Introduction
Lung cancer is an aggressive and globally prevalent
disease, with ~2.48 million new cases and 1.82 million
cancer-associated deaths worldwide in 2022 (1). Globally, it is the primary cause of
cancer-associated death in men, whilst being the third most common
type of cancer among women (behind breast and colorectal cancer)
and the second most fatal behind breast cancer (2). Despite notable progress in the
diagnostic and therapeutic methods of non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC), the 5-year survival rates for lung cancer have only shown
limited improvements over the past decades (3). For NSCLC specifically, survival rates
improved from around 23% in the early 2010s to 26.4% in recent
analyses (4). A considerable
portion of patients with lung cancer are first diagnosed already at
an advanced cancer stage, contributing to poor prognosis (3). Furthermore, although tobacco use
persists as the primary risk factor, several other factors have
been identified, including environmental exposures (such as biomass
fuels, radon, industrial carcinogens and air pollution) and
genetics (such as EGFR alterations) (5). Notably, ~25% patients with lung cancer
are non-smokers (5,6). Consequently, exploring novel avenues
to pinpoint high-risk cohorts presents itself as a promising
strategy for the prevention and early detection of lung cancer to
reduce both morbidity and mortality.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a leading cause of
global mortality, with an increase from 12.1 million in 1990,
reaching 18.6 million in 2019 in 204 countries (7). In particular, hypertension is a key
contributor of CVDs that has emerged as the primary driver of
mortality, accounting for 7.6 million deaths annually worldwide
reported by the World Health Organization in 2009 (8). The incidence of hypertension has
increased two-fold from 1975 (594 million) to 2015 (1.13 billion)
in 200 countries, largely due to an aging population (9). Individuals with CVD may face an
elevated risk of cancer, given the presence of shared risk factors,
such as tobacco smoking and excessive body weight, coupled with
common pathogenic mechanisms, including inflammation, hypoxia and
clonal hematopoiesis (10–14). Notably, individuals with CVD exhibit
a 67% increased susceptibility to lung cancer and a 95% elevated
risk of lung cancer-related mortality (15). Among male individuals who smoke and
have hypertension, an association has been found between high blood
pressure levels and an elevated risk of developing lung cancer
(16). Moreover, findings from a
Dutch study revealed that women with hypertensive disorders faced a
2.19-fold increased risk of mortality compared with those without
such conditions in lung cancer (17). A close link between high blood
pressure and lung cancer mortality was also observed in a South
Korea study (18). However, these
studies were epidemiological, not genetic. To the best of our
knowledge, it remains to be determined whether and how high blood
pressure can affect somatic mutations in patients with NSCLC.
Environmental exposures, including biomass fuels,
arsenic (As), radon, industrial carcinogens and air pollution, can
all contribute to the morbidity and mortality associated with lung
cancer (5). Several studies have
posited an association between environmental exposure to heavy
metals [such as As, cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), iron,
mercury (Hg), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn)] and the onset
of lung cancer (19–23). Perturbations in metal homeostasis
have the potential to induce oncogenic signaling pathways, impede
DNA repair mechanisms, increase oxidative stress and alter
epigenetic inheritance (19–22).
Additionally, exposure to heavy metals, such as As, Cd, Hg and Pb,
has been associated with elevated blood pressure levels (24–27).
The underlying mechanisms involve oxidative stress, compromised
nitric oxide signaling, altered vascular responses to
neurotransmitters, disruptions in vascular muscle Ca2+
signaling, renal damage and interference with the renin-angiotensin
system (24–26,28–31).
However, previous epidemiological studies have primarily focused on
the associations between heavy metals and the occurrence of a
single disease (24–27), whilst, to the best of our knowledge,
no studies have assessed the distributional differences in heavy
metals between patients with NSCLC with and without
hypertension.
Therefore, in the present study, targeted
next-generation sequencing (NGS) of 82 tumor-associated genes and
inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) detection of
18 heavy metals were performed on tissue DNA and serum samples,
respectively, from patients with NSCLC with and without
hypertension. The primary objectives of the present study were to
elucidate the following: i) Disparities in genomic alterations,
somatic interactions and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
(KEGG) and Gene Ontology (GO) enriched signaling pathways between
patients with NSCLC with and without hypertension; ii) heavy metal
profiles in patients with NSCLC with or without hypertension; and
iii) how the different heavy metals associate with somatic
mutations, demographics and clinical characteristics, in addition
to other heavy metals in patients with NSCLC with hypertension.
Materials and methods
Patients and sample collection
A total of 64 patients with NSCLC from the
Department of Thoracic Surgery at The First People's Hospital of
Ping Ding Shan (Pingdingshan, China) were recruited between October
2019 and October 2021. The pathological diagnosis was confirmed by
three separate pulmonary pathologists (XZ, HS and YW) using The
Fourth Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of
Lung Tumors (32). The NGS data
were acquired from 64 formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE)
tumor specimens. The tumor tissue specimens were fixed with 10%
neutral buffered formalin at room temperature (~25°C) for 24–48 h
immediately after surgical removal. The present study adhered to
the Code of Ethics established by the World Medical Association
(Declaration of Helsinki) (33),
and was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of First People's
Hospital of Ping Ding Shan (approval no. PYLL20190806;
Pingdingshan, China).
The inclusion criteria were: i) Age >18 years;
ii) an initial diagnosis of NSCLC by histological examination; iii)
an enhanced CT scan of the chest and abdomen, MRI of the brain, and
whole-body bone scan (emission CT) results were available; iv)
diagnosed primary NSCLC; and v) no history of tumor treatment.
The exclusion criteria were: i) Patients had been
subjected to tumor treatments, including chemotherapy,
radiotherapy, targeted therapy or immunotherapy; ii) history of
exposure to trace elements, toxic elements or heavy metals; iii)
patients used antioxidants, vitamins or dietary supplements; iv)
patients had undergone surgery within the past year; v) patients
had comorbidities, such as autoimmune disease, gout, chronic liver
disease, chronic kidney disease, protein-energy malnutrition,
thyroid disease or vitamin A/D deficiency; or vi) patients had
additional comorbidities deemed inappropriate for the present study
by the research team, such as uncontrolled diabetes, psychiatric
disorders, and substance abuse.
Assessment of hypertension
To be diagnosed with hypertension, patients must
have met at least one of the following three criteria: i)
Affirmative response from the patient to the question of whether
they had a prior diagnosis of hypertension from a medical
professional; ii) individuals exhibiting a systolic blood pressure
(SBP) of ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of ≥90
mmHg; and iii) individuals currently using blood pressure-lowering
medications, including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors,
angiotensin II receptor blockers, calcium channel blockers,
diuretics and beta-blockers. Hypertensive participants were
categorized into three hypertension grades based on their blood
pressure readings: i) Grade 1, 140≤ SBP <160 mmHg and/or 90≤ DBP
<100 mmHg; ii) grade 2, 160≤ SBP <180 mmHg and/or 100≤ DBP
<110 mmHg; and iii) grade 3, SBP ≥180 mmHg and/or DBP ≥110 mmHg
(34). In addition, the categorized
criteria of patients with optimal, normal and high normal blood
pressure readings were as follows: Optimal, SBP <120 mmHg and
DBP <80 mmHg; normal, 120≤ SBP <130 mmHg and/or 80≤ DBP
<85 mmHg; high normal, 130≤ SBP <140 mmHg and/or 85≤ DBP
<90 mmHg.
DNA extraction and quality
control
The extraction of genomic DNA (gDNA) from the FFPE
tumor specimens was performed using a GeneRead DNA FFPE Kit (Qiagen
GmbH). gDNA quantity and purity were assessed using a
Qubit® 3.0 Fluorometer (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) and a NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer instrument
(Agilent Technologies, Inc.) was used to evaluate DNA integrity
using High Sensitivity DNA Reagent (Agilent Technologies,
Inc.).
Library preparation, hybridization
capture and Illumina sequencing
Firstly, 300 ng gDNA from each FFPE tumor specimen
was mechanically fragmented by an E220 focused ultrasonicator
Covaris (Covaris, LLC) at 75W peak incident power, 20% duty factor,
1000 cycles per burst and a 7°C water bath temperature for 95 sec
treatment time. The DNA fragments were broken into fragments of
150–200 bp. Secondly, the KAPA library preparation kit (cat. No.
KK8500; Kapa Biosystems; Roche Diagnostics) was employed to
construct libraries using 10–100 ng gDNA fragments. Finally, the
xGen Lockdown Probe pool (Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc.) was
used to capture the NGS libraries, followed by amplification of the
captured DNA fragments using 1× KAPA HiFi Hot Start Ready Mix (Kapa
Biosystems; Roche Diagnostics). The sequences of the forward and
reverse primers were 5′-AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACAC-3′ (Illumina
P5 primer) and 5′-CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGAT-3′ (Illumina P7 primer).
The thermal cycling protocol was as follows: Initial denaturation
step at 98°C for 45 sec, followed by 13 cycles of 15 sec at 98°C,
30 sec at 60°C and 30 sec at 72°C. The final extension was
conducted at 72°C for 60 sec. The fragment length of library
amplification products was analyzed by Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer
(Agilent Technologies, Inc.) and High Sensitivity DNA Kit (cat. No.
5067-4626; Agilent Technologies, Inc.). The library concentrations
were determined by Qubit® 3.0 Fluorometer (Invitrogen;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and the final library concentration
for sequencing was 1.8 pM. Illumina NextSeq CN500 platform
(Illumina Inc.) and NextSeq CN500 Mid Output v2 Kit (150 cycles)
(cat. no. R0151; Illumina Inc.) were adopted to perform sequence
with a 75 bp pair end mode.
Bioinformatics analysis
Fastp software (v.0.23.2; OpenGene Bioinformatics)
was applied to remove low-quality reads [the proportion of
low-quality bases (quality below Q15) in a read exceeds 40%],
resulting in clean data. Burrows-Wheeler-Alignment Tool (BWA
v.0.7.12; Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute) was used to align all
filtered reads using the human genome as the reference (University
of California Santa Cruz ID: hg19). Subsequently, Picard tools
(v.1.130; Broad Institute) and Genome Analysis Toolkit (v.3.2.2;
Broad Institute) were used to remove duplicates, perform indel
realignment and recalibrate the base quality scores (35,36).
The CollectTargetedPcrMetrics tool of Genome Analysis Toolkit was
employed to generate quality statistics. Finally, VarDict (v.1.6.0;
GitHub, Inc.) was used to verify single nucleotide variations and
insertions/deletions (37).
ANNOVAR (v. 20210202; http://annovar.openbioinformatics.org/en/latest/)
software was used to annotate somatic mutations (38). The identification of somatic
mutation candidates was performed using the following filtering
criteria: i) Removal of the variants coverage depth (VDP) <10;
ii) variant sites with a mutant allele frequency (MAF) >0.001 in
the 1,000 Genomes databases were removed (1,000 Genomes Project
Consortium; http://www.internationalgenome.org/); iii) variant
sites with a MAF ≥0.001 and <0.1 in the 1,000 Genomes databases,
accompanied by COSMIC (http://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic) evidence, were
retained; iv) variations in the exonic or splicing region (10 bp
upstream and downstream of splicing sites) were retained; v)
synonymous mutations were excluded; vi) variants with an unknown
classification were excluded; and vii) functionally benign variant
sites as predicted by PolyPhen 2 (Polymorphism Phenotyping v2;
http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/) were excluded.
KEGG pathway and GO term enrichment analysis were performed using
the R package clusterProfiler (v3.10.1), and P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference
(39).
Detection of traditional serum
biomarkers
To obtain serum, a minimum of 10 ml whole blood from
each patient at initial diagnosis was centrifuged at 1,690 × g for
10 min at 4°C. Serum samples were stored at −80°C. The preparation
of standard solutions of CEA, cytokeratin-19 fragments (CYFRA21-1)
and neuron-specific enolase (NSE) was performed by serial dilution
with a buffer solution (pH 7.5). Chemiluminescence immunoassays
were used to measure the concentrations of these three
aforementioned conventional serum biomarkers for tumors, as
previously described (40,41). An automated chemiluminescence
immunoassay analyzer (COBAS 8000 E 801; Roche Diagnostics GmbH) was
used for analysis, with Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) Assay Kit
(Electrochemiluminescence Method) (cat. no. 07027079190),
Cytokeratin 19 Fragment (CYFRA 21-1) Assay Kit
(Electrochemiluminescence Method) (cat. no. 07299966190) and
Neuron-Specific Enolase (NSE) Assay Kit (Electrochemiluminescence
Method) (cat. no. 07299982190), all sourced from Roche Diagnostics
GmbH.
Detection of heavy metals
The serum levels of 18 heavy metals [As, barium
(Ba), Cd, cobalt (Co), Cr, Cu, gallium, Hg, manganese (Mn), Ni, Pb,
antimony (Sb), selenium (Se), stannum (Sn), strontium (Sr),
thallium (Tl), vanadium and Zn] were determined by ICP-MS,
utilizing an Agilent 7800 instrument (Agilent Technologies, Inc.)
with an SPS 4 Series autosampler (Agilent Technologies, Inc.) and a
peristaltic pump for injecting samples. The Agilent ICP-MS 7800
instrument (Agilent Technologies, Inc.) was chosen for its
capability to analyze multiple elements, with specific detection
procedures detailed in the manufacturer's instructions (42).
For sample preparation, ≥2 ml whole blood was
collected from each patient at initial diagnosis and centrifuged at
1,690 × g for 10 min at room temperature to obtain the serum. Serum
samples were stored at −20°C until use. Subsequently, 500 µl serum
and 500 µl internal standard solution (10 µg/ml; cat. no.
5191-4570; Agilent Technologies, Inc.) were added to 4,000 µl
diluent consisting of 0.1% nitric acid (cat. no. 1.00456;
MilliporeSigma) and 0.1% Triton™ X-100 (cat. no. 93443;
MilliporeSigma). All components were then mixed and stored at 4°C
until analysis.
The analysis of 18 heavy metals was performed using
helium gas mode, with the instrument parameters shown in Table I. Sample analysis was preceded by an
autotuning system using a tuning solution (1 µg/l cerium, Co,
lithium, magnesium, Tl and yttrium; cat. no. 5185-5959; Agilent
Technologies, Inc.), with the following major parameters: i) The
mass 7 sensitivity should be >3,000 counts/sec; ii) the mass 89
sensitivity should be >10,000 counts/sec; iii) the mass 205
sensitivity should be >6,000 counts/sec; iv) for the
aforementioned measurements, the relative standard deviation should
be <15%, the oxide ratio <2%, the doubly charged ratio <3%
and the peak height at 10% width between 0.65 and 0.8; and v) in
helium mode, the Co intensity count should be >2,400. System
control and data acquisition and processing were conducted using
the MassHunter 4.4 Workstation® version C.01.04 software
(Agilent Technologies, Inc.).
 | Table I.Inductively coupled plasma mass
spectrometry instrument parameters for helium gas mode. |
Table I.
Inductively coupled plasma mass
spectrometry instrument parameters for helium gas mode.
| A, Plasma
parameters |
|---|
|
|---|
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| RF power, W | 1,550 |
| RF matching, V | 1.55 |
| Sample depth,
mm | 8.0 |
| Carrier gas,
l/min | 0.7 |
| Option
gasa | 0 |
| Nebulizer pump,
rps | 0.25 |
| S/C temperature,
°C | 2 |
| Gas switch | Makeup gas |
| Makeup/dilution
gas, l/min | 0.38 |
|
| B, Lens
parameters |
|
|
Parameter | Value |
|
| Extract 1, V | 0.0 |
| Extract 2, V | −180.0 |
| Omega bias, V | −110 |
| Omega lens, V | 10.5 |
| Cell entrance,
V | −50 |
| Cell exit, V | −70 |
| Deflect, V | −2.9 |
| Plate bias, V | −50 |
|
| C, Cell
parameters |
|
|
Parameter | Value |
|
| Use gas | True |
| Helium flow,
ml/min | 4.5 |
| H2 flow,
ml/min | 0.0 |
| Third gas flow | 0 |
| OctP bias, V | −18.0 |
| OctP RF, V | 180 |
| Energy
discrimination, V | 2.0 |
Statistical analysis
The ‘maftools’ package (version 2.6.05) within the R
software environment (version 4.0.3; R Core Team; http://www.r-project.org) was used to visualize
genomic landscapes, lollipop plots and spectra of co-occurring and
mutually exclusive genomic alterations (43). Statistical differences in the
categorical variables between patients with and without
hypertension were assessed using χ2 test or Fisher's
exact test in SPSS (version 22.0; IBM Corp.). Continuous variables
are presented as the median and interquartile range (IQR), where
comparisons between two groups were conducted using an unpaired
Student's t-test or a Mann-Whitney U test using GraphPad Prism
(version 7.0; Dotmatics). Spearman's rank correlation analysis by
the R software (version 4.0.3; R Core Team; http://www.r-project.org) was used to assess the
correlations among age, BMI, three traditional serum biomarkers and
18 heavy metals. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
Patient characteristics
In the present study, the number of patients with
primary NSCLC with stage 0, I, II, III and IV was 1, 33, 7, 17 and
6, respectively. Regarding hypertension status, 16 patients were
confirmed to have hypertension (aged 39–82 years, median 64.50;
referred to as Hyp group), and 48 patients did not have
hypertension (aged 33–80 years, median 61.50; referred to as
non-Hyp group). All 16 hypertensive patients were taking
antihypertensive drugs, where the numbers of patients with
different hypertension grades were 0 in optimal, 4 in normal, 3 in
high normal, 5 in grade 1, 4 in grade 2 and 0 in grade 3. Among the
64 patients (Hyp group vs. non-Hyp group, 16 vs. 48), serum samples
from 56 patients (Hyp group vs. non-Hyp group, 14 vs. 42) were used
for the detection of conventional serum biomarkers, whereas serum
samples from 62 patients (Hyp group vs. non-Hyp group, 16 vs. 46)
were used for the assessment of 18 heavy metals. For the
unaccounted for serum samples, 2 were excluded due to hemolysis
during storage, and 6 patients provided an insufficient volume of
serum, making it impossible to perform all planned analyses. No
significant differences were observed regarding age, height,
weight, BMI, sex distribution, the incidence of EGFR or TP53
mutations, pulmonary infection history, smoking history, drinking
history, cancer staging, blood vessel invasion, nerve invasion,
distant metastasis status, CEA, CYFRA21-1 and NSE levels between
the Hyp group and the non-Hyp group, but significant differences
were observed for other chronic diseases (including coronary heart
disease, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, Parkinson's disease and
chronic gastritis) (P<0.001; Table
II).
 | Table II.Clinical characteristics of patients
categorized based on hypertension status. |
Table II.
Clinical characteristics of patients
categorized based on hypertension status.
|
| Hypertension
status |
|
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Clinical
characteristics | No. of patients
(n=64) | Yes (n=16) | No (n=48) | P-value |
|---|
| Sex, N |
|
|
| 0.561 |
|
Male | 25 | 5 | 20 |
|
|
Female | 39 | 11 | 28 |
|
| EGFR
mutations, N |
|
|
| 0.757 |
|
Yes | 44 | 12 | 32 |
|
| No | 20 | 4 | 16 |
|
| TP53
mutations, N |
|
|
| 0.776 |
|
Yes | 33 | 9 | 24 |
|
| No | 31 | 7 | 24 |
|
| Pulmonary infection
history, N |
|
|
| 0.667 |
|
Yes | 8 | 1 | 7 |
|
| No | 56 | 15 | 41 |
|
| Other chronic
disease, N |
|
|
|
<0.001a |
|
Yes | 7 | 7 | 0 |
|
| No | 57 | 9 | 48 |
|
| Smoking history,
N |
|
|
| 0.093 |
|
Former | 5 | 3 | 2 |
|
|
Now | 11 | 1 | 10 |
|
|
Never | 48 | 12 | 36 |
|
| Drinking history,
N |
|
|
| 0.459 |
|
Former | 2 | 1 | 1 |
|
|
Now | 8 | 3 | 5 |
|
|
Never | 54 | 12 | 42 |
|
| Cancer staging,
N |
|
|
| 0.428 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
|
| I | 33 | 8 | 25 |
|
| II | 7 | 1 | 6 |
|
|
III | 17 | 5 | 12 |
|
| IV | 6 | 1 | 5 |
|
| Vascular invasion,
N |
|
|
| 0.498 |
|
Yes | 15 | 5 | 10 |
|
| No | 49 | 11 | 38 |
|
| Nerve invasion,
N |
|
|
| >0.999 |
|
Yes | 12 | 3 | 9 |
|
| No | 52 | 13 | 39 |
|
| Distant metastasis,
N |
|
|
| >0.999 |
|
Yes | 6 | 1 | 5 |
|
| No | 58 | 15 | 43 |
|
| CEA at baseline,
N |
|
|
| >0.999 |
| Normal,
0–4.3 ng/ml | 42 | 10 | 32 |
|
|
Elevated, >4.3 ng/ml | 18 | 4 | 14 |
|
|
Unknown | 4 | 2 | 2 |
|
| CYFRA21-1 at
baseline, N |
|
|
| 0.121 |
| Normal,
0–3.3 ng/ml | 34 | 11 | 23 |
|
|
Elevated, >3.3 ng/ml | 24 | 3 | 21 |
|
|
Unknown | 6 | 2 | 4 |
|
| NSE at baseline,
N |
|
|
| 0.431 |
| Normal,
0–15.2 ng/ml | 49 | 13 | 36 |
|
|
Elevated, >15.2 ng/ml | 9 | 1 | 8 |
|
|
Unknown | 6 | 2 | 4 |
|
| Median age, years
(IQR) | 62.000
(54.250–65.000) | 64.500
(58.250–75.750) | 61.500
(54.000–65.000) | 0.056 |
| Median height, m
(IQR) | 1.600
(1.600–1.680) | 1.625
(1.600–1.698) | 1.600
(1.600–1.675) | 0.700 |
| Median weight, kg
(IQR) | 60.500
(55.000–69.750) | 63.500
(58.500–74.000) | 60.000
(55.000–68.500) | 0.206 |
| Median BMI,
kg/m2 (IQR) | 23.220
(21.340–25.800) | 23.550
(21.900–25.790) | 22.940
(20.600–25.800) | 0.199 |
Disparities in genomic alterations
between patients with NSCLC with and without hypertension
Despite the considerable advantages observed when
targeted therapies (such as gefitinib, afatinib and osimertinib)
are used for the treatment of patients with NSCLC harboring driver
gene mutations (44,45), there remains a knowledge gap
regarding the differences in genomic profiles between individuals
with hypertension and those without. To explore these differences,
somatic mutations in the tumor tissues of 16 hypertensive patients
and 48 non-hypertensive patients were examined using an NGS panel
comprising 82 tumor-related genes, which were related to the
occurrence, progression and treatment of solid tumors, mainly
derived from the NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology, the
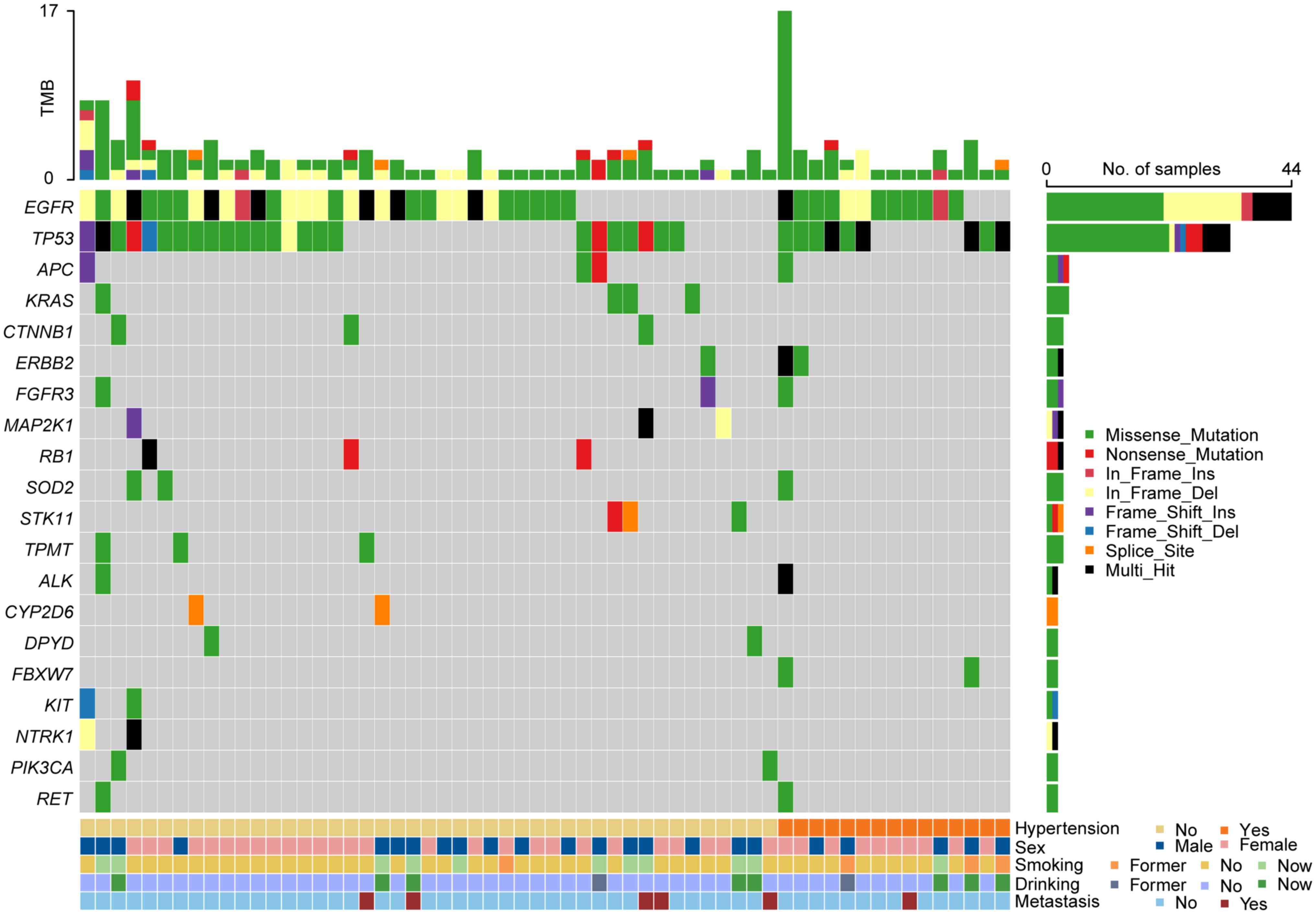
cancer knowledgebase database and the oncokb database (Table SI). In total, 47 somatic mutations
involving 14 mutant genes were detected in all 16 patients with
hypertension (100%). In comparison, 113 somatic mutations affecting
26 mutant genes were identified in 45 of the 48 patients without
hypertension (93.75%; Fig. 1;
Table SII, Table SIII, Table IV). Among the identified mutant
genes, FBXW7, CBR3, CDKN2A, HRAS, SMO and UGT1A1 were
exclusively observed in patients with hypertension, whilst 18
mutant genes (including KRAS, MAP2K1, RB1, CTNNB1, STK11, TPMT,
NTRK1, CYP2D6, DPYD, KIT, PIK3CA, BRAF, ESR1, FGFR2, GNAS, NOS3,
NOTCH1 and PDGFRA) were only observed in patients without
hypertension.
In addition, although EGFR, TP53, ERBB2, ALK,
APC, FGFR3, RET and SOD2 mutations were detected in both
groups, their mutation frequencies and sites markedly differed
between the Hyp group and the non-Hyp group (Fig. S1; Table SV). For TP53 mutations,
whilst ~50% of the patients in both the Hyp group (56.25%; 9/16)
and the non-Hyp group (50%; 24/48; Fig.
1), notable differences were identified in the mutation types
and sites (Fig. S1). Specifically,
except for the G245D mutation, the other 26 mutant sites differed
between the two groups (Hyp group: R273L, A159P, T125K, E221Q,
Q192X, D148H, C141W, P152T, 187_193del, and 187_192del; non-hyp
group: S241F, R196G, D42fs, S241Y, L344P, E286G, R158L, C275F,
131_132del, T284P, Y236C, E298X, R196X, R306X, R273C, and V203M).
Moreover, the mutation rate of EGFR was found to be higher
in patients with hypertension (75.00%; 12/16) compared with those
without (66.67%; 32/48).
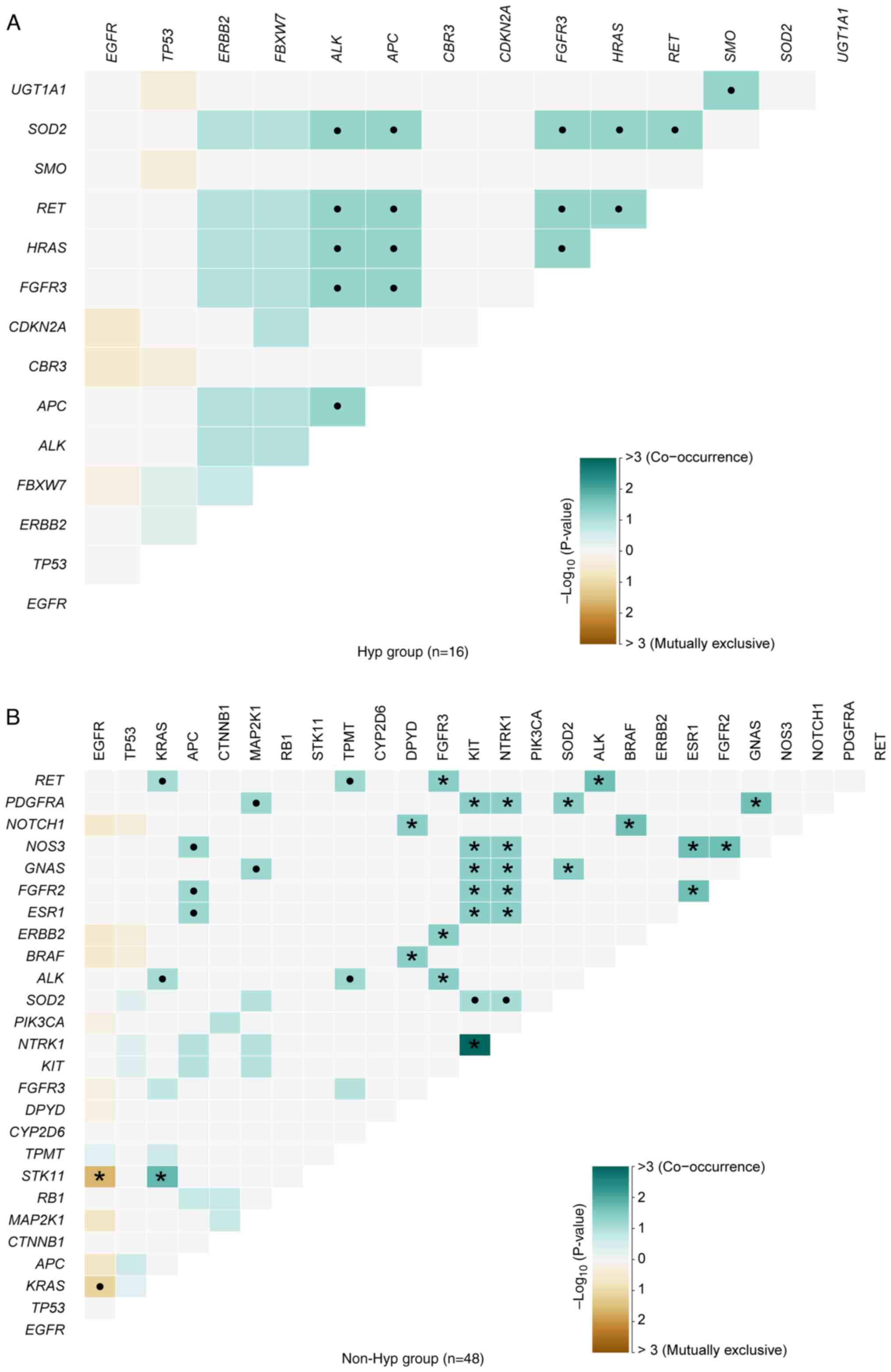
Disparities in somatic interactions
between patients with NSCLC with and without hypertension
In NSCLC, mutations in EGFR and KRAS
tended to occur independently, with instances of patients harboring
both mutations exhibiting resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase
inhibitors (46). In the present
cohort, the somatic interactions identified in hypertensive
patients differed from those observed in non-hypertensive patients.
In the non-Hyp group, mutually exclusive interactions were observed
between EGFR and STK11 (P=0.0240; Fig. 2B; Table
SVI). However, no significant mutually exclusive interactions
were found in the Hyp group (Fig.
2A; Table SVI). By contrast,
notable disparities were observed in the sets of co-occurring genes
between the two groups. APC and ALK (P=0.0588),
FGFR3 and ALK (P=0.0588), HRAS and ALK
(P=0.0588), and another 13 pairs of genes were markedly
co-occurring in hypertensive patients (Fig. 2A; Table
SVI). The significant sets of co-occurring genes in patients
without hypertension were as follows: NTRK1 and KIT
(P=0.0010), KRAS and STK11 (P=0.0169), RET and
ALK (P=0.0217) and another 22 pairs of genes (Fig. 2B; Table
SVI).
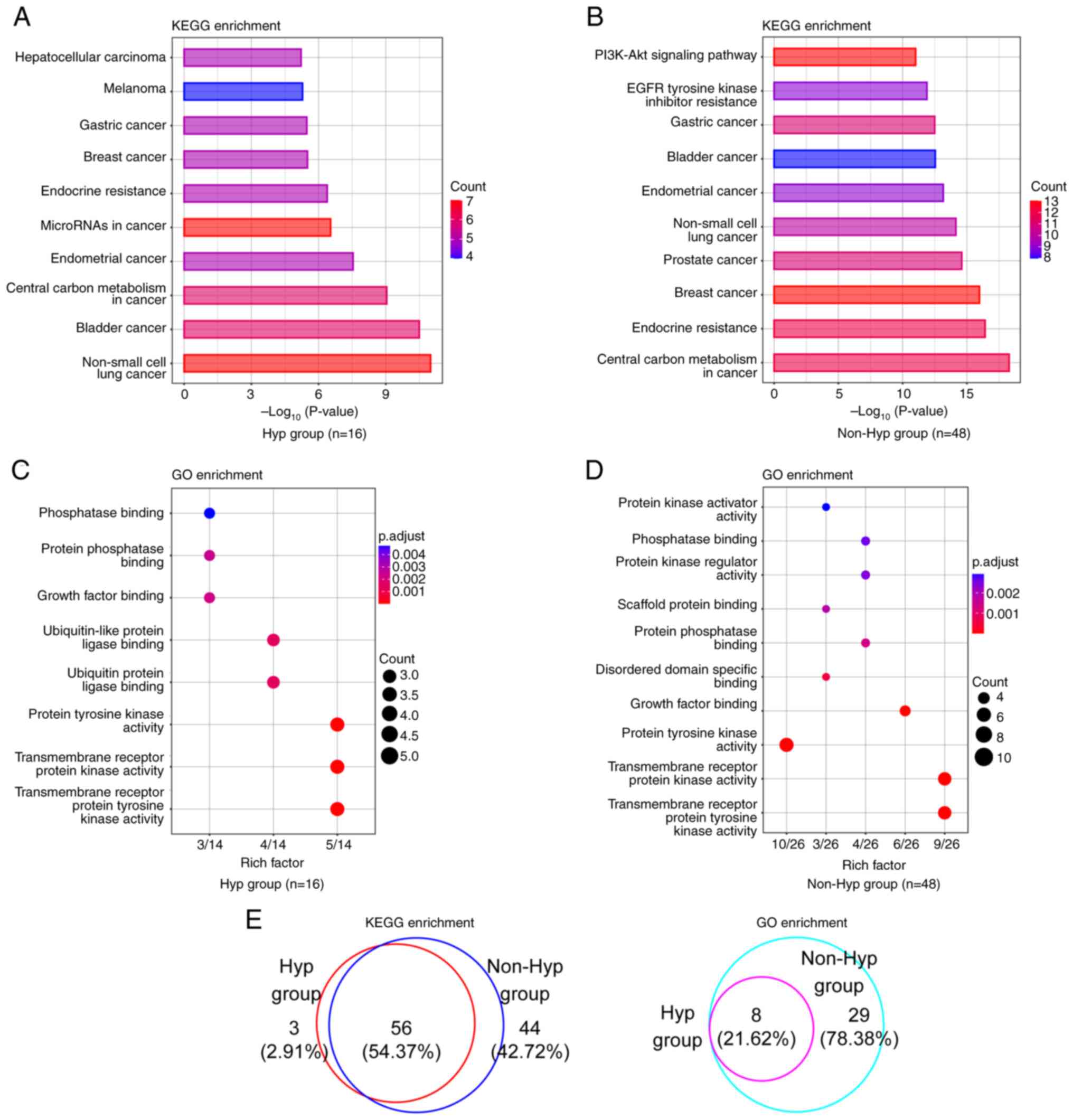
Disparities in key signaling pathways
and biological functional categories between patients with NSCLC
with and without hypertension
To obtain a deeper understanding of the functional
biological distinctions between the Hyp and the non-Hyp group, KEGG
and GO analyses were performed. The top 10 KEGG signaling pathways
based on both gene counts and P-values were identified, where the
majority of the signaling pathways found were closely associated
with cancer (Fig. 3A and B;
Table SVII). ‘Non-small cell lung
cancer’ was the top KEGG pathway in hypertensive patients, whereas
‘central carbon metabolism in cancer’ was the top pathway in
patients without hypertension. In the GO enrichment analysis, the
most prevalent functional category in both groups was
‘transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity’ (Fig. 3C and D; Table SVII). In addition, the proportions
of altered signaling pathways and altered functional terms shared
between these two groups were 54.37% (56/103) and 21.62% (8/37),
respectively (Fig. 3E).
Unexpectedly, all functional terms in the Hyp group were also
identified in the non-Hyp group.
Disparities in levels of heavy metals
between patients with NSCLC with and without hypertension
To further examine the differences between the
groups of patients with NSCLC based on hypertension status, a
comparative analysis of three conventional serum biomarkers between
individuals with hypertension (n=14) and those without hypertension
(n=42) was performed. The serum levels of CEA, CYFRA21-1 and NSE
were all found to be similar between the Hyp group and the non-Hyp
group (Table SVIII and IX). Subsequently, the serum
concentrations of 18 heavy metals in the Hyp group (n=16) and the
non-Hyp group (n=46) were compared, revealing a significant
difference in Cr, with no significant difference found in the other
17 heavy metals (Fig. 4). The
median concentrations (IQR) for Cr were as follows: 2.635 µg/l
(1.678–3.438 µg/l) in the Hyp group and 1.97 µg/l (1.525–2.483
µg/l) in the non-Hyp group (Fig.
4E).
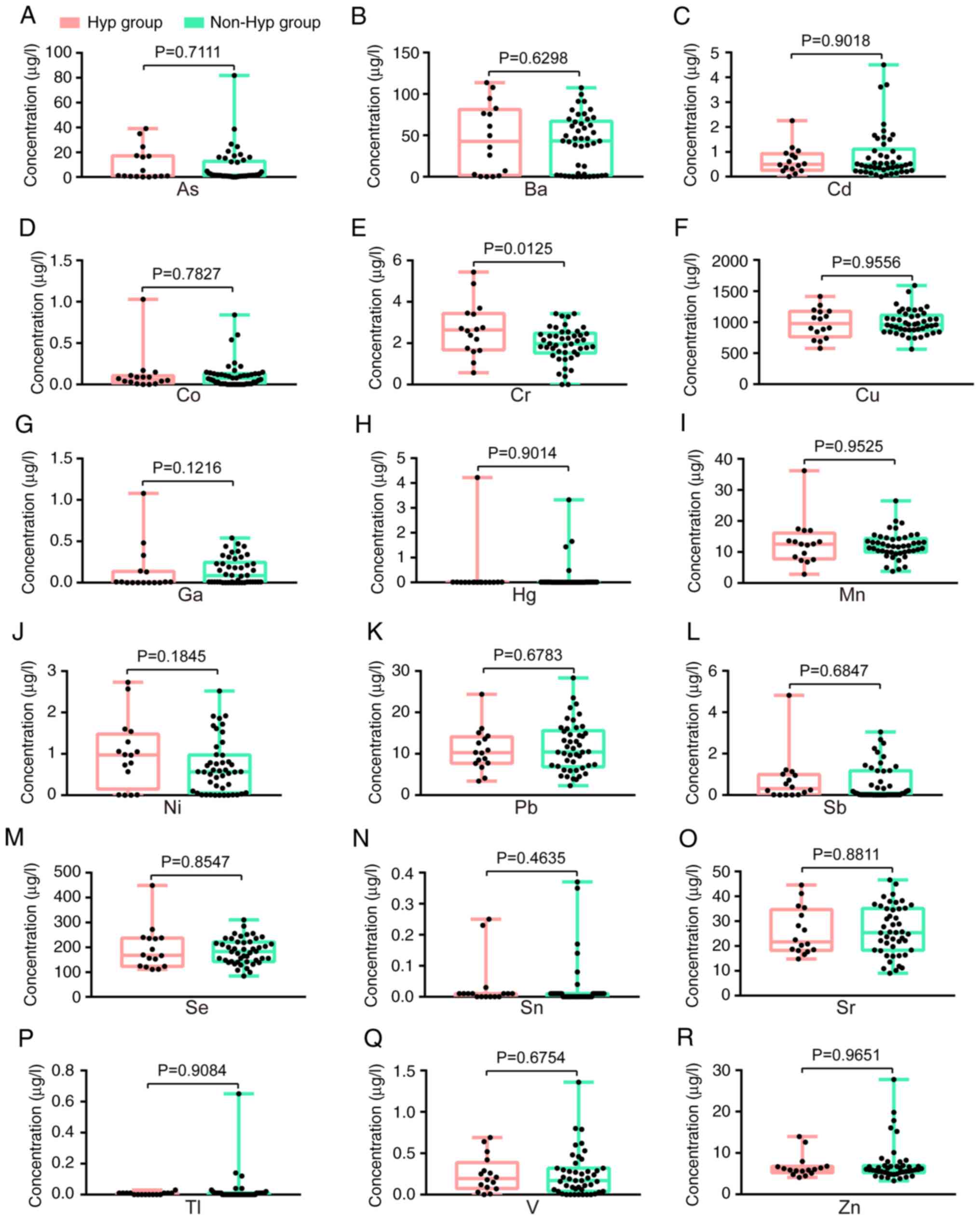 | Figure 4.Comparative evaluation of 18 heavy
metals in patients with non-small cell lung cancer with and without
hypertension. (A) As, (B) Ba, (C) Cd, (D) Co, (E) Cr, (F) Cu, (G)
Ga, (H) Hg, (I) Mn, (J) Ni, (K) Pb, (L) Sb, (M) Se, (N) Sn, (O) Sr,
(P) Tl, (Q) V and (R) Zn. A two-tailed unpaired t-test was applied
for Cr, Pb and Sr, whilst a two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test was used
for the remaining 15 heavy metals. As, arsenic; Ba, barium; Cd,
cadmium; Co, cobalt; Cr, chromium; Cu, copper; Ga, gallium; Hg,
mercury; Hyp group, hypertension group; Mn, manganese; Ni, nickel;
non-Hyp group, non-hypertension group; Pb, lead; Sb, antimony; Se,
selenium; Sn, stannum; Sr, strontium; Tl, thallium; V, vanadium;
Zn, zinc. |
Correlations among somatic mutations,
demographic and clinical characteristics, traditional serum
biomarkers and heavy metals in patients with NSCLC with
hypertension
In the male group, the proportion of smokers
(P=0.0049) and drinkers (P=0.0049) were significantly higher than
those in the female group (Fig.
S2; Table SVIII). Compared
with the non-smoking group, the proportion of drinkers in the
smoking group was significantly higher (P=0.0009; Fig. S2; Table SVIII). In addition, compared with
that in patients without EGFR mutations, a significant
decrease in Sn levels was observed in patients with EGFR
mutations (P=0.0110) according to the two-tailed Mann-Whitney U
test (Fig. S3; Table SVIII). However, none of the three
traditional serum biomarkers, CEA, CYFRA21-1 and NSE, or 18 heavy
metals exhibited significant differences between patients with and
without TP53 mutations, between patients with and without
other chronic diseases, between male and female sex, between
non-smokers and smokers or between non-drinkers and drinkers
(Fig. S4, Fig. S5, Fig.
S6, Fig. S7, Fig. S8). In addition, Spearman's rank
correlation analysis was next performed to examine the correlations
among age, BMI, three traditional serum biomarkers and 18 heavy
metals in the 14 hypertensive patients. Significant correlations
were observed between traditional serum biomarkers and heavy
metals, including between CEA and Cr (r=−0.67; P<0.01), between
CYFRA21-1 and Zn (r=−0.64; P<0.01), between NSE and As (r=−0.66;
P<0.01), between NSE and Ba (r=−0.76; P<0.01), between NSE
and Pb (r=0.66; P<0.01) and between NSE and Se (r=0.58;
P<0.05). In addition, significant correlations were observed
between some of the 18 heavy metals, such as between As and Sr
(r=0.54; P<0.05), between Ba and Hg (r=−0.59; P<0.05) and
between Cd and Cu (r=0.58; P<0.05; Fig. 5).
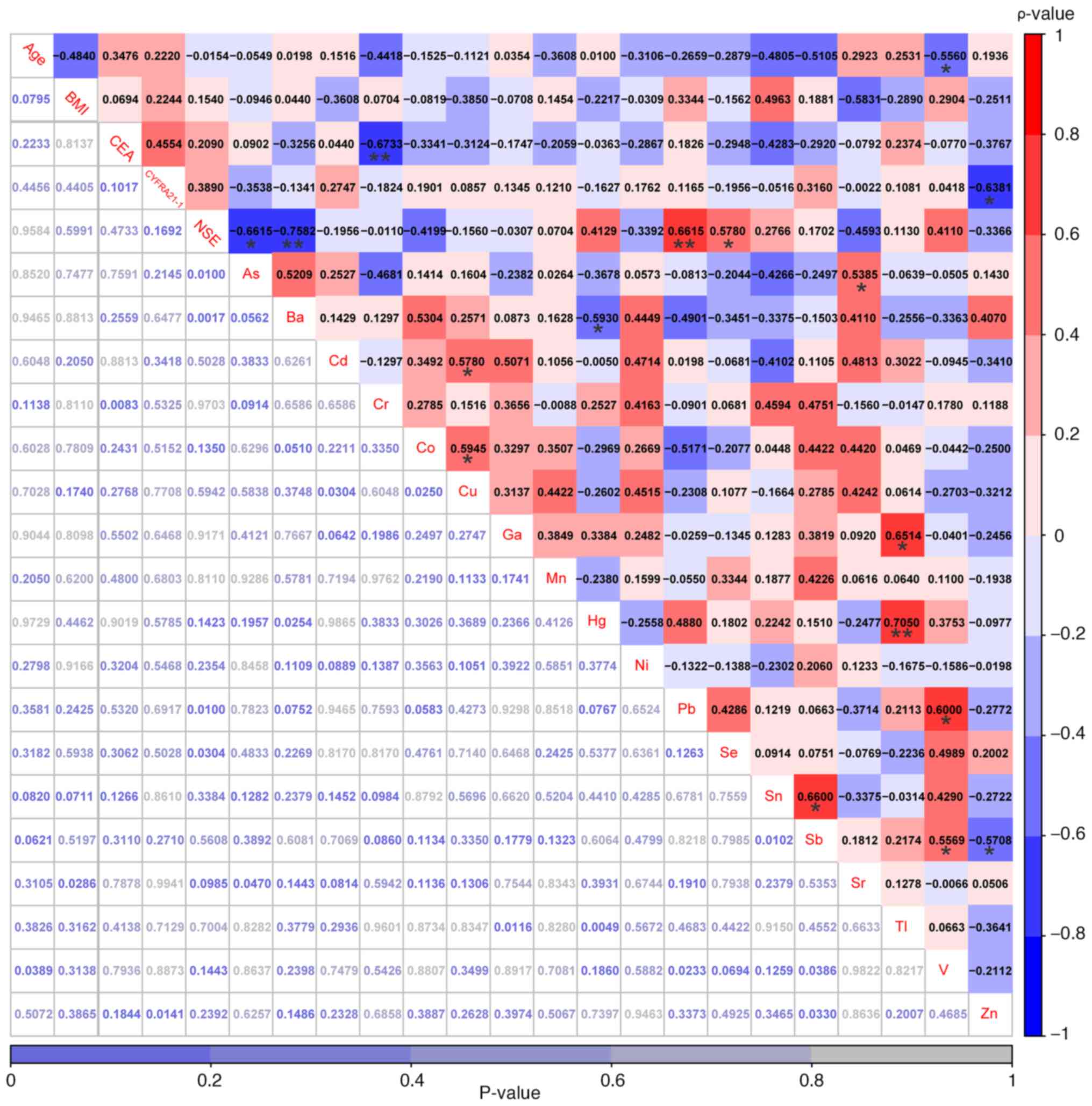 | Figure 5.Correlations among age, BMI, three
conventional serum biomarkers and 18 heavy metals were explored in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer with hypertension. The
values highlighted in various colors are the correlation
coefficients, with the scale on the right. The values at the bottom
are the P-values. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01. As, arsenic; Ba,
barium; Cd, cadmium; Co, cobalt; Cr, chromium; Cu, copper;
CYFRA21-1, cytokeratin-19 fragments; Ga, gallium; Hg, mercury; Mn,
manganese; Ni, nickel; NSE, neuron-specific enolase; Pb, lead; Sb,
antimony; Se, selenium; Sn, stannum; Sr, strontium; Tl, thallium;
V, vanadium; Zn, zinc. |
Correlations among somatic mutations,
demographic and clinical characteristics, traditional serum
biomarkers, and heavy metals in patients with NSCLC without
hypertension
Compared with patients with EGFR mutations,
the proportion of KRAS mutations (P=0.0192) and smokers
(P=0.0265) were significantly increased in patients without
EGFR mutations (Fig. S9;
Table SIX). The proportion of
women in patients with TP53 mutations was significantly
higher than in patients without TP53 mutations (P=0.0300)
(Fig. S9; Table SIX). In addition, a significant
decrease of Zn was observed in patients with EGFR mutations
in comparison with that in patients without EGFR mutations
(P=0.0280) according to the two-tailed unpaired t-test (Fig. S10; Table SIX). Compared with patients
without TP53 mutations, patients with TP53 mutations
exhibited a significantly lower level of As and significantly
higher levels of Cu and CEA (Fig.
S11). The serum levels of Co, Cr and Ni in patients with
KRAS mutations were significantly higher than those in
patients without KRAS mutations (Fig. S12). Compared with female patients,
male patients exhibited significantly lower levels of Cu and Mn as
well as significantly higher levels of Pb and Sn (Fig. S13). Compared with non-smokers,
smokers exhibited a significantly lower level of Mn, and
significantly higher levels of As, Cd, Pb and Sr (Fig. S14). Compared with non-drinkers,
drinkers exhibited significantly lower levels of Ga and Mn, and a
significantly higher level of Pb (Fig.
S15). Spearman's rank correlation analysis was next performed
to examine the correlations among age, BMI, three traditional serum
biomarkers and 18 heavy metals in 42 patients without hypertension.
BMI was found to be weakly negatively correlated with the serum
concentrations of Cu (r=−0.3227; P=0.0371), but no significant
correlations were observed between age and other factors (Fig. 6; Table
SIX). Furthermore, CYFRA21-1 was significantly positively
correlated with NSE (r=0.60; P<0.001), weakly but positively
correlated with As (r=0.35; P<0.05) and Pb (r=0.39; P<0.01),
whilst being negatively correlated with Cr (r=−0.39; P<0.01),
differing from only a significant negative correlation between
CYFRA21-1 and Zn observed in patients with hypertension. Among the
18 heavy metals, significant correlations were found in Fig. 6, such as between As and Sr (r=0.51;
P<0.001), between Ba and Sr (r=0.52; P<0.001), and between Hg
and Sn (r=0.64; P<0.001; Fig.
6).
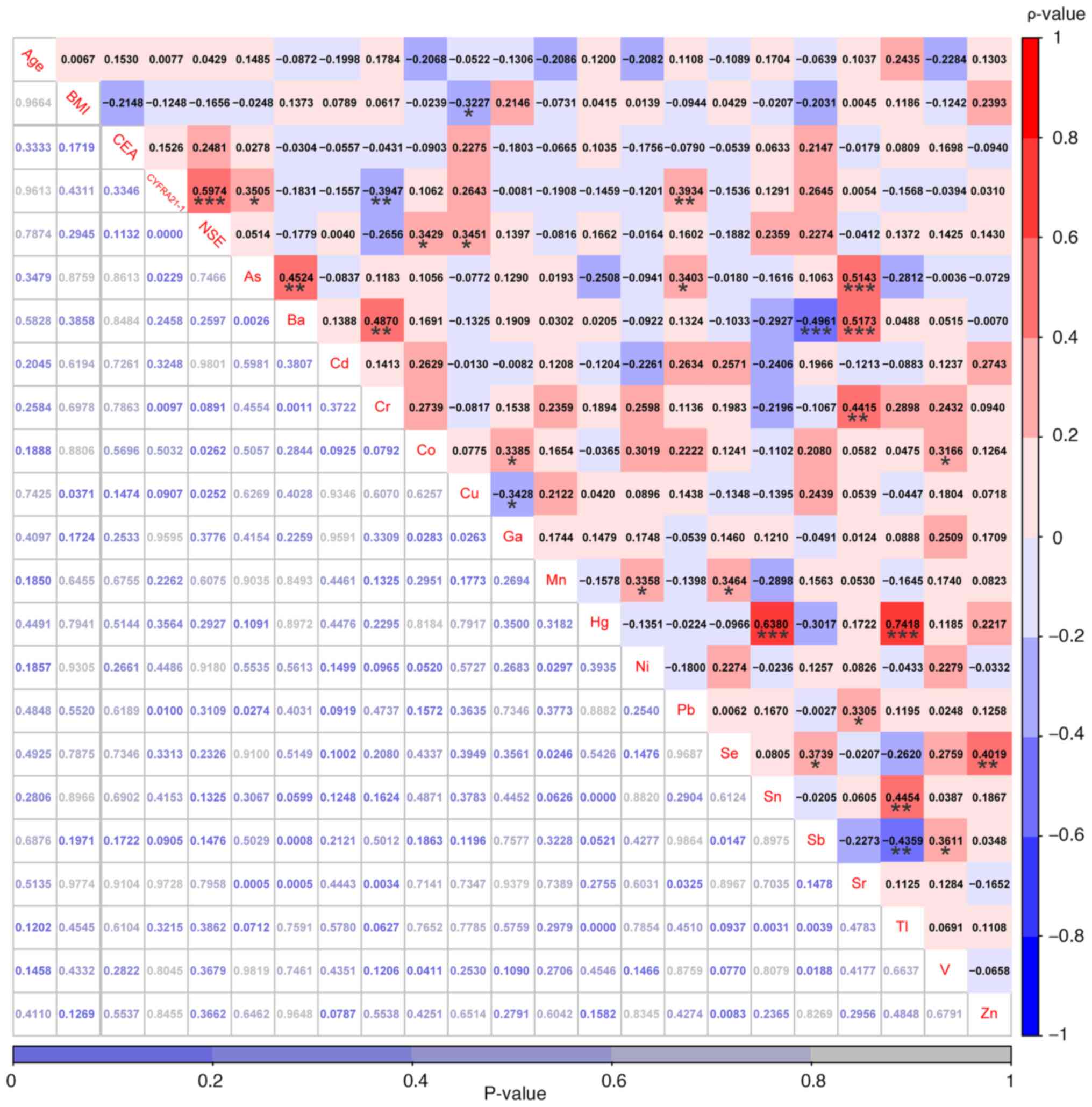 | Figure 6.Correlations among age, BMI, three
conventional serum biomarkers and 18 heavy metals were examined in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer without hypertension. The
values highlighted in various colors are the correlation
coefficients, with the scale on the right. The values at the bottom
are the P-values. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. As,
arsenic; Ba, barium; Cd, cadmium; Co, cobalt; Cr, chromium; Cu,
copper; CYFRA21-1, cytokeratin-19 fragments; Ga, gallium; Hg,
mercury; Mn, manganese; Ni, nickel; NSE, neuron-specific enolase;
Pb, lead; Sb, antimony; Se, selenium; Sn, stannum; Sr, strontium;
Tl, thallium; V, vanadium; Zn, zinc. |
Discussion
Over the past decades, there has been notable
improvements in the prognosis and survival of patients with NSCLC
(47,48). However, this progress has come with
a new set of challenges, since patients, particularly patients with
preexisting high blood pressure, the elderly and those with a high
body mass index, now face lasting cardiovascular ramifications
associated with targeted agents (49–51).
Among cancer survivors, CVD stands out as a prominent contributor
to morbidity and mortality, ranking second after cancer recurrence
(50). This evolving landscape of
NSCLC treatment outcomes underscores the importance of addressing
long-term cardiovascular implications, emphasizing the necessity
for tailored strategies, especially for individuals with specific
risk factors.
In the present study, 64 patients with primary NSCLC
were recruited, including 16 hypertensive patients and 48
non-hypertensive patients. No significant differences were found
regarding the distribution of sex, EGFR mutation status,
TP53 mutation status, pulmonary infection history, smoking
history, drinking history, cancer staging, presence of blood vessel
invasion, nerve invasion, distant metastasis status, CEA levels,
CYFRA21-1 levels and NSE levels between patients with and without
hypertension, with the only significant difference being the
incidence of other chronic diseases (including coronary heart
disease, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, Parkinson's disease and
chronic gastritis). A total of 47 somatic mutations involving 14
mutant genes were detected in all 16 hypertensive patients
(100.00%), whilst 113 somatic mutations involving 26 mutant genes
were found in 45 out of the 48 non-hypertensive patients (93.75%).
Differences in genomic alterations, somatic interactions, key
signaling pathways and enriched biological functional categories
were identified between these two groups. Furthermore, the serum
concentrations of Cr were significantly elevated in hypertensive
patients compared with those in non-hypertensive patients. Finally,
significant negative correlations were observed between Cr and CEA,
between CYFRA21-1 and Zn, and between NSE and As in patients with
hypertension, which were not observed in patients without
hypertension. This suggests the existence of differences in the
interactive profiles among somatic mutations, traditional serum
biomarkers and heavy metals between the Hyp group and the non-Hyp
group. To the best of our knowledge, the present study was the
first to identify these significant negative correlations between
Cr and CEA, between CYFRA21-1 and Zn, and between NSE and As in
patients with NSCLC and hypertension in an Eastern Asian
cohort.
The prevalence of both lung cancer incidence and
mortality exhibits an upward trend in the presence of hypertensive
conditions. Previous cohort studies conducted in Finland, Sweden,
Norway and Austria indicated an association between hypertension
and an elevated risk of lung cancer in both sexes (13,16).
Stocks et al (13) further
suggested that elevated blood pressure levels were associated with
an increased risk of mortality, particularly in men rather than
women. Conversely, findings from a Dutch study involving 11,075
participants with lung cancer previously revealed that women with
hypertensive disorders faced a 2.19-fold increased risk of
mortality compared with those without such conditions (17). Additionally, a study in South Korea
identified a link between high blood pressure and lung cancer
mortality, but subsequent analyses categorized by smoking status
implied that the heightened risk was confined to current smokers
(18). However, there were no
significant differences observed regarding sex distribution and
smoking status between hypertensive patients and non-hypertensive
patients in the present study. This could be attributed in part to
the limited sample size, regional variations or differences in
disease status among various studies.
Cigarette smoking is the predominant modifiable risk
factor contributing to the onset of lung cancer, which is
responsible for ~66% of all lung cancer cases worldwide (52). Nevertheless, the incidence of lung
cancer among individuals who have never smoked is also steadily
increasing, constituting up to 25% of all diagnosed cases globally
(53–55). Several studies have previously
indicated a higher propensity for lung adenocarcinoma development
in female Chinese patients harboring EGFR mutations,
particularly among those with no prior history of smoking or
alcohol consumption (56–58). In the present study, smoking history
was more likely to be observed in men compared with women, which
was identified in both the hypertensive and non-hypertensive
groups. However, non-smoking patients were more likely to carry
EGFR mutations than smoking patients, and a significant
negative correlation between EGFR mutations and smoking
history was only observed in patients without hypertension,
indicating the difference in interaction characteristics between
patients with and without hypertension.
Although inflammation, hypoxia and clonal
hematopoiesis are recognized as pivotal players in the intricate
relationship between CVD and cancer, the specific mechanisms
underpinning the connection between hypertension and an increased
incidence of lung cancer remain elusive (59). In the present study, FBXW7, CBR3,
CDKN2A, HRAS, SMO and UGT1A1 mutations were solely found
in hypertensive patients, where the somatic interactions identified
in patients with and without hypertension differed markedly. F-Box
and WD repeat domain containing 7 (FBXW7), also known as FBW7 or
hCDC4, operates as a crucial component within the
Skp1-Cdc53/Cullin-F-box-protein complex (60,61).
Its function lies in facilitating the phosphorylation-dependent
ubiquitination and subsequent proteasome degradation of
oncoproteins (61–63). Numerous studies have indicated that
the absence of FBXW7 is strongly associated with tumorigenesis, the
metastatic spread of tumors, an adverse prognosis and increased
resistance to chemotherapy, radiation and immunotherapy, including
breast cancer (64,65), cervical cancer (66), colorectal cancer (62,67),
gastric cancer (67,68), glioma (69), hepatocellular carcinoma (68), lung cancer (67,70),
nasopharyngeal carcinoma (68) and
oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (62). Recently, Wang et al (71) reported that the induction of
glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 by the microRNA
(miR)-27b-3p/FBXW7/Kruppel-like transcription factor 5 axis may
promote pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats. In myeloma
fibroblasts, upregulation of miR-27b-3p was found to increase
proliferation and resistance to apoptosis via the action of FBXW7
(72). However, to the best of our
knowledge, whether miR-27b-3p is involved in the development of
NSCLC, particularly in patients with hypertension, remain unclear.
These aforementioned results improve our understanding of the
pathogenesis of patients with NSCLC with hypertension. In addition,
evidence from both experimental animal models and tumor databases
(cBioPortal for Cancer Genomics, https://www.cbioportal.org; The Cancer Genome Atlas
Program, http://www.cancer.gov/ccg/research/genome-sequencing/tcga)
indicated an association between FBXW7 mutations and a worse
prognosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma (62,73),
suggesting that FBXW7 may be regarded as an independent prognostic
indicator for this disease. To examine this hypothesis, we are
collecting prognostic data from patients with NSCLC with various
comorbidities, including hypertension, bone metastases and brain
metastases, to be analyzed in future studies.
Whilst the precise mechanisms by which heavy metals
induce hypertension remain incompletely understood, there is
evidence indicating that blood levels of Cr are independently
associated with hypertension (74,75).
Prolonged living or working in environments (such as manufacturing
shop and maintenance shop of a factory) with elevated Cr exposure
is associated with an increased risk of developing hypertension
(74,76). Furthermore, plasma concentrations of
Cr showed significant correlations with specific clinical markers
of pulmonary arterial hypertension severity, including the 6-min
walk distance (r=−0.55; P=0.014) and the most recent brain
natriuretic peptide level (r=0.463; P=0.039) (77). Consistent with the aforementioned
studies, the serum levels of Cr were found to be significantly
higher in hypertensive patients compared with those in
non-hypertensive patients in the present study. However,
contradictory findings also exist. In a previous cross-sectional
analysis, serum Cr levels in hypertensive individuals were reported
to be significantly lower compared with those in healthy controls
(75). In a case-control study,
patients with diabetes displayed significant increases in
low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, total cholesterol,
triglyceride, very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, insulin,
high sensitive C-reactive protein, and homeostasis model assessment
of insulin resistance, and a significant decrease in plasma levels
of Cr (78). Moreover, a lower Cr
level was correlated with high blood pressure, obesity and lipid
dysregulation. Overall, large-scale and multi-center studies are
required to verify the distributional differences of serum Cr
between patients with NSCLC with and without hypertension, which
may further refine the management of NSCLC subgroups with different
clinical characteristics.
In the present study, a number of limitations must
be acknowledged. The NGS data of tumor tissues were obtained from
individuals lacking corresponding normal tissues for comparison.
This approach was driven by the consideration that a single sample
provides sufficient clinically actionable genomic alterations under
the appropriate filtering conditions (79–87).
It is imperative to acknowledge that opting for the collection of
several types of tissues or biopsies from multiple regions incurs
higher costs compared with a single-sample approach. The present
study also exclusively scrutinized the overall levels of heavy
metals in serum, without delving into the repercussions of various
forms of a single metal. Additionally, there was a lack of detailed
exploration into the sources of exposure, such as soil, water or
air, an aspect that falls outside the scope of the present type of
study. The assessment of heavy metal concentrations was confined to
only serum samples, without corresponding analyses of matched
samples (such as urine, hair and nails). Due to the direct
reservoirs of certain heavy metals in hair and nails, exploration
of the levels of heavy metals in future studies using several
different source samples from the same individual is recommended.
Furthermore, the sample size in the present study was relatively
small, where the demographic diversity of the patients recruited
was low. Therefore, the recruitment of several cohorts from
multiple institutes from different countries is required to
validate the applicability of the findings of the present
study.
In conclusion, differences were observed in the
presence of genomic mutations, somatic interactions and the serum
levels of Cr between patients with NSCLC with and without
hypertension in the present study. Furthermore, patients with
hypertension exhibited significant negative correlations between Cr
and CEA, between CYFRA21-1 and Zn, and between NSE and As,
indicating that heavy metals may contribute to the progression of
NSCLC in patients with different hypertensive statuses.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Scientific Instruments
Application Methods Project of the Shanghai Science and Technology
Innovation Action Plan (grant no. 19142200800).
Availability of data and materials
The sequencing data generated in the present study
may be found in the National Center for Biotechnology Information
BioProject database under accession number PRJNA904839 or at the
following URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/?term=PRJNA904839.
The other data generated in the present study may be requested from
the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
XZ, JY and HJ were involved in the conception and
design of the study. XZ, HS and YW supplied patient samples, and
analyzed and interpreted the clinicopathological data. JY, MW, LJ
and HJ carried out data collection and analysis. All authors were
involved in writing the manuscript and revising it critically. XZ,
JY and HJ confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors
read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
For the use of human samples, the present study was
approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of The First People's
Hospital of Ping Ding Shan (approval no. PYLL20190806;
Pingdingshan, China). Written informed consent was obtained from
all patients.
Patient consent for publication
All patients provided written consent for the
publication of data.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
The Lancet: Lung cancer: Some progress,
but still a lot more to do. Lancet. 394:18802019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ganti AK, Klein AB, Cotarla I, Seal B and
Chou E: Update of incidence, prevalence, survival, and initial
treatment in patients with non-small cell lung cancer in the US.
JAMA Oncol. 7:1824–1832. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Leiter A, Veluswamy RR and Wisnivesky JP:
The global burden of lung cancer: Current status and future trends.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 20:624–639. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pallis AG and Syrigos KN: Lung cancer in
never smokers: Disease characteristics and risk factors. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 88:494–503. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato
G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, Barengo NC, Beaton AZ, Benjamin EJ,
Benziger CP, et al: Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and
risk factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 76:2982–3021. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arima H, Barzi F and Chalmers J: Mortality
patterns in hypertension. J Hypertens. 29:S3–S7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC),
. Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015: A pooled
analysis of 1479 population-based measurement studies with 19.1
million participants. Lancet. 389:37–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
van Kruijsdijk RC, van der Graaf Y,
Peeters PH and Visseren FL; Second Manifestations of ARTerial
disease (SMART) study group, : Cancer risk in patients with
manifest vascular disease: Effects of smoking, obesity, and
metabolic syndrome. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 22:1267–1277.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hatlen P, Langhammer A, Carlsen SM,
Salvesen O and Amundsen T: Self-reported cardiovascular disease and
the risk of lung cancer, the HUNT study. J Thorac Oncol. 9:940–946.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sorensen HT, Svaerke C, Farkas DK,
Christiansen CF, Pedersen L, Lash TL, Prandoni P and Baron JA:
Superficial and deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism and
subsequent risk of cancer. Eur J Cancer. 48:586–593. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stocks T, Van Hemelrijck M, Manjer J,
Bjørge T, Ulmer H, Hallmans G, Lindkvist B, Selmer R, Nagel G,
Tretli S, et al: Blood pressure and risk of cancer incidence and
mortality in the Metabolic Syndrome and Cancer Project.
Hypertension. 59:802–810. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Buck C and Donner A: Cancer incidence in
hypertensives. Cancer. 59:1386–1390. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang C, Lu D, Cronin-Fenton D, Huang C,
Liew Z, Wei D, Qin G, Yu Y and Li J: Cardiovascular disease and
risk of lung cancer incidence and mortality: A nationwide matched
cohort study. Front Oncol. 12:9509712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lindgren A, Pukkala E, Nissinen A and
Tuomilehto J: Blood pressure, smoking, and the incidence of lung
cancer in hypertensive men in North Karelia, Finland. Am J
Epidemiol. 158:442–447. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peeters PH, van Noord PA, Hoes AW and
Grobbee DE: Hypertension, antihypertensive drugs, and mortality
from cancer among women. J Hypertens. 16:941–947. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee SY, Kim MT, Jee SH and Im JS: Does
hypertension increase mortality risk from lung cancer? A
prospective cohort study on smoking, hypertension and lung cancer
risk among Korean men. J Hypertens. 20:617–622. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huff MO, Todd SL, Smith AL, Elpers JT,
Smith AP, Murphy RD, Bleser-Shartzer AS, Hoerter JE, Radde BN and
Klinge CM: Arsenite and cadmium activate MAPK/ERK via membrane
estrogen receptors and G-protein coupled estrogen receptor
signaling in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Toxicol Sci.
152:62–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hartwig A, Asmuss M, Ehleben I, Herzer U,
Kostelac D, Pelzer A, Schwerdtle T and Bürkle V: Interference by
toxic metal ions with DNA repair processes and cell cycle control:
molecular mechanisms. Environ Health Perspect. 110 (Suppl):797–799.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim HS, Kim YJ and Seo YR: An overview of
carcinogenic heavy metal: Molecular toxicity mechanism and
prevention. J Cancer Prev. 20:232–240. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Caffo M, Caruso G, Fata GL, Barresi V,
Visalli M, Venza M and Venza I: Heavy metals and epigenetic
alterations in brain tumors. Curr Genomics. 15:457–463. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Coyle YM, Minahjuddin AT, Hynan LS and
Minna JD: An ecological study of the association of metal air
pollutants with lung cancer incidence in Texas. J Thorac Oncol.
1:654–661. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Satarug S, Nishijo M, Ujjin P,
Vanavanitkun Y and Moore MR: Cadmium-induced nephropathy in the
development of high blood pressure. Toxicol Lett. 157:57–68. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Swaddiwudhipong W, Mahasakpan P,
Limpatanachote P and Krintratun S: Correlations of urinary cadmium
with hypertension and diabetes in persons living in
cadmium-contaminated villages in northwestern Thailand: A
population study. Environ Res. 110:612–616. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Valera B, Dewailly E and Poirier P:
Environmental mercury exposure and blood pressure among Nunavik
Inuit adults. Hypertension. 54:981–986. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang Z: Association between blood lead
level with high blood pressure in US (NHANES 1999–2018). Front
Public Health. 10:8363572022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vaziri ND and Sica DA: Lead-induced
hypertension: Role of oxidative stress. Curr Hypertens Rep.
6:314–320. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bunderson M, Coffin JD and Beall HD:
Arsenic induces peroxynitrite generation and cyclooxygenase-2
protein expression in aortic endothelial cells: Possible role in
atherosclerosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 184:11–18. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
da Cunha Martins A, Jr, Carneiro MFH,
Grotto D, Adeyemi JA and Barbosa F Jr: Arsenic, cadmium, and
mercury-induced hypertension: Mechanisms and epidemiological
findings. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 21:61–82. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Torres AD, Rai AN and Hardiek ML: Mercury
intoxication and arterial hypertension: Report of two patients and
review of the literature. Pediatrics. 105:E342000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG,
Yatabe Y, Austin JHM, Beasley MB, Chirieac LR, Dacic S, Duhig E,
Flieder DB, et al: The 2015 World health organization
classification of lung tumors: Impact of genetic, clinical and
radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol.
10:1243–1260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gandevia B and Tovell A: Declaration of
Helsinki. Med J Aust. 2:320–321. 1964. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Rosei
EA, Azizi M, Burnier M, Clement DL, Coca A, de Simone G, Dominiczak
A, et al: 2018 ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial
hypertension. Eur Heart J. 39:3021–3104. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li H and Durbin R: Fast and accurate
long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics.
26:589–595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A,
Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly
M and DePristo MA: The genome analysis toolkit: A MapReduce
framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome
Res. 20:1297–1303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lai Z, Markovets A, Ahdesmaki M, Chapman
B, Hofmann O, McEwen R, Johnson J, Dougherty B, Barrett JC and Dry
JR: VarDict: A novel and versatile variant caller for
next-generation sequencing in cancer research. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:e1082016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang K, Li M and Hakonarson H: ANNOVAR:
Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput
sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:e1642010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qu S, Liu J, Luo J, Huang Y, Shi W, Wang B
and Cai X: A rapid and highly sensitive portable chemiluminescent
immunosensor of carcinoembryonic antigen based on immunomagnetic
separation in human serum. Anal Chim Acta. 766:94–99. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gong X and Zhang H: Diagnostic and
prognostic values of anti-elicobacter pylori antibody combined with
serum CA724, CA19 and CEA for young patients with early gastric
cancer. J Clin Lab Anal. 34:e232682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao S, Cao S, Luo L, Zhang Z, Yuan G,
Zhang Y, Yang Y, Guo W, Wang L, Chen F, et al: A preliminary
investigation of metal element profiles in the serum of patients
with bloodstream infections using inductively-coupled plasma mass
spectrometry (ICP-MS). Clin Chim Acta. 485:323–332. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mayakonda A, Lin DC, Assenov Y, Plass C
and Koeffler HP: Maftools: Efficient and comprehensive analysis of
somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res. 28:1747–1756. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Riely GJ, Wood DE, Ettinger DS, Aisner DL,
Akerley W, Bauman JR, Bharat A, Bruno DS, Chang JY, Chirieac LR, et
al: Non-small cell lung cancer, version 4.2024, NCCN clinical
practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
22:249–274. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Guo H, Zhang J, Qin C, Yan H, Liu T, Hu H,
Tang S, Tang S and Zhou H: Biomarker-targeted therapies in
non-small cell lung cancer: Current status and perspectives. Cells.
11:32002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pao W, Wang TY, Riely GJ, Miller VA, Pan
Q, Ladanyi M, Zakowski MF, Heelan RT, Kris MG and Varmus HE: KRAS
mutations and primary resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to
gefitinib or erlotinib. PLoS Med. 2:e172005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang M, Herbst RS and Boshoff C: Toward
personalized treatment approaches for non-small-cell lung cancer.
Nat Med. 27:1345–1356. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tan AC and Tan DSW: Targeted therapies for
lung cancer patients with oncogenic driver molecular alterations. J
Clin Oncol. 40:611–625. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hamnvik OP, Choueiri TK, Turchin A, McKay
RR, Goyal L, Davis M, Kaymakcalan MD and Williams JS: Clinical risk
factors for the development of hypertension in patients treated
with inhibitors of the VEGF signaling pathway. Cancer. 121:311–319.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Essa H, Dobson R, Wright D and Lip GYH:
Hypertension management in cardio-oncology. J Hum Hypertens.
34:673–681. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen F, Chen N, Yu Y and Cui J: Efficacy
and safety of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors
plus antiangiogenic agents as first-line treatments for patients
with advanced EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: A
meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 10:9042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
GBD 2019 Respiratory Tract Cancers
Collaborators, . Global, regional, and national burden of
respiratory tract cancers and associated risk factors from 1990 to
2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study
2019. Lancet Respir Med. 9:1030–1049. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cheng ES, Weber MF, Steinberg J, Canfell K
and Yu XQ: Evaluating risk factors for lung cancer among
never-smoking individuals using two Australian studies. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 148:2827–2840. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rivera GA and Wakelee H: Lung cancer in
never smokers. Adv Exp Med Biol. 893:43–57. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang T, Joubert P, Ansari-Pour N, Zhao W,
Hoang PH, Lokanga R, Moye AL, Rosenbaum J, Gonzalez-Perez A,
Martínez-Jiménez F, et al: Genomic and evolutionary classification
of lung cancer in never smokers. Nat Genet. 53:1348–1359. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang XC, Wang J, Shao GG, Wang Q, Qu X,
Wang B, Moy C, Fan Y, Albertyn Z, Huang X, et al: Comprehensive
genomic and immunological characterization of Chinese non-small
cell lung cancer patients. Nat Commun. 10:17722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ha SY, Choi SJ, Cho JH, Choi HJ, Lee J,
Jung K, Irwin D, Liu X, Lira ME, Mao M, et al: Lung cancer in
never-smoker Asian females is driven by oncogenic mutations, most
often involving EGFR. Oncotarget. 6:5465–5474. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li C, Fang R, Sun Y, Han X, Li F, Gao B,
Iafrate AJ, Liu XY, Pao W, Chen H and Ji H: Spectrum of oncogenic
driver mutations in lung adenocarcinomas from East Asian never
smokers. PLoS One. 6:e282042011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Aboumsallem JP, Moslehi J and de Boer RA:
Reverse cardio-oncology: Cancer development in patients with
cardiovascular disease. J Am Heart Assoc. 9:e0137542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hao B, Oehlmann S, Sowa ME, Harper JW and
Pavletich NP: Structure of a Fbw7-Skp1-cyclin E complex:
Multisite-phosphorylated substrate recognition by SCF ubiquitin
ligases. Mol Cell. 26:131–143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhou Z, He C and Wang J: Regulation
mechanism of Fbxw7-related signaling pathways (Review). Oncol Rep.
34:2215–2224. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fan J, Bellon M, Ju M, Zhao L, Wei M, Fu L
and Nicot C: Clinical significance of FBXW7 loss of function in
human cancers. Mol Cancer. 21:872022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yeh CH, Bellon M and Nicot C: FBXW7: A
critical tumor suppressor of human cancers. Mol Cancer. 17:1152018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gasca J, Flores ML, Giraldez S,
Ruiz-Borrego M, Tortolero M, Romero F, Japón MA and Sáez C: Loss of
FBXW7 and accumulation of MCL1 and PLK1 promote paclitaxel
resistance in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:52751–52765. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen S, Leng P, Guo J and Zhou H: FBXW7 in
breast cancer: Mechanism of action and therapeutic potential. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 42:2262023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chen S, Lin J, Zhao J, Lin Q, Liu J, Wang
Q, Mui R and Ma L: FBXW7 attenuates tumor drug resistance and
enhances the efficacy of immunotherapy. Front Oncol.
13:11472392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang W, Jiang K, Liu X, Li J, Zhou W, Wang
C, Cui J and Liang T: FBXW7 and human tumors: Mechanisms of drug
resistance and potential therapeutic strategies. Front Pharmacol.
14:12780562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shen W, Zhou Q, Peng C, Li J, Yuan Q, Zhu
H, Zhao M, Jiang X, Liu W and Ren C: FBXW7 and the hallmarks of
cancer: Underlying mechanisms and prospective strategies. Front
Oncol. 12:8800772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xing L, Xu L, Zhang Y, Che Y, Wang M, Shao
Y, Qiu D, Yu H, Zhao F and Zhang J: Recent insight on regulations
of FBXW7 and its role in immunotherapy. Front Oncol. 12:9250412022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yokobori T, Yokoyama Y, Mogi A, Endoh H,
Altan B, Kosaka T, Yamaki E, Yajima T, Tomizawa K, Azuma Y, et al:
FBXW7 mediates chemotherapeutic sensitivity and prognosis in
NSCLCs. Mol Cancer Res. 12:32–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang Q, Chai L, Zhang Q, Wang J, Liu J,
Chen H, Wang Y, Chen Y, Shen N, Xie X and Li M: Induction of GLI1
by miR-27b-3p/FBXW7/KLF5 pathway contributes to pulmonary arterial
hypertension. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 171:16–29. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Frassanito MA, Desantis V, Di Marzo L,
Craparotta I, Beltrame L, Marchini S, Annese T, Visino F, Arciuli
M, Saltarella I, et al: Bone marrow fibroblasts overexpress miR-27b
and miR-214 in step with multiple myeloma progression, dependent on
tumour cell-derived exosomes. J Pathol. 247:241–253. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ruiz EJ, Diefenbacher ME, Nelson JK,
Sancho R, Pucci F, Chakraborty A, Moreno P, Annibaldi A, Liccardi
G, Encheva V, et al: LUBAC determines chemotherapy resistance in
squamous cell lung cancer. J Exp Med. 216:450–465. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Qian H, Li G, Luo Y, Fu X, Wan S, Mao X,
Yin W, Min Z, Jiang J, Yi G and Tan X: Relationship between
occupational metal exposure and hypertension risk based on
conditional logistic regression analysis. Metabolites. 12:12592022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhang Z, Zhao S, Wu H, Qin W, Zhang T,
Wang Y, Tang Y, Qi S, Cao Y and Gao X: Cross-sectional study:
Relationship between serum trace elements and hypertension. J Trace
Elem Med Biol. 69:1268932022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Xu J, White AJ, Niehoff NM, O'Brien KM and
Sandler DP: Airborne metals exposure and risk of hypertension in
the Sister Study. Environ Res. 191:1101442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
El-Kersh K, Hopkins CD, Wu X, Rai SN, Cave
MC, Smith MR, Go YM, Jones DP, Cai L and Huang J: Metallomics in
pulmonary arterial hypertension patients. Pulm Circ. 13:e122022023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ngala RA, Awe MA and Nsiah P: The effects
of plasma chromium on lipid profile, glucose metabolism and
cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A case-control
study. PLoS One. 13:e01979772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Adzhubei I, Jordan DM and Sunyaev SR:
Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using
PolyPhen-2. Curr Protoc Hum Genet Chapter 7. Unit7 20. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
1000 Genomes Project Consortium, . Auton
A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Garrison EP, Kang HM, Korbel JO, Marchini
JL, McCarthy S, McVean GA and Abecasis GR: A global reference for
human genetic variation. Nature. 526:68–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Kircher M, Witten DM, Jain P, O'Roak BJ,
Cooper GM and Shendure J: A general framework for estimating the
relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat Genet.
46:310–315. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Ng PC and Henikoff S: SIFT: Predicting
amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res.
31:3812–3814. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Schwarz JM, Rodelsperger C, Schuelke M and
Seelow D: MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of
sequence alterations. Nat Methods. 7:575–576. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
McNulty SN, Parikh BA, Duncavage EJ,
Heusel JW and Pfeifer JD: Optimization of population frequency
cutoffs for filtering common germline polymorphisms from tumor-only
next-generation sequencing data. J Mol Diagn. 21:903–912. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Sukhai MA, Misyura M, Thomas M, Garg S,
Zhang T, Stickle N, Virtanen C, Bedard PL, Siu LL, Smets T, et al:
Somatic tumor variant filtration strategies to optimize tumor-only
molecular profiling using targeted next-generation sequencing
panels. J Mol Diagn. 21:261–273. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hiltemann S, Jenster G, Trapman J, van der
Spek P and Stubbs A: Discriminating somatic and germline mutations
in tumor DNA samples without matching normals. Genome Res.
25:1382–1390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Teer JK, Zhang Y, Chen L, Welsh EA, Cress
WD, Eschrich SA and Berglund AE: Evaluating somatic tumor mutation
detection without matched normal samples. Hum Genomics. 11:222017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|