|
1
|
Sung PS, Park DJ, Roh PR, Mun KD, Cho SW,
Lee GW, Jung ES, Lee SH, Jang JW, Bae SH, et al: Intrahepatic
inflammatory IgA+PD-L1high monocytes in
hepatocellular carcinoma development and immunotherapy. J
Immunother Cancer. 10:e0036182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mun K, Han J, Roh P, Park J, Kim G, Hur W,
Jang J, Choi J, Yoon S, You Y, et al: Isolation and
characterization of cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor
microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Liver Cancer.
23:341–349. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tumen D, Heumann P, Gulow K, Demirci CN,
Cosma LS, Muller M and Kandulski A: Pathogenesis and current
treatment strategies of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomedicines.
10:32022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alawyia B and Constantinou C:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: A narrative review on current knowledge
and future prospects. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 24:711–724. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thandra KC and Barsouk A, Saginala K,
Aluru JS, Rawla P and Barsouk A: Epidemiology of non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. Clin Exp Hepatol. 6:289–294. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim GA, Moon JH and Kim W: Critical
appraisal of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver
disease: Implication of Janus-faced modernity. Clin Mol Hepatol.
29:831–843. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gallego-Durán R, Albillos A, Ampuero J,
Arechederra M, Bañares R, Blas-García A, Berná G, Caparrós E,
Delgado TC, Falcón-Pérez JM, et al: Metabolic-associated fatty
liver disease: From simple steatosis toward liver cirrhosis and
potential complications. Proceedings of the third translational
hepatology meeting, organized by the Spanish association for the
study of the liver (AEEH). Gastroenterol Hepatol. 45:724–734.
2022.(In English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Angeli-Pahim I, Chambers A, Duarte S and
Zarrinpar A: Current trends in surgical management of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 15:53782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yoon JH and Choi SK: Management of
early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: Challenges and strategies for
optimal outcomes. J Liver Cancer. 23:300–315. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jost-Brinkmann F, Demir M, Wree A, Luedde
T, Loosen SH, Müller T, Tacke F, Roderburg C and Mohr R:
Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma: Results from a German real-world cohort. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 57:1313–1325. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sung PS: Crosstalk between
tumor-associated macrophages and neighboring cells in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol. 28:333–350. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Li G, Liu X, Song Y, Xie J, Li G,
Ren J, Wang H, Mou J, Dai J, et al: Sorafenib inhibited cell growth
through the MEK/ERK signaling pathway in acute promyelocytic
leukemia cells. Oncol Lett. 15:5620–5626. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Habiba YH, Omran GA, Helmy MW and Houssen
ME: Antitumor effects of rhamnazinon sorafenib-treated human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines via modulation of VEGF
signaling and PI3K/NF-κB p38/caspase-3 axes cross talk. Life Sci.
297:1204432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Xuan S, Dong P, Xiang Z, Gao C, Li
M, Huang L and Wu J: Immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma:
Recent progress and new strategy. Front Immunol. 14:11925062023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tian X, Yan T, Liu F, Liu Q, Zhao J, Xiong
H and Jiang S: Link of sorafenib resistance with the tumor
microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanistic insights.
Front Pharmacol. 13:9910522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hiebinger F, Kudulyte A, Chi H, Burbano De
Lara S, Ilic D, Helm B, Welsch H, Dao Thi VL, Klingmüller U and
Binder M: Tumour cells can escape antiproliferative pressure by
interferon-β through immunoediting of interferon receptor
expression. Cancer Cell Int. 23:3152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Blaszczyk K, Nowicka H, Kostyrko K,
Antonczyk A, Wesoly J and Bluyssen HAR: The unique role of STAT2 in
constitutive and IFN-induced transcription and antiviral responses.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 29:71–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Au-Yeung N, Mandhana R and Horvath CM:
Transcriptional regulation by STAT1 and STAT2 in the interferon
JAK-STAT pathway. JAKSTAT. 2:e239312013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Platanitis E, Demiroz D, Schneller A,
Fischer K, Capelle C, Hartl M, Gossenreiter T, Muller M,
Novatchkova M and Decker T: A molecular switch from STAT2-IRF9 to
ISGF3 underlies interferon-induced gene transcription. Nat Commun.
10:29212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee CJ, An HJ, Cho ES, Kang HC, Lee JY,
Lee HS and Cho YY: Stat2 stability regulation: An intersection
between immunity and carcinogenesis. Exp Mol Med. 52:1526–1536.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sung PS, Cheon H, Cho CH, Hong SH, Park
DY, Seo HI, Park SH, Yoon SK, Stark GR and Shin EC: Roles of
unphosphorylated ISGF3 in HCV infection and interferon
responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:10443–10448. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheon H, Holvey-Bates EG, Schoggins JW,
Forster S, Hertzog P, Imanaka N, Rice CM, Jackson MW, Junk DJ and
Stark GR: IFNβ-dependent increases in STAT1, STAT2, and IRF9
mediate resistance to viruses and DNA damage. EMBO J. 32:2751–2763.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheon H, Wang YX, Wightman SM, Jackson MW
and Stark GR: How cancer cells make and respond to interferon-I.
Trends Cancer. 9:83–92. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jung H, Choi J, Park J and Ahn J: A novel
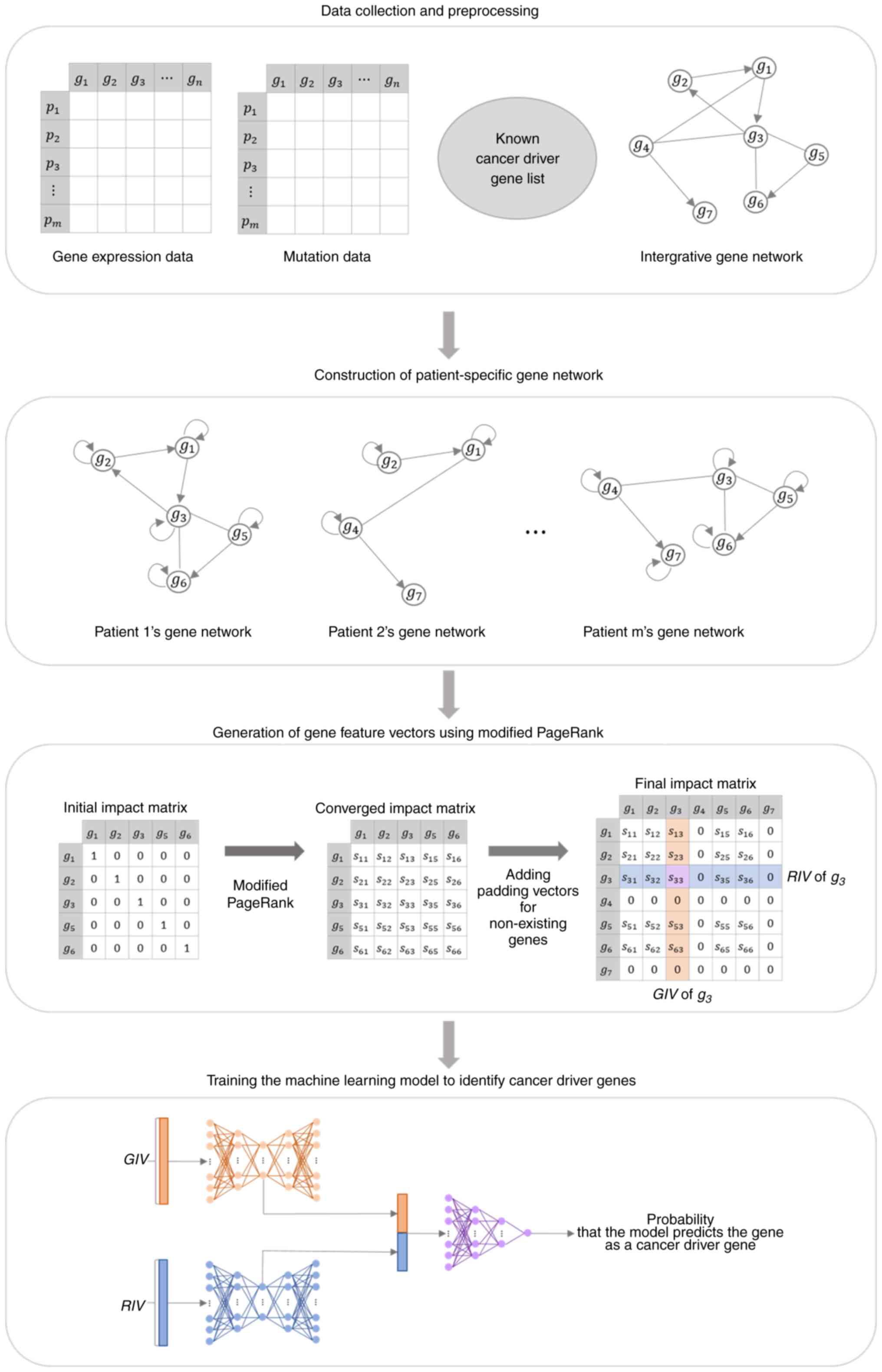
machine learning model for identifying patient-specific cancer
driver genes. IEEE Access. 10:54245–54253. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tomczak K, Czerwińska P and Wiznerowicz M:
The cancer genome atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of
knowledge. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 19:A68–A77. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Croft D, O'Kelly G, Wu G, Haw R, Gillespie
M, Matthews L, Caudy M, Garapati P, Gopinath G, Jassal B, et al:
Reactome: A database of reactions, pathways and biological
processes. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:(Database Issue). D691–D697. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu ZP, Wu C, Miao H and Wu H: RegNetwork:
An integrated database of transcriptional and post-transcriptional
regulatory networks in human and mouse. Database (Oxford).
2015:bav0952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sondka Z, Bamford S, Cole CG, Ward SA,
Dunham I and Forbes SA: The COSMIC cancer gene census: Describing
genetic dysfunction across all human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer.
18:696–705. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gundem G, Perez-Llamas C, Jene-Sanz A,
Kedzierska A, Islam A, Deu-Pons J, Furney SJ and Lopez-Bigas N:
IntOGen: Integration and data mining of multidimensional
oncogenomic data. Nat Methods. 7:92–93. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ewels P, Magnusson M, Lundin S and Käller
M: MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and
samples in a single report. Bioinformatics. 32:3047–3048. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bray NL, Pimentel H, Melsted P and Pachter
L: Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat
Biotechnol. 34:525–527. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Marx V: Genomics in the clouds. Nat
Methods. 10:941–945. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang W, Yin Y, Xu L, Su J, Huang F, Wang
Y, Boor PPC, Chen K, Wang W, Cao W, et al: Unphosphorylated ISGF3
drives constitutive expression of interferon-stimulated genes to
protect against viral infections. Sci Signal. 10:eaah42482017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhou W, Lou W, Chen J, Ding B, Chen B, Xie
H, Zhou L, Zheng S and Jiang D: AG-1024 sensitizes
sorafenib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib via
enhancing G1/S arrest. Onco Targets Ther. 14:1049–1059. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guo L, Hu C, Yao M and Han G: Mechanism of
sorafenib resistance associated with ferroptosis in HCC. Front
Pharmacol. 14:12074962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhai B and Sun XY: Mechanisms of
resistance to sorafenib and the corresponding strategies in
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 5:345–352. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xia S, Pan Y, Liang Y, Xu J and Cai X: The
microenvironmental and metabolic aspects of sorafenib resistance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine. 51:1026102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun T, Liu H and Ming L: Multiple roles of
autophagy in the sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:716–727. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|