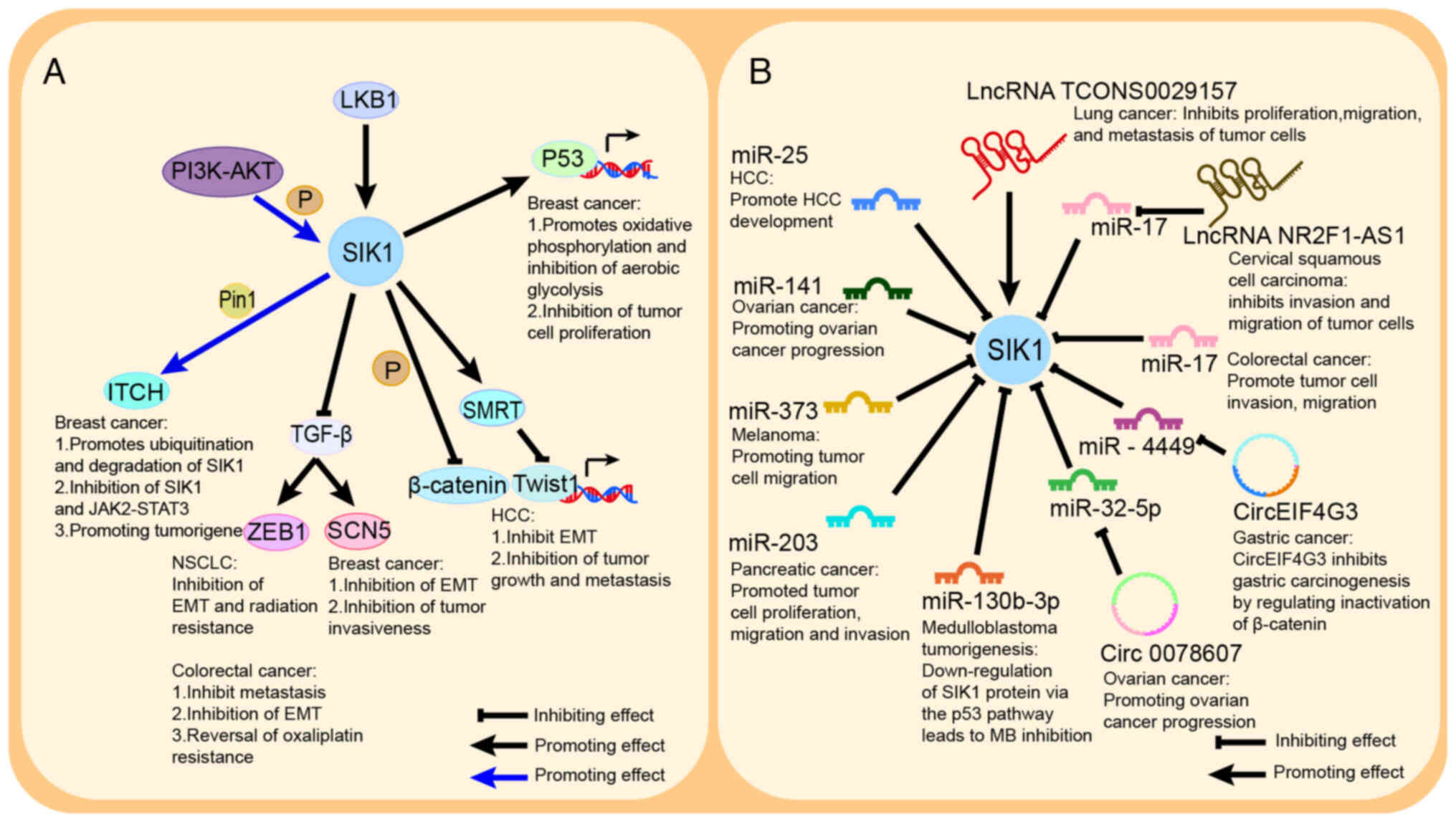
|
1
|
Hollstein PE, Eichner LJ, Brun SN,
Kamireddy A, Svensson RU, Vera LI, Ross DS, Rymoff TJ, Hutchins A,
Galvez HM, et al: The AMPK-related kinases SIK1 and SIK3 mediate
key tumor-suppressive effects of LKB1 in NSCLC. Cancer Discov.
9:1606–1627. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bright NJ, Thornton C and Carling D: The
regulation and function of mammalian AMPK-related kinases. Acta
Physiol (Oxf). 196:15–26. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun Z, Jiang Q, Li J and Guo J: The potent
roles of Salt-inducible kinases (SIKs) in metabolic homeostasis and
tumorigenesis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:1502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wein MN, Foretz M, Fisher DE, Xavier RJ
and Kronenberg HM: Salt-inducible kinases: Physiology, regulation
by cAMP, and therapeutic potential. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
29:723–735. 2028. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Z, Takemori H, Halder SK, Nonaka Y
and Okamoto M: Cloning of a novel kinase (SIK) of the SNF1/AMPK
family from high salt diet-treated rat adrenal. FEBS Lett.
453:135–139. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Okamoto M, Takemori H and Katoh Y:
Salt-inducible kinase in steroidogenesis and adipogenesis. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 15:21–26. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Feldman JD, Vician L, Crispino M, Hoe W,
Baudry M and Herschman HR: The salt-inducible kinase, SIK, is
induced by depolarization in brain. J Neurochem. 74:2227–2238.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Horike N, Takemori H, Katoh Y, Doi J, Min
L, Asano T, Sun XJ, Yamamoto H, Kasayama S, Muraoka M, et al:
Adipose-specific expression, phosphorylation of Ser794 in insulin
receptor substrate-1, and activation in diabetic animals of
salt-inducible kinase-2. J Biol Chem. 278:18440–18447. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen F, Chen L, Qin Q and Sun X:
Salt-Inducible Kinase 2: An oncogenic signal transmitter and
potential target for cancer therapy. Front Oncol. 9:182019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song D, Yin L, Wang C and Wen X:
Adenovirus-mediated expression of SIK1 improves hepatic glucose and
lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. PLoS One.
14:e02109302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang C, Song D, Fu J and Wen X: SIK1
Regulates CRTC2-Mediated gluconeogenesis signaling pathway in human
and mouse liver cells. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 11:5802020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao WW, Tang HV, Cheng Y, Chan CP, Chan CP
and Jin DY: Suppression of gluconeogenic gene transcription by
SIK1-induced ubiquitination and degradation of CRTC1. Biochim
Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 1861:211–223. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song D, Yin L, Wang C and Wen X: Zhenqing
recipe attenuates Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating
the SIK1/CRTC2 signaling in experimental diabetic rats. BMC
Complement Med Ther. 20:272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Takemori H, Wang C, Fu J, Xu M,
Xiong L, Li N and Wen X: Role of salt inducible kinase 1 in high
glucose-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells and metformin
intervention. Life Sci. 173:107–115. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng H, Liu P, Wang ZC, Zou L, Santiago
S, Garbitt V, Gjoerup OV, Iglehart JD, Miron A, Richardson AL, et
al: SIK1 couples LKB1 to p53-dependent anoikis and suppresses
metastasis. Sci Signal. 2:ra352009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park M, Miyoshi C, Fujiyama T, Kakizaki M,
Ikkyu A, Honda T, Choi J, Asano F, Mizuno S, Takahashi S, et al:
Loss of the conserved PKA sites of SIK1 and SIK2 increases sleep
need. Sci Rep. 10:86762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Darling NJ and Cohen P: Nuts and bolts of
the salt-inducible kinases (SIKs). Biochem J. 478:1377–1397. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pires NM, Igreja B and Soares-da-Silva P:
Antagonistic modulation of SIK1 and SIK2 isoforms in high blood
pressure and cardiac hypertrophy triggered by high-salt intake.
Clin Exp Hypertens. 43:428–435. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jaitovich A and Bertorello AM:
Intracellular sodium sensing: SIK1 network, hormone action and high
blood pressure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1802:1140–1149. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hansen J, Snow C, Tuttle E, Ghoneim DH,
Yang CS, Spencer A, Gunter SA, Smyser CD, Gurnett CA, Shinawi M, et
al: De novo mutations in SIK1 cause a spectrum of developmental
epilepsies. Am J Hum Genet. 96:682–690. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pröschel C, Hansen JN, Ali A, Tuttle E,
Lacagnina M, Buscaglia G, Halterman MW and Paciorkowski AR:
Epilepsy-causing sequence variations in SIK1 disrupt synaptic
activity response gene expression and affect neuronal morphology.
Eur J Hum Genet. 25:216–221. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peng L, Li C, Tang X, Xiang Y, Xu Y, Cao
W, Zhou H and Li S: Blocking salt-inducible kinases with YKL-06-061
prevents PTZ-induced seizures in mice. Brain Behav. 13:e33052023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Babbe H, Sundberg TB, Tichenor M,
Seierstad M, Bacani G, Berstler J, Chai W, Chang L, Chung M, Coe K,
et al: Identification of highly selective SIK1/2 inhibitors that
modulate innate immune activation and suppress intestinal
inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 121:e23070861202024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ponnusamy L and Manoharan R: Distinctive
role of SIK1 and SIK3 isoforms in aerobic glycolysis and cell
growth of breast cancer through the regulation of p53 and mTOR
signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1868:1189752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qu C, He D, Lu X, Dong L, Zhu Y, Zhao Q,
Jiang X, Chang P, Jiang X, Wang L, et al: Salt-inducible Kinase
(SIK1) regulates HCC progression and WNT/β-catenin activation. J
Hepatol. 64:1076–1089. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xin L, Liu C, Liu Y, Mansel RE, Ruge F,
Davies E, Jiang WG and Martin TA: SIKs suppress tumor function and
regulate drug resistance in breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res.
11:3537–3557. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang C, Liu J, Xu L, Hu W, Wang J, Wang M
and Yao X: MicroRNA-17 promotes cell proliferation and migration in
human colorectal cancer by downregulating SIK1. Cancer Manag Res.
11:3521–3534. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ren ZG, Dong SX, Han P and Qi J: miR-203
promotes proliferation, migration and invasion by degrading SIK1 in
pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:1365–1374. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zang X, Jiang J, Gu J, Chen Y, Wang M,
Zhang Y, Fu M, Shi H, Cai H, Qian H, et al: Circular RNA EIF4G3
suppresses gastric cancer progression through inhi bition of
β-catenin by promoting δ-catenin ubiquitin degradation and u
pregulating SIK1. Mol Cancer. 21:1412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang S, Xue P, Han X, Zhang C, Yang L,
Liu L, Wang X, Li H, Fu J and Zhou Y: Exosomal miR-130b-3p targets
SIK1 to inhibit medulloblastoma tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis.
11:4082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hartono AB, Kang HJ, Shi L, Phipps W,
Ungerleider N, Giardina A, Chen W, Spraggon L, Somwar R, Moroz K,
et al: Salt-inducible Kinase 1 is a potential therapeutic target in
desmoplastic small round cell tumor. Oncogenesis. 11:182022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Katoh Y, Takemori H, Horike N, Doi J,
Muraoka M, Min L and Okamoto M: Salt-inducible kinase (SIK)
isoforms: Their involvement in steroidogenesis and adipogenesis.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 217:109–112. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lizcano JM, Göransson O, Toth R, Deak M,
Morrice NA, Boudeau J, Hawley SA, Udd L, Mäkelä TP, Hardie DG and
Alessi DR: LKB1 is a master kinase that activates 13 kinases of the
AMPK subfamily, including MARK/PAR-1. EMBO J. 23:833–843. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sakamoto K, Bultot L and Göransson O: The
Salt-inducible kinases: Emerging metabolic regulators. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 29:827–840. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Taub M, Springate JE and Cutuli F:
Targeting of renal proximal tubule Na,K-ATPase by Salt-inducible
kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 393:339–344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Feng S, Wei F, Shi H, Chen S, Wang B,
Huang D and Luo L: Roles of Salt-inducible kinases in cancer
(Review). Int J Oncol. 63:1182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Katoh Y, Takemori H, Lin XZ, Tamura M,
Muraoka M, Satoh T, Tsuchiya Y, Min L, Doi J, Miyauchi A, et al:
Silencing the constitutive active transcription factor CREB by the
LKB1-SIK signaling cascade. FEBS J. 273:2730–2748. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Clark K, MacKenzie KF, Petkevicius K,
Kristariyanto Y, Zhang J, Choi HG, Peggie M, Plater L, Pedrioli PG,
McIver E, et al: Phosphorylation of CRTC3 by the salt-inducible
kinases controls the interconversion of classically activated and
regulatory macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:16986–16991.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hashimoto YK, Satoh T, Okamoto M and
Takemori H: Importance of autophosphorylation at Ser186 in the
A-loop of salt inducible kinase 1 for its sustained kinase
activity. J Cell Biochem. 104:1724–1739. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bertorello AM and Zhu JK: SIK1/SOS2
networks: Decoding sodium signals via calcium-responsive protein
kinase pathways. Pflugers Arch. 458:613–619. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jaleel M, Villa F, Deak M, Toth R,
Prescott AR, Van Aalten DM and Alessi DR: The Ubiquitin-associated
domain of AMPK-related kinases regulates conformation and
LKB1-mediated phosphorylation and activation. Biochem J.
394:545–555. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jaleel M, McBride A, Lizcano JM, Deak M,
Toth R, Morrice NA and Alessi DR: Identification of the sucrose
non-fermenting related kinase SNRK, as a novel LKB1 substrate. FEBS
Lett. 579:1417–1423. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Al-Hakim AK, Göransson O, Deak M, Toth R,
Campbell DG, Morrice NA, Prescott AR and Alessi DR: 14-3-3
cooperates with LKB1 to regulate the activity and localization of
QSK and SIK. J Cell Sci. 118:5661–5673. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Berggreen C, Henriksson E, Jones HA,
Morrice N and Göransson O: cAMP-elevation mediated by β-adrenergic
stimulation inhibits salt-inducible kinase (SIK) 3 activity in
adipocytes. Cell Signal. 24:1863–1871. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Matsumoto S, Iwakawa R, Takahashi K, Kohno
T, Nakanishi Y, Matsuno Y, Suzuki K, Nakamoto M, Shimizu E, Minna
JD and Yokota J: Prevalence and specificity of LKB1 genetic
alterations in lung cancers. Oncogene. 26:5911–5918. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shackelford DB: Unravelling the connection
between metabolism and tumorigenesis through studies of the liver
kinase B1 tumour suppressor. J Carcinog. 12:162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Eneling K, Brion L, Pinto V, Pinho MJ,
Sznajder JI, Mochizuki N, Emoto K, Soares-da-Silva P and Bertorello
AM: Salt-inducible kinase 1 regulates E-cadherin expression and
intercellular junction stability. FASEB J. 26:3230–3239. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Grahame Hardie D: AMP-activated protein
kinase: A key regulator of energy balance with many roles in human
disease. J Intern Med. 276:543–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Taub M: Salt inducible kinase signaling
networks: Implications for acute kidney injury and therapeutic
potential. Int J Mol Sci. 20:32192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yang Z, Wang C, Xue Y, Liu X, Chen S, Song
C, Yang Y and Guo Y: Calcium-activated 14-3-3 proteins as a
molecular switch in salt stress tolerance. Nat Commun. 10:11992019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sonntag T, Vaughan JM and Montminy M:
14-3-3 proteins mediate inhibitory effects of cAMP on
salt-inducible kinases (SIKs). FEBS J. 285:467–480. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Thommesen L, Nørsett K, Sandvik AK, Hofsli
E and Laegreid A: Regulation of inducible cAMP early repressor
expression by gastrin and cholecystokinin in the pancreatic cell
line AR42J. J Biol Chem. 275:4244–4250. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Thommesen L, Hofsli E, Paulssen RH,
Anthonsen MW and Laegreid A: Molecular mechanisms involved in
gastrin-mediated regulation of cAMP-responsive promoter elements.
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 281:E1316–E1325. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Berdeaux R, Goebel N, Banaszynski L,
Takemori H, Wandless T, Shelton GD and Montminy M: SIK1 is a class
II HDAC kinase that promotes survival of skeletal myocytes. Nat
Med. 13:597–603. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Selvik LK, Rao S, Steigedal TS, Haltbakk
I, Misund K, Bruland T, Prestvik WS, Lægreid A and Thommesen L:
Salt-inducible kinase 1 (SIK1) is induced by gastrin and inhibits
migration of gastric adenocarcinoma cells. PLoS One. 9:e1124852014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
van der Linden AM, Nolan KM and Sengupta
P: KIN-29 SIK regulates chemoreceptor gene expression via an MEF2
transcription factor and a class II HDAC. EMBO J. 26:358–370. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chan JK, Sun L, Yang XJ, Zhu G and Wu Z:
Functional characterization of an amino-terminal region of HDAC4
that possesses MEF2 binding and transcriptional repressive
activity. J Biol Chem. 278:23515–23521. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Haberland M, Montgomery RL and Olson EN:
The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and
physiology: Implications for disease and therapy. Nat Rev Genet.
10:32–42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Longin S, Jordens J, Martens E, Stevens I,
Janssens V, Rondelez E, De Baere I, Derua R, Waelkens E, Goris J,
et al: An inactive protein phosphatase 2A population is associated
with methylesterase and can be re-activated by the phosphotyrosyl
phosphatase activator. Biochem J. 380:111–119. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Pagel P, Zatti A, Kimura T, Duffield A,
Chauvet V, Rajendran V and Caplan MJ: Ion pump-interacting
proteins: Promising new partners. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 986:360–368.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sjöström M, Stenström K, Eneling K,
Zwiller J, Katz AI, Takemori H and Bertorello AM: SIK1 is part of a
cell sodium-sensing network that regulates active sodium transport
through a calcium-dependent process. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:16922–16927. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang Y, Gao W, Yang K, Tao H and Yang H:
Salt-Inducible Kinase 1 (SIK1) is induced by alcohol and suppresses
microglia inflammation via NF-κB signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem.
47:1411–1421. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Norman P: The use of salt-inducible kinase
inhibitors to treat autoimmune and inflammatory diseases:
Evaluation of WO2013136070. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 24:943–946. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sundberg TB, Liang Y, Wu H, Choi HG, Kim
ND, Sim T, Johannessen L, Petrone A, Khor B, Graham DB, et al:
Development of chemical probes for investigation of Salt-inducible
kinase function in vivo. ACS Chem Biol. 11:2105–2111. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
McIver Edward G, Bryans Justin S,
Smiljanic ELA, Lewis Stephen J, Hough J and Drake T: Pyrimidine
derivatives capable of inhibiting one or more kinases. 2009.
|
|
66
|
Raposo TP, Beirão BC, Pang LY, Queiroga FL
and Argyle DJ: Inflammation and cancer: Till death tears them
apart. Vet J. 205:161–174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chai EZ, Siveen KS, Shanmugam MK, Arfuso F
and Sethi G: Analysis of the intricate relationship between chronic
inflammation and cancer. Biochem J. 468:1–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Hu J, Qiao J, Yu Q, Liu B, Zhen J, Liu Y,
Ma Q, Li Y, Wang Q, Wang C, et al: Role of SIK1 in the transition
of acute kidney injury into chronic kidney disease. J Transl Med.
19:692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Meng J, Li N, Liu X, Qiao S, Zhou Q, Tan
J, Zhang T, Dong Z, Qi X, Kijlstra A, et al: NLRP3 attenuates
intraocular inflammation by inhibiting AIM2-mediated pyroptosis
through the phosphorylated salt-inducible kinase 1/Sterol
regulatory element binding transcription factor 1 pathway.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 75:842–855. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pirie E, Cauntay P, Fu W, Ray S, Pan C,
Lusis AJ, Hsiao J, Burel SA, Narayanan P, Crooke RM, et al: Hybrid
mouse diversity panel identifies genetic architecture associated
with the acute antisense oligonucleotide-mediated inflammatory
response to a 2'-O-Methoxyethyl antisense oligonucleotide. Nucleic
Acid Ther. 29:266–277. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lombardi MS, Gilliéron C, Dietrich D and
Gabay C: SIK inhibition in human myeloid cells modulates TLR and
IL-1R signaling and induces an anti-inflammatory phenotype. J
Leukoc Biol. 99:711–721. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Cai X, Wang L, Yi Y, Deng D, Shi M, Tang
M, Li N, Wei H, Zhang R, Su K, et al: Discovery of
pyrimidine-5-carboxamide derivatives as novel salt-inducible
kinases (SIKs) inhibitors for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
treatment. Eur J Med Chem. 256:1154692023
|
|
73
|
Qu C and Qu Y: Down-regulation of
salt-inducible kinase 1 (SIK1) is mediated by RNF2 in
hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 8:3144–3155. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Murray CW, Brady JJ, Tsai MK, Li C,
Winters IP, Tang R, Andrejka L, Ma RK, Kunder CA, Chu P and Winslow
MM: An LKB1-SIK axis suppresses lung tumor growth and controls
differentiation. Cancer Discov. 9:1590–1605. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Cheng D, Wang J, Wang Y, Xue Y, Yang Q,
Yang Q, Zhao H, Huang J and Peng X: Chemokines: Function and
therapeutic potential in bone metastasis of lung cancer. Cytokine.
172:1564032023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Fu X, Tang Y, Wu W, Ouyang Y, Tan D and
Huang Y: Exosomal microRNA-25 released from cancer cells targets
SIK1 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis. Dig Liver
Dis. 54:954–963. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Gao Y, Li H, Wang P, Wang J and Yao X:
SIK1 suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis and chemoresistance
via the TGF-β signaling pathway. J Cancer. 14:2455–2467. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Jin Y and Wang H: Circ_0078607 inhibits
the progression of ovarian cancer via regulating the miR-32-5p/SIK1
network. J Ovarian Res. 15:32022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Kou B, Wang XD, Sun XP, Qi Q, Yang M, Yun
YN, Zhou JS and Liu W: LKB1 inhibits proliferation, metastasis and
angiogenesis of thyroid cancer by upregulating SIK1. J Cancer.
13:2872–2883. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Li B, Chen Y, Wang F, Guo J, Fu W, Li M,
Zheng Q, Liu Y, Fan L, Li L and Xu C: Bmi1 drives
hepatocarcinogenesis by repressing the TGFβ2/SMAD signalling axis.
Oncogene. 39:1063–1079. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
De Faveri LE, Hurst CD, Roulson JA, Wood
H, Sanchez-Carbayo M, Knowles MA and Chapman EJ: Polycomb repressor
Complex 1 member, BMI1 contributes to urothelial tumorigenesis
through p16-independent mechanisms. Transl Oncol. 8:387–399. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang Q, Wu Y, Lin M, Wang G, Liu J, Xie M,
Zheng B, Shen C and Shen J: BMI1 promotes osteosarcoma
proliferation and metastasis by repressing the transcription of
SIK1. Cancer Cell Int. 22:1362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Nguyen K, Hebert K, McConnell E, Cullen N,
Cheng T, Awoyode S, Martin E, Chen W, Wu T, Alahari SK, et al: LKB1
signaling and patient survival outcomes in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Pharmacol Res. 192:1067572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Yao YH, Cui Y, Qiu XN, Zhang LZ, Zhang W,
Li H and Yu JM: Attenuated LKB1-SIK1 signaling promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and radioresistance of non-small
cell lung cancer cells. Chin J Cancer. 35:502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Seoane J and Gomis RR: TGF-β Family
signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 9:a0222772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Kowanetz M, Lönn P, Vanlandewijck M,
Kowanetz K, Heldin CH and Moustakas A: TGFbeta induces SIK to
negatively regulate type I receptor kinase signaling. J Cell Biol.
182:655–662. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ang HL, Mohan CD, Shanmugam MK, Leong HC,
Makvandi P, Rangappa KS, Bishayee A, Kumar AP and Sethi G:
Mechanism of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer and its
regulation by natural compounds. Med Res Rev. 43:1141–1200. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Saitoh M: Transcriptional regulation of
EMT transcription factors in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 97:21–29.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Gradek F, Lopez-Charcas O, Chadet S,
Poisson L, Ouldamer L, Goupille C, Jourdan ML, Chevalier S,
Moussata D, Besson P, et al: Sodium Channel Na(v)1.5 controls
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and invasiveness in breast
cancer cells through its regulation by the salt-inducible Kinase-1.
Sci Rep. 9:186522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Lönn P, Vanlandewijck M, Raja E, Kowanetz
M, Watanabe Y, Kowanetz K, Vasilaki E, Heldin CH and Moustakas A:
Transcriptional induction of salt-inducible kinase 1 by
transforming growth factor β leads to negative regulation of type I
receptor signaling in cooperation with the Smurf2 ubiquitin ligase.
J Biol Chem. 287:12867–12878. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sánchez-Tilló E, Liu Y, de Barrios O,
Siles L, Fanlo L, Cuatrecasas M, Darling DS, Dean DC, Castells A
and Postigo A: EMT-activating transcription factors in cancer:
Beyond EMT and tumor invasiveness. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:3429–3456.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Nelson M, Yang M, Millican-Slater R and
Brackenbury WJ: Nav1.5 regulates breast tumor growth and metastatic
dissemination in vivo. Oncotarget. 6:32914–32929. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Yang M, Kozminski DJ, Wold LA, Modak R,
Calhoun JD, Isom LL and Brackenbury WJ: Therapeutic potential for
phenytoin: Targeting Na(v)1.5 sodium channels to reduce migration
and invasion in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
134:603–615. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Zhu QQ, Ma C, Wang Q, Song Y and Lv T: The
role of TWIST1 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancers.
Tumour Biol. 37:185–197. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Sun Z, Jiang Q, Gao B, Zhang X, Bu L, Wang
L, Lin Y, Xie W, Li J and Guo J: AKT blocks SIK1-mediated
repression of STAT3 to promote breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Res.
83:1264–1279. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Chen JL, Chen F, Zhang TT and Liu NF:
Suppression of SIK1 by miR-141 in human ovarian cancer cell lines
and tissues. Int J Mol Med. 37:1601–1610. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Bai X, Yang M and Xu Y: MicroRNA-373
promotes cell migration via targeting salt-inducible kinase 1
expression in melanoma. Exp Ther Med. 16:4759–4764. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Peng J, Hou F, Zhu W, Li J and Teng Z:
lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 regulates miR-17/SIK1 axis to suppress the
invasion and migration of cervical squamous cell carcinoma cells.
Reprod Sci. 27:1534–1539. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Bawa P, Zackaria S, Verma M, Gupta S,
Srivatsan R, Chaudhary B and Srinivasan S: Integrative analysis of
normal long intergenic non-coding RNAs in prostate cancer. PLoS
One. 10:e01221432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Bon H, Wadhwa K, Schreiner A, Osborne M,
Carroll T, Ramos-Montoya A, Ross-Adams H, Visser M, Hoffmann R,
Ahmed AA, et al: Salt-inducible kinase 2 regulates mitotic
progression and transcription in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res.
13:620–635. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Gao T, Zhang X, Zhao J, Zhou F, Wang Y,
Zhao Z, Xing J, Chen B, Li J and Liu S: SIK2 promotes reprogramming
of glucose metabolism through PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α pathway and
Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission in ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett.
469:89–101. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zhou J, Alfraidi A, Zhang S,
Santiago-O'Farrill JM, Yerramreddy Reddy VK, Alsaadi A, Ahmed AA,
Yang H, Liu J, Mao W, et al: A novel compound ARN-3236 inhibits
Salt-inducible kinase 2 and sensitizes ovarian cancer cell lines
and xenografts to paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res. 23:1945–1954. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Du WQ, Zheng JN and Pei DS: The diverse
oncogenic and tumor suppressor roles of salt-inducible kinase (SIK)
in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 20:477–485. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Charoenfuprasert S, Yang YY, Lee YC, Chao
KC, Chu PY, Lai CR, Hsu KF, Chang KC, Chen YC, Chen LT, et al:
Identification of salt-inducible kinase 3 as a novel tumor antigen
associated with tumorigenesis of ovarian cancer. Oncogene.
30:3570–3584. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Zhou X, Xu B, Gu Y, Ji N, Meng P and Dong
L: Long noncoding RNA SNHG1 protects brain microvascular
endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose
deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury by sponging miR-298 and
upregulating SIK1 expression. Biotechnol Lett. 43:1163–1174. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|