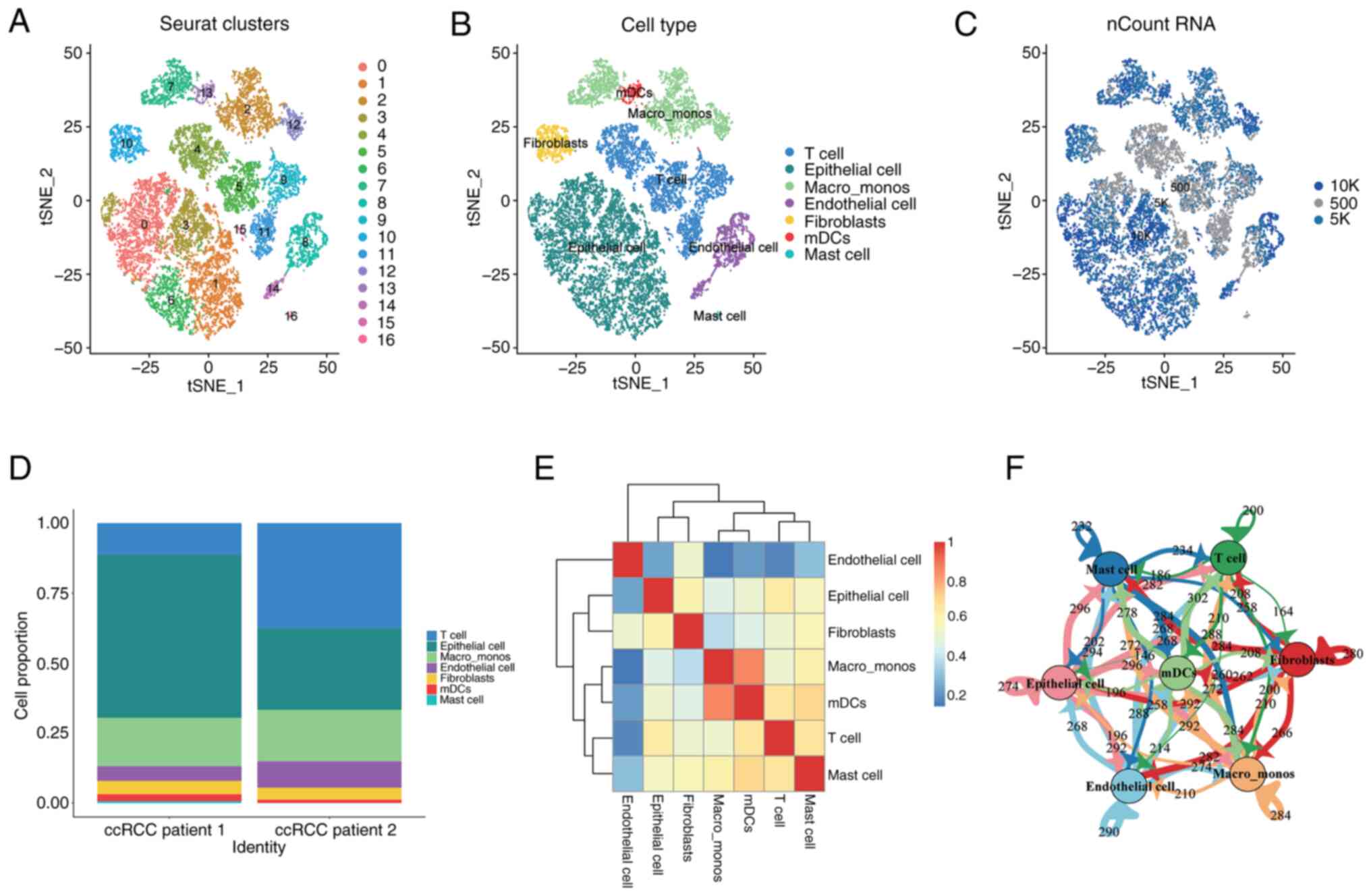
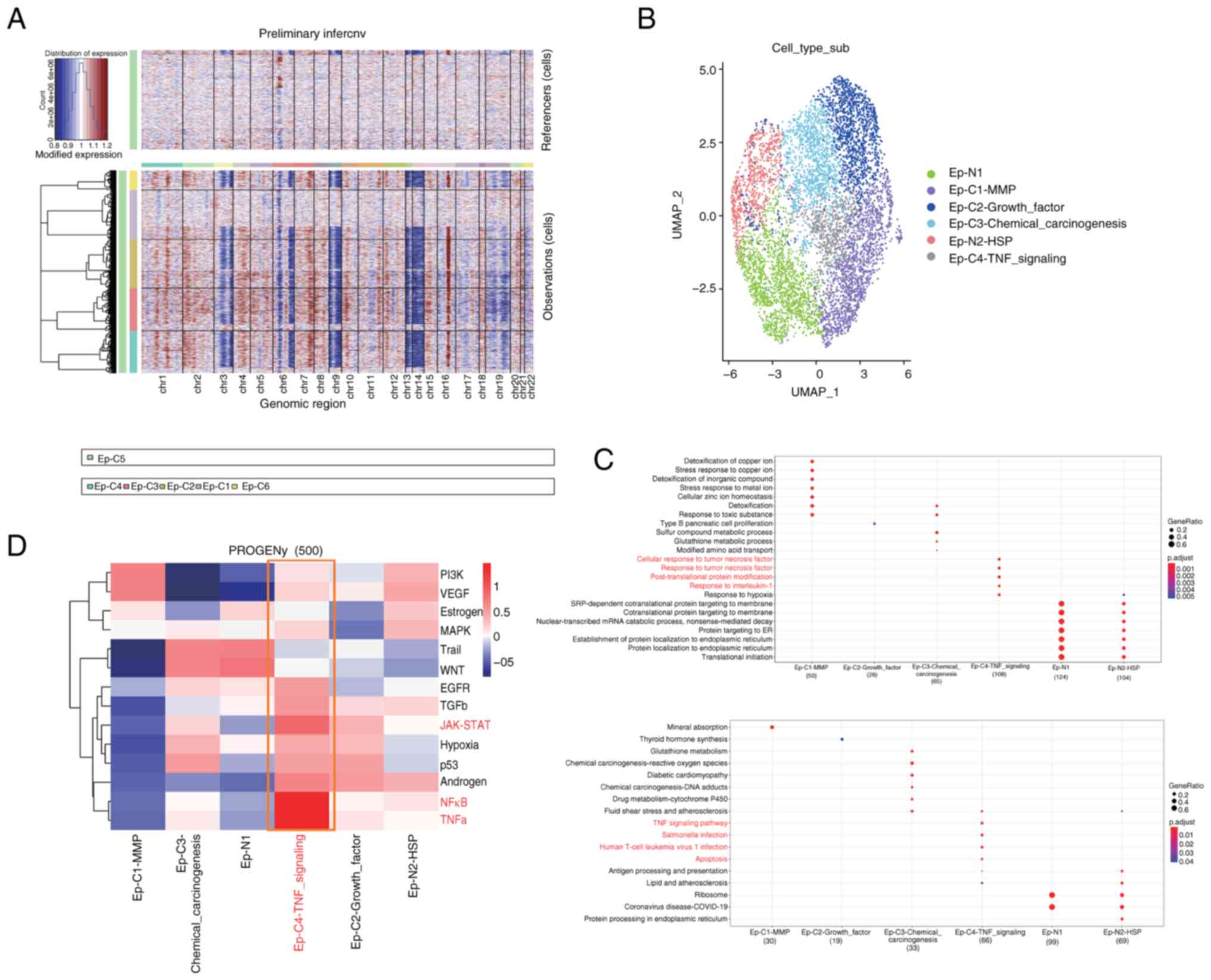
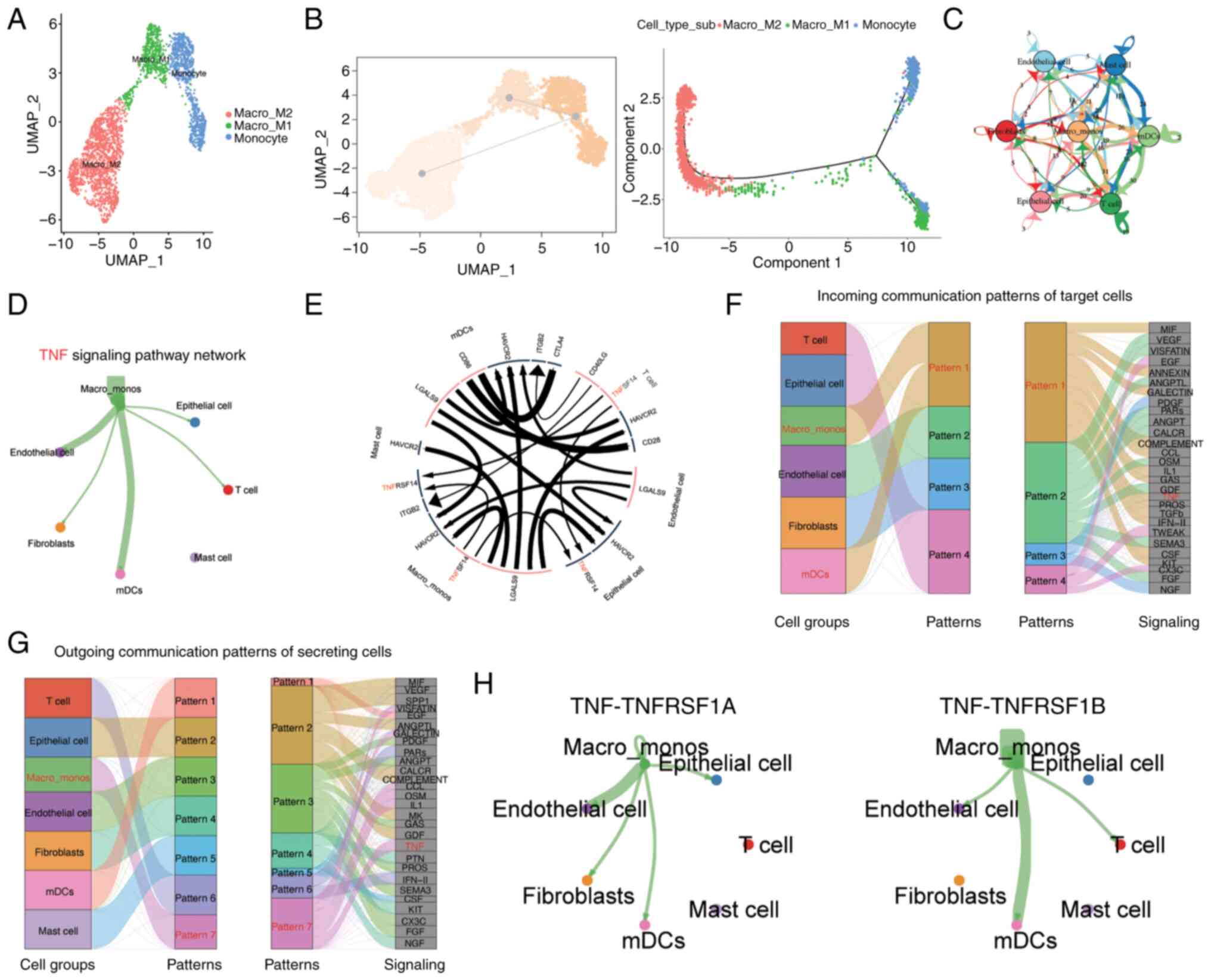
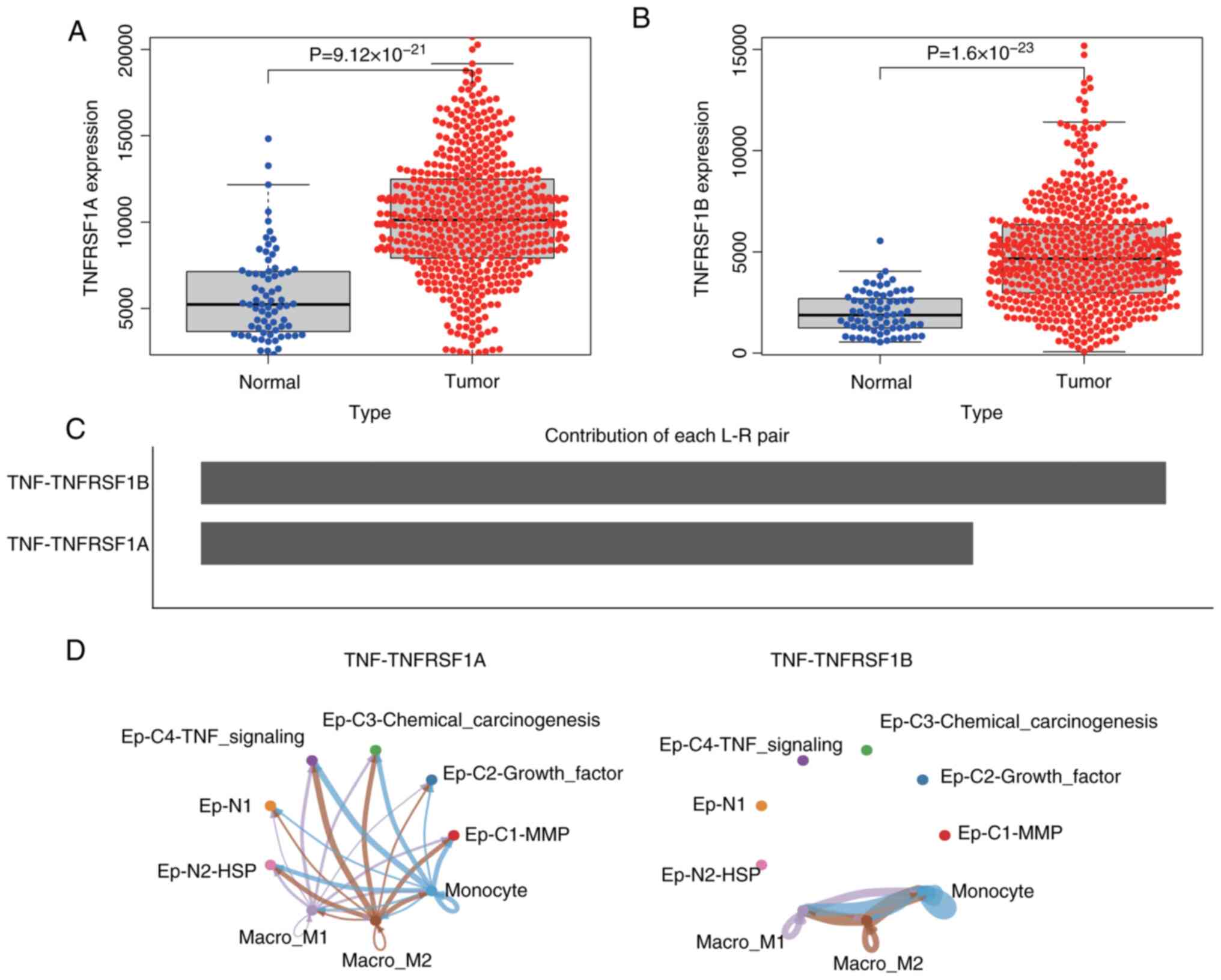
|
1
|
Capitanio U, Bensalah K, Bex A, Boorjian
SA, Bray F, Coleman J, Gore JL, Sun M, Wood C and Russo P:
Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 75:74–84. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cirillo L, Innocenti S and Becherucci F:
Global epidemiology of kidney cancer. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
39:920–928. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Choueiri TK: Renal cell carcinoma. Hematol
Oncol Clin North Am. 25:xiii–xiv. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Diaz-Montero CM, Rini BI and Finke JH: The
immunology of renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Nephrol. 16:721–735.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chowdhury N and Drake CG: Kidney cancer:
An overview of current therapeutic approaches. Urol Clin North Am.
47:419–431. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bahadoram S, Davoodi M, Hassanzadeh S,
Bahadoram M, Barahman M and Mafakher L: Renal cell carcinoma: An
overview of the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. G Ital
Nefrol. 39:2022–vol3. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gray RE and Harris GT: Renal cell
carcinoma: Diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 99:179–184.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hancock SB and Georgiades CS: Kidney
cancer. Cancer J. 22:387–392. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li F, Aljahdali IAM, Zhang R, Nastiuk KL,
Krolewski JJ and Ling X: Kidney cancer biomarkers and targets for
therapeutics: Survivin (BIRC5), XIAP, MCL-1, HIF1alpha, HIF2alpha,
NRF2, MDM2, MDM4, p53, KRAS and AKT in renal cell carcinoma. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 40:2542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sharma R, Kadife E, Myers M, Kannourakis
G, Prithviraj P and Ahmed N: Determinants of resistance to VEGF-TKI
and immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:1862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tonooka A and Ohashi R: Current trends in
anti-cancer molecular targeted therapies: Renal complications and
their histological features. J Nippon Med Sch. 89:128–138. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miao D, Margolis CA, Gao W, Voss MH, Li W,
Martini DJ, Norton C, Bossé D, Wankowicz SM, Cullen D, et al:
Genomic correlates of response to immune checkpoint therapies in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Science. 359:801–806. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Topalian SL, Taube JM, Anders RA and
Pardoll DM: Mechanism-driven biomarkers to guide immune checkpoint
blockade in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:275–287. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fischer R, Kontermann RE and Pfizenmaier
K: Selective targeting of TNF receptors as a novel therapeutic
approach. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:4012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu W, Yan B, Yu H, Ren J, Peng M, Zhu L,
Wang Y, Jin X and Yi L: OTUD1 stabilizes PTEN to inhibit the
PI3K/AKT and TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB signaling pathways and sensitize
ccRCC to TKIs. Int J Biol Sci. 18:1401–1414. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Richter F, Williams SK, John K, Huber C,
Vaslin C, Zanker H, Fairless R, Pichi K, Marhenke S, Vogel A, et
al: The TNFR1 antagonist atrosimab is therapeutic in mouse models
of acute and chronic inflammation. Front Immunol. 12:7054852021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su C, Lv Y, Lu W, Yu Z, Ye Y, Guo B, Liu
D, Yan H, Li T, Zhang Q, et al: Single-Cell RNA sequencing in
multiple pathologic types of renal cell carcinoma revealed novel
potential tumor-specific markers. Front Oncol. 11:7195642021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu J, Fan Z, Zhao W and Zhou X: Machine
intelligence in single-cell data analysis: Advances and new
challenges. Front Genet. 12:6555362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Street K, Risso D, Fletcher RB, Das D,
Ngai J, Yosef N, Purdom E and Dudoit S: Slingshot: Cell lineage and
pseudotime inference for single-cell transcriptomics. BMC Genomics.
19:4772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Armingol E, Officer A, Harismendy O and
Lewis NE: Deciphering cell-cell interactions and communication from
gene expression. Nat Rev Genet. 22:71–88. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jin S, Guerrero-Juarez CF, Zhang L, Chang
I, Ramos R, Kuan CH, Myung P, Plikus MV and Nie Q: Inference and
analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat. Nat Commun.
12:10882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chandrashekar DS, Karthikeyan SK, Korla
PK, Patel H, Shovon AR, Athar M, Netto GJ, Qin ZS, Kumar S, Manne
U, et al: UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis
platform. Neoplasia. 25:18–27. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Balkwill F: Tumour necrosis factor and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:361–371. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saha P and Smith A: TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis
Factor-α). Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 38:2542–2543. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Eisenman ST, Gibbons SJ, Verhulst PJ,
Cipriani G, Saur D and Farrugia G: Tumor necrosis factor alpha
derived from classically activated ‘M1’ macrophages reduces
interstitial cell of Cajal numbers. Neurogastroenterol Motil.
29:10.1111. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S,
Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, Seifi B, Mohammadi
A, Afshari JT and Sahebkar A: Macrophage plasticity, polarization,
and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 233:6425–6440.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Garancher A, Suzuki H, Haricharan S, Chau
LQ, Masihi MB, Rusert JM, Norris PS, Carrette F, Romero MM,
Morrissy SA, et al: Tumor necrosis factor overcomes immune evasion
in p53-mutant medulloblastoma. Nat Neurosci. 23:842–853. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Masola V, Greco N, Tozzo P, Caenazzo L and
Onisto M: The role of SPATA2 in TNF signaling, cancer, and
spermatogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 13:9772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H and Hu H:
Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and
clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:2092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Balkwill F: TNF-alpha in promotion and
progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:409–416. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tacke F and Zimmermann HW: Macrophage
heterogeneity in liver injury and fibrosis. J Hepatol.
60:1090–1096. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Takahashi H, Yoshimatsu G and Faustman DL:
The roles of TNFR2 signaling in cancer cells and the tumor
microenvironment and the potency of TNFR2 targeted therapy. Cells.
11:19522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Speeckaert MM, Speeckaert R, Laute M,
Vanholder R and Delanghe JR: Tumor necrosis factor receptors:
Biology and therapeutic potential in kidney diseases. Am J Nephrol.
36:261–270. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hwang HS, Park YY, Shin SJ, Go H, Park JM,
Yoon SY, Lee JL and Cho YM: Involvement of the TNF-α pathway in TKI
resistance and suggestion of TNFR1 as a predictive biomarker for
TKI responsiveness in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Korean Med
Sci. 35:e312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dong B, Miao J, Wang Y, Luo W, Ji Z, Lai
H, Zhang M, Cheng X, Wang J, Fang Y, et al: Single-cell analysis
supports a luminal-neuroendocrine transdifferentiation in human
prostate cancer. Commun Biol. 3:7782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Couturier CP, Ayyadhury S, Le PU, Nadaf J,
Monlong J, Riva G, Allache R, Baig S, Yan X, Bourgey M, et al:
Single-cell RNA-seq reveals that glioblastoma recapitulates a
normal neurodevelopmental hierarchy. Nat Commun. 11:34062020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Braun DA, Hou Y, Bakouny Z, Ficial M,
Angelo MS, Forman J, Ross-Macdonald P, Berger AC, Jegede OA,
Elagina L, et al: Interplay of somatic alterations and immune
infiltration modulates response to PD-1 blockade in advanced clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat Med. 26:909–918. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Au L, Hatipoglu E, de Massy M, Litchfield
K, Beattie G, Rowan A, Schnidrig D, Thompson R, Byrne F, Horswell
S, et al: Determinants of anti-PD-1 response and resistance in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 39:1497–1518.
e14112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wajant H: The role of TNF in cancer.
Results Probl Cell Differ. 49:1–15. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gao M, Li X, Yang M, Feng W, Lin Y and He
T: TNFAIP3 mediates FGFR1 activation-induced breast cancer
angiogenesis by promoting VEGFA expression and secretion. Clin
Transl Oncol. 24:2453–2465. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Messeha SS, Zarmouh NO, Antonie L and
Soliman KFA: Sanguinarine inhibition of TNF-α-induced CCL2,
IKBKE/NF-κB/ERK1/2 signaling pathway, and cell migration in human
triple-negative breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 23:83292022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tomolonis JA, Xu X, Dholakia KH, Zhang C,
Guo L, Courtney AN, Wang S, Balzeau J, Barragán GA, Tian G, et al:
Interaction between tumor cell TNFR2 and monocyte membrane-bound
TNF-α triggers tumorigenic inflammation in neuroblastoma. J
Immunother Cancer. 11:e0054782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Naserian S, Abdelgawad ME, Bakshloo MA, Ha
G, Arouche N, Cohen JL, Salomon BL and Uzan G: The TNF/TNFR2
signaling pathway is a key regulatory factor in endothelial
progenitor cell immunosuppressive effect. Cell Commun Signal.
18:942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Siegmund D, Wagner J and Wajant H: TNF
receptor associated factor 2 (TRAF2) signaling in cancer. Cancers
(Basel). 14:40552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hira K and Begum AS: Methods for
evaluation of TNF-α inhibition effect. Methods Mol Biol.
2248:271–279. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xing-Rong W, Sheng-Qian X, Wen L, Shan Q,
Fa-Ming P and Jian-Hua X: Role of TNFRSF1A and TNFRSF1B
polymorphisms in susceptibility, severity, and therapeutic efficacy
of etanercept in human leukocyte antigen-B27-positive Chinese Han
patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Medicine (Baltimore).
97:e116772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shi G and Hu Y: TNFR1 and TNFR2, which
link NF-κB activation, drive lung cancer progression, cell
dedifferentiation, and metastasis. Cancers (Basel). 15:42992023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Miller PG, Bonn MB and McKarns SC:
Transmembrane TNF-TNFR2 impairs Th17 differentiation by promoting
Il2 expression. J Immunol. 195:2633–2647. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|