remodeling. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:7833222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Potter LR: Guanylyl cyclase structure,
function and regulation. Cell Signal. 23:1921–1926. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kaneko K, Miyamoto Y, Tsukuura R, Sasa K,
Akaike T, Fujii S, Yoshimura K, Nagayama K, Hoshino M, Inoue S, et
al: 8-Nitro-cGMP is a promoter of osteoclast differentiation
induced by RANKL. Nitric Oxide. 72:46–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wagner BM, Robinson JW, Prickett TCR,
Espiner EA, Khosla S, Gaddy D, Suva LJ and Potter LR: Guanylyl
Cyclase-B dependent bone formation in mice is associated with
youth, increased osteoblasts, and decreased osteoclasts. Calcif
Tissue Int. 111:506–518. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li Y, Xiao W, Luo W, Zeng C, Deng Z, Ren
W, Wu G and Lei G: Alterations of amino acid metabolism in
osteoarthritis: Its implications for nutrition and health. Amino
Acids. 48:907–914. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rucci N, Capulli M, Ventura L, Angelucci
A, Peruzzi B, Tillgren V, Muraca M, Heinegård D and Teti A:
Proline/arginine-rich end leucine-rich repeat protein N-terminus is
a novel osteoclast antagonist that counteracts bone loss. J Bone
Miner Res. 28:1912–1924. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li Z, Yang X, Fu R, Wu Z, Xu S, Jiao J,
Qian M, Zhang L, Wu C, Xie T, et al: Kisspeptin-10 binding to Gpr54
in osteoclasts prevents bone loss by activating Dusp18-mediated
dephosphorylation of Src. Nat Commun. 15:13002024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shao H, Shen J, Wang M, Cui J, Wang Y, Zhu
S, Zhang W, Yang H, Xu Y and Geng D: Icariin protects against
titanium particle-induced osteolysis and inflammatory response in a
mouse calvarial model. Biomaterials. 60:92–99. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Deng Z, Wang S, Li M, Fu G, Liu C, Li S,
Jin J, Lyu FJ, Ma Y and Zheng Q: A modified murine calvarial
osteolysis model exposed to ti particles in aseptic loosening.
Biomed Res Int. 25:34034892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jiang H, Wang Y, Deng Z, Jin J, Meng J,
Chen S, Wang J, Qiu Y, Guo T and Zhao J: Construction and
evaluation of a murine calvarial osteolysis model by exposure to
CoCrMo particles in aseptic loosening. J Vis Exp. 17:562762018.
|