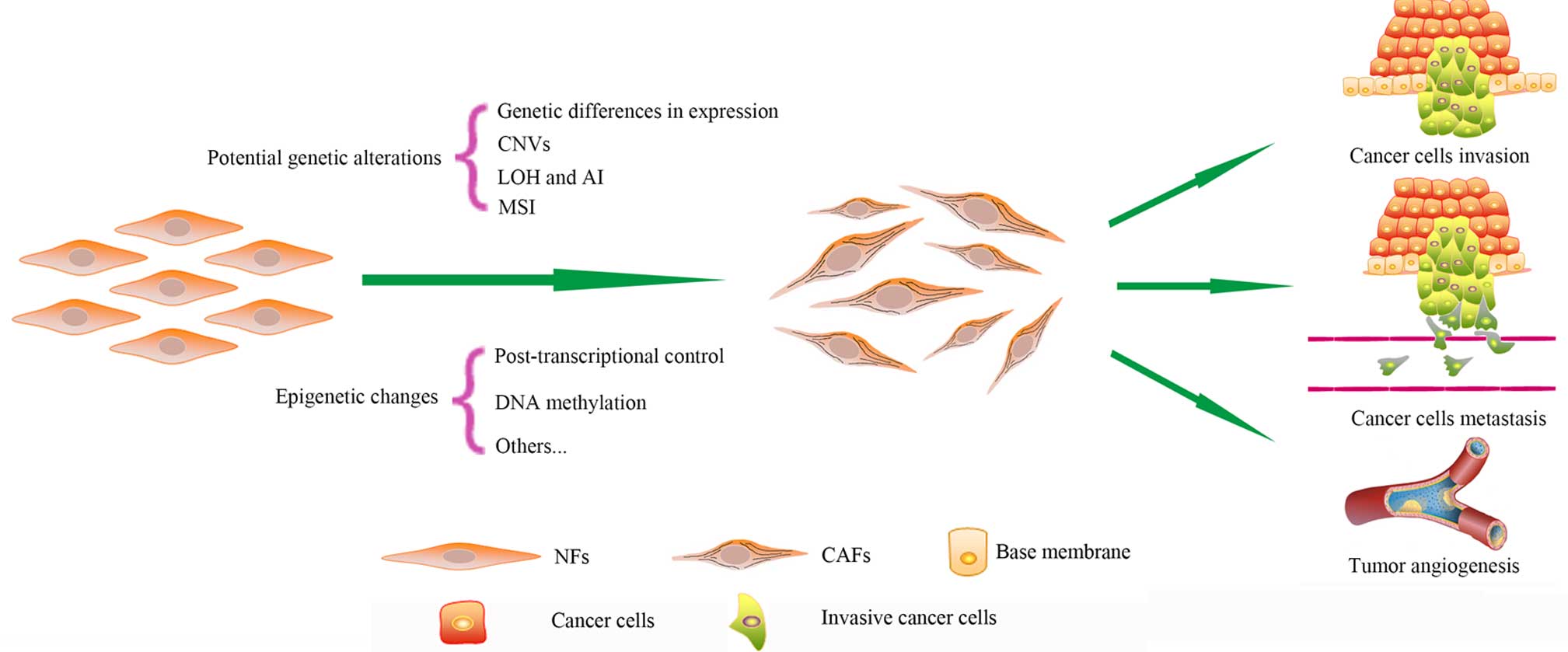
|
1
|
Lengauer C, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B:
Genetic instabilities in human cancers. Nature. 396:643–649. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Crispo E, Moore JS, Lee-Yaw JA, Gray SM
and Haller BC: Broken barriers: Human-induced changes to gene flow
and introgression in animals: An examination of the ways in which
humans increase genetic exchange among populations and species and
the consequences for biodiversity. Bioessays. 33:508–518. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Verde C, di Prisco G and Convey P:
Molecular and genetic advances to understanding evolution and
biodiversity in the polar regions. Mar Genomics. 8:1–2. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jia CC, Wang TT, Liu W, Fu BS, Hua X, Wang
GY, Li TJ, Li X, Wu XY, Tai Y, et al: Cancer-associated fibroblasts
from hepatocellular carcinoma promote malignant cell proliferation
by HGF secretion. PLoS One. 8:e632432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xing F, Saidou J and Watabe K: Cancer
associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in tumor microenvironment. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 15:166–179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Franco OE, Shaw AK, Strand DW and Hayward
SW: Cancer associated fibroblasts in cancer pathogenesis. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 21:33–39. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Castello-Cros R, Bonnuccelli G, Molchansky
A, Capozza F, Witkiewicz AK, Birbe RC, Howell A, Pestell RG,
Whitaker-Menezes D, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Matrix remodeling
stimulates stromal autophagy, ‘fueling’ cancer cell mitochondrial
metabolism and metastasis. Cell Cycle. 10:2021–2034. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Balliet RM, Capparelli C, Guido C, Pestell
TG, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Lin Z, Whitaker-Menezes D, Chiavarina
B, Pestell RG, Howell A, et al: Mitochondrial oxidative stress in
cancer-associated fibroblasts drives lactate production, promoting
breast cancer tumor growth: Understanding the aging and cancer
connection. Cell Cycle. 10:4065–4073. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bonuccelli G, Tsirigos A, Whitaker-Menezes
D, Pavlides S, Pestell RG, Chiavarina B, Frank PG, Flomenberg N,
Howell A, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, et al: Ketones and lactate ‘fuel’
tumor growth and metastasis: Evidence that epithelial cancer cells
use oxidative mitochondrial metabolism. Cell Cycle. 9:3506–3514.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qiu W, Hu M, Sridhar A, Opeskin K, Fox S,
Shipitsin M, Trivett M, Thompson ER, Ramakrishna M, Gorringe KL, et
al: No evidence of clonal somatic genetic alterations in
cancer-associated fibroblasts from human breast and ovarian
carcinomas. Nat Genet. 40:650–655. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bauer M, Su G, Casper C, He R, Rehrauer W
and Friedl A: Heterogeneity of gene expression in stromal
fibroblasts of human breast carcinomas and normal breast. Oncogene.
29:1732–1740. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakagawa H, Liyanarachchi S, Davuluri RV,
Auer H, Martin EW Jr, de la Chapelle A and Frankel WL: Role of
cancer-associated stromal fibroblasts in metastatic colon cancer to
the liver and their expression profiles. Oncogene. 23:7366–7377.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sato N, Maehara N and Goggins M: Gene
expression profiling of tumor-stromal interactions between
pancreatic cancer cells and stromal fibroblasts. Cancer Res.
64:6950–6956. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamada C, Aikawa T, Okuno E, Miyagawa K,
Amano K, Takahata S, Kimata M, Okura M, Iida S and Kogo M: TGF-β in
jaw tumor fluids induces RANKL expression in stromal fibroblasts.
Int J Oncol. 49:499–508. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Singer CF, Gschwantler-Kaulich D,
Fink-Retter A, Haas C, Hudelist G, Czerwenka K and Kubista E:
Differential gene expression profile in breast cancer-derived
stromal fibroblasts. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 110:273–281. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Navab R, Strumpf D, Bandarchi B, Zhu CQ,
Pintilie M, Ramnarine VR, Ibrahimov E, Radulovich N, Leung L,
Barczyk M, et al: Prognostic gene-expression signature of
carcinoma-associated fibroblasts in non-small cell lung cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:7160–7165. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ and Balmain A:
TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat
Genet. 29:117–129. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wakefield LM and Roberts AB: TGF-beta
signaling: Positive and negative effects on tumorigenesis. Curr
Opin Genet Dev. 12:22–29. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zavadil J and Böttinger EP: TGF-beta and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. Oncogene. 24:5764–5774.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Katsuno Y, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-β signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer
progression. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:76–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Herrera M, Islam AB, Herrera A, Martín P,
García V, Silva J, Garcia JM, Salas C, Casal I, de Herreros AG, et
al: Functional heterogeneity of cancer-associated fibroblasts from
human colon tumors shows specific prognostic gene expression
signature. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5914–5926. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Migneco G, Whitaker-Menezes D, Chiavarina
B, Castello-Cros R, Pavlides S, Pestell RG, Fatatis A, Flomenberg
N, Tsirigos A, Howell A, et al: Glycolytic cancer associated
fibroblasts promote breast cancer tumor growth, without a
measurable increase in angiogenesis: Evidence for
stromal-epithelial metabolic coupling. Cell Cycle. 9:2412–2422.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Leiherer A, Geiger K, Muendlein A and
Drexel H: Hypoxia induces a HIF-1α dependent signalling cascade to
make a complex metabolic switch in SGBS-adipocytes. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 383:21–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu C, Wang Z, Zhai L, Yang M, Shan L, Chai
C, Liu M and Wang L: Effects of cancer-associated fibroblasts on
the migration and invasion abilities of SGC-7901 gastric cancer
cells. Oncol Lett. 5:609–612. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim SH, Choe C, Shin YS, Jeon MJ, Choi SJ,
Lee J, Bae GY, Cha HJ and Kim J: Human lung cancer-associated
fibroblasts enhance motility of non-small cell lung cancer cells in
co-culture. Anticancer Res. 33:2001–2009. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cao M, Seike M, Soeno C, Mizutani H,
Kitamura K, Minegishi Y, Noro R, Yoshimura A, Cai L and Gemma A:
MiR-23a regulates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
by targeting E-cadherin in lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
41:869–875. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schveigert D, Cicenas S, Bruzas S,
Samalavicius NE, Gudleviciene Z and Didziapetriene J: The value of
MMP-9 for breast and non-small cell lung cancer patients' survival.
Adv Med Sci. 58:73–82. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nagasaki T, Hara M, Nakanishi H, Takahashi
H, Sato M and Takeyama H: Interleukin-6 released by colon
cancer-associated fibroblasts is critical for tumour angiogenesis:
Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody suppressed angiogenesis and
inhibited tumour-stroma interaction. Br J Cancer. 110:469–478.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Al-Ansari MM, Hendrayani SF, Tulbah A,
Al-Tweigeri T, Shehata AI and Aboussekhra A: P16INK4A represses
breast stromal fibroblasts migration/invasion and their
VEGF-A-dependent promotion of angiogenesis through Akt inhibition.
Neoplasia. 14:1269–1277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC,
Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, Carey VJ, Richardson AL
and Weinberg RA: Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human
breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through
elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell. 121:335–348. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Finak G, Bertos N, Pepin F, Sadekova S,
Souleimanova M, Zhao H, Chen H, Omeroglu G, Meterissian S, Omeroglu
A, et al: Stromal gene expression predicts clinical outcome in
breast cancer. Nat Med. 14:518–527. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sadlonova A, Bowe DB, Novak Z, Mukherjee
S, Duncan VE, Page GP and Frost AR: Identification of molecular
distinctions between normal breast-associated fibroblasts and
breast cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Microenviron. 2:9–21.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tchou J, Kossenkov AV, Chang L, Satija C,
Herlyn M, Showe LC and Puré E: Human breast cancer associated
fibroblasts exhibit subtype specific gene expression profiles. BMC
Med Genomics. 5:392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ma XJ, Dahiya S, Richardson E, Erlander M
and Sgroi DC: Gene expression profiling of the tumor
microenvironment during breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer
Res. 11:R72009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Park SU, Choi ES, Jang YS, Hong SH, Kim IH
and Chang DK: Effects of chromosomal polyploidy on survival of
colon cancer cells. Korean J Gastroenterol. 57:150–157. 2011.(In
Korean). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zheng XH, Liu Y, Zhou HM, Chen QM and Li
BQ: Analysis of chromosome karyotype of oral carcinoma-associated
Fibroblasts. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 23:159–160. 2005.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dudley AC, Shih SC, Cliffe AR, Hida K and
Klagsbrun M: Attenuated p53 activation in tumour-associated stromal
cells accompanies decreased sensitivity to etoposide and
vincristine. Br J Cancer. 99:118–125. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang G, Rosen DG, Zhang Z, Bast RC Jr,
Mills GB, Colacino JA, Mercado-Uribe I and Liu J: The chemokine
growth-regulated oncogene 1 (Gro-1) links RAS signaling to the
senescence of stromal fibroblasts and ovarian tumorigenesis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:16472–16477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Capparelli C, Whitaker-Menezes D, Guido C,
Balliet R, Pestell TG, Howell A, Sneddon S, Pestell RG,
Martinez-Outschoorn U, Lisanti MP and Sotgia F: CTGF drives
autophagy, glycolysis and senescence in cancer-associated
fibroblasts via HIF1 activation, metabolically promoting tumor
growth. Cell Cycle. 11:2272–2284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Erenpreisa J and Cragg MS: Three steps to
the immortality of cancer cells: Senescence, polyploidy and
self-renewal. Cancer Cell Int. 13:922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bowcock AM: Invited review DNA copy number
changes as diagnostic tools for lung cancer. Thorax. 69:495–496.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tuhkanen H, Anttila M, Kosma VM, Heinonen
S, Juhola M, Helisalmi S, Kataja V and Mannermaa A: Frequent gene
dosage alterations in stromal cells of epithelial ovarian
carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 119:1345–1353. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pelham RJ, Rodgers L, Hall I, Lucito R,
Nguyen KC, Navin N, Hicks J, Mu D, Powers S, Wigler M and Botstein
D: Identification of alterations in DNA copy number in host stromal
cells during tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:19848–19853. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Carles-Kinch K, Kilpatrick KE, Stewart JC
and Kinch MS: Antibody targeting of the EphA2 tyrosine kinase
inhibits malignant cell behavior. Cancer Res. 62:2840–2847.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mao W, Luis E, Ross S, Silva J, Tan C,
Crowley C, Chui C, Franz G, Senter P, Koeppen H and Polakis P:
EphB2 as a therapeutic antibody drug target for the treatment of
colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 64:781–788. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rummel S, Valente AL, Kane JL, Shriver CD
and Ellsworth RE: Genomic (in)stability of the breast tumor
microenvironment. Mol Cancer Res. 10:1526–1531. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rohrbach H, Haas CJ, Baretton GB,
Hirschmann A, Diebold J, Behrendt RP and Löhrs U: Microsatellite
instability and loss of heterozygosity in prostatic carcinomas:
Comparison of primary tumors and of corresponding recurrences after
androgen-deprivation therapy and lymph-node metastases. Prostate.
40:20–27. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Smith HS, Lu Y, Deng G, Martinez O, Krams
S, Ljung BM, Thor A and Lagios M: Molecular aspects of early stages
of breast cancer progression. J Cell Biochem Suppl 17G. 144–152.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Agapova LS, Ivanov AV, Sablina AA, Kopnin
PB, Sokova OI, Chumakov PM and Kopnin BP: P53-dependent effects of
RAS oncogene on chromosome stability and cell cycle checkpoints.
Oncogene. 18:3135–3142. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Matsumoto N, Yoshida T and Okayasu I: High
epithelial and stromal genetic instability of chromosome 17 in
ulcerative colitis-associated carcinogenesis. Cancer Res.
63:6158–6161. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wernert N, Löcherbach C, Wellmann A,
Behrens P and Hügel A: Presence of genetic alterations in
microdissected stroma of human colon and breast cancers. Anticancer
Res. 21:2259–2264. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Moinfar F, Man YG, Arnould L, Bratthauer
GL, Ratschek M and Tavassoli FA: Concurrent and independent genetic
alterations in the stromal and epithelial cells of mammary
carcinoma: Implications for tumorigenesis. Cancer Res.
60:2562–2566. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Paterson RF, Ulbright TM, MacLennan GT,
Zhang S, Pan CX, Sweeney CJ, Moore CR, Foster RS, Koch MO, Eble JN
and Cheng L: Molecular genetic alterations in the
laser-capture-microdissected stroma adjacent to bladder carcinoma.
Cancer. 98:1830–1836. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tuhkanen H, Anttila M, Kosma VM,
Ylä-Herttuala S, Heinonen S, Kuronen A, Juhola M, Tammi R, Tammi M
and Mannermaa A: Genetic alterations in the peritumoral stromal
cells of malignant and borderline epithelial ovarian tumors as
indicated by allelic imbalance on chromosome 3p. Int J Cancer.
109:247–252. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kurose K, Gilley K, Matsumoto S, Watson
PH, Zhou XP and Eng C: Frequent somatic mutations in PTEN and TP53
are mutually exclusive in the stroma of breast carcinomas. Nat
Genet. 32:355–357. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Patocs A, Zhang L, Xu Y, Weber F, Caldes
T, Mutter GL, Platzer P and Eng C: Breast-cancer stromal cells with
TP53 mutations and nodal metastases. N Engl J Med. 357:2543–2551.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Fukino K, Shen L, Patocs A, Mutter GL and
Eng C: Genomic instability within tumor stroma and
clinicopathological characteristics of sporadic primary invasive
breast carcinoma. JAMA. 297:2103–2111. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fukino K, Shen L, Matsumoto S, Morrison
CD, Mutter GL and Eng C: Combined total genome loss of
heterozygosity scan of breast cancer stroma and epithelium reveals
multiplicity of stromal targets. Cancer Res. 64:7231–7236. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kurose K, Hoshaw-Woodard S, Adeyinka A,
Lemeshow S, Watson PH and Eng C: Genetic model of multi-step breast
carcinogenesis involving the epithelium and stroma: Clues to
tumour-microenvironment interactions. Hum Mol Genet. 10:1907–1913.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Hill R, Song Y, Cardiff RD and Van Dyke T:
Selective evolution of stromal mesenchyme with p53 loss in response
to epithelial tumorigenesis. Cell. 123:1001–1011. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hawsawi NM, Ghebeh H, Hendrayani SF,
Tulbah A, Al-Eid M, Al-Tweigeri T, Ajarim D, Alaiya A, Dermime S
and Aboussekhra A: Breast carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and
their counterparts display neoplastic-specific changes. Cancer Res.
68:2717–2725. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chung JH, Rho JK, Xu X, Lee JS, Yoon HI,
Lee CT, Choi YJ, Kim HR, Kim CH and Lee JC: Clinical and molecular
evidences of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in acquired
resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Lung Cancer. 73:176–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Shang Y, Cai X and Fan D: Roles of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer drug resistance. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 13:915–929. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Schmid JO, Dong M, Haubeiss S, Friedel G,
Bode S, Grabner A, Ott G, Mürdter TE, Oren M, Aulitzky WE and van
der Kuip H: Cancer cells cue the p53 response of cancer-associated
fibroblasts to cisplatin. Cancer Res. 72:5824–5832. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Assadian S, El-Assaad W, Wang XQ, Gannon
PO, Barrès V, Latour M, Mes-Masson AM, Saad F, Sado Y, Dostie J and
Teodoro JG: P53 inhibits angiogenesis by inducing the production of
Arresten. Cancer Res. 72:1270–1279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ghahremani M Farhang, Goossens S, Nittner
D, Bisteau X, Bartunkova S, Zwolinska A, Hulpiau P, Haigh K,
Haenebalcke L, Drogat B, et al: P53 promotes VEGF expression and
angiogenesis in the absence of an intact p21-Rb pathway. Cell Death
Differ. 20:888–897. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Teodoro JG, Parker AE, Zhu X and Green MR:
P53-mediated inhibition of angiogenesis through up-regulation of a
collagen prolyl hydroxylase. Science. 313:968–971. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Heinimann K: Toward a molecular
classification of colorectal cancer: The role of microsatellite
instability status. Front Oncol. 3:2722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Matsumoto N, Yoshida T, Yamashita K,
Numata Y and Okayasu I: Possible alternative carcinogenesis pathway
featuring microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer stroma.
Br J Cancer. 89:707–712. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yagishita H, Yoshida T, Ishiguro K, Numata
Y and Okayasu I: Epithelial and stromal genetic instability linked
to tumor suppressor genes in ulcerative colitis-associated
tumorigenesis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 43:559–566. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu X, Goldblum JR, Zhao Z, Landau M,
Heald B, Pai R and Lin J: Distinct clinicohistologic features of
inflammatory bowel disease-associated colorectal adenocarcinoma: in
comparison with sporadic microsatellite-stable and Lynch
syndrome-related colorectal adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol.
36:1228–1233. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Shiraishi H, Mikami T, Yoshida T, Tanabe
S, Kobayashi N, Watanabe M and Okayasu I: Early genetic instability
of both epithelial and stromal cells in esophageal squamous cell
carcinomas, contrasted with Barrett's adenocarcinomas. J
Gastroenterol. 41:1186–1196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chomyn A and Attardi G: MtDNA mutations in
aging and apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 304:519–529. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Liu VW, Shi HH, Cheung AN, Chiu PM, Leung
TW, Nagley P, Wong LC and Ngan HY: High incidence of somatic
mitochondrial DNA mutations in human ovarian carcinomas. Cancer
Res. 61:5998–6001. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Habano W, Sugai T, Nakamura SI, Uesugi N,
Yoshida T and Sasou S: Microsatellite instability and mutation of
mitochondrial and nuclear DNA in gastric carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 118:835–841. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Habano W, Nakamura S and Sugai T:
Microsatellite instability in the mitochondrial DNA of colorectal
carcinomas: Evidence for mismatch repair systems in mitochondrial
genome. Oncogene. 17:1931–1937. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Suzuki M, Toyooka S, Miyajima K, Iizasa T,
Fujisawa T, Bekele NB and Gazdar AF: Alterations in the
mitochondrial displacement loop in lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res.
9:5636–5641. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Kim HS, Lim HS, Lee SH, Lee JW, Nam SW,
Park WS, Lee YS, Lee JY and Yoo NJ: Mitochondrial microsatellite
instability of colorectal cancer stroma. Int J Cancer.
119:2607–2611. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Dey P: Epigenetic changes in tumor
microenvironment. Indian J Cancer. 48:507–512. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ting AH, McGarvey KM and Baylin SB: The
cancer epigenome-components and functional correlates. Genes Dev.
20:3215–3231. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Lund AH and van Lohuizen M: Epigenetics
and cancer. Genes Dev. 18:2315–2335. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Di Leva G and Croce CM: Roles of small
RNAs in tumor formation. Trends Mol Med. 16:257–267. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhao L, Sun Y, Hou Y, Peng Q, Wang L, Luo
H, Tang X, Zeng Z and Liu M: MiRNA expression analysis of
cancer-associated fibroblasts and normal fibroblasts in breast
cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:2051–2059. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Bronisz A, Godlewski J, Wallace JA,
Merchant AS, Nowicki MO, Mathsyaraja H, Srinivasan R, Trimboli AJ,
Martin CK, Li F, et al: Reprogramming of the tumour
microenvironment by stromal PTEN-regulated miR-320. Nat Cell Biol.
14:159–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Rask L, Balslev E, Jørgensen S, Eriksen J,
Flyger H, Møller S, Høgdall E, Litman T and Nielsen BS: High
expression of miR-21 in tumor stroma correlates with increased
cancer cell proliferation in human breast cancer. APMIS.
119:663–673. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Pathmanathan N and Balleine RL: Ki67 and
proliferation in breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 66:512–516. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Yamamichi N, Shimomura R, Inada K, Sakurai
K, Haraguchi T, Ozaki Y, Fujita S, Mizutani T, Furukawa C,
Fujishiro M, et al: Locked nucleic acid in situ hybridization
analysis of miR-21 expression during colorectal cancer development.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:4009–4016. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Nouraee N, Roosbroeck K, Vasei M, Semnani
S, Samaei NM, Naghshvar F, Omidi AA, Calin GA and Mowla SJ:
Expression, tissue distribution and function of miR-21 in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e730092013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Dobreva G, Dambacher J and Grosschedl R:
SUMO modification of a novel MAR-binding protein, SATB2, modulates
immunoglobulin mu gene expression. Genes Dev. 17:3048–3061. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Patani N, Jiang W, Mansel R, Newbold R and
Mokbel K: The mRNA expression of SATB1 and SATB2 in human breast
cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 9:182009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Aprelikova O, Yu X, Palla J, Wei BR, John
S, Yi M, Stephens R, Simpson RM, Risinger JI, Jazaeri A and
Niederhuber J: The role of miR-31 and its target gene SATB2 in
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Cycle. 9:4387–4398. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Aprelikova O, Palla J, Hibler B, Yu X,
Greer YE, Yi M, Stephens R, Maxwell GL, Jazaeri A, Risinger JI, et
al: Silencing of miR-148a in cancer-associated fibroblasts results
in WNT10B-mediated stimulation of tumor cell motility. Oncogene.
32:3246–3253. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wei J, Melichian D, Komura K, Hinchcliff
M, Lam AP, Lafyatis R, Gottardi CJ, MacDougald OA and Varga J:
Canonical Wnt signaling induces skin fibrosis and subcutaneous
lipoatrophy: A novel mouse model for scleroderma? Arthritis Rheum.
63:1707–1717. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Enkelmann A, Heinzelmann J, von Eggeling
F, Walter M, Berndt A, Wunderlich H and Junker K: Specific protein
and miRNA patterns characterise tumour-associated fibroblasts in
bladder cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:751–759. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Schepeler T, Reinert JT, Ostenfeld MS,
Christensen LL, Silahtaroglu AN, Dyrskjøt L, Wiuf C, Sørensen FJ,
Kruhøffer M, Laurberg S, et al: Diagnostic and prognostic microRNAs
in stage II colon cancer. Cancer Res. 68:6416–6424. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Lee KH, Lotterman C, Karikari C, Omura N,
Feldmann G, Habbe N, Goggins MG, Mendell JT and Maitra A:
Epigenetic silencing of MicroRNA miR-107 regulates cyclin-dependent
kinase 6 expression in pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 9:293–301.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, Lu R, Rader JS,
Meyers C and Zheng ZM: Aberrant expression of oncogenic and
tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for
cancer cell growth. PLoS One. 3:e25572008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Mitra AK, Zillhardt M, Hua Y, Tiwari P,
Murmann AE, Peter ME and Lengyel E: MicroRNAs reprogram normal
fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts in ovarian cancer.
Cancer Discov. 2:1100–1108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Long H, Xie R, Xiang T, Zhao Z, Lin S,
Liang Z, Chen Z and Zhu B: Autocrine CCL5 signaling promotes
invasion and migration of CD133+ovarian cancer stem-like cells via
NF-κB-mediated MMP-9 upregulation. Stem Cells. 30:2309–2319. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Naito Y, Sakamoto N, Oue N, Yashiro M,
Sentani K, Yanagihara K, Hirakawa K and Yasui W: MicroRNA-143
regulates collagen type III expression in stromal fibroblasts of
scirrhous type gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 105:228–235. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Musumeci M, Coppola V, Addario A, Patrizii
M, Maugeri-Saccà M, Memeo L, Colarossi C, Francescangeli F, Biffoni
M, Collura D, et al: Control of tumor and microenvironment
cross-talk by miR-15a and miR-16 in prostate cancer. Oncogene.
30:4231–4242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Sun P, Hu JW, Xiong WJ and Mi J: MiR-186
regulates glycolysis through Glut1 during the formation of
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:4245–4250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Pavlides S, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Castello-Cros R, Flomenberg N, Witkiewicz AK, Frank PG, Casimiro
MC, Wang C, Fortina P, Addya S, et al: The reverse Warburg effect:
Aerobic glycolysis in cancer associated fibroblasts and the tumor
stroma. Cell Cycle. 8:3984–4001. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Sotgia F, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Pavlides
S, Howell A, Pestell RG and Lisanti MP: Understanding the Warburg
effect and the prognostic value of stromal caveolin-1 as a marker
of a lethal tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. 13:2132011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Sotgia F, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Howell
A, Pestell RG, Pavlides S and Lisanti MP: Caveolin-1 and cancer
metabolism in the tumor microenvironment: Markers, models, and
mechanisms. Annu Rev Pathol. 7:423–467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Razani B, Zhang XL, Bitzer M, von
Gersdorff G, Böttinger EP and Lisanti MP: Caveolin-1 regulates
transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta/SMAD signaling through an
interaction with the TGF-beta type I receptor. J Biol Chem.
276:6727–6738. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The fundamental
role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 3:415–428.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Wilson AS, Power BE and Molloy PL: DNA
hypomethylation and human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1775:138–162. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Adany R, Heimer R, Caterson B, Sorrell JM
and Iozzo RV: Altered expression of chondroitin sulfate
proteoglycan in the stroma of human colon carcinoma.
Hypomethylation of PG-40 gene correlates with increased PG-40
content and mRNA levels. J Biol Chem. 265:11389–11396.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Adany R and Iozzo RV: Altered methylation
of versican proteoglycan gene in human colon carcinoma. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 171:1402–1413. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Adany R and Iozzo RV: Hypomethylation of
the decorin proteoglycan gene in human colon cancer. Biochem J.
276:301–306. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Kekeeva TV, Popova OP, Shegaĭ PV, Alekseev
BIa, Adnreeva IuIu, Zaletaev DV and Nemtsova MV: Abberant
methylation of p16, HIC1, N33 and GSTP1 genes in tumor epitelium
and tumor-associated stromal cells of prostate cancer. Mol Biol
(Mosk). 41:79–85. 2007.(In Russian). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Rodriguez-Canales J, Hanson JC, Tangrea
MA, Erickson HS, Albert PS, Wallis BS, Richardson AM, Pinto PA,
Linehan WM, Gillespie JW, et al: Identification of a unique
epigenetic sub-microenvironment in prostate cancer. J Pathol.
211:410–419. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Ye F, Zhang SF, Xie X and Lu WG: OPCML
gene promoter methylation and gene expression in tumor and stroma
cells of invasive cervical carcinoma. Cancer Invest. 26:569–574.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Matsunoki A, Kawakami K, Kotake M, Kaneko
M, Kitamura H, Ooi A, Watanabe G and Minamoto T: LINE-1 methylation
shows little intra-patient heterogeneity in primary and synchronous
metastatic colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 12:5742012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Fiegl H, Millinger S, Goebel G,
Müller-Holzner E, Marth C, Laird PW and Widschwendter M: Breast
cancer DNA methylation profiles in cancer cells and tumor stroma:
Association with HER-2/neu status in primary breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 66:29–33. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Dawsey SP, Roth MJ, Adams L, Hu N, Wang
QH, Taylor PR and Woodson K: COX-2 (PTGS2) gene methylation in
epithelial, subepithelial lymphocyte and stromal tissue
compartments in a spectrum of esophageal squamous neoplasia. Cancer
Detect Prev. 32:135–139. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhuang J, Jones A, Lee SH, Ng E, Fiegl H,
Zikan M, Cibula D, Sargent A, Salvesen HB, Jacobs IJ, et al: The
dynamics and prognostic potential of DNA methylation changes at
stem cell gene loci in women's cancer. PLoS Genet. 8:e10025172012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Jiang L, Gonda TA, Gamble MV, Salas M,
Seshan V, Tu S, Twaddell WS, Hegyi P, Lazar G, Steele I, et al:
Global hypomethylation of genomic DNA in cancer-associated
myofibroblasts. Cancer Res. 68:9900–9908. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Wasserkort R, Kalmar A, Valcz G, Spisak S,
Krispin M, Toth K, Tulassay Z, Sledziewski AZ and Molnar B:
Aberrant septin 9 DNA methylation in colorectal cancer is
restricted to a single CpG island. BMC Cancer. 13:3982013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Hanson JA, Gillespie JW, Grover A, Tangrea
MA, Chuaqui RF, Emmert-Buck MR, Tangrea JA, Libutti SK, Linehan WM
and Woodson KG: Gene promoter methylation in prostate
tumor-associated stromal cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 98:255–261.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Kim YI, Fawaz K, Knox T, Lee YM, Norton R,
Arora S, Paiva L and Mason JB: Colonic mucosal concentrations of
folate correlate well with blood measurements of folate status in
persons with colorectal polyps. Am J Clin Nutr. 68:866–872.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Momparler RL: Cancer epigenetics.
Oncogene. 22:6479–6483. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Hayes J, Peruzzi PP and Lawler S:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol
Med. 20:460–469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Nielsen BS, Jørgensen S, Fog JU, Søkilde
R, Christensen IJ, Hansen U, Brünner N, Baker A, Møller S and
Nielsen HJ: High levels of microRNA-21 in the stroma of colorectal
cancers predict short disease-free survival in stage II colon
cancer patients. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:27–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Dou L, Zheng D, Li J, Li Y, Gao L, Wang L
and Yu L: Methylation-mediated repression of microRNA-143 enhances
MLL-AF4 oncogene expression. Oncogene. 31:507–517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Liu R, Liao J, Yang M, Sheng J, Yang H,
Wang Y, Pan E, Guo W, Pu Y, Kim SJ and Yin L: The cluster of
miR-143 and miR-145 affects the risk for esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma through co-regulating fascin homolog 1. PLoS One.
7:e339872013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Zhu H, Dougherty U, Robinson V, Mustafi R,
Pekow J, Kupfer S, Li YC, Hart J, Goss K, Fichera A, et al: EGFR
signals downregulate tumor suppressors miR-143 and miR-145 in
Western diet-promoted murine colon cancer: role of G1 regulators.
Mol Cancer Res. 9:960–975. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Wang Q, Cai J, Wang J, Xiong C and Zhao J:
MiR-143 inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent osteosarcoma invasion.
Tumour Biol. 35:12743–12748. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Wang X, Baumgartner C, Shields DC, Deng HW
and Beckmann JS: Application of Clinical Bioinformatics. Springer;
Netherlands: pp. 1262016
|
|
135
|
Anestopoulos I, Voulgaridou GP,
Georgakilas AG, Franco R, Pappa A and Panayiotidis MI: Epigenetic
therapy as a novel approach in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacol
Ther. 145:103–119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Corver WE, Ter Haar NT, Fleuren GJ and
Oosting J: Cervical carcinoma-associated fibroblasts are DNA
diploid and do not show evidence for somatic genetic alterations.
Cell Oncol (Dordr). 34:553–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Walter K, Omura N, Hong SM, Griffith M and
Goggins M: Pancreatic cancer associated fibroblasts display normal
allelotypes. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:882–888. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Erez N, Truitt M, Olson P, Arron ST and
Hanahan D: Cancer-associated fibroblasts are activated in incipient
neoplasia to orchestrate tumor-promoting inflammation in an
NF-kappaB-dependent manner. Cancer Cell. 17:135–147. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Whitaker-Menezes
D, Lin Z, Flomenberg N, Howell A, Pestell RG, Lisanti MP and Sotgia
F: Cytokine production and inflammation drive autophagy in the
tumor microenvironment: Role of stromal caveolin-1 as a key
regulator. Cell Cycle. 10:1784–1793. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Servais C and Erez N: From sentinel cells
to inflammatory culprits: Cancer-associated fibroblasts in
tumour-related inflammation. J Pathol. 229:198–207. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Shiels MS, Engels EA, Shi J, Landi MT,
Albanes D, Chatterjee N, Chanock SJ, Caporaso NE and Chaturvedi AK:
Genetic variation in innate immunity and inflammation pathways
associated with lung cancer risk. Cancer. 118:5630–5636. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Pavlides S, Tsirigos A, Vera I, Flomenberg
N, Frank PG, Casimiro MC, Wang C, Fortina P, Addya S, Pestell RG,
et al: Loss of stromal caveolin-1 leads to oxidative stress, mimics
hypoxia and drives inflammation in the tumor microenvironment,
conferring the ‘reverse Warburg effect’ a transcriptional
informatics analysis with validation. Cell Cycle. 9:2201–2219.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Lehmann U and Kreipe H: Real-time PCR
analysis of DNA and RNA extracted from formalin-fixed and
paraffin-embedded biopsies. Methods. 25:409–418. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Ale-Agha N, Dyballa-Rukes N, Jakob S,
Altschmied J and Haendeler J: Cellular functions of the
dual-targeted catalytic subunit of telomerase, telomerase reverse
transcriptase-potential role in senescence and aging. Exp Gerontol.
56:189–193. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Urquidi V, Tarin D and Goodison S: Role of
telomerase in cell senescence and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Med.
51:65–79. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Shawi M and Autexier C: Telomerase,
senescence and ageing. Mech Ageing Dev. 129:3–10. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|