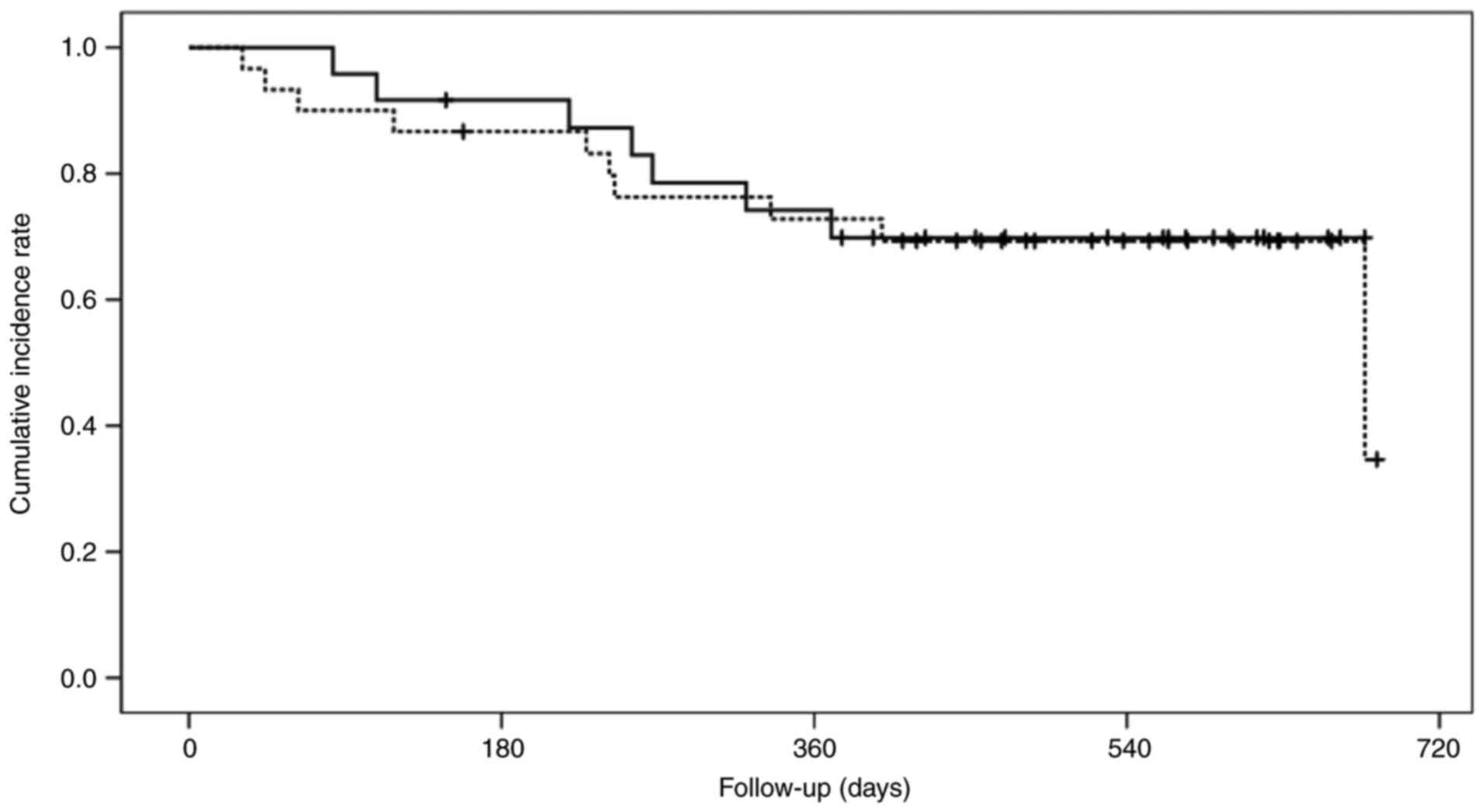
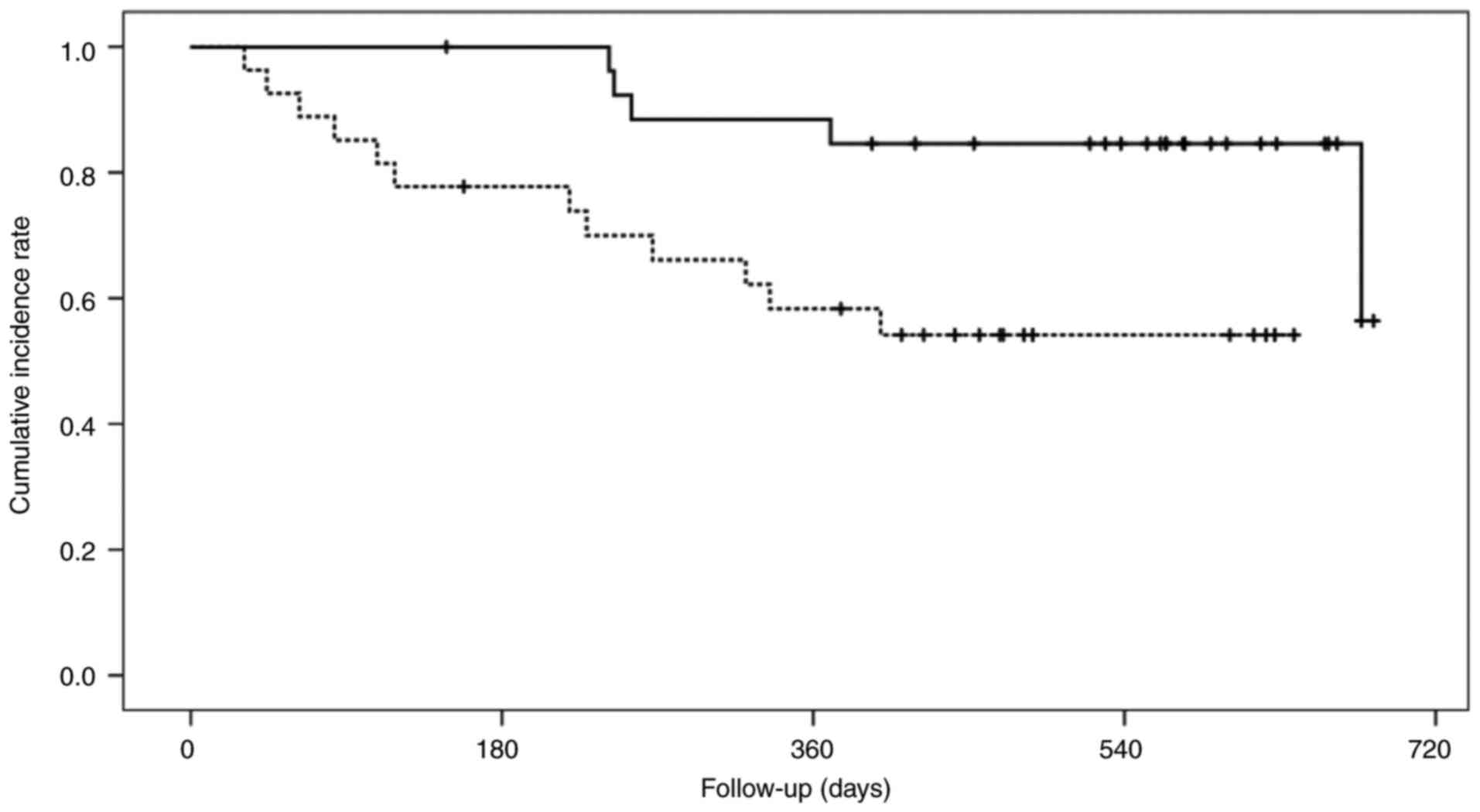
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun L, Quan XQ and Yu S: An
epidemiological survey of cachexia in advanced cancer patients and
analysis on its diagnostic and treatment status. Nutr Cancer.
67:1056–1062. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fearon K, Strasser F, Anker SD, Bosaeus I,
Bruera E, Fainsinger RL, Jatoi A, Loprinzi C, MacDonald N,
Mantovani G, et al: Definition and classification of cancer
cachexia: An international consensus. Lancet Oncol. 12:489–495.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Iwai N, Okuda T, Sakagami J, Harada T,
Ohara T, Taniguchi M, Sakai H, Oka K, Hara T, Tsuji T, et al:
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predicts prognosis in unresectable
pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep. 10:187582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iwai N, Okuda T, Oka K, Sakagami J, Harada
T, Ohara T, Hattori C, Taniguchi M, Sakai H, Hara T, et al:
Depletion of psoas muscle mass after systemic chemotherapy is
associated with poor prognosis in patients with unresectable
pancreatic cancer. Cancers (Basel). 13:38602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jafri SH, Previgliano C, Khandelwal K and
Shi R: Cachexia index in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
patients. Clin Med Insights Oncol. 9:87–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakashima K, Haruki K, Kamada T, Takahashi
J, Nakaseko Y, Ohdaira H, Furukawa K, Suzuki Y and Ikegami T:
Usefulness of the cachexia index as a prognostic indicator for
patients with gastric cancer. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 7:733–740.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hamura R, Haruki K, Shirai Y, Tanji Y,
Taniai T, Okui N, Furukawa K, Shiozaki H, Onda S and Ikegami T:
Preoperative cachexia index can predict the prognosis of
extrahepatic biliary tract cancer after resection. Surg Oncol.
44:1018252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shimagaki T, Sugimachi K, Mano Y, Onishi
E, Iguchi T, Nakashima Y, Sugiyama M, Yamamoto M, Morita M and Toh
Y: Cachexia index as a prognostic predictor after resection of
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann Gastroenterol Surg.
7:977–986. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kamada T, Haruki K, Nakashima K, Takahashi
J, Nakaseko Y, Suzuki N, Ohdaira H, Eto K, Ikegami T and Suzuki Y:
Prognostic significance of the cachexia index in patients with
stage I–III colorectal cancer who underwent laparoscopic surgery.
Surg Today. 53:1064–1072. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Goh MJ, Kang W, Jeong WK, Sinn DH, Gwak
GY, Paik YH, Choi MS, Lee JH, Koh KC and Paik SW: Prognostic
significance of cachexia index in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma treated with systemic chemotherapy. Sci
Rep. 12:76472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matsunaga T, Satio H, Sakano Y, Makinoya
M, Shimizu S, Shishido Y, Miyatani K, Hanaki T, Kihara K, Yamamoto
M, et al: Prognostic significance of the cachexia index in patients
with unresectable advanced gastric cancer receiving palliative
chemotherapy: A retrospective single-center study. Surg Today.
54:231–239. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gong C, Wan Q, Zhao R, Zuo X, Chen Y and
Li T: Cachexia index as a prognostic indicator in patients with
gastric cancer: A retrospective study. Cancers (Basel).
14:44002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tanji Y, Furukawa K, Haruki K, Taniai T,
Onda S, Tsunematsu M, Shirai Y, Yanagaki M, Igarashi Y and Ikegami
T: Significant impact of cachexia index on the outcomes after
hepatic resection for colorectal liver metastases. Ann
Gastroenterol Surg. 6:804–812. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aleixo GFP, Shachar SS, Nyrop KA, Muss HB,
Battaglini CL and Williams GR: Bioelectrical impedance analysis for
the assessment of sarcopenia in patients with cancer: A systematic
review. Oncologist. 25:170–182. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Okubo S, Shinmura K, Kadota S, Nakayasu M,
Kurosawa S, Nakayama H, Sakurai A, Ito C, Aisa Y and Nakazato T:
Evaluation of the cachexia index using a bioelectrical impedance
analysis in elderly patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: A
single-center prospective study. Ann Hematol. 103:823–831. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen LK, Liu LK, Woo J, Assantachai P,
Auyeung TW, Bahyah KS, Chou MY, Chen LY, Hsu PS, Krairit O, et al:
Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus report of the Asian working group for
sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 15:95–101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen LK, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung TW,
Chou MY, Iijima K, Jang HC, Kang L, Kim M, Kim S, et al: Asian
working group for sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus update on sarcopenia
diagnosis and treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 21:300–307.e2. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Caillet P, Liuu E, Raynaud Simon A,
Bonnefoy M, Guerin O, Berrut G, Lesourd B, Jeandel C, Ferry M,
Rolland Y and Paillaud E: Association between cachexia,
chemotherapy and outcomes in older cancer patients: A systematic
review. Clin Nutr. 36:1473–1482. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Basile D, Parnofiello A, Vitale MG,
Cortiula F, Gerratana L, Fanotto V, Lisanti C, Pelizzari G, Ongaro
E, Bartoletti M, et al: The IMPACT study: Early loss of skeletal
muscle mass in advanced pancreatic cancer patients. J Cachexia
Sarcopenia Muscle. 10:368–377. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang H, Tang X, Zhang J, Man C, Jiang D,
Xu Y, Zhang W, Gong D and Fan Y: Cachexia index as a predictor of
reduced survival in patients with gastrointestinal cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Cancer. 76:815–823. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Go SI, Park MJ and Lee GW: Clinical
significance of the cachexia index in patients with small cell lung
cancer. BMC Cancer. 21:5632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Go SI, Park MJ, Park S, Kang MH, Kim HG,
Kang JH, Kim JH and Lee GW: Cachexia index as a potential biomarker
for cancer cachexia and a prognostic indicator in diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 12:2211–2219. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Karmali R, Alrifai T, Fughhi IAM, Ng R,
Chukkapalli V, Shah P, Basu S, Nathan S, Szymanski-Grant K, Gordon
LI, et al: Impact of cachexia on outcomes in aggressive lymphomas.
Ann Hematol. 96:951–956. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Iwai N, Sakai H, Oka K, Sakagami J, Okuda
T, Hattori C, Taniguchi M, Hara T, Tsuji T, Komaki T, et al:
Predictors of response to anamorelin in gastrointestinal cancer
patients with cachexia: A retrospective study. Support Care Cancer.
31:1152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kikuchi N, Uojima H, Hidaka H, Iwasaki S,
Wada N, Kubota K, Nakazawa T, Shibuya A, Kako M, Take A, et al:
Evaluation of skeletal muscle mass in patients with chronic liver
disease shows different results based on bioelectric impedance
analysis and computed tomography. Ann Nutr Metab. 78:336–344. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|