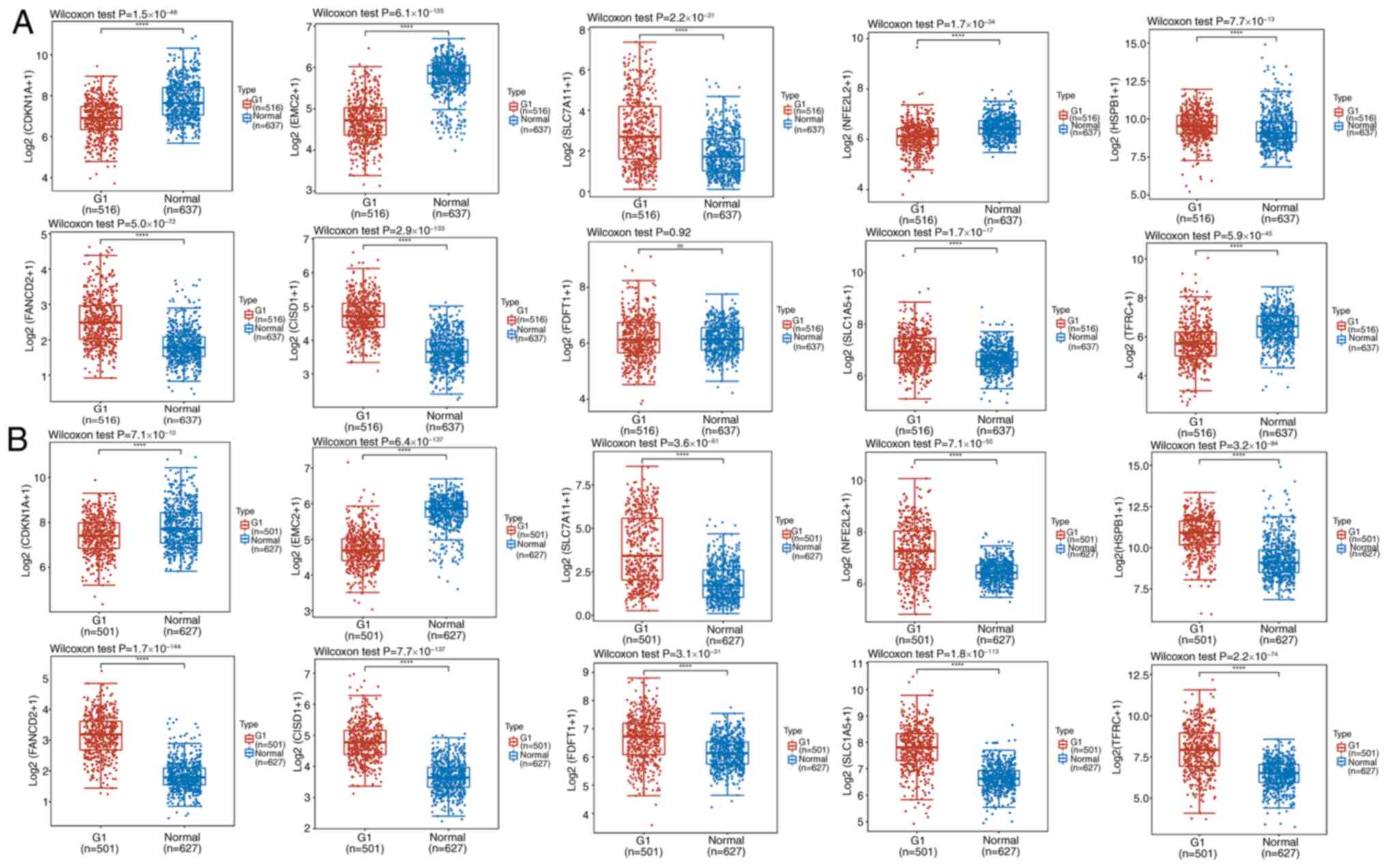
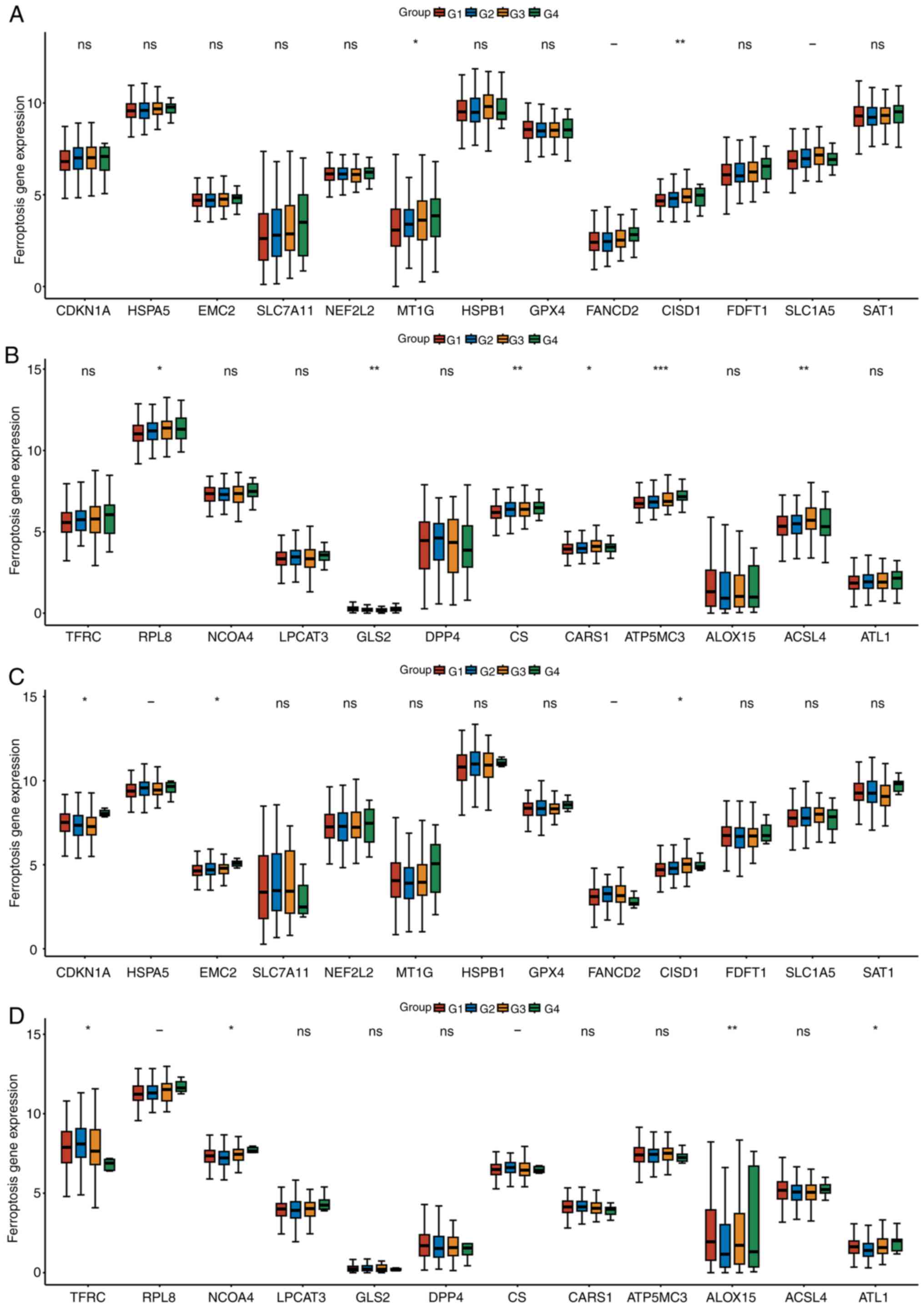
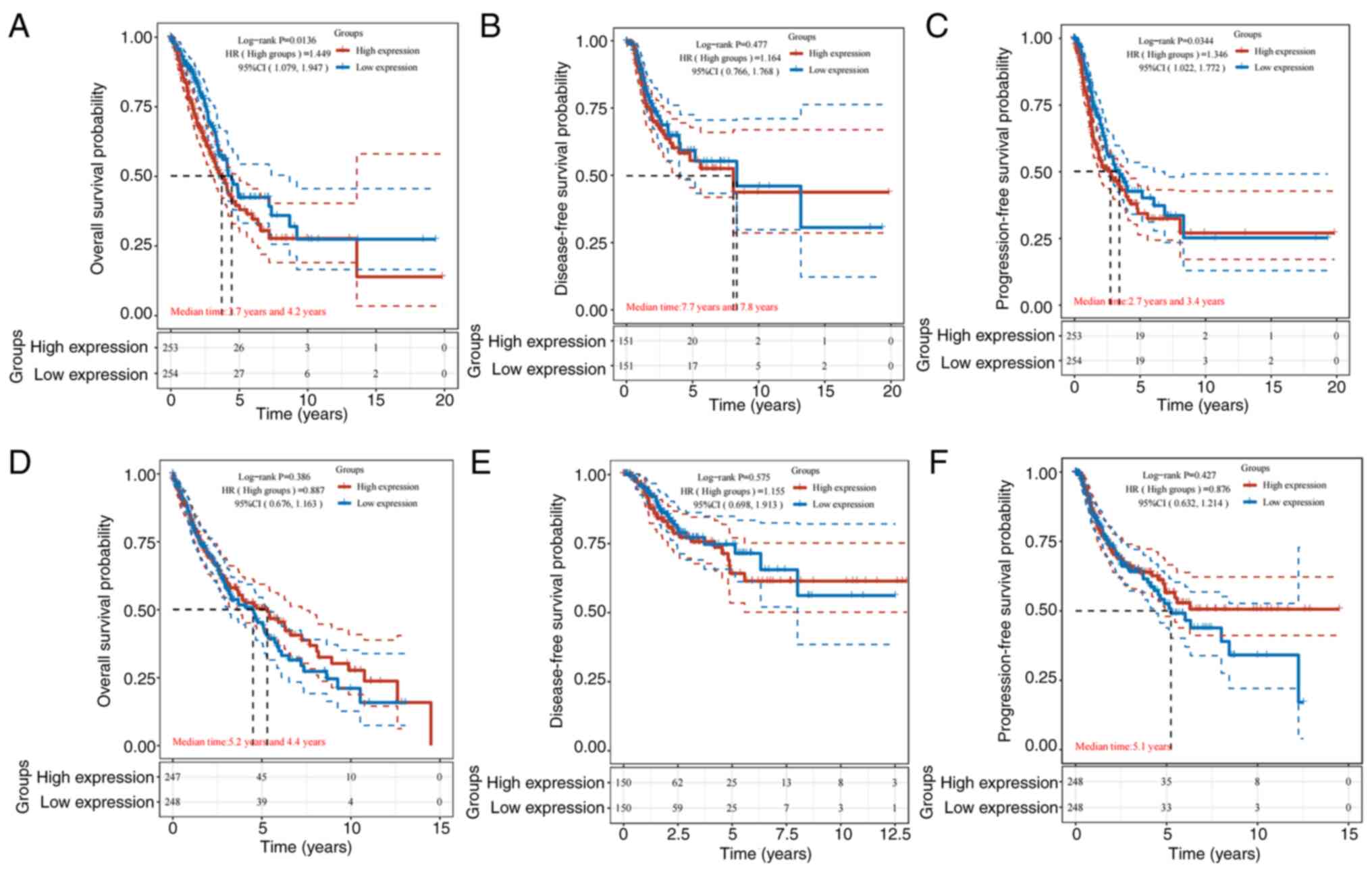
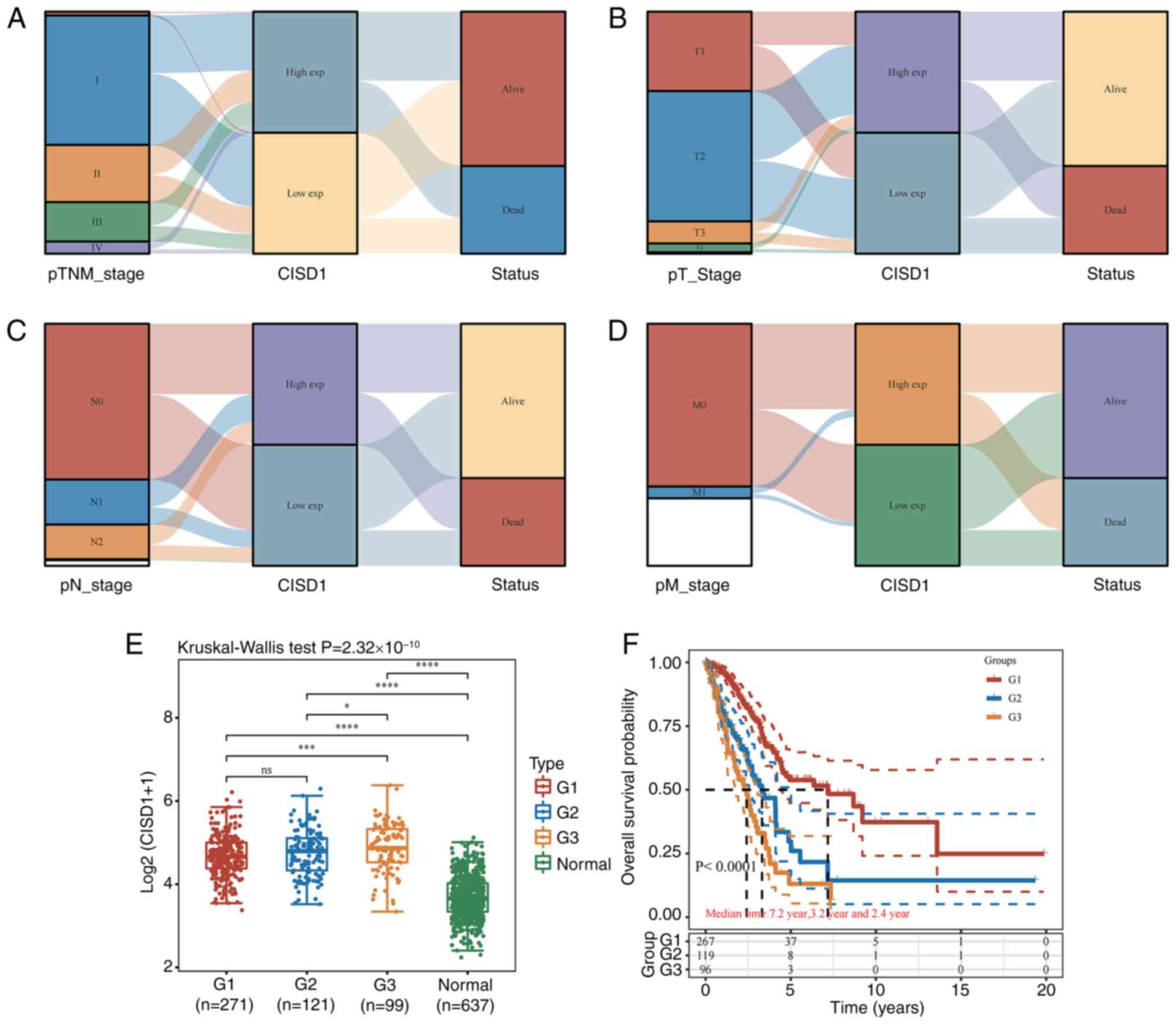
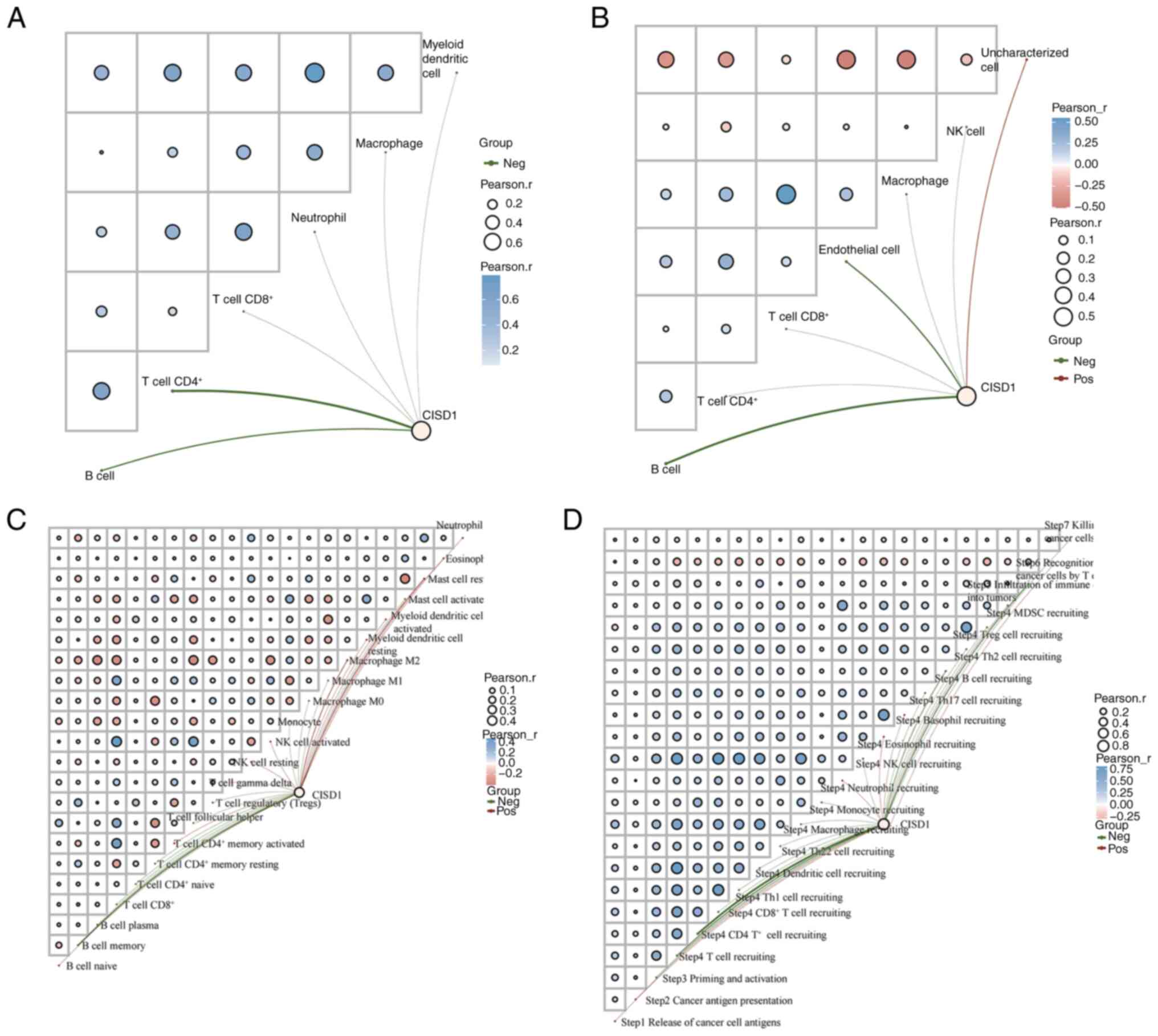
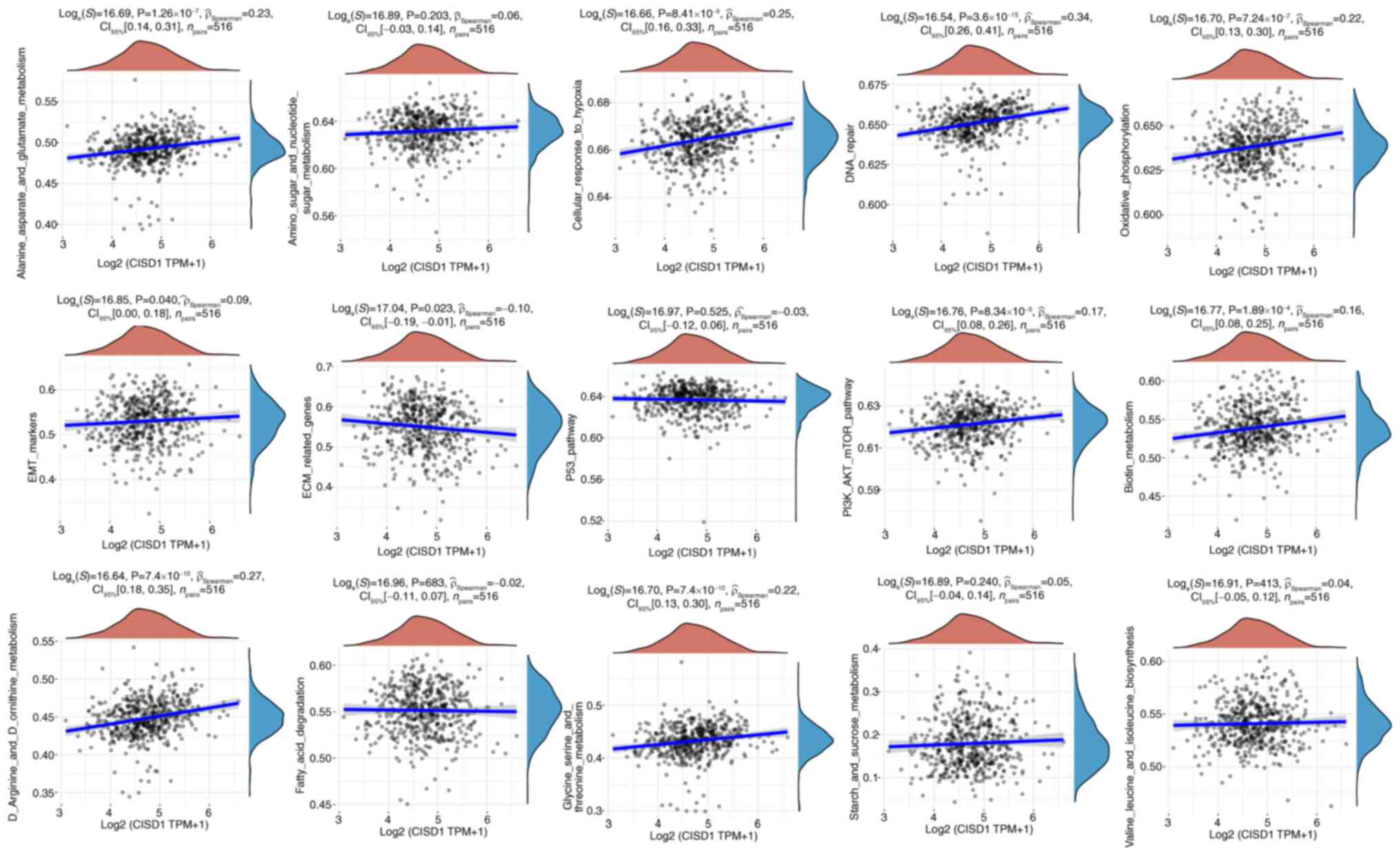
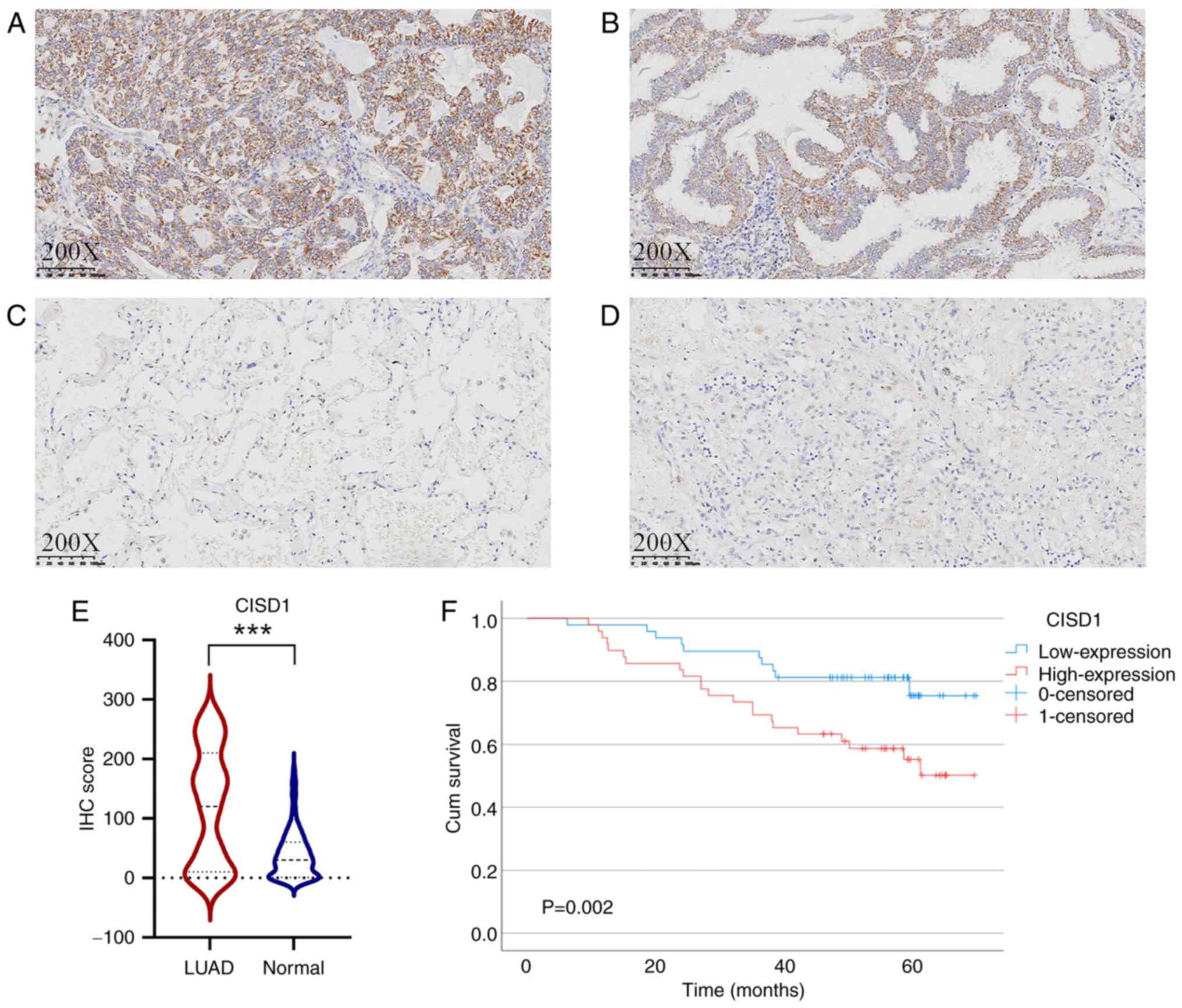
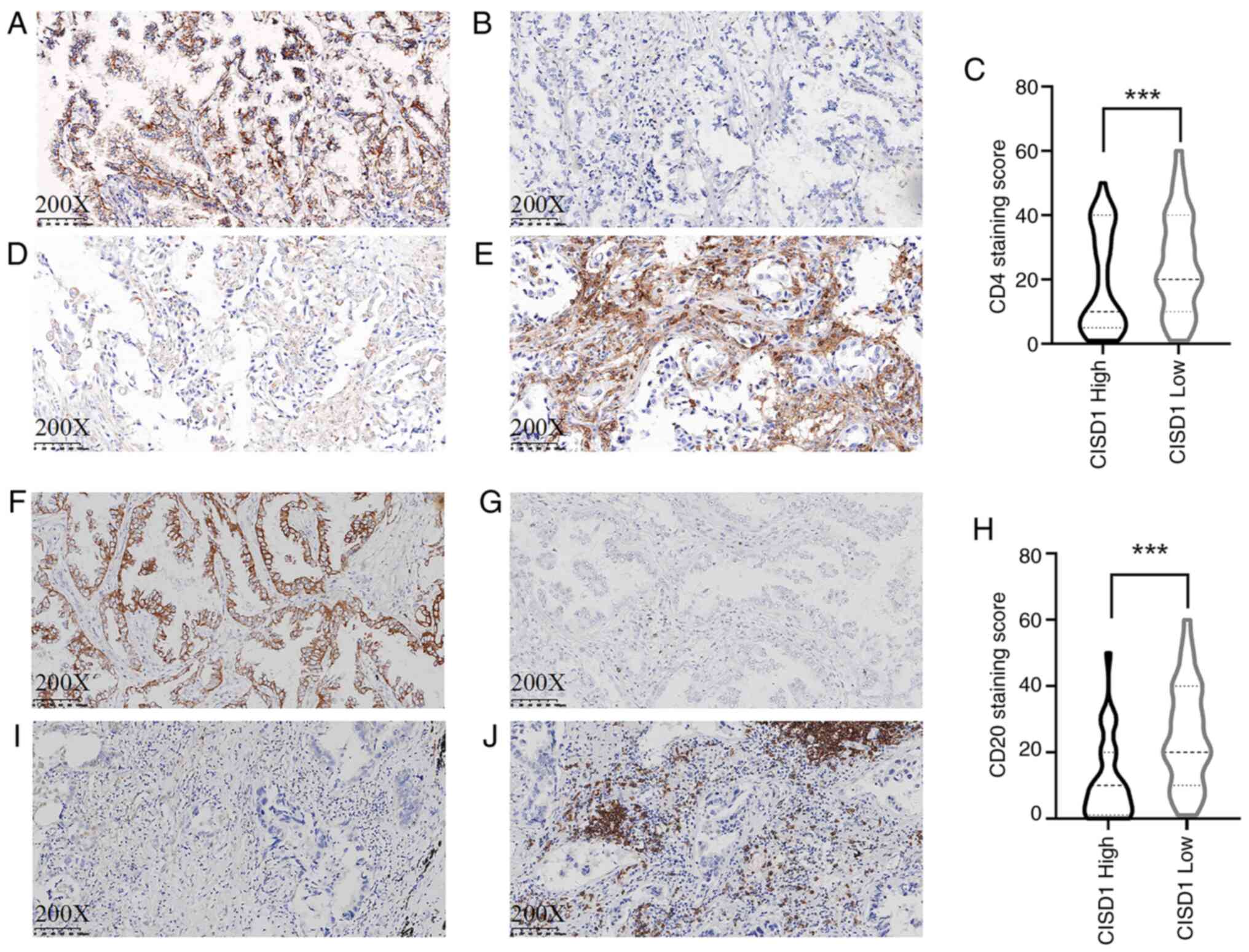
|
1
|
Han B, Zheng R, Zeng H, Wang S, Sun K,
Chen R, Li L, Wei W and He J: Cancer incidence and mortality in
China, 2022. J Natl Cancer Cent. 4:47–53. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li C, Lei S, Ding L, Xu Y, Wu X, Wang H,
Zhang Z, Gao T, Zhang Y and Li L: Global burden and trends of lung
cancer incidence and mortality. Chin Med J (Engl). 136:1583–1590.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley
W, Bauman J, Chirieac LR, D'Amico TA, DeCamp MM, Dilling TJ,
Dobelbower M, et al: Non-small cell lung cancer, version 5.2017,
NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 15:504–535. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lim ZF and Ma PC: Emerging insights of
tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance mechanisms in lung cancer
targeted therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 12:1342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Iron death: An iron dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park E and Chung SW: Ros-mediated
autophagy increases intracellular iron levels and ferropositis by
ferritin and transferrin receptor regulation. Cell death Dis.
10:8222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Conche C, Finkelmeier F, PEšIć M, Nicolas
AM, Böttger TW, Kennel KB, Denk D, Ceteci F, Mohs K, Engel E, et
al: Combining osteoporosis induction with MDSC blockade renders
primary tumours and metals in liver sensitive to immune checkpoint
blockade. Gut. 7:1774–1782. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang F, Xiao Y, Ding JH, Jin X, Ma D, Li
DQ, Shi JX, Huang W, Wang YP, Jiang YZ and Shao ZM: Ferroptosis
heterogeneity in triple-negative breast cancer reveals an
innovative immunotherapy combination strategy. Cell Metab.
35:84–100.e8. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Q, Deng T, Zhang H, Zuo D, Zhu Q,
Bai M, Liu R, Ning T, Zhang L, Yu Z, et al: Adipocyte-derived
exosomal MTTP suppresses ferrooposis and promotes chemoresistance
in colorectal cancer. Adv SCI (Weinh). 9:e22033572022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang J, Wang L, Pang Z, Ge Q, Wu Y and Qi
X: Integrated analysis of ferroptosis and immunity-related genes
associated with diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes.
16:3773–3793. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hsieh SS, Cook DA, Inoue A, Gong H, Sudhir
Pillai P, Johnson MP, Leng S, Yu L, Fidler JL, Holmes DR III, et
al: Understanding reader variability: A 25-radiologist study on
liver metastasis detection at CT. Radiology. 306:e2202662023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Messori A: Synthetizing published evidence
on survival by reconstruction of patient-level data and generation
of a multi-trial kaplan-meier curve. Cureus.
13:e194222021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cao L, Liu M, Ma X, Rong P, Zhang J and
Wang W: Comprehensive scRNA-seq analysis and identification of
CD8_+T cell related gene markers for predicting prognosis and drug
resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Med Chem.
31:2414–2430. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kalemkerian GP, Narula N, Kennedy EB,
Biermann WA, Donington J, Leighl NB, Lew M, Pantelas J, Ramalingam
SS, Reck M, et al: Molecular testing guideline for the selection of
lung cancer patients for treatment with targeted thyroid kinase
inhibitors: American society of clinical oncology endowment summary
of the college of American physicians/international association for
the study of lung cancer/association for molecular pathology
clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 36:911–919. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fukui T, Taniguchi T, Kawaguchi K,
Fukumoto K, Nakamura S, Sakao Y and Yokoi K: Comparisons of the
clinicopathological features and survival outcomes between lung
cancer patients with adenocarcinoma and rectangular cell carcinoma.
Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 63:507–513. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang BY, Huang JY, Chen HC, Lin CH, Lin
SH, Hung WH and Cheng YF: The comparison between adenocarcinoma and
rectangular cell carcinoma in lung cancer patients. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 146:43–52. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wiley SE, Murphy AN, Ross SA, van der Geer
P and Dixon JE: Mitoneet is an iron containing outer mitochondrial
membrane protein that regulates oxidative capacity. Proc Natl Acad
SCI USA. 104:5318–5323. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Inupakutika MA, Sengupta S, Nechushtai R,
Jennings PA, Onuchic JN, Azad RK, Padilla P and Mittler R:
Phylogenetic analysis of eucaryotic neet proteins uncovers a link
between a key gene duplication event and the evolution of
vertebrates. Sci Rep. 7:425712017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kunk C, Kruger J, Mendoza G, Markitan J,
Bias T, Mann A, Nath A, Geldenhuys WJ, Menze MA and Konkle ME:
Mitoneet's reactivity of lys55 toward pyrooxidative phosphate
demonstrations its activity as a transaminase enzyme. ACS Chem
Biol. 1:2716–2722. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Colca JR, McDonald WG, Waldon DJ, Leone
JW, Lull JM, Bannow CA, Lund ET and Mathews WR: Identification of a
novel mitochondrial protein (‘mitoNEET’) cross linked specifically
by a thiazolidinedione photoprobe. Am J Physical Endocrinol Metab.
286:e252–e260. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu F, Dong Y, Zhong F, Guo H and Dong P:
CISD1 is a breast cancer diagnostic biomarker associated with
diabetes mellitus. Biomolecules. 13:372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liang Y, Ye F, Xu C, Zou L, Hu Y, Hu J and
Jiang H: A novel survival model based on a paradox related gene
signature for predicting overall survival in bladder cancer. BMC
Cancer. 2:9432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang J, Wei X, Hu F, Dong W and Sun L:
Development and validation of a novel 3-gene diagnostic model for
pancreatic adenocarcinoma based on ferrosis related genes. Cancer
Cell Int. 22:212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang H, Jia Y, Gu J, Chen O and Yue S:
Iron death-related genes are involved in ashma and regulate the
immune microenvironment. Front Pharmacol. 14:10875572023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu MN, Zhou DM, Jiang CY, Chen WW, Chen
JC, Zou YM, Han T and Zhou LJ: Genetic analysis of potential
biomarkers and therapeutic targets in ferroptosis from psoriasis.
Front Immunol. 13:11044622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao J, Dong M, Tian W, Xia J, Qian Y,
Jiang Z, Chen Z and Shen Y: The role of CISD1 reduction in
macrophages in promoting COPD development through M1 polarization
and mitochondrial dysfunction. Eur J Med Res. 29:5412024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu ZH, Tang Y, Yu H and Li HD: The role of
ferroptosis in breast cancer patients: A comprehensive analysis.
Cell Death Discov. 7:932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lu T, Li C, Xiang C, Gong Y, Peng W and
Chen C: Overexpression of CISD1 predicts worse survival in
hepatocarcinoma patients. Biomed Res Int. 2022:78231912022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zang J, Cui M, Xiao L, Zhang J and Jing R:
Overexpression of ferroptosis-related genes FSP1 and CISD1 is
related to prognosis and tumor immune infiltration in gastric
cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 25:2532–2544. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lei G, Zhuang L and Gan B: Targeting
ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
22:381–396. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Igarashi K, Shoji Y, Sekine Suzuki E, Ueno
M, Matsumoto KI, Nakanishi I and Fukui K: Importance of locations
of iron ions to elicit cytotoxicity induced by a fenton type
reaction. Cancers (Basel). 14:36422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Searle AJ and Wilson RL: Stimulation of
microscopic lipid peroxidation by iron and cysteine
characterization and the role of free radios. Biochem J.
21:549–554. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ploumi C, Kyriakakis E and Tavernarakis N:
Coupling of autophagy and the mitochondrial intrinsic apoptosis
pathway modulates proteostasis and ageing in Caenorhabditis
elegans. Cell Death Dis. 14:1102023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hsiung KC, Tang HY, Cheng ML, Hung LM,
Chin-Ming Tan B and Lo SJ: Mitochondrial bioenergetics deficiency
in CISD-1 mutants is linked to AMPK-mediated lipid metabolism.
Biomed J. 7:1008062024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Furihata T, Takada S, Kakutani N, Maekawa
S, Tsuda M, Matsumoto J, Mizushima W, Fukushima A, Yokota T, Enzan
N, et al: Cardiac-specific loss of mitoNEET expression is linked
with age-related heart failure. Commun Biol. 4:1382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Martinez A, Sanchez-Martinez A, Pickering
JT, Twyning MJ, Terriente-Felix A, Chen PL, Chen CH and Whitworth
AJ: Mitochondrial CISD1/CISD accumulation blocks mitophagy and
genetic or pharmacological inhibition rescues neurodegenerative
phenotypes in Pink1/parkin models. Mol Neurodegener. 19:122024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ham SJ, Yoo H, Woo D, Lee DH, Park KS and
Chung J: PINK1 and Parkin regulate IP3R-mediated ER calcium
release. Nat Commun. 14:52022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang ZB, Xiong LL, Xue LL, Deng YP, Du
RL, Hu Q, Xu Y, Yang SJ and Wang TH: MiR-127-3p targeting CISD1
regulates autophagy in hypoxic-ischemic cortex. Cell Death Dis.
12:2792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tang CF, Ding H, Wu YQ, Miao ZA, Wang ZX,
Wang WX, Pan Y and Kong LD: Gastrodin attenuates high
fructose-induced sweet taste preference decrease by inhibiting
hippocampal neural stem cell ferroptosis. J Adv Res. Sep
29–2024.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang X, Peng T, Li C, Ai C, Wang X, Lei
X, Li G and Li T: Inhibition of CISD1 alleviates mitochondrial
dysfunction and ferroptosis in mice with acute lung injury. Int
Immunopharmacol. 130:1116852024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang C, Yang Y, Hu X, Tang Q, Zhang J,
Zhang P, Lu X, Xu J, Li S, Dong Z, et al: Loss of GCN5L1
exacerbates damage in alcoholic liver disease through ferroptosis
activation. Liver Int. 44:1924–1936. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dong W, Jiang Y, Yao Q, Xu M, Jin Y, Dong
L, Li Z and Yu D: Inhibition of CISD1 attenuates cisplatin-induced
hearing loss in mice via the PI3K and MAPK pathways. Biochem
Pharmacol. 223:1161322024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Geldenhuys WJ, Piktel D, Moore JC, Rellick
SL, Meadows E, Pinti MV, Hollander JM, Ammer AG, Martin KH and
Gibson LF: Loss of the redox mitochondrial protein mitoNEET leads
to mitochondrial dysfunction in B-cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Free Radic Biol Med. 175:226–235. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Efimova I, Catanzaro E, Van der Meeren L,
Turubanova VD, Hammad H, Mishchenko TA, Vedunova MV, Fimognari C,
Bachert C, Coppieters F, et al: Vaccination with early atrophic
cancer cells induce effective antitumor immunity. J Immunother
Cancer. 8:e0013692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|