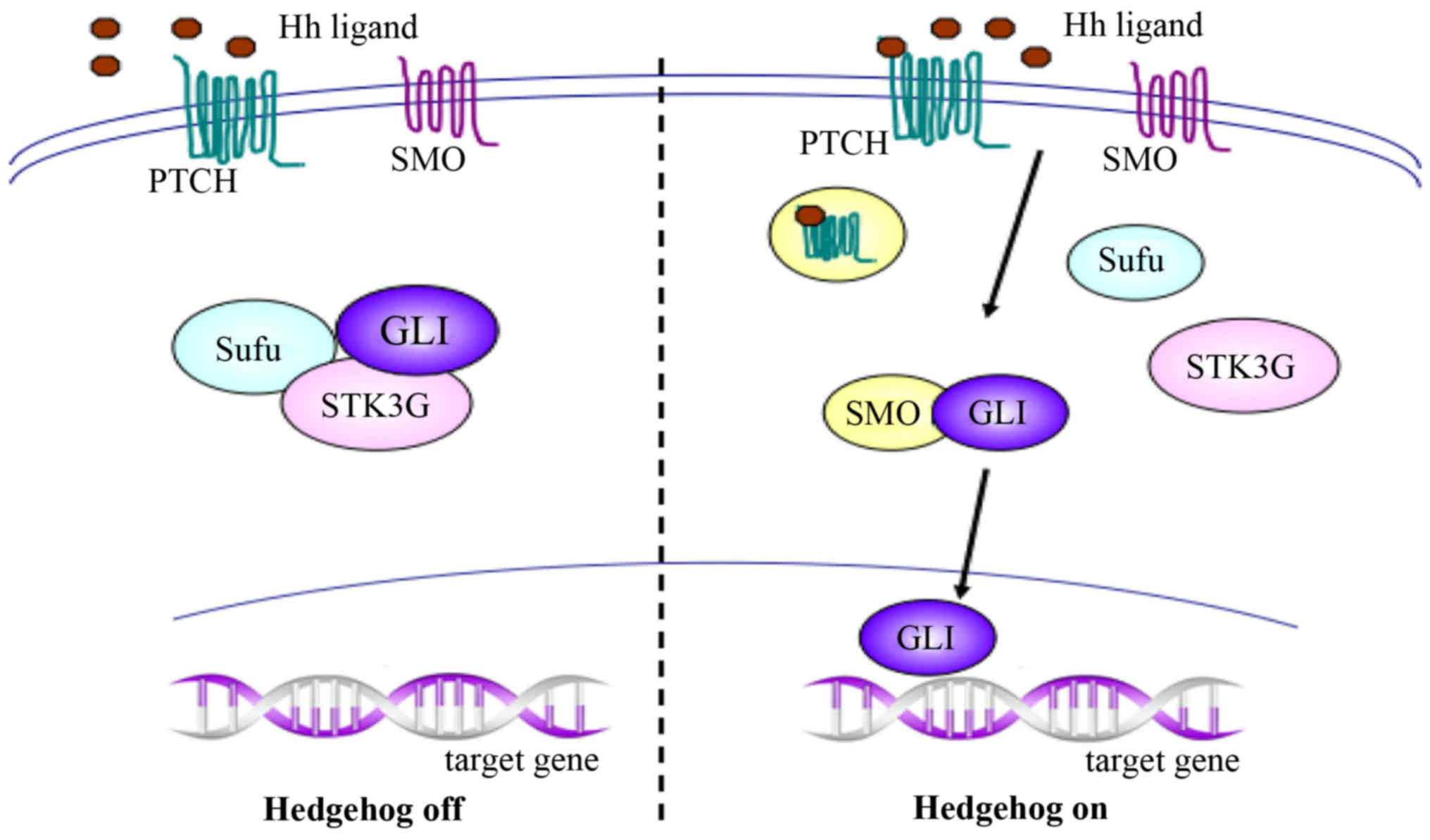
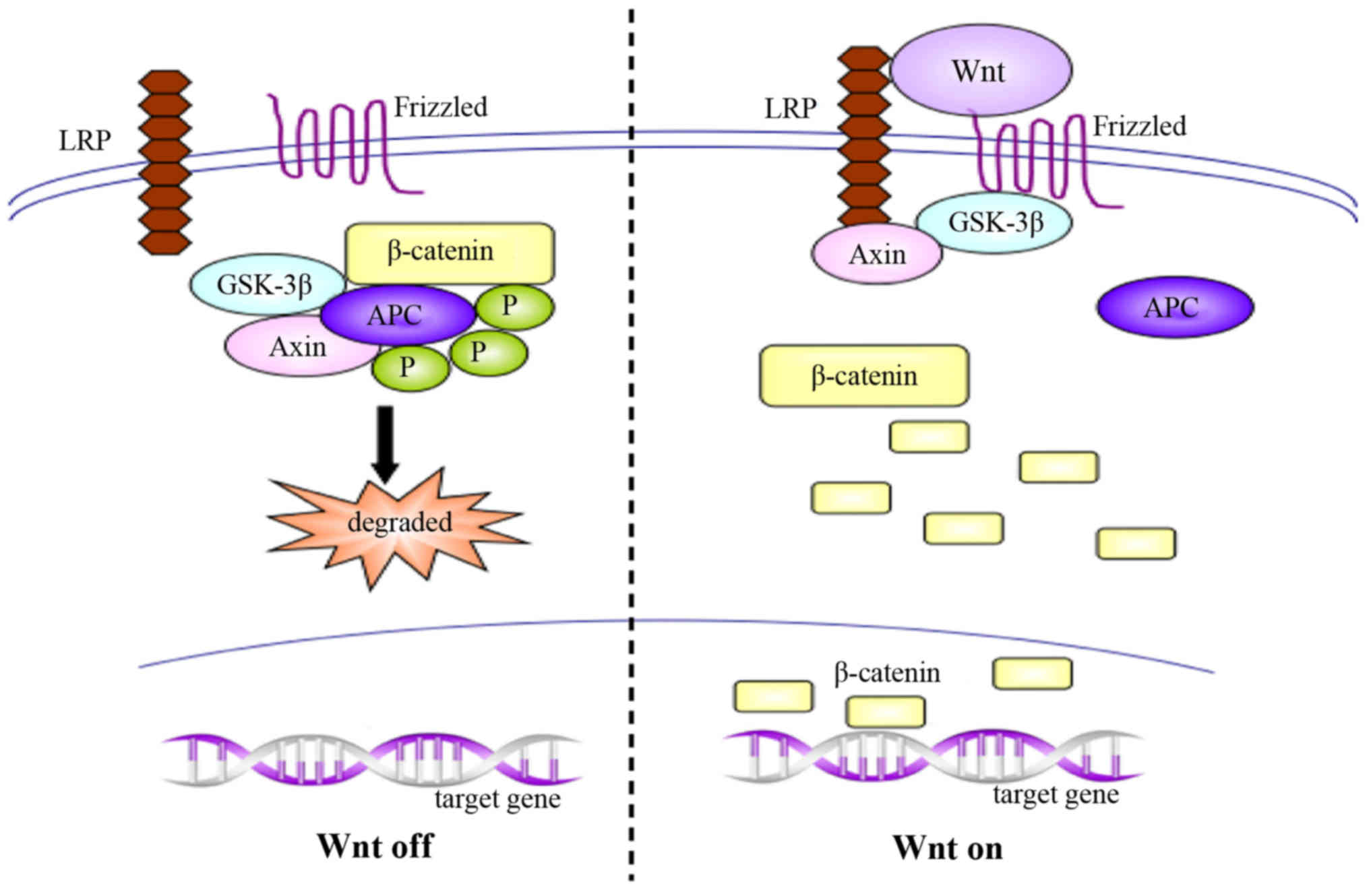
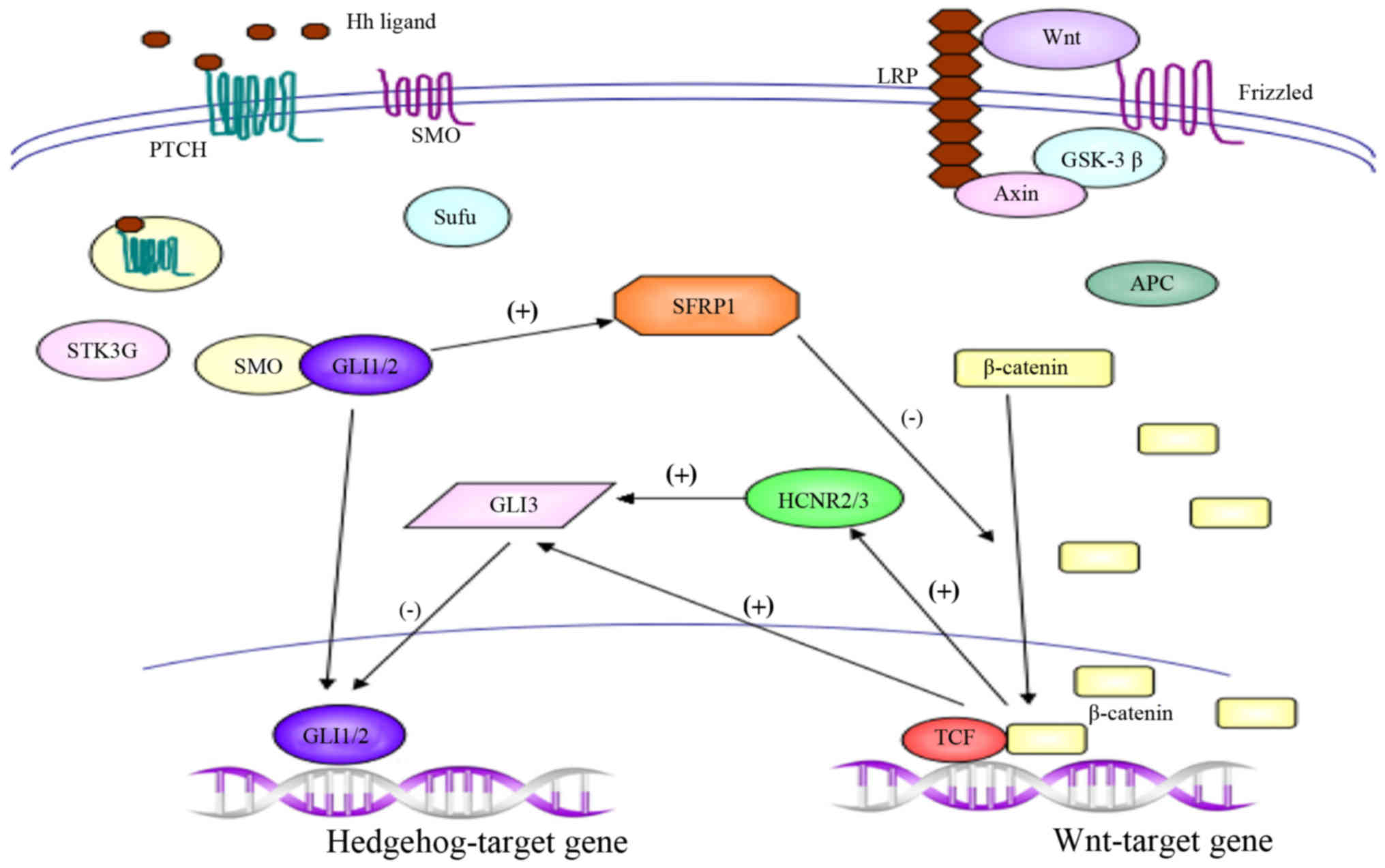
|
1
|
Parmigiani G, Boca S, Lin J, Kinzler KW,
Velculescu V and Vogelstein B: Design and analysis issues in
genome-wide somatic mutation studies of cancer. Genomics. 93:17–21.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sjöblom T, Jones S, Wood LD, Parsons DW,
Lin J, Barber TD, Mandelker D, Leary RJ, Ptak J, Silliman N, et al:
The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal
cancers. Science. 314:268–274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Greenman CP, Stephens P, Smith R,
Dalgliesh GL, Hunter C, Bignell G, Davies H, Teague J, Butler A,
Stevens C, et al: Patterns of somatic mutation in human cancer
genomes. Nature. 446:153–158. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thomas RK, Baker AC, Debiasi RM, Winckler
W, Laframboise T, Lin WM, Wang M, Feng W, Zander T, MacConaill L,
et al: High-throughput oncogene mutation profiling in human cancer.
Nat Genet. 39:347–351. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mangelberger D, Kern D, Loipetzberger A,
Eberl M and Aberger F: Cooperative Hedgehog-EGFR signaling. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 17:90–99. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matsushita S, Onishi H, Nakano K,
Nagamatsu I, Imaizumi A, Hattori M, Oda Y, Tanaka M and Katano M:
Hedgehog signaling pathway is a potential therapeutic target for
gallbladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 105:272–280. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rubin LL and de Sauvage FJ: Targeting the
Hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:1026–1033. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takebe N, Harris PJ, Warren RQ and Ivy SP:
Targeting cancer stem cells by inhibiting Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog
pathways. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:1–106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Karamboulas C and Ailles L: Developmental
signaling pathways in cancer stem cells of sol-id tumors. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1830:2481–2495. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dodge ME and Lum L: Drugging the cancer
stem cell compartment: Lessons learned from the hedgehog and Wnt
signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
51:289–310. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
JP IV Morris, Wang SC and Hebrok M: KRAS,
Hedgehog, Wnt and the twisted developmental biology of pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:683–695. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Katoh Y and Katoh M: WNT antagonist,
SFRP1, is Hedgehog signaling target. Int J Mol Med. 17:171–175.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bovolenta P, Esteve P, Ruiz JM, Cisneros E
and Lopez-Rios J: Beyond Wnt inhibition: New functions of secreted
Frizzled-related proteins in development and disease. J Cell Sci.
121:737–746. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nüsslein-Volhard C and Wieschaus E:
Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila.
Nature. 287:795–801. 1980. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Varjosalo M and Taipale J: Hedgehog
signaling. J Cell Sci. 120:3–6. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wilson CW and Chuang PT: Mechanism and
evolution of cytosolic Hedgehog signal transduction. Development.
137:2079–2094. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rohatgi R, Milenkovic L, Corcoran RB and
Scott MP: Hedgehog signal transduction by Smoothened: Pharmacologic
evidence for a 2-step activation process. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:pp. 3196–3201. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Varjosalo M and Taipale J: Hedgehog:
Functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev. 22:2454–2472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rohatgi R, Milenkovic L and Scott MP:
Patched1 regulate hedgehog signaling at the primary cilium.
Science. 317:372–376. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Marigo V and Tabin CJ: Regulation of
patched by sonic hedgehog in the developing neural tube. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 93:pp. 9346–9351. 1996; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bellusci S, Furuta Y, Rush MG, Henderson
R, Winnier G and Hogan BL: Involvement of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) in
mouse embryonic lung growth and morphogenesis. Development.
124:53–63. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hardcastle Z, Mo R, Hui CC and Sharpe PT:
The Shh signalling pathway in tooth development: Defects in Gli2
and Gli3 mutants. Development. 125:2803–2811. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Litingtung Y, Lei L, Westphal H and Chiang
C: Sonic hedgehog is essential to foregut development. Nat Genet.
20:58–61. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
St-Jacques B, Dassule HR, Karavanova I,
Botchkarev VA, Li J, Danielian PS, McMahon JA, Lewis PM, Paus R and
McMahon AP: Sonic hedgehog signaling is essential for hair
development. Curr Biol. 8:1058–1068. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vortkamp A, Lee K, Lanske B, Segre GV,
Kronenberg HM and Tabin CJ: Regulation of rate of cartilage
differentiation by Indian hedgehog and PTH-related protein.
Science. 273:613–622. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bitgood MJ, Shen L and McMahon AP: Sertoli
cell signaling by Desert hedgehog regulates the male germline. Curr
Biol. 6:298–304. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen Y and Jiang J: Decoding the
phosphorylation code in Hedgehog signal transduction. Cell Res.
23:186–200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Merchant JL: Hedgehog signaling in gut
development, physiology and cancer. J Physiol. 590:421–432. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bertrand FE, Angus CW, Partis WJ and
Sigounas G: Developmental pathways in colon cancer: Crosstalk
between WNT, BMP, Hedgehog and Notch. Cell Cycle. 11:4344–4351.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Niu Y, Li F, Tang B, Shi Y, Hao Y and Yu
P: Clinicopathological correlation and prognostic significance of
sonic hedgehog protein overexpression in human gastric cancer. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:5144–5153. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kai K, Aishima S and Miyazaki K:
Gallbladder cancer: Clinical and pathological approach. World J
Clin Cases. 2:515–521. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nigam A: Breast cancer stem cells,
pathways and therapeutic perspectives 2011. Indian J Surg.
75:170–180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hwang J, Kang MH, Yoo YA, Quan YH, Kim HK,
Oh SC and Choi YH: The effects of sonic hedgehog signaling pathway
components on non-small-cell lung cancer progression and clinical
outcome. World J Surg Oncol. 12:2682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ok CY, Singh RR and Vega F: Aberrant
activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway in malignant
hematological neoplasms. Am J Pathol. 180:2–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Irvine DA and Copland M: Targeting
hedgehog in hematologic malignancy. Blood. 119:2196–2204. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Harwood CA, Attard NR, O'Donovan P,
Chambers P, Perrett CM, Proby CM, McGregor JM and Karran P: PTCH
mutations in basal cell carcinomas from azathioprine-treated organ
transplant recipients. Br J Cancer. 99:1276–1284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Soufir N, Gerard B, Portela M, Brice A,
Liboutet M, Saiag P, Descamps V, Kerob D, Wolkenstein P, Gorin I,
et al: PTCH mutations and deletions in patients with typical nevoid
basal cell carcinoma syndrome and in patients with a suspected
genetic predisposition to basal cell carcinoma: A French study. Br
J Cancer. 95:548–553. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nitzki F, Tolosa EJ, Cuvelier N, Frommhold
A, Salinas-Riester G, Johnsen SA, Fernandez-Zapico ME and Hahn H:
Overexpression of mutant Ptch in rhabdomyosarcomas is associated
with promoter hypomethylation and increased Gli1 and H3K4me3
occupancy. Oncotarget. 6:9113–9124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lim CB, Prêle CM, Cheah HM, Cheng YY,
Klebe S, Reid G, Watkins DN, Baltic S, Thompson PJ and Mutsaers SE:
Mutational analysis of hedgehog signaling pathway genes in human
malignant mesothelioma. PLoS One. 8:e666852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen Y, Li S, Tong C, Zhao Y, Wang B, Liu
Y, Jia J and Jiang J: G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 promotes
high-level Hedgehog signaling by regulating the active state of Smo
through kinase-dependent and kinase-independent mechanisms in
Drosophila. Genes Dev. 24:2054–2067. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhou X, Liu Z, Jang F, Xiang C, Li Y and
He Y: Autocrine Sonic hedgehog attenuates inflammation in
cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice via upregulation of
IL-10. PLoS One. 7:e441212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ertao Z, Jianhui C, Chuangqi C, Changjiang
Q, Sile C, Yulong H, Hui W and Shirong C: Autocrine Sonic hedgehog
signaling promotes gastric cancer proliferation through induction
of phospholipase Cy1 and the ERK1/2 pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35:632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Levi B, James AW, Nelson ER, Li S, Peng M,
Commons GW, Lee M, Wu B and Longaker MT: Human adipose-derived
stromal cells stimulate autogenous skeletal repair via paracrine
Hedgehog signaling with calvarial osteoblasts. Stem Cells Dev.
20:243–257. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chan IS, Guy CD, Chen Y, Lu J,
Swiderska-Syn M, Michelotti GA, Karaca G, Xie G, Krüger L, Syn WK,
et al: Paracrine Hedgehog signaling drives metabolic changes in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 72:6344–6350. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Scales SJ and de Sauvage FJ: Mechanisms of
Hedgehog pathway activation in cancer and implications for therapy.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 30:303–312. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Rudin CM, Hann CL, Laterra J, Yauch RL,
Callahan CA, Fu L, Holcomb T, Stinson J, Gould SE, Coleman B, et
al: Treatment of medulloblastoma with hedgehog pathway inhibitor
GDC-0449. N Engl J Med. 361:1173–1178. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Von Hoff DD, LoRusso PM, Rudin CM, Reddy
JC, Yauch RL, Tibes R, Weiss GJ, Borad MJ, Hann CL, Brahmer JR, et
al: Inhibition of the hedgehog pathway in advanced basal-cell
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 361:1164–1172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dubey AK, Dubey S, Handu SS and Qazi MA:
Vismodegib: The first drug approved for advanced and metastatic
basal cell carcinoma. J Postgrad Med. 59:48–50. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Stecca B, Ruiz I and Altaba A:
Context-dependent regulation of the GLI code in cancer by HEDGEHOG
and non-HEDGEHOG signals. J Mol Cell Biol. 2:84–95. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lauth M and Toftgård R: Non-canonical
activation of GLI transcription factors: Implications for targeted
anti-cancer therapy. Cell Cycle. 6:2458–2463. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Riobo NA, Lu K and Emerson CP Jr: Hedgehog
signal transduction: Signal integration and cross talk in
development and cancer. Cell Cycle. 5:1612–1615. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Muñoz-Descalzo S, Hadjantonakis AK and
Arias AM: Wnt/ß-catenin signalling and the dynamics of fate
decisions in early mouse embryos and embryonic stem (ES) cells.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 47-48:1–109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sokol SY: Maintaining embryonic stem cell
pluripotency with Wnt signaling. Development. 138:4341–4350. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yang K, Wang X, Zhang H, Wang Z, Nan G, Li
Y, Zhang F, Mohammed MK, Haydon RC, Luu HH, et al: The evolving
roles of canonical WNT signaling in stem cells and tumorigenesis:
Implications in targeted cancer therapies. Lab Invest. 96:116–136.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mohammed MK, Shao C, Wang J, Wei Q, Wang
X, Collier Z, Tang S, Liu H, Zhang F, Huang J, et al: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling plays an ever-expanding role in stem cell self-renewal,
tumorigenesis and cancer chemoresistance. Genes Dis. 3:11–40. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kalderon D: Similarities between the
Hedgehog and Wnt signaling pathways. Trends Cell Biol. 12:523–531.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
He X, Semenov M, Tamai K and Zeng X: LDL
receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling:
Arrows point the way. Development. 131:1663–1677. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Peifer M and McEwen DG: The ballet of
morphogenesis: Unveiling the hidden choreographers. Cell.
109:271–274. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Shigemitsu K, Sekido Y, Usami N, Mori S,
Sato M, Horio Y, Hasegawa Y, Bader SA, Gazdar AF, Minna JD, et al:
Genetic alteration of the beta-catenin gene (CTNNBI) in human lung
cancer and malignant mesothelioma and identification of a new
3p21.3 homozygous deletion. Oncogene. 20:4249–4257. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kimura Y, Furuhata T, Mukaiya M, Kihara C,
Kawakami M, Okita K, Yanai Y, Zenbutsu H, Satoh M, Ichimiya S and
Hirata K: Frequent beta-catenin alteration in gallbladder
carcinomas. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 22:321–328. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Coscio A, Chang DW, Roth JA, Ye Y, Gu J,
Yang P and Wu X: Genetic variants of the Wnt signaling pathway as
predictors of recurrence and survival in early-stage non-small cell
lung cancer patients. Carcinogenesis. 35:1284–1291. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li S, Li S, Sun Y and Li L: The expression
of β-catenin in different subtypes of breast cancer and its
clinical significance. Tumour Biol. 35:7693–7698. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lu D, Choi MY, Yu J, Castro JE, Kipps TJ
and Carson DA: Salinomycin inhibits Wnt signaling and selectively
induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Proc Matl
Acad Sci USA. 108:pp. 13253–13257. 2011; View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Price MA: CKI, there's more than one:
casein kinase I family members in Wnt and Hedgehog signaling. Genes
Dev. 20:399–410. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Rhee CS, Sen M, Lu D, Wu C, Leoni L, Rubin
J, Corr M and Carson DA: Wnt and frizzled receptors as potential
targets for immunotherapy in head and neck squamous cell
carcinomas. Oncogene. 21:6598–6605. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Collu GM, Hidalgo-Sastre A and Brennan K:
Wnt-Notch signaling crosstalk in development and disease. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 71:3553–3567. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Xu F, Zhang J and Ma D: Crosstalk of
Hippo/YAP and Wnt/β-catenin pathways. Yi Chuan. 36:95–102. 2014.(In
Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Shimobayashi M and Hall MN: Making new
contacts: The mTOR network in metabolism and signalling crosstalk.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:155–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Moussaif M and Sze JY: Intraflagellar
transport/Hedgehog-related signaling components couple sensory
cilium morphology and serotonin biosynthesis in Caenorhabditis
elegans. J Neurosci. 29:4065–4075. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Brás-Pereira C, Potier D, Jacobs J, Aerts
S, Casares F and Janody F: dachshund Potentiates Hedgehog Signaling
during Drosophila Retinogenesis. PLoS Genet. 12:e10062042016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Poss KD, Keating MT and Nechiporuk A:
Tales of regeneration in zebrafish. Dev Dyn:. 226:202–210. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Akimenko MA, Mari-Beffa M, Becerra J and
Géraudie J: Old questions, new tools, and some answers to the
mystery of fin regeneration. Dev Dyn. 226:190–201. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Stoick-Cooper CL, Weidinger G, Riehle KJ,
Hubbert C, Major MB, Fausto N and Moon RT: Distinct Wnt signaling
pathways have opposing roles in appendage regeneration.
Development. 134:479–489. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Singh BN, Doyle MJ, Weaver CV,
Koyano-Nakagawa N and Garry DJ: Hedgehog and Wnt coordinate
signaling in myogenic progenitors and regulate limb regeneration.
Dev Biol. 371:23–34. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Day TF and Yang Y: Wnt and hedgehog
signaling pathways in bone development. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 90
Suppl 1:S19–S24. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Liu B, Chen S, Cheng D, Jing W and Helms
JA: Primary cilia integrate hedgehog and Wnt signaling during tooth
development. J Dent Res. 93:475–482. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Oberhofer G, Grossmann D, Siemanowski JL,
Beissbarth T and Bucher G: Wnt/β-catenin signaling integrates
patterning and metabolism of the insect growth zone. Development.
141:4740–4750. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Shin K, Lee J, Guo N, Kim J, Lim A, Qu L,
Mysorekar IU and Beachy PA: Hedgehog/Wnt feedback supports
regenerative proliferation of epithelial stem cells in bladder.
Nature. 472:110–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Xu Q, D'Amore PA and Sokol SY: Functional
and biochemical interactions of Wnts with FrzA, a secreted Wnt
antagonist. Development. 125:4767–4776. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
He J, Sheng T, Stelter AA, Li C, Zhang X,
Sinha M, Luxon BA and Xie J: Suppressing Wnt signalling by the
hedgehog pathway through sFRP-1. J Biol Chem. 281:35598–35602.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Alvarez-Medina R, Le Dreau G, Ros M and
Marti E: Hedgehog activation is required upstream of Wnt signalling
to control neural progenitor proliferation. Development.
136:3301–3309. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Borday C, Cabochette P, Parain K, Mazurier
N, Janssens S, Tran HT, Sekkali B, Bronchain O, Vleminckx K, Locker
M and Perron M: Antagonistic cross-regulation between Wnt and
Hedgehog signalling pathways controls post-embryonic retinal
proliferation. Development. 139:3499–3509. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kim JH, Shin HS, Lee SH, Lee I, Lee YS,
Park JC, Kim YJ, Chung JB and Lee YC: Contrasting activity of
Hedgehog and Wnt pathways according to gastric cancer cell
differentiation: Relevance of crosstalk mechanisms. Cancer Sci.
101:328–335. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kurosaka H, Lulianella A, Williams T and
Trainor PA: Disrupting hedgehog and WNT signaling interactions
promotes cleft lip pathogenesis. J Clin Invest. 124:1660–1671.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Fu X, Shi L, Zhang W, Zhang X, Peng Y,
Chen X, Tang C, Li X and Zhou X: Expression of Indian hedgehog is
negatively correlated with APC gene mutation in colorectal tumors.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:2150–2155. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Xuan YH, Jung HS, Choi YL, Shin YK, Kim
HJ, Kim KH, Kim WJ, Lee YJ and Kim SH: Enhanced expression of
hedgehog signaling molecules in squamous cell carcinoma of uterine
cervix and its precursor lesions. Mod Patho. 19:1139–1147.
2006.
|
|
88
|
Yanai K, Nakamura M, Akiyoshi T, Nagai S,
Wada J, Koga K, Noshiro H, Nagai E, Tsuneyoshi M, Tanaka M and
Katano M: Crosstalk of hedgehog and Wnt pathways in gastric cancer.
Cancer Lett. 263:145–156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Jacob J and Briscoe J: Gli proteins and
the control of spinal-cord patterning. EMBO Rep. 4:761–765. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Alvarez-Medina R, Cayuso J, Okubo T,
Takada S and Marti E: Wnt canonical pathway restricts graded
Shh/Gli patterning activity through the regulation of Gli3
expression. Development. 135:237–247. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Muroyama Y, Fujihara M, Ikeya M, Kondoh H
and Takada S: Wnt signalling plays an essential role in neuronal
specification of the dorsal spinal cord. Genes Dev. 16:548–553.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Abbasi AA, Paparidis Z, Malik S, Goode DK,
Callaway H, Elgar G and Grzeschick KH: Human GLI3 intragenic
conserved non-coding sequences are tissue-specific enhancers. PLoS
One. 2:e3662007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Meijer L, Skaltsounis AL, Magiatis P,
Polychronopoulos P, Knockaert M, Leost M, Ryan XP, Vonica CA,
Brivanlou A, Dajani R, et al: GSK-3-selective inhibitors derived
from Tyrian purple indirubins. Chem Biol. 10:1255–1266. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Chen B, Dodge ME, Tang W, Lu J, Ma Z, Fan
CW, Wei S, Hao W, Kilgore J, Williams NS, et al: Small
molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signalling in tissue
regeneration and cancer. Nat Chem Biol. 5:100–107. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Pöschl J, Bartels M, Ohli J, Bianchi E,
Kuteykin-Teplyakov K, Grammel D, Ahlfeld J and Schüller U:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibits the Shh pathway and impairs tumor
growth in Shh-dependent medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol.
127:605–607. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|