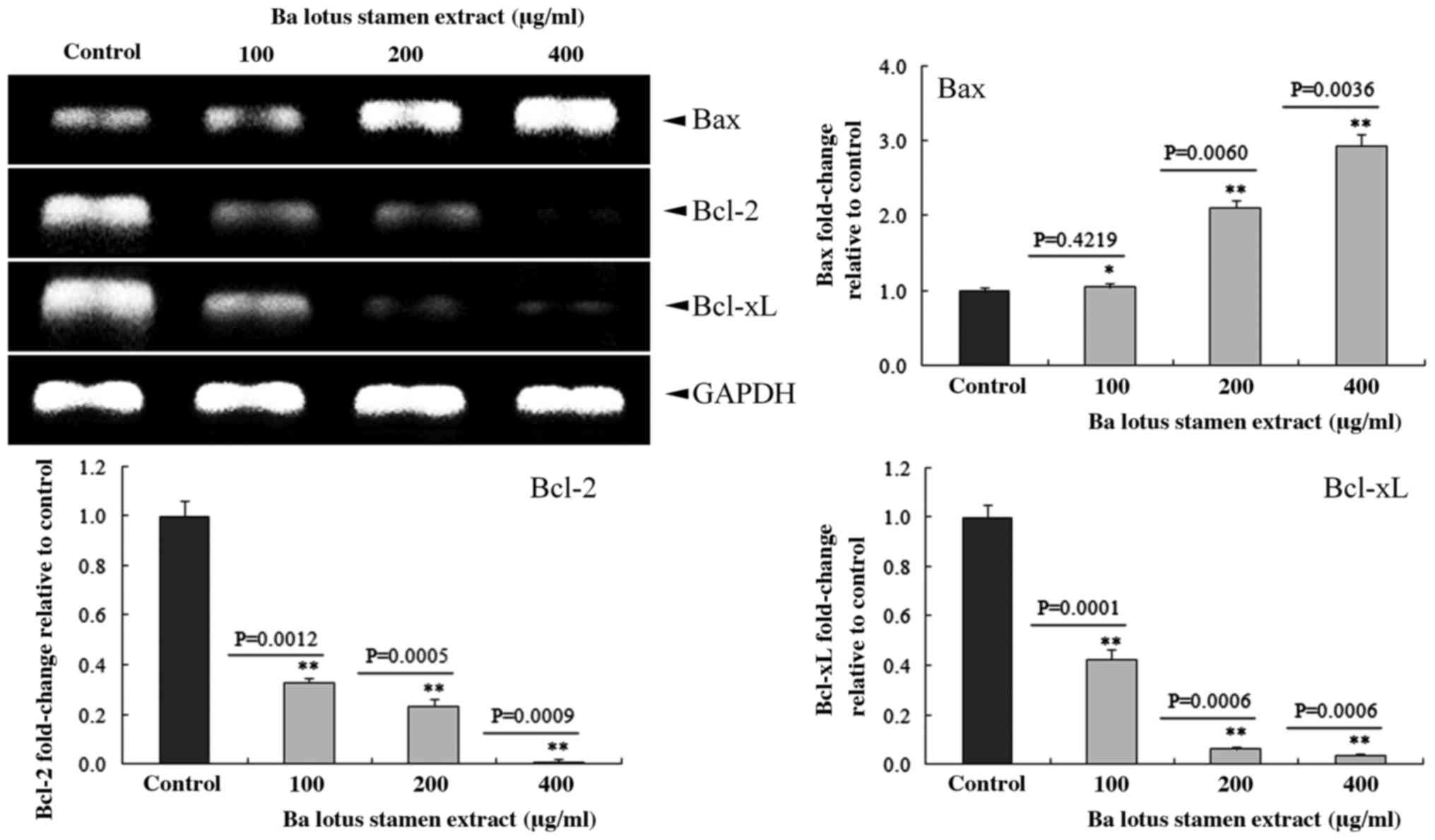
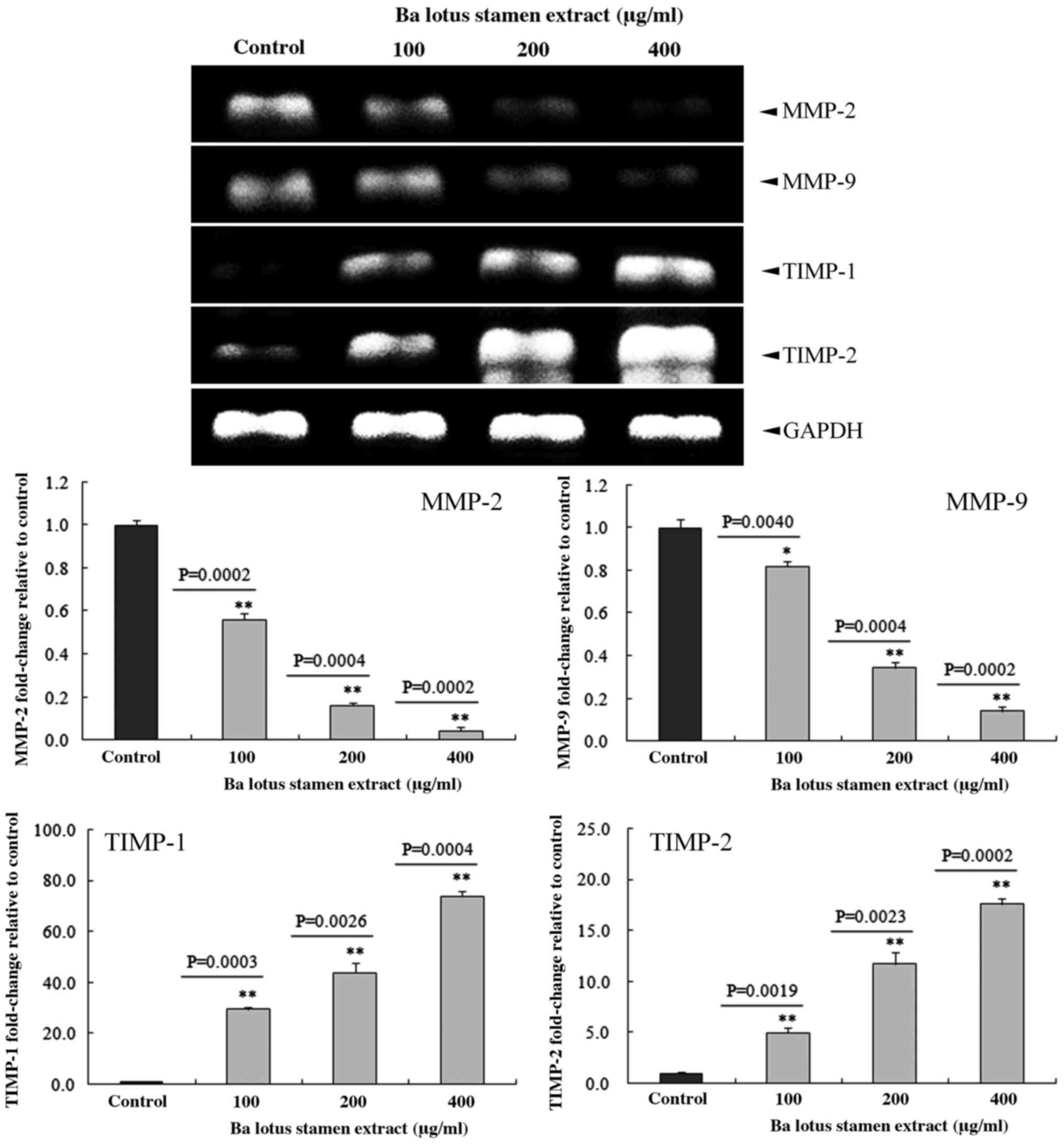
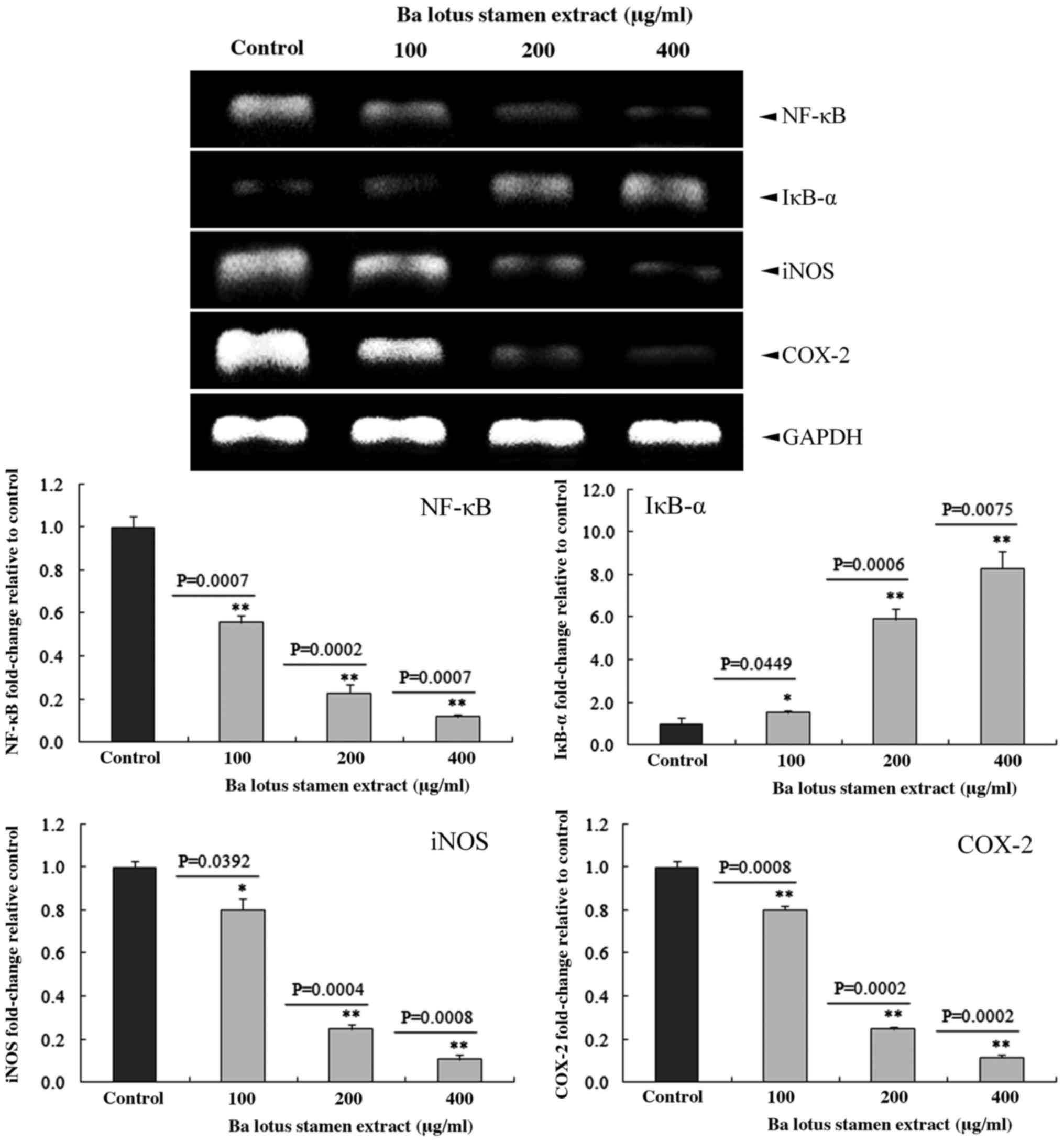
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Long N, Moore M, Chen W, Gao CM, Lai MS,
Mizoue T, Oyunchimeg D, Park S, Shin HR, Tajima K, et al: Cancer
epidemiology and control in north-East Asia-past, present and
future. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 11:(Suppl 2). S107–S148. 2010.
|
|
3
|
Wang ZX, Cao JX, Liu ZP, Cui YX, Li CY, Li
D, Zhang XY, Liu JL and Li JL: Combination of chemotherapy and
immunotherapy for colon cancer in China: A meta-analysis. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:1095–1060. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wong RS: Apoptosis in cancer: From
pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:872011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ola MS, Nawaz M and Ahsan H: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol
Cell Biochem. 351:41–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Volkmann N, Marassi FM, Newmeyer DD and
Hanein D: The rheostat in the membrane: BCL-2 family proteins and
apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 206–215. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peter ME and Krammer PH: The
CD95(APO-1/Fas) DISC and beyond. Cell Death Differ. 10:26–35. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Martinou JC and Youle RJ: Mitochondria in
apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev
Cell. 21:92–101. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cullen SP and Martin SJ: Caspase
activation pathways: Some recent progress. Cell Death Differ.
16:935–938. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao Y, Lei M, Wang Z, Qiao G, Yang T and
Zhang J: TCR-induced, PKC-θ-mediated NF-κB activation is regulated
by a caspase-8-caspase-9-caspase-3 cascade. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 450:526–531. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gordaliza M: Natural products as leads to
anticancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol. 9:767–776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsiao WL and Liu L: The role of
traditional Chinese herbal medicines in cancer therapy-from TCM
theory to mechanistic insights. Planta Med. 76:1118–1131. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qi F, Li A, Inagaki Y, Gao J, Li J, Kokudo
N, Li XK and Tang W: Chinese herbal medicines as adjuvant treatment
during chemo-or radio-therapy for cancer. Biosci Trends. 4:297–307.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Parsons ME and Keeling DJ: Novel
approaches to the pharmacological blockade of gastric acid
secretion. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 14:411–421. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Talukder MJ and Nessa J: Effect of Nelumbo
nucifera rhizome extract on the gastrointestinal tract of rat.
Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull. 24:6–9. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kuo YC, Lin YL, Liu CP and Tsai WJ: Herpes
simplex virus type 1 propagation in HeLa cells interrupted by
Nelumbo nucifera. J Biomed Sci. 12:1021–1034. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ono Y, Hattori E, Fukaya Y, Imai S and
Ohizumi Y: Anti-obesity effect of Nelumbo nucifera leaves extract
in mice and rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 106:238–244. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin HY, Kuo YH, Lin YL and Chiang W:
Antioxidative effect and active components from leaves of Lotus
(Nelumbo nucifera). J Agric Food Chem. 57:6623–6629. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu CH, Yang MY, Chan KC, Chung PJ, Ou TT
and Wang CJ: Improvement in high-fat diet-induced obesity and body
fat accumulation by a Nelumbo nucifera leaf flavonoid-rich extract
in mice. J Agric Food Chem. 58:7075–7081. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Du H, You JS, Zhao X, Park JY, Kim SH and
Chang KJ: Antiobesity and hypolipidemic effects of lotus leaf hot
water extract with taurine supplementation in rats fed a high fat
diet. J Biomed Sci. 17:(Suppl 1). S422010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee JS, Shukla S, Kim JA and Kim M:
Anti-angiogenic effect of Nelumbo nucifera leaf extracts in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells with antioxidant potential. PLoS
One. 10:e01185522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sohn DH, Kim YC, Oh SH, Park EJ, Li X and
Lee BH: Hepatoprotective and free radical scavenging effects of
Nelumbo nucifera. Phytomedicine. 10:165–169. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu CP, Tsai WJ, Lin YL, Liao JF, Chen CF
and Kuo YC: The extracts from Nelumbo Nucifera suppress cell cycle
progression, cytokine genes expression, and cell proliferation in
human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Life Sci. 75:699–716.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang CF, Chen YW, Yang CY, Lin HY, Way
TD, Chiang W and Liu SH: Extract of lotus leaf (Nelumbo nucifera)
and its active constituent catechin with insulin secretagogue
activity. J Agric Food Chem. 59:1087–1094. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
O'Reilly LA, Tai L, Lee L, Kruse EA,
Grabow S, Fairlie WD, Haynes NM, Tarlinton DM, Zhang JG, Belz GT,
et al: Membrane-bound Fas ligand only is essential for Fas-induced
apoptosis. Nature. 461:659–663. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Waring P and Müllbacher A: Cell death
induced by the Fas/Fas ligand pathway and its role in pathology.
Immunol Cell Biol. 77:312–317. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang S and El-Deiry WS: TRAIL and
apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene.
22:8628–8633. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang L and Fang B: Mechanisms of
resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther.
12:228–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Scaffidi C, Medema JP, Krammer PH and
Peter ME: FLICE is predominantly expressed as two functionally
active isoforms, caspase-8/a and caspase-8/b. J Biol Chem.
272:26953–26958. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pan G, O'Rourke K and Dixit VM: Caspase-9,
Bcl-XL, and Apaf-1 form a ternary complex. J Biol Chem.
273:5841–5845. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hu Y, Benedict MA, Wu D, Inohara N and
Núñez G: Bcl-XL interacts with Apaf-1 and inhibits Apaf-1-dependent
caspase-9 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:4386–4391. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Letai A, Bassik MC, Walensky LD,
Sorcinelli MD, Weiler S and Korsmeyer SJ: Distinct BH3 domains
either sensitize or activate mitochondrial apoptosis, serving as
prototype cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell. 2:183–192. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Finucane DM, BossyWetzel E, Waterhouse NJ,
Cotter TG and Green DR: Bax-induced caspase activation and
apoptosis via cytochrome c release from mitochondria is inhibitable
by Bcl-xL. J Biol Chem. 274:2225–2233. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moss LA Shuman, JensenTaubman S and
Stetler-Stevenson WG: Matrix metalloproteinases: Changing roles in
tumor progression and metastasis. Am J Pathol. 181:1895–1899. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD and Karamanos NK:
Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their
pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 278:16–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Groblewska M, Mroczko B, Gryko M,
Pryczynicz A, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K, Kędra B, Kemona A and
Szmitkowski M: Serum levels and tissue expression of matrix
metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) and tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinases 2 (TIMP-2) in colorectal cancer patients. Tumour
Biol. 35:3793–3802. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang B, Tang F, Zhang B, Zhao Y, Feng J
and Rao Z: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 overexpression is closely
related to poor prognosis in patients with colon cancer. World J
Surg Oncol. 12:242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Seo EY and Kim WK: Red ginseng extract
reduced metastasis of colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J
Ginseng Res. 35:315–324. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Deng W, Sui H, Wang Q, He N, Duan C, Han
L, Li Q, Lu M and Lv S: A Chinese herbal formula, Yi-Qi-Fu-Sheng,
inhibits migration/invasion of colorectal cancer by down-regulating
MMP-2/9 via inhibiting the activation of ERK/MAPK signaling
pathways. BMC Complement Altern Med. 13:652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao X, Sun P, Qian Y and Suo H: D.
candidum has in vitro anticancer effects in HCT-116 cancer cells
and exerts in vivo anti-metastatic effects in mice. Nutr Res Pract.
8:487–493. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li BH, Zhao P, Liu SZ, Yu YM, Han M and
Wen JK: Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of
metallo-proteinase-2 in colorectal carcinoma invasion and
metastasis. World J Gastroenterol. 11:3046–3050. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Murnane MJ, Cai J, Shuja S, McAneny D,
Klepeis V and Willett JB: Active MMP-2 effectively identifies the
presence of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 125:2893–2902. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mroczko B, Groblewska M, Okulczyk B, Kędra
B and Szmitkowski M: The diagnostic value of matrix
metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and tissue inhibitor of matrix
metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1) determination in the sera of
colorectal adenoma and cancer patients. Int J Colorectal Dis.
25:1177–1184. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rayet B and Gélinas C: Aberrant rel/nfkb
genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene. 18:6938–6947. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J and
Matias-Guiu X: NF-kB in development and progression of human
cancer. Virchows Arch. 446:475–482. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ohshima K, Sugihara M, Haraoka S, Suzumiya
J, Kanda M, Kawasaki C, Shimazaki K and Kikuchi M: Possible
immortalization of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells: Telomerase
expression, lengthening of telomere, and inhibition of apoptosis by
NF-kappaB expression. Leuk Lymphoma. 41:367–376. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ghosh S and Karin M: Missing pieces in the
NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell. 109(Suppl): S81–S96. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tak PP and Firestein GS: NF-kappaB: A key
role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 107:7–11. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Van Antwerp DJ, Martin SJ, Verma IM and
Green DR: Inhibition of TNF-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB. Trends
Cell Biol. 8:107–111. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen C, Edelstein LC and Gélinas C: The
Rel/NF-kappaB family directly activates expression of the apoptosis
inhibitor Bcl-x(L). Mol Cell Biol. 20:2687–2695. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lin A and Karin M: NF-kappaB in cancer: A
marked target. Semin Cancer Biol. 13:107–114. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tergaonkar V, Bottero V, Ikawa M, Li Q and
Verma IM: IkappaB kinase-independent IkappaBalpha degradation
pathway: Functional NF-kappaB activity and implications for cancer
therapy. Mol Cell Biol. 23:8070–8083. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lee CH, Jeon YT, Kim SH and Song YS:
NF-kappaB as a potential molecular target for cancer therapy.
Biofactors. 29:19–35. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|