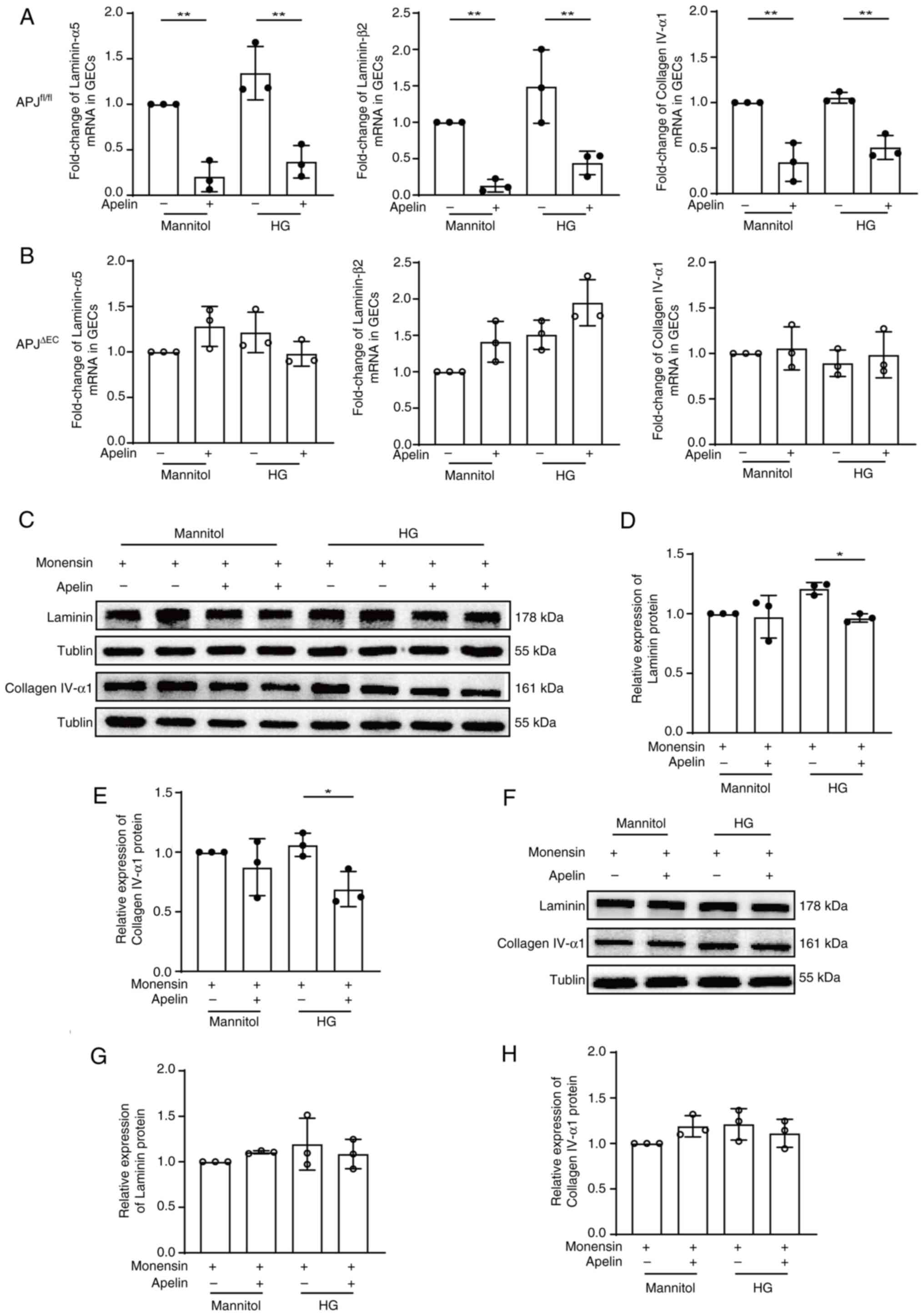
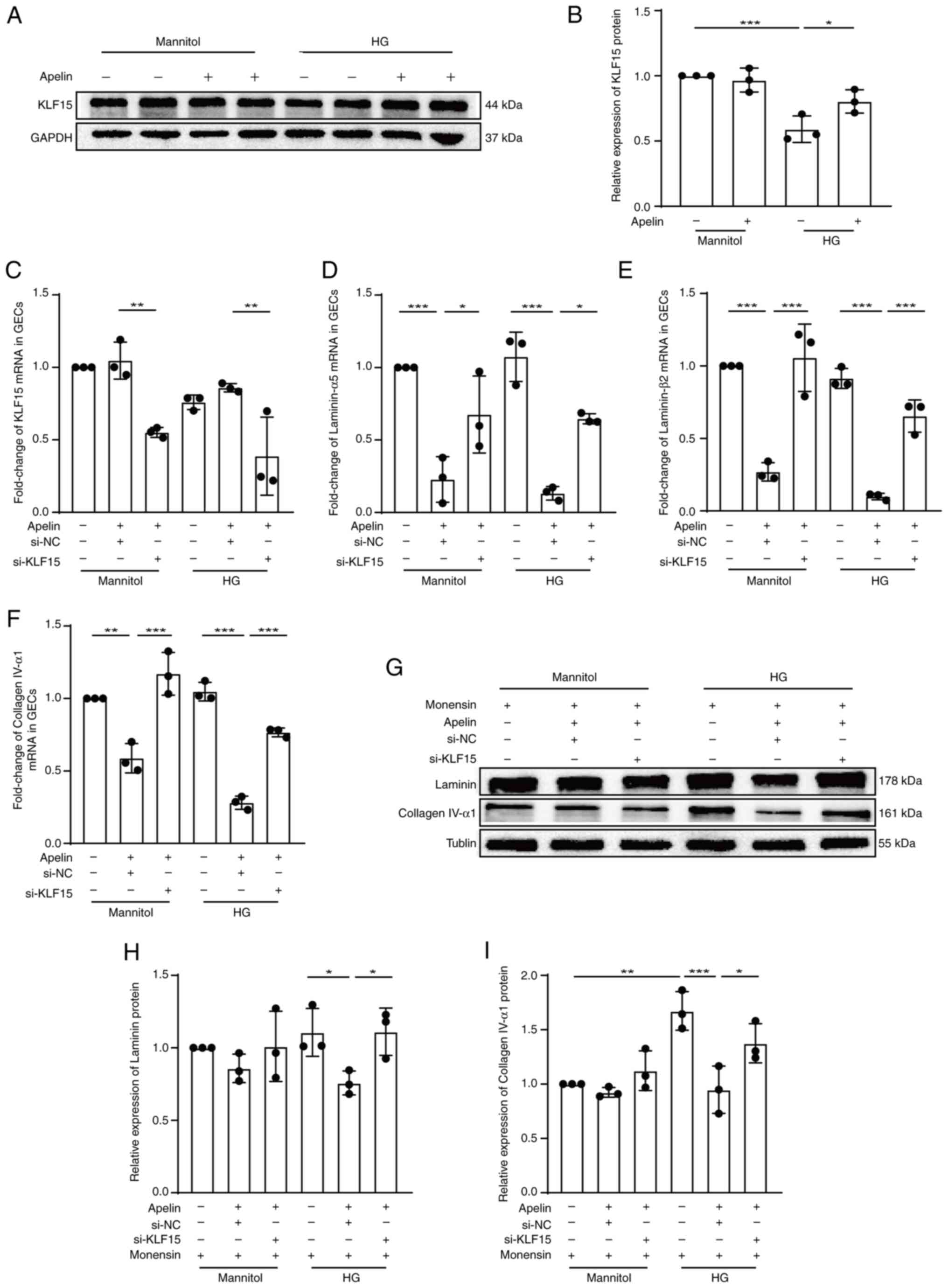
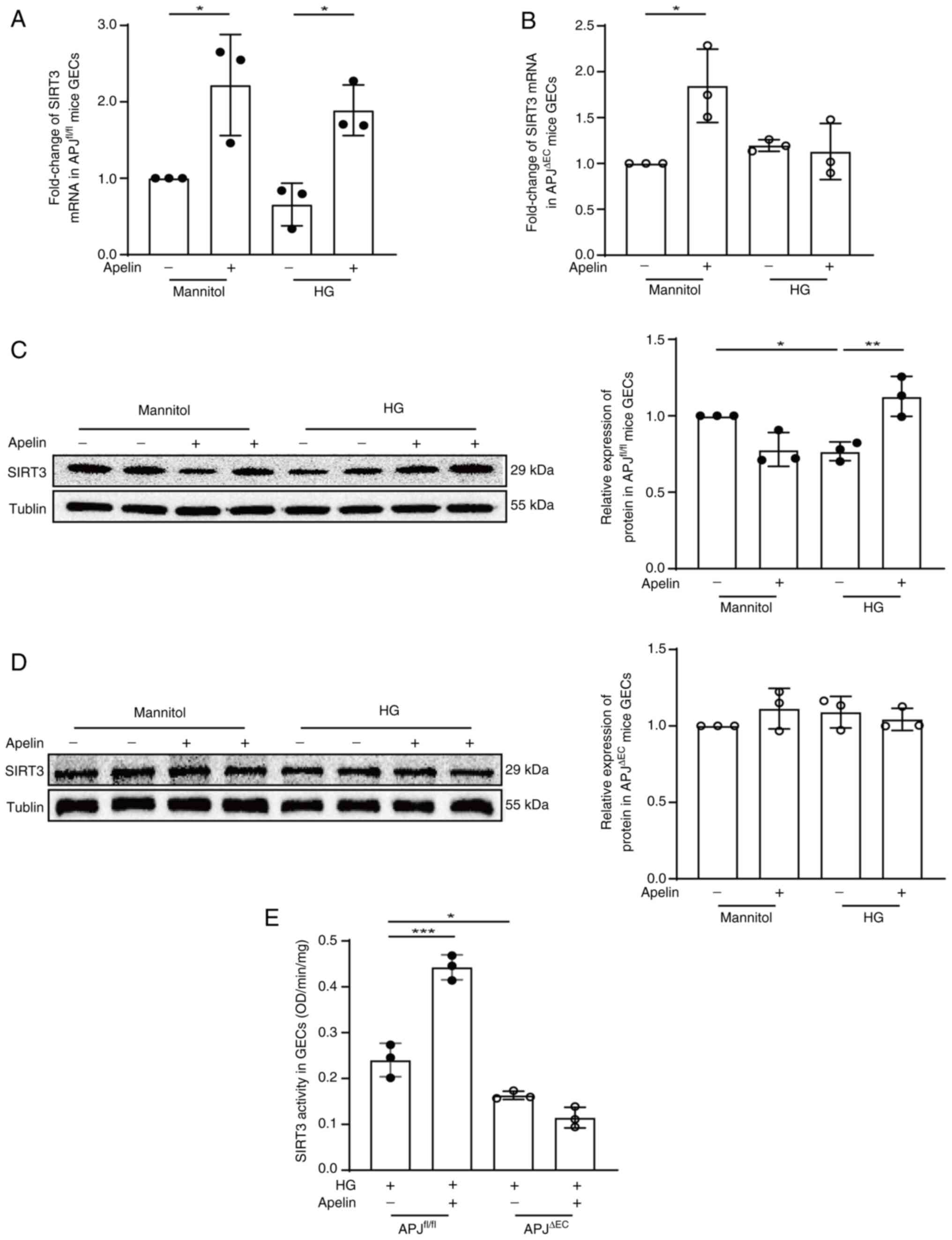
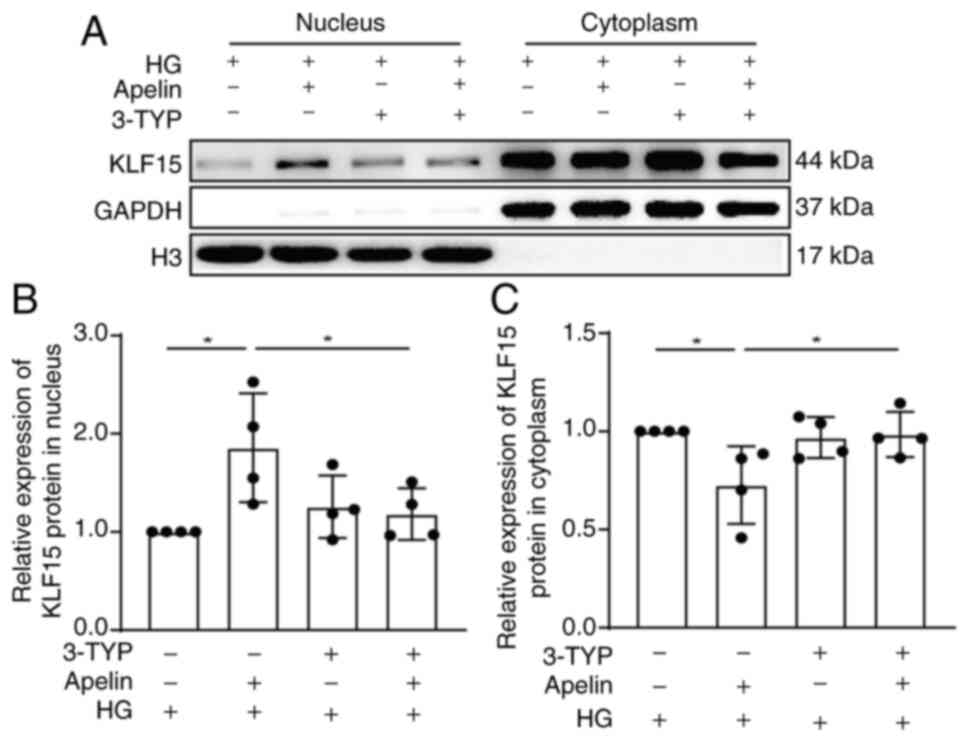
|
1
|
Papadopoulou-Marketou N, Chrousos GP and
Kanaka-Gantenbein C: Diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes: A
review of early natural history, pathogenesis, and diagnosis.
Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 33:28412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alicic RZ, Rooney MT and Tuttle KR:
Diabetic kidney disease: Challenges, progress, and possibilities.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 7:2032–2045. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Naylor RW, Morais MRPT and Lennon R:
Complexities of the glomerular basement membrane. Nat Rev Nephrol.
17:112–127. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marshall CB: Rethinking glomerular
basement membrane thickening in diabetic nephropathy: Adaptive or
pathogenic? Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 311:F831–F843. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tuleta I and Frangogiannis NG: Diabetic
fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis. 1867:1660442021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Petrazzuolo A, Sabiu G, Assi E, Maestroni
A, Pastore I, Lunati ME, Montefusco L, Loretelli C, Rossi G, Ben
Nasr M, et al: Broadening horizons in mechanisms, management, and
treatment of diabetic kidney disease. Pharmacol Res.
190:106710:2021.
|
|
7
|
St John PL and Abrahamson DR: Glomerular
endothelial cells and podocytes jointly synthesize laminin-1 and
−11 chains. Kidney Int. 60:1037–1046. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kriz W, Löwen J, Federico G, van den Born
J, Gröne E and Gröne HJ: Accumulation of worn-out GBM material
substantially contributes to mesangial matrix expansion in diabetic
nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 312:F1101–F1111. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stefan G, Stancu S, Zugravu A, Petre N,
Mandache E and Mircescu G: Histologic predictors of renal outcome
in diabetic nephropathy: Beyond renal pathology society
classification. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e163332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lenoir O, Jasiek M, Hénique C, Guyonnet L,
Hartleben B, Bork T, Chipont A, Flosseau K, Bensaada I, Schmitt A,
et al: Endothelial cell and podocyte autophagy synergistically
protect from diabetes-induced glomerulosclerosis. Autophagy.
11:1130–1145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wardle EN: How does hyperglycaemia
predispose to diabetic nephropathy? QJM. 89:943–951. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
DeFronzo RA, Reeves WB and Awad AS:
Pathophysiology of diabetic kidney disease: impact of SGLT2
inhibitors. Nat Rev Nephrol. 17:319–334. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eringa EC, Serne EH, Meijer RI, Schalkwijk
CG, Houben AJ, Stehouwer CD, Smulders YM and van Hinsbergh VW:
Endothelial dysfunction in (pre) diabetes: Characteristics,
causative mechanisms and pathogenic role in type 2 diabetes. Rev
Endocr Metab Disord. 14:39–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
El Husseny MW, Mamdouh M, Shaban S,
Ibrahim Abushouk A, Zaki MM, Ahmed OM and Abdel-Daim MM:
Adipokines: Potential therapeutic targets for vascular dysfunction
in type II Diabetes mellitus and obesity. J Diabetes Res.
2017:80959262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim S, Kim S, Hwang AR, Choi HC, Lee JY
and Woo CH: Apelin-13 inhibits methylglyoxal-induced unfolded
protein responses and endothelial dysfunction via regulating AMPK
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 21:40692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheng J, Luo X, Huang Z and Chen L:
Apelin/APJ system: A potential therapeutic target for endothelial
dysfunction-related diseases. J Cell Physiol. 234:12149–12160.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mariappan MM: Signaling mechanisms in the
regulation of renal matrix metabolism in diabetes. Exp Diabetes
Res. 2012:7498122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ni T, Lin N, Huang X, Lu W, Sun Z, Zhang
J, Lin H, Chi J and Guo H: Icariin ameliorates diabetic
cardiomyopathy through apelin/sirt3 signalling to improve
mitochondrial dysfunction. Front Pharmacol. 11:2562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guan YM, Diao ZL, Huang HD, Zheng JF,
Zhang QD, Wang LY and Liu WH: Bioactive peptide apelin rescues
acute kidney injury by protecting the function of renal tubular
mitochondria. Amino Acids. 53:1229–1240. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li N, Zhang J, Yan X, Zhang C, Liu H, Shan
X, Li J, Yang Y, Huang C, Zhang P, et al: SIRT3-KLF15 signaling
ameliorates kidney injury induced by hypertension. Oncotarget.
8:39592–39604. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rane MJ, Zhao Y and Cai L: Krϋppel-like
factors (KLFs) in renal physiology and disease. EBioMedicine.
40:743–750. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao X, Huang L, Grosjean F, Esposito V, Wu
J, Fu L, Hu H, Tan J, He C, Gray S, et al: Low-protein diet
supplemented with ketoacids reduces the severity of renal disease
in 5/6 nephrectomized rats: A role for KLF15. Kidney Int.
79:987–996. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tervaert TW, Mooyaart AL, Amann K, Cohen
AH, Cook HT, Drachenberg CB, Ferrario F, Fogo AB, Haas M, de Heer
E, et al: Renal pathology society. pathologic classification of
diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:556–563. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Zhang R, Shen H, Kong J and Lv X:
Pioglitazone protects blood vessels through inhibition of the
apelin signaling pathway by promoting KLF4 expression in rat models
of T2DM. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201903172019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yin J, Wang Y, Chang J, Li B, Zhang J, Liu
Y, Lai S, Jiang Y, Li H and Zeng X: Apelin inhibited
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of podocytes in diabetic mice
through downregulating immunoproteasome subunits β5i. Cell Death
Dis. 9:10312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Abrahamson DR: Role of the podocyte (and
glomerular endothelium) in building the GBM. Semin Nephrol.
32:342–349. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lennon R, Byron A, Humphries JD, Randles
MJ, Carisey A, Murphy S, Knight D, Brenchley PE, Zent R and
Humphries MJ: Global analysis reveals the complexity of the human
glomerular extracellular matrix. J Am Soc Nephrol. 25:939–951.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miner JH: Type IV collagen and diabetic
kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 16:3–4. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Seo K, Parikh VN and Ashley EA:
Stretch-induced biased signaling in angiotensin ii type 1 and
apelin receptors for the mediation of cardiac contractility and
hypertrophy. Front Physiol. 11:1812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eleftheriadis T, Antoniadi G, Pissas G,
Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis I: The renal endothelium in diabetic
nephropathy. Ren Fail. 35:592–599. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Swärd P and Rippe B: Acute and sustained
actions of hyperglycaemia on endothelial and glomerular barrier
permeability. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 204:294–307. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jaimes EA, Hua P, Tian RX and Raij L:
Human glomerular endothelium: Interplay among glucose, free fatty
acids, angiotensin II, and oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 298:F125–F132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li N, Ma X, Ban T, Xu S, Ma Y, Ason B and
Hu LA: Loss of APJ mediated β-arrestin signalling improves high-fat
diet induced metabolic dysfunction but does not alter cardiac
function in mice. Biochem J. 477:3313–3327. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|