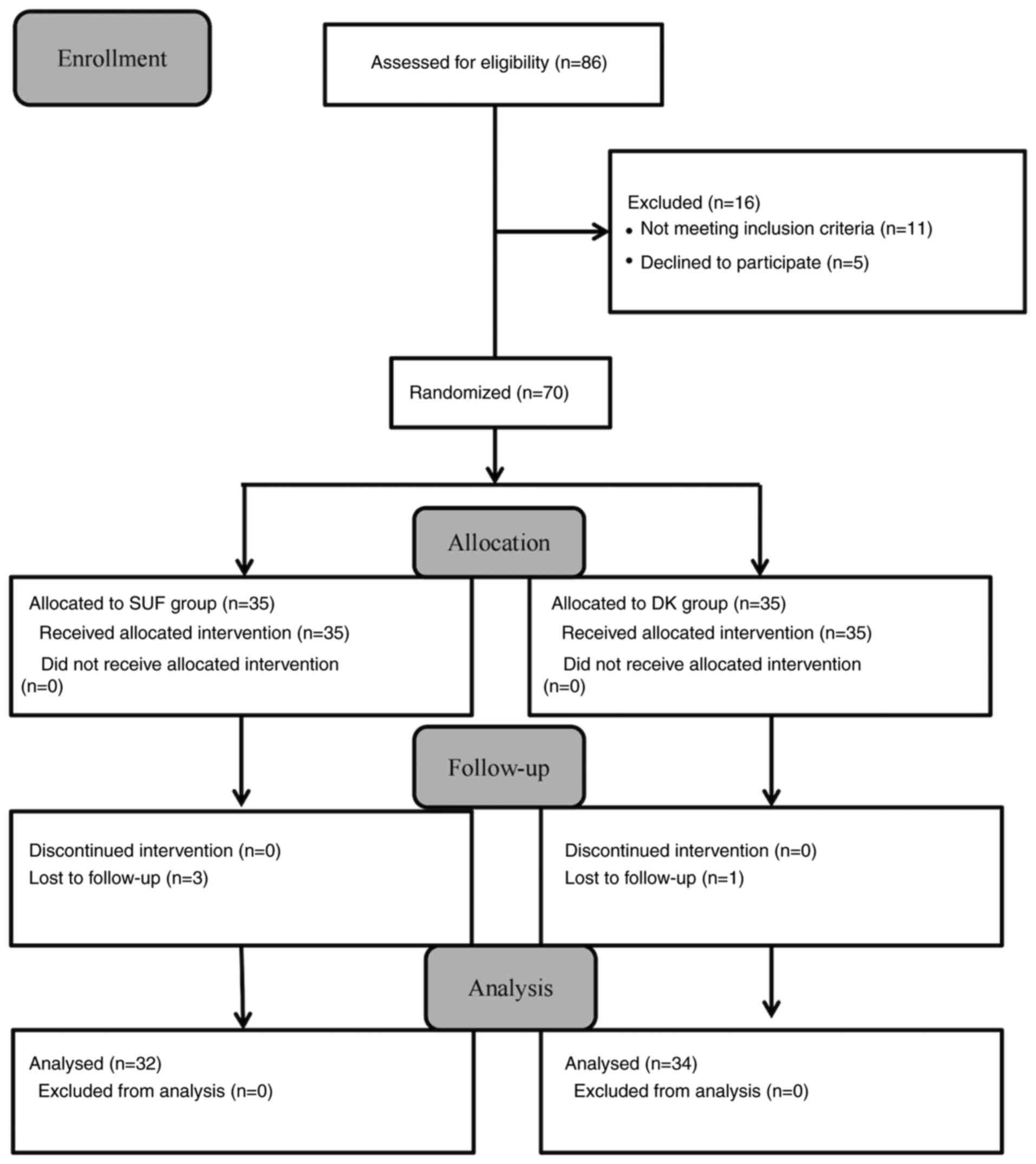
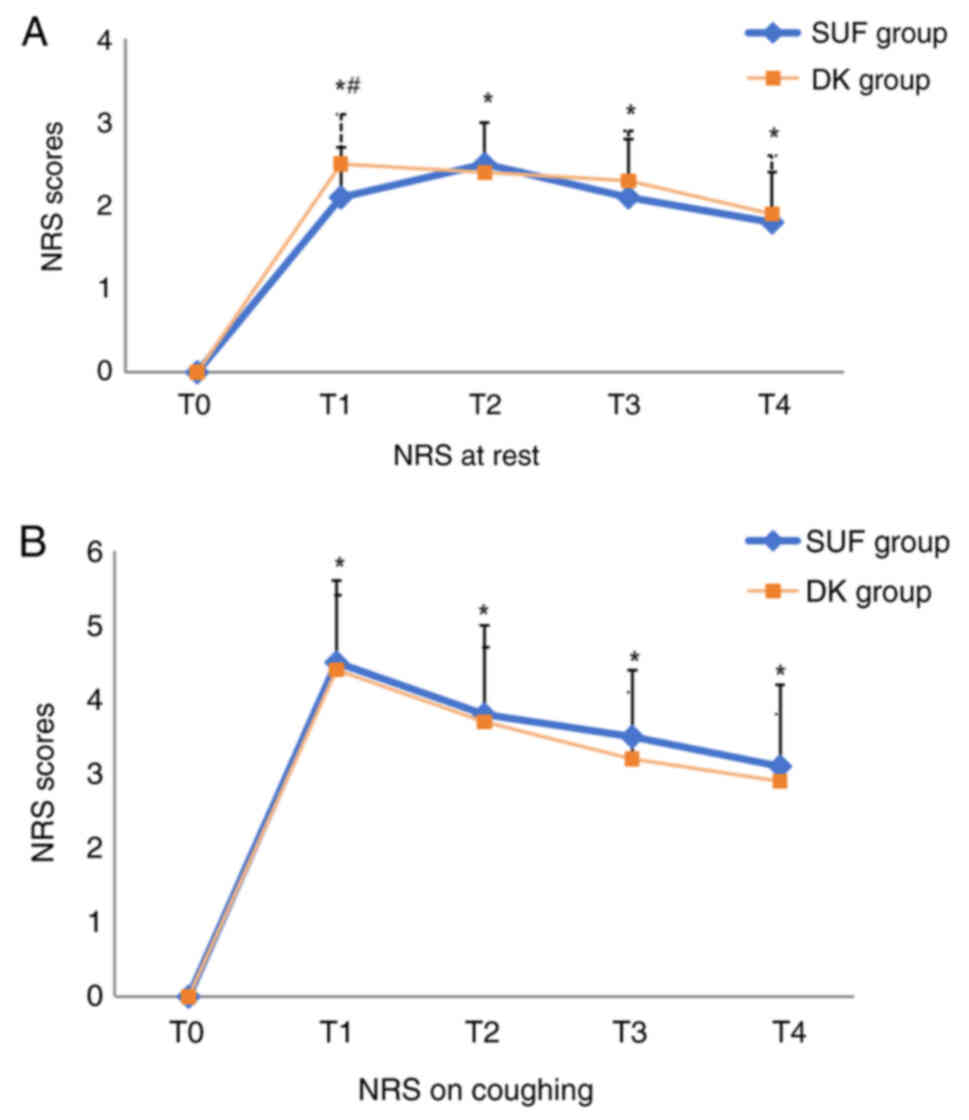
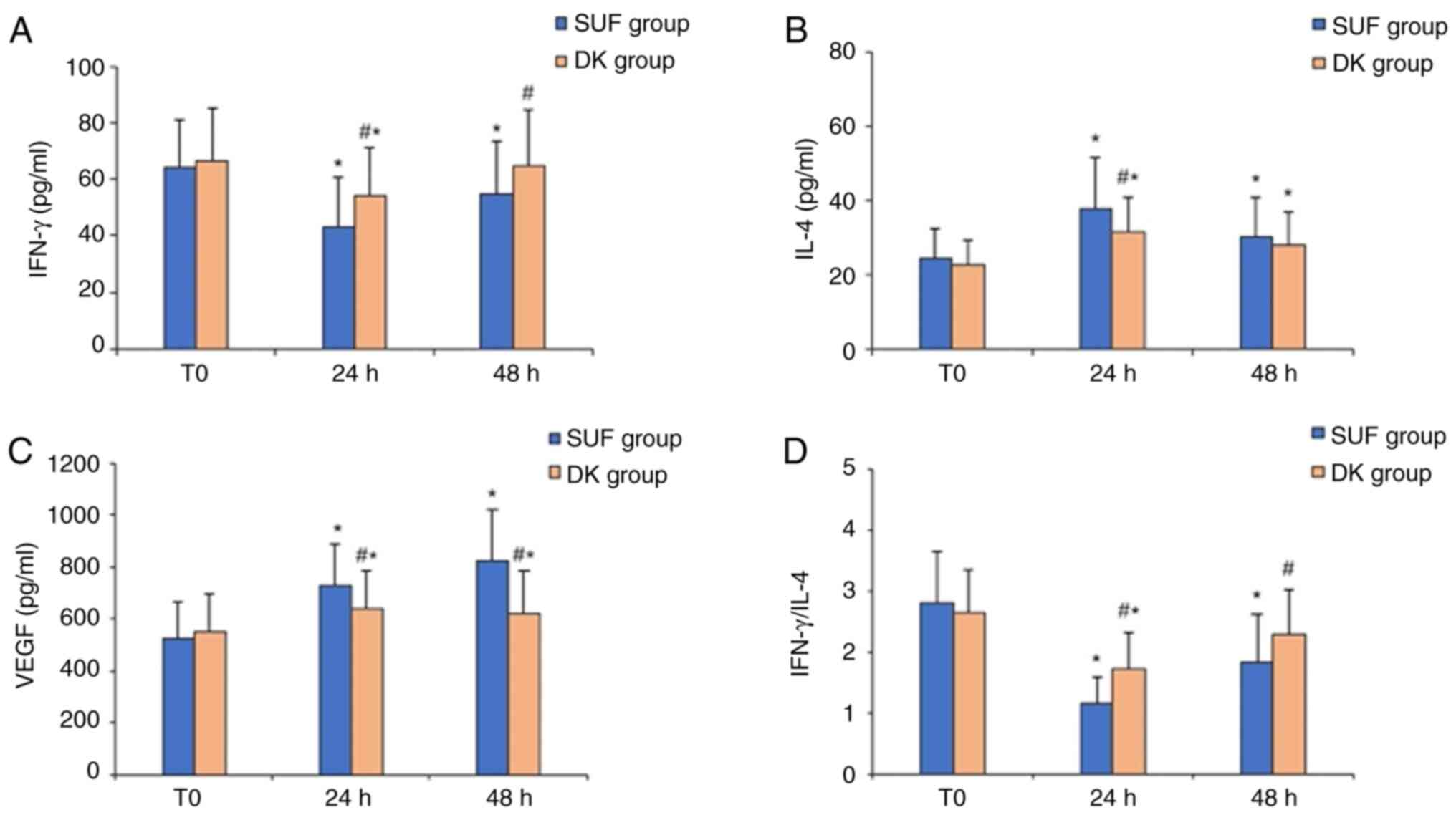
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hiller JG, Perry NJ, Poulogiannis G,
Riedel B and Sloan EK: Perioperative events influence cancer
recurrence risk after surgery. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018.15:205–218.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Manders P, Beex LV, Tjan-Heijnen VC, Span
PN and Sweep CG: Vascular endothelial growth factor is associated
with the efficacy of endocrine therapy in patients with advanced
breast carcinoma. Cancer. 98:2125–2132. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cho JS, Lee MH, Kim SI, Park S, Park HS,
Oh E, Lee JH and Koo BN: The effects of perioperative anesthesia
and analgesia on immune function in patients undergoing breast
cancer resection: A prospective randomized study. Int J Med Sci.
14:970–976. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Snyder GL and Greenberg S: Effect of
anaesthetic technique and other perioperative factors on cancer
recurrence. Br J Anaesth. 105:106–115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ogawa K, Hirai M, Katsube T, Murayama M,
Hamaguchi K, Shimakawa T, Naritake Y, Hosokawa T and Kajiwara T:
Suppression of cellular immunity by surgical stress. Surgery.
127:329–336. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shafi S, Collinsworth AW, Copeland LA,
Ogola GO, Qiu T, Kouznetsova M, Liao IC, Mears N, Pham AT, Wan GJ
and Masica AL: Association of opioid-related adverse drug events
with clinical and cost outcomes among surgical patients in a large
integrated health care delivery system. JAMA Surg. 153:757–763.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Xu X, Liu H and Ji F: Effects of
dexmedetomidine on patients undergoing radical gastrectomy. J Surg
Res. 194:147–153. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li B, Li Y, Tian S, Wang H, Wu H, Zhang A
and Gao C: Anti-inflammatory effects of perioperative
dexmedetomidine administered as an adjunct to general anesthesia: A
meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 5:123422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rainsford KD: Ibuprofen: Pharmacology,
efficacy and safety. Inflammopharmacology. 17:275–342. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cepeda MS, Carr DB, Miranda N, Diaz A,
Silva C and Morales O: Comparison of morphine, ketorolac, and their
combination for postoperative pain. Anesthesiology. 103:1225–1232.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Foekens JA, Peters HA, Grebenchtchikov N,
Look MP, Meijer-van Gelder ME, Geurts-Moespot A, van der Kwast TH,
Sweep CG and Klijn JG: High tumor levels of vascular endothelial
growth factor predict poor response to systemic therapy in advanced
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 61:5407–5414. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Jiang L, Wang J, Chai Z and Xiong
W: Morphine promotes angiogenesis by activating PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α
pathway and upregulating VEGF in hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Gastrointest Oncol. 12:1761–1772. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singleton PA and Moss J: Effect of
perioperative opioids on cancer recurrence: A hypothesis. Future
Oncol. 6:1237–1242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Singleton PA, Garcia JG and Moss J:
Synergistic effects of methylnaltrexone with 5-fluorouracil and
bevacizumab on inhibition of vascular endothelial growth
factor-induced angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:1669–1679. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martinez L, Ekman E and Nakhla N:
Perioperative opioid-sparing strategies: Utility of Conventional
NSAIDs in Adults. Clin Ther. 41:2612–2628. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Adurthi S, Mukherjee G, Krishnamurthy H,
Sudhir K, Bafna UD, Umadevi K and Jayshree RS: Functional tumor
infiltrating TH1 and TH2 effectors in large early-stage cervical
cancer are suppressed by regulatory T cells. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
22:1130–1107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ma J, Liu H and Wang X: Effect of ginseng
polysaccharides and dendritic cells on the balance of Th1/Th2 T
helper cells in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Tradit
Chin Med. 34:641–645. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guideline for Good Clinical Practice
E6(R1) 1996, . International Conference on Harmonization of
Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for
Human Use. ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guideline. Accessed May 12,
2015. http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Efficacy/E6/E6_R1_Guideline.pdf
|
|
20
|
American Society of Anesthesiologists, .
ASA physical status classification system. November
23–2018https://www.asahq.org/resources/AmericanSociety of
Anesthesiologists.
|
|
21
|
Green JS and Tsui BC: Impact of anesthesia
for cancer surgery: Continuing professional development. Can J
Anaesth. 60:1248–1269. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wen Y, Wang M, Yang J, Wang Y, Sun H, Zhao
J, Liu W, Zhou Z, Deng H, Castillo-Pedraza C, et al: A comparison
of fentanyl and flurbiprofen axetil on serum VEGF-C, TNF-α, and
IL-1ß concentrations in women undergoing surgery for breast cancer.
Pain Practice. 15:530–537. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hudson LG, Cook LS, Grimes MM, Muller CY,
Adams SF and Wandinger-Ness A: Dual actions of ketorolac in
metastatic ovarian cancer. Cancers (Basel). 11:10492019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Butcher B, Hutchings E, Fazekas B, Clark
K, Rowett D and Currow D: Opioid-sparing effects of ketorolac in
palliative care patients receiving opioids for chronic
cancer-related pain: A systematic literature review. Palliat Med.
36:71–80. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang W, Pan Y, Gou P, Zhou C, Ma L, Liu
Q, Du Y, Yang J and Wang Q: Effect of xanthohumol on Th1/Th2
balance in a breast cancer mouse model. Oncol Rep. 39:280–288.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hao CJ, Li J, Liu P, Li XL, Hu YQ, Sun JC
and Wei Y: Effects of the balance between type 1 and type 2 T
helper cells on ovarian cancer. Genet Mol Res. 15:2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Webster NR and Galley HF: Immunomodulation
in the critically ill. Br J Anaesth. 103:70–81. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liao W, Lin JX and Leonard WJ: IL-2 family
cytokines: New insights into the complex roles of IL-2 as a broad
regulator of T helper cell differentiation. Curr Opin Immunol.
23:598–604. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kurosawa S and Kato M: Anesthetics, immune
cells, and immune responses. J Anesth. 22:263–277. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cardinale F, Chinellato I, Caimmi S,
Peroni DG, Franceschini F, Miraglia Del Giudice M and Bernardini R:
Perioperative Period: Immunological Modifications. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 24 (3 Suppl):S3–S12. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ueki M, Kawasaki T, Habe K, Hamada K,
Kawasaki C and Sata T: The effects of dexmedetomidine on
inflammatory mediators after cardiopulmonary bypass. Anaesthesia.
69:693–700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Hu B, Zou Y, Bo L, Wang J, Li J
and Luo Y: Dexmedetomidine premedication attenuates concanavalin
A-induced hepatitis in mice. J Toxicol Sci. 39:755–764. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee JM, Han HJ, Choi WK, Yoo S, Baek S and
Lee J: Immunomodulatory effects of intraoperative dexmedetomidine
on T helper 1, T helper 2, T helper 17 and regulatory T cells
cytokine levels and their balance: A prospective, randomised,
double-blind, dose-response clinical study. BMC Anesthesiol.
18:1642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Forget P, Vandenhende J, Berliere M,
MacHiels JP, Nussbaum B, Legrand C and De Kock M: Do intraoperative
analgesics influence breast cancer recurrence after mastectomy? A
retrospective analysis. Anesth Analg. 110:1630–1635. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guo Y, Kenney SR, Muller CY, Adams S,
Rutledge T, Romero E, Murray-Krezan C, Prekeris R, Sklar LA, Hudson
LG and Wandinger-Ness A: R-Ketorolac Targets Cdc42 and Rac1 and
alters ovarian cancer cell behaviors critical for invasion and
metastasis. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:2215–2227. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tsuboi I, Tanaka H, Nakao M, Shichijo S
and Itoh K: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs differentially
regulate cytokine production in human lymphocytes: Up-regulation of
TNF, IFN-gamma and IL-2, in contrast to down-regulation of IL-6
production. Cytokine. 7:372–379. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma XD, Li BP, Wang DL and Yang WS:
Postoperative benefits of dexmedetomidine combined with
flurbiprofen axetil after thyroid surgery. Exp Ther Med.
14:2148–2152. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang EV, Kim SJ, Donovan EL, Chen M, Gross
AC, Webster Marketon JI, Barsky SH and Glaser R: Norepinephrine
upregulates VEGF, IL-8, and IL-6 expression in human melanoma tumor
cell lines: Implications for stress-related enhancement of tumor
progression. Brain Behav Immun. 23:267–275. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gadducci A, Tana R, Cosio S and Genazzani
AR: The serum assay of tumour markers in the prognostic evaluation,
treatment monitoring and follow-up of patients with cervical
cancer: A review of the literature. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
66:10–20. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mitsuhashi A, Suzuka K, Yamazawa K, Matsui
H, Seki K and Sekiya S: Serum vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF) and VEGF-C levels as tumor markers in patients with cervical
carcinoma. Cancer. 103:724–730. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
van Trappen PO, Steele D, Lowe DG, Baithun
S, Beasley N, Thiele W, Weich H, Krishnan J, Shepherd JH, Pepper
MS, et al: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF)-C and VEGF-D, and their receptor VEGFR-3, during different
stages of cervical carcinogenesis. J Pathol. 201:544–554. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kotowicz B, Fuksiewicz M, Jonska-Gmyrek J,
Bidzinski M and Kowalska M: The assessment of the prognostic value
of tumor markers and cytokines as SCCAg, CYFRA 21.1, IL-6, VEGF and
sTNF receptors in patients with squamous cell cervical cancer,
particularly with early stage of the disease. Tumour Biol.
37:1271–1278. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Moon HS, Kim SC, Ahn JJ and Woo BH:
Concentration of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and
transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) in the serum of
patients with cervical cancer: Prediction of response. Int J
Gynecol Cancer. 10:151–156. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mabeta P and Steenkamp V: The VEGF/VEGFR
axis revisited: Implications for cance therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
23:155852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Garcia J, Hurwitz HI, Sandler AB, Miles D,
Coleman RL, Deurloo R and Chinot OL: Bevacizumab
(Avastin®) in cancer treatment: A review of 15 years of
clinical experience and future outlook. Cancer Treat Rev.
86:1020172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mirzaei A, Rashedi S, Akbari MR, Khatami F
and Aghamir SMK: Combined anticancer effects of simvastatin and
arsenic trioxide on prostate cancer cell lines via downregulation
of the VEGF and OPN isoforms genes. J Cell Mol Med. 26:2728–2740.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wei L, Sun C, Zhang Y, Han N and Sun S:
miR-503-5p inhibits colon cancer tumorigenesis, angiogenesis, and
lymphangiogenesis by directly downregulating VEGF-A. Gene Ther.
29:28–40. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ji C, Xiong Y, Pan X, Guo X, Li Z, Qian S,
Xu C, Yu DH and Liao WQ: Effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs on the increasing the incidence of colonic anastomosis in
rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6126–6134. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Farooqui M, Li Y, Rogers T, Poonawala T,
Griffin RJ, Song CW and Gupta K: COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib prevents
chronic morphine-induced promotion of angiogenesis, tumour growth,
metastasis and mortality, without compromising analgesia. Br J
Cancer. 97:1523–1531. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Davies G, Martin LA, Sacks N and Dowsett
M: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), aromatase and breast cancer:a possible
role for COX-2 inhibitors in breast cancer chemoprevention. Ann
Oncol. 13:669–678. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Su X, Fan Y, Yang L, Huang J, Qiao F, Fang
Y and Wang J: Dexmedetomidine expands monocytic myeloid-derived
suppressor cells and promotes tumour metastasis after lung cancer
surgery. J Transl Med. 16:3472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|