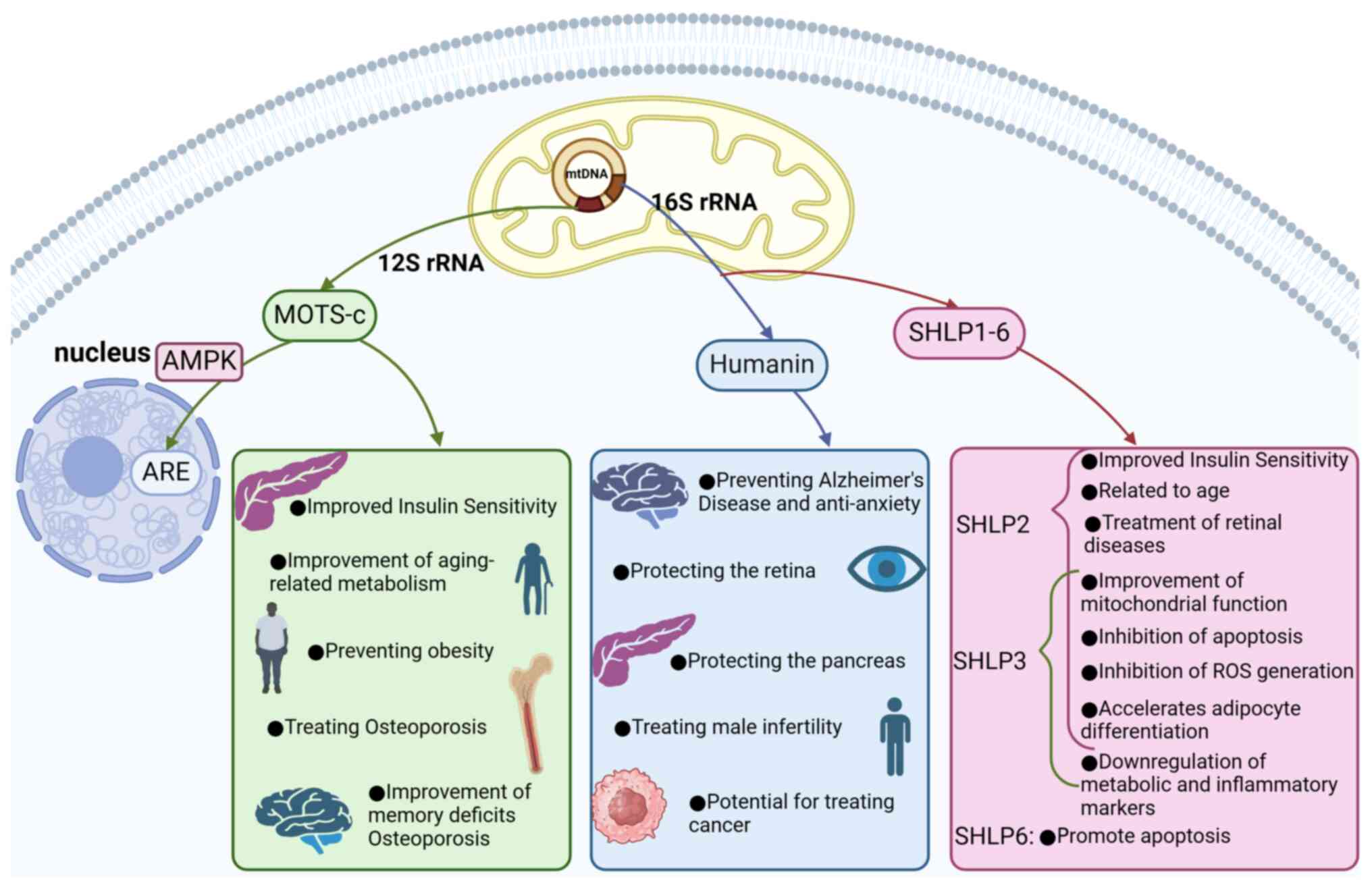
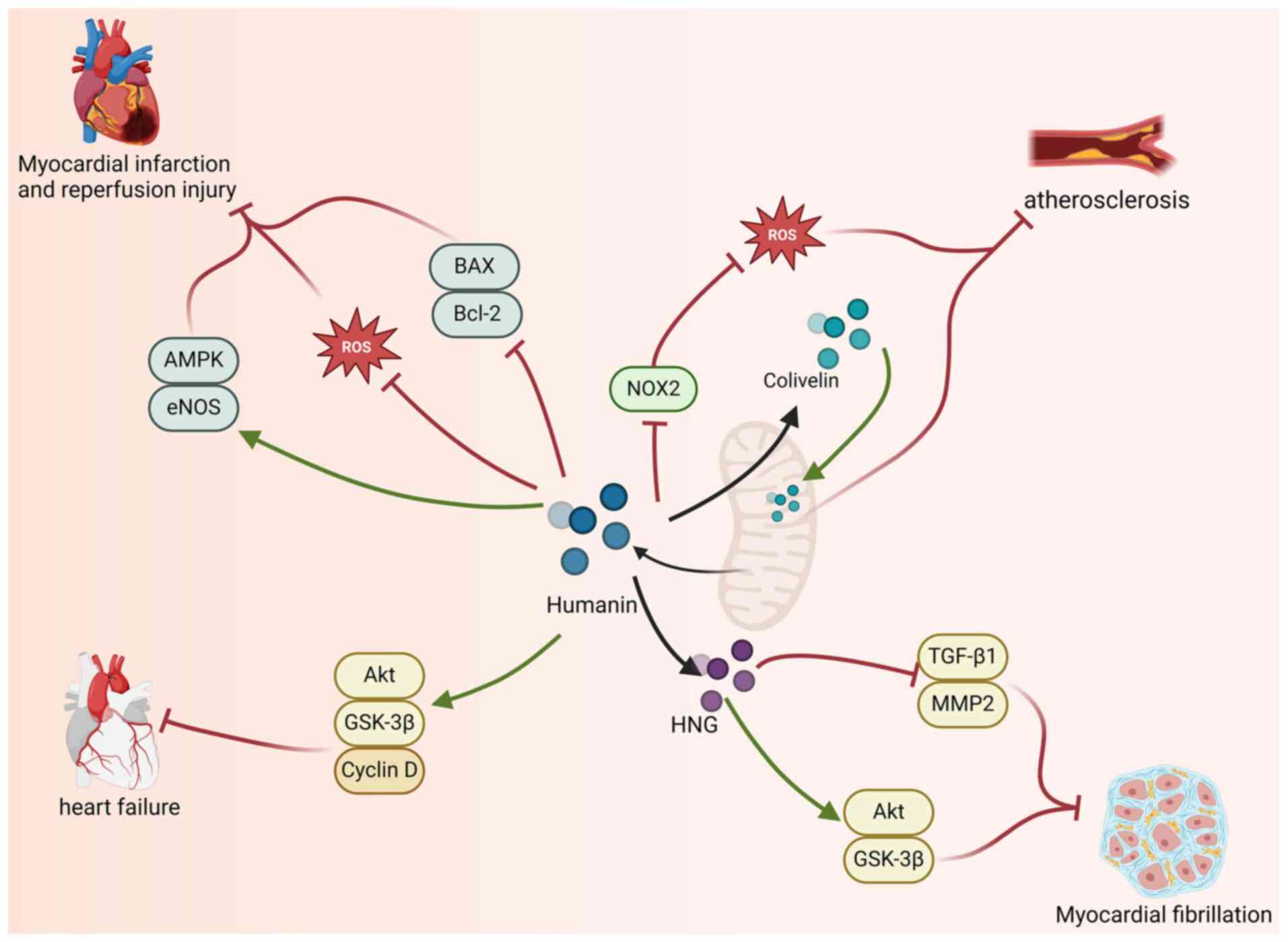
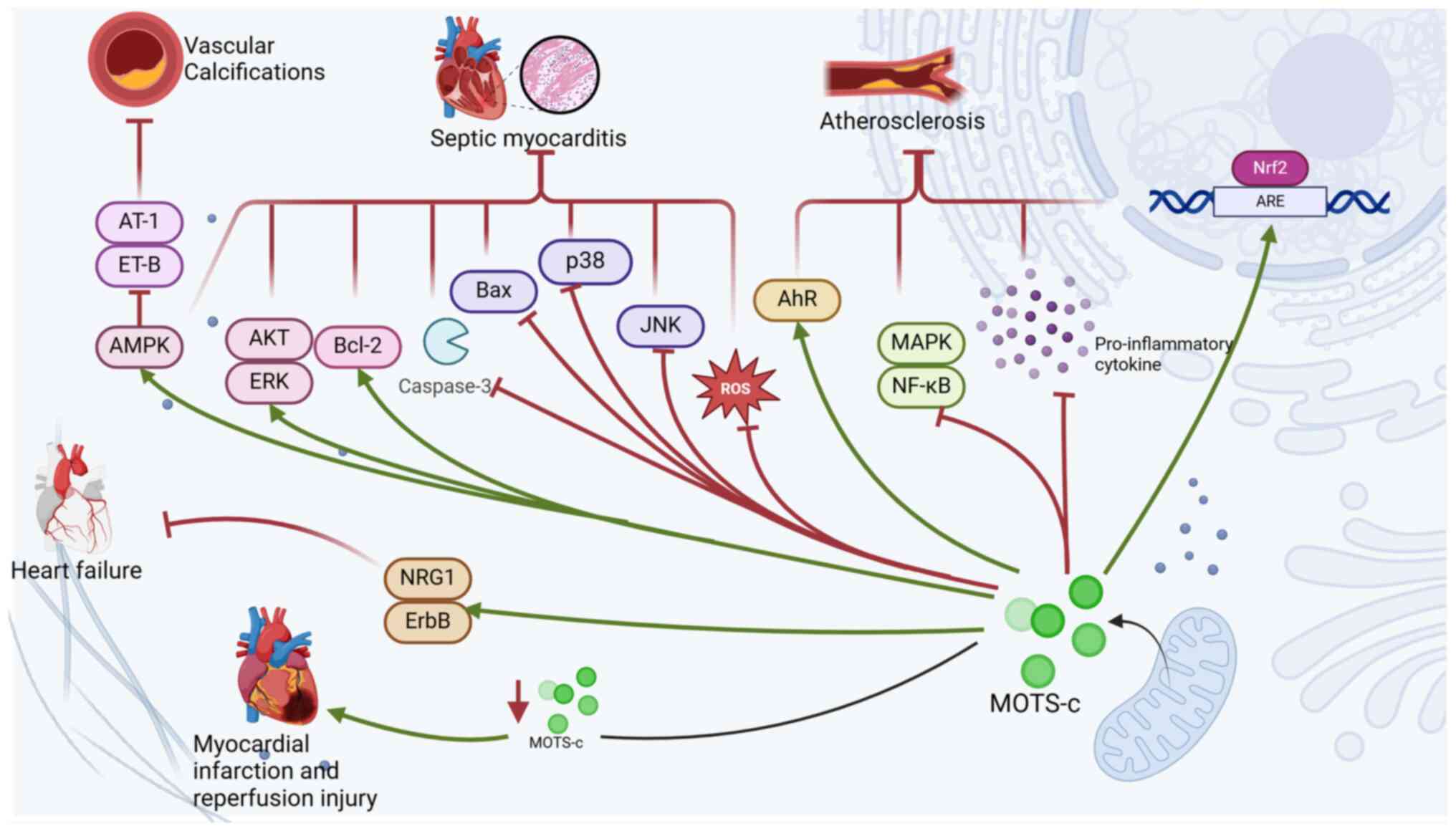
|
1
|
Crick F: Central dogma of molecular
biology. Nature. 227:561–563. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van den Akker GGH, Caron MMJ, Peffers MJ
and Welting TJM: Ribosome dysfunction in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin
Rheumatol. 34:61–67. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carninci P, Kasukawa T, Katayama S, Gough
J, Frith MC, Maeda N, Oyama R, Ravasi T, Lenhard B, Wells C, et al:
The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science.
309:1559–1563. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Plaza S, Menschaert G and Payre F: In
search of lost small peptides. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 33:391–416.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Leong AZX, Lee PY, Mohtar MA, Syafruddin
SE, Pung YF and Low TY: Short open reading frames (sORFs) and
microproteins: An update on their identification and validation
measures. J Biomed Sci. 29:192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang J, Hao J, Wang P and Xu Y: The role
of mitochondrial dysfunction in CKD-related vascular calcification:
From mechanisms to therapeutics. Kidney Int Rep. 9:2596–2607. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pang B, Dong G, Pang T, Sun X, Liu X, Nie
Y and Chang X: Advances in pathogenesis and treatment of vascular
endothelial injury-related diseases mediated by mitochondrial
abnormality. Front Pharmacol. 15:14226862024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chang X, Lochner A, Wang HH, Wang S, Zhu
H, Ren J and Zhou H: Coronary microvascular injury in myocardial
infarction: Perception and knowledge for mitochondrial quality
control. Theranostics. 11:6766–6785. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang B, Wu H, Zhang J, Cong C and Zhang
L: The study of the mechanism of non-coding RNA regulation of
programmed cell death in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol Cell Biochem.
479:1673–1696. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao J, Yang T, Yi J, Hu H, Lai Q, Nie L,
Liu M, Chu C and Yang J: AP39 through AMPK-ULK1-FUNDC1 pathway
regulates mitophagy, inhibits pyroptosis, and improves
doxorubicin-induced myocardial fibrosis. iScience. 27:1093212024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jin Y, Liu Y, Xu L, Xu J, Xiong Y, Peng Y,
Ding K, Zheng S, Yang N, Zhang Z, et al: Novel role for caspase 1
inhibitor VX765 in suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and
atherosclerosis via promoting mitophagy and efferocytosis. Cell
Death Dis. 13:5122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zang GY, Yin Q, Shao C, Sun Z, Zhang LL,
Xu Y, Li LH and Wang ZQ: CD137 signaling aggravates myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting mitophagy mediated NLRP3
inflammasome activation. J Geriatr Cardiol. 20:223–237. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Forte M, Schirone L, Ameri P, Basso C,
Catalucci D, Modica J, Chimenti C, Crotti L, Frati G, Rubattu S, et
al: The role of mitochondrial dynamics in cardiovascular diseases.
Br J Pharmacol. 178:2060–2076. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ramachandra CJA, Hernandez-Resendiz S,
Crespo-Avilan GE, Lin YH and Hausenloy DJ: Mitochondria in acute
myocardial infarction and cardioprotection. EBioMedicine.
57:1028842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu X, Tan H, Liu X and Wu Q: Correlation
between the expression of Drp1 in vascular endothelial cells and
inflammatory factors in hypertension rats. Exp Ther Med.
15:3892–3898. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brown DA, Perry JB, Allen ME, Sabbah HN,
Stauffer BL, Shaikh SR, Cleland JGF, Colucci WS, Butler J, Voors
AA, et al: Expert consensus document: Mitochondrial function as a
therapeutic target in heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. 14:238–250.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bensasson D, Zhang D, Hartl DL and Hewitt
GM: Mitochondrial pseudogenes: Evolution's misplaced witnesses.
Trends Ecol Evol. 16:314–321. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Popov LD: Mitochondrial
peptides-appropriate options for therapeutic exploitation. Cell
Tissue Res. 377:161–165. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Benayoun BA and Lee C: MOTS-c: A
mitochondrial-encoded regulator of the nucleus. Bioessays.
41:e19000462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mercer TR, Neph S, Dinger ME, Crawford J,
Smith MA, Shearwood AM, Haugen E, Bracken CP, Rackham O,
Stamatoyannopoulos JA, et al: The human mitochondrial
transcriptome. Cell. 146:645–658. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim SJ, Xiao J, Wan J, Cohen P and Yen K:
Mitochondrially derived peptides as novel regulators of metabolism.
J Physiol. 595:6613–6621. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Son JM and Lee C: Mitochondria:
Multifaceted regulators of aging. BMB Rep. 52:13–23. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hashimoto Y, Niikura T, Tajima H, Yasukawa
T, Sudo H, Ito Y, Kita Y, Kawasumi M, Kouyama K, Doyu M, et al: A
rescue factor abolishing neuronal cell death by a wide spectrum of
familial Alzheimer's disease genes and Abeta. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 98:6336–6341. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cobb LJ, Lee C, Xiao J, Yen K, Wong RG,
Nakamura HK, Mehta HH, Gao Q, Ashur C, Huffman DM, et al: Naturally
occurring mitochondrial-derived peptides are age-dependent
regulators of apoptosis, insulin sensitivity, and inflammatory
markers. Aging (Albany NY). 8:796–809. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee C, Zeng J, Drew BG, Sallam T,
Martin-Montalvo A, Wan J, Kim SJ, Mehta H, Hevener AL, de Cabo R,
et al: The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c promotes metabolic
homeostasis and reduces obesity and insulin resistance. Cell Metab.
21:443–454. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Miller B, Kim SJ, Mehta HH, Cao K, Kumagai
H, Thumaty N, Leelaprachakul N, Braniff RG, Jiao H, Vaughan J, et
al: Mitochondrial DNA variation in Alzheimer's disease reveals a
unique microprotein called SHMOOSE. Mol Psychiatry. 28:1813–1826.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Martin SS, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Anderson
CAM, Arora P, Avery CL, Baker-Smith CM, Barone Gibbs B, Beaton AZ,
Boehme AK, et al: 2024 Heart disease and stroke statistics: A
report of US and global data from the american heart association.
Circulation. 149:e347–e913. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, Benjamin
EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Cheng
S, Delling FN, et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021
update: A report from the american heart association. Circulation.
143:e254–e743. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Westman PC, Lipinski MJ, Luger D, Waksman
R, Bonow RO, Wu E and Epstein SE: Inflammation as a driver of
adverse left ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial
infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 67:2050–2060. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Roy P, Orecchioni M and Ley K: How the
immune system shapes atherosclerosis: Roles of innate and adaptive
immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 22:251–265. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yamagishi Y, Hashimoto Y, Niikura T and
Nishimoto I: Identification of essential amino acids in humanin, a
neuroprotective factor against Alzheimer's disease-relevant
insults. Peptides. 24:585–595. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thiankhaw K, Chattipakorn K, Chattipakorn
SC and Chattipakorn N: Roles of humanin and derivatives on the
pathology of neurodegenerative diseases and cognition. Biochim
Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1866:1300972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Niikura T: Humanin and Alzheimer's
disease: The beginning of a new field. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen
Subj. 1866:1300242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao H, Sonada S, Yoshikawa A, Ohinata K
and Yoshikawa M: Rubimetide, humanin, and MMK1 exert
anxiolytic-like activities via the formyl peptide receptor 2 in
mice followed by the successive activation of DP1, A2A, and GABAA
receptors. Peptides. 83:16–20. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Murakami M, Nagahama M, Maruyama T and
Niikura T: Humanin ameliorates diazepam-induced memory deficit in
mice. Neuropeptides. 62:65–70. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hashimoto Y, Ito Y, Niikura T, Shao Z,
Hata M, Oyama F and Nishimoto I: Mechanisms of neuroprotection by a
novel rescue factor humanin from Swedish mutant amyloid precursor
protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 283:460–468. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gong Z, Tasset I, Diaz A, Anguiano J, Tas
E, Cui L, Kuliawat R, Liu H, Kühn B, Cuervo AM and Muzumdar R:
Humanin is an endogenous activator of chaperone-mediated autophagy.
J Cell Biol. 217:635–647. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sreekumar PG, Ishikawa K, Spee C, Mehta
HH, Wan J, Yen K, Cohen P, Kannan R and Hinton DR: The
mitochondrial-derived peptide humanin protects RPE cells from
oxidative stress, senescence, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:1238–1253. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gong Z and Tasset I: Humanin enhances the
cellular response to stress by activation of chaperone-mediated
autophagy. Oncotarget. 9:10832–10833. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qin Q, Jin J, He F, Zheng Y, Li T, Zhang Y
and He J: Humanin promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in pancreatic
MIN6 β-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 497:292–297. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sreekumar PG and Kannan R: Mechanisms of
protection of retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidant injury
by humanin and other mitochondrial-derived peptides: Implications
for age-related macular degeneration. Redox Biol. 37:1016632020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Muzumdar RH, Huffman DM, Atzmon G,
Buettner C, Cobb LJ, Fishman S, Budagov T, Cui L, Einstein FH,
Poduval A, et al: Humanin: A novel central regulator of peripheral
insulin action. PLoS One. 4:e63342009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hoang PT, Park P, Cobb LJ,
Paharkova-Vatchkova V, Hakimi M, Cohen P and Lee KW: The
neurosurvival factor humanin inhibits beta-cell apoptosis via
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation and
delays and ameliorates diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice.
Metabolism. 59:343–349. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lue Y, Swerdloff R, Jia Y and Wang C: The
emerging role of mitochondrial derived peptide humanin in the
testis. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1865:1300092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mottaghi-Dastjerdi N, Soltany-Rezaee-Rad
M, Sepehrizadeh Z, Roshandel G, Ebrahimifard F and Setayesh N:
Genome expression analysis by suppression subtractive hybridization
identified overexpression of humanin, a target gene in gastric
cancer chemoresistance. Daru. 22:142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Omar NN, Tash RF, Shoukry Y and ElSaeed
KO: Breaking the ritual metabolic cycle in order to save acetyl
CoA: A potential role for mitochondrial humanin in T2 bladder
cancer aggressiveness. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 29:69–76. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang SF, Chen S, Tseng LM and Lee HC: Role
of the mitochondrial stress response in human cancer progression.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 245:861–878. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim KH, Son JM, Benayoun BA and Lee C: The
mitochondrial-encoded peptide MOTS-c translocates to the nucleus to
regulate nuclear gene expression in response to metabolic stress.
Cell Metab. 28:516–524.e17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Steinberg GR and Kemp BE: AMPK in health
and disease. Physiol Rev. 89:1025–1078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wu Y, Sun L, Zhuang Z, Hu X and Dong D:
Mitochondrial-derived peptides in diabetes and its complications.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12:8081202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bonkowski MS and Sinclair DA: Slowing
ageing by design: The rise of NAD+ and
sirtuin-activating compounds. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:679–690.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Imai S and Guarente L: NAD+ and sirtuins
in aging and disease. Trends Cell Biol. 24:464–471. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Che N, Qiu W, Wang JK, Sun XX, Xu LX, Liu
R and Gu L: MOTS-c improves osteoporosis by promoting the synthesis
of type I collagen in osteoblasts via TGF-β/SMAD signaling pathway.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:3183–3189. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yan Z, Zhu S, Wang H, Wang L, Du T, Ye Z,
Zhai D, Zhu Z, Tian X, Lu Z and Cao X: MOTS-c inhibits osteolysis
in the mouse calvaria by affecting osteocyte-osteoclast crosstalk
and inhibiting inflammation. Pharmacol Res. 147:1043812019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sartori M, Vincenzi F, Ravani A, Cepollaro
S, Martini L, Varani K, Fini M and Tschon M: RAW 264.7 co-cultured
with ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene particles
spontaneously differentiate into osteoclasts: An in vitro model of
periprosthetic osteolysis. J Biomed Mater Res A. 105:510–520. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mohtashami Z, Singh MK, Salimiaghdam N,
Ozgul M and Kenney MC: MOTS-c, the most recent mitochondrial
derived peptide in human aging and age-related diseases. Int J Mol
Sci. 23:119912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jiang J, Chang X, Nie Y, Shen Y, Liang X,
Peng Y and Chang M: Peripheral administration of a cell-penetrating
MOTS-c analogue enhances memory and attenuates Aβ1-42-
or LPS-induced memory impairment through inhibiting
neuroinflammation. ACS Chem Neurosci. 12:1506–1518. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhai D, Ye Z, Jiang Y, Xu C, Ruan B, Yang
Y, Lei X, Xiang A, Lu H, Zhu Z, et al: MOTS-c peptide increases
survival and decreases bacterial load in mice infected with MRSA.
Mol Immunol. 92:151–160. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jiang J, Chang X, Nie Y, Xu L, Yang L,
Peng Y and Chang M: Orally administered MOTS-c analogue ameliorates
dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by inhibiting inflammation
and apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 939:1754692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Xiao J, Zhang Q, Shan Y, Ye F, Zhang X,
Cheng J, Wang X, Zhao Y, Dan G, Chen M and Sai Y: The
mitochondrial-derived peptide (MOTS-c) interacted with Nrf2 to
defend the antioxidant system to protect dopaminergic neurons
against rotenone exposure. Mol Neurobiol. 60:5915–5930. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yang L, Li M, Liu Y, Bai Y, Yin T, Chen Y,
Jiang J and Liu S: MOTS-c is an effective target for treating
cancer-induced bone pain through the induction of AMPK-mediated
mitochondrial biogenesis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
56:1323–1339. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yin Y, Li Y, Ma B, Ren C, Zhao S and Li J,
Gong Y, Yang H and Li J: Mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c
suppresses ovarian cancer progression by attenuating USP7-mediated
LARS1 deubiquitination. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e24056202024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li Y, Li Z, Ren Y, Lei Y, Yang S, Shi Y,
Peng H, Yang W, Guo T, Yu Y and Xiong Y: Mitochondrial-derived
peptides in cardiovascular disease: Novel insights and therapeutic
opportunities. J Adv Res. 64:99–115. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Okada AK, Teranishi K, Lobo F, Isas JM,
Xiao J, Yen K, Cohen P and Langen R: The mitochondrial-derived
peptides, HumaninS14G and small humanin-like peptide 2, exhibit
chaperone-like activity. Sci Rep. 7:78022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Nashine S and Kenney MC: Effects of
mitochondrial-derived peptides (MDPs) on mitochondrial and cellular
health in AMD. Cells. 9:11022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Shin JH, Kim HW, Rhyu IJ, Song KJ and Kee
SH: Axin expression reduces staurosporine-induced
mitochondria-mediated cell death in HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res.
318:2022–2033. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Emser SV, Schaschl H, Millesi E and
Steinborn R: Extension of mitogenome enrichment based on single
long-range PCR: mtDNAs and putative mitochondrial-derived peptides
of five rodent hibernators. Front Genet. 12:6858062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Monteiro JP, Bennett M, Rodor J,
Caudrillier A, Ulitsky I and Baker AH: Endothelial function and
dysfunction in the cardiovascular system: The long non-coding road.
Cardiovasc Res. 115:1692–1704. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kinlay S, Libby P and Ganz P: Endothelial
function and coronary artery disease. Curr Opin Lipidol.
12:383–389. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Rhee M, Lee J, Lee EY, Yoon KH and Lee SH:
Lipid variability induces endothelial dysfunction by increasing
inflammation and oxidative stress. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul).
39:511–520. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Pober JS and Sessa WC: Evolving functions
of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:803–815.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lüscher TF and Barton M: Biology of the
endothelium. Clin Cardiol. 20 (11 Suppl 2):II-3-10. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Choi BJ, Prasad A, Gulati R, Best PJ,
Lennon RJ, Barsness GW, Lerman LO and Lerman A: Coronary
endothelial dysfunction in patients with early coronary artery
disease is associated with the increase in intravascular lipid core
plaque. Eur Heart J. 34:2047–2054. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Maseri A:
Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105:1135–1143. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Choi BJ, Matsuo Y, Aoki T, Kwon TG, Prasad
A, Gulati R, Lennon RJ, Lerman LO and Lerman A: Coronary
endothelial dysfunction is associated with inflammation and vasa
vasorum proliferation in patients with early atherosclerosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:2473–2477. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kashiwagi M, Kitabata H, Ozaki Y, Imanishi
T and Akasaka T: Fatty streak assessed by optical coherence
tomography: Early atherosclerosis detection. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc
Imaging. 14:1092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bonetti PO, Lerman LO and Lerman A:
Endothelial dysfunction: A marker of atherosclerotic risk.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:168–175. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Madamanchi NR, Vendrov A and Runge MS:
Oxidative stress and vascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 25:29–38. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Galle J, Hansen-Hagge T, Wanner C and
Seibold S: Impact of oxidized low density lipoprotein on vascular
cells. Atherosclerosis. 185:219–226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hansson GK: Inflammation, atherosclerosis,
and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 352:1685–1695. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
van Dijk RA, Virmani R, von der Thusen JH,
Schaapherder AF and Lindeman JHN: The natural history of aortic
atherosclerosis: A systematic histopathological evaluation of the
peri-renal region. Atherosclerosis. 210:100–106. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Widmer RJ, Flammer AJ, Herrmann J,
Rodriguez-Porcel M, Wan J, Cohen P, Lerman LO and Lerman A:
Circulating humanin levels are associated with preserved coronary
endothelial function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
304:H393–H397. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Coradduzza D, Cruciani S, Di Lorenzo B, De
Miglio MR, Zinellu A, Maioli M, Medici S, Erre GL and Carru C:
Plasma humanin and non-coding RNAs as biomarkers of endothelial
dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis: A pilot study. Noncoding RNA.
11:52025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Balan AI, Halatiu VB and Scridon A:
Oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction: A
link between obesity and atrial fibrillation. Antioxidants (Basel).
13:1172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kusminski CM and Scherer PE: Mitochondrial
dysfunction in white adipose tissue. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
23:435–443. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Teodoro JS, Nunes S, Rolo AP, Reis F and
Palmeira CM: Therapeutic options targeting oxidative stress,
mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation to hinder the
progression of vascular complications of diabetes. Front Physiol.
9:18572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Cai H and Harrison DG: Endothelial
dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: The role of oxidant stress.
Circ Res. 87:840–844. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Bachar AR, Scheffer L, Schroeder AS,
Nakamura HK, Cobb LJ, Oh YK, Lerman LO, Pagano RE, Cohen P and
Lerman A: Humanin is expressed in human vascular walls and has a
cytoprotective effect against oxidized LDL-induced oxidative
stress. Cardiovasc Res. 88:360–366. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hannun YA and Obeid LM: Principles of
bioactive lipid signalling: Lessons from sphingolipids. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:139–150. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Cai H, Liu Y, Men H and Zheng Y:
Protective mechanism of humanin against oxidative stress in
aging-related cardiovascular diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
12:6831512021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Chiba T, Yamada M, Hashimoto Y, Sato M,
Sasabe J, Kita Y, Terashita K, Aiso S, Nishimoto I and Matsuoka M:
Development of a femtomolar-acting humanin derivative named
colivelin by attaching activity-dependent neurotrophic factor to
its N terminus: Characterization of colivelin-mediated
neuroprotection against Alzheimer's disease-relevant insults in
vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci. 25:10252–10261. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Urban C, Hayes HV, Piraino G, Wolfe V,
Lahni P, O'Connor M, Phares C and Zingarelli B: Colivelin, a
synthetic derivative of humanin, ameliorates endothelial injury and
glycocalyx shedding after sepsis in mice. Front Immunol.
13:9842982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Kirkman DL, Robinson AT, Rossman MJ, Seals
DR and Edwards DG: Mitochondrial contributions to vascular
endothelial dysfunction, arterial stiffness, and cardiovascular
diseases. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 320:H2080–H2100. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Thummasorn S, Shinlapawittayatorn K,
Chattipakorn SC and Chattipakorn N: High-dose humanin analogue
applied during ischemia exerts cardioprotection against
ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing mitochondrial dysfunction.
Cardiovasc Ther. 35:2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Rentrop KP and Feit F: Reperfusion therapy
for acute myocardial infarction: Concepts and controversies from
inception to acceptance. Am Heart J. 170:971–980. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Dabravolski SA, Nikiforov NG, Starodubova
AV, Popkova TV and Orekhov AN: The role of mitochondria-derived
peptides in cardiovascular diseases and their potential as
therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 22:87702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Thummasorn S, Apaijai N, Kerdphoo S,
Shinlapawittayatorn K, Chattipakorn SC and Chattipakorn N: Humanin
exerts cardioprotection against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury
through attenuation of mitochondrial dysfunction. Cardiovasc Ther.
34:404–414. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Arrigo M, Price S, Baran DA, Pöss J,
Aissaoui N, Bayes-Genis A, Bonello L, François B, Gayat E, Gilard
M, et al: Optimising clinical trials in acute myocardial infarction
complicated by cardiogenic shock: A statement from the 2020
critical care clinical trialists workshop. Lancet Respir Med.
9:1192–1202. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Muzumdar RH, Huffman DM, Calvert JW, Jha
S, Weinberg Y, Cui L, Nemkal A, Atzmon G, Klein L, Gundewar S, et
al: Acute humanin therapy attenuates myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
30:1940–1948. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
McDermott-Roe C, Ye J, Ahmed R, Sun XM,
Serafin A, Ware J, Bottolo L, Muckett P, Cañas X, Zhang J, et al:
Endonuclease G is a novel determinant of cardiac hypertrophy and
mitochondrial function. Nature. 478:114–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Rizzi E, Guimaraes DA, Ceron CS, Prado CM,
Pinheiro LC, Martins-Oliveira A, Gerlach RF and Tanus-Santos JE:
β1-Adrenergic blockers exert antioxidant effects, reduce matrix
metalloproteinase activity, and improve renovascular
hypertension-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Free Radic Biol Med.
73:308–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Maillet M, van Berlo JH and Molkentin JD:
Molecular basis of physiological heart growth: Fundamental concepts
and new players. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:38–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Lu J, McKinsey TA, Nicol RL and Olson EN:
Signal-dependent activation of the MEF2 transcription factor by
dissociation from histone deacetylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:4070–4075. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Dai DF, Johnson SC, Villarin JJ, Chin MT,
Nieves-Cintron M, Chen T, Marcinek DJ, Dorn GW II, Kang YJ, Prolla
TA, et al: Mitochondrial oxidative stress mediates angiotensin
II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and Galphaq overexpression-induced
heart failure. Circ Res. 108:837–846. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Blasco N, Cámara Y, Núñez E, Beà A, Barés
G, Forné C, Ruíz-Meana M, Girón C, Barba I, García-Arumí E, et al:
Cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by Endonuclease G deficiency
requires reactive oxygen radicals accumulation and is inhibitable
by the micropeptide humanin. Redox Biol. 16:146–156. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Blasco N, Beà A, Barés G, Girón C,
Navaridas R, Irazoki A, López-Lluch G, Zorzano A, Dolcet X, Llovera
M and Sanchis D: Involvement of the mitochondrial nuclease EndoG in
the regulation of cell proliferation through the control of
reactive oxygen species. Redox Biol. 37:1017362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Eghbali M, Blumenfeld OO, Seifter S,
Buttrick PM, Leinwand LA, Robinson TF, Zern MA and Giambrone MA:
Localization of types I, III and IV collagen mRNAs in rat heart
cells by in situ hybridization. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 21:103–113.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Kong P, Christia P and Frangogiannis NG:
The pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
71:549–574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Edgley AJ, Krum H and Kelly DJ: Targeting
fibrosis for the treatment of heart failure: A role for
transforming growth factor-β. Cardiovasc Ther. 30:e30–e40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Piera-Velazquez S, Li Z and Jimenez SA:
Role of endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) in the
pathogenesis of fibrotic disorders. Am J Pathol. 179:1074–1080.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Zeisberg EM and Kalluri R: Origins of
cardiac fibroblasts. Circ Res. 107:1304–1312. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Travers JG, Kamal FA, Robbins J, Yutzey KE
and Blaxall BC: Cardiac fibrosis: The fibroblast awakens. Circ Res.
118:1021–1040. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Liguori TTA, Liguori GR, Moreira LFP and
Harmsen MC: Fibroblast growth factor-2, but not the adipose
tissue-derived stromal cells secretome, inhibits TGF-β1-induced
differentiation of human cardiac fibroblasts into myofibroblasts.
Sci Rep. 8:166332018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Biernacka A and Frangogiannis NG: Aging
and cardiac fibrosis. Aging Dis. 2:158–173. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Sangaralingham SJ, Wang BH, Huang L, Kumfu
S, Ichiki T, Krum H and Burnett JC Jr: Cardiorenal fibrosis and
dysfunction in aging: Imbalance in mediators and regulators of
collagen. Peptides. 76:108–114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Biernacka A, Dobaczewski M and
Frangogiannis NG: TGF-β signaling in fibrosis. Growth Factors.
29:196–202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Qin Q, Mehta H, Yen K, Navarrete G,
Brandhorst S, Wan J, Delrio S, Zhang X, Lerman LO, Cohen P and
Lerman A: Chronic treatment with the mitochondrial peptide humanin
prevents age-related myocardial fibrosis in mice. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 315:H1127–H1136. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Zavadzkas JA, Plyler RA, Bouges S, Koval
CN, Rivers WT, Beck CU, Chang EI, Stroud RE, Mukherjee R and
Spinale FG: Cardiac-restricted overexpression of extracellular
matrix metalloproteinase inducer causes myocardial remodeling and
dysfunction in aging mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
295:H1394–H1402. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Juhaszova M, Zorov DB, Yaniv Y, Nuss HB,
Wang S and Sollott SJ: Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in
cardioprotection. Circ Res. 104:1240–1252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Hirotani S, Zhai P, Tomita H, Galeotti J,
Marquez JP, Gao S, Hong C, Yatani A, Avila J and Sadoshima J:
Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta during heart failure
is protective. Circ Res. 101:1164–1174. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, Antunes MJ,
Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Bueno H, Caforio ALP, Crea F, Goudevenos JA,
Halvorsen S, et al: 2017 ESC guidelines for the management of acute
myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment
elevation: The task force for the management of acute myocardial
infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the
European society of cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 39:119–177.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Choo EH, Kim PJ, Chang K, Ahn Y, Jeon DS,
Lee JM, Kim DB, Her SH, Park CS, Kim HY, et al: The impact of
no-reflow phenomena after primary percutaneous coronary
intervention: a time-dependent analysis of mortality. Coron Artery
Dis. 25:392–398. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Wong DT, Puri R, Richardson JD, Worthley
MI and Worthley SG: Myocardial ‘no-reflow’-diagnosis,
pathophysiology and treatment. Int J Cardiol. 167:1798–1806. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Çakmak T, Yaşar E, Çakmak E, Tekin S,
Karakuş Y, Türkoğlu C and Yüksel F: Evaluation of coronary flow
level with mots-C in patients with STEMI undergoing primary PCI.
Arq Bras Cardiol. 120:e202203582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Marulanda J, Alqarni S and Murshed M:
Mechanisms of vascular calcification and associated diseases. Curr
Pharm Des. 20:5801–5810. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Zhang L, Yao J, Yao Y and Boström KI:
Contributions of the endothelium to vascular calcification. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 9:6208822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Liu W, Zhang Y, Yu CM, Ji QW, Cai M, Zhao
YX and Zhou YJ: Current understanding of coronary artery
calcification. J Geriatr Cardiol. 12:668–675. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
McCullough PA, Chinnaiyan KM, Agrawal V,
Danielewicz E and Abela GS: Amplification of atherosclerotic
calcification and Mönckeberg's sclerosis: A spectrum of the same
disease process. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 15:396–412. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Rasheed A and Cummins CL: Beyond the foam
cell: The role of LXRs in preventing atherogenesis. Int J Mol Sci.
19:23072018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Andrews J, Psaltis PJ, Bartolo BAD,
Nicholls SJ and Puri R: Coronary arterial calcification: A review
of mechanisms, promoters and imaging. Trends Cardiovasc Med.
28:491–501. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Zhang X, Xiao J, Li R, Qin X, Wang F, Mao
Y, Liang W, Sheng X, Guo M, Song Y and Ji X: Metformin alleviates
vascular calcification induced by vitamin D3 plus nicotine in rats
via the AMPK pathway. Vascul Pharmacol. 81:83–90. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Xu M, Liu L, Song C, Chen W and Gui S:
Ghrelin improves vascular autophagy in rats with vascular
calcification. Life Sci. 179:23–29. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Li KX, Du Q, Wang HP and Sun HJ:
Death-associated protein kinase 3 deficiency alleviates vascular
calcification via AMPK-mediated inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 852:90–98. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Wei M, Gan L, Liu Z, Liu L, Chang JR, Yin
DC, Cao HL, Su XL and Smith WW: Mitochondrial-derived peptide
MOTS-c attenuates vascular calcification and secondary myocardial
remodeling via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase
signaling pathway. Cardiorenal Med. 10:42–50. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Honda J, Kimura T, Sakai S, Maruyama H,
Tajiri K, Murakoshi N, Homma S, Miyauchi T and Aonuma K: The
glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist liraglutide improves
hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice partly via
normalization of reduced ET(B) receptor expression. Physiol Res. 67
(Suppl 1):S175–S184. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Boccellino M, Di Domenico M, Donniacuo M,
Bitti G, Gritti G, Ambrosio P, Quagliuolo L and Rinaldi B:
AT1-receptor blockade: Protective effects of irbesartan in
cardiomyocytes under hypoxic stress. PLoS One. 13:e02022972018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Qin Q, Delrio S, Wan J, Jay Widmer R,
Cohen P, Lerman LO and Lerman A: Downregulation of circulating
MOTS-c levels in patients with coronary endothelial dysfunction.
Int J Cardiol. 254:23–27. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Shen C, Wang J, Feng M, Peng J, Du X, Chu
H and Chen X: The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c attenuates
oxidative stress injury and the inflammatory response of H9c2 cells
through the Nrf2/ARE and NF-κB pathways. Cardiovasc Eng Technol.
13:651–661. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Li H, Ren K, Jiang T and Zhao GJ: MOTS-c
attenuates endothelial dysfunction via suppressing the MAPK/NF-κB
pathway. Int J Cardiol. 268:402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Chen M, Fu H, Zhang J, Huang H and Zhong
P: CIRP downregulation renders cardiac cells prone to apoptosis in
heart failure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 517:545–550. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Zhong P, Peng J, Hu Y, Zhang J and Shen C:
Mitochondrial derived peptide MOTS-c prevents the development of
heart failure under pressure overload conditions in mice. J Cell
Mol Med. 26:5369–5378. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Hage C, Wärdell E, Linde C, Donal E, Lam
CSP, Daubert C, Lund LH and Månsson-Broberg A: Circulating
neuregulin1-β in heart failure with preserved and reduced left
ventricular ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail. 7:445–455. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Hedhli N, Huang Q, Kalinowski A, Palmeri
M, Hu X, Russell RR and Russell KS: Endothelium-derived neuregulin
protects the heart against ischemic injury. Circulation.
123:2254–2262. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Brero A, Ramella R, Fitou A, Dati C,
Alloatti G, Gallo MP and Levi R: Neuregulin-1beta1 rapidly
modulates nitric oxide synthesis and calcium handling in rat
cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 88:443–452. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Li S, Wang M, Ma J, Pang X, Yuan J, Pan Y,
Fu Y and Laher I: MOTS-c and exercise restore cardiac function by
activating of NRG1-ErbB signaling in diabetic rats. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:8120322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Shankar-Hari M, Phillips GS, Levy ML,
Seymour CW, Liu VX, Deutschman CS, Angus DC, Rubenfeld GD and
Singer M; Sepsis Definitions Task Force, : Developing a new
definition and assessing new clinical criteria for septic shock:
For the third international consensus definitions for sepsis and
septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA. 315:775–787. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Hollenberg SM and Singer M:
Pathophysiology of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Cardiol.
18:424–434. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Shen Q, Yuan Y, Li Z, Ling Y, Wang J, Gao
M, Wang P, Li M, Lai L and Jin J: Berberine ameliorates septic
cardiomyopathy through protecting mitochondria and upregulating
Notch1 signaling in cardiomyocytes. Front Pharmacol.
15:15023542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford
KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer
S, et al: Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and
mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease
study. Lancet. 395:200–211. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Ehrman RR, Sullivan AN, Favot MJ, Sherwin
RL, Reynolds CA, Abidov A and Levy PD: Pathophysiology,
echocardiographic evaluation, biomarker findings, and prognostic
implications of septic cardiomyopathy: A review of the literature.
Crit Care. 22:1122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Ravikumar N, Sayed MA, Poonsuph CJ, Sehgal
R, Shirke MM and Harky A: Septic cardiomyopathy: From basics to
management choices. Curr Probl Cardiol. 46:1007672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Carbone F, Liberale L, Preda A, Schindler
TH and Montecucco F: Septic cardiomyopathy: From pathophysiology to
the clinical setting. Cells. 11:28332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Khalid N, Patel PD, Alghareeb R, Hussain A
and Maheshwari MV: The effect of sepsis on myocardial function: A
review of pathophysiology, diagnostic criteria, and treatment.
Cureus. 14:e261782022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Liu YC, Yu MM, Shou ST and Chai YF:
Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms and treatments. Front
Immunol. 8:10212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Wu J, Xiao D, Yu K, Shalamu K, He B and
Zhang M: The protective effect of the mitochondrial-derived peptide
MOTS-c on LPS-induced septic cardiomyopathy. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 55:285–294. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Liu C, Shen YJ, Tu QB, Zhao YR, Guo H,
Wang J, Zhang L, Shi HW and Sun Y: Pedunculoside, a novel
triterpene saponin extracted from Ilex rotunda, ameliorates
high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia in rats. Biomed Pharmacother.
101:608–616. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Su Z, Li K, Luo X, Zhu Y, Mai SY, Zhu Q,
Yang B, Zhou X and Tao H: Aromatic acids and leucine derivatives
produced from the deep-sea actinomycetes streptomyceschumphonensis
SCSIO15079 with antihyperlipidemic activities. Mar Drugs.
20:2592022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Bai X, Wang H, Li J, Xu J and Cai P:
Correlation analysis of the risk of ischemic stroke with related
risk factors in a health examination population. Pak J Med Sci.
40:2533–2537. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Huang L, Liu Z, Zhang H, Li D, Li Z, Huang
J, He J, Lu L, Wen H, Yuan H, et al: The association between serum
lipid profile levels and hypertension grades: A cross-sectional
study at a health examination center. High Blood Press Cardiovasc
Prev. 32:87–98. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Hannun YA and Obeid LM: Sphingolipids and
their metabolism in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
19:175–191. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Russo SB, Ross JS and Cowart LA:
Sphingolipids in obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic disease.
Handb Exp Pharmacol. 373–401. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Wang P, Zhang SY, Dong
Y, Zeng G, Yan Y, Sun L, Wu Q, Liu H, et al: Adipocyte
hypoxia-inducible factor 2α suppresses atherosclerosis by promoting
adipose ceramide catabolism. Cell Metab. 30:937–951.e5. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Mehta HH, Xiao J, Ramirez R, Miller B, Kim
SJ, Cohen P and Yen K: Metabolomic profile of diet-induced obesity
mice in response to humanin and small humanin-like peptide 2
treatment. Metabolomics. 15:882019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Yen K, Miller B, Kumagai H, Silverstein A
and Cohen P: Mitochondrial-derived microproteins: From discovery to
function. Trends Genet. 41:132–145. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Merry TL, Chan A, Woodhead JST, Reynolds
JC, Kumagai H, Kim SJ and Lee C: Mitochondrial-derived peptides in
energy metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 319:E659–E666.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Kim SJ, Miller B, Kumagai H, Silverstein
AR, Flores M and Yen K: Mitochondrial-derived peptides in aging and
age-related diseases. Geroscience. 43:1113–1121. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Gao Y, Wei X, Wei P, Lu H, Zhong L, Tan J,
Liu H and Liu Z: MOTS-c functionally prevents metabolic disorders.
Metabolites. 13:1252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Verma S, Goand UK, Husain A, Katekar RA,
Garg R and Gayen JR: Challenges of peptide and protein drug
delivery by oral route: Current strategies to improve the
bioavailability. Drug Dev Res. 82:927–944. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Mitragotri S, Burke PA and Langer R:
Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals:
Formulation and delivery strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
13:655–672. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|