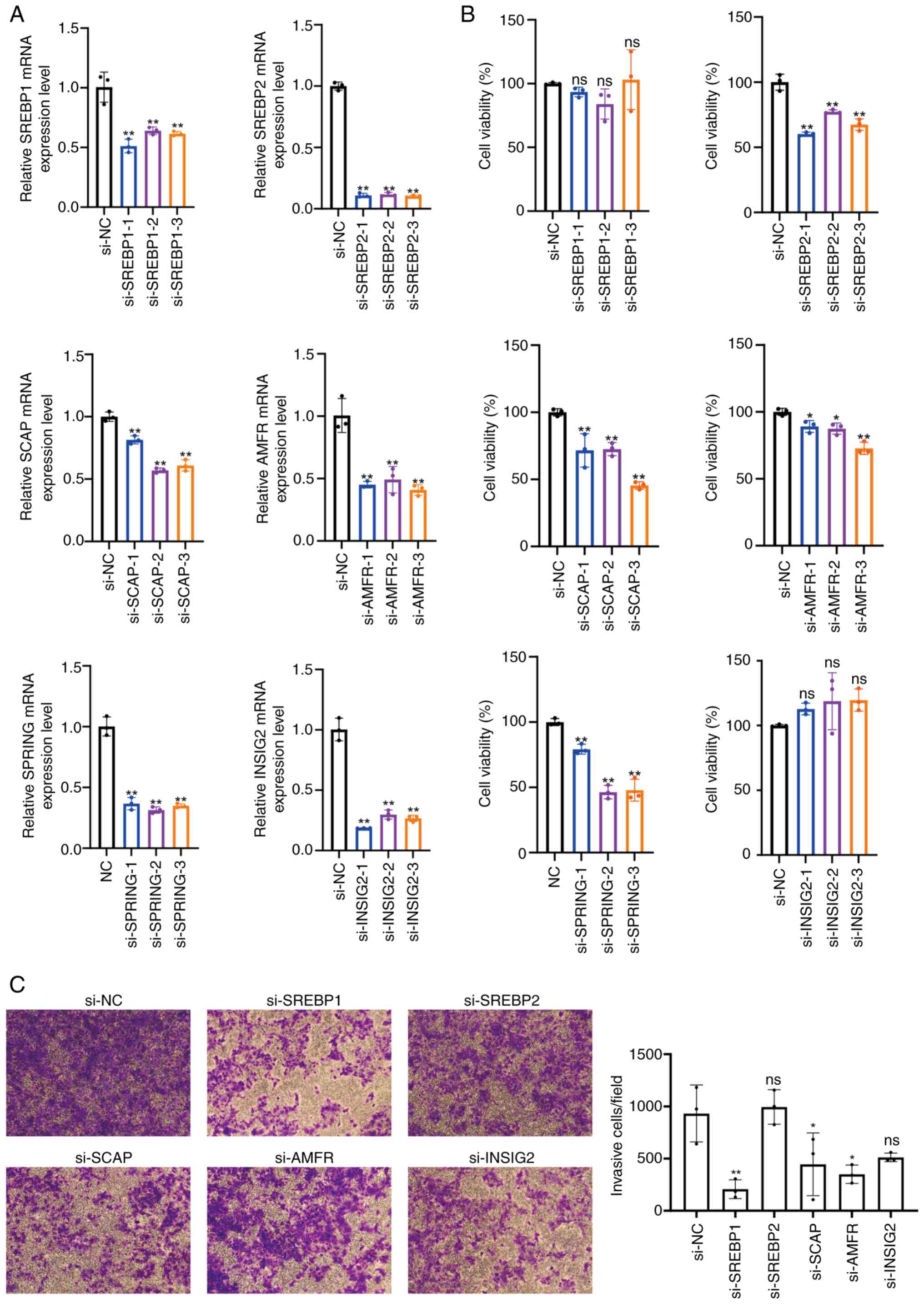
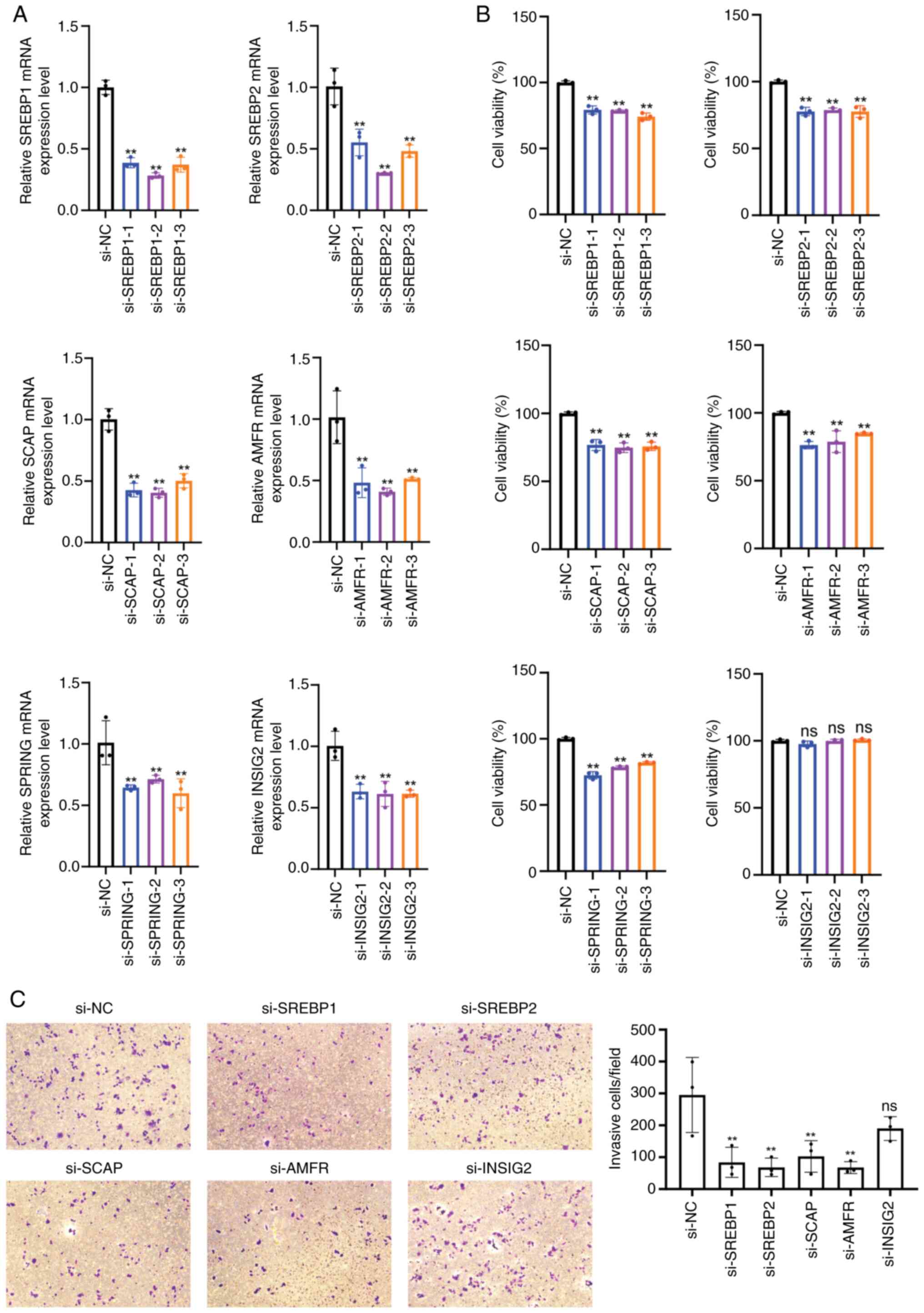
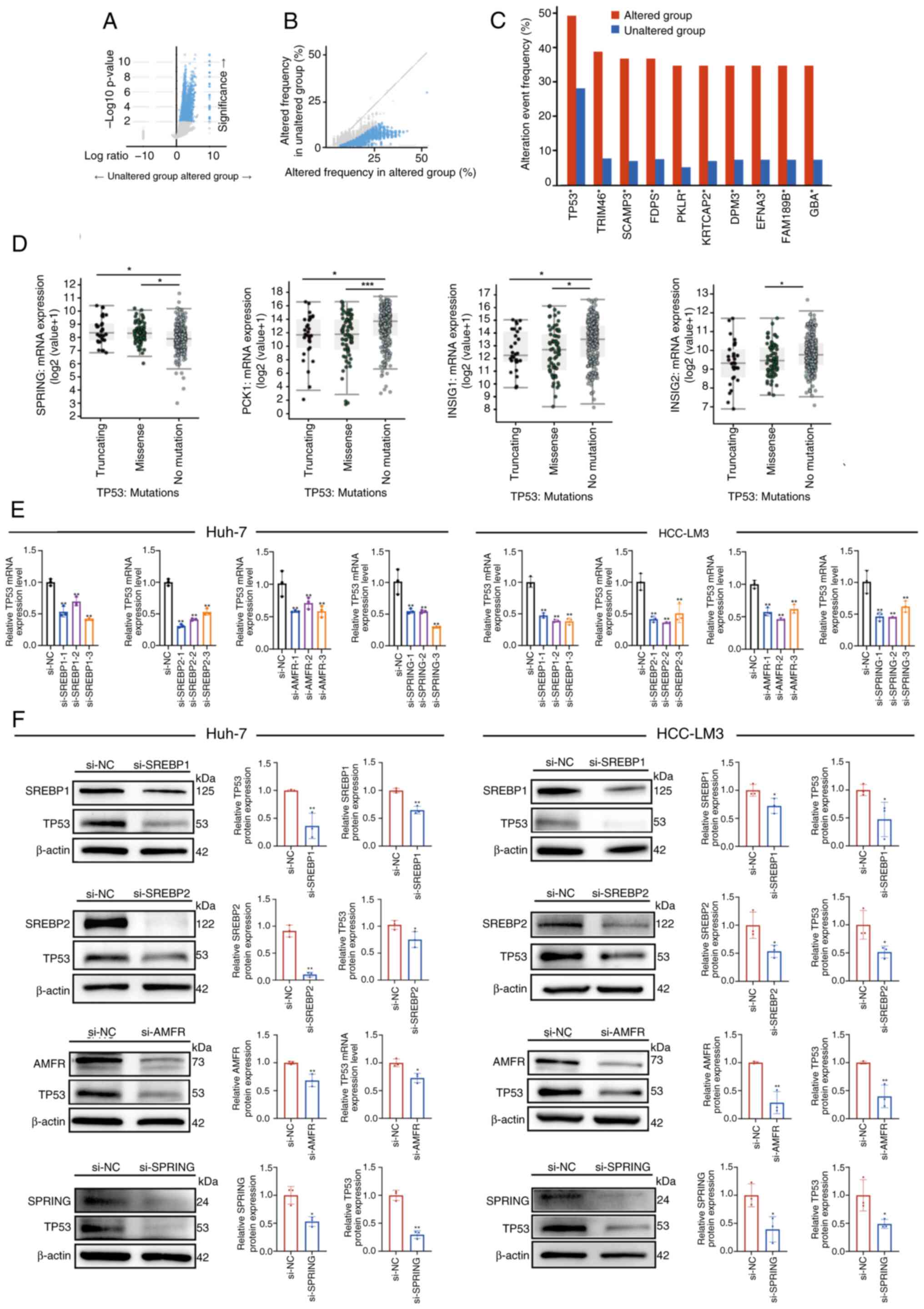
|
1
|
Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E,
Sangro B, Schwartz M, Sherman M and Gores G: Hepatocellular
carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2:160182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Villanueva A: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 380:1450–1462. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal
AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, Lencioni R, Koike K, Zucman-Rossi J and
Finn RS: Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 7:62021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Berndt N, Eckstein J, Heucke N, Gajowski
R, Stockmann M, Meierhofer D and Holzhutter HG: Characterization of
lipid and lipid droplet metabolism in human HCC. Cells. 8:5122019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nakagawa H, Hayata Y, Kawamura S, Yamada
T, Fujiwara N and Koike K: Lipid metabolic reprogramming in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 10:4472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hao Y, Li D, Xu Y, Ouyang J, Wang Y, Zhang
Y, Li B, Xie L and Qin G: Investigation of lipid metabolism
dysregulation and the effects on immune microenvironments in
pan-cancer using multiple omics data. BMC Bioinformatics. 20 (Suppl
7):S1952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu B, Lin JZ, Yang XB and Sang XT:
Aberrant lipid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells as well
as immune microenvironment: A review. Cell Prolif. 53:e127722020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Biswas SK: Metabolic reprogramming of
immune cells in cancer progression. Immunity. 43:435–449. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Smulan LJ, Ding W, Freinkman E, Gujja S,
Edwards YJK and Walker AK: Cholesterol-Independent SREBP-1
maturation is linked to ARF1 inactivation. Cell Rep. 16:9–18. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Daemen S, Kutmon M and Evelo CT: A pathway
approach to investigate the function and regulation of SREBPs.
Genes Nutr. 8:289–300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yokoyama C, Wang X, Briggs MR, Admon A, Wu
J, Hua X, Goldstein JL and Brown MS: SREBP-1, a
basic-helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein that controls
transcription of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene. Cell.
75:187–197. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang T, Espenshade PJ, Wright ME, Yabe D,
Gong Y, Aebersold R, Goldstein JL and Brown MS: Crucial step in
cholesterol homeostasis: Sterols promote binding of SCAP to
INSIG-1, a membrane protein that facilitates retention of SREBPs in
ER. Cell. 110:489–500. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yabe D, Brown MS and Goldstein JL:
Insig-2, a second endoplasmic reticulum protein that binds SCAP and
blocks export of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:12753–12758. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee JN, Song B, DeBose-Boyd RA and Ye J:
Sterol-regulated degradation of Insig-1 mediated by the
membrane-bound ubiquitin ligase gp78. J Biol Chem. 281:39308–39315.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Krycer JR, Sharpe LJ, Luu W and Brown AJ:
The Akt-SREBP nexus: Cell signaling meets lipid metabolism. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 21:268–276. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Duvel K, Yecies JL, Menon S, Raman P,
Lipovsky AI, Souza AL, Triantafellow E, Ma Q, Gorski R, Cleaver S,
et al: Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream
of mTOR complex 1. Mol Cell. 39:171–183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li N, Li X, Ding Y, Liu X, Diggle K,
Kisseleva T and Brenner DA: SREBP regulation of lipid metabolism in
liver disease, and therapeutic strategies. Biomedicines.
11:32802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li N, Zhou ZS, Shen Y, Xu J, Miao HH,
Xiong Y, Xu F, Li BL, Luo J and Song BL: Inhibition of the sterol
regulatory element-binding protein pathway suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing inflammation in mice.
Hepatology. 65:1936–1947. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang JJ, Li JG, Qi W, Qiu WW, Li PS, Li BL
and Song BL: Inhibition of SREBP by a small molecule, betulin,
improves hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance and reduces
atherosclerotic plaques. Cell Metab. 13:44–56. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu D, Wang Z, Xia Y, Shao F, Xia W, Wei Y,
Li X, Qian X, Lee JH, Du L, et al: The gluconeogenic enzyme PCK1
phosphorylates INSIG1/2 for lipogenesis. Nature. 580:530–535. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Loregger A, Raaben M, Nieuwenhuis J, Tan
JME, Jae LT, van den Hengel LG, Hendrix S, van den Berg M, Scheij
S, Song JY, et al: Haploid genetic screens identify SPRING/C12ORF49
as a determinant of SREBP signaling and cholesterol metabolism. Nat
Commun. 11:11282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N,
Lisacek F, Sanchez JC and Müller M: pROC: An open-source package
for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics.
12:772011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M and Rimm DL:
X-tile: A new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and
outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res.
10:7252–7259. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kawamura S, Matsushita Y, Kurosaki S,
Tange M, Fujiwara N, Hayata Y, Hayakawa Y, Suzuki N, Hata M, Tsuboi
M, et al: Inhibiting SCAP/SREBP exacerbates liver injury and
carcinogenesis in murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Clin
Invest. 132:e1518952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y and Gu J: fastp: an
ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics.
34:884–890. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow
J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M and Gingeras TR: STAR:
Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 29:15–21.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pertea M, Pertea GM, Antonescu CM, Chang
TC, Mendell JT and Salzberg SL: StringTie enables improved
reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat
Biotechnol. 33:290–295. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT and
Salzberg SL: Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat Protoc.
11:1650–1667. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kovaka S, Zimin AV, Pertea GM, Razaghi R,
Salzberg SL and Pertea M: Transcriptome assembly from long-read
RNA-seq alignments with StringTie2. Genome Biol. 20:2782019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Menyhart O, Nagy A and Gyorffy B:
Determining consistent prognostic biomarkers of overall survival
and vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. R Soc Open Sci.
5:1810062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gyorffy B: Integrated analysis of public
datasets for the discovery and validation of survival-associated
genes in solid tumors. Innovation (Camb). 5:1006252024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gyorffy B: Transcriptome-level discovery
of survival-associated biomarkers and therapy targets in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Pharmacol. 181:362–374. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Harding JJ, Nandakumar S, Armenia J,
Khalil DN, Albano M, Ly M, Shia J, Hechtman JF, Kundra R, El Dika
I, et al: Prospective genotyping of hepatocellular carcinoma:
Clinical implications of next-generation sequencing for matching
patients to targeted and immune therapies. Clin Cancer Res.
25:2116–2126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schulze K, Imbeaud S, Letouze E,
Alexandrov LB, Calderaro J, Rebouissou S, Couchy G, Meiller C,
Shinde J, Soysouvanh F, et al: Exome sequencing of hepatocellular
carcinomas identifies new mutational signatures and potential
therapeutic targets. Nat Genet. 47:505–511. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ahn SM, Jang SJ, Shim JH, Kim D, Hong SM,
Sung CO, Baek D, Haq F, Ansari AA, Lee SY, et al: Genomic portrait
of resectable hepatocellular carcinomas: Implications of RB1 and
FGF19 aberrations for patient stratification. Hepatology.
60:1972–1982. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
You M and Crabb DW: Molecular mechanisms
of alcoholic fatty liver: Role of sterol regulatory element-binding
proteins. Alcohol. 34:39–43. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen M, Zhang J, Sampieri K, Clohessy JG,
Mendez L, Gonzalez-Billalabeitia E, Liu XS, Lee YR, Fung J, Katon
JM, et al: An aberrant SREBP-dependent lipogenic program promotes
metastatic prostate cancer. Nat Genet. 50:206–218. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wen YA, Xiong X, Zaytseva YY, Napier DL,
Vallee E, Li AT, Wang C, Weiss HL, Evers BM and Gao T:
Downregulation of SREBP inhibits tumor growth and initiation by
altering cellular metabolism in colon cancer. Cell Death Dis.
9:2652018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shimano H and Sato R: SREBP-regulated
lipid metabolism: Convergent physiology-divergent pathophysiology.
Nat Rev Endocrinol. 13:710–730. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang Y, Hao J, Zheng Y and Jing D: SREBP:
A potential therapeutic target for cancer. Front Oncol.
11:6415782021.
|
|
42
|
Ahmad I, Muneer S and Sharif A: Role of
SREBP pathway and its therapeutic potential in autoimmune diseases.
Immunol Let. 233:1–9. 2021.
|
|
43
|
Kim Y and Park C: SREBPs as potential
therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis. BMB Reports. 51:1–7.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li X, Chen YT, Hu P and Huang WC:
Fatostatin displays high antitumor activity in prostate cancer by
blocking SREBP-regulated metabolic pathways and androgen receptor
signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:855–866. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lo AK, Lung RW, Dawson CW, Young LS, Ko
CW, Yeung WW, Kang W, To KF and Lo KW: Activation of sterol
regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1)-mediated lipogenesis
by the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1)
promotes cell proliferation and progression of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. J Pathol. 246:180–190. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shi Z, Zhou Q, Gao S, Li W, Li X, Liu Z,
Jin P and Jiang J: Silibinin inhibits endometrial carcinoma via
blocking pathways of STAT3 activation and SREBP1-mediated lipid
accumulation. Life Sci. 217:70–80. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang N, Zhang H, Liu Y, Su P, Zhang J,
Wang X, Sun M, Chen B, Zhao W, Wang L, et al: SREBP1, targeted by
miR-18a-5p, modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast
cancer via forming a co-repressor complex with Snail and HDAC1/2.
Cell Death Differ. 26:843–859. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yin F, Feng F, Wang L, Wang X, Li Z and
Cao Y: SREBP-1 inhibitor betulin enhances the antitumor effect of
sorafenib on hepatocellular carcinoma via restricting cellular
glycolytic activity. Cell Death Dis. 10:6722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li C, Yang W, Zhang J, Zheng X, Yao Y, Tu
K and Liu Q: SREBP-1 has a prognostic role and contributes to
invasion and metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Mol Sci. 15:7124–7138. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Moon SH, Huang CH, Houlihan SL, Regunath
K, Freed-Pastor WA, Morris JP IV, Tschaharganeh DF, Kastenhuber ER,
Barsotti AM, Culp-Hill R, et al: p53 Represses the mevalonate
pathway to mediate tumor suppression. Cell. 176:564–580. e192019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Restle A, Färber M, Baumann C, Böhringer
M, Scheidtmann KH, Müller-Tidow C and Wiesmüller L: Dissecting the
role of p53 phosphorylation in homologous recombination provides
new clues for gain-of-function mutants. Nucleic Acids Res.
36:5362–5375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Guo P, Qiu Y, Ma X, Li T, Ma X, Zhu L, Lin
Y and Han L: Tripartite motif 31 promotes resistance to anoikis of
hepatocarcinoma cells through regulation of p53-AMPK axis. Exp Cell
Res. 368:59–66. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cui X, Lin Z, Chen Y, Mao X, Ni W, Liu J,
Zhou H, Shan X, Chen L, Lv J, et al: Upregulated TRIM32 correlates
with enhanced cell proliferation and poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 421:127–137. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Vu T, Fowler A and McCarty N:
Comprehensive analysis of the prognostic significance of the TRIM
family in the context of TP53 mutations in cancers. Cancers
(Basel). 15:37922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Abulihaiti Z, Li W, Yang L, Zhang H, Du A,
Tang N, Lu Y and Zeng J: Hypoxia-driven lncRNA CTD-2510F5.4: A
potential player in hepatocellular carcinoma's prognostic
stratification, cellular behavior, tumor microenvironment, and
therapeutic response. Mol Biol Rep. 51:9052024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Huang S, Dong C, Zhang J, Fu S, Lv Y and
Wu J: A comprehensive prognostic and immunological analysis of
ephrin family genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Mol Biosci.
9:9433842022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|