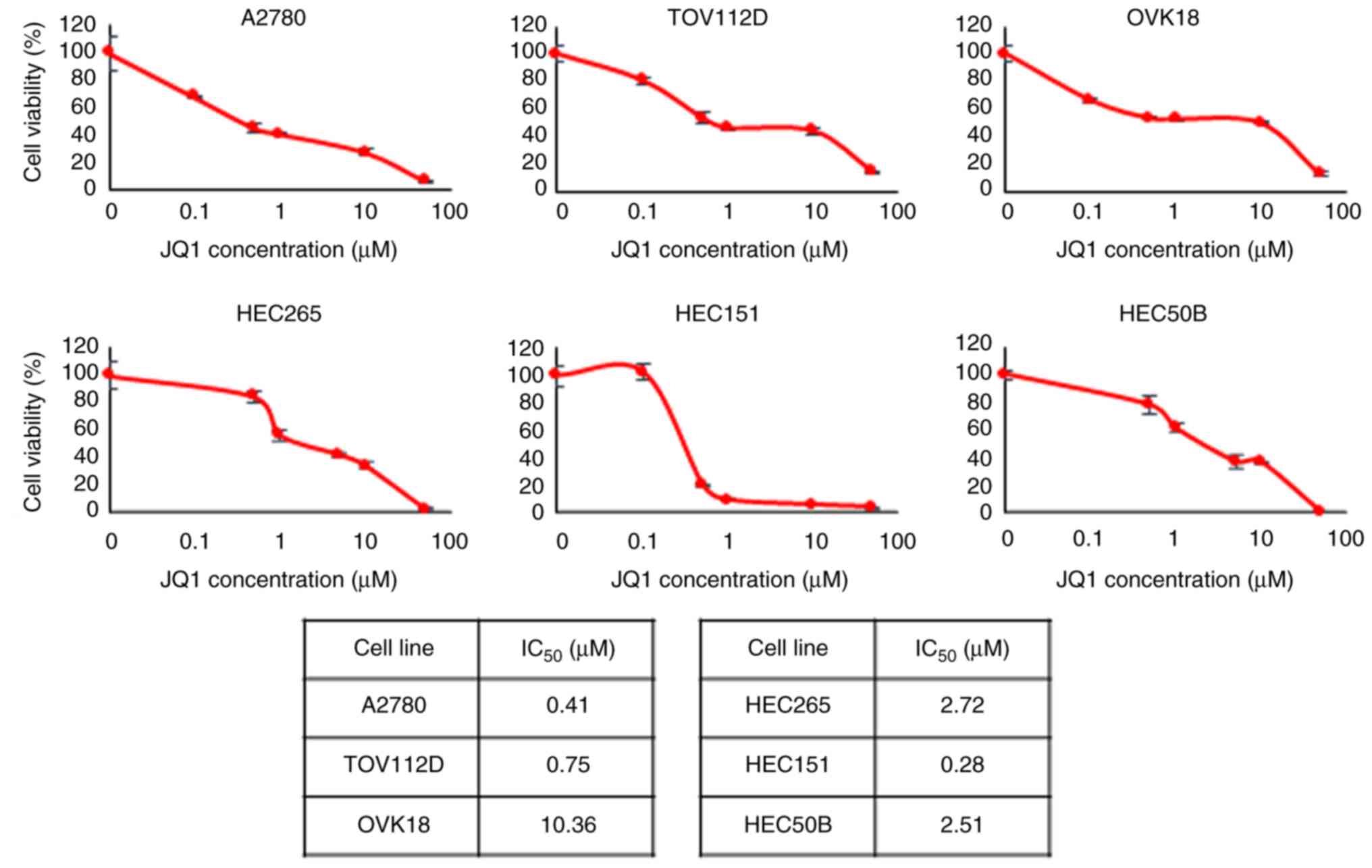
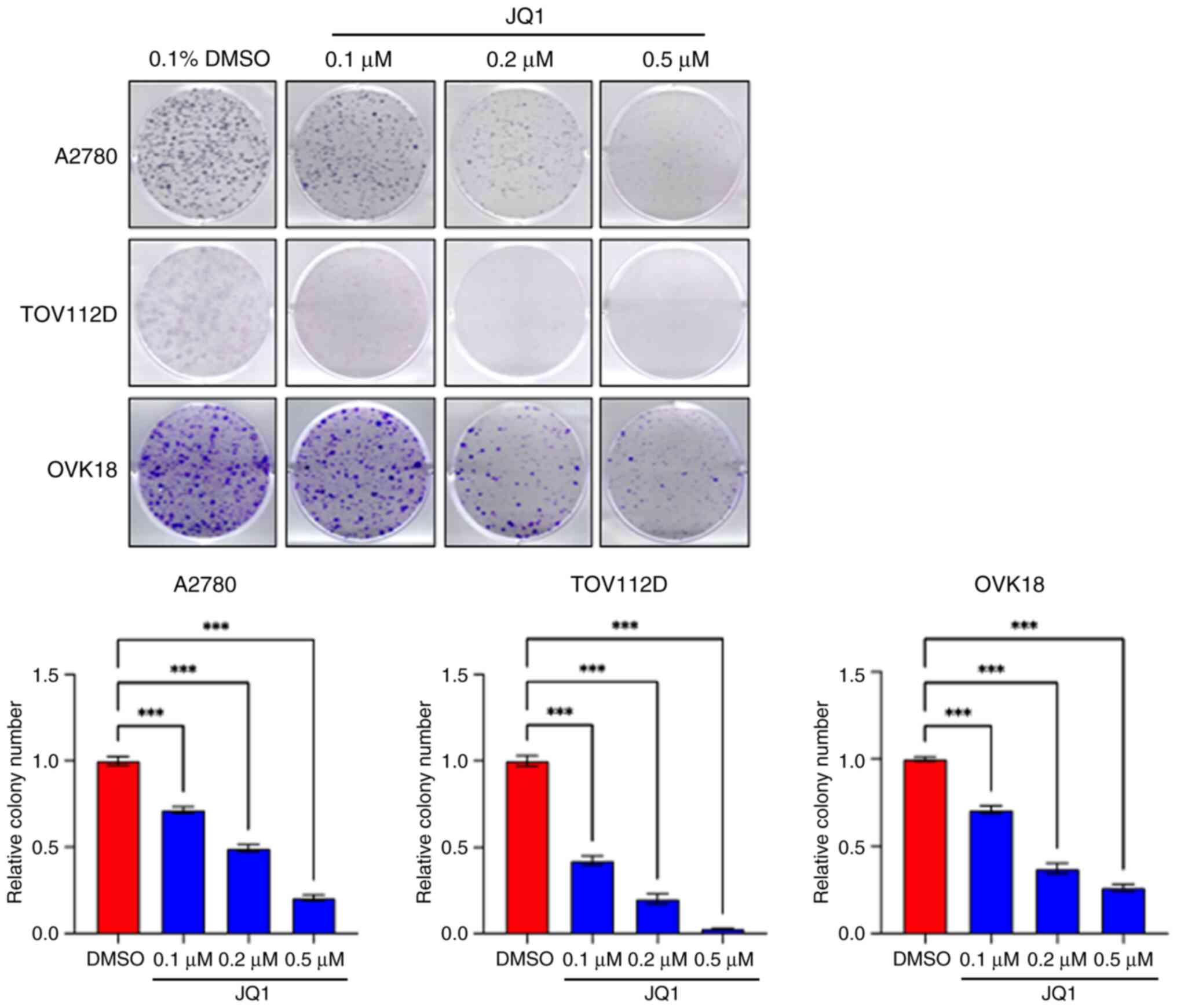
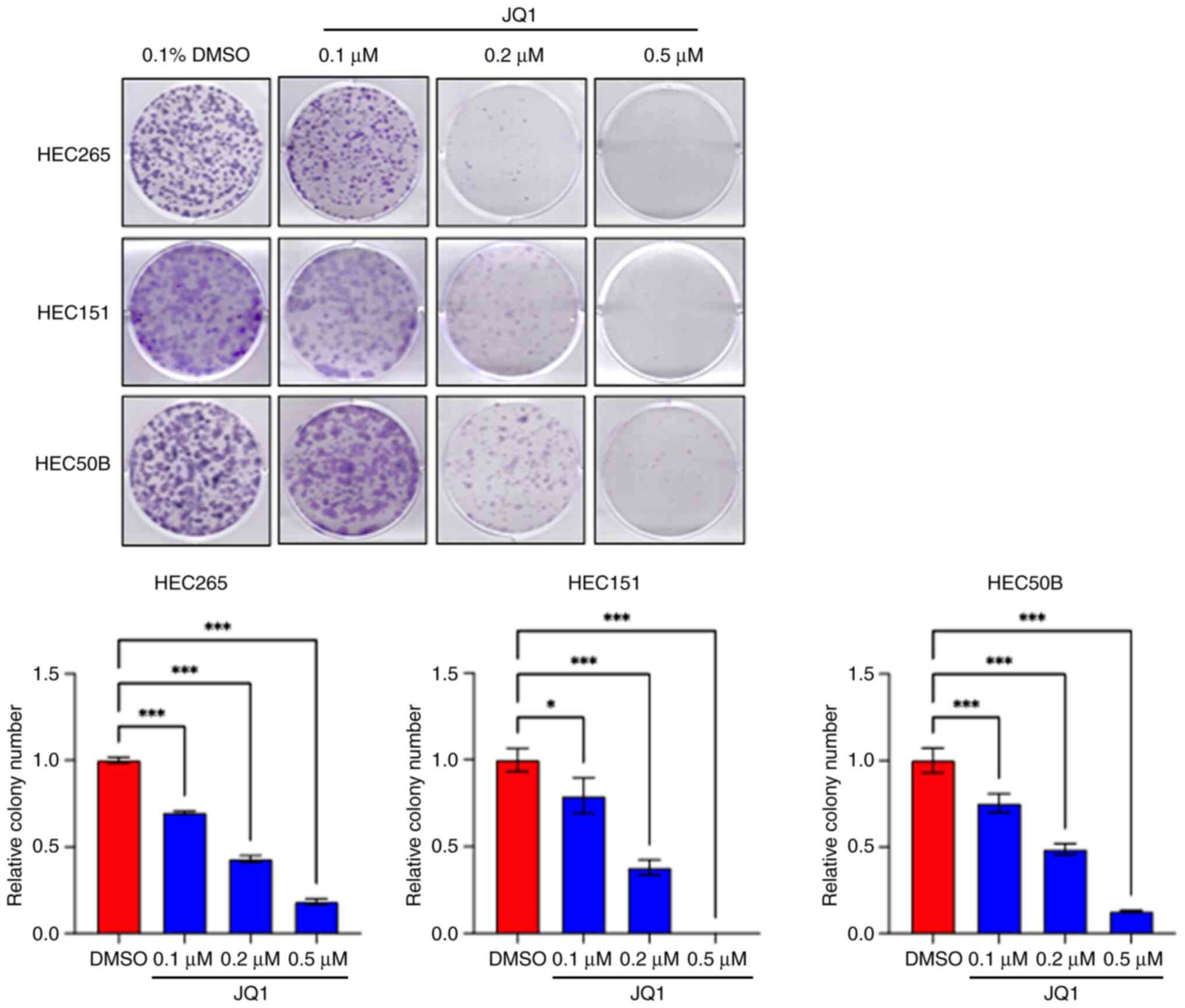
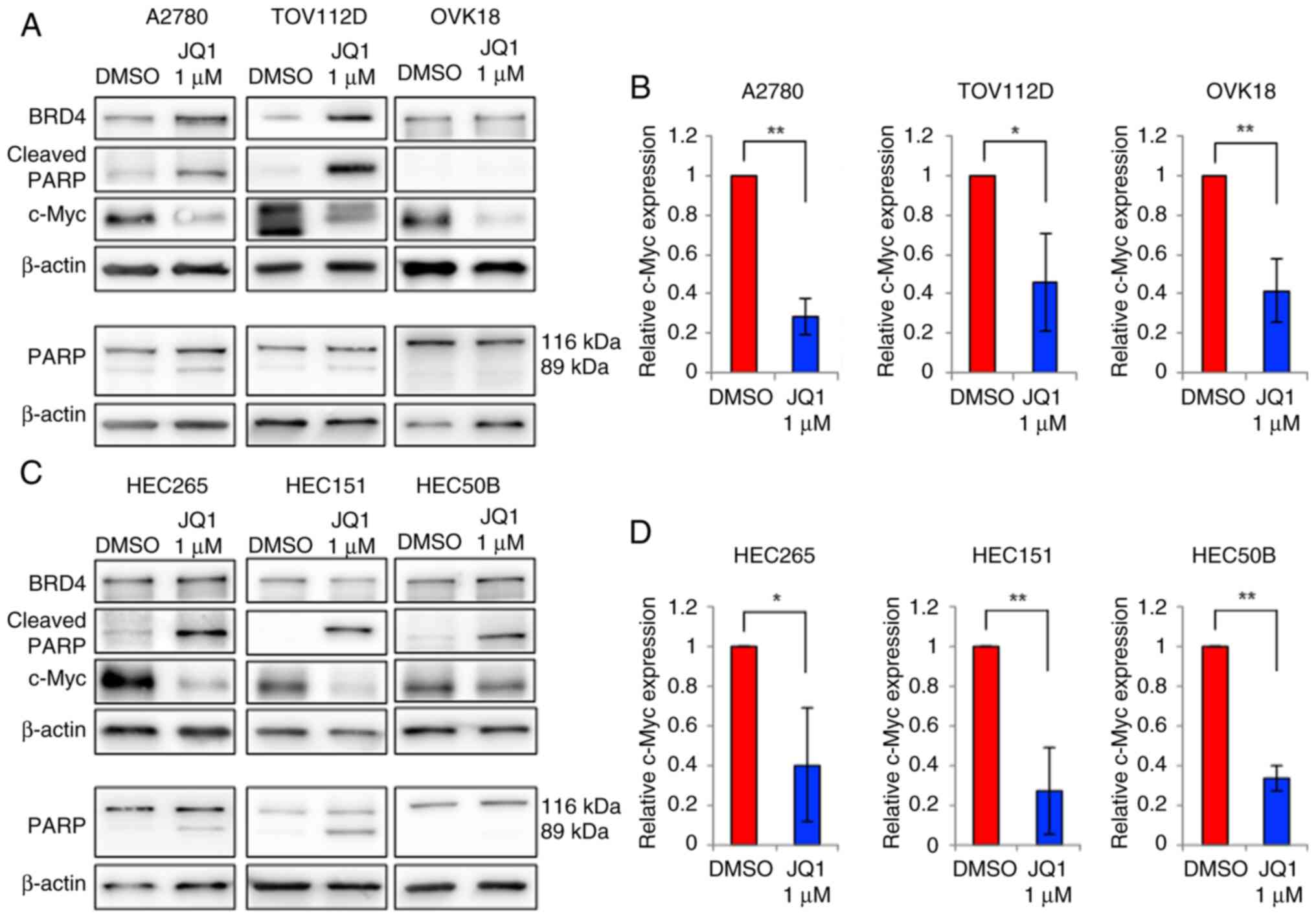
|
1
|
Karst AM and Drapkin R: Ovarian cancer
pathogenesis: A model in evolution. J Oncol.
2021:9323712010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seidman JD, Horkayne-Szakaly I, Haiba M,
Boice CR, Kurman RJ and Ronnett BM: The histologic type and stage
distribution of ovarian carcinomas of surface epithelial origin.
Int J Gynecol Pathol. 23:41–44. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Winterhoff B, Hamidi H, Wang C, Kalli KR,
Fridley BL, Dering J, Chen HW, Cliby WA, Wang HJ, Dowdy S, et al:
Molecular classification of high grade endometrioid and clear cell
ovarian cancer using TCGA gene expression signatures. Gynecol
Oncol. 141:95–100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coburn SB, Bray F, Sherman ME and Trabert
B: International patterns and trends in ovarian cancer incidence,
overall and by histologic subtype. Int J Cancer. 140:2451–2460.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Murakami K, Kotani Y, Nakai H and
Matsumura N: Endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer: The origin
and targeted therapy. Cancers (Basel). 12:16762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nakamura K, Banno K, Yanokura M, Iida M,
Adachi M, Masuda K, Ueki A, Kobayashi Y, Nomura H, Hirasawa A, et
al: Features of ovarian cancer in Lynch syndrome (Review). Mol Clin
Oncol. 2:909–916. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Łaniewski P, Ilhan ZE and Herbst-Kralovetz
MM: The microbiome and gynaecological cancer development,
prevention and therapy. Nat Rev Urol. 17:232–250. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rodolakis A, Thomakos N, Akrivos N,
Sotiropoulou M, Ioannidis I, Haidopoulos D, Vlachos G and Antsaklis
A: Clinicopathologic insight of simultaneously detected primary
endometrial and ovarian carcinomas. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
285:817–821. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang L, Lu Q and Chang C: Epigenetics in
health and disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1253:3–55. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Margueron R, Trojer P and Reinberg D: The
key to development: Interpreting the histone code? Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 15:163–176. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brownell JE, Zhou J, Ranalli T, Kobayashi
R, Edmondson DG, Roth SY and Allis CD: Tetrahymena histone
acetyltransferase A: a homolog to yeast Gcn5p linking histone
acetylation to gene activation. Cell. 84:843–851. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zaware N and Zhou MM: Bromodomain biology
and drug discovery. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 26:870–879. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Taunton J, Hassig CA and Schreiber SL:
Mammalian histone deacetylase related to the yeast transcriptional
regulator Rpd3p. Science. 272:408–411. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu SY and Chiang CM: The double
bromodomain-containing chromatin adaptor brd4 and transcriptional
regulation. J Biol Chem. 282:13141–13145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Belkina AC and Denis GV: BET domain
co-regulators in obesity, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:465–477. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang L, Zhang Y, Shan W, Hu Z, Yuan J, Pi
J, Wang Y, Fan L, Tang Z, Li C, et al: Repression of BET activity
sensitizes homologous recombination-proficient cancers to PARP
inhibition. Sci Transl Med. 9:eaal16452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mertz JA, Conery AR, Bryant BM, Sandy P,
Balasubramanian S, Mele DA, Bergeron L and Sims RJ III: Targeting
MYC dependence in cancer by inhibiting BET bromodomains. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:16669–16674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Doroshow DB, Eder JP and LoRusso PM: BET
inhibitors: A novel epigenetic approach. Ann Oncol. 28:1776–1787.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expres- sion data using real-time quantitative PCR
and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature.
474:609–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network,
. Weinstein JN, Collisson EA, Mills GB, Shaw KR, Ozenberger BA,
Ellrott K, Shmulevich I, Sander C and Stuart JM: The cancer genome
atlas pan-cancer analysis project. Nat Genet. 45:1113–1120. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou S, Zhang S, Wang L, Huang S, Yuan Y,
Yang J, Wang H, Li X, Wang P, Zhou L, et al: BET protein inhibitor
JQ1 downregulates chromatin accessibility and suppresses metastasis
of gastric cancer via inactivating RUNX2/NID1 signaling.
Oncogenesis. 9:332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Delmore JE, Issa GC, Lemieux ME, Rahl PB,
Shi J, Jacobs HM, Kastritis E, Gilpatrick T, Paranal RM, Qi J, et
al: BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target
c-Myc. Cell. 146:904–917. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen YR, Ouyang SS, Chen YL, Li P, Xu HW
and Zhu SL: BRD4/8/9 are prognostic biomarkers and associated with
immune infiltrates in hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY).
12:17541–17567. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dhanasekaran R, Deutzmann A,
Mahauad-Fernandez WD, Hansen AS, Gouw AM and Felsher DW: The MYC
oncogene-the grand orchestrator of cancer growth and immune
evasion. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 19:23–36. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Donati B, Lorenzini E and Ciarrocchi A:
BRD4 and Cancer: Going beyond transcriptional regulation. Mol
Cancer. 17:1642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hai R, He L, Shu G and Yin G:
Characterization of histone deacetylase mechanisms in cancer
development. Front Oncol. 11:7009472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ren Q and Gao W: Current status in the
discovery of dual BET/HDAC inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
31:1276712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Andrikopoulou A, Liontos M, Koutsoukos K,
Dimopoulos MA and Zagouri F: Clinical perspectives of BET
inhibition in ovarian cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 44:237–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karakashev S, Zhu H, Yokoyama Y, Zhao B,
Fatkhutdinov N, Kossenkov AV, Wilson AJ, Simpkins F, Speicher D,
Khabele D, et al: BET bromodomain inhibition synergizes with PARP
inhibitor in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cell Rep. 21:3398–3405.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu A, Fan D and Wang Y: The BET
bromodomain inhibitor i-BET151 impairs ovarian cancer metastasis
and improves antitumor immunity. Cell Tissue Res. 374:577–585.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Momeny M, Eyvani H, Barghi F, Ghaffari HS,
Javadikooshesh S, Hassanvand Jamadi R, Esmaeili F, Alishahi Z,
Zaghal A, Bashash D, et al: Inhibition of the bromodomain and
extra-terminal domains reduces the growth and invasive
characteristics of chemoresistant ovarian carcinoma cells.
Anticancer Drugs. 29:1011–1020. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen S, Li Y, Qian L, Deng S, Liu L, Xiao
W and Zhou Y: A review of the clinical characteristics and novel
molecular subtypes of endometrioid ovarian cancer. Front Oncol.
11:6681512021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ishizaka A, Taguchi A, Tsuruga T, Maruyama
M, Kawata A, Miyamoto Y, Tanikawa M, Ikemura M, Sone K, Mori M, et
al: Endometrial cancer with concomitant endometriosis is highly
associated with ovarian endometrioid carcinoma: A retrospective
cohort study. BMC Women's Health. 22:3322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Symons LK, Miller JE, Kay VR, Marks RM,
Liblik K, Koti M and Tayade C: The immunopathophysiology of
endometriosis. Trends Mol Med. 24:748–762. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sampson JA: Metastatic or embolic
endometriosis, due to the menstrual dissemination of endometrial
tissue into the venous circulation. Am J Pathol. 3:93–110.43.
1927.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wendel JRH, Wang X and Hawkins SM: The
endometriotic tumor microenvironment in ovarian cancer. Cancers
(Basel). 10:2612018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
McConechy MK, Ding J, Senz J, Yang W,
Melnyk N, Tone AA, Prentice LM, Wiegand KC, McAlpine JN, Shah SP,
et al: Ovarian and endometrial endometrioid carcinomas have
distinct CTNNB1 and PTEN mutation profiles. Mod Pathol. 27:128–134.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bauer K, Berger D, Zielinski CC, Valent P
and Grunt TW: Hitting two oncogenic machineries in cancer cells:
Cooperative effects of the multi-kinase inhibitor ponatinib and the
BET bromodomain blockers JQ1 or dBET1 on human carcinoma cells.
Oncotarget. 9:26491–26506. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Berns K, Caumanns JJ, Hijmans EM,
Gennissen AMC, Severson TM, Evers B, Wisman GBA, Jan Meersma G,
Lieftink C, Beijersbergen RL, et al: ARID1A mutation sensitizes
most ovarian clear cell carcinomas to BET inhibitors. Oncogene.
37:4611–4625. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qiu H, Li J, Clark LH, Jackson AL, Zhang
L, Guo H, Kilgore JE, Gehrig PA, Zhou C and Bae-Jump VL: JQ1
suppresses tumor growth via PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway in endometrial
cancer. Oncotarget. 7:66809–66821. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pang Y, Bai G, Zhao J, Wei X, Li R, Li J,
Hu S, Peng L, Liu P and Mao H: The BRD4 inhibitor JQ1 suppresses
tumor growth by reducing c-Myc expression in endometrial cancer. J
Transl Med. 20:3362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Filippakopoulos P, Qi J, Picaud S, Shen Y,
Smith WB, Fedorov O, Morse EM, Keates T, Hickman TT, Felletar I, et
al: Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature.
468:1067–1073. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Qiu H, Jackson AL, Kilgore JE, Zhong Y,
Chan LL, Gehrig PA, Zhou C and Bae-Jump VL: JQ1 suppresses tumor
growth through downregulating LDHA in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget.
6:6915–6930. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bonazzoli E, Predolini F, Cocco E, Bellone
S, Altwerger G, Menderes G, Zammataro L, Bianchi A, Pettinella F,
Riccio F, et al: Inhibition of BET bromodomain proteins with
GS-5829 and GS-626510 in uterine serous carcinoma, a biologically
aggressive variant of endometrial cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
24:4845–4853. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sarnik J, Popławski T and Tokarz P: BET
proteins as attractive targets for cancer therapeutics. Int J Mol
Sci. 22:111022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dang CV, Le A and Gao P: MYC-induced
cancer cell energy metabolism and therapeutic opportunities. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:6479–6483. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vita M and Henriksson M: The Myc
oncoprotein as a therapeutic target for human cancer. Semin Cancer
Biol. 16:318–330. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Luan W, Pang Y, Li R, Wei X, Jiao X, Shi
J, Yu J, Mao H and Liu P: Akt/mTOR-mediated autophagy confers
resistance to BET inhibitor JQ1 in ovarian cancer. Onco Targets
Ther. 12:8063–8074. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|