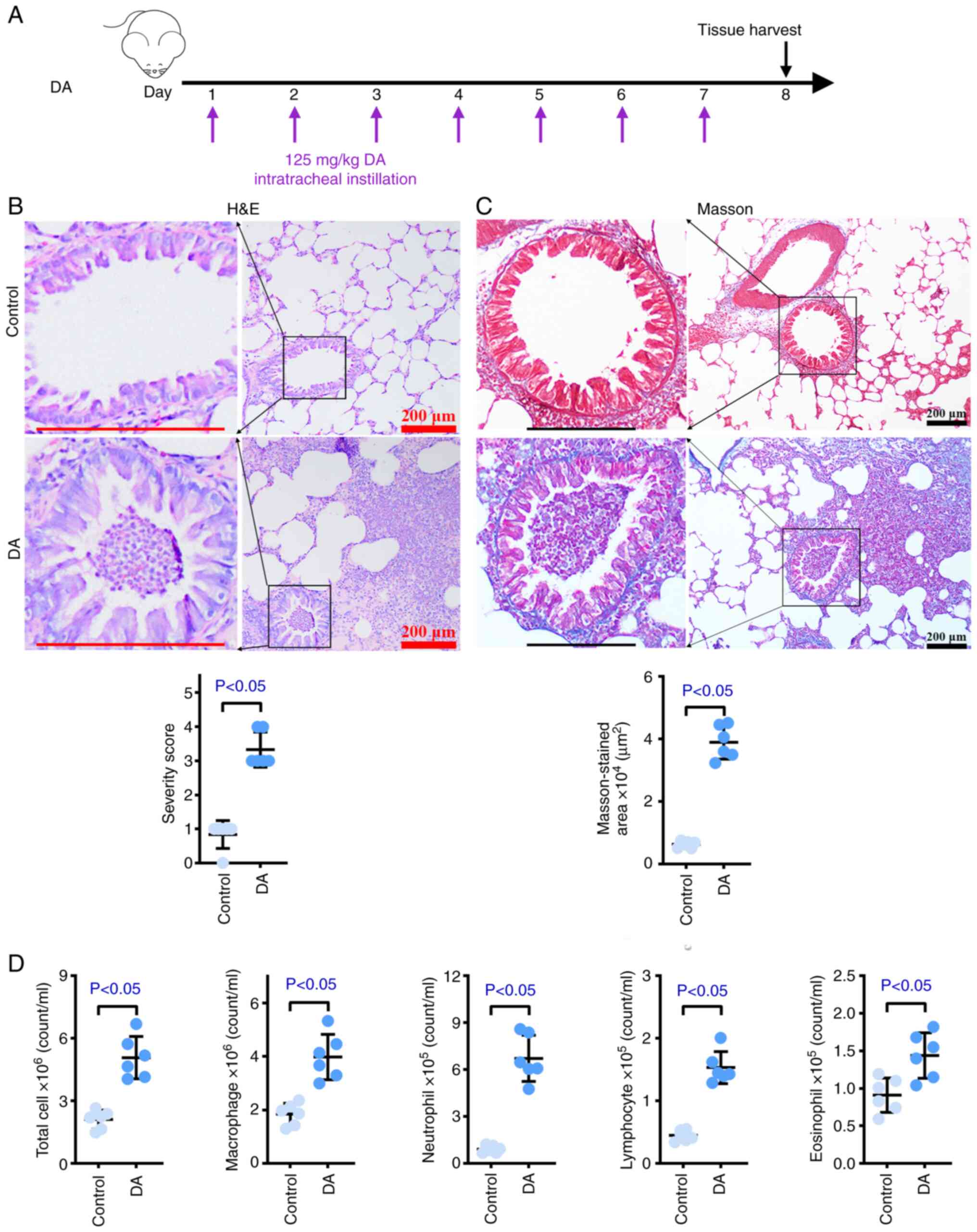
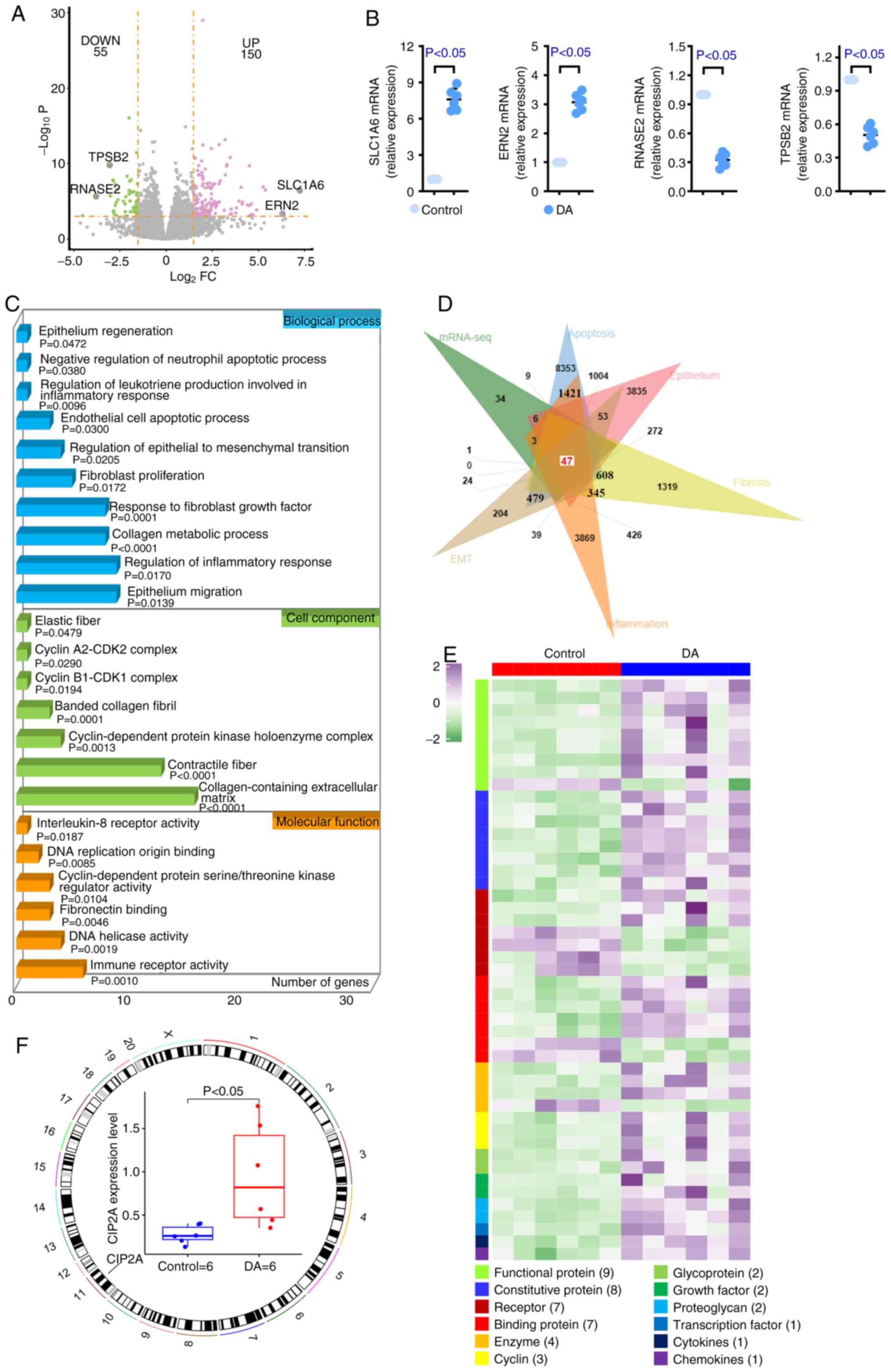
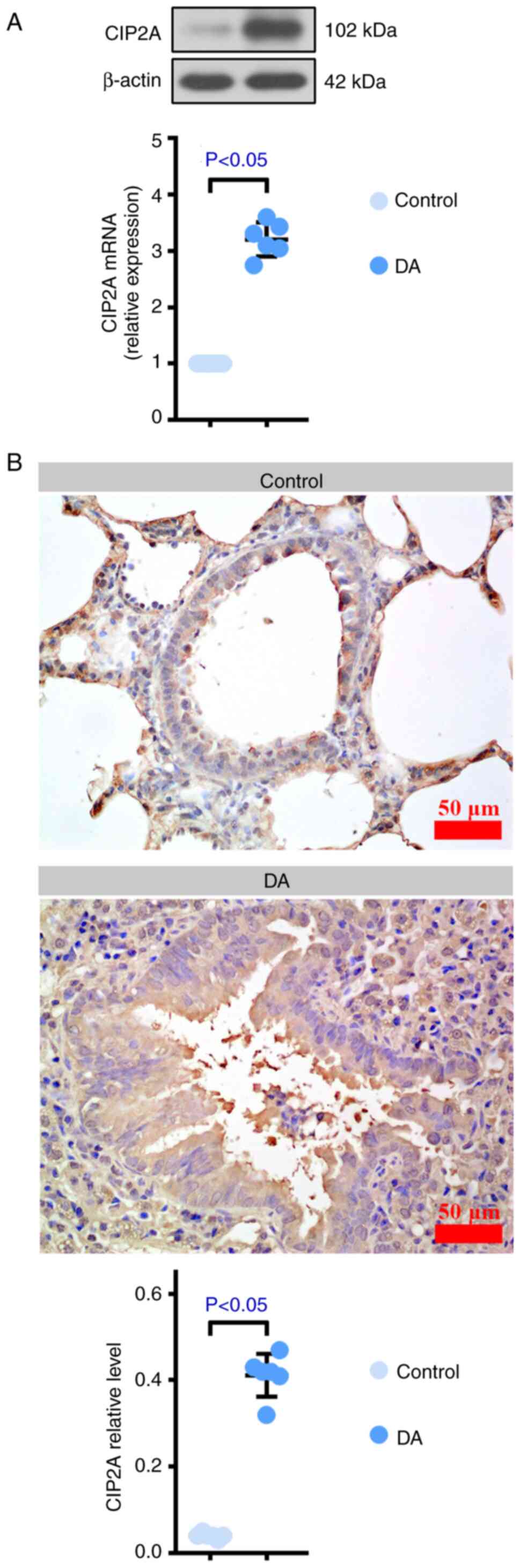
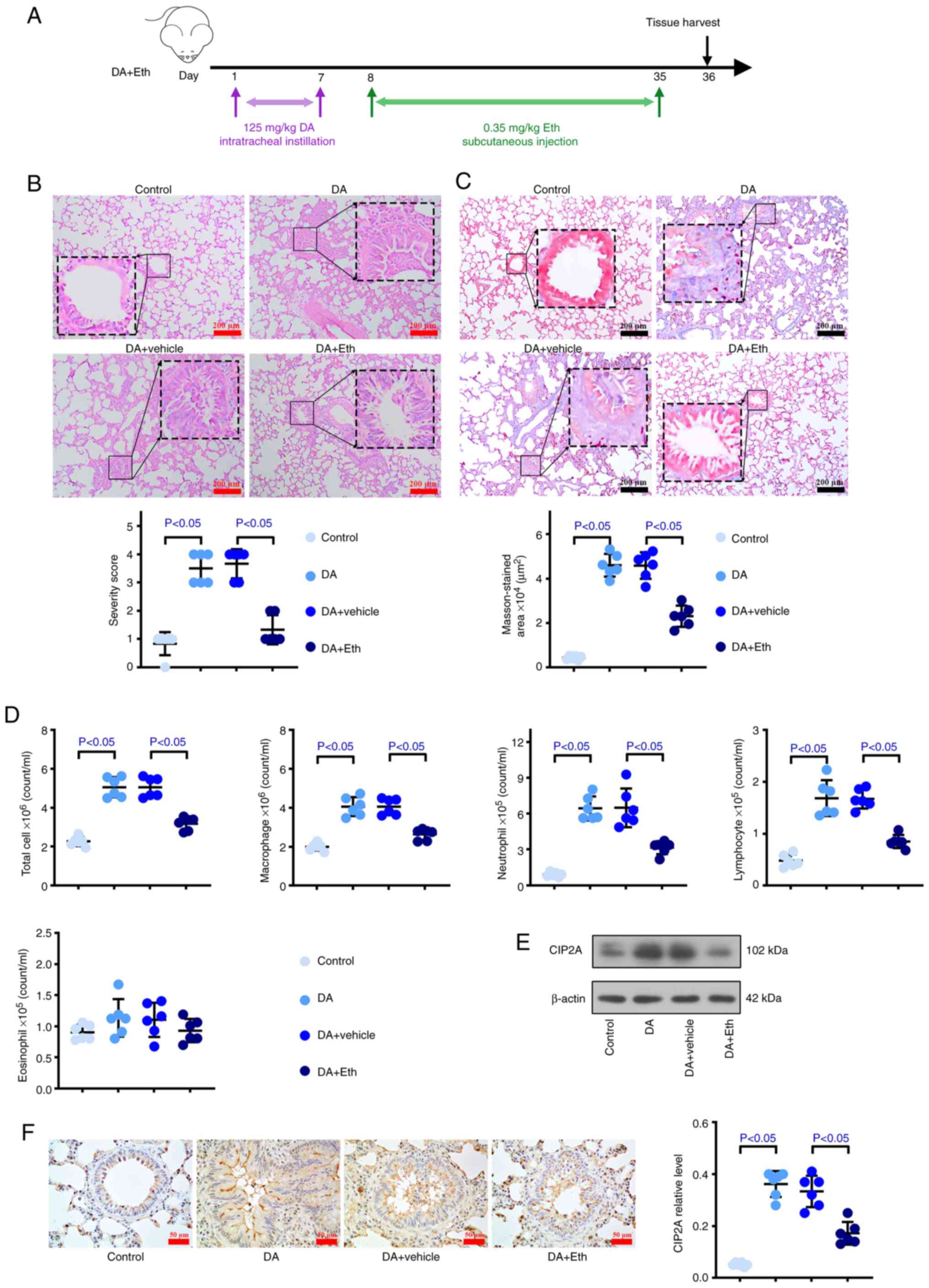
|
1
|
Chu CY, Kim SY, Pryhuber GS, Mariani TJ
and McGraw MD: Single-cell resolution of human airway epithelial
cells exposed to bronchiolitis obliterans-associated chemicals. Am
J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 326:L135–Ll148. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Colom AJ and Teper AM: Post-infectious
bronchiolitis obliterans. Pediatr Pulmonol. 54:212–219. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Flake GP and Morgan DL: Pathology of
diacetyl and 2,3-pentanedione airway lesions in a rat model of
obliterative bronchiolitis. Toxicology. 388:40–47. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Boehler A and Estenne M: Post-transplant
bronchiolitis obliterans. Eur Respir J. 22:1007–1018. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Laohaburanakit P, Chan A and Allen RP:
Bronchiolitis obliterans. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 25:259–274.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
D'Amico R, Fusco R, Cordaro M, Siracusa R,
Peritore AF, Gugliandolo E, Crupi R, Scuto M, Cuzzocrea S, Di Paola
R and Impellizzeri D: Modulation of NLRP3 inflammasome through
formyl peptide receptor 1 (Fpr-1) pathway as a new therapeutic
target in bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. Int J Mol Sci.
21:21442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang C, Niu Y, Yu L, Lv W, Xu H,
Abuduwufuer A, Cao J and Hu J: The role of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in the post-lung transplantation bronchiolitis
obliterans. J Cardiothorac Surg. 12:1192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hakim A, Cooke KR, Pavletic SZ, Khalid M,
Williams KM and Hashmi SK: Diagnosis and treatment of bronchiolitis
obliterans syndrome accessible universally. Bone Marrow Transplant.
54:383–392. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hodge S, Holmes M, Banerjee B, Musk M,
Kicic A, Waterer G, Reynolds PN, Hodge G and Chambers DC:
Posttransplant bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome is associated with
bronchial epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Am J Transplant.
9:727–733. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang J, Kim SY, House E, Olson HM,
Johnston CJ, Chalupa D, Hernady E, Mariani TJ, Clair G, Ansong C,
et al: Repetitive diacetyl vapor exposure promotes ubiquitin
proteasome stress and precedes bronchiolitis obliterans pathology.
Arch Toxicol. 95:2469–2483. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Palmer SM, Flake GP, Kelly FL, Zhang HL,
Nugent JL, Kirby PJ, Foley JF, Gwinn WM and Morgan DL: Severe
airway epithelial injury, aberrant repair and bronchiolitis
obliterans develops after diacetyl instillation in rats. PLoS One.
6:e176442011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kelly FL, Sun J, Fischer BM, Voynow JA,
Kummarapurugu AB, Zhang HL, Nugent JL, Beasley RF, Martinu T and
Gwinn WM: Diacetyl induces amphiregulin shedding in pulmonary
epithelial cells and in experimental bronchiolitis obliterans. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 51:568–574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kreiss K, Gomaa A, Kullman G, Fedan K,
Simoes EJ and Enright PL: Clinical bronchiolitis obliterans in
workers at a microwave-popcorn plant. N Engl J Med. 347:330–338.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
van Rooy FGBGJ, Rooyackers JM, Prokop M,
Houba R, Smit LAM and Heederik DJJ: Bronchiolitis obliterans
syndrome in chemical workers producing diacetyl for food
flavorings. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 176:498–504. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao F, Xu T, Wang X, Zhong S, Chen S,
Zhang M, Zhang X, Shen Y, Wang X, Xu C and Shen Z: CIP2A mediates
fibronectin-induced bladder cancer cell proliferation by
stabilizing β-catenin. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen W, Liang JL, Zhou K, Zeng QL, Ye JW
and Huang MJ: Effect of CIP2A and its mechanism of action in the
malignant biological behavior of colorectal cancer. Cell Commun
Signal. 18:672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Laine A, Nagelli SG, Farrington C, Butt U,
Cvrljevic AN, Vainonen JP, Feringa FM, Grönroos TJ, Gautam P, Khan
S, et al: CIP2A interacts with TopBP1 and drives Basal-like breast
cancer tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 81:4319–4331. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu WT, Liuyang ZY, Tian Y, Liang JW, Zhang
XL, Zhang HL, Wang G, Huo Y, Shentu YP, Wang JZ, et al: CIP2A
deficiency promotes depression-like behaviors in mice through
inhibition of dendritic arborization. EMBO Rep. 23:e549112022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou Y, Yang D, Chen H, Zheng C, Jiang H,
Liu X, Huang X, Ye S, Song S, Jiang N, et al: Polyphyllin I
attenuates cognitive impairments and reduces AD-like pathology
through CIP2A-PP2A signaling pathway in 3XTg-AD mice. FASEB J.
34:16414–16431. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou Y, Liu X, Ma S, Zhang N, Yang D, Wang
L, Ye S, Zhang Q, Ruan J, Ma J, et al: ChK1 activation induces
reactive astrogliosis through CIP2A/PP2A/STAT3 pathway in
Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J. 36:e222092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang Q, Wang Q, Zeng G, Li Q, Jiang T,
Zhang Z, Zheng W and Wang K: Overexpression of CIP2A in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma promotes cellular epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and is associated with poor prognosis. Oncol Rep.
34:2515–2522. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu Y, Gu TT and Zheng PS: CIP2A cooperates
with H-Ras to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
cervical-cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 356:646–655. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seppälä M, Tervo S, Pohjola K, Laranne J,
Huhtala H, Toppila-Salmi S and Paavonen T: The association and
prognostic relevance of cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase
2A and inflammation in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. APMIS.
123:1007–1015. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nath S, Ohlmeyer M, Salathe MA, Poon J,
Baumlin N, Foronjy RF and Geraghty P: Chronic Cigarette smoke
exposure subdues PP2A activity by enhancing expression of the
oncogene CIP2A. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 59:695–705. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jin L, Si Y, Hong X, Liu P, Zhu B, Yu H,
Zhao X, Qin S, Xiong M, Liu Y, et al: Ethoxysanguinarine inhibits
viability and induces apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by
inhibiting CIP2A. Int J Oncol. 52:1569–1578. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
House EL, Kim SY, Johnston CJ, Groves AM,
Hernady E, Misra RS and McGraw MD: Diacetyl vapor inhalation
induces mixed, granulocytic lung inflammation with increased
CD4+CD25+ T cells in the rat. Toxics. 9:3592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
National Research Council Committee for
the Update of the Guide for the C and Use of Laboratory A, . The
National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National
Institutes of Health. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals National Academies Press (US) Copyright © 2011. National
Academy of Sciences; Washington (DC): 2011, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin J, Deng H, Zhang Y, Zou L, Fu Z and
Dai J: Effect of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem
cells on murine model of bronchiolitis obliterans like injury.
Pediatr Pulmonol. 56:129–137. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ueno-Iio T, Shibakura M, Iio K, Tanimoto
Y, Kanehiro A, Tanimoto M and Kataoka M: Effect of fudosteine, a
cysteine derivative, on airway hyperresponsiveness, inflammation,
and remodeling in a murine model of asthma. Life Sci. 92:1015–1023.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Foster MW, Gwinn WM, Kelly FL, Brass DM,
Valente AM, Moseley MA, Thompson JW, Morgan DL and Palmer SM:
Proteomic analysis of primary human airway epithelial cells exposed
to the respiratory toxicant diacetyl. J Proteome Res. 16:538–549.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Z, Ma L, Wen ZS, Cheng YX and Zhou GB:
Ethoxysanguinarine induces inhibitory effects and downregulates
CIP2A in lung cancer cells. ACS Med Chem Lett. 5:113–118. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wynn TA and Ramalingam TR: Mechanisms of
fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat Med.
18:1028–1040. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kalluri R: EMT: When epithelial cells
decide to become mesenchymal-like cells. J Clin Invest.
119:1417–1419. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Smith B and Bhowmick N: Role of EMT in
metastasis and therapy resistance. J Clin Med. 5:172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Borthwick LA, Parker SM, Brougham KA,
Johnson GE, Gorowiec MR, Ward C, Lordan JL, Corris PA, Kirby JA and
Fisher AJ: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and airway
remodelling after human lung transplantation. Thorax. 64:770–777.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen XD, Tang SX, Zhang JH, Zhang LT and
Wang YW: CIP2A, an oncoprotein, is associated with cell
proliferation, invasion and migration in laryngeal carcinoma cells.
Oncol Rep. 38:1005–1012. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu X, Sun Z, Deng J, Liu J, Ma K, Si Y,
Zhang T, Feng T, Liu Y and Tan Y: Polyphyllin I inhibits invasion
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via CIP2A/PP2A/ERK signaling
in prostate cancer. Int J Oncol. 53:1279–1288. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang Y, Huang P, Liu X, Xiang Y, Zhang T,
Wu Y, Xu J, Sun Z, Zhen W, Zhang L, et al: Polyphyllin I inhibits
growth and invasion of cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer cells by
partially inhibiting CIP2A/PP2A/Akt signaling axis. J Pharmacol
Sci. 137:305–312. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fujiki H, Sueoka E, Watanabe T, Komori A
and Suganuma M: Cancer progression by the okadaic acid class of
tumor promoters and endogenous protein inhibitors of PP2A, SET and
CIP2A. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149:9425–9433. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nader CP, Cidem A, Verrills NM and Ammit
AJ: Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A): a key phosphatase in the
progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to lung
cancer. Respir Res. 20:2222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Marquardt JU, Gomez-Quiroz L, Arreguin
Camacho LO, Pinna F, Lee YH, Kitade M, Domínguez MP, Castven D,
Breuhahn K, Conner EA, et al: Curcumin effectively inhibits
oncogenic NF-κB signaling and restrains stemness features in liver
cancer. J Hepatol. 63:661–669. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cai L, Ming D, Chen W, Zhao Y, Li Y, Sun
W, Pi Y, Jiang X and Li X: Silybin alleviated hepatic injury by
regulating redox balance, inflammatory response, and mitochondrial
function in weaned piglets under Paraquat-induced oxidative stress.
Antioxidants (Basel). 13:3242024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gardner A, Fisher AJ, Richter C, Johnson
GE, Moisey EJ, Brodlie M, Ward C, Krippner-Heidenreich A, Mann DA
and Borthwick LA: The critical role of TAK1 in accentuated
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in obliterative bronchiolitis
after lung transplantation. Am J Pathol. 180:2293–2308. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mohanakumar T, Sharma M, Bansal S,
Ravichandran R, Smith MA and Bremner RM: A novel mechanism for
immune regulation after human lung transplantation. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 157:2096–2106. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Farivar AS, Mackinnon-Patterson B, Woolley
S, Namkung J, Shimamoto A, Verrier ED and Mulligan MS: FR167653
reduces obliterative airway disease in rats. J Heart Lung
Transplant. 23:985–992. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Farivar AS, Woolley SM, Naidu BV, Fraga
CH, Byrne K, Thomas R, Salzman AL, Szabo CS and Mulligan MS: Poly
(ADP) ribose synthetase inhibition reduces obliterative airway
disease in rat tracheal allografts. J Heart Lung Transplant.
23:993–1002. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ohmori K, Takeda S, Miyoshi S, Minami M,
Nakane S, Ohta M, Sawa Y and Matsuda H: Attenuation of lung injury
in allograft rejection using NF-ĸB decoy transfection-novel
strategy for use in lung transplantation. Eur J Cardio-Thoracic
Surg. 27:23–27. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lei N, Peng B and Zhang JY: CIP2A
regulates cell proliferation via the AKT signaling pathway in human
lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:1689–1694. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Monga J, Suthar SK, Rohila D, Joseph A,
Chauhan CS and Sharma M: (+)-Cyanidan-3-ol inhibits epidermoid
squamous cell carcinoma growth via inhibiting AKT/mTOR signaling
through modulating CIP2A-PP2A axis. Phytomedicine. 101:1541162022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Peng B, Chai Y, Li Y, Liu X and Zhang J:
CIP2A overexpression induces autoimmune response and enhances JNK
signaling pathway in human lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 15:8952015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Che Y, Zhang H, Li H and Wu X: CIP2A
interacts with AKT1 to promote the malignant biological behaviors
of oral squamous cell carcinoma by upregulating the
GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway. Exp Ther Med. 26:5142023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Son HE and Jang WG: Cip2A modulates
osteogenic differentiation via the ERK-Runx2 pathway in MG63 cells.
Biofactors. 47:658–664. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|