Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause
of cancer-related deaths, and its incidence (~9.39%) and mortality
rates (~10.01%) in China have also been increasing (1,2). Most
patients with CRC are already in the middle or late stage when
diagnosed (3). The commonly used
treatment methods for CRC include surgery, chemotherapy and
targeted therapy (4). Chemotherapy
is the main treatment method, and the commonly used chemotherapy
drugs in clinical practice include oxaliplatin (OXA),
5-fluorouracil (5-FU), capecitabine and calcium folinate (5). Although most patients can experience
favorable therapeutic effects through chemotherapy drugs, some
patients succumb because of the development of drug resistance and
ineffective chemotherapy within a few cycles (6,7).
Targeted therapy works by blocking specific molecules involved in
the growth and spread of cancer cells (8). The main types of targeted drugs are
monoclonal antibodies and small molecule inhibitors, which target
molecules involved in tumorigenesis and their related signaling
pathways in cancer cells, inhibiting cancer development (9). In addition, a recently added treatment
method in the CRC treatment regimen is immune checkpoint
inhibitors. In the treatment of metastatic CRC, this treatment
approach has exhibited promising clinical responses in patients
with high microsatellite instability in mismatch repair genes
(10).
Tumor drug-resistance mostly occurs after receiving
initial chemotherapy. The MDR1 gene encodes the multidrug
resistance-associated protein ABCB1, also known as P-gp, which is a
member of the ABC binding cassette transporter superfamily and
plays an important role in tumor resistance (11,12).
OXA is a third-generation platinum-based antitumor drug, and its
antitumor mechanism involves entering tumor cells, where it causes
cell cycle arrest and induces cell apoptosis (13). P-gp can pump antitumor drugs that
enter the cell out of the cell, thereby playing an important role
in the formation of chemotherapy resistance (14).
Methyltransferase 3 (METTL3) is a key N6
methyladenosine (m6A) methyltransferase that plays a major
catalytic role in m6A modification (15). It plays an important role in
regulating biological processes such as cell cycle, proliferation,
apoptosis, differentiation, invasion and migration, and
inflammatory response (16). METTL3
also has an antagonistic effect on 5-FU, leading to the development
of drug resistance (15). This is
consistent with our previous experimental results. METTL3
expression is increased in patients resistant to OXA chemotherapy.
Concurrently, it was found that Huaier can inhibit the expression
of METTL3. Therefore, it was decided to focus on METTL3 to explore
the mechanism by which Huaier affects chemotherapy resistance in
CRC.
Although there has been significant progress in the
diagnosis and treatment of CRC, issues such as postoperative
sequelae, chemotherapy resistance, toxic side effects, high rate of
metastasis, and recurrence rates have critically affected the
quality of life of patients (17,18).
An increasing number of studies have revealed that traditional
Chinese medicine has favorable therapeutic effects in treating
cancer. Traditional Chinese medicine can exert anti-CRC effects on
multiple targets and pathways, while improving the toxic side
effects caused by surgical chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted
therapy and immunotherapy, and prolonging the survival time of
patients (19). Previously,
research has found that Huaier has anticancer effects on various
types of tumors (20–23). Huaier is a fungus that grows on
various trees such as Huai Shu and Qing Tan. It contains various
organic components and minerals, and has a history of over 1,600
years as a traditional Chinese medicine (24). The main component of Huaier is
polysaccharide protein, which achieves antitumor effects by
affecting tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, drug sensitivity,
autophagy and other aspects (25–29).
It has been revealed that Huaier can inhibit the proliferation of
CRC tumor stem cells by downregulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway (30). However, it is
currently unclear whether Huaier can regulate the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway to reduce P-gp expression and thereby decrease
resistance to OXA-based chemotherapy regimens in CRC through
METTL3.
In the present study, the mechanism by which Huaier
regulates drug resistance in CRC was further investigated. It was
demonstrated that Huaier inhibited the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway by downregulating the expression of METTL3, thereby
increasing the sensitivity of CRC to OXA. This provides a
theoretical basis for the treatment of resistance to chemotherapy
in CRC by utilizing the traditional Chinese medicine Huaier.
Materials and methods
Public data
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) queue data were
accessed in the UCSC Xena database (https://xenabrowser.net/datapages/). The GSE28702 and
GSE17536 datasets were downloaded from the GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). The GSE28702
dataset contains tumor-tissue RNA expression profile data from 42
patients with CRC who responded to the FOLFOX chemotherapy regimen
and 41 patients with CRC who did not respond to this regimen. The
GSE17536 dataset contains complete survival information for 177
patients with CRC.
Chemicals
Huaier was purchased from Qidong Gaitianli
Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Huaier particles (2 grams) were dissolved
in 20 ml of PRMI-1640 medium (Procell Life Science & Technology
Co., Ltd.), filtered with a 0.22-µm filter (MilliporeSigma) to
obtain 100 mg/ml of the original solution, and then stored at
−40°C. OXA was purchased from MedChemExpress. Wnt agonist 1 (AMBMP)
was purchased from Selleck Chemicals. AMBMP is a cell permeable Wnt
signaling pathway activator that induces transcriptional activity
dependent on β-catenin and TCF. It stabilizes the intracellular
β-catenin by disrupting the Axin/β-catenin interaction, thereby
activating the Wnt signaling pathway.
Cell lines and cell culture
NCM460 cells (cat. no. JNO-H0138) were purchased
from Guangzhou Jennio Biotech Co., Ltd. HCT-8 cells (cat. no.
PC193) were purchased from Procell Life Science & Technology
Co., Ltd. The resistant cells of HCT-8/L-OHP (HCT-8/L) were
manufactured by Shanghai Aolu Biotechnology. Both cell lines were
cultured in PRMI-1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum
(Procell Life Science & Technology Co., Ltd.) and placed at
37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator.
Cell transfection
Targeted METTL3 [small interfering (si)-METTL3#1 and
si-METTL3#2] and negative control siRNA oligonucleotides (si-NC)
were designed and synthesized by Guangzhou RiboBio Co., Ltd. The
sequences were as follows: si-NC, 5′-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGU-3′;
si-METTL3#1, 5′-CAAGUAUGUUCACUAUGAA-3′; and si-METTL3#2,
5′-GACUGCUCUUUCCUUAAUA-3′. Overexpression of METTL3 was
accomplished using the expression plasmid PCMV3 synthesized by
SinoBiological, with empty vector as negative control. HCT-8/L
cells were inoculated into 6-well plates. After the cells adhered
to the wall, they were transfected with si-NC, si-METTL3#1,
si-METTL3#2, pC-NC, or pC-METTL3 (2.5 µg per well) using Lipofiter
3.0 (HanBio Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) transfection reagent at 37°C,
following the manufacturer's protocol. After 48 h, reverse
transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and western blotting were
used to detect the knockdown and overexpression efficiency.
Cell viability assay [Cell counting
kit-8 (CCK-8) assay]
Cell viability was detected using CCK-8 (APeXBIO
Technology LLC). In a 96-well plate, ~3,000 cells were inoculated
into each well. After overnight cultivation at 37°C and 5%
CO2, the cells were treated with different
concentrations (0, 5, 10, 20, 30 and 40 µmol/l) of OXA for 24 and
48 h. Then, a mixed solution of CCK-8 (10 µl CCK-8 and 100 µl
PRMI-1640 medium per well) was added and incubated in a dark
incubator for 2 h at 37°C and 5% CO2. Finally, the
absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader. In
addition, HCT-8/L cells were treated with Huaier at the following
concentrations: 0, 6, 9, 12, 15 and 18 (mg/ml). All measurements
were repeated three times. Cell viability was calculated as
follows: [As Ab)/(Ac Ab)] ×100%, where As is the absorbance of the
experimental group; Ac is the absorbance of the control group; and
Ab represents the absorbance of the blank group.
Immunofluorescence
Cells (~50–60% confluency) were cultivated in a
24-well plate at 37°C and 5% CO2. Each well contained
sterile treated cover slips, allowing the cells to adhere to the
cover slips overnight. The cells on the cover glass were washed for
three times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Then, they were
fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature for 15 min and
washed again with PBS. After penetrating with 0.1% TritonX-100
(Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd.) on ice for 15
min, the cells were blocked at room temperature for 2 h with 75%
bovine serum albumin (BSA; Beijing Solarbio Science &
Technology Co., Ltd.), and then incubated with anti-β-catenin
antibodies (1:2,000; cat. no. 8814s; Cell Signaling Technology,
Inc.) at 4°C overnight. Finally, after washing three times with
PBS, the goat anti-rabbit IgG labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 (1:100;
cat. no. AS053; ABclonal Biotech Co., Ltd.) was incubated at room
temperature for 1 h. After 15 min of DAPI (2 µg/ml) staining at
room temperature, the slides were placed under a fluorescence
microscope (Olympus Corporation) for observation.
Western blotting
Total cell proteins were extracted using RIPA cell
lysate (Report Biotech; http://www.ruipate.com/) containing 1%
phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (Report Biotech) and placed on ice
for 15 min. The BCA protein concentration assay kit (Shandong
Sparkjade Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd.) was used to determine
protein concentration, and the proteins were separated by 12%
SDS-PAGE electrophoresis with a sample size of 30 µg per well.
After SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, the protein sample was transferred
to a PVDF membrane (MilliporeSigma) under constant pressure of 100
V. A total of 5% BSA was used to block the membrane at room
temperature for 2 h. Then, an appropriate mass of primary
antibodies against METTL3 (1:2,000; cat. no. A19079; ABclonal
Biotech Co., Ltd.), P-gp (1:1,000; cat. no. 13342S; Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc.), Wnt 3a (1:2,000; cat. no. bs-1700R; BIOSS),
β-catenin (1:1,000; cat. no. 8814S; Cell Signaling Technology,
Inc.), Bax (1:2,000; cat. no. A0207; ABclonal Biotech Co., Ltd.),
Bcl-2 (1:2,000; cat. no. A0208; ABclonal Biotech Co., Ltd.),
Caspase3 (1;2,000; cat. no. 19677-1-AP; Proteintech Group, Inc.),
β-catenin (1:100,000; cat. no. AC026; ABclonal Biotech Co., Ltd.)
and Histone H3 (1:2,000; cat. no. AF0863; Affinity Biosciences) was
added and incubated at 4°C overnight. Then, the HRP-conjugated goat
anti-rabbit IgG (H + L) secondary antibody (1:10,000; cat. no.
AS014; ABclonal Biotech Co., Ltd.) was incubated for 1 h at room
temperature. Finally, the target protein was exposed and developed
using an enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) reagent (Biosharp Life
Sciences) in a 1:1 ratio of solution A and solution B.
Densitometric analysis was performed using Image Lab software
(version 5.2.1; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.).
RT-qPCR
Total RNA was extracted from the cells using TRIzol
reagent (Biosharp Life Sciences), and cDNA was synthesized using
SPARKscript II ALL-in-one RT SuperMix for qPCR (Shandong Sparkjade
Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd.) according to the manufacturer's
protocol. mRNA expression levels were detected using SYBR Green
qPCR Mix (Shandong Sparkjade Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd.). The
qPCR cycling conditions were as follows: Denaturation at 94°C for 2
min, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 10 sec,
primer annealing and extension at 60°C for 30 sec. Each experiment
was repeated at least three times, and the experimental data were
analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCq method (31). The specific primer sequences were as
follows: METTL3 forward, 5′-GTGATCGTAGCTGAGGTTCGT-3′ and reverse,
5′-GGGTTGCACATTGTGTGGTC-3′; P-gp forward,
5′-TCTATGGTTGGCAACTAACACT-3′ and reverse,
5′-CTCCTGAGTCAAAGAAACAACG-3′; β-catenin forward,
5′-ATGGCTTGGAATGAGACTGCT-3′ and reverse,
5′-GGGTCCATACCCAAGGCATC-3′; and GAPDH forward,
5′-GCACCGTCAAGGCTGAGAAC-3′ and reverse,
5′-TGGTGAAGACGCCAGTGGA-3′.
Flow cytometry
Detection of cell apoptosis was accomplished through
flow cytometry. The cells (~90% confluency) were digested with
trypsin, collected in centrifuge tubes, and washed twice with PBS.
After centrifugation at 1,000 × g for 5 min at room temperature,
the supernatant was discarded completely and staining was performed
with the Annexin V-FITC/PI dual staining apoptosis detection kit
(APeXBIO Technology LLC), avoiding light at room temperature until
5 min. Subsequently, apoptosis was analyzed using BD FACSCalibur
flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and modify software (BD
Biosciences).
Nuclear cytoplasmic separation
Cytoplasmic proteins and nuclear proteins were
separated using a nuclear protein and cytoplasmic protein
preparation kit (Applygen Technologies, Inc.). After removing the
cells from the incubator, they were washed 2–3 times with PBS and
CEB-A reagent was added for scraping; the cells were transferred to
a precooled centrifuge tube with a pipette, shook, and resuspended,
and centrifuged at 12,000 × g at 4°C for 5 min. The precipitate was
retained and the supernatant was collected into a new centrifuge
tube, which was the cytoplasmic protein component. Reagents CEB-A
and CEB-B (Applygen Technologies, Inc.) were added to centrifuge
tubes containing cell precipitates, shook and resuspended, and
centrifuged at 1,000 × g at 4°C for 5 min. All supernatants were
discarded and the precipitate was retained. Then, the reagent NEB
was added to the precipitate, placed it on ice for 30 min,
centrifuged it at 12,000 × g at 4°C for 5 min, and finally the
supernatant was collected, which was now the nuclear protein
component.
Statistical analysis
All results were based on at least three independent
experiments. The results were expressed as mean ± standard
deviation (SD). Unpaired Student's t-test, Welch's t-test, one-way
ANOVA (followed by Bonferroni post hoc test) and Mann-Whitney U
test were used to test the significance of differences. Survival
analysis was conducted using the Kaplan-Meier method followed by
the log-rank test. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS (version
20; IBM Corp.) and GraphPad Prism 8 (Dotmatics). P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
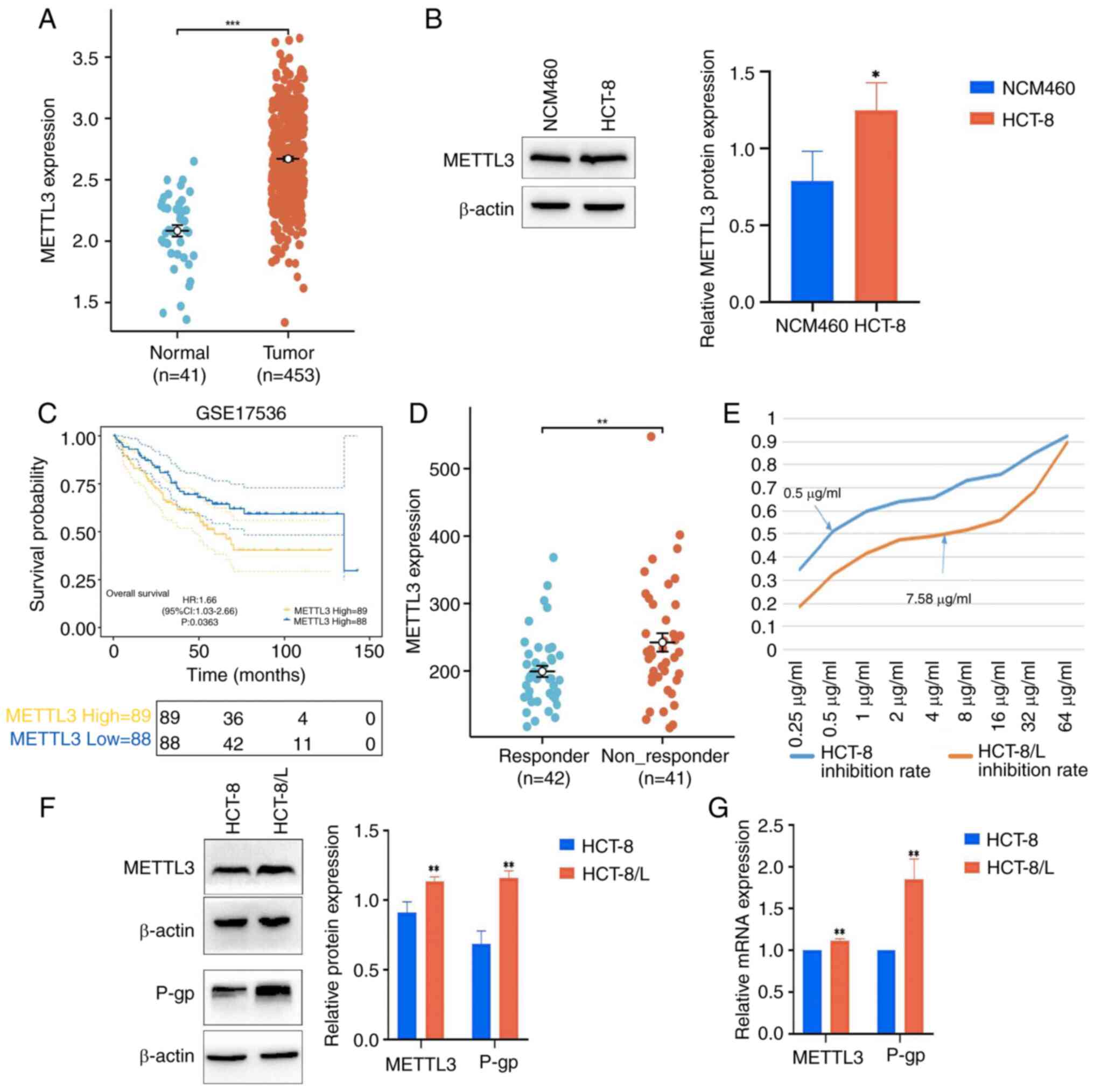
METTL3 expression increases in CRC and
is associated with drug resistance and poor prognosis
By downloading the TCGA queue data from the UCSC
Xena database, it was found that the expression level of METTL3 in
CRC tissue significantly increased, compared with that in normal
tissue (Fig. 1A). Meanwhile,
western blot analysis revealed a significant increase in the
expression level of METTL3 in HCT-8 cells (Fig. 1B). Furthermore, it was found in the
GSE17536 dataset that patients with high METTL3 expression levels
had shorter overall survival time (Fig.
1C). To clarify the relationship between METTL3 and drug
resistance, the GSE28702 dataset was downloaded and it was found
that the expression level of METTL3 increased in FOLFOX
chemotherapy-unresponsive patients, but not in FOLFOX
chemotherapy-sensitive patients (Fig.
1D). The CCK-8 experiment demonstrated that after OXA
treatment, the IC50 of HCT-8 cells was 0.5 µg/ml, and
the IC50 of HCT-8/L cells was 7.58 µg/ml. The resistance
index was ~15.16-fold, indicating high resistance (Fig. 1E). Western blotting and RT-qPCR
showed that the protein expression levels and mRNA expression
levels of METTL3 and P-gp in HCT-8/L cells significantly increased,
compared with those in HCT-8 cells (Fig. 1F and G).
Knocking down METTL3 inhibits the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and increases the sensitivity of
HCT-8/L cells to OXA
Given the increased expression of METTL3 in HCT-8/L
cells, it was hypothesized that regulating METTL3 can alter the
sensitivity of HCT-8/L cells to OXA. To confirm this hypothesis, a
knockdown model of METTL3 was constructed using si-METTL3 siRNA in
HCT-8/L cells. Western blotting and RT-qPCR showed that the protein
and mRNA expression levels of METTL3 in si-METTL3#1 and si-METTL3#2
were significantly downregulated, compared with those in si-NCs
(Fig. 2A and B). The CCK-8
experiment identified that knocking down METTL3 significantly
decreased the activity of HCT-8/L cells and increased their
sensitivity to OXA (Fig. 2C).
Concurrently, western blotting and RT-qPCR demonstrated a
significant decrease in both P-gp protein and mRNA expression
levels (Fig. 2D and F). The effect
of METTL3 on apoptosis of HCT-8/L cells was further investigated.
Through flow cytometry, it was found that the apoptotic rate of the
si-METTL3#1 group and si-METTL3#2 group were significantly higher
than that of the si-NC group (Fig.
2E). This was further supported by the results of western
blotting. Knocking down METTL3 resulted in a significant increase
in Bax protein expression level and a significant decrease in Bcl-2
protein expression level. The expression levels of cleaved caspase
3/total caspase 3 were also increased (Fig. 2F). To explore the effect of METTL3
on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, western blotting was used.
The results showed that the expression levels of Wnt 3a and
β-catenin proteins significantly decreased after knocking down
METTL3 (Fig. 2F). RT-qPCR also
revealed that the expression levels of β-catenin mRNA were
significantly downregulated (Fig.
2D). Furthermore, immunofluorescence revealed that knocking
down METTL3 inhibited the entry of β-catenin into the nucleus
(Fig. 2G). By separating the
cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins of HCT-8/L cells, it was found
that knocking down METTL3 resulted in no significant change in the
expression of β-catenin in the cytoplasm, whereas the expression of
β-catenin in the nucleus decreased (Fig. 2H). The aforementioned results
indicated that knocking down METTL3 inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway in HCT-8/L cells, promotes cell apoptosis, and
increases sensitivity to OXA.
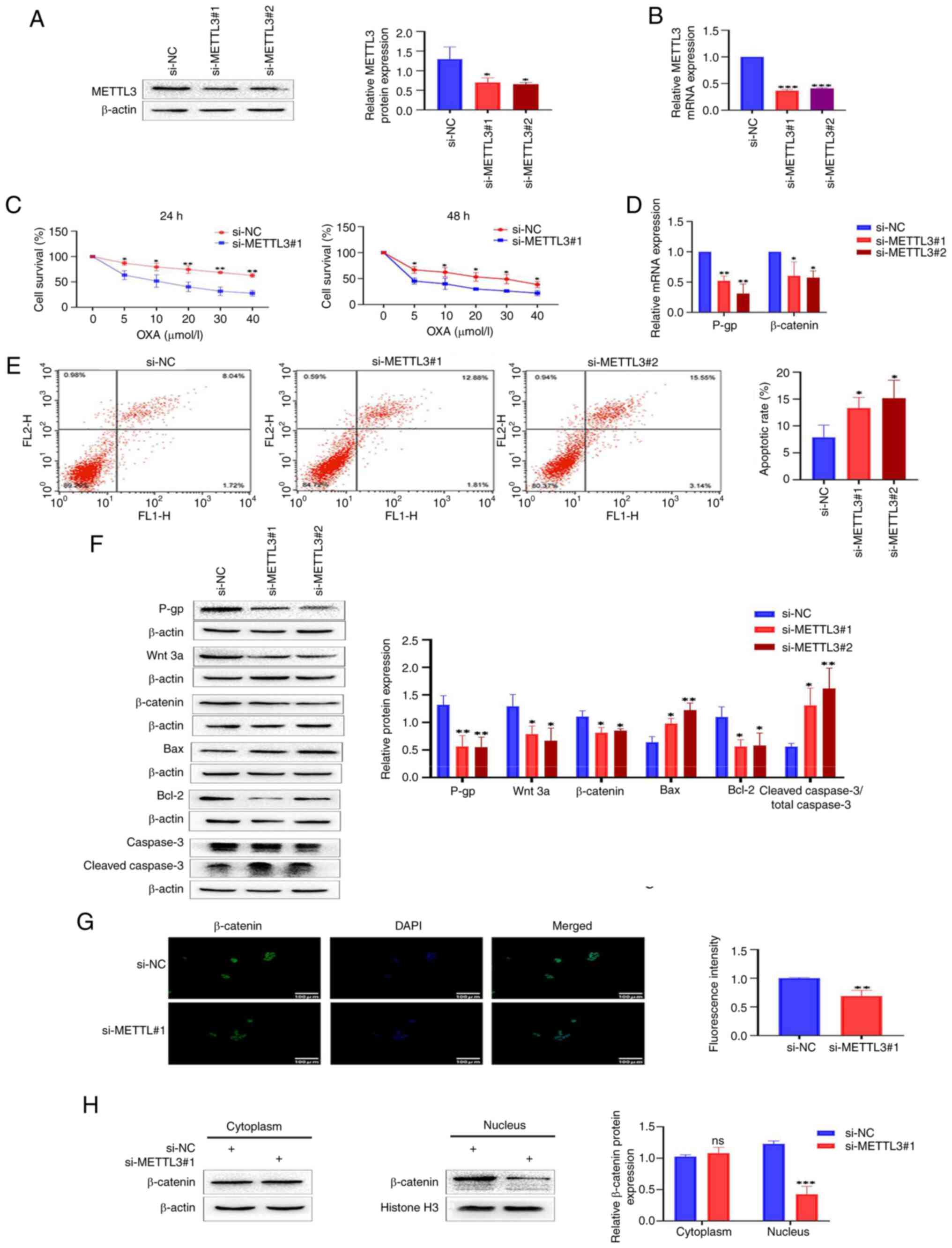 | Figure 2.Knocking down METTL3 inhibits the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, making colorectal cancer cells
sensitive to OXA. (A) Western blot detection of METTL3 knockdown
efficiency. (B) RT-qPCR detection of METTL3 knockdown efficiency.
(C) Cell survival analysis of si-METTL3#1 and control si-NC treated
with different concentrations of OXA. (D) Reverse
transcription-quantitative PCR was used to detect the mRNA
expression changes of P-gp and β-catenin after knocking down
METTL3. (E) Flow cytometric analysis of cell apoptosis. (F) Western
blot analysis was used to detect the expression changes of P-gp,
Wnt 3a, β-catenin, Bax, Bcl-2 and cleaved caspase3/total caspase 3
proteins after knocking down METTL3. (G) Immunofluorescence
analysis of β-catenin's entry into the nucleus. (H) Western
blotting was used to detect the expression of β-catenin in the
cytoplasm and nucleus of HCT-8/L cells. The data are expressed as
the mean ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 compared
with the si-NC group. METTL3, methyltransferase 3; OXA,
oxaliplatin; si-, small interfering; NC, negative control. |
Knocking down METTL3 increases
sensitivity of HCT-8/L cells to OXA by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway
To further elucidate the impact of METTL3 on the
sensitivity of HCT-8/L cells to OXA by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway, AMBMP was used in the present study. The results
of flow cytometry showed that the apoptotic rate of HCT-8/L cells
in the si-METTL3#1 group was significantly higher than that in the
si-NC group, while knocking down METTL3 and adding AMBMP caused no
significant change in the apoptotic rate of HCT-8/L cells, compared
with the negative control group (Fig.
3A). The use of AMBMP has weakened this trend. The RT-qPCR
results revealed that knocking down METTL3 resulted in a decrease
in the mRNA expression levels of β-catenin and P-gp, while AMBMP
upregulated the mRNA expression levels of β-catenin and P-gp. There
was no significant difference in the mRNA expression levels of
METTL3. After knocking down METTL3 and adding AMBMP, compared with
the si-METTL3#1 group, the mRNA expression levels of β-catenin and
P-gp both increased, while there was no significant change in the
mRNA expression level of METTL3 (Fig.
3B). Western blot results identified that knocking down METTL3
inhibited the expression of Wnt 3a, β-catenin, Bcl-2 and P-gp, and
enhanced the expression of Bax and cleaved caspase 3/total caspase
3; whereas AMBMP upregulated the expression of Wnt 3a, β-catenin,
Bcl-2 and P-gp, and reduced the expression of Bax and cleaved
caspase 3/total caspase 3. There was no significant difference in
METTL3 expression. Compared with the si-METTL3#1 group, knocking
down METTL3 and adding AMBMP enhanced the expression of Wnt 3a,
β-catenin, Bcl-2 and P-gp, and inhibited the expression of Bax and
cleaved caspase 3/total caspase 3, whereas the expression of METTL3
remained unchanged (Fig. 3C). The
immunofluorescence results showed that knocking down METTL3
inhibited the entry of β-catenin into the nucleus, whereas AMBMP
promoted the entry of β-catenin into the nucleus. After knocking
down METTL3 and adding AMBMP, compared with the si-METTL3#1 group,
the entry of β-catenin into the nucleus increased (Fig. 3D). By separating the cytoplasmic and
nuclear proteins of HCT-8/L cells, it was found that knocking down
METTL3 downregulated the expression of β-catenin in the nucleus,
while showing no significant changes in the cytoplasm. AMBMP
upregulated β-catenin in both the cytoplasm and nucleus. Knocking
down METTL3 and adding AMBMP resulted in upregulation of β-catenin
in both the cytoplasm and nucleus, compared with the si-METTL3#1
group. Compared with the group that was only supplemented with
AMBMP, knocking out METTL3 and adding AMBMP did not significantly
change β-catenin in the cytoplasm, but inhibited β-catenin in the
nucleus compared with the si-NC + AMBMP group (Fig. 3E). The aforementioned results
indicated that METTL3 can affect the sensitivity of HCT-8/L cells
to OXA by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
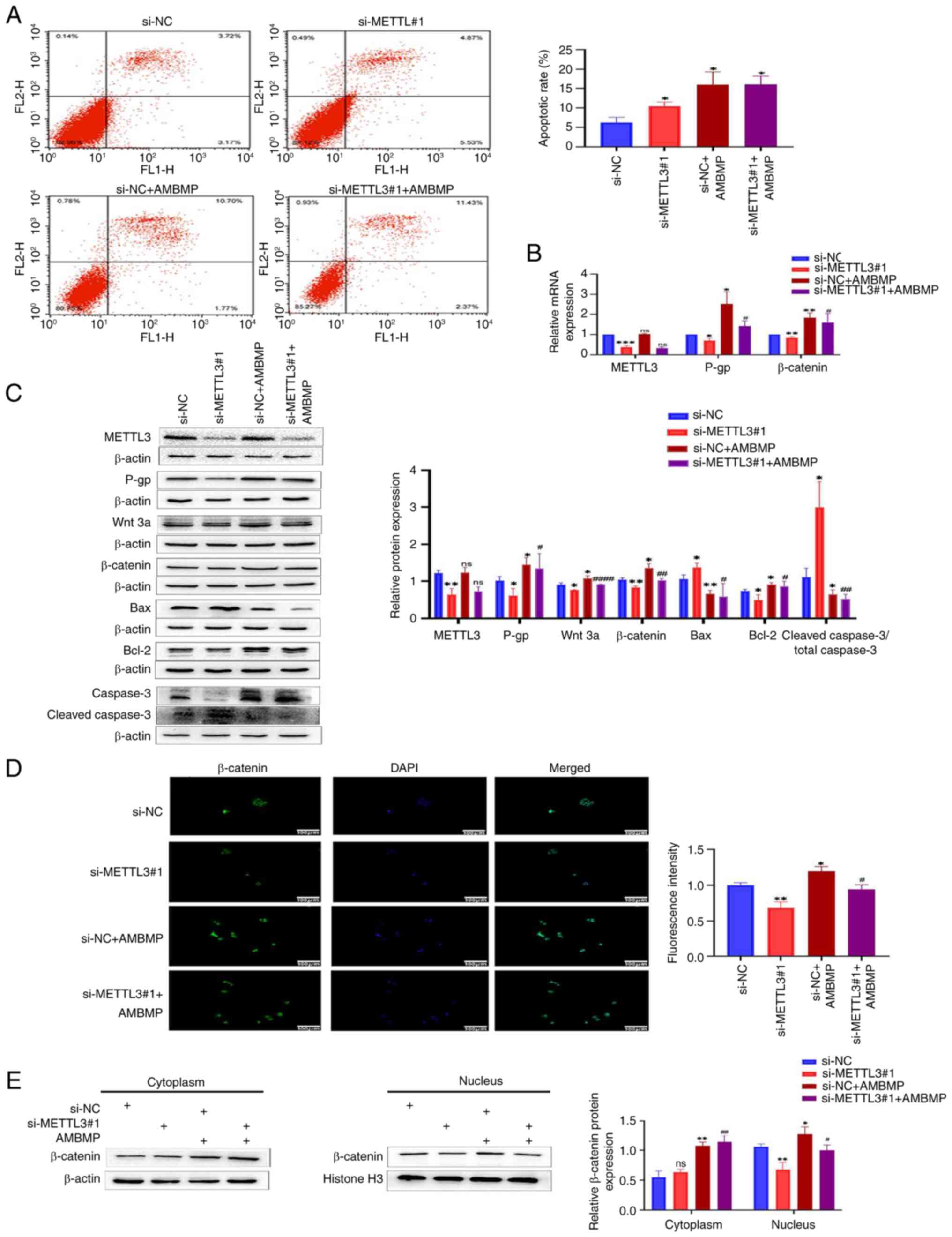 | Figure 3.Knocking down METTL3 increases the
sensitivity of HCT-8/L cells to oxaliplatin by inhibiting the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of
cell apoptosis. (B) Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR was used
to detect changes in mRNA expression of METTL3, P-gp and β-catenin.
(C) Western blotting was used to detect the protein expression
changes of METTL3, P-gp, Wnt 3a, β-catenin, Bax, Bcl-2 and cleaved
caspase3/total caspase 3. (D) Immunofluorescence analysis of
β-catenin's entry into the nucleus. (E) Western blot analysis of
the expression of β-catenin in the cytoplasm and nucleus of HCT-8/L
cells. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P<0.05,
**P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 compared with the si-NC group;
#P<0.05, ##P<0.01 and
####P<0.0001 compared with the si-METTL3#1 group.
METTL3, methyltransferase 3; si-, small interfering; NC, negative
control; ns, not significant. |
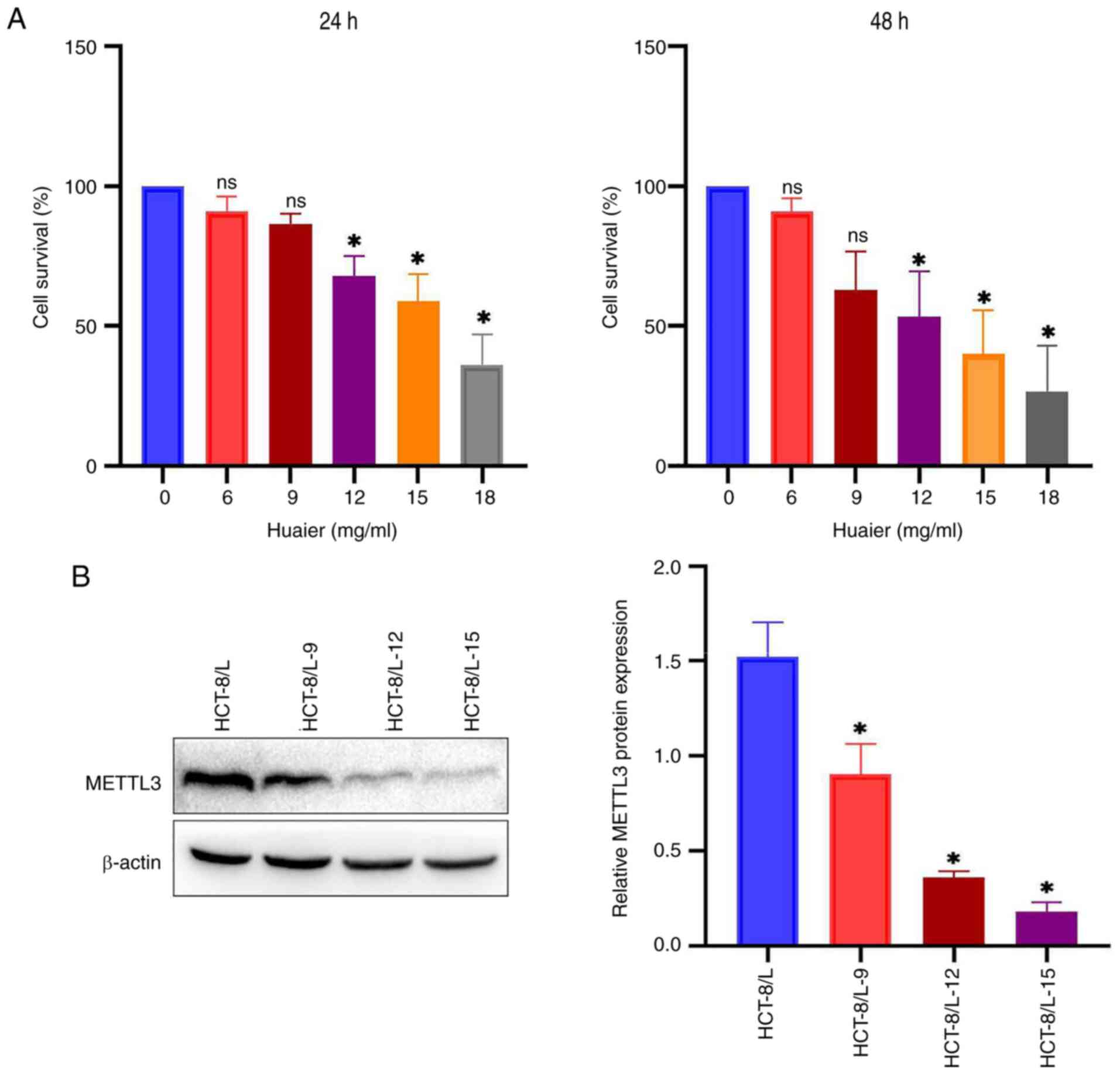
Huaier reduces the expression of
METTL3 and the vitality of HCT-8/L cells
CCK-8 method was used to detect the effect of Huaier
on the viability of HCT-8/L cells. It was found that the activity
of HCT-8/L cells decreased in a dose-dependent manner with
different doses of Huaier (0, 6, 9, 12, 15 and 18 mg/ml) (Fig. 4A). After 24 h of treatment with
Huaier, the IC50 value of HCT-8/L cells was 15.74 mg/ml,
and after 48 h, the IC50 value of HCT-8/L cells was
12.35 mg/ml. To investigate whether Huaier affects the expression
of METTL3, western blotting was used. Under different doses (0, 9,
12 and 15 mg/ml) of Huaier, the expression level of METTL3
gradually decreased with increasing concentration of Huaier
(Fig. 4B). The aforementioned
results indicated that Huaier can inhibit the expression of METTL3
and reduce the activity of HCT-8/L cells. The concentration of 12
mg/ml was selected for subsequent experiments with Huaier.
Huaier downregulates the expression of
METTL3, inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and increases
the sensitivity of HCT-8/L cells to OXA
Considering that Huaier can inhibit the expression
of METTL3, it was further analyzed whether Huaier can inhibit the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and increase the sensitivity of
HCT-8/L cells to OXA. It was found through CCK-8 experiments that
Huaier significantly increased the sensitivity of HCT-8/L cells to
OXA (Fig. 5A), while western
blotting and RT-qPCR showed a significant decrease in the protein
and mRNA expression levels of P-gp (Fig. 5B and D). The results of flow
cytometry demonstrated that under the action of Huaier, the
apoptotic rate of the cells significantly increased (Fig. 5C), and the results of western blot
supported this finding. The expression level of Bax and cleaved
caspase 3/total caspase 3 significantly increased, whereas the
expression level of Bcl-2 significantly decreased (Fig. 5D).
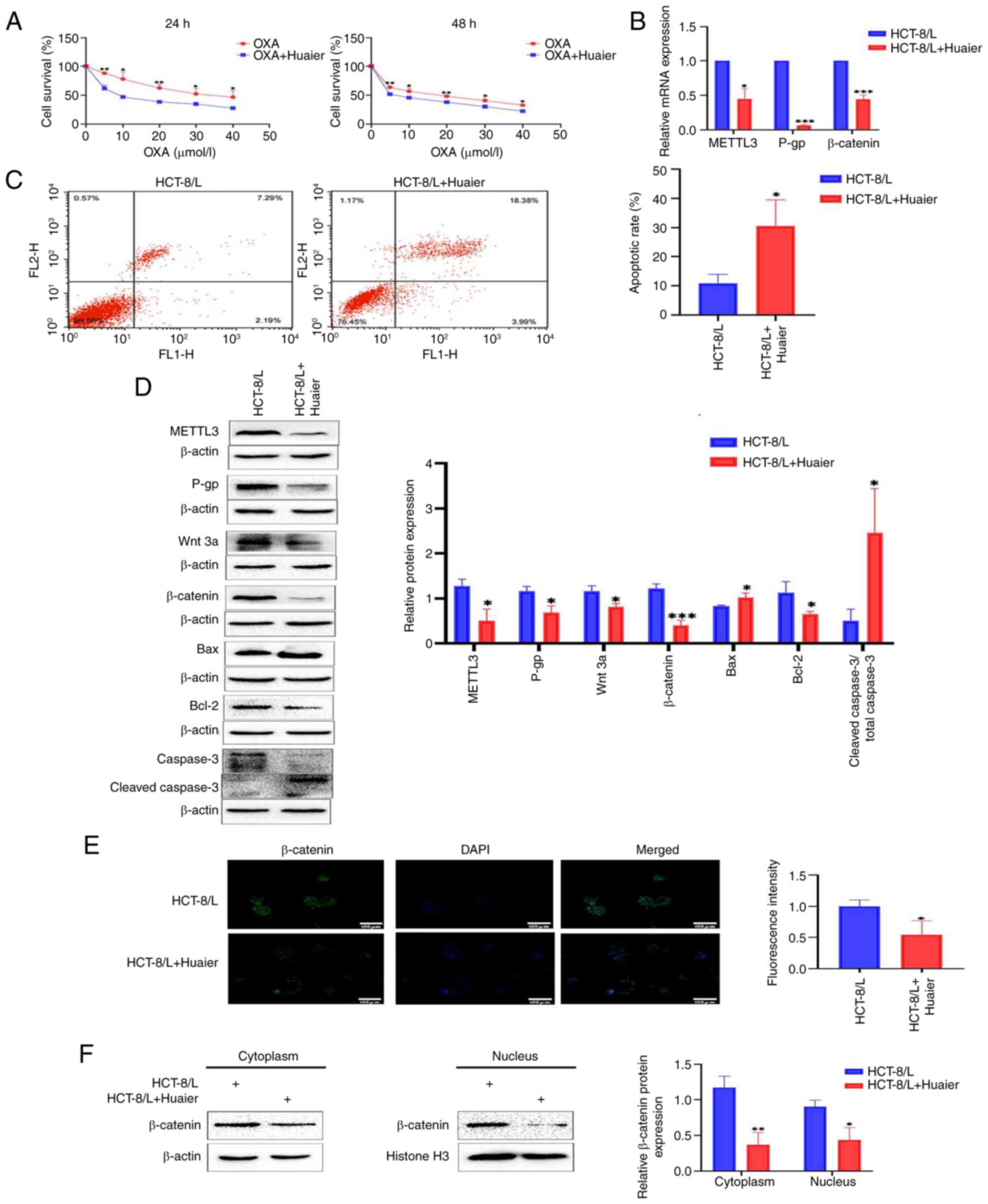 | Figure 5.Huaier downregulates the expression
of METTL3, inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and
renders HCT-8/L cells sensitive to OXA. (A) Survival analysis of
HCT-8/L cells treated with different concentrations of OXA after
treatment with Huaier. (B) Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
was used to detect the effect of Huaier on the mRNA expression of
METTL3, P-gp and β-catenin. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of cell
apoptosis. (D) Western blot was used to detect the effects of
Huaier on the protein expression of METTL3, P-gp, Wnt 3a,
β-catenin, Bax, Bcl-2 and cleaved caspase3/total caspase 3. (E)
Immunofluorescence analysis of β-catenin's entry into the nucleus.
(F) Western blotting was used to detect the expression of β-catenin
in the cytoplasm and nucleus of HCT-8/L cells. The data are
expressed as the mean ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and
***P<0.001 compared with the HCT-8/L group. METTL3,
methyltransferase 3; OXA, oxaliplatin. |
Subsequently, it was identified using western
blotting that Huaier inhibited the expression levels of METTL3, Wnt
3a and β-catenin (Fig. 5D). The
RT-qPCR results revealed a significant decrease in the expression
levels of METTL3 and β-catenin mRNA after the action of Huaier
(Fig. 5B). Immunofluorescence
experiments showed that Huaier inhibited the entry of β-catenin
into the nucleus (Fig. 5E). By
extracting cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins from HCT-8/L cells, it
was found that Huaier inhibited the expression of β-catenin in the
cytoplasm and nucleus (Fig. 5F).
This indicated that Huaier downregulates the expression of METTL3,
inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and increases the
sensitivity of HCT-8/L cells to OXA.
Huaier suppresses the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway by downregulating the expression of METTL3,
rendering HCT-8/L cells sensitive to OXA
To further elucidate whether Huaier inhibits the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by downregulating the expression of
METTL3, rendering HCT-8/L cells sensitive to OXA, a model
overexpressing METTL3 in HCT-8/L cells was constructed. Western
blotting and RT-qPCR showed that the protein and mRNA expression
levels of METTL3 in the pC-METTL3 group significantly increased,
compared with those in the pC-NC group (Fig. 6A and B). The results of flow
cytometry revealed that the apoptotic rate of HCT-8/L cells in the
pC-METTL3 group was significantly reduced, compared with that in
the pC-NC group, while Huaier increased the apoptotic rate of
HCT-8/L cells. Compared with the pC-METTL3 group, the addition of
Huaier after overexpression of METTL3 increased the apoptotic rate
of HCT-8/L cells (Fig. 6C). Western
blot results demonstrated that overexpression of METTL3 upregulated
the expression of METTL3, Wnt 3a, β-catenin, Bcl-2 and P-gp, and
inhibited the expression of Bax and cleaved caspase 3/total caspase
3. Huaier inhibited the expression of METTL3, Wnt 3a, β-catenin,
Bcl-2 and P-gp, and enhanced the expression of Bax and cleaved
caspase 3/total caspase 3. Compared with the pC-METTL3 group,
adding Huaier after overexpressing METTL3 inhibited the expression
of METTL3, Wnt 3a, β-catenin, Bcl-2 and P-gp, and upregulated the
expression of Bax and cleaved caspase 3/total caspase 3 (Fig. 6E). The RT-qPCR results showed that
after overexpression of METTL3, the mRNA expression levels of
METTL3, β-catenin and P-gp were all upregulated. After the action
of Huaier, the mRNA expression levels of METTL3, β-catenin and P-gp
were all reduced. Compared with the pC-METTL3 group, overexpression
of METTL3 followed by the addition of Huaier inhibited the mRNA
expression levels of METTL3, β-catenin and P-gp (Fig. 6D). The immunofluorescence results
identified that overexpression of METTL3 promoted the entry of
β-catenin into the nucleus, whereas Huaier inhibited the entry of
β-catenin into the nucleus. After overexpressing METTL3 and adding
Huaier, compared with the pC-METTL3 group, the entry of β-catenin
into the nucleus was reduced (Fig.
6F). After separating the cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins of
HCT-8/L cells, it was found that overexpression of METTL3
upregulated the expression of β-catenin in the nucleus, whereas
there was no significant change in β-catenin in the cytoplasm.
Huaier downregulated β-catenin in both the cytoplasm and nucleus.
After overexpressing METTL3, the use of Huaier resulted in
downregulation of β-catenin in both the cytoplasm and nucleus
compared with the pC-METTL3 group (Fig.
6G). These data indicated that Huaier can downregulate the
expression of METTL3, thereby inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway and rendering HCT-8/L cells sensitive to OXA.
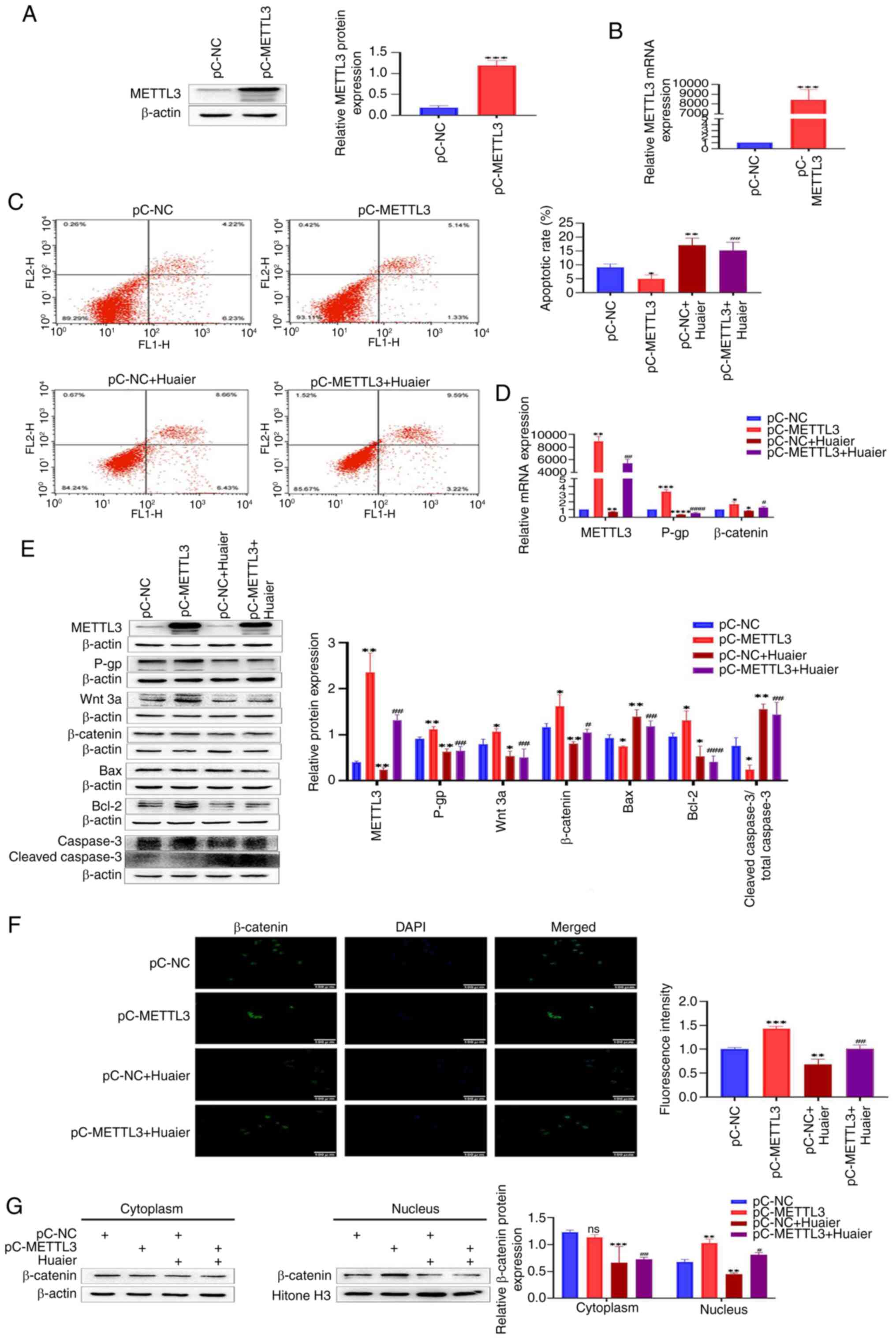 | Figure 6.Huaier inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway by downregulating the expression of METTL3,
rendering HCT-8/L cells sensitive to OXA. (A) Western blotting was
used to detect the overexpression efficiency of METTL3. (B) RT-qPCR
was used to detect the overexpression efficiency of METTL3. (C)
Flow cytometric analysis of cell apoptosis. (D) RT-qPCR was used to
detect changes in mRNA expression of METTL3, P-gp and β-catenin.
(E) Western blotting was used to detect the protein expression
changes of METTL3, P-gp, Wnt 3a, β-catenin, Bax, Bcl-2 and cleaved
caspase3/total caspase 3. (F) Immunofluorescence analysis of
β-catenin's entry into the nucleus. (G) Western blot analysis of
the expression of β-catenin in the cytoplasm and nucleus of HCT-8/L
cells. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P<0.05,
**P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001 compared with the
pC-NC group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01,
###P<0.001 and ####P<0.0001 compared
with the pC-METTL3. METTL3, methyltransferase 3; OXA, oxaliplatin;
RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; NC, negative
control; ns, not significant. |
Discussion
CRC is the third most common malignant tumor
worldwide, and its incidence rate has increased in recent years
(32). The mortality rate of CRC is
second only to that of lung cancer (33). Most patients have a hidden onset and
are already in the middle or late stage when discovered (3). Chemotherapy is a commonly used
treatment for middle- and late-stage CRC in traditional Chinese
medicine (34). The first-line
chemotherapy drug commonly used in clinical practice for the
treatment of CRC is mainly OXA. However, chemotherapy resistance
developed during the treatment process has become a common cause of
treatment failure. Due to the unclear mechanism of OXA chemotherapy
resistance, patients with CRC lack effective treatment methods.
METTL3 is the first reported m6A methyltransferase
and has been identified as the main methyltransferase involved in
the methylation process (35). Peng
et al (36) have found that
METTL3 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of CRC,
and affects the prognosis of patients with CRC. According to Li
et al (15), inhibition of
METTL3 makes CRC cells sensitive to 5-FU, and overcomes 5-FU
resistance in CRC cells by downregulating the expression of
RAD51-related protein 1, enhancing DNA damage accumulation, and
promoting cell apoptosis.
In the present study, a database analysis was first
conducted and it was found that METTL3 expression is elevated in
CRC chemotherapy-tolerant patients and that high expression of
METTL3 is closely related to poor prognosis in patients. HCT-8/L
cells were selected as the research object and it was found that
METTL3 expression was elevated in HCT-8/L cells. Knockdown of
METTL3 downregulated the expression of P-gp and Bcl-2, increased
the expression of Bax, promoted the sensitivity of HCT-8/L cells to
OXA, and facilitated cell apoptosis. In addition, it was revealed
that METTL3 has a regulatory effect on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in HCT-8/L cells. Knocking down METTL3 can inhibit the
expression of Wnt3a and β-catenin and suppress the nuclear entry of
β-catenin. Then, AMBMP was used to further validate the regulatory
effect of METTL3 on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. It was
found that compared with those in the AMBMP group, knocking down
METTL3 and adding AMBMP downregulated the expression of Wnt3a,
β-catenin, Bcl-2 and P-gp; increased the expression of Bax; and
inhibited the nuclear entry of β-catenin. Under the action of
AMBMP, there was no significant difference in the expression of
METTL3. It is considered that AMBMP activates the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway, but as METTL3 is an upstream gene, AMBMP does
not significantly affect the expression of METTL3. The
aforementioned experimental results confirm that METTL3 can promote
the sensitivity of HCT-8/L cells to OXA by regulating the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Although the knockout of METTL3 cannot completely
reverse drug resistance, current data at least suggest that
inhibiting METTL3 can partially overcome OXA resistance in HCT-8/L
cells by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. As a key
methyltransferase in m6A methylation modification, METTL3 may also
interact with other genes to contribute to drug resistance in CRC.
Liu et al (37) found that
METTL3-mediated m6A modification of Sec62 mRNA upregulated Sec62
expression in CRC. Subsequently, Sec62 potentiates Wnt signaling
through repressing β-catenin binding to APC complex. This was
consistent with the present results. However, further research is
needed to clarify the specific mechanisms of the relationship
between METTL3 and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, as well as
its connection to chemotherapy resistance, which includes gathering
more clinical tissue samples for analysis.
Since artemisinin was proven to treat malaria,
traditional Chinese medicine has garnered considerable attention.
Traditional Chinese medicine is the main source of natural
medicines and herbal products and an important source for
developing anti-CRC drugs (38).
The active ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine can disrupt
the living environment of cancer cells, promote cell apoptosis,
enhance individual immunity and eliminate pathogens through the
autoimmune system, thereby achieving anticancer effects (39–41).
An increasing amount of evidence suggests that Huaier has
anticancer effects on various types of tumors. Zhou et al
(42) found that Huaier could slow
down the growth of pancreatic cancer and reduce the invasion,
migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic
cancer cells by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Sun
et al (43) reported that
Huaier significantly reduced the tumor development of HT-29 CRC
cell line transplanted into nude mice by downregulating the
expression of PI3KR1, AKT, Wnt1, CTTNB1 and Notch genes. Cong et
al (44) found that Huaier can
inhibit the development of cholangiocarcinoma by regulating the
Twist1/FBP1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling axis.
The present study found through CCK-8 experiments
that Huaier can inhibit the proliferation activity and drug
resistance of HCT-8/L cells. The use of Huaier downregulated the
expression of METTL3, P-gp and Bcl-2 in HCT-8/L cells; upregulated
the expression of Bax; promoted the sensitivity of HCT-8/L cells to
OXA; and facilitated cell apoptosis. Moreover, Huaier has a
regulatory effect on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Huaier
inhibited the expression of Wnt3a and β-catenin in HCT-8/L cells
and inhibited the entry of β-catenin into the nucleus. Then, an
overexpression METTL3 model was constructed in HCT-8/L cells to
further explore the mechanism by which Huaier affects HCT-8/L
cells. It was found that after overexpression of METTL3 in Huaier,
the expression of METTL3, P-gp, Wnt3a, β-catenin, and Bcl-2
decreased, whereas the expression of BAX increased. The nuclear
entry of β-catenin was also inhibited, and cell apoptosis
increased. The aforementioned experimental results confirmed that
Huaier can suppress the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and render
HCT-8/L cells sensitive to OXA by downregulating the expression of
METTL3.
The present study indicated that the fungus Huaier
has a certain inhibitory effect on CRC; however, the current
results are based on cellular experiments but have not been
validated in the second cell line. Further research to verify the
clinical efficacy of Huaier is needed. More in-depth research is
still required regarding the safety, effectiveness, metabolism,
side effects and toxicity of Huaier in patients with CRC.
Meanwhile, the effect of Huaier on normal colon cells will be
explored in future studies.
In summary, Huaier downregulates the expression of
METTL3, inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and increases
the sensitivity of OXA-resistant CRC cells to OXA. The present
study provides a theoretical basis for the treatment of CRC
chemotherapy-induced drug resistance with the traditional Chinese
medicine Huaier.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Yixin Liu for
her support and companionship.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Project Funding of Hebei
Provincial Education Department (grant no. ZD2020137), the Key
Discipline Construction Project of Hebei Provincial Universities
[grant no. Ji Jiao Gao-2013-(4)-2012-37] and basic scientific
research business expenses of Chengde Medical College for
outstanding students.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
MH and JZ conceived and designed the study. MH and
ZG collected data. MH supervised the study. MH and GW analyzed and
interpreted the data. MH, ZH and JZ performed statistical analysis.
MH, JZ and ZH wrote the draft of the manuscript. MH and JZ
critically revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved
the final version of the manuscript, participated sufficiently in
the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
MH and JZ confirm the authenticity of all the raw data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Xi Y and Xu P: Global colorectal cancer
burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl Oncol.
14:1011742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang Z, Dan W, Zhang N, Fang J and Yang Y:
Colorectal cancer and gut microbiota studies in China. Gut
Microbes. 15:22363642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He K, Wang Y, Zhong Y, Pan X, Si L and Lu
J: KRAS codon 12 mutation is associated with more aggressive
invasiveness in synchronous metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC):
Retrospective research. Onco Targets Ther. 13:12601–12613. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van der Jeught K, Xu HC, Li YJ, Lu XB and
Ji G: Drug resistance and new therapies in colorectal cancer. World
J Gastroenterol. 24:3834–3848. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD,
Navarro M, James RD, Karasek P, Jandik P, Iveson T, Carmichael J,
Alakl M, et al: Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with
fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic
colorectal cancer: A multicentre randomised trial. Lancet.
355:1041–1047. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Giacchetti S, Perpoint B, Zidani R, Le
Bail N, Faggiuolo R, Focan C, Chollet P, Llory JF, Letourneau Y,
Coudert B, et al: Phase III multicenter randomized trial of
oxaliplatin added to chronomodulated fluorouracil-leucovorin as
first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol.
18:136–147. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee YT, Tan YJ and Oon CE: Molecular
targeted therapy: Treating cancer with specificity. Eur J
Pharmacol. 834:188–196. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ohishi T, Kaneko MK, Yoshida Y, Takashima
A, Kato Y and Kawada M: Current targeted therapy for metastatic
colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 24:17022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ganesh K, Stadler ZK, Cercek A, Mendelsohn
RB, Shia J, Segal NH and Diaz LA Jr: Immunotherapy in colorectal
cancer: Rationale, challenges and potential. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 16:361–375. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Overman MJ, Ernstoff MS and Morse MA:
Where we stand with immunotherapy in colorectal cancer: Deficient
mismatch repair, proficient mismatch repair, and toxicity
management. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 38:239–247. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szakács G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA,
Booth-Genthe C and Gottesman MM: Targeting multidrug resistance in
cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:219–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dean M, Rzhetsky A and Allikmets R: The
human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. Genome
Res. 11:1156–1166. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma Y, Guo C, Wang X, Wei X and Ma J:
Impact of chemotherapeutic agents on liver microenvironment:
Oxaliplatin create a pro-metastatic landscape. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 42:2372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu CP, Calcagno AM and Ambudkar SV:
Reversal of ABC drug transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in
cancer cells: Evaluation of current strategies. Curr Mol Pharmacol.
1:93–105. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li M, Xia M, Zhang Z, Tan Y, Li E, Guo Z,
Fang M, Zhu Y and Hu Z: METTL3 antagonizes 5-FU chemotherapy and
confers drug resistance in colorectal carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
61:1062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu S, Zhuo L, Wang J, Zhang Q, Li Q, Li
G, Yan L, Jin T, Pan T, Sui X, et al: METTL3 plays multiple
functions in biological processes. Am J Cancer Res. 10:1631–1646.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
El-Shami K, Oeffinger KC, Erb NL, Willis
A, Bretsch JK, Pratt-Chapman ML, Cannady RS, Wong SL, Rose J,
Barbour AL, et al: American cancer society colorectal cancer
survivorship care guidelines. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:428–455. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pachman DR, Qin R, Seisler DK, Smith EML,
Beutler AS, Ta LE, Lafky JM, Wagner-Johnston ND, Ruddy KJ, Dakhil
S, et al: Clinical course of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy:
Results from the randomized phase III trial N08CB (alliance). J
Clin Oncol. 33:3416–3422. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen JF, Wu SW, Shi ZM and Hu B:
Traditional Chinese medicine for colorectal cancer treatment:
Potential targets and mechanisms of action. Chin Med. 18:142023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen Y, Wu H, Wang X, Wang C, Gan L, Zhu
J, Tong J and Li Z: Huaier Granule extract inhibit the
proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer cells through
down-regulation of MTDH, JAK2/STAT3 and MAPK signaling pathways.
Biomed Pharmacother. 101:311–321. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu B, Yan W, Wang M, Cui X, Hu Y, Chen Q,
Zhang Y, Qi X and Jiang J: Huaier polysaccharide inhibits the
stem-like characteristics of ERα-36high triple negative
breast cancer cells via inactivation of the ERα-36 signaling
pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 15:1358–1367. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Z, Liu C, Yan K, Liu J, Fang Z and Fan
Y: Huaier extract inhibits prostate cancer growth via targeting
AR/AR-V7 pathway. Front Oncol. 11:6155682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Su D, Jiang B, Yang Y, Miao Y, Fu Q and
Zhang F: Effect of Huaier on melanoma invasion, metastasis, and
angiogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2020:81638392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pan J, Yang C, Jiang Z and Huang J:
Trametes robiniophila Murr: A traditional Chinese medicine with
potent anti-tumor effects. Cancer Manag Res. 11:1541–1549. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu DQ, Yuan XJ, Toyoda H and Hirayama M:
Anti-tumor effect of Huaier extract against neuroblastoma cells in
vitro. Int J Med Sci. 18:1015–1023. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ji D, Zheng W, Huang P, Yao Y, Zhong X,
Kang P, Wang Z, Shi G, Xu Y and Cui Y: Huaier restrains
cholangiocarcinoma progression in vitro and in vivo through
modulating lncRNA TP73-AS1 and inducing oxidative stress. Onco
Targets Ther. 13:7819–7837. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luo Z, Hu X, Xiong H, Qiu H, Yuan X, Zhu
F, Wang Y and Zou Y: A polysaccharide from Huaier induced apoptosis
in MCF-7 breast cancer cells via down-regulation of MTDH protein.
Carbohydr Polym. 151:1027–1033. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hu Z, Yang A, Fan H, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Zha
X, Zhang H and Tu P: Huaier aqueous extract sensitizes cells to
rapamycin and cisplatin through activating mTOR signaling. J
Ethnopharmacol. 186:143–150. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fang L, Zhang Y, Zang Y, Chai R, Zhong G,
Li Z, Duan Z, Ren J and Xu Z: HP-1 inhibits the progression of
ccRCC and enhances sunitinib therapeutic effects by suppressing
EMT. Carbohydr Polym. 223:1151092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan X, Lyu T, Jia N, Yu Y, Hua K and Feng
W: Huaier aqueous extract inhibits ovarian cancer cell motility via
the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. PLoS One. 8:e637312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA
and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin.
73:233–254. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang Z, Zhang X, Bai X, Xi X, Liu W and
Zhong W: Anti-angiogenesis in colorectal cancer therapy. Cancer
Sci. 115:734–751. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu T, Guo F, Yu Y, Sun T, Ma D, Han J,
Qian Y, Kryczek I, Sun D, Nagarsheth N, et al: Fusobacterium
nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to colorectal cancer by
modulating autophagy. Cell. 170:548–563.e16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Visvanathan A, Patil V, Arora A, Hegde AS,
Arivazhagan A, Santosh V and Somasundaram K: Essential role of
METTL3-mediated m6A modification in glioma stem-like
cells maintenance and radioresistance. Oncogene. 37:522–533. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Peng W, Li J, Chen R, Gu Q, Yang P, Qian
W, Ji D, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Tang J and Sun Y: Upregulated METTL3
promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer via miR-1246/SPRED2/MAPK
signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu X, Su K, Sun X, Jiang Y, Wang L, Hu C,
Zhang C, Lu M, Du X and Xing B: Sec62 promotes stemness and
chemoresistance of human colorectal cancer through activating
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:1322021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kong MY, Li LY, Lou YM, Chi HY and Wu JJ:
Chinese herbal medicines for prevention and treatment of colorectal
cancer: From molecular mechanisms to potential clinical
applications. J Integr Med. 18:369–384. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yan Z, Lai Z and Lin J: Anticancer
properties of traditional Chinese medicine. Comb Chem High
Throughput Screen. 20:423–429. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Liu X, Yu M, Xu M, Xiao Y, Ma W,
Huang L, Li X and Ye X: Berberine inhibits proliferation and
induces G0/G1 phase arrest in colorectal cancer cells by
downregulating IGF2BP3. Life Sci. 260:1184132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qiao L, Han M, Gao S, Shao X, Wang X, Sun
L, Fu X and Wei Q: Research progress on nanotechnology for delivery
of active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicines. J Mater
Chem B. 8:6333–6351. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou C, Li J, Qian W, Yue Y, Xiao Y, Qin
T, Ma Q and Li X: Huaier extract restrains pancreatic cancer by
suppressing Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
127:1101262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun WW, Dou JX, Zhang L, Qiao LK, Shen N,
Zhao Q and Gao WY: Killing effects of Huaier Granule combined with
DC-CIK on nude mice transplanted with colon carcinoma cell line.
Oncotarget. 8:46081–46089. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cong L, Shi J, Zhao J, Li K, Dai D, Zhang
B and Zhao W: Huaier inhibits cholangiocarcinoma cells through the
twist1/FBP1/Wnt/β-catenin axis. Mol Biol Rep. 51:8422024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|