|
1
|
Toumazis I, Bastani M, Han SS and
Plevritis SK: Risk-based lung cancer screening: A systematic
review. Lung Cancer. 147:154–186. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chen P, Liu Y, Wen Y and Zhou C: Non-small
cell lung cancer in China. Cancer Commun (Lond). 42:937–970. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang M, Herbst RS and Boshoff C: Toward
personalized treatment approaches for non-small-cell lung cancer.
Nat Med. 27:1345–1356. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Osarogiagbon RU, Veronesi G, Fang W, Ekman
S, Suda K, Aerts JG and Donington J: Early-stage NSCLC: Advances in
thoracic oncology 2018. J Thorac Oncol. 14:968–978. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhou C: Lung cancer molecular epidemiology
in China: Recent trends. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 3:270–279.
2014.
|
|
6
|
Lima ABC, Macedo LT and Sasse AD: Addition
of bevacizumab to chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung
cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One.
6:e226812011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Han B, Li K, Wang Q, Zhang L, Shi J, Wang
Z, Cheng Y, He J, Shi Y, Zhao Y, et al: Effect of anlotinib as a
third-line or further treatment on overall survival of patients
with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: The ALTER 0303 phase 3
randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 4:1569–1575. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Apte RS, Chen DS and Ferrara N: VEGF in
signaling and disease: Beyond discovery and development. Cell.
176:1248–1264. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jiang T, Su C, Li X, Zhao C, Zhou F, Ren
S, Zhou C and Zhang J: EGFR TKIs plus WBRT demonstrated no survival
benefit other than that of TKIs alone in patients with NSCLC and
EGFR mutation and brain metastases. J Thorac Oncol. 11:1718–1728.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lee JH, Chen HY, Hsu FM, Chen JS, Liao WY,
Shih JY, Yu CJ, Chen KY, Tsai TH and Yang JC: Cranial irradiation
for patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant
lung cancer who have brain metastases in the era of a new
generation of EGFR inhibitors. Oncologist. 24:e1417–e1425. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang C, Lu X, Zhou Z, Wang J, Hui Z, Liang
J, Feng Q, Chen D, Xiao Z, Lv J, et al: The efficacy of upfront
intracranial radiation with TKI compared to TKI alone in the NSCLC
patients harboring EGFR mutation and brain metastases. J Cancer.
10:1985–1990. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gao Y, Liu P and Shi R: Anlotinib as a
molecular targeted therapy for tumors. Oncol Lett. 20:1001–1014.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mross K, Frost A, Steinbild S, Hedbom S,
Büchert M, Fasol U, Unger C, Krätzschmar J, Heinig R, Boix O and
Christensen O: A phase I dose-escalation study of regorafenib (BAY
73–4506), an inhibitor of oncogenic, angiogenic, and stromal
kinases, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
18:2658–2667. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Strumberg D, Richly H, Hilger RA,
Schleucher N, Korfee S, Tewes M, Faghih M, Brendel E, Voliotis D,
Haase CG, et al: Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of the
Novel Raf kinase and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
inhibitor BAY 43–9006 in patients with advanced refractory solid
tumors. J Clin Oncol. 23:965–972. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen XZ: Anlotinib for refractory advanced
non-small cell lung cancer in China. JAMA Oncol. 5:116–117. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhong R, Wang Y, Han B, et al:
Interpretation of the clinical diagnosis and treatment guidelines
for lung cancer (2022 edition) of the Chinese medical association.
Chin J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 29:1402–1406. 2022.
|
|
17
|
Chhetri P, Giri A, Shakya S, Shakya S,
Sapkota B and Pramod KC: Current development of anti-cancer drug
S-1. J Clin Diagn Res. 10:XE01–XE05. 2016.
|
|
18
|
Ma PQ: Research progress of new anti-tumor
drug Tegafur potassium. Chin J Med Guide. 499–502. 2007.
|
|
19
|
Cheng XW, Leng WH and Mu CL: Efficacy and
safety of S-1 maintenance therapy in advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer patients. World J Clin Cases. 8:5172–5179. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kawahara M: Efficacy of S-1 in non-small
cell lung cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 15:1927–1942. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Yi Y, Lin A, Luo P and Zhang J: A
comparison of the efficacy of antiangiogenic agents combined with
chemotherapy for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: A
network meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 20:5482020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Garon EB, Ciuleanu TE, Arrieta O, Prabhash
K, Syrigos KN, Goksel T, Park K, Gorbunova V, Kowalyszyn RD, Pikiel
J, et al: Ramucirumab plus docetaxel versus placebo plus docetaxel
for second-line treatment of stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer
after disease progression on platinum-based therapy (REVEL): A
multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet.
384:665–673. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Horn L and Sandler A: Chemotherapy and
antiangiogenic agents in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung
Cancer. 8 (Suppl 2):S68–S73. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
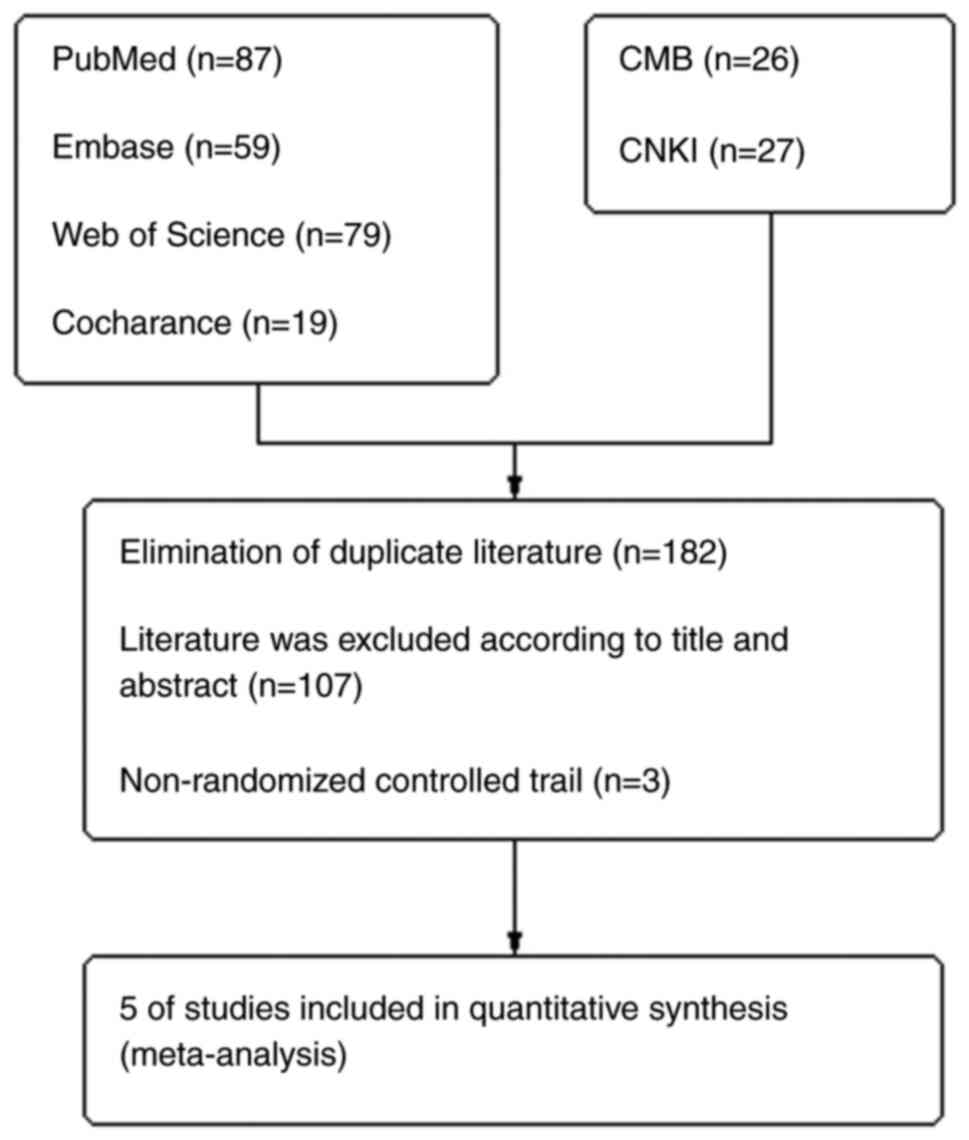
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG; PRISMA Group, : Preferred reporting items for systematic
reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int J Surg.
8:336–341. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
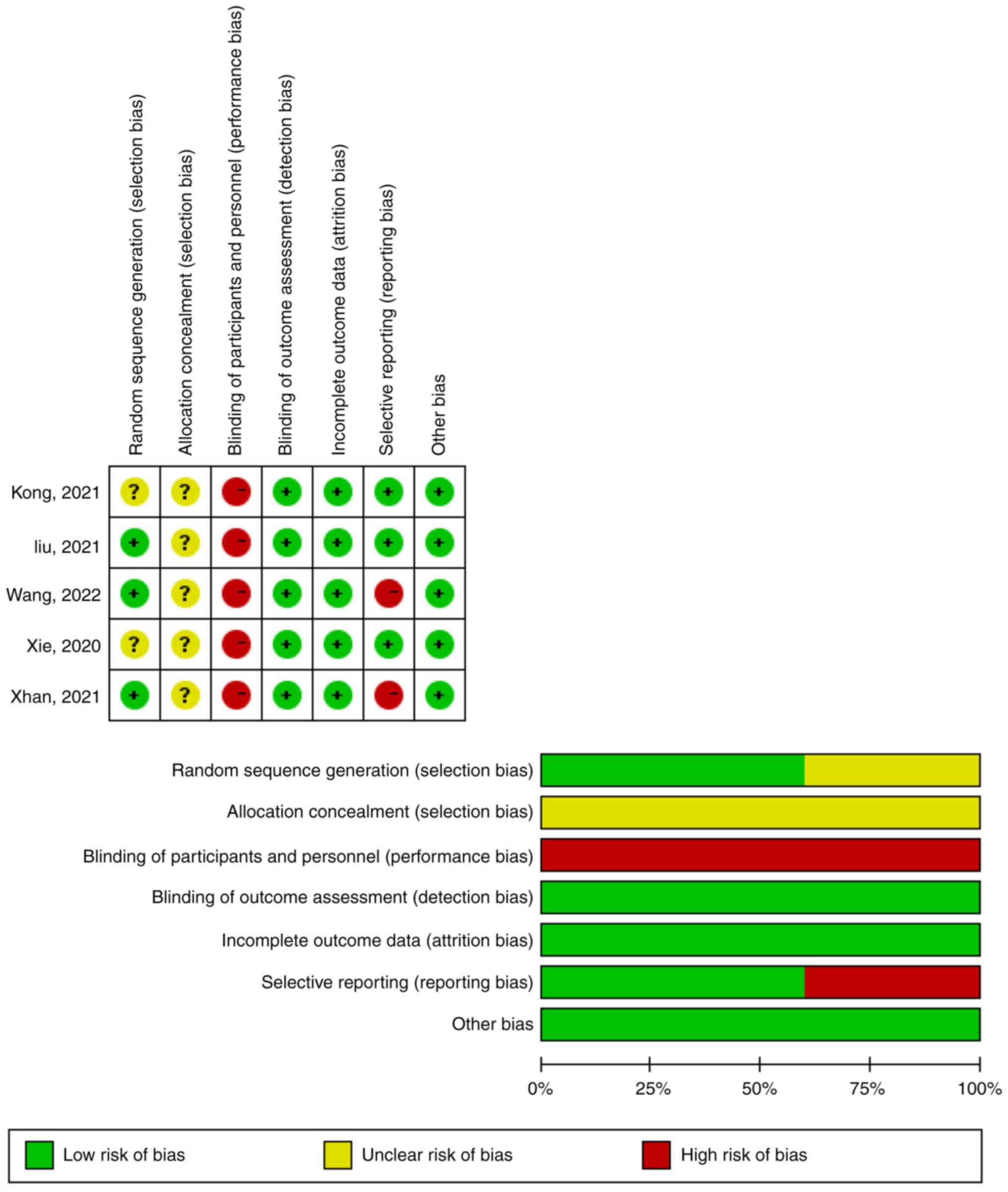
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni
P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA, et
al: The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 343:d59282011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J,
Welch VA, Higgins JP and Thomas J: Updated guidance for trusted
systematic reviews: A new edition of the Cochrane handbook for
systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
10:ED0001422019.
|
|
27
|
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J,
Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ and Welch VA: Cochrane handbook for
systematic reviews of interventions. 2nd edition. Chichester (UK):
John Wiley & Sons Ltd; 2019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang D, Zhai JX, Mou ZY, Zong HX, Zhao XD,
Wang XY and Gu P: Discussing on the research of heterogeneity in
meta-analysis. Chin J Evid-Based Med. 9:1115–1118. 2009.
|
|
29
|
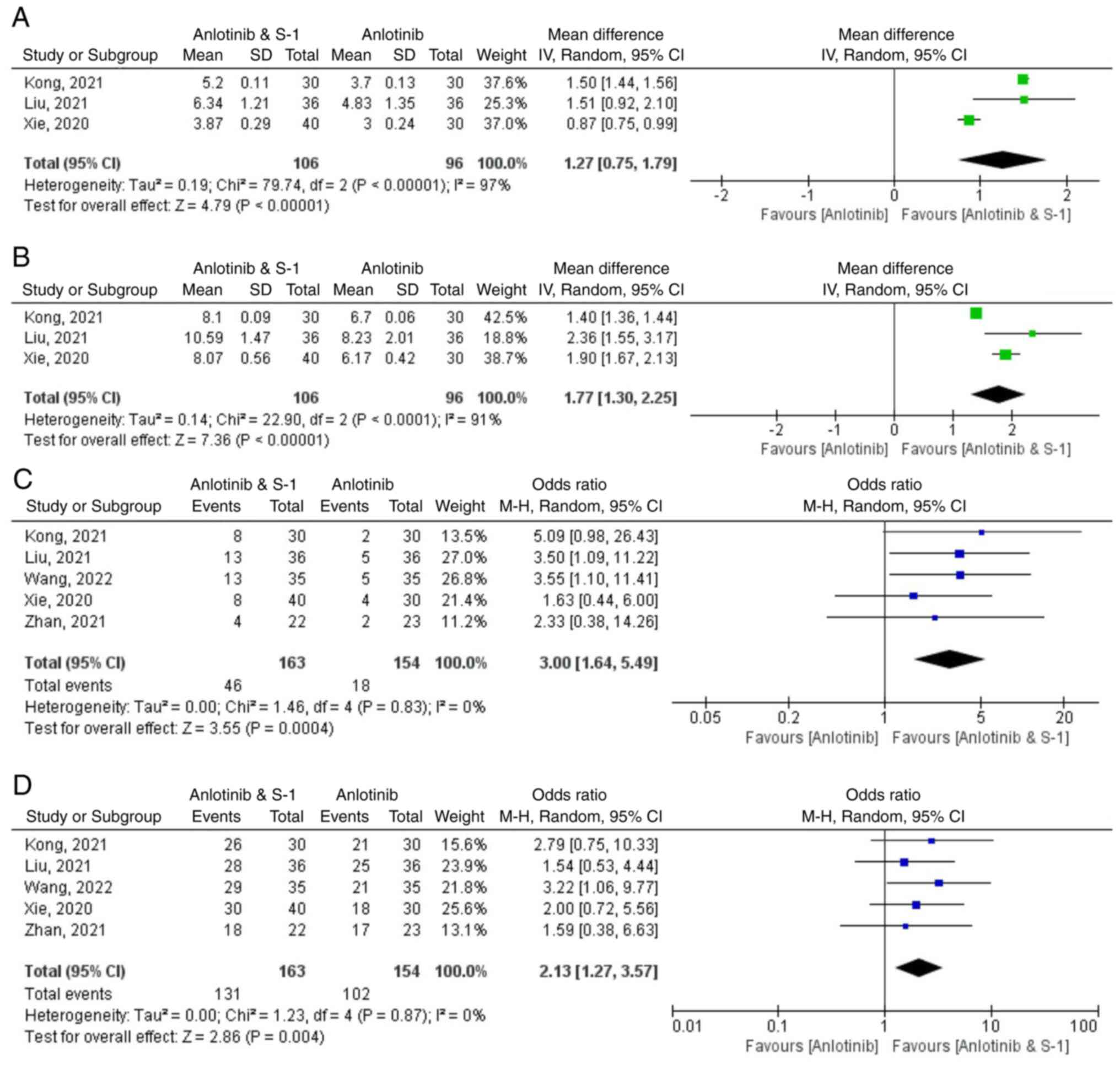
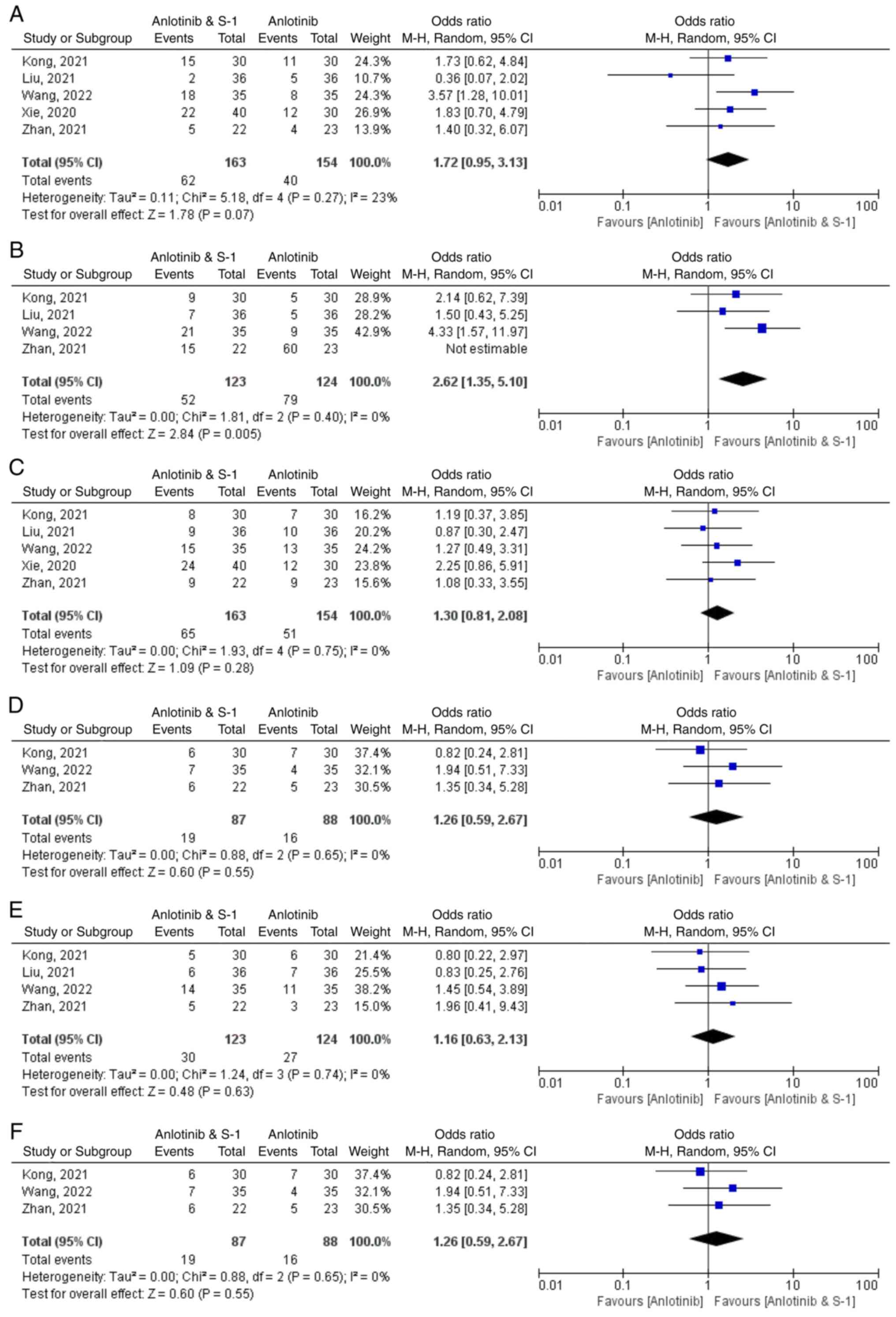
Xie XH, Wang F, Lin XQ, Qin YY, Xie ZH,
Zhang JX, Ouyang M and Zhou CZ: Anlotinib plus S-1 for patients
with EGFR mutation-negative advanced squamous cell lung cancer with
ps scores of 2–3 after progression of second-line or later-line
treatment. Cancer Manag Res. 12:12709–12714. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu KL: Efficacy analysis of antirotinib
combined with S-1 in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung
cancer. Chin J Mod Drug Appl. 15:162–164. 2021.
|
|
31
|
Kong DH: Efficacy and safety of anlotinib
combined with tegafur in the treatment of third-line and later
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. China Med Univ; 2021
|
|
32
|
Zhan LF, Yang QL and Li YY: Effects of
combination therapy with anlotinib and S-1 in thirdly-line
treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Guide China Med.
19:95–96+99. 2021.
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Li XZ, Jang SL, et al: Clinical
efficacy of anlotinib combined with S-1 of advanced non-small cell
lung cancer after second-line treatment. Anhui Med J. 43:36–40.
2022.
|
|
34
|
Wu F, Wang L and Zhou C: Lung cancer in
China: Current and prospect. Curr Opin Oncol. 33:40–46. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shen G, Zheng F, Ren D, Du F, Dong Q, Wang
Z, Zhao F, Ahmad R and Zhao J: Anlotinib: A novel multi-targeting
tyrosine kinase inhibitor in clinical development. J Hematol Oncol.
11:1202018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang L, Dong X, Ren Y, Luo J, Liu P, Su D
and Yang X: Targeting EHMT2 reverses EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC
by epigenetically regulating the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway. Cell
Death Dis. 9:1292018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jiang W, Sun W, Li W, Gao J, Wang H, Zhou
W, Liang J, Aa L and Wang L: Real-world treatment pattern and
comprehensive comparative effectiveness of Endostar plus different
chemotherapy in advanced patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
Sci Rep. 12:108412022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang HY, Chu JF, Zhao Y, Tang H, Wang LL,
Zhou MQ, Yan Z, Liu YY and Yao ZH: A trial of the safety and
efficacy of chemotherapy plus anlotinib vs chemotherapy alone as
second- or third-line salvage treatment for advanced non-small cell
lung cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 12:3827–3834. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Meng L, Zeng Q, Meng Q, et al: Clinical
effect of antirotinib and bevacizumab combined with paclitaxel plus
carboplatin in the treatment of advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Chin
Med. 14:1164–1168. 2019.
|
|
40
|
Lugano R, Ramachandran M and Dimberg A:
Tumor angiogenesis: Causes, consequences, challenges and
opportunities. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:1745–1770. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liang L, Hui K, Hu C, Wen Y, Yang S, Zhu
P, Wang L, Xia Y, Qiao Y, Sun W, et al: Autophagy inhibition
potentiates the anti-angiogenic property of multikinase inhibitor
anlotinib through JAK2/STAT3/VEGFA signaling in non-small cell lung
cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:712019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Xu Q, Wang J, Sun Y, Lin Y, Liu J, Zhuo Y,
Huang Z, Huang S, Chen Y, Chen L, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sintilimab plus anlotinib for PD-L1-positive recurrent or
metastatic cervical cancer: A multicenter, single-arm, prospective
phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 40:1795–1805. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Su Y, Luo B, Lu Y, Wang D, Yan J, Zheng J,
Xiao J, Wang Y, Xue Z, Yin J, et al: Anlotinib induces a T
cell-inflamed tumor microenvironment by facilitating vessel
normalization and enhances the efficacy of PD-1 checkpoint blockade
in neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 28:793–809. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Dallavalle S, Dobričić V, Lazzarato L,
Gazzano E, Machuqueiro M, Pajeva I, Tsakovska I, Zidar N and
Fruttero R: Improvement of conventional anti-cancer drugs as new
tools against multidrug resistant tumors. Drug Resist Updat.
50:1006822020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Freites-Martinez A, Santana N,
Arias-Santiago S and Viera A: Using the common terminology criteria
for adverse events (CTCAE-version 5.0) to evaluate the severity of
adverse events of anticancer therapies. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl
Ed). 112:90–92. 2021.(In English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lin H, Xie Q, Zhong AH, et al: Efficacy
and safety of S-1 in postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy for
non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Chin Foreign Med Res.
18:1–6. 2020.
|
|
47
|
Chen J, Wang J, Wu X, Che X, Zou Y, Weng
M, Miao Q and Zheng Q: Meta-analysis for the efficacy of S-1-based
regimens as the first-line treatment in Asian chemotherapy-naive
patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol.
13:2195–2207. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Li Y, Ji Y and Peng X: Efficacy and
tolerability of S-1 and 5-FU on advanced rectal cancer
chemotherapy. J Colorectal Anal Surg (China). 23:194–197. 2017.
|
|
49
|
Exarchakou A, Rachet B, Belot A, Maringe C
and Coleman MP: Impact of national cancer policies on cancer
survival trends and socioeconomic inequalities in England,
1996–2013: Population based study. BMJ. 360:K7642018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wang JD: Guangdong has ranked first in GDP
for 32 consecutive years. Insight China. 38–39. 2021.
|
|
51
|
Begg CB and Berlin JA: Publication bias
and dissemination of clinical research. J Natl Cancer Inst.
81:107–115. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ioannidis JPA: Why most published research
findings are false. PLoS Med. 2:e1242005. View Article : Google Scholar
|