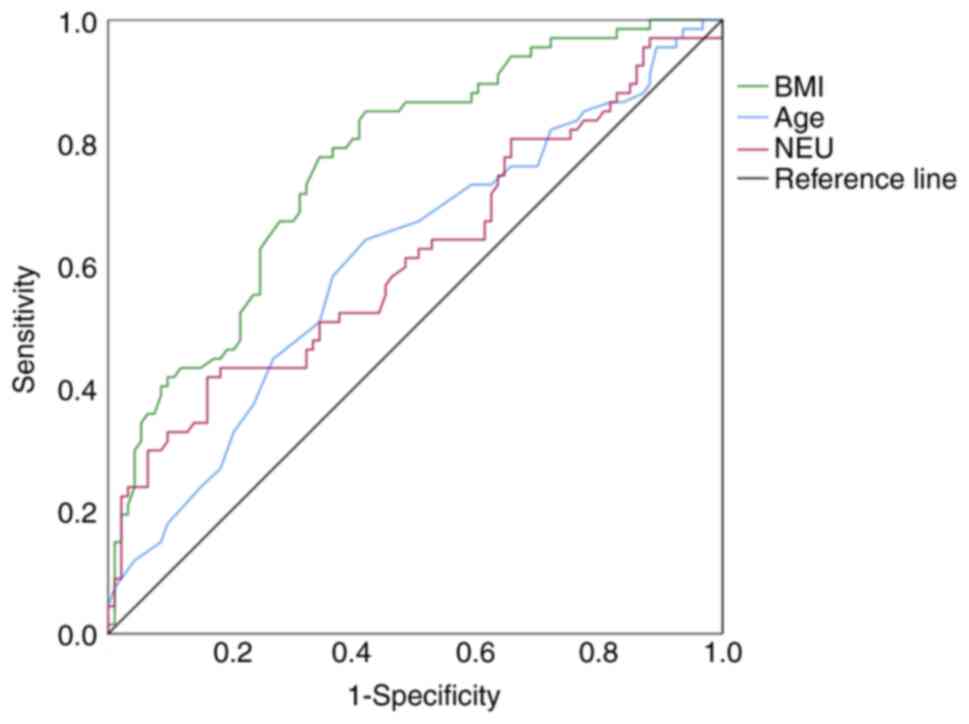
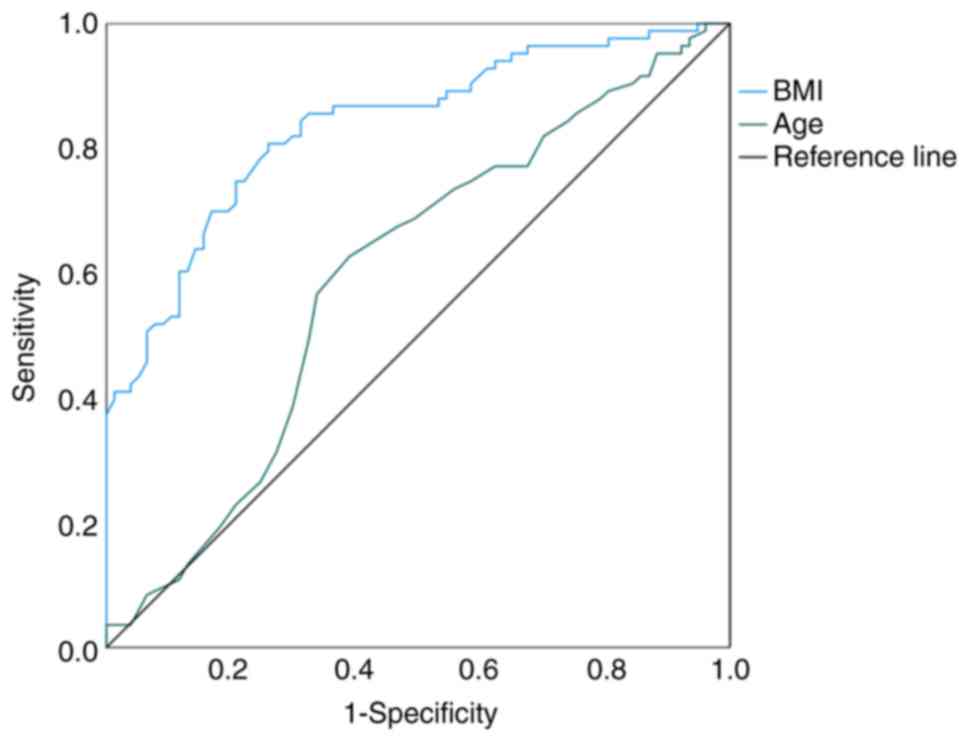
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cao J, Xu H, Li W, Guo Z, Lin Y, Shi Y, Hu
W, Ba Y, Li S, Li Z, et al: Nutritional assessment and risk factors
associated to malnutrition in patients with esophageal cancer. Curr
Probl Cancer. 45:1006382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamano T, Yoshimura M, Kobayashi M, Beppu
N, Hamanaka M, Babaya A, Tsukamoto K, Noda M, Matsubara N and
Tomita N: Malnutrition in rectal cancer patients receiving
preoperative chemoradiotherapy is common and associated with
treatment tolerability and anastomotic leakage. Int J Colorectal
Dis. 31:877–884. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Illa P, Tomiskova M and Skrickova J:
Nutritional risk screening predicts tumor response in lung cancer
patients. J Am Coll Nutr. 34:425–429. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cederholm T, Bosaeus I, Barazzoni R, Bauer
J, Van Gossum A, Klek S, Muscaritoli M, Nyulasi I, Ockenga J,
Schneider SM, et al: Diagnostic criteria for malnutrition - An
ESPEN consensus statement. Clin Nutr. 34:335–340. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cederholm T, Jensen GL, Correia MITD,
Gonzalez MC, Fukushima R, Higashiguchi T, Baptista G, Barazzoni R,
Blaauw R, Coats AJS, et al: GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of
malnutrition-A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition
community. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 10:207–217. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kondrup J, Rasmussen HH, Hamberg O and
Stanga Z; Ad Hoc ESPEN Working Group, : Nutritional risk screening
(NRS 2002): A new method based on an analysis of controlled
clinical trials. Clin Nutr. 22:321–336. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ottery FD: Rethinking nutritional support
of the cancer patient: The new field of nutritional oncology. Semin
Oncol. 21:770–778. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Detsky AS, McLaughlin JR, Baker JP,
Johnston N, Whittaker S, Mendelson RA and Jeejeebhoy KN: What is
subjective global assessment of nutritional status? JPEN J Parenter
Enteral Nutr. 11:8–13. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jager-Wittenaar H and Ottery FD: Assessing
nutritional status in cancer: Role of the patient-generated
subjective global assessment. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.
20:322–329. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pirozzolo G, Gisbertz SS, Castoro C, van
Berge Henegouwen MI and Scarpa M: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as
prognostic marker in esophageal cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. 11:3136–3145. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hong X, Cui B, Wang M, Yang Z, Wang L and
Xu Q: Systemic immune-inflammation index, based on platelet counts
and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, is useful for predicting prognosis
in small cell lung cancer. Tohoku J Exp Med. 236:297–304. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK and
Wittekind C: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 8th Edition.
Wiley-Blackwell; Chichester: 2017
|
|
14
|
Noghrehchi F, Stoklosa J, Penev S and
Warton DI: Selecting the model for multiple imputation of missing
data: Just use an IC! Stat Med. 40:2467–2497. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Isenring E, Cross G, Kellett E, Koczwara B
and Daniels L: Nutritional status and information needs of medical
oncology patients receiving treatment at an Australian public
hospital. Nutr Cancer. 62:220–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clark AB, Reijnierse EM, Lim WK and Maier
AB: Prevalence of malnutrition comparing the GLIM criteria, ESPEN
definition and MST malnutrition risk in geriatric rehabilitation
patients: RESORT. Clin Nutr. 39:3504–3511. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu M, Lian XJ, Jia JM, Cao WT, Yan N, Xin
YM, Liu ZR, Li HY, Fan ZF and Sun P: The role of the
Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA) and
biochemical markers in predicting anemia patients with cancer.
Support Care Cancer. 27:1443–1448. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huo Z, Chong F, Yin L, Li N, Liu J, Zhang
M, Guo J, Fan Y, Zhang L, Lin X, et al: Comparison of the
performance of the GLIM criteria, PG-SGA and mPG-SGA in diagnosing
malnutrition and predicting survival among lung cancer patients: A
multicenter study. Clin Nutr. 42:1048–1058. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou L, Fu J, Ding Z, Jin K, Wu R and Ye
LX: Comparison of GLIM, SGA, PG-SGA, and PNI in diagnosing
malnutrition among hepatobiliary-pancreatic surgery patients. Front
Nutr. 10:11162432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rosnes KS, Henriksen C, Hoidalen A and
Paur I: Agreement between the GLIM criteria and PG-SGA in a mixed
patient population at a nutrition outpatient clinic. Clin Nutr.
40:5030–5037. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Physical status: The use and
interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO expert committee.
World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 854:1–452. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Martin L, Senesse P, Gioulbasanis I,
Antoun S, Bozzetti F, Deans C, Strasser F, Thoresen L, Jagoe RT,
Chasen M, et al: Diagnostic criteria for the classification of
cancer-associated weight loss. J Clin Oncol. 33:90–99. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Song C, Cao J, Zhang F, Wang C, Guo Z, Lin
Y, Shi Y, Hu W, Ba Y, Xu H, et al: Nutritional risk assessment by
scored patient-generated subjective global assessment associated
with demographic characteristics in 23,904 common malignant tumors
patients. Nutr Cancer. 71:50–60. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Howard EE, Pasiakos SM, Blesso CN, Fussell
MA and Rodriguez NR: Divergent roles of inflammation in skeletal
muscle recovery from injury. Front Physiol. 11:872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Puppa MJ, White JP, Sato S, Cairns M,
Baynes JW and Carson JA: Gut barrier dysfunction in the ApcMin/+
mouse model of colon cancer cachexia. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1812:1601–1606. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rupert JE, Narasimhan A, Jengelley DHA,
Jiang Y, Liu J, Au E, Silverman LM, Sandusky G, Bonetto A, Cao S,
et al: Tumor-derived IL-6 and trans-signaling among tumor, fat, and
muscle mediate pancreatic cancer cachexia. J Exp Med.
218:e201904502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pototschnig I, Feiler U, Diwoky C, Vesely
PW, Rauchenwald T, Paar M, Bakiri L, Pajed L, Hofer P, Kashofer K,
et al: Interleukin-6 initiates muscle- and adipose tissue wasting
in a novel C57BL/6 model of cancer-associated cachexia. J Cachexia
Sarcopenia Muscle. 14:93–107. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bonetto A, Aydogdu T, Jin X, Zhang Z, Zhan
R, Puzis L, Koniaris LG and Zimmers TA: JAK/STAT3 pathway
inhibition blocks skeletal muscle wasting downstream of IL-6 and in
experimental cancer cachexia. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
303:E410–E421. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Haddad F, Zaldivar F, Cooper DM and Adams
GR: IL-6-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. J Appl Physiol (1985).
98:911–917. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun Q, van de Lisdonk D, Ferrer M,
Gegenhuber B, Wu M, Park Y, Tuveson DA, Tollkuhn J, Janowitz T and
Li B: Area postrema neurons mediate interleukin-6 function in
cancer cachexia. Nat Commun. 15:46822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schéle E, Benrick A, Grahnemo L, Egecioglu
E, Anesten F, Pálsdóttir V and Jansson JO: Inter-relation between
interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6 and body fat regulating circuits of the
hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. J Neuroendocrinol. 25:580–589. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Penafuerte CA, Gagnon B, Sirois J, Murphy
J, MacDonald N and Tremblay ML: Identification of
neutrophil-derived proteases and angiotensin II as biomarkers of
cancer cachexia. Br J Cancer. 114:680–687. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Trobec K, von Haehling S, Anker SD and
Lainscak M: Growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor 1, and
insulin signaling-a pharmacological target in body wasting and
cachexia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2:191–200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deng M, Aberle MR, van Bijnen AAJHM, van
der Kroft G, Lenaerts K, Neumann UP, Wiltberger G, Schaap FG, Olde
Damink SWM and Rensen SS: Lipocalin-2 and neutrophil activation in
pancreatic cancer cachexia. Front Immunol. 14:11594112023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Olson B, Zhu X, Norgard MA, Levasseur PR,
Butler JT, Buenafe A, Burfeind KG, Michaelis KA, Pelz KR, Mendez H,
et al: Lipocalin 2 mediates appetite suppression during pancreatic
cancer cachexia. Nat Commun. 12:20572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McLoughlin TJ, Tsivitse SK, Edwards JA,
Aiken BA and Pizza FX: Deferoxamine reduces and nitric oxide
synthase inhibition increases neutrophil-mediated myotube injury.
Cell Tissue Res. 313:313–319. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liang H, Peng H and Chen L: Prognostic
value of sarcopenia and systemic inflammation markers in patients
undergoing definitive radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Cancer
Manag Res. 13:181–192. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ruan HC, Wu XH, Huang DL, Fu XB, Zhang C,
Zhou K, Zhu GY, Liu D, Cai JT and Tan MH: The Role of the PNI and
NLR in nutritional risk screening and assessment of gastric cancer
patients. J Nutr Oncol. 7:192–198. 2022.
|
|
39
|
Lipshitz M, Visser J, Anderson R, Nel DG,
Smit T, Steel HC and Rapoport B: Emerging markers of cancer
cachexia and their relationship to sarcopenia. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 149:17511–17527. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Giese MA, Hind LE and Huttenlocher A:
Neutrophil plasticity in the tumor microenvironment. Blood.
133:2159–2167. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lipshitz M, Visser J, Anderson R, Nel DG,
Smit T, Steel HC and Rapoport BL: Relationships of emerging
biomarkers of cancer cachexia with quality of life, appetite, and
cachexia. Support Care Cancer. 32:3492024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lin J, Zhang W, Huang Y, Chen W, Wu R,
Chen X, Lou N and Wang P: Sarcopenia is associated with the
neutrophil/lymphocyte and platelet/lymphocyte ratios in operable
gastric cancer patients: A prospective study. Cancer Manag Res.
10:4935–4944. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang P, Chen X, Liu Q, Liu X and Li Y:
Good performance of the Global Leadership Initiative on
Malnutrition criteria for diagnosing and classifying malnutrition
in people with esophageal cancer undergoing esophagectomy.
Nutrition. 91-92:1114202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu N, Chen G, Hu H, Pang L and Chen Z: Low
pretherapeutic serum albumin as a risk factor for poor outcome in
esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Nutr Cancer. 67:481–485. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Onodera T, Goseki N and Kosaki G:
Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of
malnourished cancer patients. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi.
85:1001–1005. 1984.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ignacio de Ulíbarri J, González-Madroo A,
de Villar NG, González P, González B, Mancha A, Rodríguez F and
Fernández G: CONUT: A tool for controlling nutritional status.
First validation in a hospital population. Nutr Hosp. 20:38–45.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yoshida N, Harada K, Baba Y, Kosumi K,
Iwatsuki M, Kinoshita K, Nakamura K, Sakamoto Y, Miyamoto Y,
Karashima R, et al: Preoperative controlling nutritional status
(CONUT) is useful to estimate the prognosis after esophagectomy for
esophageal cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 402:333–341. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|