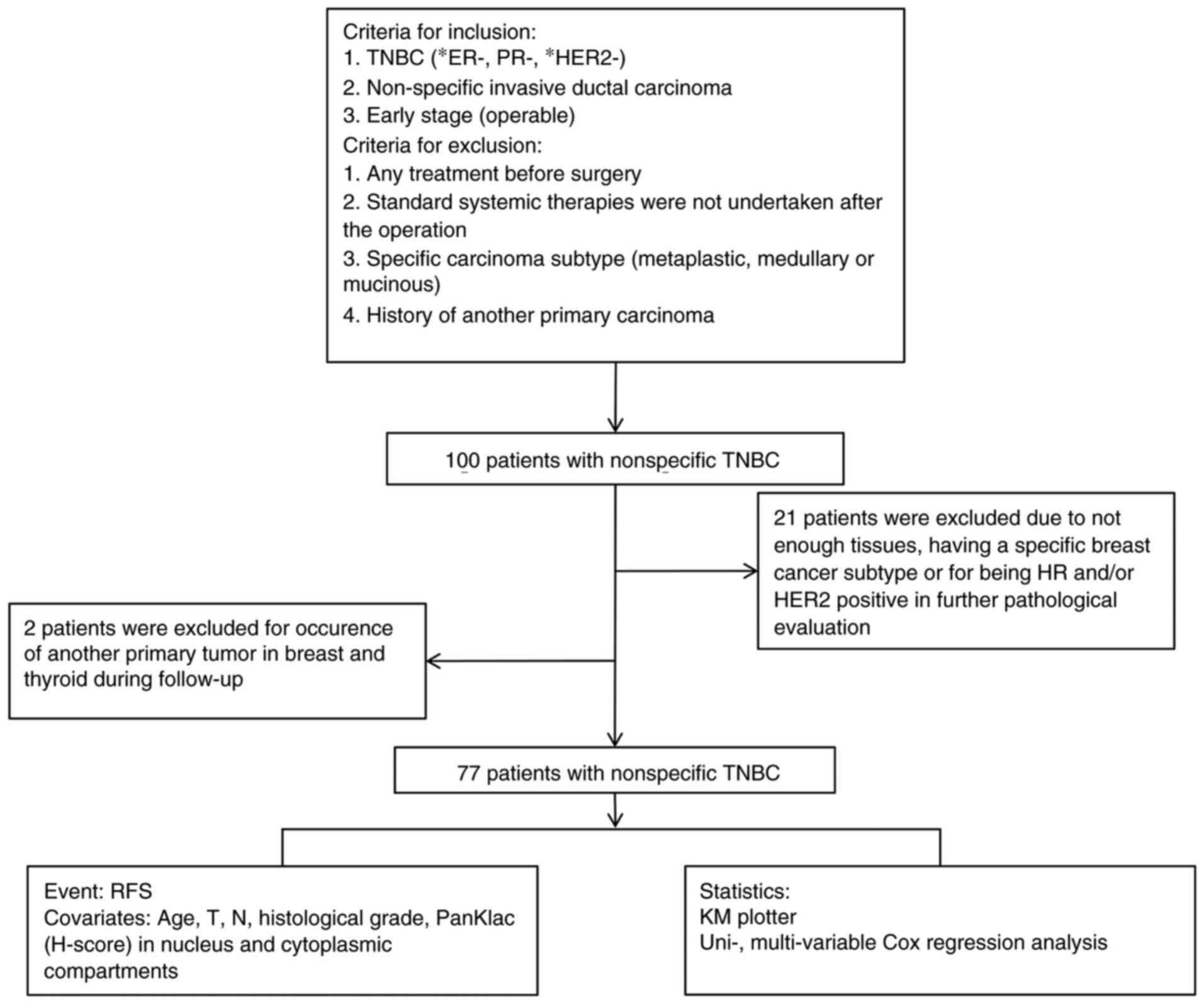
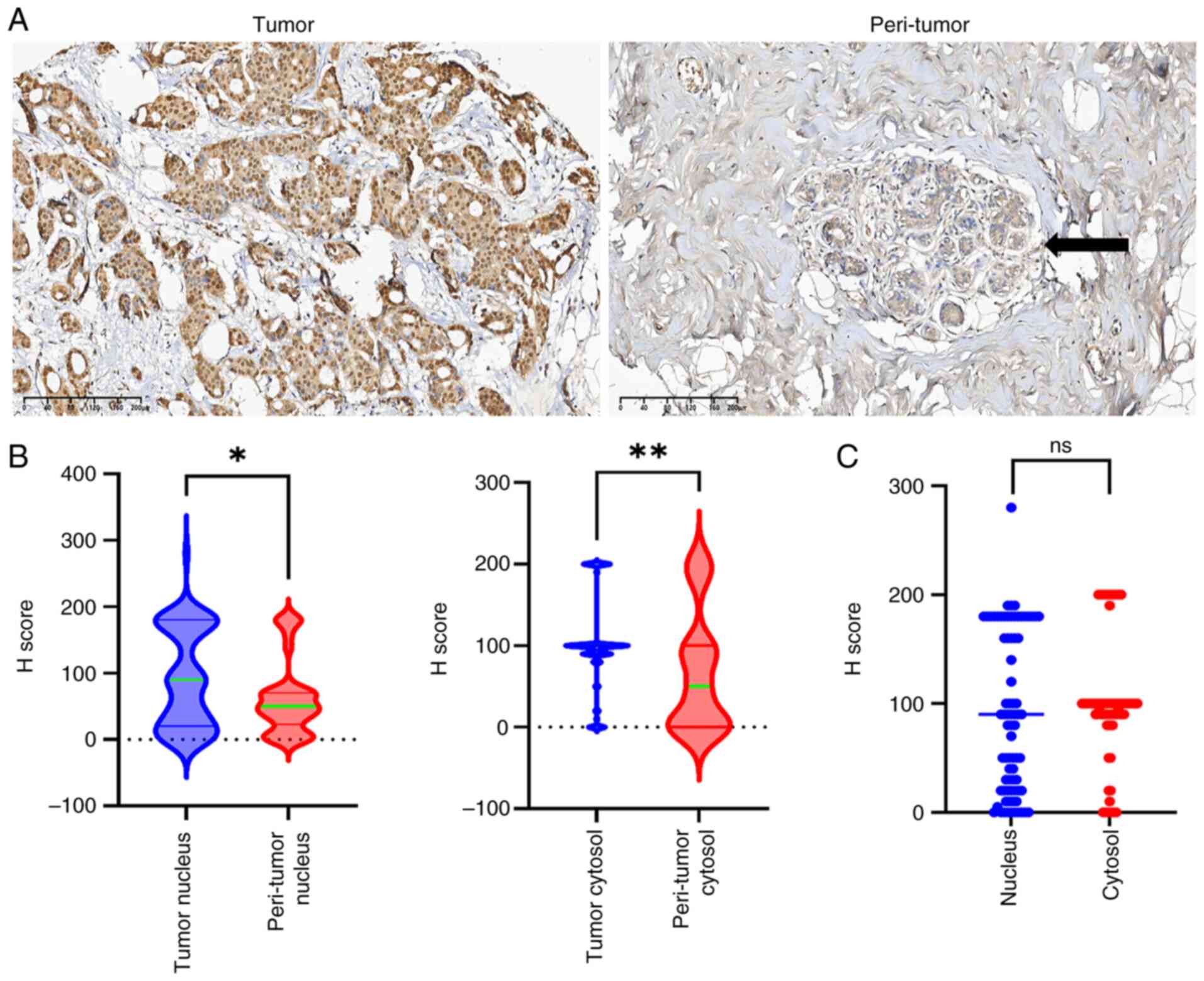
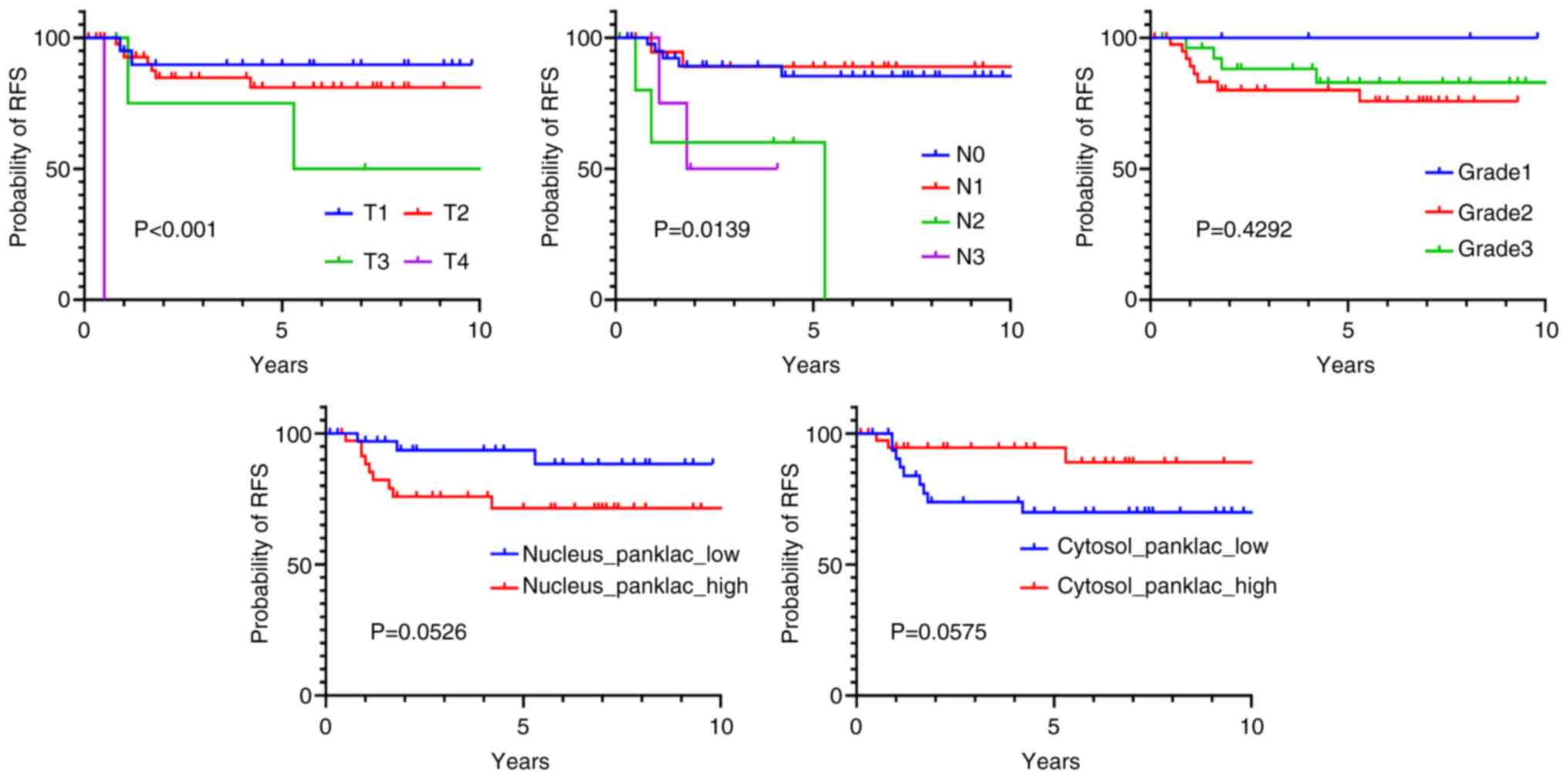
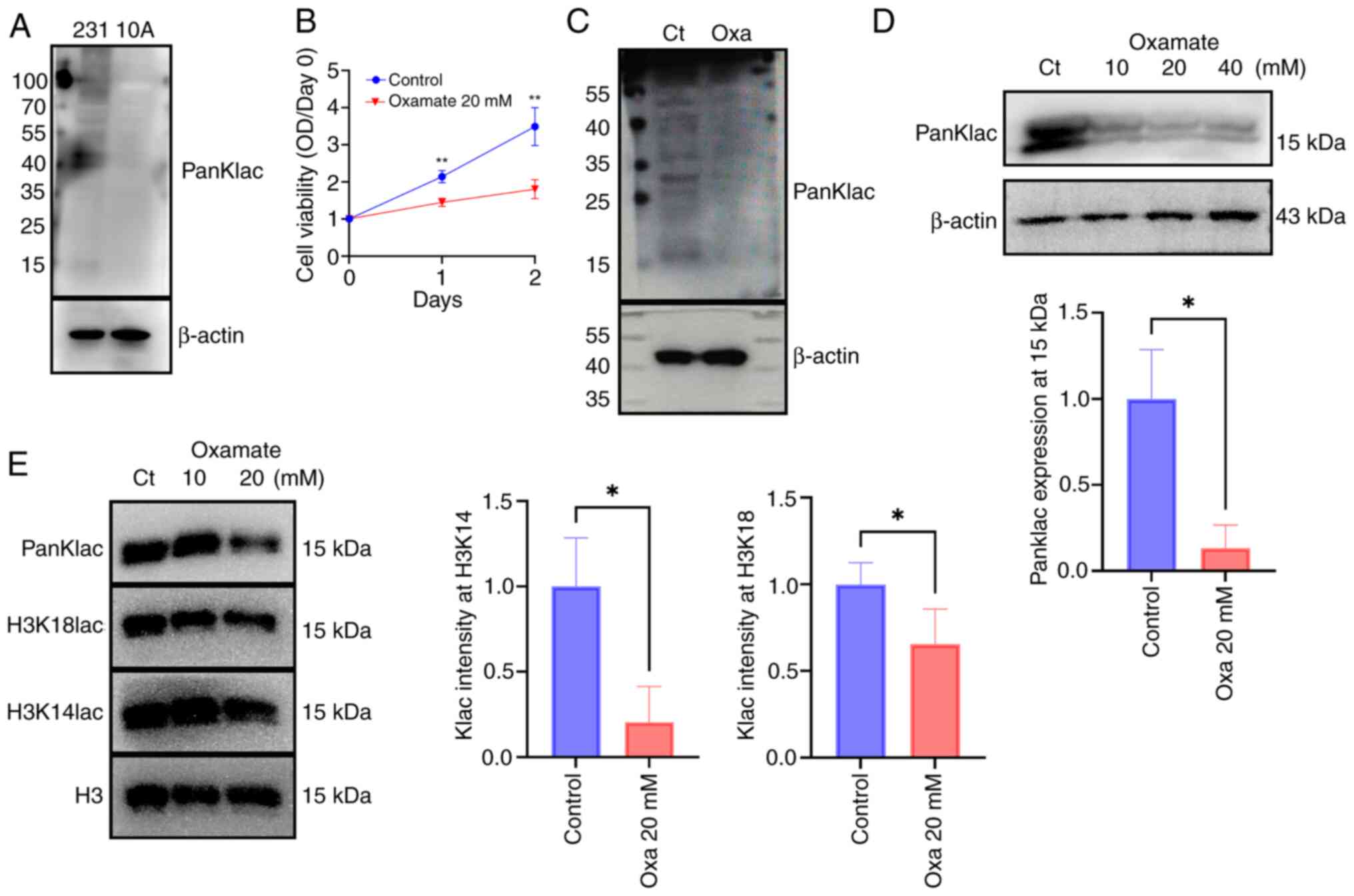
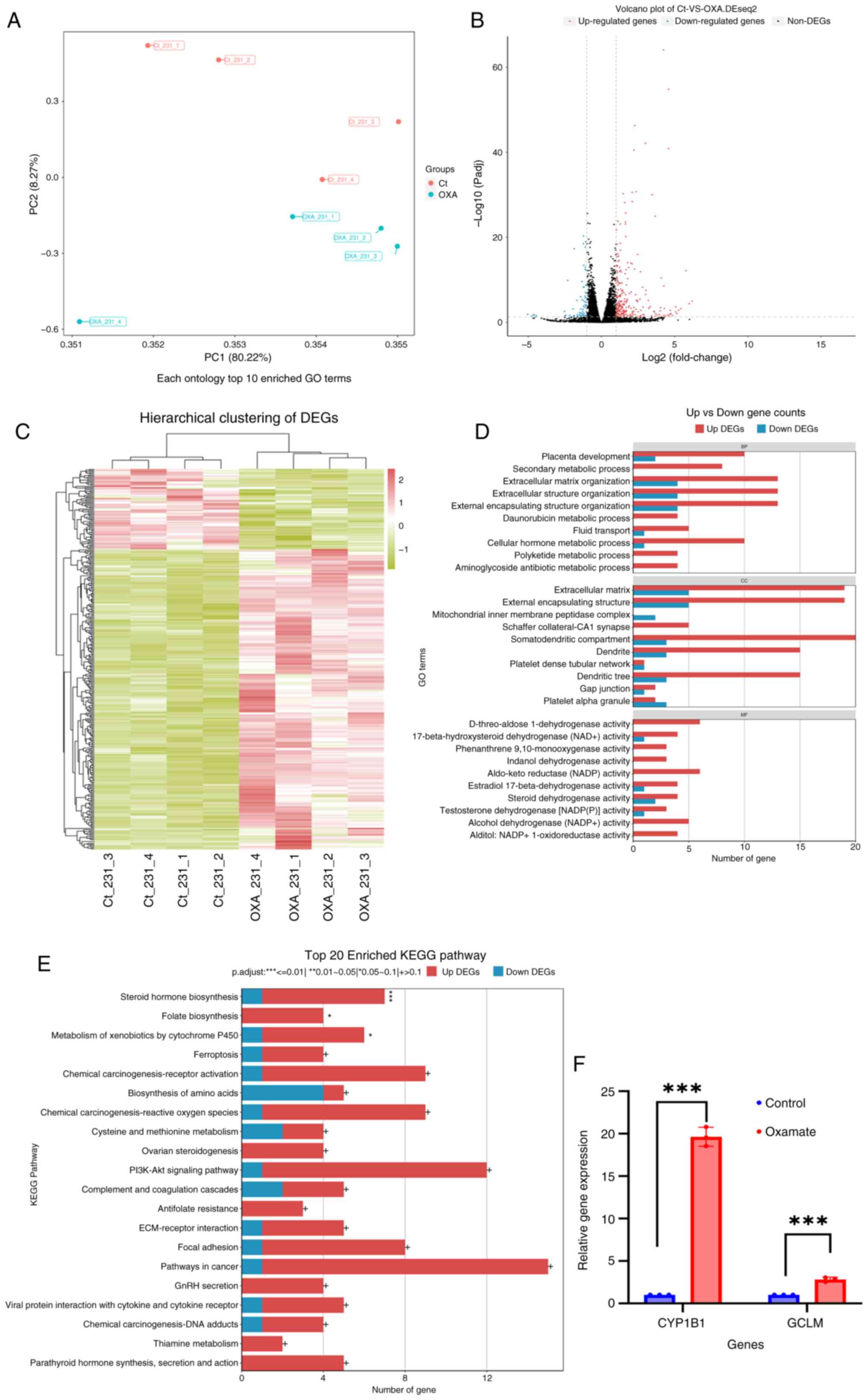
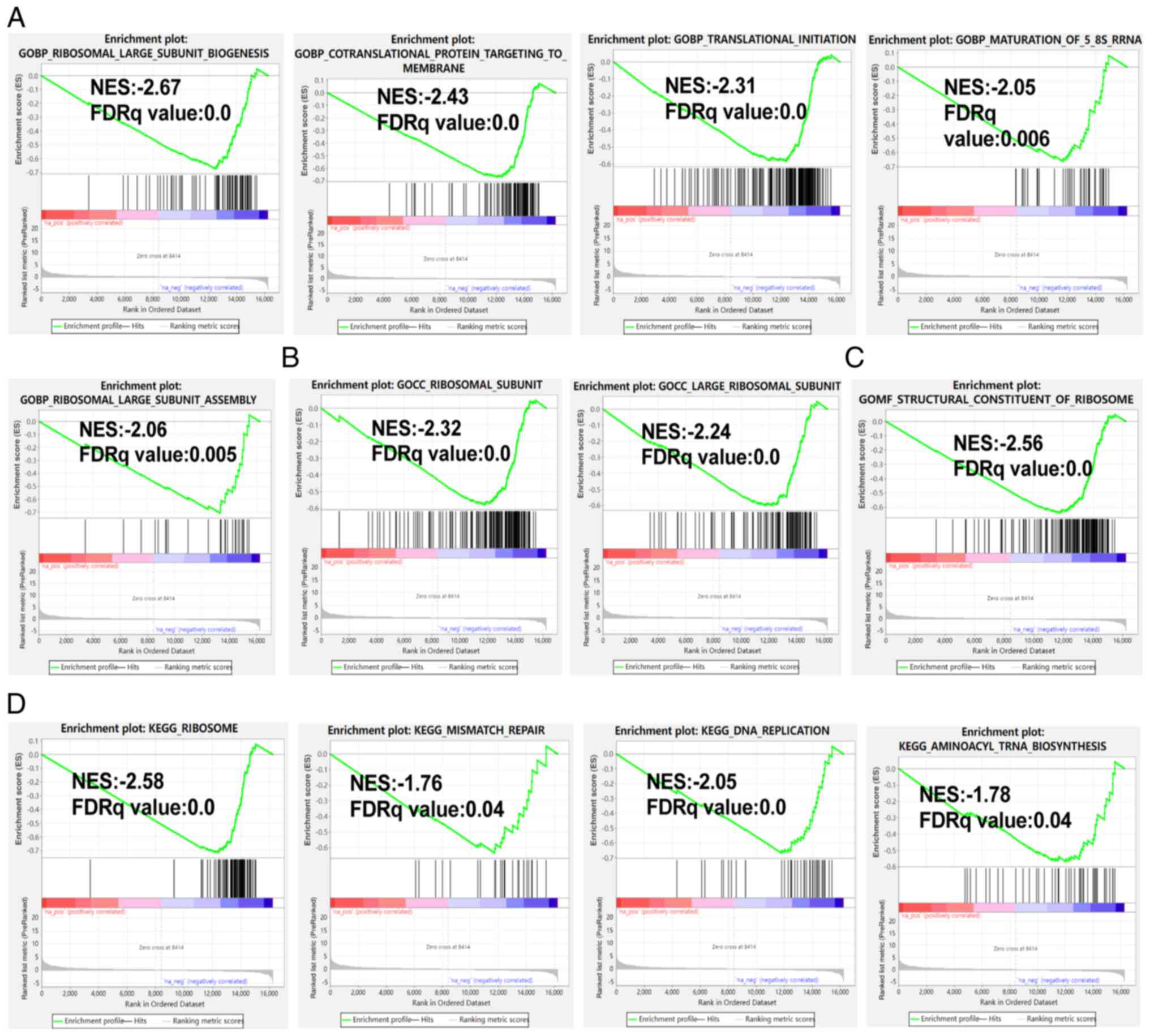
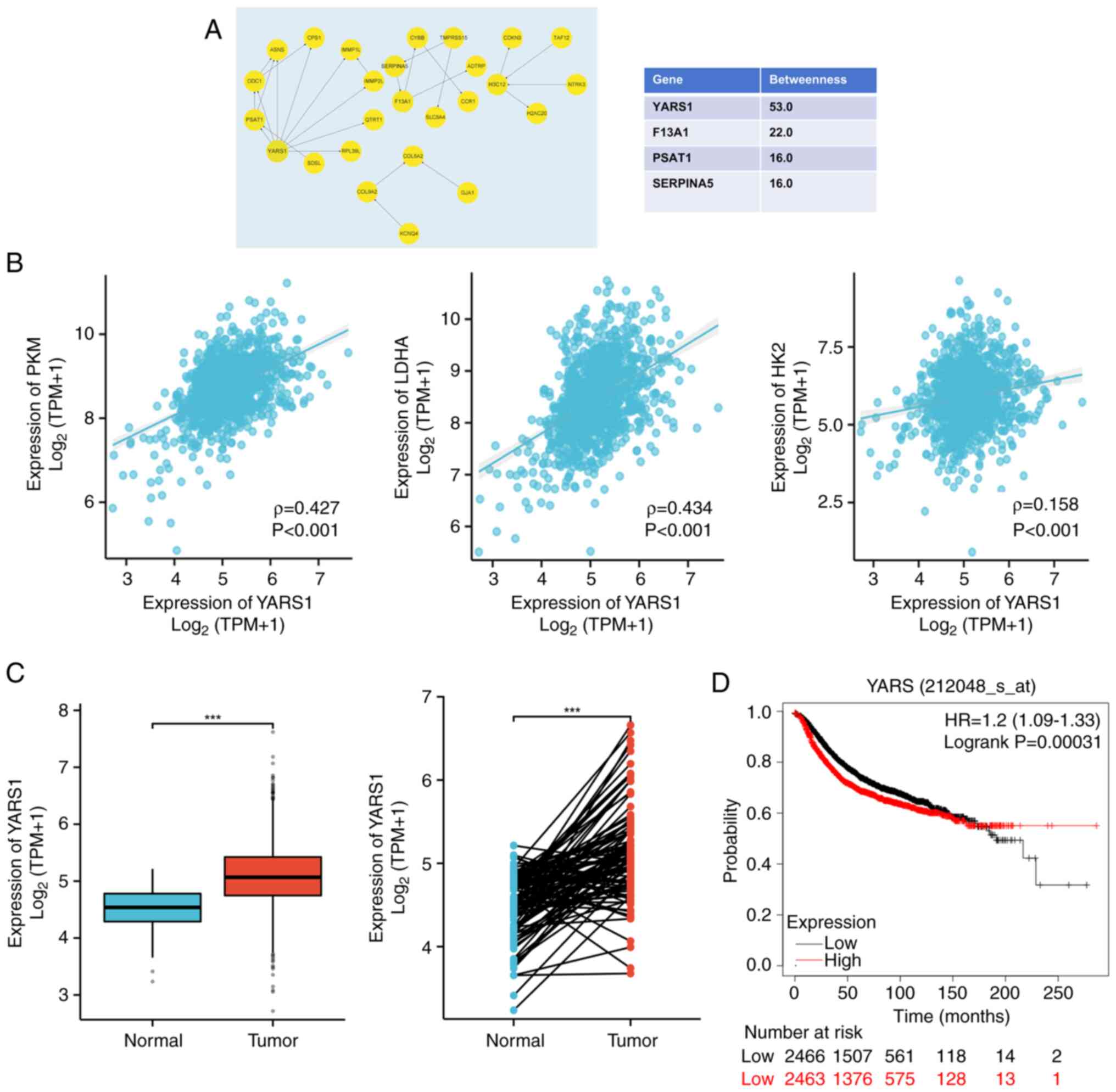
|
1
|
Arnold M, Morgan E, Rumgay H, Mafra A,
Singh D, Laversanne M, Vignat J, Gralow JR, Cardoso F, Siesling S
and Soerjomataram I: Current and future burden of breast cancer:
Global statistics for 2020 and 2040. Breast. 66:15–23. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Derakhshan F and Reis-Filho JS:
Pathogenesis of triple-negative breast cancer. Annu Rev Pathol.
17:181–204. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bianchini G, De Angelis C, Licata L and
Gianni L: Treatment landscape of triple-negative breast
cancer-expanded options, evolving needs. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
19:91–113. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mittendorf EA, Zhang H, Barrios CH, Saji
S, Jung KH, Hegg R, Koehler A, Sohn J, Iwata H, Telli ML, et al:
Neoadjuvant atezolizumab in combination with sequential
nab-paclitaxel and anthracycline-based chemotherapy versus placebo
and chemotherapy in patients with early-stage triple-negative
breast cancer (IMpassion031): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3
trial. Lancet. 396:1090–1100. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Winer EP, Lipatov O, Im SA, Goncalves A,
Muñoz-Couselo E, Lee KS, Schmid P, Tamura K, Testa L, Witzel I, et
al: Pembrolizumab versus investigator-choice chemotherapy for
metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (KEYNOTE-119): A
randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 22:499–511.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park JH, Pyun WY and Park HW: Cancer
metabolism: Phenotype, signaling and therapeutic targets. Cells.
9:23082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lunt SY and Vander Heiden MG: Aerobic
glycolysis: Meeting the metabolic requirements of cell
proliferation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:441–464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang J, Ren B, Yang G, Wang H, Chen G, You
L, Zhang T and Zhao Y: The enhancement of glycolysis regulates
pancreatic cancer metastasis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:305–321. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen Y, Zhang J, Zhang M, Song Y, Zhang Y,
Fan S, Ren S, Fu L, Zhang N, Hui H and Shen X: Baicalein
resensitizes tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells by reducing
aerobic glycolysis and reversing mitochondrial dysfunction via
inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Clin Transl Med.
11:e5772021. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao J, Jin D, Huang M, Ji J, Xu X, Wang
F, Zhou L, Bao B, Jiang F, Xu W, et al: Glycolysis in the tumor
microenvironment: A driver of cancer progression and a promising
therapeutic target. Front Cell Dev Biol. 12:14164722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang H, Zou X, Yang S, Zhang A, Li N and
Ma Z: Identification of lactylation related model to predict
prognostic, tumor infiltrating immunocytes and response of
immunotherapy in gastric cancer. Front Immunol. 14:11499892023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiao Y, Ji F, Hou L, Lv Y and Zhang J:
Lactylation-related gene signature for prognostic prediction and
immune infiltration analysis in breast cancer. Heliyon.
10:e247772024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang T, Ye Z, Li Z, Jing DS, Fan GX, Liu
MQ, Zhuo QF, Ji SR, Yu XJ, Xu XW and Qin Y: Lactate-induced protein
lactylation: A bridge between epigenetics and metabolic
reprogramming in cancer. Cell Prolif. 56:e134782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang D, Tang Z, Huang H, Zhou G, Cui C,
Weng Y, Liu W, Kim S, Lee S, Perez-Neut M, et al: Metabolic
regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation. Nature.
574:575–580. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li W, Zhou C, Yu L, Hou Z, Liu H, Kong L,
Xu Y, He J, Lan J, Ou Q, et al: Tumor-derived lactate promotes
resistance to bevacizumab treatment by facilitating autophagy
enhancer protein RUBCNL expression through histone H3 lysine 18
lactylation (H3K18la) in colorectal cancer. Autophagy. 20:114–130.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li F, Zhang H, Huang Y, Li D, Zheng Z, Xie
K, Cao C, Wang Q, Zhao X, Huang Z, et al: Single-cell transcriptome
analysis reveals the association between histone lactylation and
cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer. Drug Resist Updat.
73:1010592024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu J, Chai P, Xie M, Ge S, Ruan J, Fan X
and Jia R: Histone lactylation drives oncogenesis by facilitating
m6A reader protein YTHDF2 expression in ocular melanoma.
Genome Biol. 22:852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ju J, Zhang H, Lin M, Yan Z, An L, Cao Z,
Geng D, Yue J, Tang Y, Tian L, et al: The alanyl-tRNA synthetase
AARS1 moonlights as a lactyltransferase to promote YAP signaling in
gastric cancer. J Clin Invest. 134:e1745872024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zong Z, Xie F, Wang S, Wu X, Zhang Z, Yang
B and Zhou F: Alanyl-tRNA synthetase, AARS1, is a lactate sensor
and lactyltransferase that lactylates p53 and contributes to
tumorigenesis. Cell. 187:2375–2392.e33. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Giuliano AE, Connolly JL, Edge SB,
Mittendorf EA, Rugo HS, Solin LJ, Weaver DL, Winchester DJ and
Hortobagyi GN: Breast cancer-major changes in the American joint
committee on cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer
J Clin. 67:290–303. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred
DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, Fitzgibbons PL, Francis G, Goldstein NS,
Hayes M, et al: American society of clinical oncology/college of
American pathologists guideline recommendations for
immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors
in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:2784–2795. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wolff AC, Hammond MEH, Allison KH, Harvey
BE, Mangu PB, Bartlett JMS, Bilous M, Ellis IO, Fitzgibbons P,
Hanna W, et al: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in
breast cancer: American society of clinical oncology/college of
American pathologists clinical practice guideline focused update.
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 142:1364–1382. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bertozzi S, Londero AP, Viola L, Orsaria
M, Bulfoni M, Marzinotto S, Corradetti B, Baccarani U, Cesselli D,
Cedolini C and Mariuzzi L: TFEB, SIRT1, CARM1, beclin-1 expression
and PITX2 methylation in breast cancer chemoresistance: A
retrospective study. BMC Cancer. 21:11182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Győrffy B: Survival analysis across the
entire transcriptome identifies biomarkers with the highest
prognostic power in breast cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J.
19:4101–4109. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Knab VM, Gotthardt D, Klein K,
Grausenburger R, Heller G, Menzl I, Prinz D, Trifinopoulos J, List
J, Fux D, et al: Triple-negative breast cancer cells rely on
kinase-independent functions of CDK8 to evade NK-cell-mediated
tumor surveillance. Cell Death Dis. 12:9912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deng J and Liao X: Lysine lactylation
(Kla) might be a novel therapeutic target for breast cancer. BMC
Med Genomics. 16:2832023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cui Z, Li Y, Lin Y, Zheng C, Luo L, Hu D,
Chen Y, Xiao Z and Sun Y: Lactylproteome analysis indicates histone
H4K12 lactylation as a novel biomarker in triple-negative breast
cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 15:13286792024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang Z, Yan C, Ma J, Peng P, Ren X, Cai S,
Shen X, Wu Y, Zhang S, Wang X, et al: Lactylome analysis suggests
lactylation-dependent mechanisms of metabolic adaptation in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Metab. 5:61–79. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song F, Hou C, Huang Y, Liang J, Cai H,
Tian G, Jiang Y, Wang Z and Hou J: Lactylome analyses suggest
systematic lysine-lactylated substrates in oral squamous cell
carcinoma under normoxia and hypoxia. Cell Signal. 120:1112282024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Luo Y, Yang Z, Yu Y and Zhang P: HIF1α
lactylation enhances KIAA1199 transcription to promote angiogenesis
and vasculogenic mimicry in prostate cancer. Int J Biol Macromol.
222:2225–2243. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen Y, Wu J, Zhai L, Zhang T, Yin H, Gao
H, Zhao F, Wang Z, Yang X, Jin M, et al: Metabolic regulation of
homologous recombination repair by MRE11 lactylation. Cell.
187:294–311.e21. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang C, Lin X, Zhao Q, Wang Y, Jiang F,
Ji C, Li Y, Gao J, Li J and Shen L: YARS as an oncogenic protein
that promotes gastric cancer progression through activating
PI3K-Akt signaling. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 146:329–342. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Y, Wang J, Zhang L, He J, Ji B, Wang
J, Ding B and Ren M: Unveiling the role of YARS1 in bladder cancer:
A prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target. J Cell Mol Med.
28:1–20. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|