|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A,
Plymoth A and Roberts LR: A global view of hepatocellular
carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:589–604. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Llovet JM, Pinyol R, Kelley RK,
El-Khoueiry A, Reeves HL, Wang XW, Gores GJ and Villanueva A:
Molecular pathogenesis and systemic therapies for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Nat Cancer. 3:386–401. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang T, Dang N, Tang G, Li Z, Li X, Shi B,
Xu Z, Li L, Yang X, Xu C and Ye K: Integrating bulk and single-cell
RNA sequencing reveals cellular heterogeneity and immune
infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Oncol. 16:2195–2213.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang Q, Lou Y, Yang J, Wang J, Feng J,
Zhao Y, Wang L, Huang X, Fu Q, Ye M, et al: Integrated multiomic
analysis reveals comprehensive tumour heterogeneity and novel
immunophenotypic classification in hepatocellular carcinomas. Gut.
68:2019–2031. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ho DW, Tsui YM, Chan LK, Sze KM, Zhang X,
Cheu JW, Chiu YT, Lee JM, Chan AC, Cheung ET, et al: Single-cell
RNA sequencing shows the immunosuppressive landscape and tumor
heterogeneity of HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat
Commun. 12:36842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim E and Viatour P: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Old friends and new tricks. Exp Mol Med. 52:1898–1907.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Orea-Soufi A, Paik J, Bragança J, Donlon
TA, Willcox BJ and Link W: FOXO transcription factors as
therapeutic targets in human diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
43:1070–1084. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calissi G, Lam EWF and Link W: Therapeutic
strategies targeting FOXO transcription factors. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 20:21–38. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Galili N, Davis RJ, Fredericks WJ,
Mukhopadhyay S, Rauscher FJ, Emanuel BS, Rovera G and Barr FG:
Fusion of a fork head domain gene to PAX3 in the solid tumour
alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat Genet. 5:230–235. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Davis RJ, D'Cruz CM, Lovell MA, Biegel JA
and Barr FG: Fusion of PAX7 to FKHR by the variant t(1;13)(p36;q14)
translocation in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res.
54:2869–2872. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dansen TB and Burgering BMT: Unravelling
the tumor-suppressive functions of FOXO proteins. Trends Cell Biol.
18:421–429. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Link W and Fernandez-Marcos PJ: FOXO
transcription factors at the interface of metabolism and cancer.
Int J Cancer. 141:2379–2391. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Paik JH, Kollipara R, Chu G, Ji H, Xiao Y,
Ding Z, Miao L, Tothova Z, Horner JW, Carrasco DR, et al: FoxOs are
lineage-restricted redundant tumor suppressors and regulate
endothelial cell homeostasis. Cell. 128:309–323. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu T, Chung YM, Guan M, Ma M, Ma J, Berek
JS and Hu MCT: Reprogramming ovarian and breast cancer cells into
non-cancerous cells by low-dose metformin or SN-38 through FOXO3
activation. Sci Rep. 4:58102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang C, Chen W, Zhi X, Ma T, Xia X, Liu
H, Zhang Q, Hu Q, Zhang Y, Bai X and Liang T: Serotonin promotes
the proliferation of serum-deprived hepatocellular carcinoma cells
via upregulation of FOXO3a. Mol Cancer. 12:142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yao J, Wang J, Xu Y, Guo Q, Sun Y, Liu J,
Li S, Guo Y and Wei L: CDK9 inhibition blocks the initiation of
PINK1-PRKN-mediated mitophagy by regulating the SIRT1-FOXO3-BNIP3
axis and enhances the therapeutic effects involving mitochondrial
dysfunction in hepatocellular carcinoma. Autophagy. 18:1879–1897.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang LJ, Tang Q, Wu J, Chen Y, Zheng F,
Dai Z and Hann SS: Inter-regulation of IGFBP1 and FOXO3a unveils
novel mechanism in ursolic acid-inhibited growth of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin Z, Niu Y, Wan A, Chen D, Liang H, Chen
X, Sun L, Zhan S, Chen L, Cheng C, et al: RNA m6A methylation
regulates sorafenib resistance in liver cancer through
FOXO3-mediated autophagy. EMBO J. 39:e1031812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Colaprico A, Silva TC, Olsen C, Garofano
L, Cava C, Garolini D, Sabedot TS, Malta TM, Pagnotta SM,
Castiglioni I, et al: TCGAbiolinks: An R/bioconductor package for
integrative analysis of TCGA data. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:e712016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Friedman J, Hastie T and Tibshirani R:
Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate
descent. J Stat Softw. 33:1–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi Y, Wang Y, Dong H, Niu K, Zhang W,
Feng K, Yang R and Zhang Y: Crosstalk of ferroptosis regulators and
tumor immunity in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Novel perspective to
mRNA vaccines and personalized immunotherapy. Apoptosis.
28:1423–1435. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang G, Su L, Lv X and Yang Q: A novel
tumor doubling time-related immune gene signature for prognosis
prediction in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int.
21:5222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N,
Lisacek F, Sanchez JC and Muller M: pROC: An open-source package
for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics.
12:772011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ito K and Murphy D: Application of ggplot2
to pharmacometric graphics. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol.
2:e792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Abe S, Kawa K, Nozawa H, Hata K, Kiyomatsu
T, Tanaka T, Nishikawa T, Otani K, Sasaki K, Kaneko M, et al: Use
of a nomogram to predict the closure rate of diverting ileostomy
after low anterior resection: A retrospective cohort study. Int J
Surg. 47:83–88. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak K and Schimittgen T: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitive PCR and
the 2 (-delata delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Z, Zeng X, Wu Y, Liu Y, Zhang X and
Song Z: Cuproptosis-related risk score predicts prognosis and
characterizes the tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Front Immunol. 13:9256182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tang Y, Xu L, Ren Y, Li Y, Yuan F, Cao M,
Zhang Y, Deng M and Yao Z: Identification and validation of a
prognostic model based on three MVI-related genes in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. 18:261–275. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tian Z, Song J, She J, He W, Guo S and
Dong B: Constructing a disulfidptosis-related prognostic signature
of hepatocellular carcinoma based on single-cell sequencing and
weighted co-expression network analysis. Apoptosis. 29:1632–1647.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pu Q, Yu L, Liu X, Yan H, Xie Y, Cai X, Wu
Y, Du J and Yang Z: Prognostic value of CD8+T cells related genes
and exhaustion regulation of Notch signaling pathway in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Immunol. 15:13758642024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peng L, Xu S and Xu JL: Integration of
single-cell RNA sequencing and bulk RNA sequencing to identify an
immunogenic cell death-related 5-gene prognostic signature in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J hepatocell Carcinoma. 11:879–900. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moeini A, Cornellà H and Villanueva A:
Emerging signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver
Cancer. 1:83–93. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang G, Wang Q, Liang N, Xue H, Yang T,
Chen X, Qiu Z, Zeng C, Sun T, Yuan W, et al: Oncogenic driver genes
and tumor microenvironment determine the type of liver cancer. Cell
Death Dis. 11:3132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Uhlen M, Fagerberg L, Hallstrom B,
Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson A, Kampf C,
Sjostedt E, Asplund A, et al: Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the
human proteome. Science. 23:3472015.
|
|
37
|
Cheng K, Cai N, Zhu J, Yang X, Liang H and
Zhang W: Tumor-associated macrophages in liver cancer: From
mechanisms to therapy. Cancer Commun (Lond). 42:1112–1140. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Di Z, Zhou S, Xu G, Ren L, Li C, Ding Z,
Huang K, Liang L and Yuan Y: Single-cell and WGCNA uncover a
prognostic model and potential oncogenes in colorectal cancer. Biol
Proced Online. 24:132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lu J, Chen Y, Zhang X, Guo J, Xu K and Li
L: A novel prognostic model based on single-cell RNA sequencing
data for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 22:382022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao Z, He S, Yu X, Lai X, Tang S, Mariya
MEA, Wang M, Yan H, Huang X, Zeng S and Zha D: Analysis and
experimental validation of rheumatoid arthritis innate immunity
gene CYFIP2 and pan-cancer. Front Immunol. 13:9548482022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tang B, Zhu J, Zhao Z, Lu C, Liu S, Fang
S, Zheng L, Zhang N, Chen M, Xu M, et al: Diagnosis and prognosis
models for hepatocellular carcinoma patient's management based on
tumor mutation burden. J Adv Res. 33:153–165. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
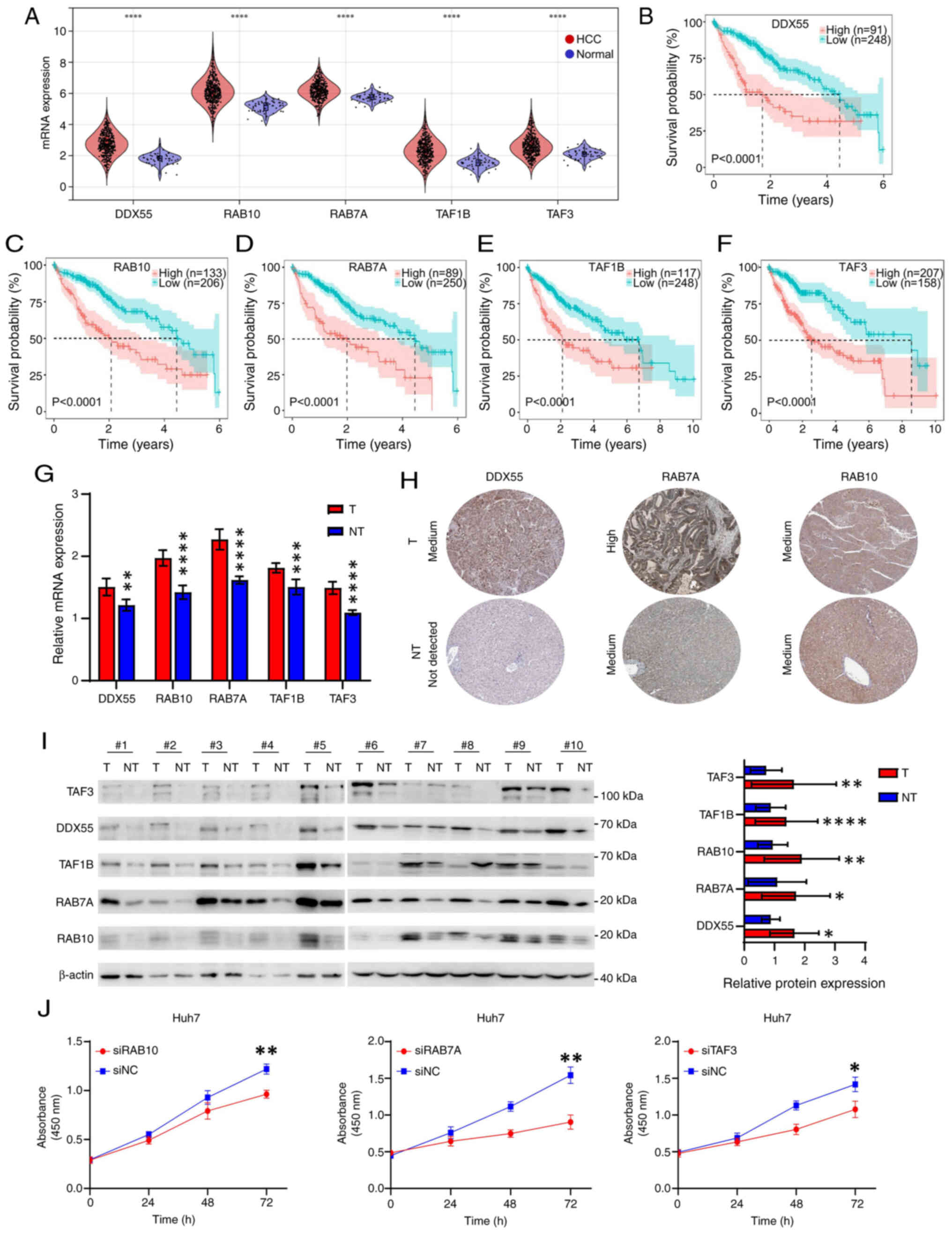
Wang W, Jia WD, Hu B and Pan YY: RAB10
overexpression promotes tumor growth and indicates poor prognosis
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:26434–26447. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lv Z, Ma G, Zhong Z, Xie X, Li B and Long
D: O-GlcNAcylation of RAB10 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. Carcinogenesis. 44:785–794. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu Y, Ma J, Wang X, Liu P, Cai C, Han Y,
Zeng S, Feng Z and Shen H: Lipophagy-related gene RAB7A is involved
in immune regulation and malignant progression in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Comput Biol Med. 158:1068622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu Z, Scannell DR, Eisen MB and Tjian R:
Control of embryonic stem cell lineage commitment by core promoter
factor, TAF3. Cell. 146:720–731. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu B, Zhou S, Long D, Ning Y, Yao H, Zhou
E and Wang Y: DDX55 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression
by interacting with BRD4 and participating in exosome-mediated
cell-cell communication. Cancer Sci. 113:3002–3017. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen HF, Gao DD, Jiang XQ, Sheng H, Wu Q,
Zheng Q, Zhai QC, Yuan L, Liu M, Xu LF, et al: TAF1B depletion
leads to apoptotic cell death by inducing nucleolar stress and
activating p53-miR-101 circuit in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front
Oncol. 13:12037752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|