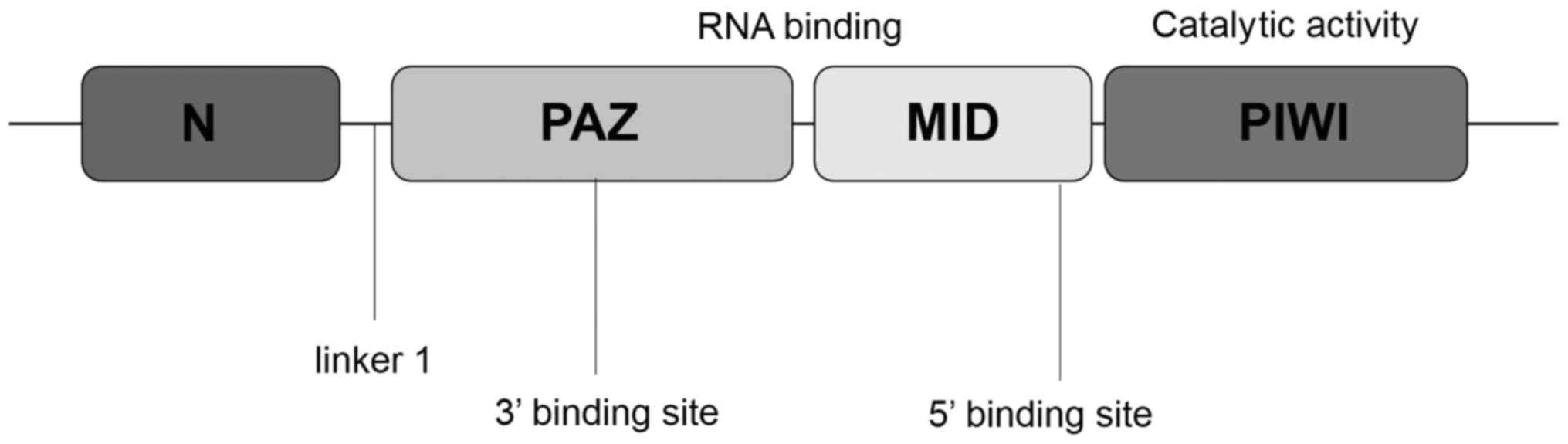
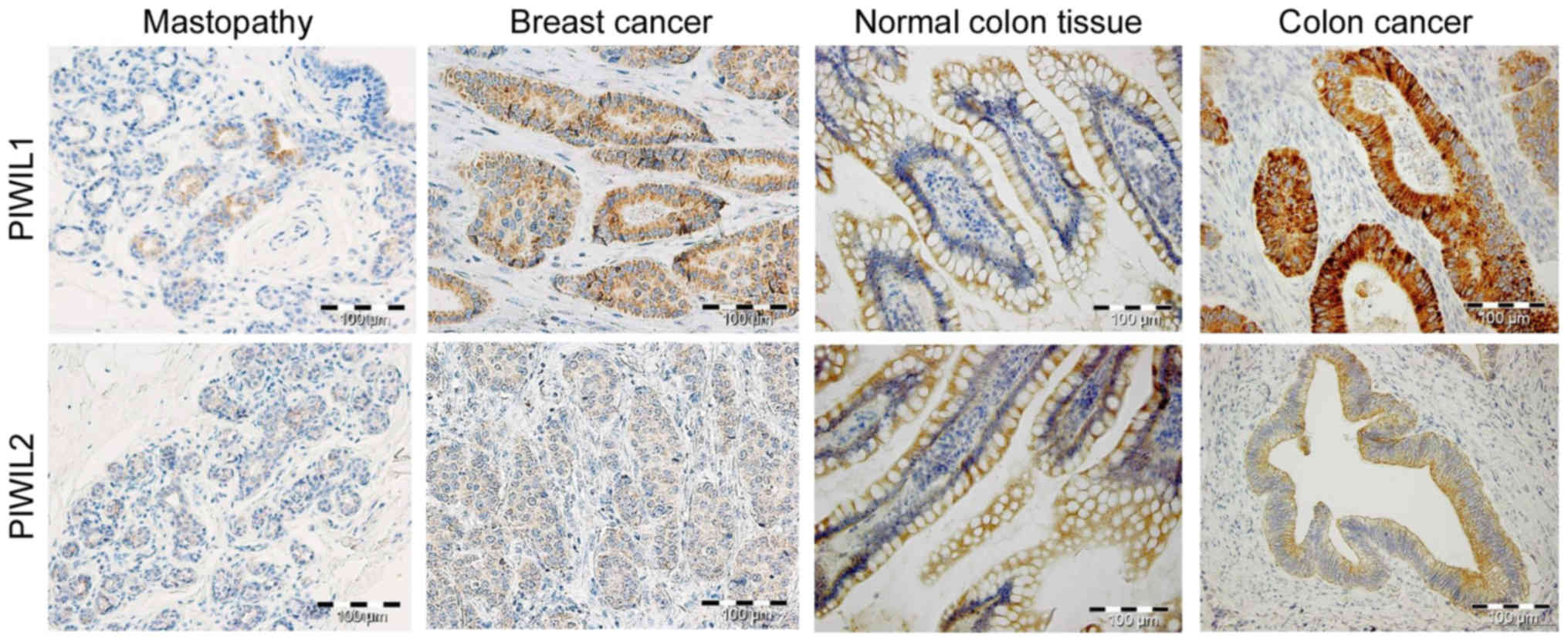
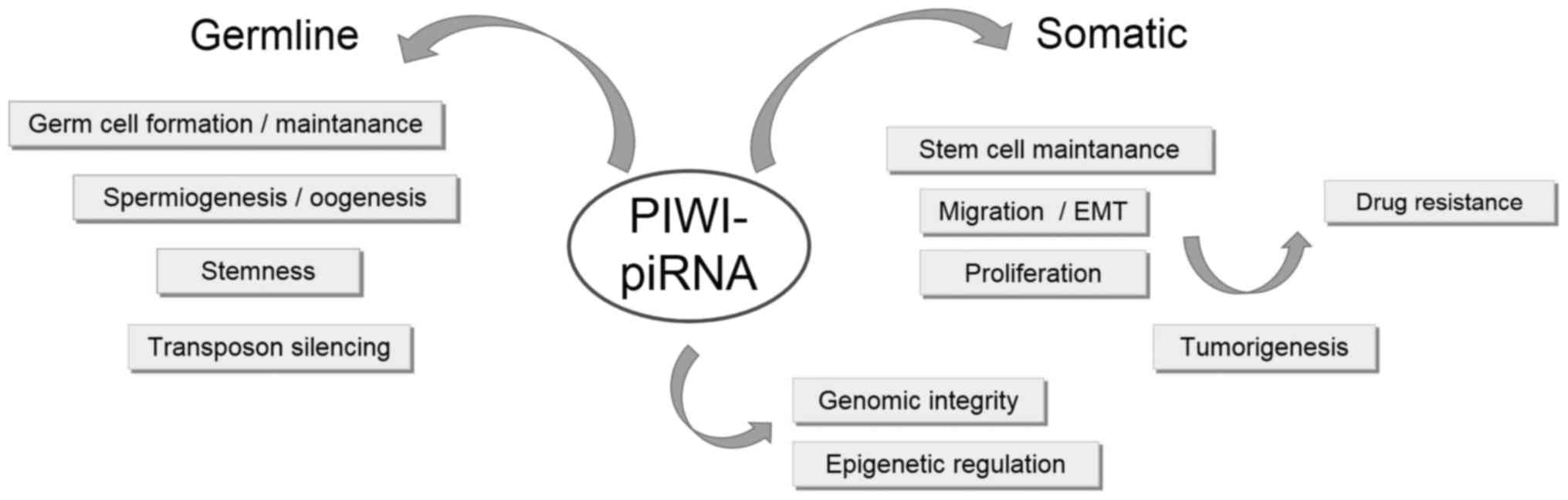
|
1
|
Kanwal R and Gupta S: Epigenetic
modifications in cancer. Clin Genet. 81:303–311. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kristensen LS, Nielsen HM and Hansen LL:
Epigenetics and cancer treatment. Eur J Pharmacol. 625:131–142.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aravin A, Gaidatzis D, Pfeffer S,
Lagos-Quintana M, Landgraf P, Iovino N, Morris P, Brownstein MJ,
Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Nakano T, et al: A novel class of small RNAs
bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature. 442:203–207.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Girard A, Sachidanandam R, Hannon GJ and
Carmell MA: A germline-specific class of small RNAs binds mammalian
Piwi proteins. Nature. 442:199–202. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grivna ST, Beyret E, Wang Z and Lin H: A
novel class of small RNAs in mouse spermatogenic cells. Genes Dev.
1:1709–1714. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Watanabe T, Takeda A, Tsukiyama T, Mise K,
Okuno T, Sasaki H, Minami N and Imai H: Identification and
characterization of two novel classes of small RNAs in the mouse
germline: Retrotransposon-derived siRNAs in oocytes and germline
small RNAs in testes. Genes Dev. 1:1732–1743. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Martinez VD, Vucic EA, Thu KL, Hubaux R,
Enfield KS, Pikor LA, Becker-Santos DD, Brown CJ, Lam S and Lam WL:
Unique somatic and malignant expression patterns implicate
PIWI-interacting RNAs in cancer-type specific biology. Sci Rep.
5:104232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suzuki R, Honda S and Kirino Y: Piwi
expression and function in cancer. Front Genet. 3:2042012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luteijn MJ and Ketting RF:
PIWI-interacting RNAs: From generation to transgenerational
epigenetics. Nat Rev Genet. 14:523–534. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Robine N, Lau NC, Balla S, Jin Z, Okamura
K, Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Blower MD and Lai EC: A broadly conserved
pathway generates 3′UTR-directed primary piRNAs. Curr Biol.
19:2066–2076. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ku HY and Lin H: PIWI proteins and their
interactors in piRNA biogenesis, germline development and gene
expression. Natl Sci Rev. 1:205–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Llave C, Kasschau KD, Rector MA and
Carrington JC: Endogenous and silencing associated small RNAs in
plants. Plant Cell. 14:1605–1619. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Djikeng A, Shi H, Tschudi C and Ullu E:
RNA interference in Trypanosoma brucei: Cloning of small
interfering RNAs provides evidence for retroposon-derived 24–26
nucleotide RNAs. RNA. 7:1522–1530. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Farazi TA, Juranek SA and Tuschl T: The
growing catalog of small RNAs and their association with distinct
Argonaute/Piwi family members. Development. 135:1201–1214. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Simon B, Kirkpatrick JP, Eckhardt S,
Reuter M, Rocha EA, Andrade-Navarro MA, Sehr P, Pillai RP and
Carlopamgno T: Recognition of 2′-O-methylated 3′-end of piRNA by
the PAZ domain of a Piwi protein. Structure. 19:172–180. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jinek M and Doudna JA: A three dimensional
view of the molecular machinery of RNA interference. Nature.
457:405–412. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kirino Y, Kim N, de Planell-Saguer M,
Khandros E, Chiorean S, Klein PS, Rigoutsos I, Jongens TA and
Mourelatos Z: Arginine methylation of Piwi proteins catalysed by
dPRMT5 is required for Ago3 and Aub stability. Nat Cell Biol.
11:652–658. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vagin VV, Wohlschlegel J, Qu J, Jonsson Z,
Huang X, Chuma S, Girard A, Sachidanandam R, Hannon GJ and Aravin
AA: Proteomic analysis of murine Piwi proteins reveals a role for
arginine methylation in specifying interaction with Tudor family
members. Genes Dev. 23:1749–1762. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hashim A, Rizzo F, Marchese G, Ravo M,
Taralllo R, Nassa G, Giurato G, Santamaria G, Cordella A,
Cantarella C and Weisz A: RNA sequencing identifies specific
PIWI-interacting small non-coding RNA expression patterns in breast
cancer. Oncotarget. 5:9901–9910. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Juliano C, Wang J and Lin H: Uniting
germline and stem cells: The function of Piwi proteins and the
piRNA pathway in diverse organisms. Annu Rev Genet. 45:447–469.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thomson T and Lin H: The biogenesis and
function PIWI proteins and piRNAs: Progress and prospect. Annu Rev
Cell Dev Biol. 25:355–376. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sasaki T, Shiiohama A, Minoshima S and
Shimizu N: Identification of eight members of the Argonaute family
in the human genome. Genomics. 82:323–330. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Williams RW and Rubin GM: Argonautel is
required for efficient RNA interference in Drosophila
embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:6889–6894. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carmell MA, Xuan Y, Yhang MQ and Hannon
HJ: The Argonaute family: Tentacles that reach into RNAi,
developmental control, stem cell maintenance, and tumorigenesis.
Genes Dev. 16:2733–2742. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Carmell MA, Girard A, van de Kant HJ,
Bourc'his D, Bestor TH, de Rooij DG and Hannon GJ: MIWI2 is
essential for spermatogenesis and repression of transposons in the
mouse male germline. Dev Cell. 12:503–514. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Kimura T, Ijiri TW,
Isobe T, Asada N, Fujita Y, Ikawa M, Iwai N, Okabe M, Deng W, et
al: Mili, a mammalian member of piwi family gene, is essential for
spermatogenesis. Development. 131:839–849. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deng W and Lin H: Miwi, a murine homolog
of piwi, encodes a cytoplasmic protein essential for
spermatogenesis. Dev Cell. 2:819–830. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Siddiqi S and Matushansky I: Piwis and
piwi-interacting RNAs in the epigenetics of cancer. J Cell Biochem.
113:373–380. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sharma AK, Nelson MC, Brandt JE, Wessman
M, Mahmud N, Weller KP and Hoffman R: Human CD34(+) stem cells
express the HIWI gene, a human homologue of the Drosophila
gene piwi. Blood. 97:426–434. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tan Y, Liu L, Liao M, Zhang C, Hu S, Zou
M, Gu M and Li X: Emerging roles for PIWI proteins in cancer. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 47:315–324. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qiao D, Zeeman AM, Deng W, Looijenga LH
and Lin H: Molecular characterization of hiwi, a human member of
the piwi gene family whose overexpression is correlated with
seminomas. Oncogene. 21:3988–3999. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Taubert H, Greither T, Kaushal D, Würl P,
Bache M, Bartel F, Kehlen A, Lautenschläger C, Harris L, Kraemer K,
et al: Expression of the stem cell self-renewal gene Hiwi and risk
of tumour-related death in patients with soft-tissue sarcoma.
Oncogene. 15:1098–1100. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang DW, Wang ZH, Wang LL, Song Y and
Zhang GZ: Overexpression of hiwi promotes growth of human breast
cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:7553–7558. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cao J, Xu G, Lan J, Huang Q, Tang Z and
Tian L: High expression of piwi-like RNA mediated gene silencing 1
is associated with poor prognosis via regulating transforming
growth factor-β receptors and cyclin-dependent kinases in breast
cancer. Mol Med Rep. 13:2829–2835. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He W, Wang Z, Wang Q, Fan Q, Shou C, Wang
J, Giercksky KE, Nesland JM and Suo Z: Expression of HIWI in human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is significantly associated with
poorer prognosis. BMC Cancer. 9:4262009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Grochola LF, Greither T, Taubert H, Möller
P, Knippschild U, Udelnow A, Henne-Bruns D and Würl P: The stem
cell-associated Hiwi gene in human adenocarcinoma of the pancreas:
Expression and risk of tumor-related death. Br J Cancer.
99:1083–1088. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Shen X, Zhang X, Chen X,
Yang C and Gao H: The PIWI protein acts as a predictive marker for
human gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 5:315–325.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu JJ, Shen R, Chen L, Ye Y, He G, Hua K,
Jarjoura D, Nakano T, Ramesh GK, Shapiro CL, et al: Piwil2 is
expressed in various stages of breast cancers and has the potential
to be used as a novel biomarker. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 3:328–337.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zeng Y, Qu LK, Meng L, Liu CY, Dong B,
Xing XE, Wu J and Shou CC: HIWI expression profile in cancer cells
and its prognostic value for patients with colorectal cancer. Chin
Med J (Engl). 124:2144–2149. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao YM, Zhou JM, Wang LR, He HW, Wang XL,
Tao ZH, Sun HC, Wu WZ, Fan J, Tang ZY and Wang L: HIWI is
associated with prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
after curative resection. Cancer. 118:2708–2717. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu W, Gao Q, Chen K, Xue X, Li M, Chen Q,
Zhu G and Gao Y: Hiwi facilitates chemoresistance as a cancer stem
cell marker in cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:1853–1860. 2016.
|
|
42
|
Wang Y, Liu J, Wu G and Yang F:
Manipulations in HIWI levels exerts influence on the proliferation
of human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Exp Ther Med.
11:1971–1976. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang L, Bi L, Liu Q, Zhao M, Cao B, Li D
and Xiu J: Hiwi promotes the proliferation of colorectal cancer
cells via upregulating global DNA methylation. Dis Markers.
2015:3830562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ye Y, Yin DT, Chen L, Zhou Q, Shen R, He
G, Yan Q, Tong Z, Issekutz AC, Shapiro CL, et al: Identification of
Piwil2-like (PL2L) proteins that promote tumorigenesis. PLoS One.
5:e134062010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu X, Sun Y, Guo J, Ma H, Li J, Dong B,
Jin G, Zhang J, Wu J, Meng L and Shou C: Expression of hiwi gene in
human gastric cancer was associated with proliferation of cancer
cells. Int J Cancer. 118:1922–1929. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
He G, Chen L, Ye Y, Xiao Y, Hua K,
Jarjoura D, Nakano T, Barsky SH, Shen R and Gao JX: Piwil2
expressed in various stages of cervical neoplasia is a potential
complementary marker for p16. Am J Transl Res. 2:156–169.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen C, Liu J and Xu G: Overexpression of
PIWI proteins in human stage III epithelial ovarian cancer with
lymph node metastasis. Cancer Biomark. 13:315–321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang Y, Zhang X, Song D and Wei J: Piwil2
modulates the invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer by
regulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Oncol Lett. 10:1735–1740.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Oh SJ, Kim SM, Kim YO and Chang HK:
Clinicopathologic implications of PIWIL2 expression in colorectal
cancer. Korean J Pathol. 46:318–323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee JH, Jung C, Javadian-Elyaderani P,
Schweyer S, Schütte D, Shoukier M, Karimi-Busheri F, Weinfeld M,
Rasouli-Nia A, Hengstler JG, et al: Pathway of proliferation and
apoptosis driven in breast cancer stem cells by stem cell protein
piwil2. Cancer Res. 70:4569–4579. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lee JH, Schütte D, Wulf G, Füzesi L,
Radzun HJ, Schweyer S, Engel W and Nayernia K: Stem-cell protein
Piwil2 is widely expressed in tumors and inhibits apoptosis through
activation of Stat3/Bcl-XL pathway. Hum Mol Genet. 15:201–211.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gainetdinov IV, Skvortsova YV, Stukacheva
EA, Bychenko OS, Kondratieva SA, Zinovieva MV and Azhikina TL:
Expression profiles of PIWIL2 short isoforms differ in testicular
germ cell tumors of various differentiation subtypes. PLoS One.
9:e1125282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li D, Sun X, Yan D, Huang J, Luo Q, Tang H
and Peng Z: Piwil2 modulates the proliferation and metastasis of
colon cancer via regulation of matrix metallopeptidase 9
transcriptional activity. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 237:1231–1240.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Litwin M, Dubis J, Arczyńska K, Piotrowska
A, Frydlewicz A, Karczewski M, Dzięgiel P and Witkiewicz W:
Correlation of HIWI and HILI expression with cancer stem cell
markers in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 35:3317–3324.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nikpour P, Forouzandeh-Moghaddam M, Ziaee
SA, Dokun OY, Schulz WA and Mowla SJ: Absence of PIWIL2 (HILI)
expression in human bladder cancer cell lines and tissues. Cancer
Epidemiol. 33:271–275. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Su C, Ren ZJ, Wang F, Liu M, Li X and Tang
H: PIWIL4 regulates cervical cancer cell line growth and is
involved in down-regulating the expression of p14ARF and p53. FEBS
Lett. 586:1356–1362. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Al-Janabi O, Wach S, Nolte E, Weigelt K,
Rau TT, Stöhr C, Legal W, Schick S, Greither T, Hartmann A, et al:
Piwi-like 1 and 4 gene transcript levels are associated with
clinicopathological parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1842:686–690. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li D, Luo Y, Gao Y and Yang Y, Wang Y, Xu
Y, Tan S, Zhang Y, Duan J and Yang Y: piR-651 promotes tumour
formation in non-small cell lung carcinoma through the upregulation
of cyclin D1 and CDK4. Int J Mol Med. 38:927–936. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Cheng J, Guo JM, Xiao BX, Miao Y, Jaing Z,
Zhou H and Li QN: piRNA, the new non-coding RNA, is aberrantly
expressed in human cancer cells. Clinica Chim Acta. 412:1621–1625.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Huang G, Hu H, Xue X, Shen S, Gao E, Guo
G, Shen X and Zhang X: Altered expression of piRNAs and their
relation with clinicopathologic features of breast cancer. Clin
Transl Oncol. 15:563–568. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Siddigi S, Terry M and Matushansky I: Hiwi
mediated tumorigenesis is associated with DNA hypermethylation.
PLoS One. 7:e337112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Aravin AA, Sachidanandam R, Bourc'his D,
Schaefer C, Pezic D, Toth KF, Bestor T and Hannon GJ: A piRNA
pathway primed by individual transposons is linked to de novo DNA
methylation in mice. Mol Cell. 26:785–799. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Watanabe T, Gotoh K,
Totoki Y, Toyoda A, Ikawa M, Asada N, Kojima K, Yamaguchi Y, Ijiri
TW, et al: DNA methylation of retrotransposon genes is regulated by
Piwi family members MILI and MIWI2 in murine fetal testes. Genes
Dev. 22:908–917. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Brennecke J, Malone CD, Aravin AA,
Sachidanandam R, Stark A and Hannon GJ: An epigenetic role for
maternally inherited piRNAs in transposon silencing. Science.
322:1387–1392. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Saito K, Nishida KM, Mori T, Kawamura Y,
Miyoshi K, Nagami T, Siomi H and Siomi MC: Specific association of
Piwi with rasiRNAs derived from retrotransposon and heterochromatic
regions in the Drosophila genome. Genes Dev. 20:2214–2222.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Saito K: The epigenetic regulation of
transposable elements by PIWI-interacting RNAs in
Drosophila. Genes Genet Syst. 88:9–17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
van Wolfswinkel JC and Ketting RF: The
role of small non-coding RNAs in genome stability and chromatin
organization. J Cell Sci. 123:1825–1839. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lobo NA, Shimono Y, Qian D and Clarke MF:
The biology of cancer stem cells. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
23:675–699. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Pardal R, Clarke MF and Morrison SJ:
Applying the principles of stem-cell biology to cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:895–902. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Islam F, Gopalan V, Smith RA and Lam AK:
Translational potential of cancer stem cells: A review of the
detection of cancer stem cells and their roles in cancer recurrence
and cancer treatment. Exp Cell Res. 335:135–147. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yao J, Caballero OL, Yung WK, Weinstein
JN, Riggins GJ, Strausberg RL and Zhao Q: Tumor subtype-specific
cancer-testis antigens as potential biomarkers and
immunotherapeutic targets for cancers. Cancer Immunol Res.
2:371–379. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yin AH, Miraglia S, Zanjani ED,
Almeida-Porada G, Ogawa M, Leary AG, Olweus J, Kearney J and Buck
DW: AC133, a novel marker for human hematopoietic stem and
progenitor cells. Blood. 90:5002–5012. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Salven P, Mustjoki S, Alitalo R, Alitalo K
and Rafii S: VEGFR-3 and CD133 identify a population of
CD34+lymphatic/vascular endothelial precursor cells. Blood.
101:168–172. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Uchida N, Buck DW, He D, Reitsma MJ, Masek
M, Phan TV, Tsukamoto AS, Gage FH and Weissman IL: Direct isolation
of human central nervous system stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:14720–14725. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: Identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Suetsugu A, Nagaki M, Aoki H, Motohashi T,
Kunisada T and Moriwaki H: Characterization of CD133+
hepatocellular carcinoma cells as cancer stem/progenitor cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 351:820–824. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
O'Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S and
Dick JE: A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour
growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature. 445:106–110. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T, Aicher A,
Ellwart JW, Guba M, Bruns CJ and Heeschen C: Distinct populations
of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth and metastatic activity
in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 1:313–323. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Collins AT, Berry PA, Hyde C, Stower MJ
and Maitland NJ: Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate
cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 65:10946–10951. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Klonisch T, Wiechec E, Hombach-Klonisch S,
Ande SR, Wesselborg S, Schulze-Osthoff K and Los M: Cancer stem
cell markers in common cancers-therapeutic implications. Trends Mol
Med. 14:445–460. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Takebe N, Miele L, Harris PJ, Jeong W,
Bando H, Kahn M, Yang SX and Ivy SP: Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and
Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical update. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 12:445–464. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang J, Rao S, Chu J, Shen X, Levasseur
DN, Theunissen TW and Orkin SH: A protein interaction network for
pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. Nature. 444:364–368. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Niwa H, Miyazaki J and Smith AG:
Quantitative expression of Oct-3/4 defines differentiation,
dedifferentiation or self-renewal of ES cells. Nature Genet.
24:372–376. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Chiou SH, Yu CC, Huang CY, Lin SC, Liu CJ,
Tsai TH, Chou SH, Chien CS, Ku HH and Lo JF: Positive correlations
of Oct4 and Nanog in oral cancer stem-like cells and high grade
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:4085–4095. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Guo Y, Liu S, Wang P, Zhao S, Wang F, Bing
L, Zhang Y, Ling EA, Gao J and Hao A: Expression profile of
embryonic stem cell-associated genes Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog in human
glioma. Histopathology. 59:763–775. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Matsuoka J, Yashiro M, Sakuari K, Kubo N,
Tanaka H, Muguruma K, Sawada T, Ohira M and Hirakawa K: Role of the
stemness factors Sox2, Oct3/4, and Nanog in gastric carcinoma. J
Surg Res. 174:130–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Saigusa S, Tanaka K, Toiyama Y, Yokoe T,
Okugawa Y, Ioue Y, Miki C and Kusunoki M: Correlation of CD133,
OCT4, and Sox2 in rectal cancer and their association with distant
recurrence after chemoradiotherpy. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:3488–3498.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Yin X, Li YW, Jin JJ, Zhou Y, Ren ZG, Qiu
SJ and Zhang BH: The clinical and prognostic implications of
pluripotent stem cell gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncol Lett. 5:1155–1162. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Meng HM, Zheng P, Wang XY, Liu C, Sui HM,
Wu SJ, Zhou J, Ding YQ and Li J: Overexpression of Nanog predicts
tumor progression and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Cancer
Biol Ther. 9:295–302. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Sholl LM, Barletta JA, Yeap BY, Chirieac
LR and Hornick JL: Sox2 protein expression is an independent poor
prognostic indicator in stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg
Pathol. 34:1193–1198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lengerke C, Fehm T, Kurth R, Neubauer H,
Scheble V, Müller F, Schneider F, Petersen K, Wallwiener D, Kanz L,
et al: Expression of the embryonic stem cell marker SOX2 in
early-stage breast carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 11:422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Bareiss PM, Paczulla A, Wang H, Schairer
R, Wiehr S, Kohlhofer U, Rothfuss OC, Fischer A, Perner S, Staebler
A, et al: SOX2 expression associates with stem cell state in human
ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res. 73:5544–5555. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Sanada Y, Yoshida K, Ohara M, Oeda M,
Konishi K and Tsutani Y: Histopathological evaluation of stepwise
progression of pancreatic carcinoma with immunohistochemical
analysis of gastric epithelial transcription factor SOX2:
Comparison of expression patterns between invasive components and
cancerous or nonneoplastic intraductal components. Pancreas.
32:164–170. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Tiwari N, Meyer-Schaller N, Arnold P,
Antoniadis H, Pachkov M, van Nimwegen E and Christofori G: Klf4 is
a transcriptional regulator of genes critical for EMT, including
Jnk1 (Mapk8). PLoS One. 8:e573292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Thiery JP, Aclogue H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wu CY, Tsai YP, Wu MZ, Teng SC and Wu KJ:
Epigenetic reprogramming and post-transcriptional regulation during
the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Trends Genet. 28:454–463.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Esteban MA, Bao X, Zhuang Q, Zhou T, Qin B
and Pei D: The mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition in somatic cell
reprogramming. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 22:423–428. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: An emerging role axis of evil in the war
on cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Fan F, Samuel S, Evans KW, Lu J, Xia L,
Zhou Y, Sceusi E, Tozzi F, Ye XC, Mani SA and Ellis LM:
Overexpression of Snail induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and a cancer stem cell-like phenotype in human colorectal cancer
cells. Cancer Med. 1:5–16. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Chiou SH, Wang ML, Chou YT, Chen CJ, Hong
CF, Hsieh WJ, Chang HT, Chen YS, Lin TW, Hsu HS and Wu CW:
Coexpression of Oct4 and Nanog enhances malignancy in lung
adenocarcinoma by inducing cancer stem cell-like properties and
epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation. Cancer Res.
70:10433–10444. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Luo W, Li S, Peng B, Ye Y, Deng X and Yao
K: Embryonic stem cell markers SOX2, OCT4 and Nanog expression and
their correlations with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e563242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Chen KL, Pan F, Jiang H, Chen JF, Pei L,
Xie FW and Liang HJ: Highly enriched CD133(+)CD44(+) stem-like
cells with CD133(+)CD44(high) metastatic subset in HCT116 colon
cancer cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:751–763. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Zhanga H, Renb Y, Xuc H, Pengd D, Duane C
and Liua C: The expression of stem cell protein Piwil2 and piR-932
in breast cancer. Surgical Oncol. 22:217–223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Botchkina IL, Rowehl RA, Rivadeneira DE,
Karpeh MS Jr, Crawford H, Dufour A, Ju J, Wang Y, Leyfman Y and
Botchkina GI: Phenotypic subpopulations of metastatic colon cancer
stem cells: Genomic analysis. Cancer Genomic Proteomics. 6:19–30.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zou AE, Zheng H, Saad MA, Rahimy M, Ku J,
Kuo SZ, Honda TK, Wang-Rodriguez J, Xuan Y, Korrapati A, et al: The
non-coding landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:51211–51222. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Watanabe T and Lin H: Posttranscriptional
regulation of gene expression by Piwi proteins and piRNAs. Mol
Cell. 56:18–27. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Moyano M and Stefani G: piRNA involvement
in genome stability and human cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 8:382015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Ng KW, Anderson C, Marshall EA, Minatel
BC, Enfield KS, Saprunoff HL, Lam WL and Martinez VD:
Piwi-interacting RNAs in cancer: Emerging functions and clinical
utility. Mol Cancer. 15:52016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|