|
1
|
Brown ZJ, Tsilimigras DI, Ruff SM, Mohseni
A, Kamel IR, Cloyd JM and Pawlik TM: Management of hepatocellular
carcinoma: A review. JAMA Surg. 158:410–420. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chidambaranathan-Reghupaty S, Fisher PB
and Sarkar D: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Epidemiology,
etiology and molecular classification. Adv Cancer Res. 149:1–61.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kumar A, Acharya SK, Singh SP, Arora A,
Dhiman RK, Aggarwal R, Anand AC, Bhangui P, Chawla YK, Gupta SD, et
al: 2019 update of Indian national association for study of the
liver consensus on prevention, diagnosis, and management of
hepatocellular carcinoma in India: The puri II recommendations. J
Clin Exp Hepatol. 10:43–80. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K,
Piscaglia F, Baron A, Park JW, Han G, Jassem J, et al: Lenvatinib
versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3
non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 391:1163–1173. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao Y, Zhang YN, Wang KT and Chen L:
Lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma: From preclinical
mechanisms to anti-cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1874:1883912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ikeda M, Okusaka T, Mitsunaga S, Ueno H,
Tamai T, Suzuki T, Hayato S, Kadowaki T, Okita K and Kumada H:
Safety and pharmacokinetics of lenvatinib in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 22:1385–1394. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, Crocenzi
TS, Kudo M, Hsu C, Kim TY, Choo SP, Trojan J, Welling THR, et al:
Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
(CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose
escalation and expansion trial. Lancet. 389:2492–2502. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fukumura D, Kloepper J, Amoozgar Z, Duda
DG and Jain RK: Enhancing cancer immunotherapy using
antiangiogenics: Opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
15:325–340. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng AL, Hsu C, Chan SL, Choo SP and Kudo
M: Challenges of combination therapy with immune checkpoint
inhibitors for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 72:307–319.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deng H, Kan A, Lyu N, Mu L, Han Y, Liu L,
Zhang Y, Duan Y, Liao S, Li S, et al: Dual vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor and fibroblast growth factor receptor
inhibition elicits antitumor immunity and enhances programmed cell
death-1 checkpoint blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver
Cancer. 9:338–357. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kudo M: Scientific rationale for combined
immunotherapy with PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies and VEGF inhibitors in
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 12:10892020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Finn RS, Ikeda M, Zhu AX, Sung MW, Baron
AD, Kudo M, Okusaka T, Kobayashi M, Kumada H, Kaneko S, et al:
Phase Ib study of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 38:2960–2970.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cook DA and Reed DA: Appraising the
quality of medical education research methods: The medical
education research study quality instrument and the
newcastle-ottawa scale-education. Acad Med. 90:1067–1076. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bernardo WM: PRISMA statement and
PROSPERO. Int Braz J Urol. 43:383–384. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
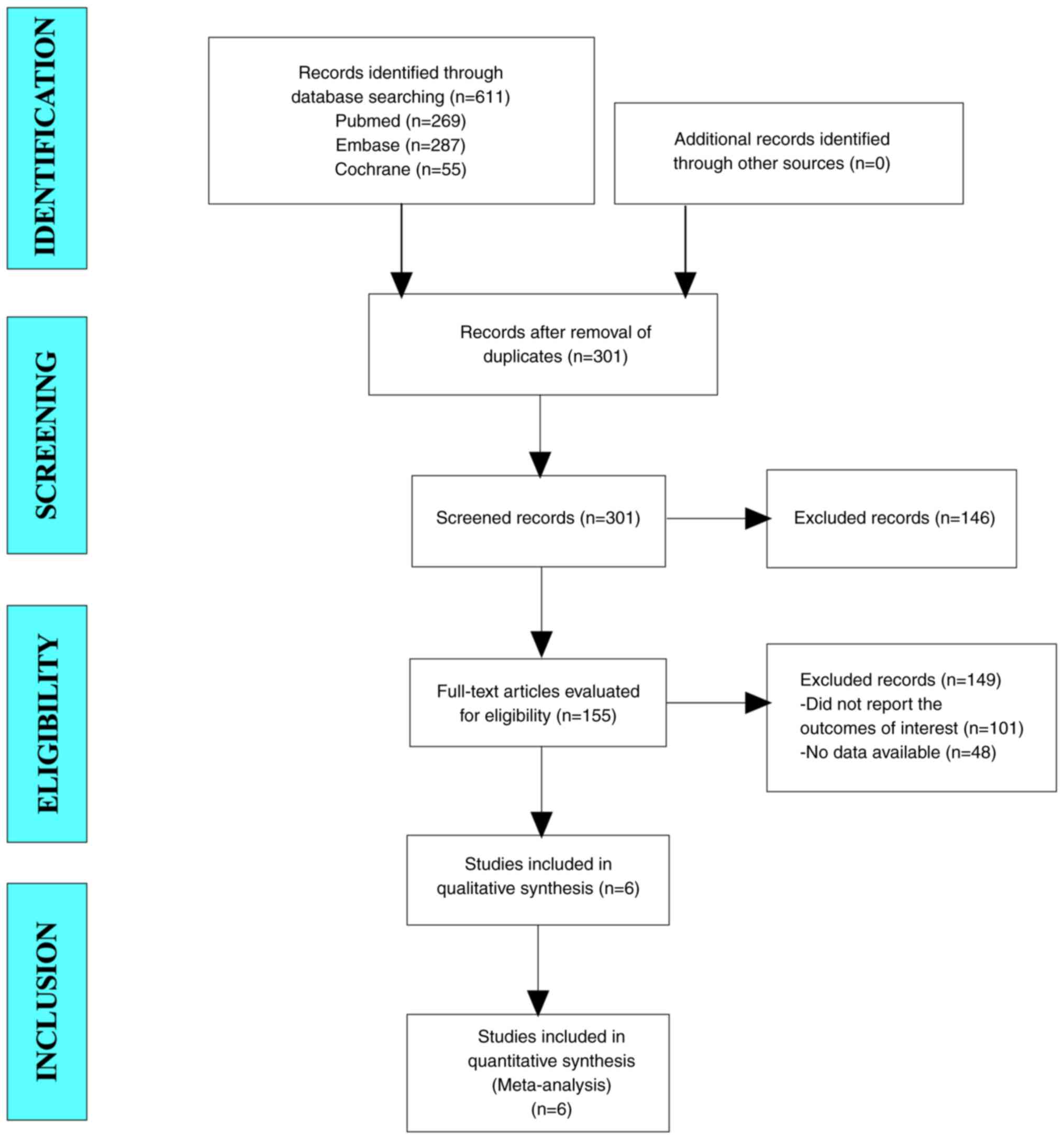
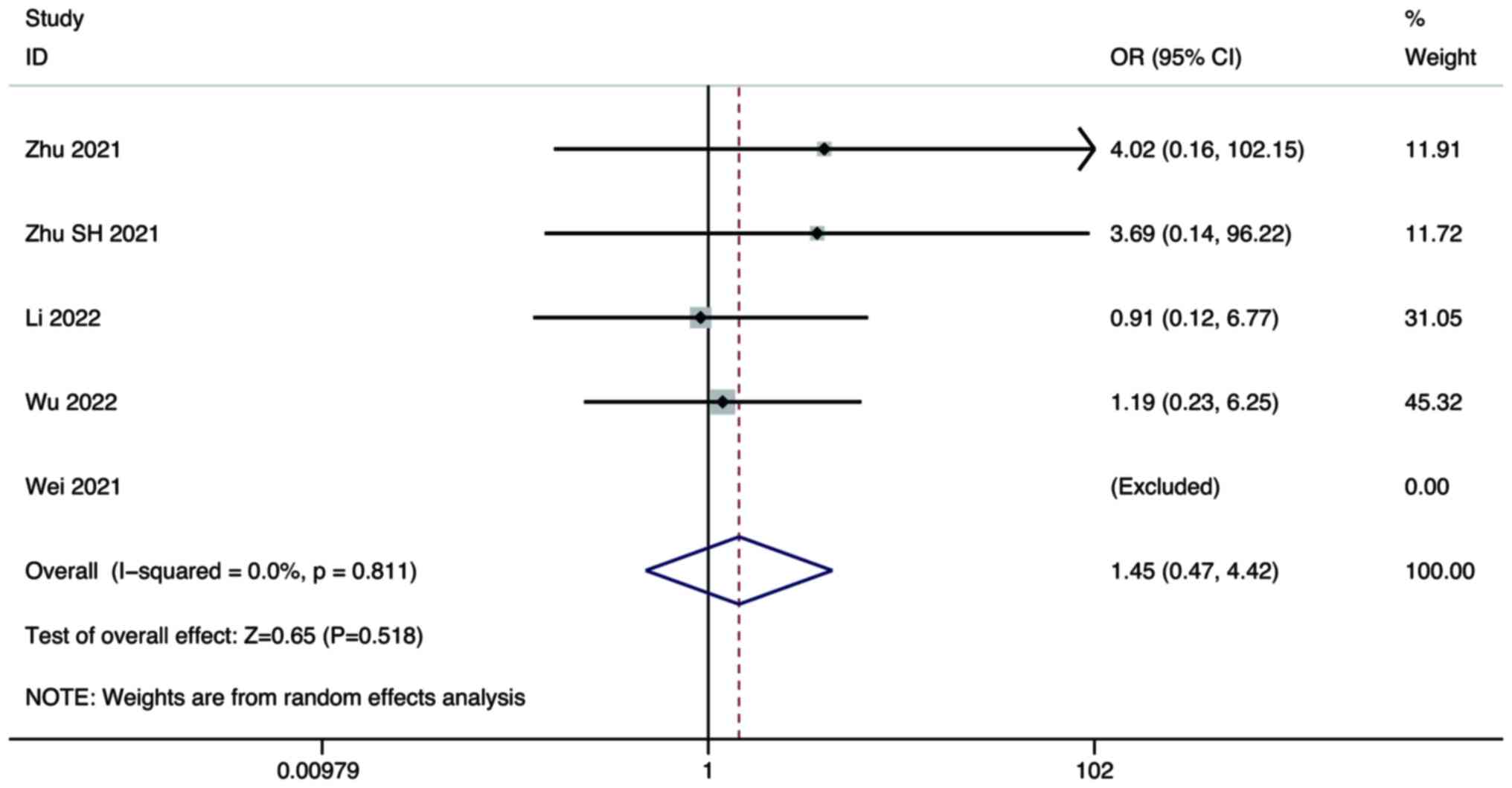
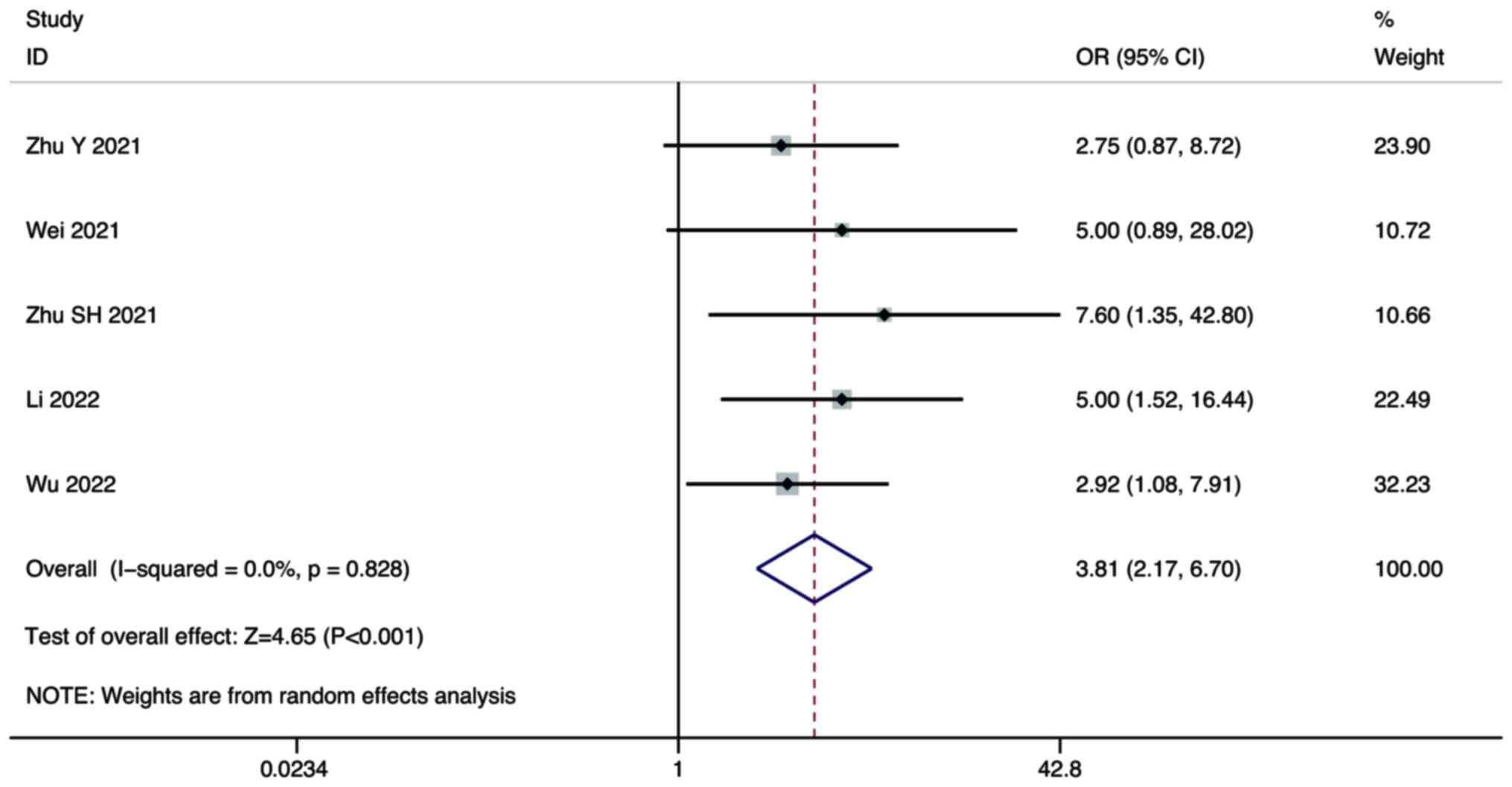
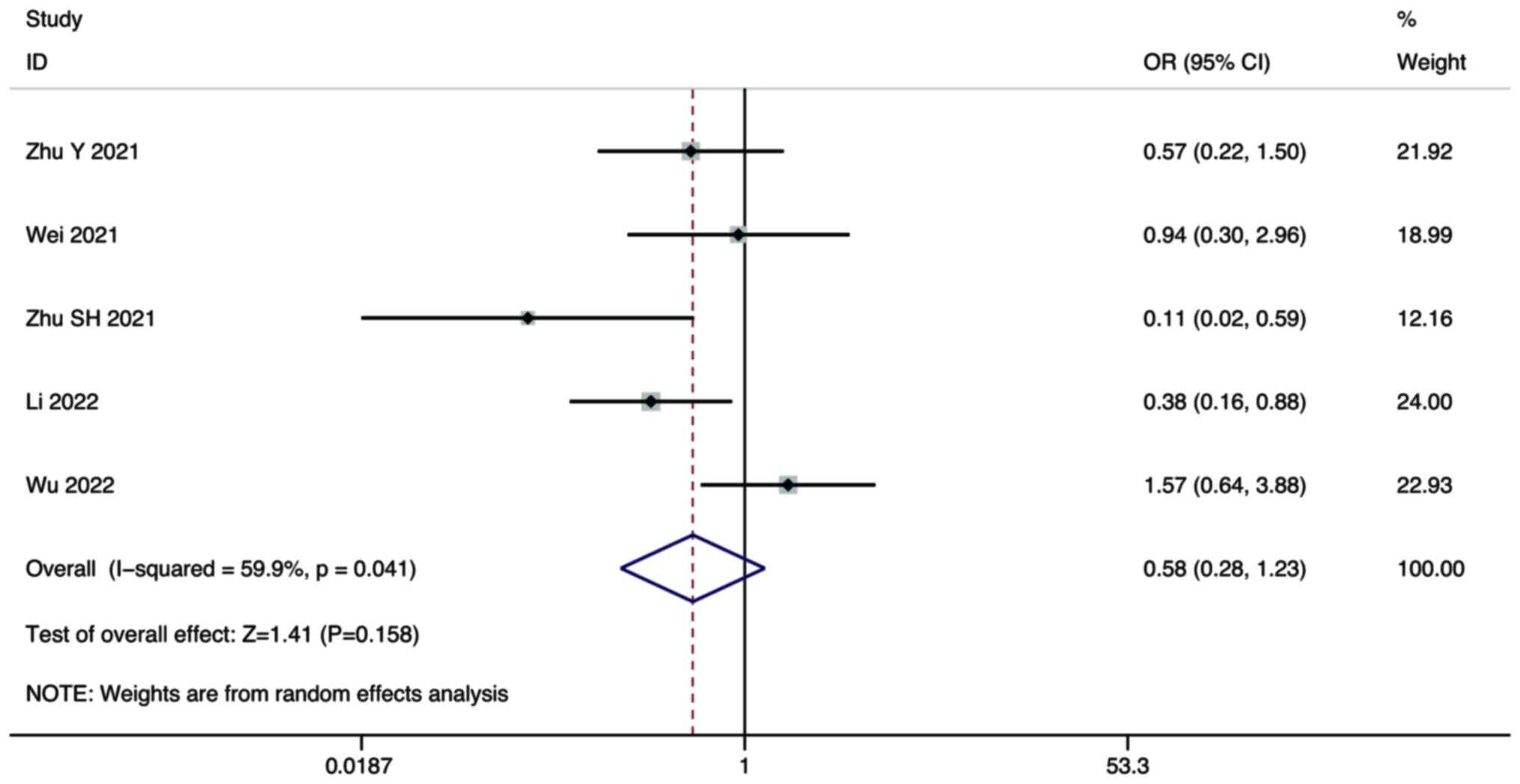
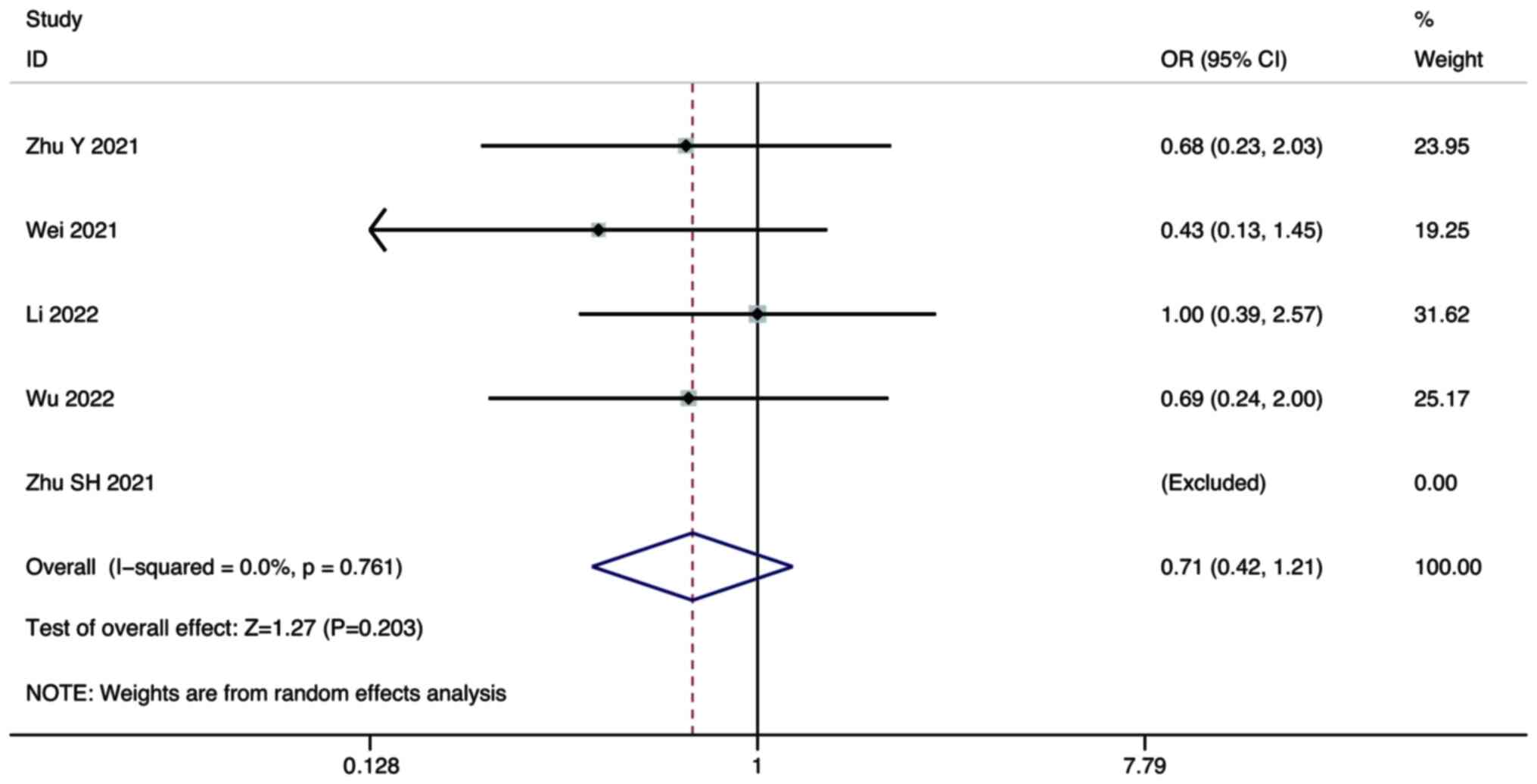
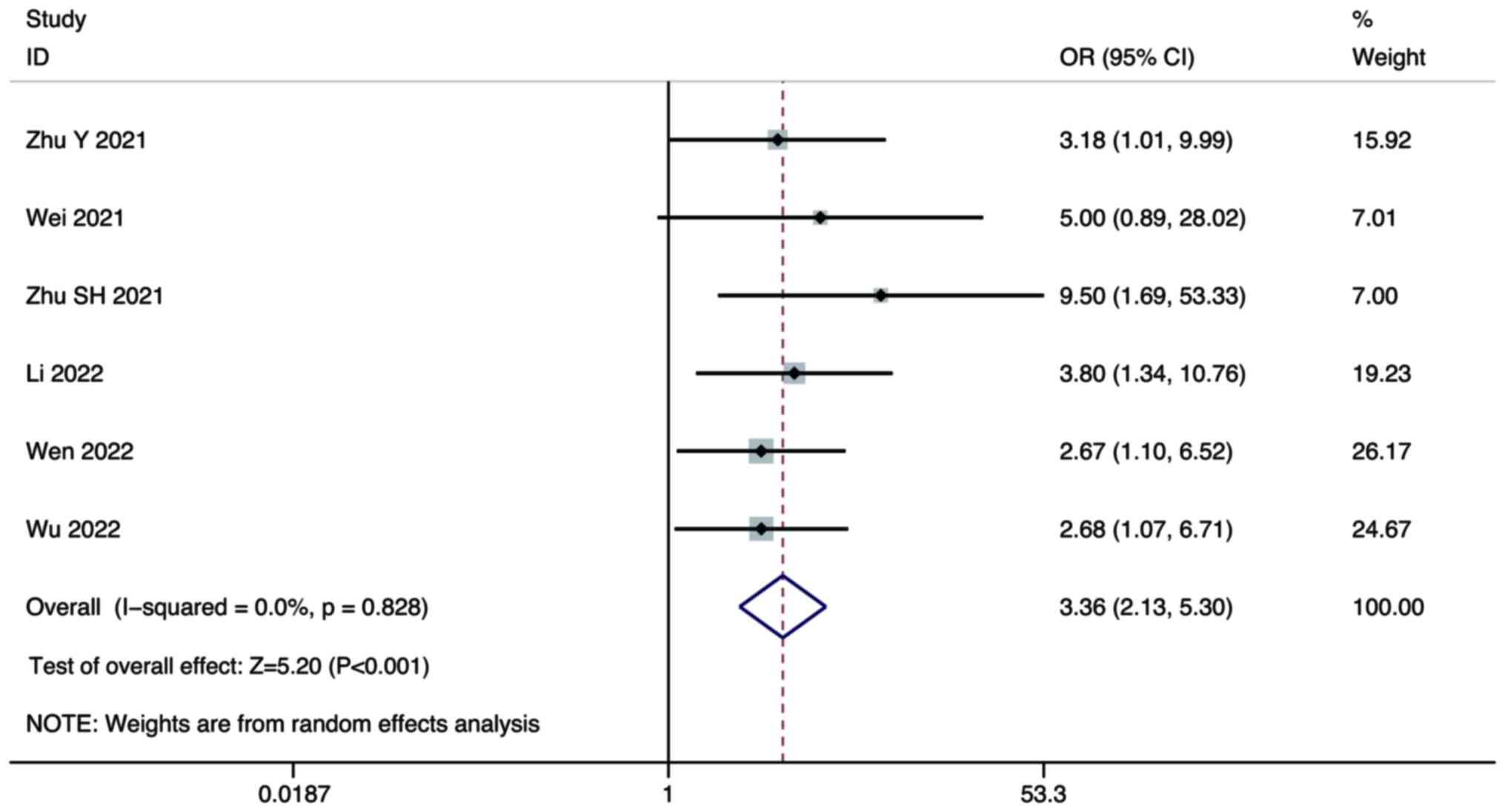
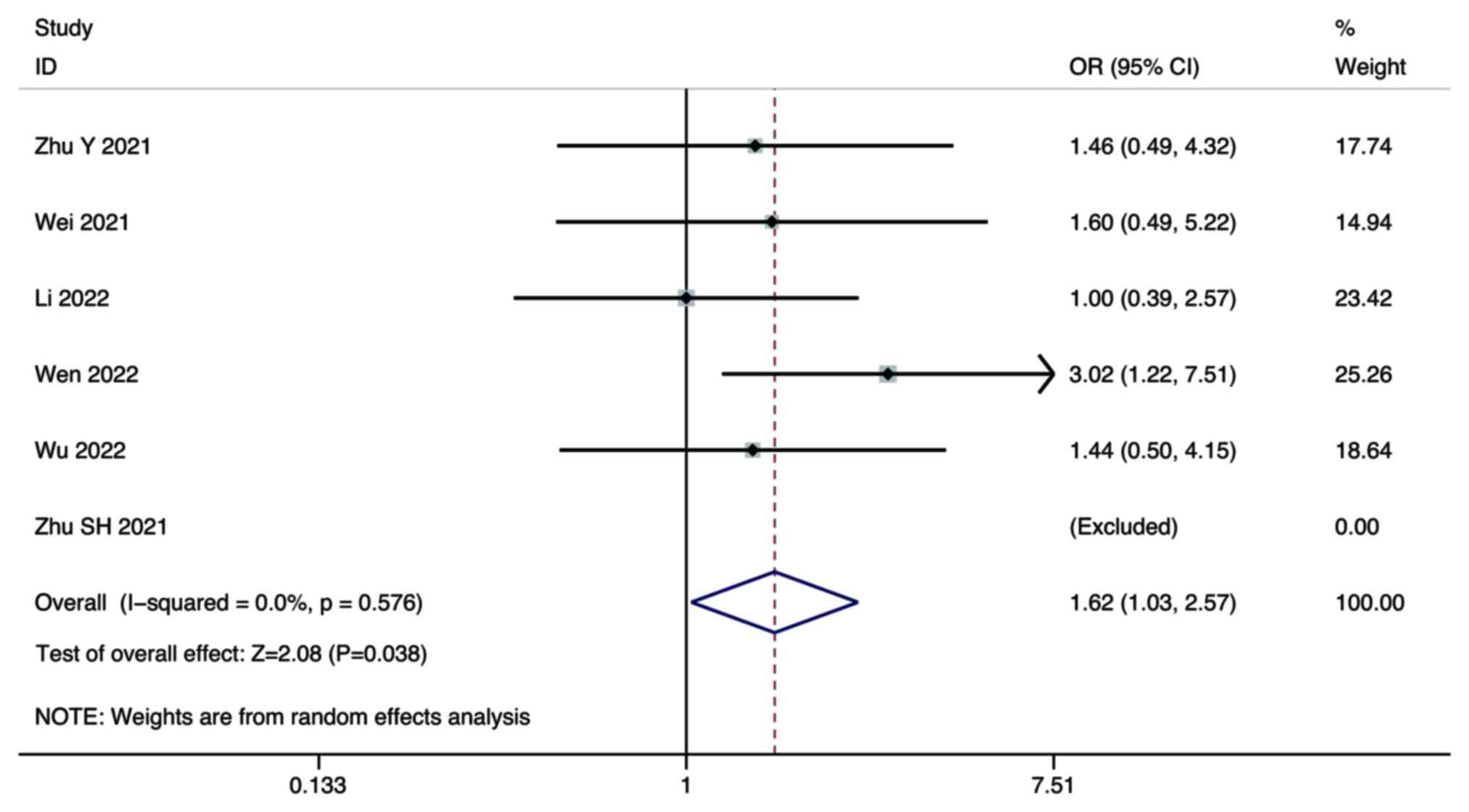
Zhu Y, Sun P, Wang K, Xiao S and Cheng Y,
Li X, Wang B, Li J, Yu W and Cheng Y: Efficacy and safety of
lenvatinib monotreatment and lenvatinib-based combination therapy
for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A
retrospective, real-world study in China. Cancer Cell Int.
21:5032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
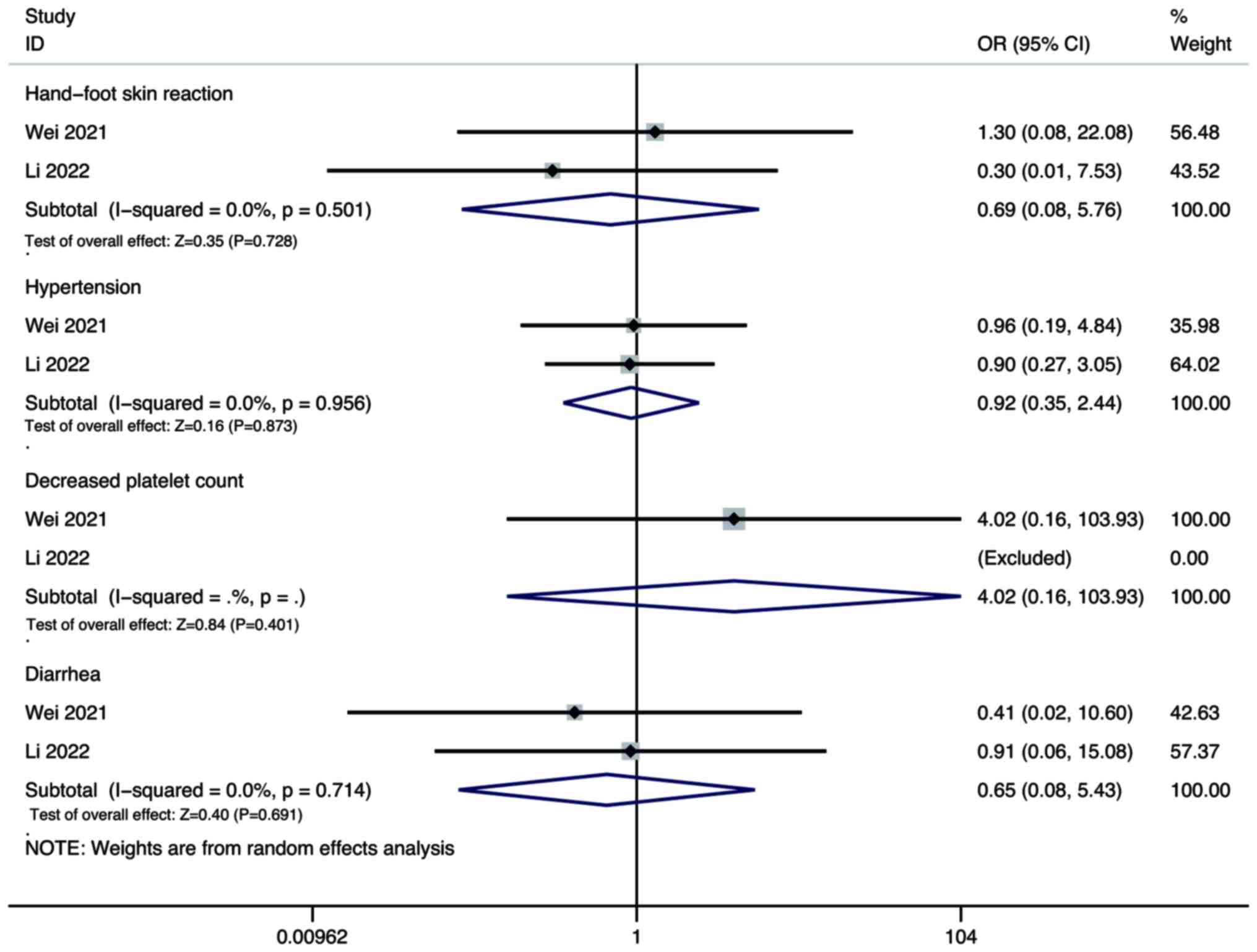
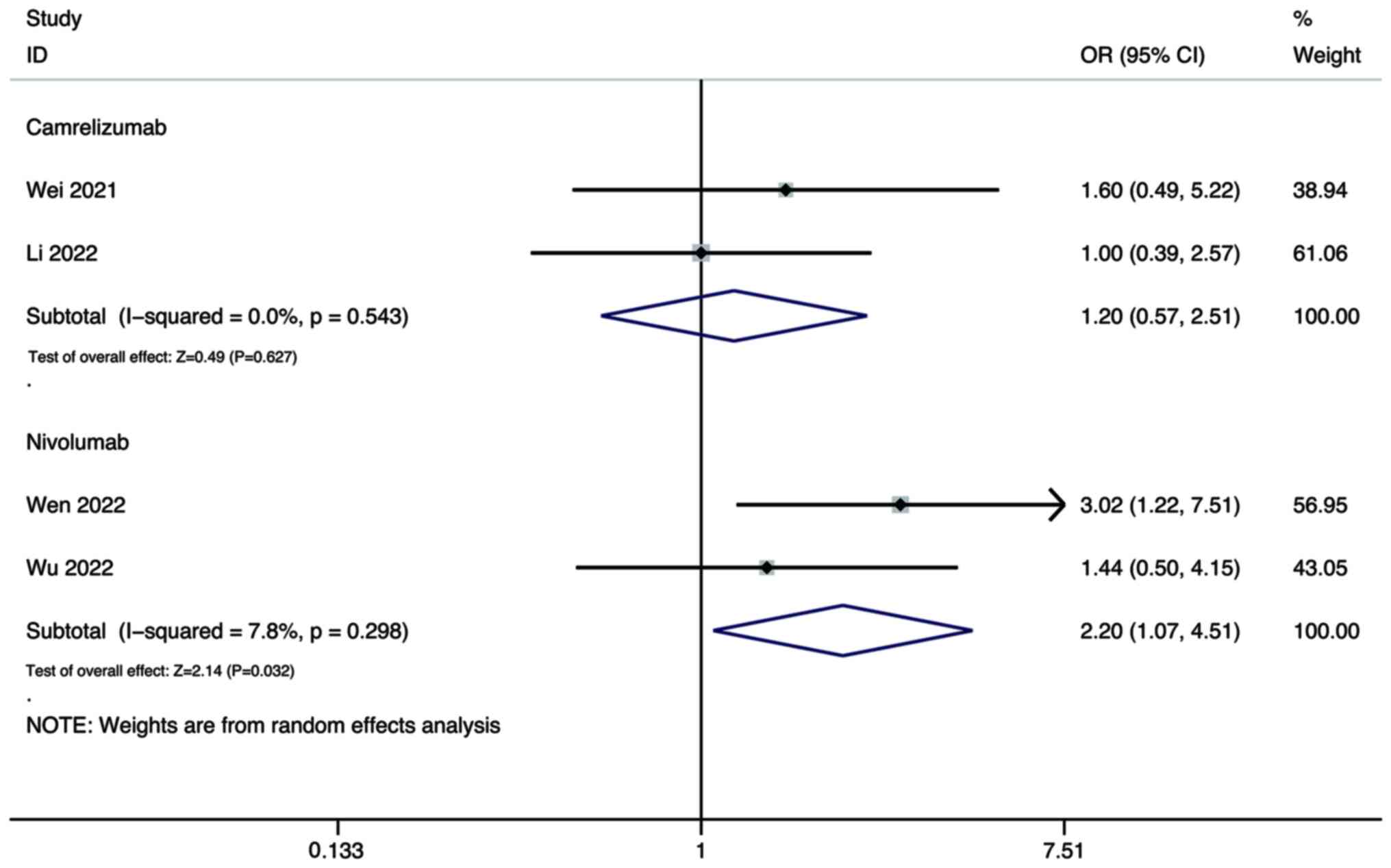
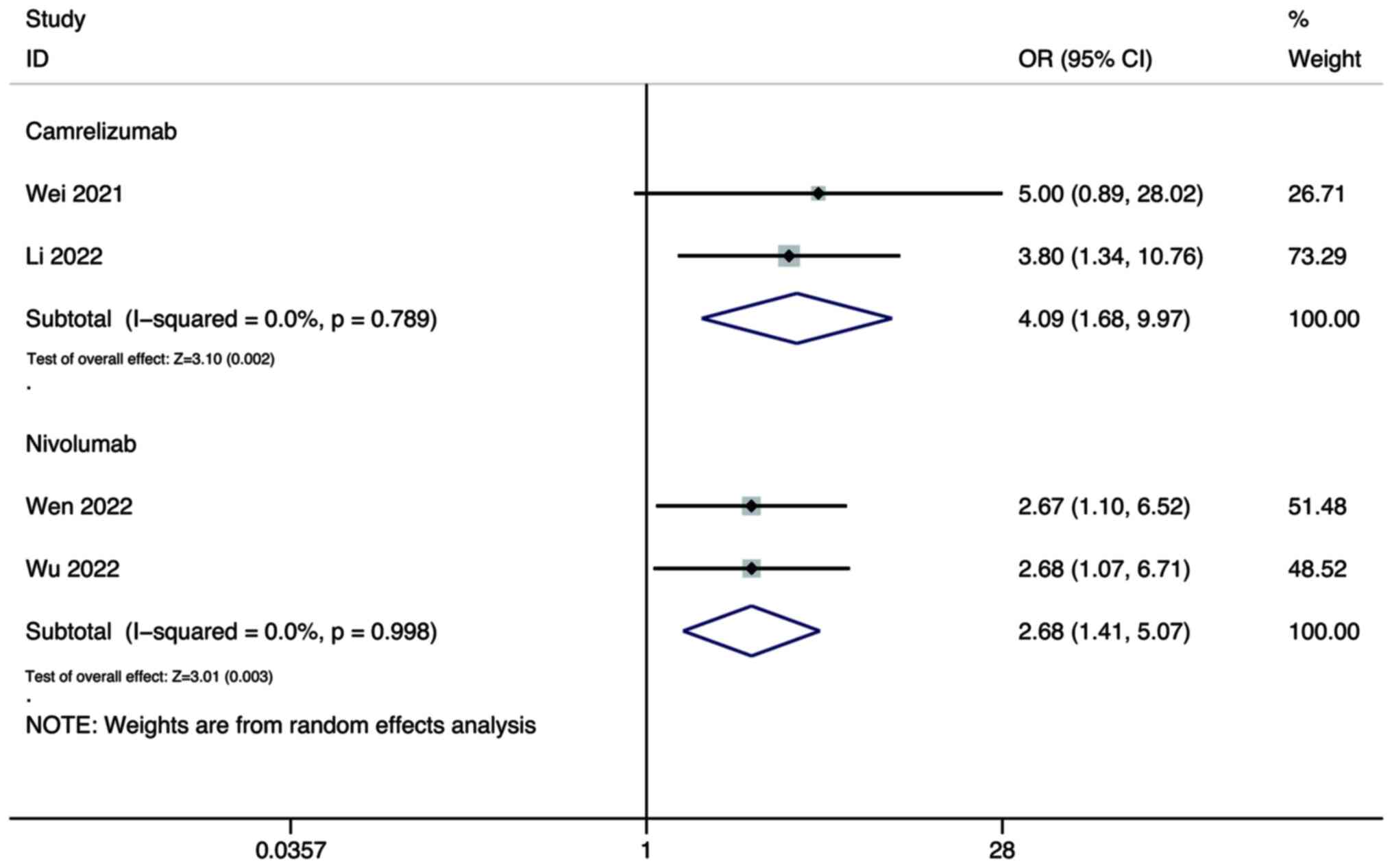
Wei F, Huang Q, He J, Luo L and Zeng Y:
Lenvatinib plus Camrelizumab versus Lenvatinib monotherapy as
post-progression treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A
short-term prognostic study. Cancer Manag Res. 13:4233–4240. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu S, Liu C, Dong Y, Shao J, Liu B and
Shen J: A retrospective study of lenvatinib monotherapy or combined
with programmed cell death protein 1 antibody in the treatment of
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma in China. Front Oncol. 11:7886352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Q, Cao M, Yuan G, Cheng X, Zang M, Chen
M, Hu X, Huang J, Li R, Guo Y, et al: Lenvatinib Plus Camrelizumab
vs. Lenvatinib Monotherapy as first-line treatment for unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicenter retrospective cohort study.
Front Oncol. 12:8097092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wen S, Zeng J, Zhong L, Ye J and Lai X:
The efficacy and adverse effects of nivolumab and lenvatinib in the
treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-grand). 68:53–57. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu WC, Lin TY, Chen MH, Hung YP, Liu CA,
Lee RC, Huang YH, Chao Y and Chen SC: Lenvatinib combined with
nivolumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma-real-world
experience. Invest New Drugs. 40:789–797. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miura S, Mitsuhashi N, Shimizu H, Kimura
F, Yoshidome H, Otsuka M, Kato A, Shida T, Okamura D and Miyazaki
M: Fibroblast growth factor 19 expression correlates with tumor
progression and poorer prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 12:562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matsuki M, Hoshi T, Yamamoto Y,
Ikemori-Kawada M, Minoshima Y, Funahashi Y and Matsui J: Lenvatinib
inhibits angiogenesis and tumor fibroblast growth factor signaling
pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma models. Cancer Med.
7:2641–2653. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin YY, Tan CT, Chen CW, Ou DL, Cheng AL
and Hsu C: Immunomodulatory effects of current targeted therapies
on hepatocellular carcinoma: Implication for the future of
immunotherapy. Semin Liver Dis. 38:379–388. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Adachi Y, Kamiyama H, Ichikawa K,
Fukushima S, Ozawa Y, Yamaguchi S, Goda S, Kimura T, Kodama K,
Matsuki M, et al: Inhibition of FGFR reactivates IFNgamma signaling
in tumor cells to enhance the combined antitumor activity of
lenvatinib with Anti-PD-1 antibodies. Cancer Res. 82:292–306. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kimura T, Kato Y, Ozawa Y, Kodama K, Ito
J, Ichikawa K, Yamada K, Hori Y, Tabata K, Takase K, et al:
Immunomodulatory activity of lenvatinib contributes to antitumor
activity in the Hepa1-6 hepatocellular carcinoma model. Cancer Sci.
109:3993–4002. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meng Y, Ye F, Nie P, Zhao Q, An L, Wang W,
Qu S, Shen Z, Cao Z, Zhang X, et al: Immunosuppressive CD10+ALPL+
neutrophils promote resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in HCC by
mediating irreversible exhaustion of T cells. J Hepatol.
79:1435–1449. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ma H, Kang Z, Foo TK, Shen Z and Xia B:
Disrupted BRCA1-PALB2 interaction induces tumor immunosuppression
and T-lymphocyte infiltration in HCC through cGAS-STING pathway.
Hepatology. 77:33–47. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|