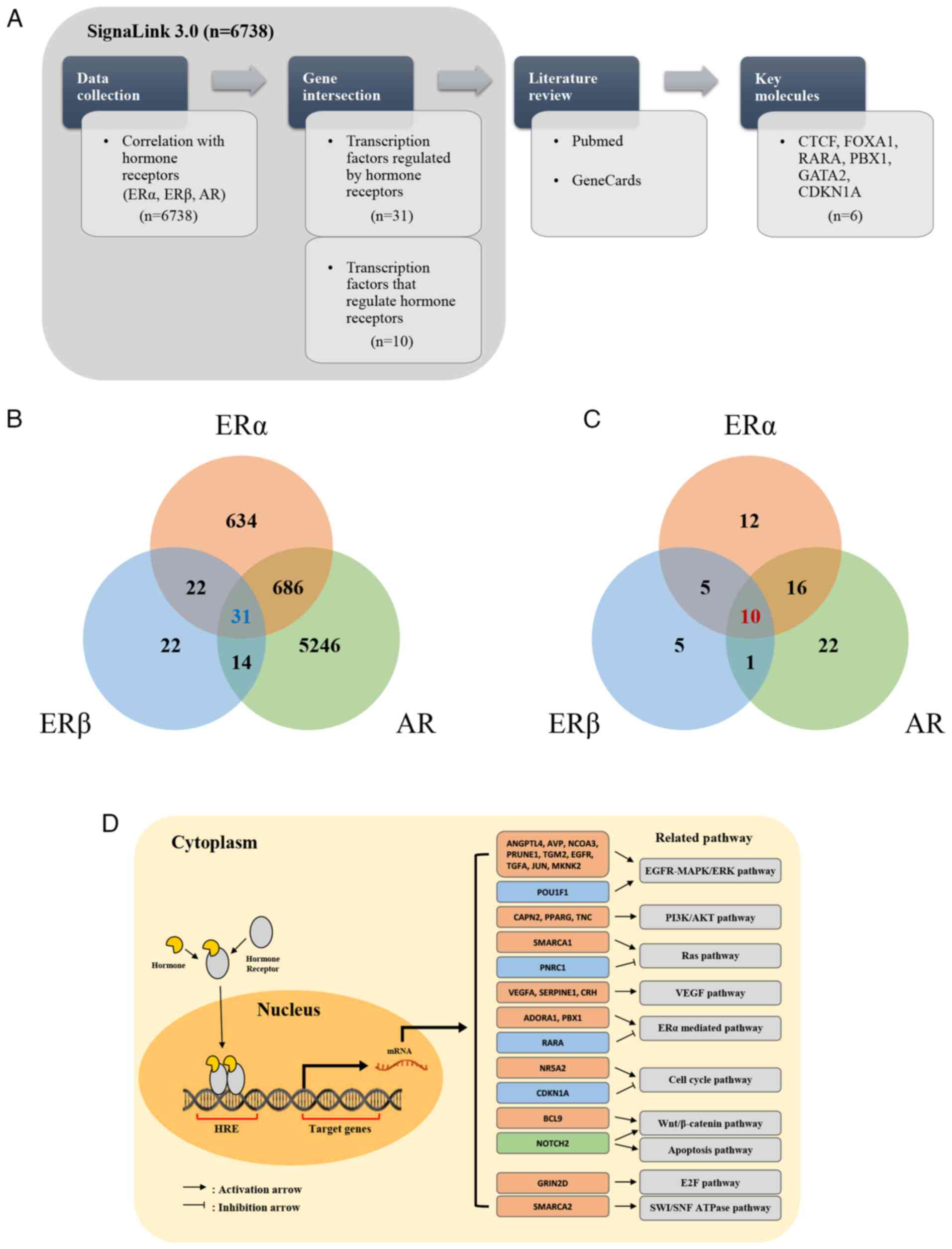
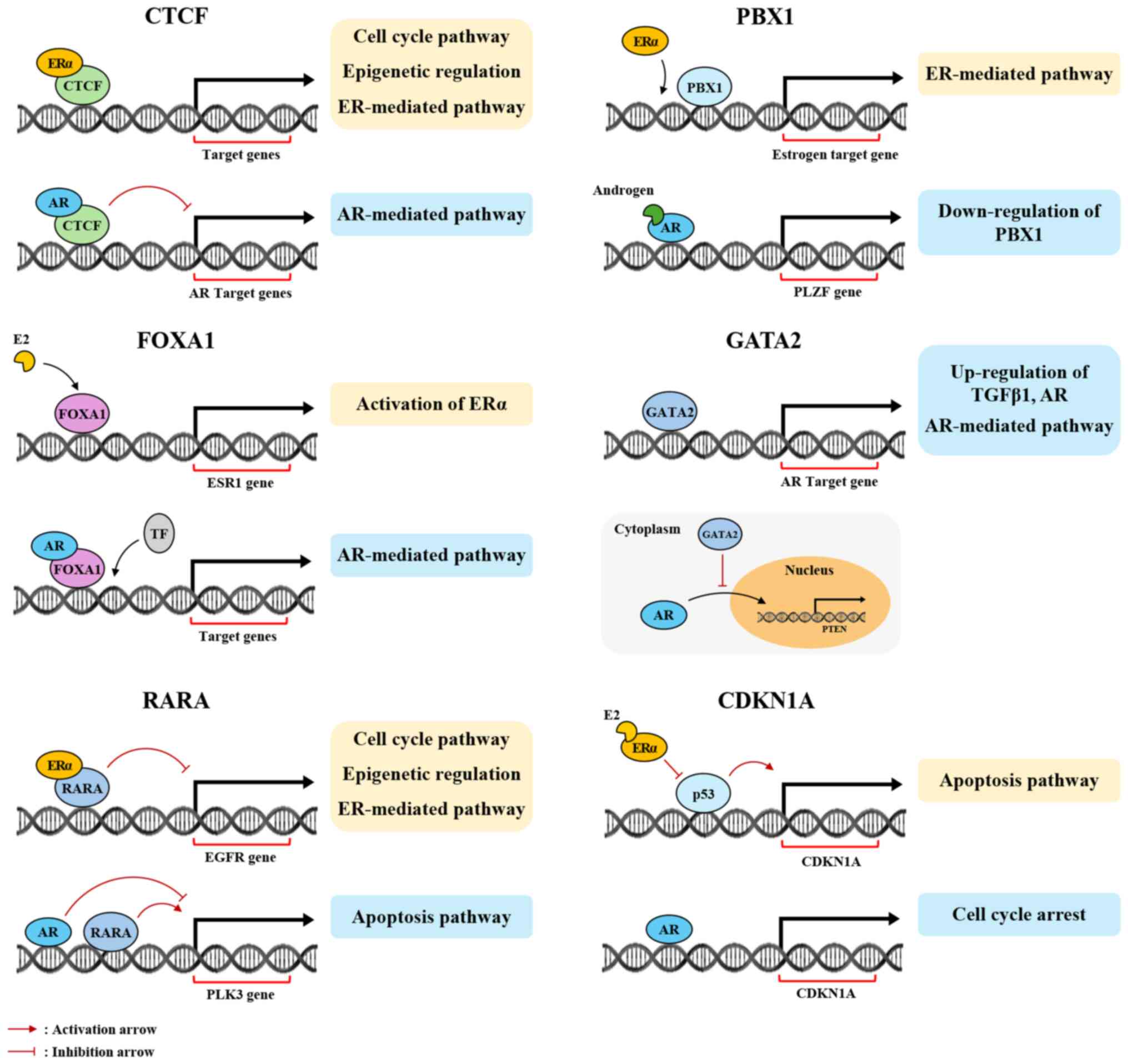
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shen X, Jain A, Aladelokun O, Yan H,
Gilbride A, Ferrucci LM, Lu L, Khan SA and Johnson CH: Asparagine,
colorectal cancer, and the role of sex, genes, microbes, and diet:
A narrative review. Front Mol Biosci. 9:9586662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fuentes N, Silva Rodriguez M and Silveyra
P: Role of sex hormones in lung cancer. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
246:2098–2110. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coelingh Bennink HJT, Prowse A, Egberts
JFM, Debruyne FMJ, Huhtaniemi IT and Tombal B: The loss of
estradiol by androgen deprivation in prostate cancer patients shows
the importance of estrogens in males. J Endocr Soc. 8:bvae1072024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Frederiksen H, Johannsen TH, Andersen SE,
Albrethsen J, Landersoe SK, Petersen JH, Andersen AN, Vestergaard
ET, Schorring ME, Linneberg A, et al: Sex-specific estrogen levels
and reference intervals from infancy to late adulthood determined
by LC-MS/MS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 105:754–768. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gates MA, Mekary RA, Chiu GR, Ding EL,
Wittert GA and Araujo AB: Sex steroid hormone levels and body
composition in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98:2442–2450. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Marriott RJ, Murray K, Adams RJ, Antonio
L, Ballantyne CM, Bauer DC, Bhasin S, Biggs ML, Cawthon PM, Couper
DJ, et al: Factors associated with circulating sex hormones in men:
Individual participant data meta-analyses. Ann Intern Med.
176:1221–1234. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Simpson ER, Misso M, Hewitt KN, Hill RA,
Boon WC, Jones ME, Kovacic A, Zhou J and Clyne CD: Estrogen-the
good, the bad, and the unexpected. Endocr Rev. 26:322–330. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gandhi N, Omer S and Harrison RE: In vitro
cell culture model for osteoclast activation during estrogen
withdrawal. Int J Mol Sci. 25:61342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hughes DE, Dai A, Tiffee JC, Li HH, Mundy
GR and Boyce BF: Estrogen promotes apoptosis of murine osteoclasts
mediated by TGF-beta. Nat Med. 2:1132–1136. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Srivastava S, Toraldo G, Weitzmann MN,
Cenci S, Ross FP and Pacifici R: Estrogen decreases osteoclast
formation by down-regulating receptor activator of NF-kappa B
ligand (RANKL)-induced JNK activation. J Biol Chem. 276:8836–8840.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gavali S, Gupta MK, Daswani B, Wani MR,
Sirdeshmukh R and Khatkhatay MI: LYN, a key mediator in
estrogen-dependent suppression of osteoclast differentiation,
survival, and function. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1865:547–557. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kharb R, Haider K, Neha K and Yar MS:
Aromatase inhibitors: Role in postmenopausal breast cancer. Arch
Pharm (Weinheim). 353:e20000812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arumugam A, Lissner EA and Lakshmanaswamy
R: The role of hormones and aromatase inhibitors on breast tumor
growth and general health in a postmenopausal mouse model. Reprod
Biol Endocrinol. 12:662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Parish SJ, Simon JA, Davis SR, Giraldi A,
Goldstein I, Goldstein SW, Kim NN, Kingsberg SA, Morgentaler A,
Nappi RE, et al: International society for the study of women's
sexual health clinical practice guideline for the use of systemic
testosterone for hypoactive sexual desire disorder in women. J Sex
Med. 18:849–867. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Van-Duyne G, Blair IA, Sprenger C,
Moiseenkova-Bell V, Plymate S and Penning TM: The androgen
receptor. Vitam Horm. 123:439–481. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsai CC, Yang YSH, Chen YF, Huang LY, Yang
YN, Lee SY, Wang WL, Lee HL, Whang-Peng J, Lin HY, et al: Integrins
and actions of androgen in breast cancer. Cells. 12:21262023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Naamneh Elzenaty R, du Toit T and Flück
CE: Basics of androgen synthesis and action. Best Pract Res Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 36:1016652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bienenfeld A, Azarchi S, Lo Sicco K,
Marchbein S, Shapiro J and Nagler AR: Androgens in women:
Androgen-mediated skin disease and patient evaluation. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 80:1497–1506. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang R, Hu K, Bai H, Liu H, Pu Y, Yang C,
Liu Q and Fan P: Increased oxidative stress is associated with
hyperandrogenemia in polycystic ovary syndrome evidenced by
oxidized lipoproteins stimulating rat ovarian androgen synthesis in
vitro. Endocrine. 84:1238–1249. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Paakinaho V and Palvimo JJ: Genome-wide
crosstalk between steroid receptors in breast and prostate cancers.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 28:R231–R250. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Amirghofran Z, Monabati A and Gholijani N:
Androgen receptor expression in relation to apoptosis and the
expression of cell cycle related proteins in prostate cancer.
Pathol Oncol Res. 10:37–41. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bodner K, Laubichler P, Kimberger O,
Czerwenka K, Zeillinger R and Bodner-Adler B: Oestrogen and
progesterone receptor expression in patients with adenocarcinoma of
the uterine cervix and correlation with various clinicopathological
parameters. Anticancer Res. 30:1341–1345. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yoon K, Park Y, Kang E, Kim E, Kim JH, Kim
SH, Suh KJ, Kim SM, Jang M, Yun BR, et al: Effect of estrogen
receptor expression level and hormonal therapy on prognosis of
early breast cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 54:1081–1090. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC,
Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, Meyer L, Gress DM, Byrd DR and
Winchester DP: The eighth edition AJCC cancer staging manual:
Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more
‘personalized’ approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin.
67:93–99. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Giuliano AE, Edge SB and Hortobagyi GN:
Eighth edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual: Breast cancer.
Ann Surg Oncol. 25:1783–1785. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cheang MCU, Chia SK, Voduc D, Gao D, Leung
S, Snider J, Watson M, Davies S, Bernard PS, Parker JS, et al: Ki67
index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 101:736–750. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs
H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M,
et al: Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2
for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med.
344:783–792. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huggins C and Hodges CV: Studies on
prostatic cancer. I. The effect of castration, of estrogen and of
androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of
the prostate. 1941. J Urol. 167:948–952. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Scher HI and Sawyers CL: Biology of
progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: Directed
therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J Clin
Oncol. 23:8253–8261. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gu G, Tian L, Herzog SK, Rechoum Y,
Gelsomino L, Gao M, Du L, Kim JA, Dustin D, Lo HC, et al: Hormonal
modulation of ESR1 mutant metastasis. Oncogene. 40:997–1011. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kolyvas EA, Caldas C, Kelly K and Ahmad
SS: Androgen receptor function and targeted therapeutics across
breast cancer subtypes. Breast Cancer Res. 24:792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Peters AA, Buchanan G, Ricciardelli C,
Bianco-Miotto T, Centenera MM, Harris JM, Jindal S, Segara D, Jia
L, Moore NL, et al: Androgen receptor inhibits estrogen
receptor-alpha activity and is prognostic in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 69:6131–6140. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hickey TE, Selth LA, Chia KM, Laven-Law G,
Milioli HH, Roden D, Jindal S, Hui M, Finlay-Schultz J, Ebrahimie
E, et al: The androgen receptor is a tumor suppressor in estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer. Nat Med. 27:310–320. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Secreto G, Girombelli A and Krogh V:
Androgen excess in breast cancer development: Implications for
prevention and treatment. Endocr Relat Cancer. 26:R81–R94. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gehrig J, Kaulfuß S, Jarry H, Bremmer F,
Stettner M, Burfeind P and Thelen P: Prospects of estrogen receptor
β activation in the treatment of castration-resistant prostate
cancer. Oncotarget. 8:34971–34979. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lung DK, Reese RM and Alarid ET: Intrinsic
and extrinsic factors governing the transcriptional regulation of
ESR1. Horm Cancer. 11:129–147. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jensen EV, Desombre ER, Kawashima T,
Suzuki T, Kyser K and Jungblut PW: Estrogen-binding substances of
target tissues. Science. 158:529–530. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kato S, Endoh H, Masuhiro Y, Kitamoto T,
Uchiyama S, Sasaki H, Masushige S, Gotoh Y, Nishida E, Kawashima H,
et al: Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation
by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science. 270:1491–1494. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bunone G, Briand PA, Miksicek RJ and
Picard D: Activation of the unliganded estrogen receptor by EGF
involves the MAP kinase pathway and direct phosphorylation. EMBO J.
15:2174–2183. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tremblay A, Tremblay GB, Labrie F and
Giguère V: Ligand-independent recruitment of SRC-1 to estrogen
receptor beta through phosphorylation of activation function AF-1.
Mol Cell. 3:513–519. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yi P, Wang Z, Feng Q, Pintilie GD, Foulds
CE, Lanz RB, Ludtke SJ, Schmid MF, Chiu W and O'Malley BW:
Structure of a biologically active estrogen receptor-coactivator
complex on DNA. Mol Cell. 57:1047–1058. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Brzozowski AM, Pike AC, Dauter Z, Hubbard
RE, Bonn T, Engström O, Ohman L, Greene GL, Gustafsson JA and
Carlquist M: Molecular basis of agonism and antagonism in the
oestrogen receptor. Nature. 389:753–758. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Heery DM, Kalkhoven E, Hoare S and Parker
MG: A signature motif in transcriptional co-activators mediates
binding to nuclear receptors. Nature. 387:733–736. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Torchia J, Rose DW, Inostroza J, Kamei Y,
Westin S, Glass CK and Rosenfeld MG: The transcriptional
co-activator p/CIP binds CBP and mediates nuclear-receptor
function. Nature. 387:677–684. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kumar R, Betney R, Li J, Thompson EB and
McEwan IJ: Induced alpha-helix structure in AF1 of the androgen
receptor upon binding transcription factor TFIIF. Biochemistry.
43:3008–3013. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bevan CL, Hoare S, Claessens F, Heery DM
and Parker MG: The AF1 and AF2 domains of the androgen receptor
interact with distinct regions of SRC1. Mol Cell Biol.
19:8383–8392. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang B, Omoto Y, Iwase H, Yamashita H,
Toyama T, Coombes RC, Filipovic A, Warner M and Gustafsson JÅ:
Differential expression of estrogen receptor alpha, beta1, and
beta2 in lobular and ductal breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:1933–1938. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Couse JF and Korach KS: Estrogen receptor
null mice: What have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr
Rev. 20:358–417. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jia M, Dahlman-Wright K and Gustafsson JÅ:
Estrogen receptor alpha and beta in health and disease. Best Pract
Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 29:557–568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Martin EC, Conger AK, Yan TJ, Hoang VT,
Miller DF, Buechlein A, Rusch DB, Nephew KP, Collins-Burow BM and
Burow ME: MicroRNA-335-5p and −3p synergize to inhibit estrogen
receptor alpha expression and promote tamoxifen resistance. FEBS
Lett. 591:382–392. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Santner SJ, Feil PD and Santen RJ: In situ
estrogen production via the estrone sulfatase pathway in breast
tumors: Relative importance versus the aromatase pathway. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 59:29–33. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jordan VC: Antiestrogenic action of
raloxifene and tamoxifen: Today and tomorrow. J Natl Cancer Inst.
90:967–971. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Arpino G, Weiss H, Lee AV, Schiff R, De
Placido S, Osborne CK and Elledge RM: Estrogen receptor-positive,
progesterone receptor-negative breast cancer: Association with
growth factor receptor expression and tamoxifen resistance. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 97:1254–1261. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Horwitz KB, Koseki Y and McGuire WL:
Estrogen control of progesterone receptor in human breast cancer:
Role of estradiol and antiestrogen. Endocrinology. 103:1742–1751.
1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dowsett M, Houghton J, Iden C, Salter J,
Farndon J, A'Hern R and Baum M: Estrogen receptor status,
progesterone receptor status, and HER2 status as biomarkers for
predicting response to endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol.
26:1814–1820. 2008.
|
|
59
|
Kumar R, Zakharov MN, Khan SH, Miki R,
Jang H, Toraldo G, Singh R, Bhasin S and Jasuja R: The dynamic
structure of the estrogen receptor. J Amino Acids. 2011:8125402011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Weihua Z, Andersson S, Cheng G, Simpson
ER, Warner M and Gustafsson JA: Update on estrogen signaling. FEBS
Lett. 546:17–24. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Flouriot G, Brand H, Denger S, Metivier R,
Kos M, Reid G, Sonntag-Buck V and Gannon F: Identification of a new
isoform of the human estrogen receptor-alpha (hER-alpha) that is
encoded by distinct transcripts and that is able to repress
hER-alpha activation function 1. EMBO J. 19:4688–4700. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Langley RE, Godsland IF, Kynaston H,
Clarke NW, Rosen SD, Morgan RC, Pollock P, Kockelbergh R, Lalani
EN, Dearnaley D, et al: Early hormonal data from a multicentre
phase II trial using transdermal oestrogen patches as first-line
hormonal therapy in patients with locally advanced or metastatic
prostate cancer. BJU Int. 102:442–445. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lau KM and To KF: Importance of estrogenic
signaling and its mediated receptors in prostate cancer. Int J Mol
Sci. 17:14342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ricke WA, McPherson SJ, Bianco JJ, Cunha
GR, Wang Y and Risbridger GP: Prostatic hormonal carcinogenesis is
mediated by in situ estrogen production and estrogen receptor alpha
signaling. FASEB J. 22:1512–1520. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Olczak M, Orzechowska MJ, Bednarek AK and
Lipiński M: The transcriptomic profiles of ESR1 and MMP3 stratify
the risk of biochemical recurrence in primary prostate cancer
beyond clinical features. Int J Mol Sci. 24:83992023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lin Q, Cao J, Du X, Yang K, Yang X, Liang
Z, Shi J and Zhang J: CYP1B1-catalyzed 4-OHE2 promotes the
castration resistance of prostate cancer stem cells by estrogen
receptor α-mediated IL6 activation. Cell Commun Signal. 20:312022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Reis LO, Zani EL and García-Perdomo HA:
Estrogen therapy in patients with prostate cancer: A contemporary
systematic review. Int Urol Nephrol. 50:993–1003. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Christoforou P, Christopoulos PF and
Koutsilieris M: The role of estrogen receptor β in prostate cancer.
Mol Med. 20:427–434. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sieh W, Köbel M, Longacre TA, Bowtell DD,
deFazio A, Goodman MT, Høgdall E, Deen S, Wentzensen N, Moysich KB,
et al: Hormone-receptor expression and ovarian cancer survival: An
ovarian tumor tissue analysis consortium study. Lancet Oncol.
14:853–862. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Park SH, Cheung LWT, Wong AST and Leung
PCK: Estrogen regulates Snail and Slug in the down-regulation of
E-cadherin and induces metastatic potential of ovarian cancer cells
through estrogen receptor alpha. Mol Endocrinol. 22:2085–2098.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chan KK, Leung TH, Chan DW, Wei N, Lau GT,
Liu SS, Siu MK and Ngan HY: Targeting estrogen receptor subtypes
(ERα and ERβ) with selective ER modulators in ovarian cancer. J
Endocrinol. 221:325–336. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Langdon SP, Herrington CS, Hollis RL and
Gourley C: Estrogen signaling and its potential as a target for
therapy in ovarian cancer. Cancers (Basel). 12:16472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
He M, Yu W, Chang C, Miyamoto H, Liu X,
Jiang K and Yeh S: Estrogen receptor α promotes lung cancer cell
invasion via increase of and cross-talk with infiltrated
macrophages through the CCL2/CCR2/MMP9 and CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling
pathways. Mol Oncol. 14:1779–1799. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Siegel DA, Fedewa SA, Henley SJ, Pollack
LA and Jemal A: Proportion of never smokers among men and women
with lung cancer in 7 US States. JAMA Oncol. 7:302–304. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hsu LH, Liu KJ, Tsai MF, Wu CR, Feng AC,
Chu NM and Kao SH: Estrogen adversely affects the prognosis of
patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 106:51–59. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Chlebowski RT, Schwartz AG, Wakelee H,
Anderson GL, Stefanick ML, Manson JE, Rodabough RJ, Chien JW,
Wactawski-Wende J, Gass M, et al: Oestrogen plus progestin and lung
cancer in postmenopausal women (Women's Health Initiative trial): A
post-hoc analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet.
374:1243–1251. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhou J, Teng R, Xu C, Wang Q, Guo J, Xu C,
Li Z, Xie S, Shen J and Wang L: Overexpression of ERα inhibits
proliferation and invasion of MKN28 gastric cancer cells by
suppressing β-catenin. Oncol Rep. 30:1622–1630. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Takano N, Iizuka N, Hazama S, Yoshino S,
Tangoku A and Oka M: Expression of estrogen receptor-alpha and
-beta mRNAs in human gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 176:129–135.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Tang W, Liu R, Yan Y, Pan X, Wang M, Han
X, Ren H and Zhang Z: Expression of estrogen receptors and androgen
receptor and their clinical significance in gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:40765–40777. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen P, Li B and Ou-Yang L: Role of
estrogen receptors in health and disease. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 13:8390052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Chen J and Iverson D: Estrogen in
obesity-associated colon cancer: Friend or foe? Protecting
postmenopausal women but promoting late-stage colon cancer. Cancer
Causes Control. 23:1767–1773. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jiang H, Teng R, Wang Q, Zhang X, Wang H,
Wang Z, Cao J and Teng L: Transcriptional analysis of estrogen
receptor alpha variant mRNAs in colorectal cancers and their
matched normal colorectal tissues. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
112:20–24. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Dai B, Geng L, Yu Y, Sui C, Xie F, Shen W,
Zheng T and Yang J: Methylation patterns of estrogen receptor α
promoter correlate with estrogen receptor α expression and
clinicopathological factors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Biol
Med (Maywood). 239:883–890. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Hou J, Xu J, Jiang R, Wang Y, Chen C, Deng
L, Huang X, Wang X and Sun B: Estrogen-sensitive PTPRO expression
represses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by control of STAT3.
Hepatology. 57:678–688. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Iyer JK, Kalra M, Kaul A, Payton ME and
Kaul R: Estrogen receptor expression in chronic hepatitis C and
hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol.
23:6802–6816. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Kuiper GG, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M,
Nilsson S and Gustafsson JA: Cloning of a novel receptor expressed
in rat prostate and ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:5925–5930.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Mal R, Magner A, David J, Datta J,
Vallabhaneni M, Kassem M, Manouchehri J, Willingham N, Stover D,
Vandeusen J, et al: Estrogen receptor beta (ERβ): A ligand
activated tumor suppressor. Front Oncol. 10:5873862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Lewandowski S, Kalita K and Kaczmarek L:
Estrogen receptor beta. Potential functional significance of a
variety of mRNA isoforms. FEBS Lett. 524:1–5. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hua H, Zhang H, Kong Q and Jiang Y:
Mechanisms for estrogen receptor expression in human cancer. Exp
Hematol Oncol. 7:242018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Haldosén LA, Zhao C and Dahlman-Wright K:
Estrogen receptor beta in breast cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
382:665–672. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Dalal H, Dahlgren M, Gladchuk S, Brueffer
C, Gruvberger-Saal SK and Saal LH: Clinical associations of ESR2
(estrogen receptor beta) expression across thousands of primary
breast tumors. Sci Rep. 12:46962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang J, Zhang C, Chen K, Tang H, Tang J,
Song C and Xie X: ERβ1 inversely correlates with PTEN/PI3K/AKT
pathway and predicts a favorable prognosis in triple-negative
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 152:255–269. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Grober OM, Mutarelli M, Giurato G, Ravo M,
Cicatiello L, De Filippo MR, Ferraro L, Nassa G, Papa MF, Paris O,
et al: Global analysis of estrogen receptor beta binding to breast
cancer cell genome reveals an extensive interplay with estrogen
receptor alpha for target gene regulation. BMC Genomics. 12:362011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Hurtado A, Pinós T, Barbosa-Desongles A,
López-Avilés S, Barquinero J, Petriz J, Santamaria-Martínez A,
Morote J, de Torres I, Bellmunt J, et al: Estrogen receptor beta
displays cell cycle-dependent expression and regulates the G1 phase
through a non-genomic mechanism in prostate carcinoma cells. Cell
Oncol. 30:349–365. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hwang NM and Stabile LP: Estrogen receptor
ß in cancer: To ß(e) or not to ß(e)? Endocrinology.
162:bqab1622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Mak P, Leav I, Pursell B, Bae D, Yang X,
Taglienti CA, Gouvin LM, Sharma VM and Mercurio AM: ERbeta impedes
prostate cancer EMT by destabilizing HIF-1alpha and inhibiting
VEGF-mediated snail nuclear localization: Implications for Gleason
grading. Cancer Cell. 17:319–332. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Mak P, Chang C, Pursell B and Mercurio AM:
Estrogen receptor β sustains epithelial differentiation by
regulating prolyl hydroxylase 2 transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 110:4708–4713. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Lim W, Cho J, Kwon HY, Park Y, Rhyu MR and
Lee Y: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha activates and is inhibited
by unoccupied estrogen receptor beta. FEBS Lett. 583:1314–1318.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Chaurasiya S, Widmann S, Botero C, Lin CY,
Gustafsson JÅ and Strom AM: Estrogen receptor β exerts tumor
suppressive effects in prostate cancer through repression of
androgen receptor activity. PLoS One. 15:e02260572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Jefferi NES, Shamhari AA, 'Azhar NKZN,
Shin JGY, Kharir NAM, Azhar MA, Hamid ZA, Budin SB and Taib IS: The
role of ERα and ERβ in castration-resistant prostate cancer and
current therapeutic approaches. Biomedicines. 11:8262023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Leung YK, Lam HM, Wu S, Song D, Levin L,
Cheng L, Wu CL and Ho SM: Estrogen receptor beta2 and beta5 are
associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer, and promote
cancer cell migration and invasion. Endocr Relat Cancer.
17:675–689. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Lazennec G: Estrogen receptor beta, a
possible tumor suppressor involved in ovarian carcinogenesis.
Cancer Lett. 231:151–157. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Bossard C, Busson M, Vindrieux D, Gaudin
F, Machelon V, Brigitte M, Jacquard C, Pillon A, Balaguer P,
Balabanian K and Lazennec G: Potential role of estrogen receptor
beta as a tumor suppressor of epithelial ovarian cancer. PLoS One.
7:e447872012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Verardi L, Fiori J, Andrisano V, Locatelli
A, Morigi R, Naldi M, Bertucci C, Strocchi E, Boga C, Micheletti G
and Calonghi N: Indole derivative interacts with estrogen receptor
beta and inhibits human ovarian cancer cell growth. Molecules.
25:44382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Chen W, Xin B, Pang H, Han L, Shen W, Zhao
Z, Duan L, Cao P, Liu L and Zhang H: Downregulation of estrogen
receptor β inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell growth. Oncol Rep.
41:2967–2974. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Liu S, Hu C, Li M, An J, Zhou W, Guo J and
Xiao Y: Estrogen receptor beta promotes lung cancer invasion via
increasing CXCR4 expression. Cell Death Dis. 13:702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Peri S and Niv Y: Estrogen receptor beta
(ERß) in gastric cancer-A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Microb Health Dis. 6:e9842024.
|
|
108
|
Zhou F, Xu Y, Shi J, Lan X, Zou X, Wang L
and Huang Q: Expression profile of E-cadherin, estrogen receptors,
and P53 in early-onset gastric cancers. Cancer Med. 5:3403–3411.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zhou F, Jin J, Zhou L, Wu L, Cao Y, Yan H,
Huang Q, Wang L and Zou X: Suppression of estrogen receptor-beta
promotes gastric cancer cell apoptosis with induction of autophagy.
Am J Transl Res. 12:4397–4409. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Gan L, He J, Zhang X, Zhang YJ, Yu GZ,
Chen Y, Pan J, Wang JJ and Wang X: Expression profile and
prognostic role of sex hormone receptors in gastric cancer. BMC
Cancer. 12:5662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Caiazza F, Ryan EJ, Doherty G, Winter DC
and Sheahan K: Estrogen receptors and their implications in
colorectal carcinogenesis. Front Oncol. 5:192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Hartman J, Edvardsson K, Lindberg K, Zhao
C, Williams C, Ström A and Gustafsson JA: Tumor repressive
functions of estrogen receptor beta in SW480 colon cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 69:6100–6106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Topi G, Satapathy SR, Dash P, Fred Mehrabi
S, Ehrnström R, Olsson R, Lydrup ML and Sjölander A:
Tumour-suppressive effect of oestrogen receptor β in colorectal
cancer patients, colon cancer cells, and a zebrafish model. J
Pathol. 251:297–309. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Konstantinopoulos PA, Kominea A, Vandoros
G, Sykiotis GP, Andricopoulos P, Varakis I, Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G
and Papavassiliou AG: Oestrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) is
abundantly expressed in normal colonic mucosa, but declines in
colon adenocarcinoma paralleling the tumour's dedifferentiation.
Eur J Cancer. 39:1251–1258. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Rudolph A, Toth C, Hoffmeister M, Roth W,
Herpel E, Jansen L, Marx A, Brenner H and Chang-Claude J:
Expression of oestrogen receptor β and prognosis of colorectal
cancer. Br J Cancer. 107:831–839. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Iavarone M, Lampertico P, Seletti C,
Donato MF, Ronchi G, Del Ninno E and Colombo M: The clinical and
pathogenetic significance of estrogen receptor-beta expression in
chronic liver diseases and liver carcinoma. Cancer. 98:529–534.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Yang W, Lu Y, Xu Y, Xu L, Zheng W, Wu Y,
Li L and Shen P: Estrogen represses hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
growth via inhibiting alternative activation of tumor-associated
macrophages (TAMs). J Biol Chem. 287:40140–40149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Marzioni M, Torrice A, Saccomanno S,
Rychlicki C, Agostinelli L, Pierantonelli I, Rhönnstad P, Trozzi L,
Apelqvist T, Gentile R, et al: An oestrogen receptor β-selective
agonist exerts anti-neoplastic effects in experimental intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 44:134–142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Handelsman DJ: History of androgens and
androgen action. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab.
36:1016292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Brinkmann AO, Faber PW, van Rooij HC,
Kuiper GG, Ris C, Klaassen P, van der Korput JA, Voorhorst MM, van
Laar JH, Mulder E, et al: The human androgen receptor: Domain
structure, genomic organization and regulation of expression. J
Steroid Biochem. 34:307–310. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Davey RA and Grossmann M: Androgen
receptor structure, function and biology: From bench to bedside.
Clin Biochem Rev. 37:3–15. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Moilanen A, Rouleau N, Ikonen T, Palvimo
JJ and Jänne OA: The presence of a transcription activation
function in the hormone-binding domain of androgen receptor is
revealed by studies in yeast cells. FEBS Lett. 412:355–358. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Ueda T, Bruchovsky N and Sadar MD:
Activation of the androgen receptor N-terminal domain by
interleukin-6 via MAPK and STAT3 signal transduction pathways. J
Biol Chem. 277:7076–7085. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Asai S, Goto Y, Tanigawa K, Tomioka Y,
Kato M, Mizuno K, Sakamoto S and Seki N: MiR-15b-5p inhibits
castration-resistant growth of prostate cancer cells by targeting
the muscarinic cholinergic receptor CHRM3. FEBS Lett.
597:1164–1175. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Martin-Caraballo M: Regulation of
molecular biomarkers associated with the progression of prostate
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 25:41712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Muralidhar A, Gamat-Huber M, Vakkalanka S
and McNeel DG: Sequence of androgen receptor-targeted vaccination
with androgen deprivation therapy affects anti-prostate tumor
efficacy. J Immunother Cancer. 12:e0088482024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhong M, Xu W, Tian P, Zhang Q, Wang Z,
Liang L, Zhang Q, Yang Y, Lu Y and Wei GH: An inherited allele
confers prostate cancer progression and drug resistance via
RFX6/HOXA10-orchestrated TGFβ signaling. Adv Sci (Weinh).
11:e24014922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Liu C, Chen B, Xu P, Yang J, Nip C, Wang
L, Shen Y, Ning S, Shang Y, Corey E, et al: Plexin D1 emerges as a
novel target in the development of neural lineage plasticity in
treatment-resistant prostate cancer. Res Sq [Preprint].
rs.3.rs-4095949. 2024.
|
|
129
|
Matsumoto K, Kosaka T, Takeda T, Fukumoto
K, Yasumizu Y, Tanaka N, Morita S, Mizuno R, Asanuma H and Oya M:
Appropriate definition of non-metastatic castration-resistant
prostate cancer (nmCRPC) and optimal timing of androgen receptor
signaling inhibitor (ARSI). Int J Clin Oncol. 29:1198–1203. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Shiota M, Ushijima M, Tsukahara S,
Nagakawa S, Okada T, Tanegashima T, Kobayashi S, Matsumoto T and
Eto M: Oxidative stress in peroxisomes induced by androgen receptor
inhibition through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
promotes enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer. Free Radic
Biol Med. 221:81–88. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Ramírez-de-Arellano A, Pereira-Suárez AL,
Rico-Fuentes C, López-Pulido EI, Villegas-Pineda JC and Sierra-Diaz
E: Distribution and effects of estrogen receptors in prostate
cancer: Associated molecular mechanisms. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 12:8115782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Palmieri C, Linden H, Birrell SN,
Wheelwright S, Lim E, Schwartzberg LS, Dwyer AR, Hickey TE, Rugo
HS, Cobb P, et al: Activity and safety of enobosarm, a novel, oral,
selective androgen receptor modulator, in androgen
receptor-positive, oestrogen receptor-positive, and HER2-negative
advanced breast cancer (Study G200802): A randomised, open-label,
multicentre, multinational, parallel design, phase 2 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 25:317–325. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Xu F, Xu K, Fan L, Li X, Liu Y, Yang F,
Zhu C and Guan X: Estrogen receptor beta suppresses the androgen
receptor oncogenic effects in triple-negative breast cancer. Chin
Med J (Engl). 137:338–349. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Cuenca-López MD, Montero JC, Morales JC,
Prat A, Pandiella A and Ocana A: Phospho-kinase profile of triple
negative breast cancer and androgen receptor signaling. BMC Cancer.
14:3022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Garay JP, Karakas B, Abukhdeir AM,
Cosgrove DP, Gustin JP, Higgins MJ, Konishi H, Konishi Y, Lauring
J, Mohseni M, et al: The growth response to androgen receptor
signaling in ERα-negative human breast cells is dependent on p21
and mediated by MAPK activation. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R272012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Chang C, Lee SO, Yeh S and Chang TM:
Androgen receptor (AR) differential roles in hormone-related tumors
including prostate, bladder, kidney, lung, breast and liver.
Oncogene. 33:3225–3234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Chadha S, Rao BR, Slotman BJ, van
Vroonhoven CC and van der Kwast TH: An immunohistochemical
evaluation of androgen and progesterone receptors in ovarian
tumors. Hum Pathol. 24:90–95. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Cardillo MR, Petrangeli E, Aliotta N,
Salvatori L, Ravenna L, Chang C and Castagna G: Androgen receptors
in ovarian tumors: Correlation with oestrogen and progesterone
receptors in an immunohistochemical and semiquantitative image
analysis study. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 17:231–237. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Kohan-Ivani K, Gabler F, Selman A, Vega M
and Romero C: Role of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) on TGF-β1 signaling
pathway in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 142:47–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Ligr M, Patwa RR, Daniels G, Pan L, Wu X,
Li Y, Tian L, Wang Z, Xu R, Wu J, et al: Expression and function of
androgen receptor coactivator p44/Mep50/WDR77 in ovarian cancer.
PLoS One. 6:e262502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Martins FC, Couturier DL, Paterson A,
Karnezis AN, Chow C, Nazeran TM, Odunsi A, Gentry-Maharaj A, Vrvilo
A, Hein A, et al: Clinical and pathological associations of PTEN
expression in ovarian cancer: A multicentre study from the ovarian
tumour tissue analysis consortium. Br J Cancer. 123:793–802. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Liu S, Hu C, Li M, Zhou W, Wang R and Xiao
Y: Androgen receptor suppresses lung cancer invasion and increases
cisplatin response via decreasing TPD52 expression. Int J Biol Sci.
19:3709–3725. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Zhou J, Wang H, Sun Q, Liu X, Wu Z, Wang
X, Fang W and Ma Z: miR-224-5p-enriched exosomes promote
tumorigenesis by directly targeting androgen receptor in non-small
cell lung cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 23:1217–1228. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Li X, Tang Y, Liang P, Sun M, Li T, Shen Z
and Sha S: Luteolin inhibits A549 cells proliferation and migration
by down-regulating androgen receptors. Eur J Med Res. 28:3532023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Recchia AG, Musti AM, Lanzino M, Panno ML,
Turano E, Zumpano R, Belfiore A, Andò S and Maggiolini M: A
cross-talk between the androgen receptor and the epidermal growth
factor receptor leads to p38MAPK-dependent activation of mTOR and
cyclinD1 expression in prostate and lung cancer cells. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 41:603–614. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Liu B, Zhou M, Li X, Zhang X, Wang Q, Liu
L, Yang M, Yang D, Guo Y, Zhang Q, et al: Interrogation of gender
disparity uncovers androgen receptor as the transcriptional
activator for oncogenic miR-125b in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis.
12:4412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Xia N, Cui J, Zhu M, Xing R and Lu Y:
Androgen receptor variant 12 promotes migration and invasion by
regulating MYLK in gastric cancer. J Pathol. 248:304–315. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Soleymani Fard S, Yazdanbod M, Sotoudeh M,
Bashash D, Mahmoodzadeh H, Saliminejad K, Mousavi SA, Ghaffari SH
and Alimoghaddam K: Prognostic and therapeutic significance of
androgen receptor in patients with gastric cancer. Onco Targets
Ther. 13:9821–9837. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Gu S, Honisch S, Kounenidakis M, Alkahtani
S, Alarifi S, Alevizopoulos K, Stournaras C and Lang F: Membrane
androgen receptor down-regulates c-src-activity and beta-catenin
transcription and triggers GSK-3beta-phosphorylation in colon tumor
cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1402–1412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Alkahtani S: Testosterone induced
apoptosis in colon cancer cells is regulated by PI3K/Rac1
signaling. Asian J Androl. 15:831–834. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Rodríguez-Santiago Y, Garay-Canales CA,
Nava-Castro KE and Morales-Montor J: Sexual dimorphism in
colorectal cancer: Molecular mechanisms and treatment strategies.
Biol Sex Differ. 15:482024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Acosta-Lopez S, Diaz-Bethencourt D,
Concepción-Massip T, Martin-Fernandez de Basoa MC, Plata-Bello A,
Gonzalez-Rodriguez A, Perez-Hernandez F and Plata-Bello J: The
androgen receptor expression and its activity have different
relationships with prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep.
10:220462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Ren QN, Zhang H, Sun CY, Zhou YF, Yang XF,
Long JW, Li XX, Mai SJ, Zhang MY, Zhang HZ, et al: Phosphorylation
of androgen receptor by mTORC1 promotes liver steatosis and
tumorigenesis. Hepatology. 75:1123–1138. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Ren H, Ren B, Zhang J, Zhang X, Li L, Meng
L, Li Z, Li J, Gao Y and Ma X: Androgen enhances the activity of
ETS-1 and promotes the proliferation of HCC cells. Oncotarget.
8:109271–109288. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Ouyang X, Feng L, Liu G, Yao L, Wang Z,
Liu S, Xiao Y and Zhang G: Androgen receptor (AR) decreases HCC
cells migration and invasion via miR-325/ACP5 signaling. J Cancer.
12:1915–1925. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Porter W, Saville B, Hoivik D and Safe S:
Functional synergy between the transcription factor Sp1 and the
estrogen receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 11:1569–1580. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Greaves E, Collins F, Critchley HOD and
Saunders PTK: ERβ-dependent effects on uterine endothelial cells
are cell specific and mediated via Sp1. Hum Reprod. 28:2490–2501.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Eisermann K, Broderick CJ, Bazarov A,
Moazam MM and Fraizer GC: Androgen up-regulates vascular
endothelial growth factor expression in prostate cancer cells via
an Sp1 binding site. Mol Cancer. 12:72013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Setlur SR, Mertz KD, Hoshida Y, Demichelis
F, Lupien M, Perner S, Sboner A, Pawitan Y, Andrén O, Johnson LA,
et al: Estrogen-dependent signaling in a molecularly distinct
subclass of aggressive prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
100:815–825. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Kohvakka A, Sattari M, Shcherban A, Annala
M, Urbanucci A, Kesseli J, Tammela TLJ, Kivinummi K, Latonen L,
Nykter M and Visakorpi T: AR and ERG drive the expression of
prostate cancer specific long noncoding RNAs. Oncogene.
39:5241–5251. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Lombardi AP, Pisolato R, Vicente CM,
Lazari MF, Lucas TF and Porto CS: Estrogen receptor beta (ERβ)
mediates expression of β-catenin and proliferation in prostate
cancer cell line PC-3. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 430:12–24. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Song LN and Gelmann EP: Interaction of
beta-catenin and TIF2/GRIP1 in transcriptional activation by the
androgen receptor. J Biol Chem. 280:37853–37867. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Dahlman-Wright K, Qiao Y, Jonsson P,
Gustafsson JÅ, Williams C and Zhao C: Interplay between AP-1 and
estrogen receptor α in regulating gene expression and proliferation
networks in breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 33:1684–1691.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Frønsdal K, Engedal N, Slagsvold T and
Saatcioglu F: CREB binding protein is a coactivator for the
androgen receptor and mediates cross-talk with AP-1. J Biol Chem.
273:31853–31859. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Sato N, Sadar MD, Bruchovsky N, Saatcioglu
F, Rennie PS, Sato S, Lange PH and Gleave ME: Androgenic induction
of prostate-specific antigen gene is repressed by protein-protein
interaction between the androgen receptor and AP-1/c-Jun in the
human prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. J Biol Chem.
272:17485–17494. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Dadiani M, Seger D, Kreizman T, Badikhi D,
Margalit R, Eilam R and Degani H: Estrogen regulation of vascular
endothelial growth factor in breast cancer in vitro and in vivo:
The role of estrogen receptor alpha and c-Myc. Endocr Relat Cancer.
16:819–834. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Paruthiyil S, Parmar H, Kerekatte V, Cunha
GR, Firestone GL and Leitman DC: Estrogen receptor beta inhibits
human breast cancer cell proliferation and tumor formation by
causing a G2 cell cycle arrest. Cancer Res. 64:423–428. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Gao L, Schwartzman J, Gibbs A, Lisac R,
Kleinschmidt R, Wilmot B, Bottomly D, Coleman I, Nelson P, McWeeney
S and Alumkal J: Androgen receptor promotes ligand-independent
prostate cancer progression through c-Myc upregulation. PLoS One.
8:e635632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Smart E, Semina SE and Frasor J: Update on
the role of NFκB in promoting aggressive phenotypes of estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer. Endocrinology. 161:bqaa1522020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Mak P, Li J, Samanta S and Mercurio AM:
ERβ regulation of NF-kB activation in prostate cancer is mediated
by HIF-1. Oncotarget. 6:40247–40254. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Zhang L, Altuwaijri S, Deng F, Chen L, Lal
P, Bhanot UK, Korets R, Wenske S, Lilja HG, Chang C, et al:
NF-kappaB regulates androgen receptor expression and prostate
cancer growth. Am J Pathol. 175:489–499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Binai NA, Damert A, Carra G, Steckelbroeck
S, Löwer J, Löwer R and Wessler S: Expression of estrogen receptor
alpha increases leptin-induced STAT3 activity in breast cancer
cells. Int J Cancer. 127:55–66. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Wang HC, Yeh HH, Huang WL, Lin CC, Su WP,
Chen HHW, Lai WW and Su WC: Activation of the signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 pathway up-regulates estrogen
receptor-beta expression in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol
Endocrinol. 25:1145–1158. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Yamamoto T, Sato N, Sekine Y, Yumioka T,
Imoto S, Junicho A, Fuse H and Matsuda T: Molecular interactions
between STAT3 and protein inhibitor of activated STAT3, and
androgen receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 306:610–615. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Csabai L, Fazekas D, Kadlecsik T,
Szalay-Bekő M, Bohár B, Madgwick M, Módos D, Ölbei M, Gul L,
Sudhakar P, et al: SignaLink3: A multi-layered resource to uncover
tissue-specific signaling networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 50(D1):
D701–D709. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Lin Z, Yin P, Reierstad S, O'Halloran M,
Coon VJS, Pearson EK, Mutlu GM and Bulun SE: Adenosine A1 receptor,
a target and regulator of estrogen receptoralpha action, mediates
the proliferative effects of estradiol in breast cancer. Oncogene.
29:1114–1122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Xu J, Wu F, Zhu Y, Wu T, Cao T, Gao W, Liu
M, Qian W, Feng G, Xi X and Hou S: ANGPTL4 regulates ovarian cancer
progression by activating the ERK1/2 pathway. Cancer Cell Int.
24:542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Zhao N, Peacock SO, Lo CH, Heidman LM,
Rice MA, Fahrenholtz CD, Greene AM, Magani F, Copello VA, Martinez
MJ, et al: Arginine vasopressin receptor 1a is a therapeutic target
for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Sci Transl Med.
11:eaaw46362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Guan B, Ma J, Yang Z, Yu F and Yao J:
LncRNA NCK1-AS1 exerts oncogenic property in gastric cancer by
targeting the miR-22-3p/BCL9 axis to activate the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling. Environ Toxicol. 36:1640–1653. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Wang X, Feng M, Xiao T, Guo B, Liu D, Liu
C, Pei J, Liu Q, Xiao Y, Rosin-Arbesfeld R, et al: BCL9/BCL9L
promotes tumorigenicity through immune-dependent and independent
mechanisms in triple negative breast cancer. Oncogene.
40:2982–2997. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Li P, Miao C, Liang C, Shao P, Wang Z and
Li J: Silencing CAPN2 expression inhibited castration-resistant
prostate cancer cells proliferation and invasion via AKT/mTOR
signal pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2017:25936742017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Fang X, Hong Y, Dai L, Qian Y, Zhu C, Wu B
and Li S: CRH promotes human colon cancer cell proliferation via
IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway and VEGF-induced tumor
angiogenesis. Mol Carcinog. 56:2434–2445. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Jin C, Han-Hua D, Qiu-Meng L, Deng N,
Peng-Chen D, Jie M, Lei X, Xue-Wu Z, Hui-Fang L, Yan C, et al:
MTDH-stabilized DDX17 promotes tumor initiation and progression
through interacting with YB1 to induce EGFR transcription in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 42:169–183. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Chen Z, Song Y, Li P and Gao W: GRIN2D
knockdown suppresses the progression of lung adenocarcinoma by
regulating the E2F signalling pathway. Cell Signal. 107:1106852023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Yan T, Huang L, Yan Y, Zhong Y, Xie H and
Wang X: MAPK/AP-1 signaling pathway is involved in the protection
mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes
against ultraviolet-induced photoaging in human dermal fibroblasts.
Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 36:98–106. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Guo Z, Peng G, Li E, Xi S, Zhang Y, Li Y,
Lin X, Li G, Wu Q and He J: MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine
kinase 2 promotes proliferation, metastasis, and predicts poor
prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 7:106122017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Gupta A, Hossain MM, Miller N, Kerin M,
Callagy G and Gupta S: NCOA3 coactivator is a transcriptional
target of XBP1 and regulates PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 signalling in breast
cancer. Oncogene. 35:5860–5871. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Baquié M, St-Onge L, Kerr-Conte J,
Cobo-Vuilleumier N, Lorenzo PI, Jimenez Moreno CM, Cederroth CR,
Nef S, Borot S, Bosco D, et al: The liver receptor homolog-1
(LRH-1) is expressed in human islets and protects {beta}-cells
against stress-induced apoptosis. Hum Mol Genet. 20:2823–2833.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Zhu J, Zou Z, Nie P, Kou X, Wu B, Wang S,
Song Z and He J: Downregulation of microRNA-27b-3p enhances
tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer by increasing NR5A2 and CREB1
expression. Cell Death Dis. 7:e24542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Kao TW, Chen HH, Lin J, Wang TL and Shen
YA: PBX1 as a novel master regulator in cancer: Its regulation,
molecular biology, and therapeutic applications. Biochim Biophys
Acta Rev Cancer. 1879:1890852024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Elix C, Pal SK and Jones JO: The role of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in prostate
cancer. Asian J Androl. 20:238–243. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Carotenuto M, De Antonellis P, Liguori L,
Benvenuto G, Magliulo D, Alonzi A, Turino C, Attanasio C, Damiani
V, Bello AM, et al: H-Prune through GSK-3β interaction sustains
canonical WNT/β-catenin signaling enhancing cancer progression in
NSCLC. Oncotarget. 5:5736–5749. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Teng F, Zhang JX, Chen Y, Shen XD, Su C,
Guo YJ, Wang PH, Shi CC, Lei M, Cao YO and Liu SQ: LncRNA
NKX2-1-AS1 promotes tumor progression and angiogenesis via
upregulation of SERPINE1 expression and activation of the VEGFR-2
signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Mol Oncol. 15:1234–1255. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Sun G, Wei Y, Zhou B, Wang M, Luan R, Bai
Y, Li H, Wang S, Zheng D, Wang C, et al: BAP18 facilitates
CTCF-mediated chromatin accessible to regulate enhancer activity in
breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 30:1260–1278. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Pospiech K, Orzechowska M, Nowakowska M,
Anusewicz D, Płuciennik E, Kośla K and Bednarek AK: TGFα-EGFR
pathway in breast carcinogenesis, association with WWOX expression
and estrogen activation. J Appl Genet. 63:339–359. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Maeda A, Nishino T, Matsunaga R, Yokoyama
A, Suga H, Yagi T and Konishi H: Transglutaminase-mediated
cross-linking of WDR54 regulates EGF receptor-signaling. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1866:285–295. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Cao L, Petrusca DN, Satpathy M, Nakshatri
H, Petrache I and Matei D: Tissue transglutaminase protects
epithelial ovarian cancer cells from cisplatin-induced apoptosis by
promoting cell survival signaling. Carcinogenesis. 29:1893–1900.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Qian Y, Liu X, Feng Y, Li X and Xuan Y:
Tenascin C regulates cancer cell glycolysis and tumor progression
in prostate cancer. Int J Urol. 29:578–585. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Wei L, Sun C, Zhang Y, Han N and Sun S:
miR-503-5p inhibits colon cancer tumorigenesis, angiogenesis, and
lymphangiogenesis by directly downregulating VEGF-A. Gene Ther.
29:28–40. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Xiao L, Parolia A, Qiao Y, Bawa P, Eyunni
S, Mannan R, Carson SE, Chang Y, Wang X, Zhang Y, et al: Targeting
SWI/SNF ATPases in enhancer-addicted prostate cancer. Nature.
601:434–439. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Kim YC, Chen C and Bolton EC: Androgen
receptor-mediated growth suppression of HPr-1AR and PC3-Lenti-AR
prostate epithelial cells. PLoS One. 10:e01382862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Zhou D, Chen B, Ye JJ and Chen S: A novel
crosstalk mechanism between nuclear receptor-mediated and growth
factor/Ras-mediated pathways through PNRC-Grb2 interaction.
Oncogene. 23:5394–5404. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Huang YL, Chou WC, Hsiung CN, Hu LY, Chu
HW and Shen CY: FGFR2 regulates Mre11 expression and double-strand
break repair via the MEK-ERK-POU1F1 pathway in breast
tumorigenesis. Hum Mol Genet. 24:3506–3517. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Hua S, Kittler R and White KP: Genomic
antagonism between retinoic acid and estrogen signaling in breast
cancer. Cell. 137:1259–1271. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
O'Neill CF, Urs S, Cinelli C, Lincoln A,
Nadeau RJ, León R, Toher J, Mouta-Bellum C, Friesel RE and Liaw L:
Notch2 signaling induces apoptosis and inhibits human MDA-MB-231
×enograft growth. Am J Pathol. 171:1023–1036. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Xiu MX and Liu YM: The role of oncogenic
Notch2 signaling in cancer: A novel therapeutic target. Am J Cancer
Res. 9:837–854. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Shen T, Wang W, Zhou W, Coleman I, Cai Q,
Dong B, Ittmann MM, Creighton CJ, Bian Y, Meng Y, et al: MAPK4
promotes prostate cancer by concerted activation of androgen
receptor and AKT. J Clin Invest. 131:e1354652021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Ross-Innes CS, Brown GD and Carroll JS: A
co-ordinated interaction between CTCF and ER in breast cancer
cells. BMC Genomics. 12:5932011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Yang SZ and Abdulkadir SA: Early growth
response gene 1 modulates androgen receptor signaling in prostate
carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 278:39906–39911. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Grinshpun A, Chen V, Sandusky ZM, Fanning
SW and Jeselsohn R: ESR1 activating mutations: From structure to
clinical application. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1878:1888302023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Barker R, Biernacka K, Kingshott G, Sewell
A, Gwiti P, Martin RM, Lane JA, McGeagh L, Koupparis A, Rowe E, et
al: Associations of CTCF and FOXA1 with androgen and IGF pathways
in men with localized prostate cancer. Growth Horm IGF Res. 69–70.
1015332023.
|
|
212
|
Pu J, Zhang D, Wang B, Zhu P, Yang W, Wang
K, Yang Z and Song Q: FOXA1/UBE2T inhibits CD8+T cell
activity by inducing mediates glycolysis in lung adenocarcinoma.
Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 29:1342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Vaclavicek A, Bermejo JL, Schmutzler RK,
Sutter C, Wappenschmidt B, Meindl A, Kiechle M, Arnold N, Weber
BHF, Niederacher D, et al: Polymorphisms in the Janus kinase 2
(JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)
genes: Putative association of the STAT gene region with familial
breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 14:267–277. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Xu WF, Ma YC, Ma HS, Shi L, Mu H, Ou WB,
Peng J, Li TT, Qin T, Zhou HM, et al: Co-targeting CK2α and YBX1
suppresses tumor progression by coordinated inhibition of the
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Cycle. 18:3472–3490. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Liu X, Xu M, Jia W, Duan Y, Ma J and Tai
W: PU.1 negatively regulates tumorigenesis in non-small-cell lung
cancer. Med Oncol. 40:792023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Tortorella E, Giantulli S, Sciarra A and
Silvestri I: AR and PI3K/AKT in prostate cancer: A tale of two
interconnected pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 24:20462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Hua S, Kallen CB, Dhar R, Baquero MT,
Mason CE, Russell BA, Shah PK, Liu J, Khramtsov A, Tretiakova MS,
et al: Genomic analysis of estrogen cascade reveals histone variant
H2A.Z associated with breast cancer progression. Mol Syst Biol.
4:1882008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Taslim C, Chen Z, Huang K, Huang TH, Wang
Q and Lin S: Integrated analysis identifies a class of
androgen-responsive genes regulated by short combinatorial
long-range mechanism facilitated by CTCF. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:4754–4764. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Zhang H, Li S, Zhou R, Dong T, Zhang X, Yu
M, Lin J, Shi M, Geng E, Li J, et al: SRCAP complex promotes lung
cancer progression by reprograming the oncogenic transcription of
Hippo-YAP/TAZ signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 585:2166672024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Stelzer G, Rosen R, Plaschkes I, Zimmerman
S, Twik M, Fishilevich S, Stein TI, Nudel R, Lieder I, Mazor Y, et
al: The GeneCards suite: From gene data mining to disease genome
sequence analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 54:1.30.1–1.30.33.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Montes-de-Oca-Fuentes EV, Jácome-López K,
Zarco-Mendoza A, Guerrero G, Ventura-Gallegos JL, Juárez-Méndez S,
Cabrera-Quintero AJ, Recillas-Targa F and Zentella-Dehesa A:
Differential DNA methylation and CTCF binding between the ESR1
promoter a of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Mol Biol
Rep. 51:1482024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Rossi EL, Dunlap SM, Bowers LW, Khatib SA,
Doerstling SS, Smith LA, Ford NA, Holley D, Brown PH, Estecio MR,
et al: Energy balance modulation impacts epigenetic reprogramming,
ERα and ERβ expression, and mammary tumor development in MMTV-neu
transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 77:2500–2511. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Chaudhary S, Krishna BM and Mishra SK: A
novel FOXA1/ESR1 interacting pathway: A study of
Oncomine™ breast cancer microarrays. Oncol Lett.
14:1247–1264. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Zhang Y, Huang YX, Wang DL, Yang B, Yan
HY, Lin LH, Li Y, Chen J, Xie LM, Huang YS, et al: LncRNA DSCAM-AS1
interacts with YBX1 to promote cancer progression by forming a
positive feedback loop that activates FOXA1 transcription network.
Theranostics. 10:10823–10837. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Wu Y, Li Z, Wedn AM, Casey AN, Brown D,
Rao SV, Omarjee S, Hooda J, Carroll JS, Gertz J, et al: FOXA1
reprogramming dictates retinoid X receptor response in ESR1-mutant
breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 21:591–604. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Lupien M, Eeckhoute J, Meyer CA, Wang Q,
Zhang Y, Li W, Carroll JS, Liu XS and Brown M: FoxA1 translates
epigenetic signatures into enhancer-driven lineage-specific
transcription. Cell. 132:958–970. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Rangel N, Fortunati N, Osella-Abate S,
Annaratone L, Isella C, Catalano MG, Rinella L, Metovic J,
Boldorini R, Balmativola D, et al: FOXA1 and AR in invasive breast
cancer: New findings on their co-expression and impact on prognosis
in ER-positive patients. BMC Cancer. 18:7032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Seachrist DD, Anstine LJ and Keri RA:
FOXA1: A pioneer of nuclear receptor action in breast cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 13:52052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Tsirigoti C, Ali MM, Maturi V, Heldin CH
and Moustakas A: Loss of SNAI1 induces cellular plasticity in
invasive triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
13:8322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Gerhardt J, Montani M, Wild P, Beer M,
Huber F, Hermanns T, Müntener M and Kristiansen G: FOXA1 promotes
tumor progression in prostate cancer and represents a novel
hallmark of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Am J Pathol.
180:848–861. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Jin HJ, Zhao JC, Ogden I, Bergan RC and Yu
J: Androgen receptor-independent function of FoxA1 in prostate
cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 73:3725–3736. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Li Z, Tuteja G, Schug J and Kaestner KH:
Foxa1 and Foxa2 are essential for sexual dimorphism in liver
cancer. Cell. 148:72–83. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Ross-Innes CS, Stark R, Holmes KA, Schmidt
D, Spyrou C, Russell R, Massie CE, Vowler SL, Eldridge M and
Carroll JS: Cooperative interaction between retinoic acid
receptor-alpha and estrogen receptor in breast cancer. Genes Dev.
24:171–182. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Salvatori L, Ravenna L, Caporuscio F,
Principessa L, Coroniti G, Frati L, Russo MA and Petrangeli E:
Action of retinoic acid receptor on EGFR gene transactivation and
breast cancer cell proliferation: Interplay with the estrogen
receptor. Biomed Pharmacother. 65:307–312. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Gorodetska I, Offermann A, Püschel J,
Lukiyanchuk V, Gaete D, Kurzyukova A, Freytag V, Haider MT, Fjeldbo
CS, Di Gaetano S, et al: ALDH1A1 drives prostate cancer metastases
and radioresistance by interplay with AR- and RAR-dependent
transcription. Theranostics. 14:714–737. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Zou A, Marschke KB, Arnold KE, Berger EM,
Fitzgerald P, Mais DE and Allegretto EA: Estrogen receptor beta
activates the human retinoic acid receptor alpha-1 promoter in
response to tamoxifen and other estrogen receptor antagonists, but
not in response to estrogen. Mol Endocrinol. 13:418–430. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Magnani L, Patten DK, Nguyen VT, Hong SP,
Steel JH, Patel N, Lombardo Y, Faronato M, Gomes AR, Woodley L, et
al: The pioneer factor PBX1 is a novel driver of metastatic
progression in ERα-positive breast cancer. Oncotarget.
6:21878–21891. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Magnani L, Ballantyne EB, Zhang X and
Lupien M: PBX1 genomic pioneer function drives ERα signaling
underlying progression in breast cancer. PLoS Genet.
7:e10023682011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Kikugawa T, Kinugasa Y, Shiraishi K, Nanba
D, Nakashiro KI, Tanji N, Yokoyama M and Higashiyama S: PLZF
regulates Pbx1 transcription and Pbx1-HoxC8 complex leads to
androgen-independent prostate cancer proliferation. Prostate.
66:1092–1099. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Shen T, Dong B, Meng Y, Moore DD and Yang
F: A COP1-GATA2 axis suppresses AR signaling and prostate cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 119:e22053501192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Yang X, Zhang Q, Li S, Devarajan R, Luo B,
Tan Z, Wang Z, Giannareas N, Wenta T, Ma W, et al: GATA2 co-opts
TGFβ1/SMAD4 oncogenic signaling and inherited variants at 6q22 to
modulate prostate cancer progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
42:1982023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Chaytor L, Simcock M, Nakjang S, Heath R,
Walker L, Robson C, Jones D and Gaughan L: The pioneering role of
GATA2 in androgen receptor variant regulation is controlled by
bromodomain and extraterminal proteins in castrate-resistant
prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 17:1264–1278. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Wang Y, He X, Ngeow J and Eng C: GATA2
negatively regulates PTEN by preventing nuclear translocation of
androgen receptor and by androgen-independent suppression of PTEN
transcription in breast cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 21:569–576. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Treeck O, Diepolder E, Skrzypczak M,
Schüler-Toprak S and Ortmann O: Knockdown of estrogen receptor β
increases proliferation and affects the transcriptome of
endometrial adenocarcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. 19:7452019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Konduri SD, Medisetty R, Liu W,
Kaipparettu BA, Srivastava P, Brauch H, Fritz P, Swetzig WM,
Gardner AE, Khan SA and Das GM: Mechanisms of estrogen receptor
antagonism toward p53 and its implications in breast cancer
therapeutic response and stem cell regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 107:15081–15086. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Fritah A, Saucier C, Mester J, Redeuilh G
and Sabbah M: p21WAF1/CIP1 selectively controls the transcriptional
activity of estrogen receptor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 25:2419–2430.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Nishimura FG, Sampaio BB, Komoto TT, da
Silva WJ, da Costa MMG, Haddad GI, Peronni KC, Evangelista AF,
Hossain M, Dimmock JR, et al: Exploring CDKN1A upregulation
mechanisms: Insights into cell cycle arrest induced by NC2603
curcumin analog in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci.
25:49892024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Mukhopadhyay UK, Oturkar CC, Adams C,
Wickramasekera N, Bansal S, Medisetty R, Miller A, Swetzig WM,
Silwal-Pandit L, Børresen-Dale AL, et al: TP53 status as a
determinant of pro-vs anti-tumorigenic effects of estrogen
receptor-beta in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 111:1202–1215.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
He Y, Alejo S, Venkata PP, Johnson JD,
Loeffel I, Pratap UP, Zou Y, Lai Z, Tekmal RR, Kost ER and Sareddy
GR: Therapeutic targeting of ovarian cancer stem cells using
estrogen receptor beta agonist. Int J Mol Sci. 23:71592022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Lee CI, Goodwin A and Wilcken N:
Fulvestrant for hormone-sensitive metastatic breast cancer.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CD0110932017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Augusto TV, Amaral C, Varela CL, Bernardo
F, da Silva ET, Roleira FFM, Costa S, Teixeira N and
Correia-da-Silva G: Effects of new C6-substituted steroidal
aromatase inhibitors in hormone-sensitive breast cancer cells: Cell
death mechanisms and modulation of estrogen and androgen receptors.
J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 195:1054862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Jacobson EM, Hugo ER, Tuttle TR, Papoian R
and Ben-Jonathan N: Unexploited therapies in breast and prostate
cancer: Blockade of the prolactin receptor. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 21:691–698. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Basile D, Cinausero M, Iacono D, Pelizzari
G, Bonotto M, Vitale MG, Gerratana L and Puglisi F: Androgen
receptor in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer: Beyond
expression. Cancer Treat Rev. 61:15–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Bonkhoff H, Fixemer T, Hunsicker I and
Remberger K: Estrogen receptor expression in prostate cancer and
premalignant prostatic lesions. Am J Pathol. 155:641–647. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
255
|
Robinson JLL, Macarthur S, Ross-Innes CS,
Tilley WD, Neal DE, Mills IG and Carroll JS: Androgen receptor
driven transcription in molecular apocrine breast cancer is
mediated by FoxA1. EMBO J. 30:3019–3027. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|