Introduction
Gastric cancer is the most common type of
gastrointestinal cancer. It significantly shortens patient survival
time, and reduces the quality of life (1,2). Studies
worldwide have shown that the treatment effect of gastric cancer is
closely related to the PTEN gene (3,4). When PTEN
expression is low, it can affect downstream proteins, contributing
to cancer cell proliferation and deterioration of the condition of
gastric cancer, thereby significantly reducing quality of life, and
shortening survival time (5,6).
Currently, surgery is the main clinical method for
treating malignant tumors. Surgical resection is one manner to
avoid cancer cell proliferation. However, it can also cause
patients to experience negative emotions, affecting treatment
efficacy (7). Previous findings
showed that when close care and nursing are provided for patients
with ovarian cancer, the therapeutic effect can be significantly
improved. However, to the best of our knowledge, no studies have
reported on whether close care and nursing can improve the
rehabilitation and prognosis of gastric cancer patients with low
PTEN expression (8,9).
In the present study, we analyzed the influence of
operating room (OR) care combined with home care on the
postoperative rehabilitation and prognosis of gastric cancer
patients with a low expression of PTEN, and analyzed the
relationship between them, to provide a theoretical basis for the
importance of patient OR and home care.
Patients and methods
Patients
Between August 2010 and July 2013, 96 patients in
the Department of Digestive Surgery of Weifang People's Hospital,
who underwent surgical treatment, and had been diagnosed with
gastric cancer were selected for this study. The male:female ratio
was 5:3, and the age of patients was 48–76 years, with a mean age
62 years. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of
Weifang People's Hospital. Signed written informed consents were
obtained from all participants before the study. Inclusion criteria
for the study were: all gastric cancer patients were diagnosed and
treated according to the criteria of the World Health Organization,
with postoperative pathological examination that confirmed the
presence of gastric cancer. Genetic testing was provided for each
patient to determine the state of PTEN expression. All the selected
participants were diagnosed without any other consumptive diseases.
A total of 96 participants, gastric cancer patients with low PTEN
expression, were selected, and informed consent was provided. The
patients were randomized into the control and observation groups,
with 48 participants each. In terms of sex and age, there were no
significant differences between the two groups (p>0.05).
Participants in the control and observation groups were given the
same preoperative monitoring of physical signs, preoperative
preparation, gastric cancer surgical treatment, postoperative drug
therapy and general care. In addition to the above care and
treatment, participants in the observation group were provided more
comprehensive OR and home care.
Selection of participants with a low
PTEN gene expression
Gastric cancer tissue samples were obtained from
patients, and centrifuged at 1,788.8 × g for 10 min. The
supernatant was then collected, and RNA was extracted using a
TRIzol kit. RNA integrity was confirmed by agarose gel
electrophoresis. The results of electrophoresis showed that the
bands corresponding to 28S, 18S, and 5S RNA were clear, and the
brightness of the 28S band was nearly double that of the 18S band,
indicating that RNA was of high integrity. Therefore, the extracted
RNA could be used for follow-up experiments. A reverse
transcription kit was utilized to obtain cDNA. The expression of
PTEN was detected via semi-quantitative polymerase chain reaction
(PCR), with GAPDH as the internal control. The reaction conditions
were: 95°C for 30 sec, 64°C for 25 sec, and 72°C for 30 sec, for 35
cycles in total. The primers were synthesized by Tiangen Biotech
(Beijing) Co., Ltd., Beijing, China. Sequences are shown in
Table I. After the reaction, samples
were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis, and the results were
observed with a UV imaging system.
 | Table I.PCR primers. |
Table I.
PCR primers.
| Gene | Sequences |
|---|
| PTEN | F:
5-CTACAATGAGCTGCGTGTGGC-3 |
|
| R:
5-CAGGTCCAGACGCAGGATGGC-3 |
| GAPDH | F: 5-GAGTCAAC
GGATTTGGTCGT-3 |
|
| R:
5-TGTGGTCATGAGTCCTTCCA-3 |
OR care and home care
OR care
Participants were provided preoperative
psychological assessment to rule out emotions such as anxiety and
fear (psychological care). Surgery was conducted in a quiet
environment throughout the entire procedure, and strictly according
to operating norms to avoid any accidents (environment care).
Patient body temperature was maintained within the normal range,
and infusion liquid was maintained at 37°C (temperature care).
Following surgery, the series intraoperative procedures were
described to the patients. Medical staff coordinated with patients
for the pull of tracheal cannula, further informed patients that
the operation went smoothly and guided the correct way to cough
(extubation care).
Home care
A home care team was established, the eating quality
of participants was asked to follow strict requirements;
participant body functional recovery training was also required;
simple yoga and jogging were performed to improve the mood of
participants, allowing them to feel good during recovery, and
reduce their burden; family members expressed support for
participants, and timely informed them of the doctors advice to
increase their information; and follow-up visits were enhanced to
strengthen the contact between patients and doctors. The family
members of participants described their recovery status to them in
detail, and health care professionals gave a detailed assessment of
participant prognosis.
Observational indicators
Both in the observation and control groups, the
operative time, bleeding volume, extubation time, and postoperative
recovery time of participants were recorded and analyzed.
Self-rating anxiety scale (SAS) and Hamilton anxiety scale (HAMA)
scores were applied 1 year after surgery to evaluate and collect
the rehabilitation and prognosis status of all the participants,
comparing changes and improvements of participant mental state
before and after care was provided. In addition, scores of
participant rehabilitation, overall quality of life, family
adaptability and cohesion were gathered for statistical analysis
(10,11). At the time of recruitment,
participants in the observation and control groups did not show
significant differences in any of the above indicators. Finally,
participant survival time within 3 years after surgery was analyzed
statistically and survival was graphed.
Effect assessment
SAS scores >50 indicated anxiety, while lower
scores showed that participants had less negative emotions. Lower
HAMA scores indicated less negative feelings experienced by
participants, lower scores of rehabilitation indicators indicated
better rehabilitation status, and the score of overall quality of
life was calculated via the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy
(FACT), where higher score suggested better quality of life during
illness. The family adaptability and cohesion score was assessed
through the Family Adaptability and Cohesion Scale. Lower score
suggested lower degree of family cohesion and poorer adaptability
(12,13).
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation
(SD). Data were analyzed with SPSS19.0 software (SPSS, Inc.,
Chicago, IL, USA). A t-test was applied to analyze numerical data,
and a χ2-test was applied to conduct intergroup analyses
of numeration data. The correlation between the expression level
and clinicopathological characteristics was analyzed in a related
program. The Kaplan-Meier log-rank test was utilized to perform
survival analysis. P≤0.05 was considered statistically
significant.
Results
Selection of participants with a low
PTEN expression
Gastric carcinoma and paracancerous tissue samples
were collected from gastric cancer patients. Semi-quantitative PCR
was used to measure the expression of PTEN. The expression of PTEN
in gastric carcinoma tissue varied significantly among patients. In
some patients, PTEN expression in gastric carcinoma tissue was
significantly lower compared with the level in paracancerous tissue
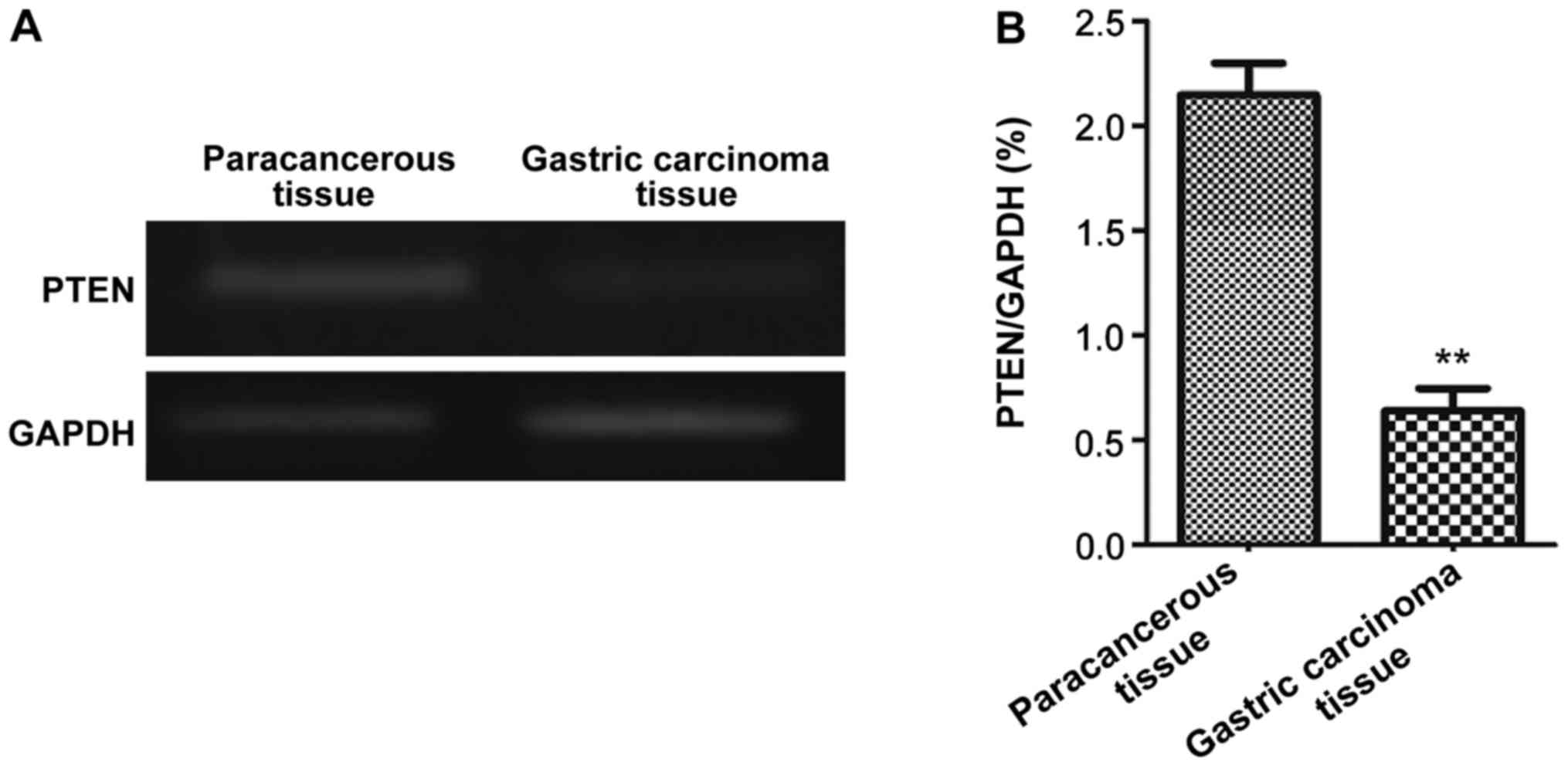
(p<0.01). Representative semi-quantitative PCR results are shown
in Fig. 1. Patients with a lower PTEN
expression in gastric carcinoma tissue compared with paracancerous
tissues were selected as participants and randomized into the
observation and control groups with 48 participants each.
Surgical indicators in participants of
the two groups
Participants in the observation and control groups
were treated by the same operation. There were no significant
differences in operative time or bleeding volume between the two
groups (p>0.05). However, there were differences between the
groups in extubation time and postoperative recovery time.
Participants in the control group underwent longer extubation time
and delayed recovery compared with the observation group
(p<0.01, Table II).
 | Table II.Comparison of surgical indicators
between groups. |
Table II.
Comparison of surgical indicators
between groups.
| Group | n | Operative time
(h) | Intraoperative
bleeding volume (ml) | Extubation time
(min) | Postoperative
recovery time (min) |
|---|
| Observation
group | 48 | 4.39±1.21 | 168.32±28.32 |
15.82±3.51a |
46.26±10.25a |
| Control group | 48 | 4.52±1.19 | 175.29±29.87 | 25.27±2.97 | 82.18±12.26 |
| P-value |
| 0.762 | 0.521 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
SAS scores of participants before and
after care
There were no significant difference in SAS scores
between groups before care was provided. After care was provided,
SAS scores in the two groups were significantly reduced
(p<0.05). Furthermore, after care was provided, the SAS scores
in the observation group were significantly lower than in the
control group (p<0.01, Table
III).
 | Table III.Comparison of SAS scores before and
after care. |
Table III.
Comparison of SAS scores before and
after care.
|
|
| SAS scores |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Group | n | Before care | After care | P-value |
|---|
| Observation
group | 48 | 45.28±5.87 | 29.32±4.85 | <0.01 |
| Control group | 48 | 46.32±5.69 | 42.98±5.04 | <0.05 |
| P-value |
| 0.426 | <0.01 |
|
HAMA scores of the two groups before
and after care
There were no significant differences in HAMA scores
between the groups before care was provided. After care, HAMA
scores in both groups were significantly reduced (p<0.05).
Furthermore, the HAMA scores in the observation group were
significantly lower than in the control group (p<0.01, Table IV).
 | Table IV.Comparison of HAMA scores before and
after care. |
Table IV.
Comparison of HAMA scores before and
after care.
|
|
| HAMA scores |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Group | n | Before care | After care | P-value |
|---|
| Observation
group | 48 | 16.32±5.28 | 7.98±3.02 | <0.01 |
| Control group | 48 | 16.63±4.92 | 12.36±3.53 | <0.01 |
| P-value |
| 0.724 | <0.01 |
|
Rehabilitation status of patients in
the two groups
Rehabilitation status of the two groups of patients
was assessed. In the observation group, the scores of stomach
discomfort, reflux, eating disorders and taste changes in
rehabilitation assessment were significantly higher than those in
the control group (p<0.01, Table
V).
 | Table V.Comparison of postoperative
rehabilitation. |
Table V.
Comparison of postoperative
rehabilitation.
| Group | n | Dysphagia | Stomach
discomfort | Reflux | Eating disorders | Taste |
|---|
| Observation
group | 48 | 18.52±13.28 |
16.32±12.32b |
23.82±17.51b |
22.26±15.25a |
16.29±12.34b |
| Control group | 48 | 17.65±14.89 | 23.29±15.87 | 32.27±21.97 | 27.18±18.26 | 22.26±19.64 |
| P-value |
| 0.762 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
Scores of overall postoperative
quality of life of the two groups of participants after care
Patients in the two groups were provided the same
treatment, but accepted different OR and home care. After care, the
scores of overall quality of life were compared between groups. The
scores of the observation group were significantly higher than
those of the control group (p<0.01). The scores related to
society/family and emotional parameters in the observation group
were significantly higher than those in the control group, while
scores of function recovery were not significantly different
between the two groups (p=0.835, Table
VI).
 | Table VI.Scores of quality of life after
care. |
Table VI.
Scores of quality of life after
care.
| Group | n | Total score of
quality of life | Society/Family | Emotion | Function |
|---|
| Observation
group | 48 |
57.89±8.26a |
22.28±4.29a |
19.76±5.23a | 15.85±3.27 |
| Control group | 48 | 47.77±7.95 | 16.83±3.67 | 15.25±4.96 | 15.69±3.56 |
| P-value |
| <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.835 |
Scores of postoperative family
adaptability and cohesion of the two groups of patients after
care
Patients in the two groups were provided the same
treatment, while different care procedures and scores of family
adaptability and cohesion were compared between the groups. The
scores of family adaptability and cohesion in the observation group
were significantly higher than those in the control group
(p<0.01, Table VII).
 | Table VII.Scores of family adaptability and
cohesion after care. |
Table VII.
Scores of family adaptability and
cohesion after care.
| Group | n | Family
cohesion | Family
adaptability |
|---|
| Observation
group | 48 |
26.83±5.26a |
24.82±4.24a |
| Control group | 48 | 18.67±4.25 | 17.67±3.85 |
| P-value |
| <0.01 | <0.01 |
Comparison of participant
postoperative survival time between groups
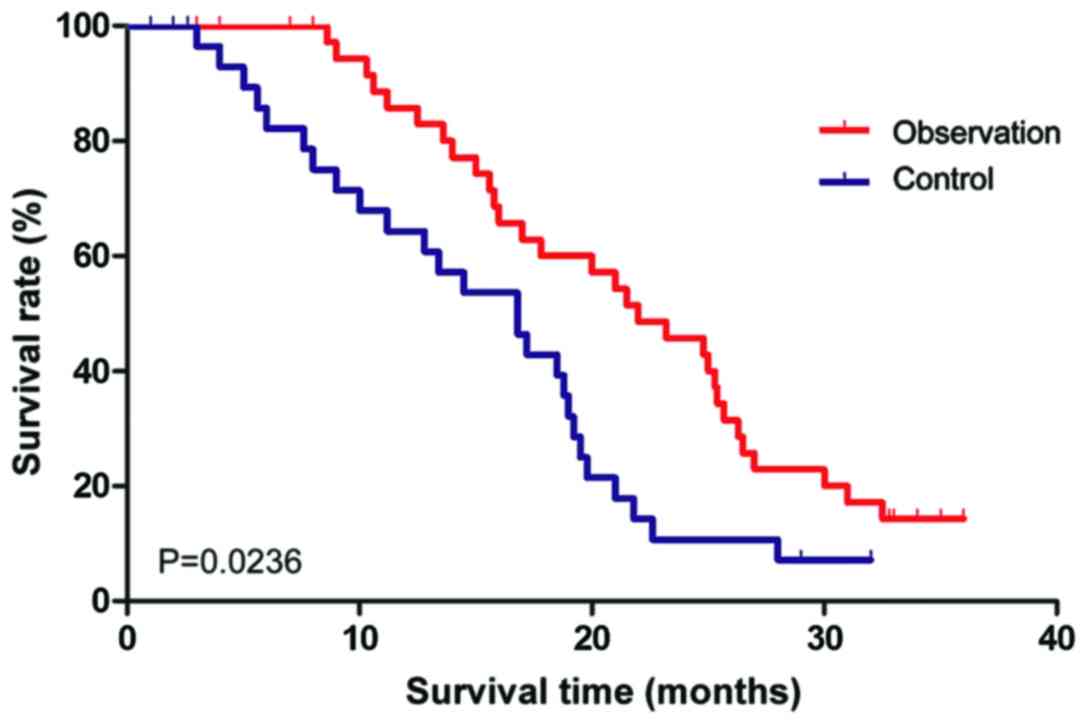
The two groups of patients were followed up for 3
years to collect detailed visit reports. In the observation group,
42 valid reports were collected while 38 in the control group. When
the participant survival time was compared between the two groups.
In the observation group, in which patients were provided OR care
combined with home care, the participant survival time was
significantly longer than that in the control group (p=0.0236,
Fig. 2).
Discussion
In recent years, a clear increase in postoperative
survival time of cancer patients has been reported with constant
improvements of surgical techniques. However, opera-tion-induced
negative emotions such as anxiety and pain severely influence the
treatment effect and postoperative rehabilitation (14). With improvements of the concepts of
patient care, many domestic and international studies have reported
that necessary OR care can ensure a smooth operation and distinctly
increases disease treatment effect (15).
In the present study, we analyzed the effect of OR
care combined with home care on postoperative rehabilitation and
prognosis of gastric cancer patients with a low PTEN expression. We
found that although thorough OR care did not shorten operative time
or reduce bleeding volume (p>0.05), it significantly reduced
postoperative extubation time and recovery time (p<0.01).
Informing patients of surgical details can effectively reduce their
negative emotions, thereby shortening their recovery time. Various
forms of care such as coordinating with patients to pull the
tracheal cannula, informing them of the right way to cough, and
providing regular backslapping are helpful for patients remove
various secretions from their mouth, avoiding respiratory tract
clogging, thus influencing prognosis (16). Comparison of SAS and HAMA scores
before and after care was provided, showing that postoperative SAS
and HAMA scores of the two groups of patients were significantly
reduced compared with their preoperative scores (p<0.05), with
the scores in the observation group reduced more significantly than
in the control group (p<0.01), demonstrating that comprehensive
OR care could relieve the negative emotions of patients and improve
prognosis. Preoperative psychological care can reduce patient
anxiety and fear caused by not understanding details of the
operation, thereby smoothing its process (17). Postoperative body temperature care
reduces the effects of low temperature on patient rehabilitation
and prognosis, excluding unfavorable factors and promoting patient
recovery (18). Various postoperative
indicators demonstrated that rehabilitation status of the
observation group was significantly better than that of the control
group (p<0.01), suggesting that OR care could effectively
improve patient rehabilitation and prognosis, which was consistent
with relevant studies (19). When
comparing the overall quality of life between the observation and
control groups, the scores of quality of life and family
adaptability and cohesion in the observation group were
significantly higher than those in the control group, demonstrating
patient improvement in these areas after care was provided
(p<0.01). Many studies from around the world have also reported
that advanced care provided in different disease treatment regimens
can significantly reduce patient anxiety and improve patient
quality of life and family cohesion (20). This was the first study to analyze the
effect of home care on postoperative quality of life in patients
with low PTEN expression. This intervention plays an important role
in improving patient quality of life and prognosis by involving
family function to increase patient confidence.
Postoperative care ensures the process of treatment
and rehabilitation. Nurses, as daily care providers, are able to
understand treatment effects, and timely communicate with doctors
to optimize the effects. Family members also play a positive role
in disease treatment by providing home care and supervising and
accompanying patients for their necessary follow-up visits
(21,22). Some studies have also demonstrated
that receiving comprehensive OR and home care significantly
improves the quality of life and family cohesion of cancer patients
(23,24). In conclusion, OR care combined with
home care is an effective form of care for gastric cancer patients
with low PTEN expression and plays a positive role in their
rehabilitation and prognosis by improving patient mood and mental
state.
References
|
1
|
Higashi T, Nakamura F, Shimada Y, Shinkai
T, Muranaka T, Kamiike W, Mekata E, Kondo K, Wada Y, Sakai H, et
al: Quality of gastric cancer care in designated cancer care
hospitals in Japan. Int J Qual Health Care. 25:418–428. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rostom A, Ross ED, Dubé C, Rutter MD, Lee
T, Valori R, Bridges RJ, Pontifex D, Webbink V, Rees C, et al:
Development and validation of a nurse-assessed patient comfort
score for colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 77:255–261. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang BG, Li JF, Yu BQ, Zhu ZG, Liu BY and
Yan M: microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in
gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncol Rep. 27:1019–1026.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang TS, Yang XH, Wang XD, Wang YL, Zhou B
and Song ZS: MiR-214 regulate gastric cancer cell proliferation,
migration and invasion by targeting PTEN. Cancer Cell Int.
13:682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Conde-Perez A and Larue L: PTEN and
melanomagenesis. Future Oncol. 8:1109–1120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bian EB, Li J and Zhao B: miR-29, a
potential therapeutic target for liver fibrosis. Gene. 544:259–260.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jin Y, Qiu MZ, Wang DS, Zhang DS, Ren C,
Bai L, Luo HY, Wang ZQ, Wang FH, Li YH, et al: Adjuvant
chemotherapy for elderly patients with gastric cancer after D2
gastrectomy. PLoS One. 8:e531492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang SI, Puc J, Li J, Bruce JN, Cairns P,
Sidransky D and Parsons R: Somatic mutations of PTEN in
glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res. 57:4183–4186. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brakebusch C and Fässler R: The
integrin-actin connection, an eternal love affair. EMBO J.
22:2324–2333. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Osaki M, Oshimura M and Ito H: PI3K-Akt
pathway: Its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yilmaz S, Zergeroglu AD, Yilmaz E,
Sofuoglu K, Delikara N and Kutlu P: Effects of sperm DNA
fragmentation on semen parameters and ICSI outcome determined by an
improved SCD test, halosperm. Int J Fertil Steril. 4:73–78.
2010.
|
|
12
|
Cong M, Liu T, Wang P, Fan X, Yang A, Bai
Y, Peng Z, Wu P, Tong X, Chen J, et al: Antifibrotic effects of a
recombinant adeno-associated virus carrying small interfering RNA
targeting TIMP-1 in rat liver fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 182:1607–1616.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Adhikari N, Mondal D, Jana M, Kumari K,
Das KJ and Julka PK: Primary neuroendocrine tumor of seminal
vesicle: An extremely rare clinical entity emphasizing diagnostic
role of 68-Ga DOTANOC PET-CT scan and therapeutic potential of long
acting depot octreotide injection in maintenance. Clin Genitourin
Cancer. 14:e539–e543. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sajant J, Heikkinen E and Majamaa K: Rapid
induction of meningeal collagen synthesis in the cerebral cisternal
and ventricular compartments after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta
Neurochir (Wien). 143:821–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thompson ME, Harver A and Eure M: A model
for integrating strategic planning and competence-based curriculum
design in establishing a public health programme: The UNC Charlotte
experience. Hum Resour Health. 7:712009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tanaka M, Lee J, Ikai H and Imanaka Y:
Development of efficiency indicators of operating room management
for multi-institutional comparisons. J Eval Clin Pract. 19:335–341.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shaffer FA and Tuttas CA: Nursing
leaderships responsibility for patient quality, safety, and
satisfaction: Current review and analysis. Nurse Lead. 3:34–43.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jansen PL, Klinge U, Jansen M and Junge K:
Risk factors for early recurrence after inguinal hernia repair. BMC
Surg. 9:182009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kayaoglu HA, Hazinedaroglu SM, Erkek A
Bulent, Kocaturk PA, Kavas GO and Aribal D: Comparison of the
plasma and hernia sac tissue copper levels in direct and indirect
inguinal hernia patients. Biol Trace Elem Res. 108:53–59. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shoulders MD and Raines RT: Collagen
structure and stability. Annu Rev Biochem. 78:929–958. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Friedman DM, Sokal SM, Chang Y and Berger
DL: Increasing operating room efficiency through parallel
processing. Ann Surg. 243:10–14. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dexter F: Impact on operating room
efficiency of reducing turnover times and anesthesia-controlled
times. Ann Surg. 245:336–337. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kurz A: Thermal care in the perioperative
period. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 22:39–62. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cook PR and Cullen JA: Caring as an
imperative for nursing education. Nurs Educ Perspect. 24:192–197.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|