Introduction
The International Agency for Research on Cancer
(IARC) reported that in 2020, ~2.2 million new cases of lung cancer
(LC) were diagnosed globally, leading to ~1.8 million related
deaths. These figures represent 11.4% of all newly diagnosed cancer
cases and 18.0% of all cancer-related mortalities (1). LC remains a significant global health
concern, with ~28% of cases being diagnosed at an early stage and
>50% of patients exhibiting distant metastasis at the time of
the initial diagnosis (1,2). Furthermore, LC is characterized by
high recurrence and metastasis rates, low cure rates and a poor
overall 5-year survival rate of 22% (2,3).
Histologically, LC is primarily classified into two primary types:
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-SCLC (NSCLC), with NSCLC
comprising ~80–85% of all LC cases. Therefore, the importance of
early detection and prompt intervention for patient is important,
as these factors are crucial for enhancing patient prognosis and
improving survival rates.
Under normal physiological conditions, the body
obtains energy through the respiratory process to maintain the
normal functioning of its structure and functions, with oxygen
serving an indispensable role in metabolic processes (4). The oxygen content in ambient air is
~21%, equivalent to an atmospheric pressure of 150 mmHg, whereas
the oxygen level in most healthy mammalian tissues is maintained
between 2–9%, averaging ~40 mmHg. By contrast, the oxygen
concentration within tumor tissue typically ranges from 1–2%
(5,6). Hypoxia is generally defined as an
oxygen concentration in tissues of ≤2%, while severe hypoxia refers
to an oxygen content of ≤0.02% (6).
Hypoxia is a characteristic of the solid tumor microenvironment
(TME) (5). Solid tumors often
exhibit acute, chronic or cyclic hypoxia, all of which stem from an
imbalance between oxygen demand and supply (7). Acute hypoxia, or perfusion-limited
hypoxia, is caused by irregular dilation of the tumor vasculature
or excessive aggregation of tumor cells leading to vascular
occlusion. Chronic hypoxia arises from the continuous proliferation
of tumor cells, which consume a large amount of oxygen near the
vasculature, resulting in inadequate oxygen supply to distal cells
(8). Intermittent hypoxia is caused
by transient occlusion of the immature and unevenly distributed
tumor vasculature, lasting from several minutes to several days
(5). The hypoxic TME is a critical
factor driving tumor progression, affecting tumor metabolism and
its surrounding microenvironment through various mechanisms,
thereby influencing tumor biological characteristics and treatment
efficacy.
Given the pivotal role of hypoxia in the progression
of NSCLC, exploring its potential molecular mechanisms and possible
therapeutic intervention strategies is important for improving
patient prognosis and survival rates. While there is increasing
awareness of the impact of hypoxia on NSCLC, the precise
localization and interaction of hypoxic conditions with tumor
biology are currently unknown. The present review integrated
previously published research findings and aimed to elucidate how
hypoxia affects the behavior of cancer cells through a series of
mechanisms, offering a solid theoretical basis and practical
operational guidance for early detection and precise targeted
therapy of NSCLC.
Mechanisms of hypoxia in NSCLC
The TME is composed of multiple components,
including tumor cells, blood vessels, immune cells,
cancer-associated fibroblasts, signaling molecules and the
extracellular matrix (ECM). All of these elements serve crucial
roles in tumor progression (9,10).
Tumor cells can actively alter the composition of the TME by
secreting extracellular signals to adapt to or respond to changes
in the host environment (11). In
the hypoxic microenvironment, the host promotes the progression of
NSCLC through various pathways.
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)
Cells adapt to hypoxic environments by modulating
the expression of certain genes. HIF, a key transcription factor
regulating gene expression, serves a central role in the hypoxic
response (5). HIF is a heterodimer
composed of an unstable, but critical, α subunit and a stable β
subunit. The alpha subunit has three subtypes: HIF-1α, HIF-2α and
HIF-3α. Although all subtypes are involved in regulating
inflammatory responses, typically only HIF-1α is expressed in
vivo (5). The structure of
HIF-1α and HIF-1β are key to their interactions and activation
during the hypoxic response (Fig.
1A). Under hypoxic conditions, HIF-α degradation is inhibited,
which allows HIF-α to translocate to the nucleus and bind with
HIF-β to form an active HIF transcription factor complex. This
complex can interact with specific sequences in >70 target gene
promoters, known as hypoxia response elements (HREs), to regulate
the transcription of protein-coding and non-coding RNA genes
(12) (Fig. 1B). These regulated genes serve
critical roles in multiple key biological processes, including
glucose uptake, tumor metabolism, angiogenesis, cell proliferation
and apoptosis, helping cells effectively adapt to hypoxic stress
(13).
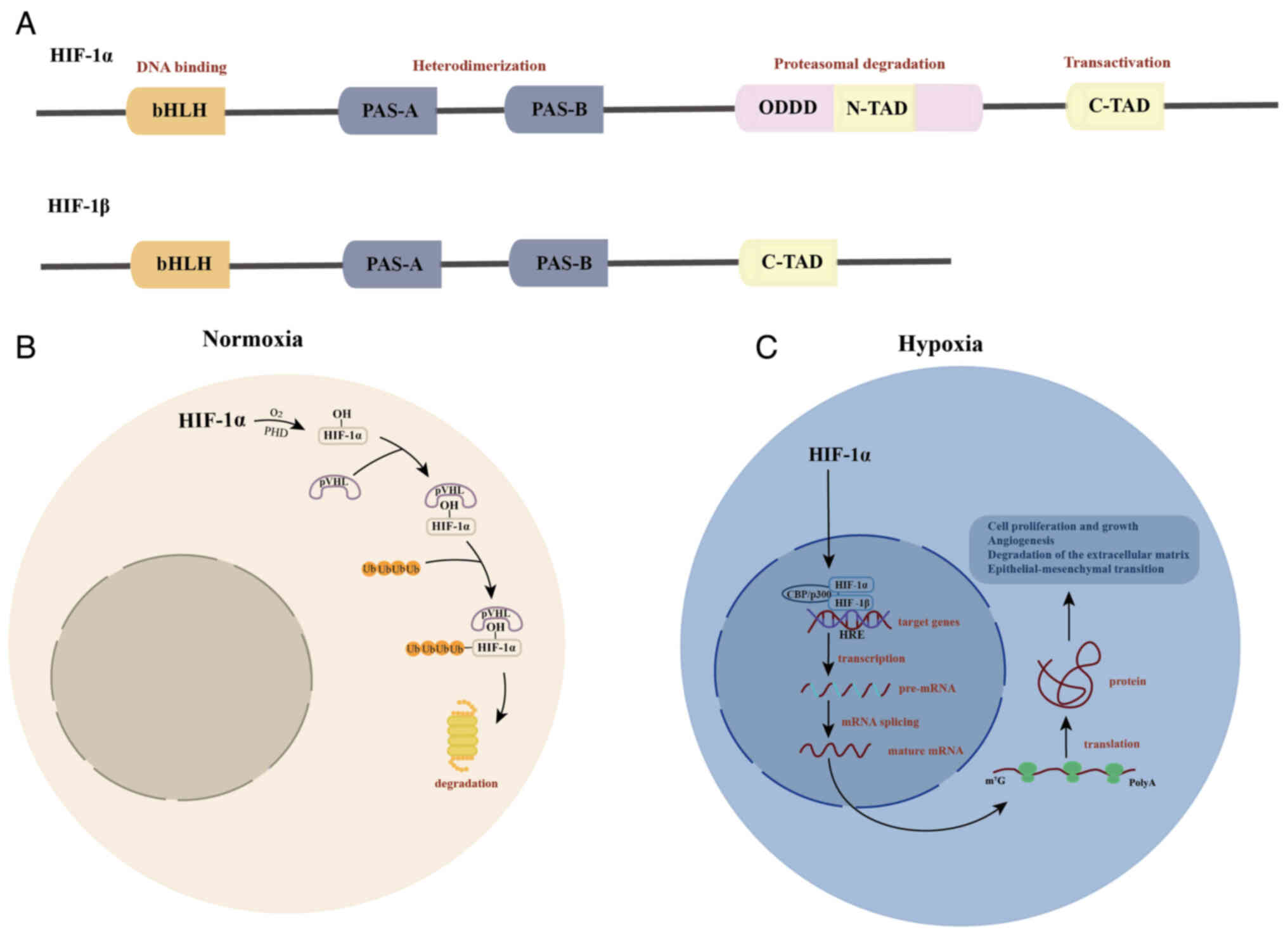 | Figure 1.Structure of HIF-1α and HIF-1β and
their role under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. (A) Structure of
HIF-1α and HIF-1β. The bHLH structural domain binds to target DNA.
The intermediate region is the PAS domain, which facilitates the
formation of heterodimers. The ODDD senses the surrounding oxygen
levels. The C-TAD enhances target gene expression by recruiting the
transcriptional co-activators CBP/p300. (B) Role of HIF under
normoxic conditions. In normoxia, PHDs hydroxylate the residues of
the ODDD, enabling the VHL tumor suppressor protein to recognize
and bind to HIF-1α, leading to its degradation via the
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. (C) Role of HIF under hypoxic
conditions. Under hypoxia, HIF-1α degradation is inhibited,
allowing it to translocate to the nucleus and dimerize with HIF-1β,
thereby activating target gene expression. PAS, Per-ARNT-Sim; ODDD,
oxygen-dependent degradation domain; C-TAD, C-terminal
transcriptional activation domain; HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor;
PHD, prolyl hydroxylase; VHL, von Hippel-Lindau; p, phosphorylated;
ub, ubiquitin. |
HIF-1α can promote the expression of various cell
proliferation factors, including insulin-like growth factor-2 and
TGF-α. Upregulation of these factors stimulates the growth and
proliferation of NSCLC cells, thereby promoting tumor development
(14). HIF-1α can also activate the
transcription of angiogenesis-related genes, including VEGF-A and
angiopoietin-2. The increased expression of these factors enhances
vasculogenesis, supplying essential oxygen and nutrients to support
both local growth and metastasis of NSCLC cells. Under the
influence of HIF-1α, the expression of proteases such as MMPs is
significantly upregulated. These enzymes can degrade the ECM,
facilitating tumor cell migration and invasion of surrounding
tissues, thereby promoting NSCLC spread and metastasis (15). Additionally, hypoxia enhances the
expansion and motility of NSCLC cells by inhibiting the expression
of connexin (CX) proteins, thereby impairing intercellular
communication. Under hypoxic conditions, the expression of certain
connexin proteins, particularly CX26 and CX43, decreases, making
these proteins more susceptible to degradation or internalization.
The disruption of intercellular communication not only disrupts
signal synchronization and metabolic exchange but also further
promotes the proliferation and migration of tumor cells. Moreover,
this communication barrier also activates the P53/MDM2
proto-oncogene signaling pathway, accelerating the malignant
progression of NSCLC (16). Under
hypoxic conditions, the activation of HIF-1α can induce EMT in
NSCLC cells. During this process, epithelial cells lose their
polarity and intercellular adhesion properties, transforming into
cells with mesenchymal features. This transformation enhances their
migration and invasion abilities, further promoting the malignant
progression of tumors (17,18).
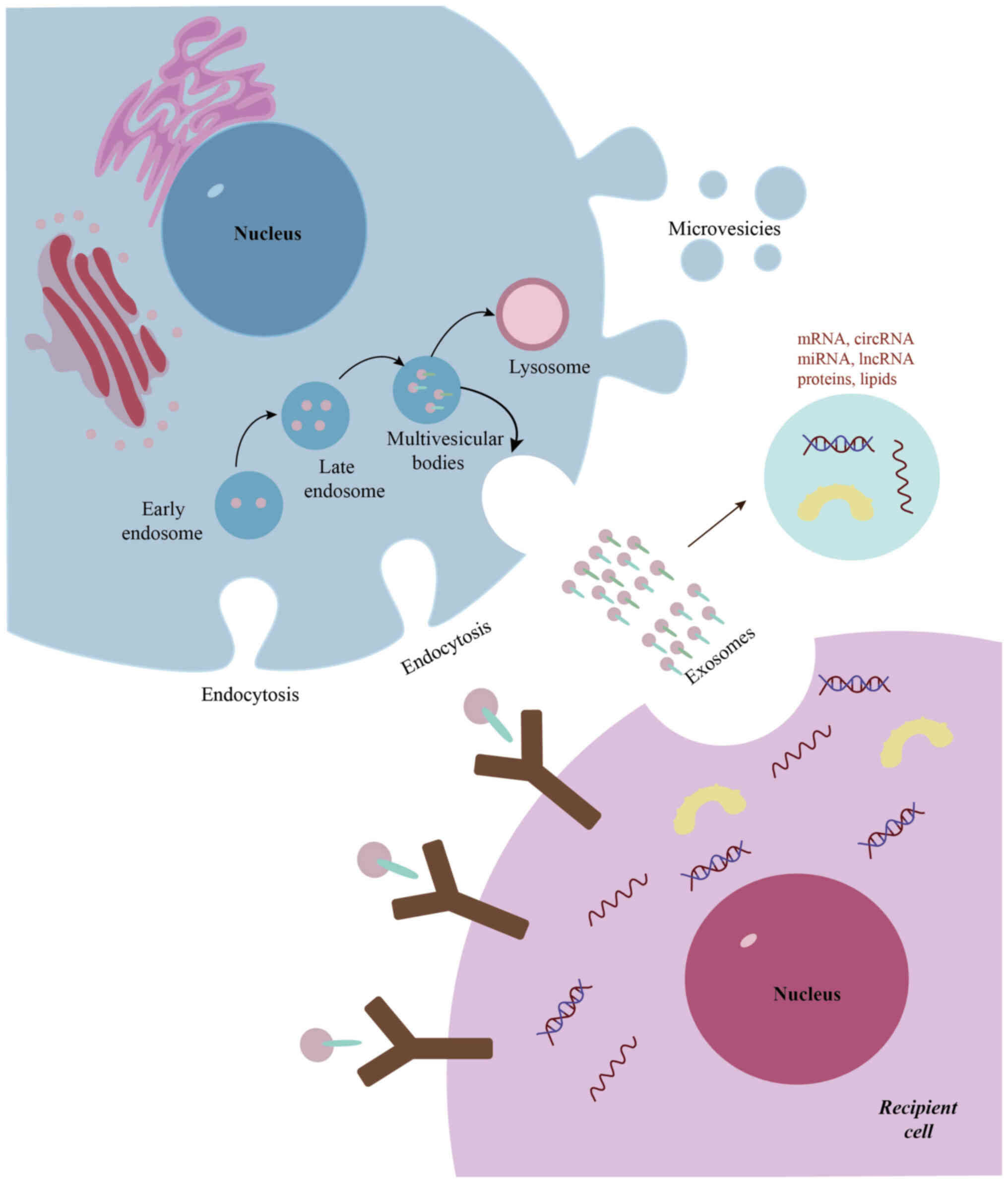
Release of exosomes
Exosomes are nanoscale extracellular vesicles
enclosed by a lipid bilayer membrane and actively secreted by
cells. Their biogenesis is a tightly regulated and complex process.
The formation of exosomes is initiated by the invagination of the
plasma membrane, leading to the generation of early endosomes.
These early endosomes undergo intracellular maturation to form late
endosomes, which subsequently give rise to multivesicular bodies
(MVBs) through intraluminal vesicle budding (19). The fusion of MVBs with the plasma
membrane facilitates the release of these vesicles into the
extracellular milieu, a process defined as exosome secretion
(Fig. 2) (19). Exosomes serve an essential role in
intercellular communication by transporting a wide range of
bioactive molecules, including mRNAs, circular RNAs (circRNAs),
long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs; miRs), proteins,
lipids and other molecular entities (20). It has been previously reported that
under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1 facilitates the release of
tumor-derived exosomes by upregulating pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2)
mRNA expression levels. PKM2, upon upregulation and phosphorylation
in tumors, functions as a protein kinase, phosphorylating
synaptosome-associated protein 23. This phosphorylation event
promotes the exocytic release of exosomes (21,22).
Exosomes, in turn, drive the growth and progression of NSCLC by
transmitting key signals that influence processes such as
glycolysis, angiogenesis, tumor cell migration, invasion and immune
infiltration (23). Tumor cells in
hypoxic environments exhibit abnormal proliferation and altered
intercellular communication, often accompanied by increased exosome
secretion. During this process, the hypoxic environment
specifically regulates the expression of certain molecular
components in exosomes, adapting to the needs of the TME by
upregulating or downregulating key molecule regulators, such as
miRNAs (23,24).
For example, miR-21 upregulates the expression and
activity of HIF-1α, further activating glycolysis-related genes and
increasing radiation resistance in NSCLC (25). HIF-1α also promotes endothelial cell
(EC) angiogenesis by downregulating miR-186-5p and upregulating
protein kinase C-α (26). Under
chronic hypoxic conditions, miR-191 accelerates the proliferation
and migration of NSCLC cells by reducing the levels of nuclear
factor I A and its downstream oncogene CCAAT enhancer binding
protein α (27). Under low oxygen
conditions, lncRNA pvt1 is overexpressed in lung cancer cells and
upregulates HIF-1α by binding to miR-199a-5p, thereby promoting
cell proliferation and malignant transformation (28). However, intermittent hypoxia
increases the expression level of miR-31-5p, activating WD
repeat-containing protein 5, thereby enhancing EMT in tumor cells
(29). Hypoxia can also stabilize
HIF-1α by promoting its binding with mutant p53 and forming a
complex that downregulates miR-129-1-3p. This, in turn, upregulates
protein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent 1D,
which dephosphorylates and inhibits p53, promoting the growth,
survival and metastasis of NSCLC cells (30).
Macrophages are key immune cells that serve a
pivotal role in early immune surveillance and response to tumors.
They recognize and eliminate tumor cells and also activate other
immune cells through antigen presentation, triggering specific
immune responses. However, tumor cells interact with macrophages by
secreting molecules such as exosomes that regulate macrophage
polarization, thereby affecting their function. Tumor-associated
macrophages (TAMs) can exhibit two distinct phenotypes: M1 and M2
(31). M1 phenotype macrophages
promote inflammatory responses and inhibit tumor growth, while M2
phenotype macrophages have anti-inflammatory effects, suppress
immune responses and promote tumor development (32). Under hypoxic conditions, LC cells
further promote M2 polarization of TAMs by upregulating miR-21 and
miR-1290. This polarization enhances angiogenesis and promotes
tumor invasion and metastasis, thereby accelerating LC progression
(33,34). Therefore, hypoxia is not only a
result of tumorigenesis but also an important driving factor for
tumor infiltration and growth (23,35).
Depending on the duration and severity of hypoxia, its impact on
tissues may be beneficial or harmful (36).
Metabolic reprogramming
Under hypoxic conditions, NSCLC cells undergo
metabolic reprogramming to adapt to the hypoxic environment and
maintain their growth and survival. This process is related to the
Warburg effect, where tumor cells convert glucose to lactate via
glycolysis, even when oxygen is abundant and mitochondrial function
is normal, rather than through the more efficient oxidative
phosphorylation pathways (37).
This metabolic transformation not only improves the efficiency of
energy production but also provides necessary biosynthetic
precursors for tumor cells to support their rapid proliferation
needs (38). In NSCLC cells, the
expression of key glycolytic enzymes, such as hexokinase,
phosphoglycerate kinase 1, lactate dehydrogenase and glucose
transporter 1 (GLUT-1) are increased, thereby promoting increased
glucose uptake and lactate production (39). Lactate is not only a product of
glycolysis but also serves multiple roles in the TME. It can create
an acidic microenvironment that is conducive to the survival and
proliferation of NSCLC cells and can also regulate certain
signaling pathways to promote tumor progression (40). Specifically, lactate can activate
the ERK/STAT3 signaling pathway, induce TAMs to polarize towards
the M2 phenotype and stimulate angiogenesis, which together promote
tumor growth and metastasis (41,42).
Additionally, lactate also has immunosuppressive effects, which can
regulate the function of immune cells, thereby limiting the
effectiveness of antitumor immune responses (43,44).
Although glycolysis is the primary energy source for NSCLC cells,
fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation
also serve important roles in cellular metabolism, signal
transduction and tumor progression (45). Mitochondria not only produce ATP
through oxidative phosphorylation but also participate in fatty
acid oxidation, redox regulation and the production of reactive
oxygen species (ROS), which affect cell proliferation, survival and
migration. Thus, NSCLC cells achieve adaptive growth in complex
TMEs and promote tumor growth and metastasis by integrating
multiple metabolic pathways such as glycolysis, lactate
accumulation and mitochondrial metabolism (45).
Antitumor treatment
Hypoxia, a common characteristic of tumor growth,
poses a significant challenge to cancer therapy. Hypoxic
environments weaken the efficacy of antitumor therapy through
various mechanisms. These mechanisms mainly include decreasing DNA
damage repair and promoting the development of invasive phenotypes
in tumor cells, thereby enhancing the survival rate of tumor cells
(46). Therefore, the hypoxic
microenvironment serves a critical role in determining the
effectiveness of radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy and
targeted therapy.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is a crucial approach for treating
tumors and its mechanism of action involves utilizing high-energy
electrons photons, such as X-rays or γ-rays, to interact with atoms
in the body and release high-energy electrons. These electrons can
trigger cellular damage, particularly DNA damage, thereby
inhibiting the proliferation and survival of tumor cells (47). The mechanism of action of
radiotherapy primarily encompasses two pathways: direct and
indirect. In the direct mechanism, radiation photons directly
interact with DNA molecules, causing single-strand or double-strand
breaks, which can prevent cell division and may induce cell
necrosis or apoptosis (48). The
indirect mechanism involves the interaction between radiation and
water molecules, generating free radicals such as hydrogen atoms,
hydroxyl radicals and hydrogen peroxide. These free radicals
further react with oxygen to generate ROS, which can damage
macromolecules such as DNA, proteins and lipids, leading to
cellular dysfunction, alterations in signal transduction and
long-term cellular damage (49).
The efficacy of radiotherapy is closely linked to the oxygen level
of tissues. In hypoxic tumor cells, due to the insufficient oxygen
available to support redox reactions, DNA repair mechanisms may not
effectively repair radiation-induced damage (50). Therefore, to achieve similar
damaging effects as in oxygen-rich cells, hypoxic tumor cells
require an increase in radiation dose by 2–3 times, a phenomenon
known as the oxygen enhancement ratio (OER) (51).
Chemotherapy
To support their rapid proliferation, tumors form an
invasive and irregular vascular system. However, these neovessels
often have abnormal structures and impaired functions, leading to
low drug delivery efficiency and reduced permeability and
distribution of chemotherapeutic agents. This significantly reduces
drug exposure to tumor cells (52).
Under hypoxic conditions, the HIF-1α and p53 genes play key roles
in regulating the resistance of NSCLC to cisplatin. Specifically,
HIF-1α promotes metabolic adaptation by enhancing glycolysis and
limiting the accumulation of ROS, thereby increasing resistance to
cisplatin. Simultaneously, p53 inhibits the progression of the cell
cycle from the G1 phase to the S phase by activating the downstream
target gene p21, further reducing the sensitivity of tumor cells to
cisplatin (53). Additionally, cell
cycle arrest under hypoxic conditions triggers metabolic
reprogramming, including upregulation of glycolysis pathways and
antioxidant responses, which further enhance cisplatin resistance
(41).
Immunotherapy
Hypoxia can also impair the antitumor immune
response. Under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1α is activated, leading to
the upregulation of CD47 expression. CD47 is a transmembrane
protein that interacts with the macrophage signal regulatory
protein α, sending a signal to macrophages to prevent degradation.
This signaling inhibits the recognition and phagocytosis of tumor
cells by macrophages, promoting immune evasion and thus
facilitating tumor growth and metastasis (54). Furthermore, dendritic cells (DCs)
serve a crucial role in activating CD4+ and
CD8+ T cells via antigen presentation, which is hindered
by chronic hypoxia (55). Key
factors such as IL-10 and VEGF induced by hypoxia can suppress the
differentiation and maturation of DCs, thereby impairing T cell
responses and reducing antitumor immunity (56,57).
In the hypoxic microenvironment, activation of the mTOR-HIF-1α
pathway also induces the upregulation of extracellular nucleotide
enzymes CD39 and CD73 in myeloid-derived suppressor cells,
converting extracellular ATP/ADP to adenosine. Conversely,
adenosine suppresses immunotherapy, induces cell apoptosis and
further impairs immune response by binding to adenosine A2A
receptors on T cells and natural killer cells (58,59).
Targeted therapies
The hypoxic microenvironment can also affect the
efficacy of targeted therapy. For example, gefitinib is a tyrosine
kinase inhibitor commonly used to treat NSCLC. However, under
hypoxic conditions, gefitinib upregulates IL-6 expression and
activates inflammatory pathways such as the TNF, NF-κB and JAK-STAT
pathways, leading to the enrichment of LC stem cells and initiation
of the EMT, ultimately enhancing resistance to gefitinib (60). In cases of NSCLC with EMAP like
4-ALK receptor tyrosine kinase (ALK) rearrangement, although ALK
inhibitors usually show good efficacy, some patients develop
resistance to agents such as crizotinib in hypoxic environments.
The emergence of this resistance is closely related to the
upregulation of HIF-1α and its downstream regulatory factor Slug
under hypoxic conditions, which promote the EMT process and
significantly enhance the migration and invasion ability of cancer
cells, thereby conferring tumors with resistance to ALK inhibitors
(61).
Hypoxia detection in NSCLC
Hypoxia serves a critical role in the progression of
NSCLC. Early detection of the hypoxic state of tumor cells can
facilitate timely intervention measures and effectively correct
these conditions (62). Currently,
hypoxia detection in laboratory cells and human tumors can be
categorized based on the types of substances measured: physical
substances, such as oxygen partial pressure and oxygen saturation,
biological substances, such as enzymes and proteins, and chemical
substances, such as signaling pathway products. Detection
technology can be categorized as direct or indirect based on the
measurement approach and can also be categorized as transient or
dynamic based on the nature of the detection process (Table I) (63).
 | Table I.Comprehensive summary of methods for
detecting hypoxia in non-small cell lung cancer. |
Table I.
Comprehensive summary of methods for
detecting hypoxia in non-small cell lung cancer.
| A, Direct
detection |
|---|
|
|---|
| Method of
detection | Analyte/marker | Techniques or
tools | Principles | Advantages | Disadvantages | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Physical | PO2 | Electrochemical
probe | Measurement of
current generated by electrode redox | Direct measurement
of tissue PO2 and is classed as the gold standard in
clinical testing | Probes may damage
tumor tissue and instantaneous detection cannot track changes over
time | (64,65) |
|
|
| Optical probe | Detecting the
intensity or lifetime of probes | High sensitivity
and resolution, non-invasive and enables real-time monitoring | Probes measure
oxygen levels in blood rather than tissues and it necessitates
particular environmental conditions | (66,67) |
|
| B, Indirect
detection |
|
| Method of
detection |
Analyte/marker | Techniques or
tools |
Principles |
Advantages |
Disadvantages | (Refs.) |
|
| Vascular system
testing | Vascular function
and morphology analysis | CT perfusion
imaging, MRI and near-infrared spectroscopy | Evaluating tumor
vascular abnormalities and blood flow | Non-invasive,
analyses vascular function and allows early detection | Uneven blood flow
and individual variations make blood flow parameters inadequate for
assessing tissue oxygen supply | (68–71) |
| Hypoxia
imaging | Oxygen metabolism
tracers imaging | Positron emission
tomography | Radiotracer
probe-based oxygen metabolism evaluation | High sensitivity
and specificity and can analyze the whole tumor tissue | Can cause radiation
hazards and has a longer half-life of the tracer | (8,73,74) |
|
|
| MRI | Blood oxygen
level-dependent-MRI uses the magnetic property comparison of
oxy-vs. deoxyhemoglobin whereas tissue oxygen level-dependent-MRI
measures tissue oxygenation via longitudinal relaxation time
changes | No radiation hazard
and enhanced clarity of soft tissue visualization | Time-consuming and
cannot be monitored in real-time | (75–78) |
|
|
| Electron
paramagnetic resonance imaging | Based on the spin
distribution of unpaired electrons in free oxygen molecules | High sensitivity,
experiences minimal interference from external factors and is
effective in detecting low concentrations of free radicals | Low spatial
resolution, rapid signal decay with tissue depth and high cost of
imaging equipment | (79,80) |
| Measurement of gene
expression levels | Hypoxia inducible
factor-1α, solute carrier family 2 member 1, Egl-9 family hypoxia
inducible factor 2, carbonic anhydrase 9 and VEGF | Quantitative PCR,
RNA sequencing and Northern blotting | Hypoxia-induced
gene expression for tumor hypoxia assessment | Can measure
molecular changes in hypoxia and is useful for tissue
sectioning | Tissue samples are
required, is unable to assess dynamic changes in vivo and
has a high cost | (81–84) |
| Measurement of
protein expression levels | Solute carrier
family 2 member 1, carbonic anhydrase 9, osteopontin and
nitroreductase | Western blotting,
immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence and ELISA | Hypoxia-related
protein expression for tumor hypoxia assessment | High sensitivity
and is appropriate for clinical and laboratory analysis | Tissue samples are
required, is unable to assess dynamic changes in vivo and
has a high cost | (78,85–88) |
Direct detection of oxygen
concentration
Physical sensors are among the most direct methods
for detecting cellular hypoxia. Electrochemical probes and optical
sensors can directly measure the oxygen partial pressure in tumor
tissue, providing accurate tissue oxygenation values. The working
principle of an electrochemical probe is to measure the oxygen
partial pressure by detecting the current generated by the oxygen
reduction reaction at the working electrode and the oxidation
reaction at the anode (64). This
technique remains the gold standard in the clinical field and with
the assistance of CT-guided oxygen partial pressure measurement, it
is now possible to detect hypoxia in deeper tumor regions (65). However, needle-based detection
methods may cause damage to tumor tissue, making it difficult to
distinguish between necrotic and hypoxic areas and these methods
can only provide transient measurements, limiting the possibility
of continuous monitoring (65).
Alternatively, optical probes detect oxygen partial pressure by
assessing the effect of oxygen partial pressure on the luminescent
intensity of fluorescent substances, a process known as quenching
(63). Metal-organic complexes,
such as Pt(II), Pd(II), Ru(II) and Ir(III), are commonly used as
phosphorescent probes (66). These
probes interact with oxygen molecules, shortening their
phosphorescence lifetime and leading to quenching phenomena. By
measuring changes in phosphorescence intensity or lifetime, in
combination with the Stern-Volmer equation, the oxygen partial
pressure in tumor tissue can be quantified (67). These phosphorescent probes offer
high sensitivity, high resolution and the ability to achieve
real-time, non-invasive monitoring, thereby demonstrating
significant advantages in effectively identifying tissue
hypoxia.
Indirect detection of hypoxic
microenvironment
Vascular system testing
The hypoxic state of tumors is closely linked to
abnormalities in their vascular system. The structural and
functional defects of the tumor vasculature lead to insufficient
oxygen supply, making it particularly important to evaluate these
vascular parameters that are critical for detecting hypoxia. The
generation of hypoxia is generally believed to be caused by three
mechanisms: i) Diffusion, due to distance from perfusing blood
vessels; ii) intermittent, fluctuations in vessel opening and
closing; and iii) perfusion-related, low blood flow efficiency
(68). Various imaging techniques,
such as cryophotometry, near-infrared spectroscopy and MRI, have
been used to evaluate tumor vascular features such as distance,
density, distribution and oxygenation status (69). Additionally, CT perfusion imaging, a
non-invasive functional imaging method, can evaluate tumor
morphology and also assess microcirculation parameters such as
blood volume, blood flow, mean transit time and permeability
surface, which provide valuable insights for understanding hypoxia
(70,71). However, due to uneven blood flow
distribution, variations in oxygen consumption between individuals
and increased hemoglobin levels caused by chronic hypoxic
adaptation, relying solely on blood flow parameters cannot fully
capture tissue-level oxygen supply and demand dynamics (72). Therefore, combining multiple
parameters to evaluate the TME is essential for a comprehensive
assessment of hypoxia.
Hypoxia imaging detection
Optical imaging provides a non-invasive and dynamic
approach to assessing tissue oxygenation. Positron emission
tomography (PET) is one of the most widely adopted methods of
optical imaging. PET assesses oxygen metabolism in tissues and
identifies preclinical or clinical hypoxia through the use of
radioactive tracer probes (73).
Unlike histological testing, PET can monitor the entire tumor
comprehensively and boasts higher sensitivity and specificity
compared with MRI, with fewer artifacts (8). Presently, two primary tracers are
employed for hypoxia detection: 18F-labeled
nitroimidazole and Cu-labeled diacetylbis (N4-methylaminothiourea)
analogs (74). The most widely used
tracer is 18F-Fluoromisonidazole (18F-FMISO), a highly
lipophilic 2-nitroimidazole analog. However, its slow plasma
clearance rate necessitates prolonged imaging times. To overcome
this, new hydrophilic tracers such as fluazomycin cytarabine and
fluorinated ethyl imidazole derivatives have been developed. These
tracers have faster plasma clearance rates, which enable quicker
imaging and improve the efficiency and accuracy of hypoxia
detection (75).
MRI includes techniques like blood oxygen
level-dependent (BOLD) and tissue oxygen level-dependent (TOLD)
imaging. Compared with PET, MRI has the advantages of high soft
tissue contrast and no radiation exposure, making it particularly
suitable for individuals with conditions that contraindicate
radiation. These include pregnant women, children, patients with
thyroid disorders and individuals with suppressed immune systems
(75). In BOLD-MRI, contrast arises
from the differing magnetic properties of oxyhemoglobin
(diamagnetic) and deoxyhemoglobin (paramagnetic), reflecting local
concentrations of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin (76). TOLD-MRI detects tissue hypoxia by
measuring free oxygen molecules within tissues. As mitochondria
consume oxygen, the remaining oxygen dissolves in the plasma,
leading to an increase in longitudinal relaxation time (T1),
thereby evaluating tissue oxygenation (77). While MRI is highly effective in the
3D mapping of tumor hypoxia, it is time-consuming and does not
allow for real-time monitoring (78).
Another method for detecting oxygen levels is
electron paramagnetic resonance imaging (EPRI). Analogous to MRI
which depicts proton distribution, EPRI measures the spin
distribution of unpaired electrons in free oxygen molecules
(76). Oxygen molecules are
paramagnetic and possess two unpaired electrons in their ground
state. When oxygen molecules interact with probes, which are
typically paramagnetic substances, the collision between the
unpaired electrons of oxygen and the probe alters the energy state
of the probe (79). Specifically,
this interaction alters the probe's spin state, which consequently
shifts its resonance frequency. EPRI detects these frequency
shifts, enabling precise the recording of oxygen levels (80). EPRI exhibits high sensitivity and is
less influenced by external factors, making it a promising tool in
clinical research.
Gene and protein markers
In the hypoxic microenvironment of NSCLC, HIF-1α
serves as a key transcription factor that regulates the expression
of various hypoxia-responsive genes. Due to the short half-life of
HIF-1α and its difficulty for use in direct labeling, studies
typically indirectly evaluate hypoxic status by measuring gene
expression levels regulated by HIF-1α. For instance, solute carrier
family 2 member 1 (SLC2A1) is a target gene of HIF-1α, which
enhances glycolytic activity by upregulating the expression of
SLC2A1, contributing to energy generation and biosynthesis in tumor
cells. The upregulation of SLC2A1 expression is strongly associated
with the prognosis of patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma
and can also serve as a key hypoxia biomarker (81). Similarly, Egl-9 family hypoxia
inducible factor 2 (EGLN2) is a HIF-1α hydroxylase that regulates
hypoxia by promoting the hydroxylation and degradation of HIF-1α.
During hypoxia, the decrease in EGLN2 activity leads to the
stabilization of HIF-1α, thereby activating the hypoxic pathway.
The expression of EGLN2 may offer diagnostic and prognostic value
in lung adenocarcinoma (82).
Additionally, genes such as carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9) and VEGF,
which are widely expressed in NSCLC, are closely correlated with
the degree of cellular hypoxia, tumor invasiveness and the
effectiveness of radiotherapy and immunotherapy (83,84).
To detect hypoxia in tumors, studies commonly employ
immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence techniques to assess
protein expression associated with hypoxia, primarily involving
biomarkers like GLUT-1 (SLC2A1), CA9 (CA-IX), osteopontin (OPN) and
nitroreductase (NTR). SLC2A1 supports glycolysis by enhancing
glucose uptake, providing tumor cells with the energy and raw
materials necessary for metabolism (85). CA-IX catalyzes the formation of
carbonic acid from carbon dioxide and water, promoting
extracellular acidification and thereby enhancing tumor
invasiveness (86). OPN, as a
hypoxia biomarker, is closely related to increased invasion and
metastasis potential in NSCLC (87,88).
NTR is an enzyme expressed only under hypoxic conditions and can
reflect the degree of tumor hypoxia based on its activity level
(78). In hypoxic environments,
nitroimidazole is reduced by intracellular NTRs to generate
reactive intermediates that disrupt DNA repair enzymes and cell
cycle regulators, thereby inhibiting tumor cell survival (76). Currently, derivatives of
2-nitroimidazole, such as pimonidazole and EF-5, have become key
tools for identifying and quantifying hypoxic regions within tumor
tissues. By detecting specific antibodies like hypoxyprobe and
ELK3-51, it is possible to efficiently map the distribution of
hypoxia in tumors (76).
Targeted hypoxia in NSCLC
In NSCLC, the hypoxic microenvironment serves a
crucial role in regulating tumor growth and invasion. Targeted
therapy strategies aimed at this microenvironment have attracted
widespread attention, as hypoxia not only affects the
proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells but also
activates a series of adaptive responses, such as angiogenesis,
metabolic reprogramming and anti-apoptotic mechanisms. These
responses enhance tumor invasiveness and lead to the development of
therapeutic resistance. Therefore, targeted hypoxia therapy not
only directly inhibits tumor progression but also has the potential
to improve the efficacy of conventional treatment methods.
Currently, several targeted therapies aimed at tumor hypoxia are
being actively researched and developed (Table II).
 | Table II.Summary of targeted hypoxia therapies
for non-small cell lung cancer. |
Table II.
Summary of targeted hypoxia therapies
for non-small cell lung cancer.
| Therapeutic
approaches | Methods and drug
treatments | Mechanism of
action | Advantages | Disadvantages | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Enhancing tissue
oxygenation | Hyperbaric oxygen
therapy, normobaric hyperoxia and aerobic exercise | Increases oxygen
levels in tumor tissues, inhibits cell proliferation and enhances
therapeutic effects | Increases oxygen
supply and enhances the effect of radiotherapy and
chemotherapy | High-concentration
oxygen induces oxygen toxicity, tissue damage and oxidative stresss
and the efficacy of aerobic exercise remains unclear | (7,89–94) |
| Reduction of oxygen
consumption | Metformin,
Atovaquone, Papaverine, heme-segregating protein 2 | Inhibition of
oxidative phosphorylation reduces the oxygen demand of tumor
cells | Improves the tumor
hypoxic environment and enhances treatment sensitivity | Can cause metabolic
toxicity and research on this therapy is currently
underdeveloped | (98–102) |
| Restoration of
blood flow | Nitroglycerin, and
Cilengitide in combination with verapamil | Improved tumor
blood flow and enhanced drug and oxygen delivery | Reduces glycolysis
and improves distribution of chemotherapy and targeted drugs | Individual
differences exist and excessive blood flow may promote tumor
spread | (104–107) |
| Targeting pathways
of HIF-1α | Acriflavine,
Polyamides, Temsirolimus, Trametinib and Bevacizumab | Inhibits HIF-1α
activity, targets HIF-1α signaling and inhibits angiogenesis | Inhibits tumor
growth and improves the tumor hypoxic microenvironment | Monotherapy may
induce resistance and the clinical efficacy and safety require
further validation | (108–117) |
| Hypoxia-activated
prodrugs | TPZ, TH-302,
PR-104, and EO9 | Targeting hypoxic
tumor regions | Precisely kills
hypoxic tumor cells while minimizing normal tissue damage | Limited reach to
avascular areas and poor clinical performance of some drugs | (121–126) |
| Improvement of
radiotherapy | Radiosensitizers,
carbon ion radiotherapy and dose painting | Enhances
radiotherapy sensitivity, higher linear energy transfer and precise
dose distribution | More precise and
higher-dose radiotherapy efficacy and minimizes impact on normal
cells | Further clinical
validation needed | (127–130) |
Enhancing tissue oxygenation
The goal of oxygen therapy is to increase the levels
of dissolved oxygen in plasma and enhance tissue oxygenation,
thereby slowing down tumor progression and improving treatment
efficacy. Currently, various key strategies including hyperbaric
oxygen therapy (HBO), normobaric hyperoxia (NBO) and aerobic
exercise are being explored to augment tissue oxygen levels. HBO
involves administering 100% oxygen at a pressure of 1.5–2.5
atmospheres absolute. Previous studies have shown that HBO can
significantly reduce the expression level of HIF-1α and its
downstream target genes, exert anti-angiogenic effects, reduce
vascular density, inhibit tumor cell proliferation and thereby
improve chemotherapy efficacy (7,89). NBO
involves the delivery of high concentrations of oxygen via masks or
shields, primarily by generating ROS to inhibit tumor growth
(90). Although NBO is not as
effective as HBO in enhancing the oxygenation of arteries and tumor
tissues, it is considered more practically valuable due to its
increased safety (91). However,
the clinical use of HBO therapy faces certain challenges, mainly
due to the possibility of causing some adverse reactions. These
reactions include barotrauma to the middle ear, paranasal sinuses
and lungs, ROS-induced damage to alveolar epithelium and pulmonary
vascular endothelium and excessive production of nitric oxide (NO)
due to aberrant activation of NO synthase. These mechanisms trigger
pro-inflammatory pathways, such as the NF-κB pathway, amplifying
local and systemic inflammation and worsening tissue damage
(92).
Additionally, aerobic exercise has been shown to
regulate the tumor vasculature and promote the relative
normalization of dysfunctional tumor blood vessels (93). Jo et al (94) reported that sustained aerobic
exercise improved lung function in NSCLC mice, increased oxygen
saturation within tumor cells and elevated HIF-1α and ROS levels,
thereby enhancing the efficacy of radiotherapy. In conclusion,
oxygen-based therapies have potential in improving tumor
oxygenation and enhancing treatment efficacy. However, a detailed
assessment of the potential risks and benefits of this approach is
particularly important for optimizing its clinical application.
Reduction of oxygen consumption
rate
Tumor cells partially produce ATP through the
mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) pathway, in which
hemoglobin serves a key role in the mitochondrial electron
transport chain (ETC) complexes II–IV, thereby promoting ATP
synthesis (95). In recent years,
certain drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration
(FDA), such as metformin, atovaquone and papaverine, have been
shown to improve the hypoxic TME by inhibiting the OXPHOS pathway
(96,97). Metformin binds to triphenylphosphine
to generate MitoMet molecules, allowing the drug to accumulate in
the mitochondria of tumor cells. MitoMet can inhibit mitochondrial
complex I, thereby disrupting the function of ETC, increasing ROS
production, inducing oxidative stress, leading to lipid
peroxidation and ultimately causing tumor cell death (98). Atovaquone is an antimalarial drug
that reduces hypoxia in NSCLC and improves cellular oxygenation by
inhibiting complex III of OXPHOS (99). Papaverine is a smooth muscle
relaxant and its derivative, papaverine pyrazole (PPV), temporarily
reduces tumor hypoxia by reversibly inhibiting complex I, thereby
enhancing the sensitivity of tumor cells to radiotherapy (100). Additionally, the inhibition
mechanism of OXPHOS is closely associated with the action of
heme-segregating proteins (HSPs), particularly HSP2. These proteins
inhibit mitochondrial OXPHOS by limiting heme uptake in tumor
cells, reducing oxygen consumption and ATP synthesis (101,102). Overall, targeting OXPHOS and
related metabolic pathways offers a promising strategy for the
treatment of NSCLC. Although these therapies have shown some
potential, their toxicity and long-term efficacy still require
further in-depth research to ensure their safety and effectiveness
in clinical applications.
Restoration of blood flow
Acute hypoxia in tumors is often caused by vascular
occlusion. Restoring blood flow can not only reduce the glycolytic
metabolism of tumor cells but also improve the distribution of
chemotherapy or targeted therapy, thereby significantly enhancing
the therapeutic effect (103).
Nitroglycerin, as a vasodilator, is primarily converted to NO
through the mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase and PI3K pathways,
thereby inducing vasodilation, improving the oxygenation status of
tumor tissue and enhancing the efficacy of anticancer drugs
(104,105). Additionally, the Arg-Gly-Asp
analogue cilengitide, can target αVβ3 and αVβ5 integrins on tumor
ECs, regulate VEGFR2 expression and promote VEGF-dependent
angiogenesis. Verapamil, a calcium channel blocker with
vasodilatory effects, can enhance chemotherapy efficacy. When used
in combination with cilengitide and gemcitabine, low-dose
cilengitide significantly enhances the cytotoxic activity of
gemcitabine against NSCLC cells (106). However, an excessive increase in
blood flow may promote tumor growth, so the efficacy of this
approach is highly dependent on tumor type and individual
differences among patients. It is crucial to dynamically adjust
treatment strategies within the time frame of vascular
normalization to achieve optimal treatment outcomes (107).
Targeting upstream and downstream
pathways of HIF-1α
HIF-1α serves a critical role in inflammation and
hypoxia and strategies targeting HIF-1α have shown potential in
reducing inhibiting the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells.
Studies have demonstrated that Acriflavine binds to the
Per-ARNT-Sim domain B subdomain of HIF-1α, thereby preventing the
dimerization of the α and β subunits. In addition, polyamides and
Echinomycin can inhibit the binding of the HIF-1 dimer to the HRE
sequence of target genes. Compounds such as Chetomin, Bortezomib
and Amphotericin B inhibit the transcriptional activity of HIF-1α
through different mechanisms, while EZN-2968 suppresses the
synthesis of the HIF-1α protein by blocking the translation process
of HIF-1α mRNA (108).
Collectively, these compounds effectively inhibit tumor growth and
angiogenesis by modulating the activity of HIF-1α (Fig. 3B) (109).
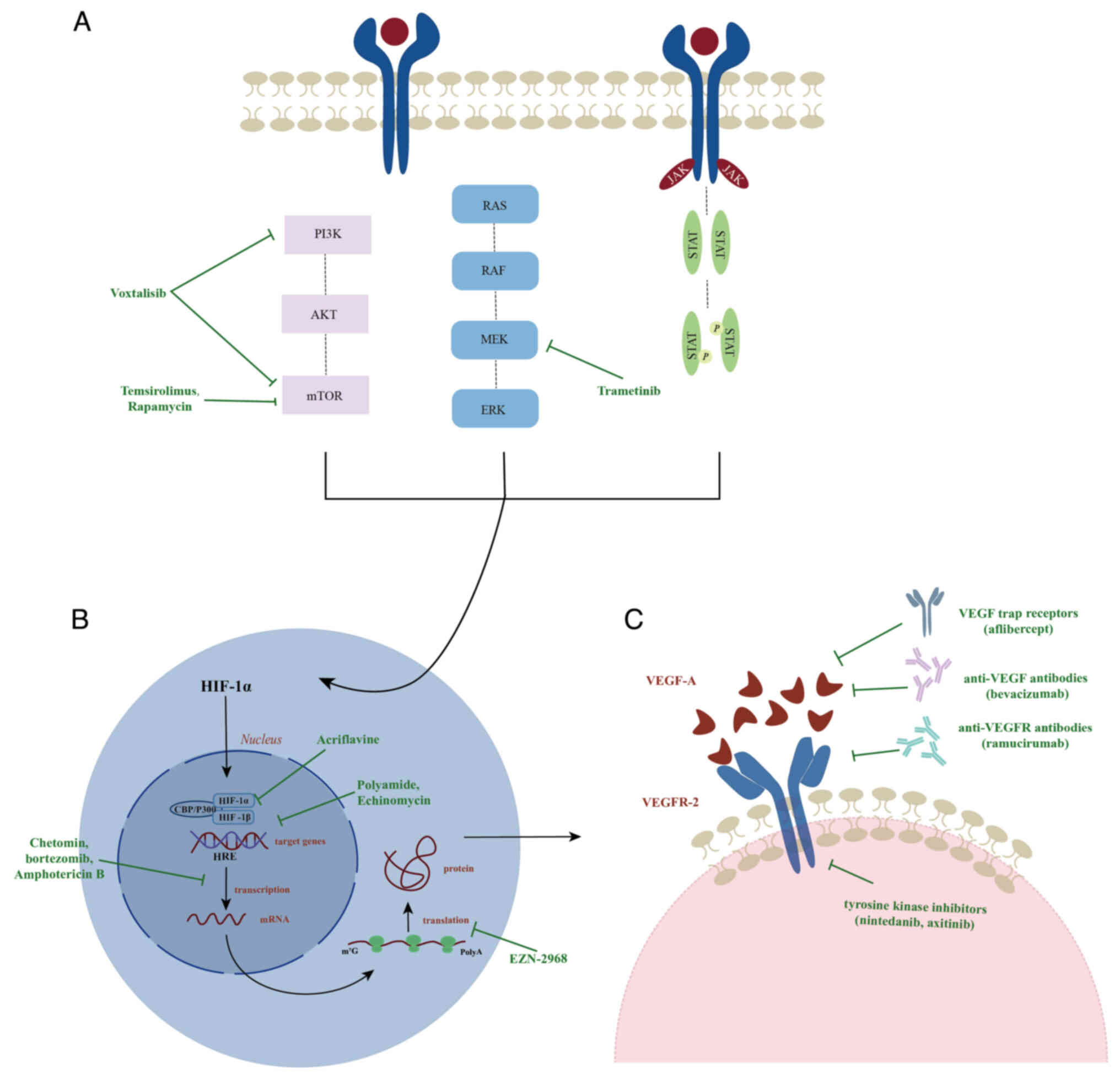
Upstream pathways
Under hypoxic conditions, signaling pathways like
PI3K-AKT-mTOR, RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK and JAK-STAT3 are activated, thereby
promoting the synthesis of the HIF-1α protein (110). Specifically, the PI3K-AKT-mTOR
pathway can enhance mRNA stability and protein synthesis
efficiency, significantly increasing the transcription level of
HIF-1α. Conversely, the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway phosphorylates the
C-terminal activation domain of HIF-1α, facilitating its
interaction with CBP/p300 and further enhancing HIF-1α-mediated
gene transcription (111).
Additionally, the STAT3 protein can be directly translocated to the
nucleus to promote the transcription of HIF-1α and it can also work
synergistically with the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway to trigger the
transcription of HIF-1α through AKT-mediated mechanisms (110,112). Clinical trials have demonstrated
that temsirolimus and rapamycin inhibit mTORC1 activity by binding
to the FKBP prolyl isomerase 1A protein, while Voxtalisib exhibits
broad antitumor activity by simultaneously inhibiting PI3K and mTOR
targets (113). Additionally, the
use of MEK inhibitors alone did not significantly improve the
survival rate of patients with NSCLC; however, when combined with
molecular targets such as VEGF, EGFR, ALK and BRAF, it shows
significant clinical efficacy. The combination therapy of
trametinib and dabrafenib has been approved by the FDA for the
treatment of these tumors (Fig. 3A)
(114).
Downstream pathways
VEGF is the only angiogenic factor consistently
expressed throughout the entire tumor cycle and serves as a key
downstream target gene of HIF-1α. When VEGF-A binds to VEGFR-2, it
initiates angiogenesis signals, fostering the survival and
proliferation of ECs and enhancing vascular permeability, all
aiding in improving tumor resistance (115). Consequently, anti-angiogenesis has
become a crucial strategy in the treatment of NSCLC. The primary
focus of this approach is to disrupt the interactions between VEGF
and VEGFR or interfere with the transmission of angiogenesis
signals to normalize the tumor vasculature. Currently,
anti-angiogenic therapies encompass a variety of drugs, including
anti-VEGF antibodies (such as bevacizumab), anti-VEGFR antibodies
(such as ramucirumab), VEGF trap receptors (such as aflibercept)
and small-molecule VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (such as
nintedanib, axitinib, sorafenib, sunitinib, vandetanib and
cediranib) (116). However, the
sole use of anti-angiogenic drugs may prompt tumor cells to develop
hypoxia-tolerant phenotypes, thereby promoting vascular remodeling
and tumor invasion, without significantly improving patient
prognosis (117). Therefore, in
clinical practice, it is more common to combine anti-angiogenic
therapy with other treatments such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy or
anti-EGFR therapy to enhance antitumor efficacy and prolong patient
survival (Fig. 3C) (116).
Hypoxia-activated prodrugs (HAPs)
HAPs, or bioreductive alkylating agents, typically
consist of five chemical groups: Nitro, quinone, aromatic,
aliphatic and transition metals (118). Due to the rarity of chronic or
severe hypoxia in normal tissues, HAPs can selectively target tumor
cells by disrupting DNA replication in the hypoxic tumor
environment (119). In
vivo, HAPs are activated by a single electron reductase system,
generating free radical intermediates. Under normoxic conditions,
these intermediates are rapidly oxidized, lose their activity or
transform into non-toxic products. However, in hypoxic
environments, the lifespan of these intermediates is prolonged,
leading to DNA alkylation, inducing cell apoptosis or necrosis and
selectively inducing tumor cell death (75,120).
Although HAPs were originally designed for hypoxic
tumor regions, they cannot reach areas far from the vascular
network, which limits their clinical efficacy (121). For instance, although the classic
HAP tirapazamine demonstrated effective hypoxic cell-killing
effects in early experiments, the overall survival rate and
response rate of patients with advanced or metastatic NSCLC did not
significantly improve in phase III trials (122). This limitation was mainly
attributed to the insufficient efficacy of tirapazamine against
normoxic tumor cells (123).
Currently, researchers are developing several new HAPs, such as
TH-302 (evofosfamide), PR-104 and Alpraziquinone (EO9), to overcome
these limitations and improve clinical efficacy (124). Combining HAPs with conventional
chemotherapy or radiotherapy can improve treatment efficacy. For
example, the combination of ezetophosamide and erlotinib has been
shown to reduce the resistance of patients with NSCLC to erlotinib
(125), while the combination of
HAPs and radiotherapy may increase the sensitivity of hypoxic tumor
cells, thereby improving overall antitumor efficacy (126).
Improvement of radiotherapy in hypoxic
NSCLC
Radiotherapy is a key component of comprehensive
treatment for various stages of NSCLC. However, to overcome its
limitations, particularly in hypoxic tumors, there is a need to
develop effective radiosensitization strategies that enhance
accuracy and improve outcomes. Radiosensitizers primarily augment
the effectiveness of radiotherapy by inhibiting radiation-induced
DNA repair, disrupting cell cycle progression, affecting organelle
function or modulating gene expression (49). For example, compounds containing
nitrogen oxides and NO act as oxygen mimetics, thereby increasing
tumor sensitivity to radiation in low-oxygen environments. These
reagents intensify the interaction between free radicals and DNA,
exacerbating DNA damage (127,128). Nanomaterials serve a significant
role in enhancing radiosensitization through multiple mechanisms,
including amplifying ROS production, modulating the cell cycle and
stimulating apoptosis (129).
Furthermore, the natural compound deguelin has shown promising
radiosensitizing effects in NSCLC. It achieves this by inhibiting
FBXO22 expression, downregulating the FOXM1/Rad51 pathway and
consequently impairing the DNA damage repair capability of tumor
cells (130).
Although radiosensitizers have enhanced the efficacy
of conventional radiotherapy, their effectiveness is still
constrained by the inability of conventional photon radiation to
effectively target radiation-resistant tumor areas. To address this
challenge, carbon ion radiotherapy (12C-ion) exhibits
heightened tumor cell-killing effects due to its higher linear
energy transfer (LET). The elevated LET of carbon ions leads to
more localized deposition of radiation energy, resulting in complex
and difficult-to-repair double-stranded DNA breaks, thereby
increasing cell lethality (131).
The advantages of carbon ion radiotherapy include: i) Increased
relative biological effectiveness with radiation-killing effects
1.2–3.5 times greater than conventional photon or proton therapy at
equivalent physical doses; ii) lower OER ensures effective
therapeutic outcomes even in hypoxic TMEs; and iii) its weak
dependence on the cell cycle renders it effective against S-phase
tumor cells, which are typically resistant to photon radiation
(132).
Despite the enhanced tumor-killing efficacy of
carbon ion radiotherapy, its therapeutic potential needs to be
optimized through precise dose distribution. Dose painting is an
advanced technique that utilizes functional imaging techniques,
such as PET and MRI, to personalize dose allocation based on
specific tumor characteristics (133). The two primary strategies for dose
painting include dose painting by contours (DPBC) and dose painting
by numbers (DPBN). DPBC classifies tumors into high-risk, requiring
higher doses, and low-risk areas, using conventional doses, based
on imaging thresholds such as PET SUV values. Although clinically
feasible, DPBC is constrained by variations in imaging thresholds,
which affect treatment consistency. DPBN assigns continuous dose
values to each voxel based on functional imaging data, more
accurately reflecting tumor heterogeneity. However, this approach
demands high image alignment precision and complex treatment
planning (134).
In summary, the development of radiosensitization
strategies and precise dose allocation techniques presents new
opportunities for improving radiotherapy for NSCLC. The combination
of efficient radiosensitizers and advanced radiotherapy approaches,
such as carbon ion therapy and dose painting, may potentially
optimize treatment strategies and enhance patient outcomes.
Discussion and conclusions
The present review summarized the role of the
hypoxic microenvironment in the progression, metabolic
reprogramming, immune escape and therapeutic resistance of NSCLC.
Hypoxia is a key driving factor for tumor progression through
multiple pathways. Specifically, HIF, as a central regulatory
factor, serves a crucial role in the proliferation, angiogenesis
and migration of tumor cells by regulating EMT and ECM degradation.
Additionally, the hypoxic environment promotes intercellular
communication through exosomes, thereby regulating processes such
as glycolysis, angiogenesis, tumor invasion and immune evasion,
which collectively promote the progression of NSCLC. At the
metabolic level, hypoxia induces metabolic reprogramming, making
NSCLC cells more inclined to rely on glycolytic pathways to
generate lactate, thus meeting their energy demands and enhancing
their adaptability to hypoxic conditions. The accumulation of
lactate not only promotes tumor cell proliferation and immune
escape but also supports tumor growth and metastasis by modulating
the TME. Moreover, under hypoxic conditions, the DNA damage repair
capability of tumor cells is reduced, and invasive phenotypes are
more likely to form, thereby increasing resistance to radiotherapy,
chemotherapy, immunotherapy and targeted therapy.
To address the challenges posed by hypoxic
microenvironments, further studies should focus on hypoxia
detection and intervention strategies. Existing methods for hypoxia
detection include electrochemical probes and optical sensors for
directly measuring oxygen partial pressure, as well as imaging
techniques such as PET, MRI and EPRI for evaluating hypoxic regions
within tumors. Additionally, gene markers, such as SLC2A1, EGLN2,
VEGF and CA9, and protein markers, such as GLUT-1, CA9 and OPN, are
currently used to detect tissue hypoxia. However, there are
currently still a number of challenges in overcoming the
heterogeneity of oxygen distribution within tumors and achieving
real-time and accurate hypoxia monitoring. Future research should
focus on developing more precise, non-invasive and real-time
hypoxia detection technologies, which may have profound
implications for clinical treatment. Regarding hypoxia treatment,
recent studies have proposed various strategies to improve TME and
enhance treatment efficacy. These strategies include increasing
tissue oxygenation, reducing tissue oxygen consumption, restoring
blood perfusion, downregulating HIF-related signaling pathways,
using HAPs and improving radiotherapy efficacy. Although these
strategies have shown some promise in preclinical studies, they
still face challenges such as inadequate targeting and potential
adverse reactions in clinical applications.
The current hypoxia detection and therapeutic
strategies have brought new perspectives to tumor treatment, but
the development of more accurate, real-time and non-invasive
monitoring techniques remains the key research area. For example,
combining high-resolution imaging technology with the detection of
hypoxia-related biomarkers can provide a dynamic and effective
method for monitoring tumor hypoxia in clinical settings.
Additionally, integrating artificial intelligence and machine
learning into image processing and data analysis is expected to
further advance real-time monitoring of the tumor hypoxic
microenvironment. In terms of treatment strategies, a single
intervention may not be sufficient to improve tumor hypoxia
effectively. Future research should explore multi-target
approaches, combined with various therapeutic approaches, to
enhance therapeutic response, alleviate tumor hypoxia and thus
improve overall treatment efficacy. However, the clinical
application of these strategies still faces many challenges,
requiring larger-scale interdisciplinary collaboration and more
clinical trials of hypoxia-targeted therapy to achieve true
therapeutic breakthroughs.
In a hypoxic microenvironment, NSCLC cells undergo a
series of adaptive changes, including enhanced growth and
metabolism, angiogenesis to maintain nutrient supply, increased
cell energy through activation of glycolysis-related genes and
enhanced invasion and migration capabilities. These adaptive
mechanisms enable tumor cells to escape the primary site and spread
to distant organs, thereby making treatment more complex and
contributing to the emergence of treatment resistance. Thus,
identifying hypoxic signals in tissues is crucial for early
diagnosis and disease monitoring of NSCLC. The best detection
method should have the characteristics of non-invasiveness,
reproducibility, high sensitivity and specificity and be able to
accurately assess hypoxia status to guide clinical decision-making.
Future therapeutic strategies should be combined with conventional
therapies and optimized for hypoxia. By improving tissue
oxygenation, modulating hypoxic genes and signaling pathways and
applying selective drug delivery methods, it is expected to enhance
the clinical treatment efficacy for patients with NSCLC.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
All authors were involved in the research design and
manuscript writing. SZ and JZ wrote the manuscript and prepared the
figures and tables. WZ and ZY were involved in collecting and
analyzing the literature for this review. PW and YZ critically
revised the article for important ideological content. Data
authentication is not applicable. All authors read and approved the
final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Steeg PS: Targeting metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 16:201–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:7–33. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu FX, Zhang YL, Liu JJ, Zhang DD and Chen
HB: Hypoxic markers in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)-A review.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:849–852. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saxena K and Jolly MK: Acute vs. chronic
vs. cyclic hypoxia: Their differential dynamics, molecular
mechanisms, and effects on tumor progression. Biomolecules.
9:3392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bertout JA, Patel SA and Simon MC: The
impact of O2 availability on human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:967–975. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meng X, Kong FM and Yu J: Implementation
of hypoxia measurement into lung cancer therapy. Lung Cancer.
75:146–150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Challapalli A, Carroll L and Aboagye EO:
Molecular mechanisms of hypoxia in cancer. Clin Transl Imaging.
5:225–253. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hinshaw DC and Shevde LA: The tumor
microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Res.
79:4557–4566. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Desai P, Takahashi N, Kumar R, Nichols S,
Malin J, Hunt A, Schultz C, Cao Y, Tillo D, Nousome D, et al:
Microenvironment shapes small-cell lung cancer neuroendocrine
states and presents therapeutic opportunities. Cell Rep Med.
5:1016102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tam FF, Ning KL, Lee M, Dumlao JM and Choy
JC: Cytokine induction of HIF-1α during normoxia in A549 human lung
carcinoma cells is regulated by STAT1 and JNK signalling pathways.
Mol Immunol. 160:12–19. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tirpe AA, Gulei D, Ciortea SM, Crivii C
and Berindan-Neagoe I: Hypoxia: Overview on hypoxia-mediated
mechanisms with a focus on the role of HIF genes. Int J Mol Sci.
20:61402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rankin EB and Giaccia AJ: The role of
hypoxia-inducible factors in tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ.
15:678–685. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Masoud GN and Li W: HIF-1α pathway: Role,
regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B.
5:378–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Della Rocca Y, Fonticoli L, Rajan TS,
Trubiani O, Caputi S, Diomede F, Pizzicannella J and Marconi GD:
Hypoxia: molecular pathophysiological mechanisms in human diseases.
J Physiol Biochem. 78:739–752. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zeng SG, Lin X, Liu JC and Zhou J:
Hypoxia-induced internalization of connexin 26 and connexin 43 in
pulmonary epithelial cells is involved in the occurrence of
non-small cell lung cancer via the P53/MDM2 signaling pathway. Int
J Oncol. 55:845–859. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hapke RY and Haake SM: Hypoxia-induced
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cancer Lett.
487:10–20. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Musleh Ud Din S, Streit SG, Huynh BT, Hana
C, Abraham AN and Hussein A: Therapeutic targeting of
hypoxia-inducible factors in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 25:20602024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu S, Zhan Y, Luo J, Feng J, Lu J, Zheng
H, Wen Q and Fan S: Roles of exosomes in the carcinogenesis and
clinical therapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 111:338–346. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang C, Xu S and Yang X: Hypoxia-driven
changes in tumor microenvironment: Insights into exosome-mediated
cell interactions. Int J Nanomedicine. 19:8211–8236. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Luo W, Hu H, Chang R, Zhong J, Knabel M,
O'Meally R, Cole RN, Pandey A and Semenza GL: Pyruvate kinase M2 is
a PHD3-stimulated coactivator for hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell.
145:732–744. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wei Y, Wang D, Jin F, Bian Z, Li L, Liang
H, Li M, Shi L, Pan C, Zhu D, et al: Pyruvate kinase type M2
promotes tumour cell exosome release via phosphorylating
synaptosome-associated protein 23. Nat Commun. 8:140412017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ji X, Zhu R, Gao C, Xie H, Gong X and Luo
J: Hypoxia-derived exosomes promote lung adenocarcinoma by
regulating HS3ST1-GPC4-mediated glycolysis. Cancers (Basel).
16:6952024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang H, Zhao H, Zhang M, He Y, Li X, Xu Y
and Liu X: Hypoxia induced changes of exosome cargo and subsequent
biological effects. Front Immunol. 13:8241882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang S, Wang R, Yan H, Jin L, Dou X and
Chen D: MicroRNA-21 modulates radiation resistance through
upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-promoted glycolysis in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:4101–4107. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Becker V, Yuan X, Boewe AS, Ampofo E,
Ebert E, Hohneck J, Bohle RM, Meese E, Zhao Y, Menger MD, et al:
Hypoxia-induced downregulation of microRNA-186-5p in endothelial
cells promotes non-small cell lung cancer angiogenesis by
upregulating protein kinase C alpha. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
31:421–436. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao J, Qiao CR, Ding Z, Sheng YL, Li XN,
Yang Y, Zhu DY, Zhang CY, Liu DL, Wu K and Zhao S: A novel pathway
in NSCLC cells: miR-191, targeting NFIA, is induced by chronic
hypoxia, and promotes cell proliferation and migration. Mol Med
Rep. 15:1319–1325. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang C, Han C, Zhang Y and Liu F: LncRNA
PVT1 regulate expression of HIF1α via functioning as ceRNA for
miR-199a-5p in non-small cell lung cancer under hypoxia. Mol Med
Rep. 17:1105–1110. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ren J: Intermittent hypoxia BMSCs-derived
exosomal miR-31-5p promotes lung adenocarcinoma development via
WDR5-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition. Sleep Breath.
27:1399–1409. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yin HL, Xu HW and Lin QY: miR129-1
regulates protein phosphatase 1D protein expression under hypoxic
conditions in non-small cell lung cancer cells harboring a TP53
mutation. Oncol Lett. 20:2239–2247. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leone RD and Powell JD: Metabolism of
immune cells in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 20:516–531. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu Z, Zou J and Xu F: Tumor-associated
macrophages affect the treatment of lung cancer. Heliyon.
10:e293322024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jin J and Yu G: Hypoxic lung cancer
cell-derived exosomal miR-21 mediates macrophage M2 polarization
and promotes cancer cell proliferation through targeting IRF1.
World J Surg Oncol. 20:2412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gu J, Yang S, Wang X, Wu Y, Wei J and Xu
J: Hypoxic lung adenocarcinoma-derived exosomal miR-1290 induces M2
macrophage polarization by targeting SOCS3. Cancer Med.
12:12639–12652. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jackson AL, Zhou B and Kim WY: HIF,
hypoxia and the role of angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:1047–1057. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Eales KL, Hollinshead KER and Tennant DA:
Hypoxia and metabolic adaptation of cancer cells. Oncogenesis.
5:e1902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dai E, Wang W and Li Y, Ye D and Li Y:
Lactate and lactylation: Behind the development of tumors. Cancer
Lett. 591:2168962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Courtnay R, Ngo DC, Malik N, Ververis K,
Tortorella SM and Karagiannis TC: Cancer metabolism and the Warburg
effect: the role of HIF-1 and PI3K. Mol Biol Rep. 42:841–851. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Luo F, Liu X, Yan N, Li S, Cao G, Cheng Q,
Xia Q and Wang H: Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1α
promotes hypoxia-induced A549 apoptosis via a mechanism that
involves the glycolysis pathway. BMC Cancer. 6:262006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shang S, Wang MZ, Xing Z, He N and Li S:
Lactate regulators contribute to tumor microenvironment and predict
prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Immunol. 13:10249252022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nisar H, Sanchidrián González PM, Brauny
M, Labonté FM, Schmitz C, Roggan MD, Konda B and Hellweg CE:
Hypoxia changes energy metabolism and growth rate in non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Cancers (Basel). 15:24722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guo Z, Hu L, Wang Q, Wang Y, Liu XP, Chen
C, Li S and Hu W: Molecular characterization and prognosis of
lactate-related genes in lung adenocarcinoma. Curr Oncol.
30:2845–2861. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang X, Liang C, Wu C, Wan S and Xu L,
Wang S, Wang J, Huang X and Xu L: A rising star involved in tumour
immunity: Lactylation. J Cell Mol Med. 28:e701462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang C, Zhou L, Zhang M, Du Y, Li C, Ren
H and Zheng L: H3K18 lactylation potentiates immune escape of
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 84:3589–3601. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Porporato PE, Filigheddu N, Pedro JMB,
Kroemer G and Galluzzi L: Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer. Cell
Res. 28:265–280. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Brustugun OT: Hypoxia as a cause of
treatment failure in non-small cell carcinoma of the lung. Semin
Radiat Oncol. 25:87–92. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Huang RX and Zhou PK: DNA damage response
signaling pathways and targets for radiotherapy sensitization in
cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen H, Han Z, Luo Q, Wang Y, Li Q, Zhou L
and Zuo H: Radiotherapy modulates tumor cell fate decisions: A
review. Radiat Oncol. 17:1962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gong L, Zhang Y, Liu C, Zhang M and Han S:
Application of radiosensitizers in cancer radiotherapy. Int J
Nanomedicine. 16:1083–1102. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhou T, Zhang LY, He JZ, Miao ZM, Li YY,
Zhang YM, Liu ZW, Zhang SZ, Chen Y, Zhou GC and Liu YQ: Review:
Mechanisms and perspective treatment of radioresistance in
non-small cell lung cancer. Front Immunol. 14:11338992023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gray LH, Conger AD, Ebert M, Hornsey S and
Scott OC: The concentration of oxygen dissolved in tissues at the
time of irradiation as a factor in radiotherapy. Br J Radiol.
26:638–648. 1953. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Herrera-Campos AB, Zamudio-Martinez E,
Delgado-Bellido D, Fernández-Cortés M, Montuenga LM, Oliver FJ and
Garcia-Diaz A: Implications of hyperoxia over the tumor
microenvironment: An overview highlighting the importance of the
immune system. Cancers (Basel). 14:27402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Guo Q, Lan F, Yan X, Xiao Z, Wu Y and
Zhang Q: Hypoxia exposure induced cisplatin resistance partially
via activating p53 and hypoxia inducible factor-1α in non-small
cell lung cancer A549 cells. Oncol Lett. 16:801–808.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Roy S, Kumaravel S, Sharma A, Duran CL,
Bayless KJ and Chakraborty S: Hypoxic tumor microenvironment:
Implications for cancer therapy. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
245:1073–1086. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hu CY, Hung CF, Chen PC, Hsu JY, Wang CT,
Lai MD, Tsai YS, Shiau AL, Shieh GS and Wu CL: Oct4 and hypoxia
dual-regulated oncolytic adenovirus armed with shRNA-targeting
dendritic cell immunoreceptor exerts potent antitumor activity
against bladder cancer. Biomedicines. 11:25982023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mancino A, Schioppa T, Larghi P,
Pasqualini F, Nebuloni M, Chen IH, Sozzani S, Austyn JM, Mantovani
A and Sica A: Divergent effects of hypoxia on dendritic cell
functions. Blood. 112:3723–3734. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Peng X, He Y, Huang J, Tao Y and Liu S:
Metabolism of dendritic cells in tumor microenvironment: For
immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 12:6134922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Eltzschig HK, Thompson LF, Karhausen J,
Cotta RJ, Ibla JC, Robson SC and Colgan SP: Endogenous adenosine
produced during hypoxia attenuates neutrophil accumulation:
Coordination by extracellular nucleotide metabolism. Blood.
104:3986–3992. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li J, Wang L, Chen X, Li L, Li Y, Ping Y,
Huang L, Yue D, Zhang Z, Wang F, et al: CD39/CD73 upregulation on
myeloid-derived suppressor cells via TGF-β-mTOR-HIF-1 signaling in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology.
6:e13200112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
An SM, Lei HM, Ding XP, Sun F, Zhang C,
Tang YB, Chen HZ, Shen Y and Zhu L: Interleukin-6 identified as an
important factor in hypoxia- and aldehyde dehydrogenase-based
gefitinib adaptive resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Oncol Lett. 14:3445–3454. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kogita A, Togashi Y, Hayashi H, Sogabe S,
Terashima M, De Velasco MA, Sakai K, Fujita Y, Tomida S, Takeyama
Y, et al: Hypoxia induces resistance to ALK inhibitors in the H3122
non-small cell lung cancer cell line with an ALK rearrangement via
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Oncol. 45:1430–1436. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Karan S, Cho MY, Lee H, Lee H, Park HS,
Sundararajan M, Sessler JL and Hong KS: Near-infrared fluorescent
probe activated by nitroreductase for in vitro and in vivo hypoxic
tumor detection. J Med Chem. 64:2971–2981. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Cheng MHY, Mo Y and Zheng G: Nano versus
molecular: Optical imaging approaches to detect and monitor tumor
hypoxia. Adv Healthc Mater. 10:e20015492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Clark LC Jr, Wolf R, Granger D and Taylor
Z: Continuous recording of blood oxygen tensions by polarography. J
Appl Physiol. 6:189–193. 1953. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sun X, Niu G, Chan N, Shen B and Chen X:
Tumor hypoxia imaging. Mol Imaging Biol. 13:399–410. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Shirmanova MV, Lukina MM, Sirotkina MA,
Shimolina LE, Dudenkova VV, Ignatova NI, Tobita S, Shcheslavskiy VI
and Zagaynova EV: Effects of photodynamic therapy on tumor
metabolism and oxygenation revealed by fluorescence and
phosphorescence lifetime imaging. Int J Mol Sci. 25:17032024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Vanderkooi JM, Maniara G, Green TJ and
Wilson DF: An optical method for measurement of dioxygen
concentration based upon quenching of phosphorescence. J Biol Chem.
262:5476–5482. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Koch CJ and Evans SM: Optimizing hypoxia
detection and treatment strategies. Semin Nucl Med. 45:163–176.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Horsman MR, Sørensen BS, Busk M and
Siemann DW: Therapeutic modification of hypoxia. Clin Oncol (R Coll
Radiol). 33:e492–e509. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Huang C, Liang J, Lei X, Xu X, Xiao Z and
Luo L: Diagnostic performance of perfusion computed tomography for
differentiating lung cancer from benign lesions: A meta-analysis.
Med Sci Monit. 25:3485–3494. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hu X, Gou J, Wang L, Lin W, Li W and Yang
F: Diagnostic accuracy of low-dose dual-input computed tomography
perfusion in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary benign and
malignant ground-glass nodules. Sci Rep. 14:170982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liao C, Liu X, Zhang C and Zhang Q: Tumor
hypoxia: From basic knowledge to therapeutic implications. Semin
Cancer Biol. 88:172–186. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Nasri D, Manwar R, Kaushik A, Er EE and
Avanaki K: Photoacoustic imaging for investigating tumor hypoxia: A
strategic assessment. Theranostics. 13:3346–3367. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Krohn KA, Link JM and Mason RP: Molecular
imaging of hypoxia. J Nucl Med. 49 (Suppl 2):129S–148S. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Brender JR, Saida Y, Devasahayam N,
Krishna MC and Kishimoto S: Hypoxia imaging as a guide for
hypoxia-modulated and hypoxia-activated therapy. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 36:144–159. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Godet I, Doctorman S, Wu F and Gilkes DM:
Detection of hypoxia in cancer models: Significance, challenges,
and advances. Cells. 11:6862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Matsumoto K, Mitchell JB and Krishna MC:
Multimodal functional imaging for cancer/tumor microenvironments
based on MRI, EPRI, and PET. Molecules. 26:16142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Qin W, Xu C, Zhao Y, Yu C, Shen S, Li L
and Huang W: Recent progress in small molecule fluorescent probes
for nitroreductase. Chin Chem Lett. 29:1451–1455. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Vikram DS, Zweier JL and Kuppusamy P:
Methods for noninvasive imaging of tissue hypoxia. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 9:1745–1756. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Epel B, Bowman MK, Mailer C and Halpern
HJ: Absolute oxygen R1e imaging in vivo with pulse electron
paramagnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med. 72:362–368. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hao B, Dong H, Xiong R, Song C, Xu C, Li N
and Geng Q: Identification of SLC2A1 as a predictive biomarker for
survival and response to immunotherapy in lung squamous cell
carcinoma. Comput Biol Med. 171:1081832024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhang R, Lai L, He J, Chen C, You D, Duan
W, Dong X, Zhu Y, Lin L, Shen S, et al: EGLN2 DNA methylation and
expression interact with HIF1A to affect survival of early-stage
NSCLC. Epigenetics. 14:118–129. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ostheimer C, Bache M, Güttler A, Kotzsch M
and Vordermark D: A pilot study on potential plasma hypoxia markers
in the radiotherapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Osteopontin,
carbonic anhydrase IX and vascular endothelial growth factor.
Strahlenther Onkol. 190:276–282. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Giatromanolaki A, Harris AL, Banham AH,
Contrafouris CA and Koukourakis MI: Carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9)
expression in non-small-cell lung cancer: Correlation with
regulatory FOXP3+T-cell tumour stroma infiltration. Br J Cancer.
122:1205–1210. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Geng H, Chen L, Lv S, Li M, Huang X, Li M
and Liu C and Liu C: Photochemically controlled release of the
glucose transporter 1 inhibitor for glucose deprivation responses
and cancer suppression research. J Proteome Res. 23:653–662. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Kim SJ, Rabbani ZN, Vollmer RT, Schreiber
EG, Oosterwijk E, Dewhirst MW, Vujaskovic Z and Kelley MJ: Carbonic
anhydrase IX in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 10:7925–7933. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Coppola D, Szabo M, Boulware D, Muraca P,
Alsarraj M, Chambers AF and Yeatman TJ: Correlation of osteopontin
protein expression and pathological stage across a wide variety of
tumor histologies. Clin Cancer Res. 10((1 Pt 1)): 184–190. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ostheimer C, Bache M, Güttler A, Reese T
and Vordermark D: Prognostic information of serial plasma
osteopontin measurement in radiotherapy of non-small-cell lung
cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:8582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Stępień K, Ostrowski RP and Matyja E:
Hyperbaric oxygen as an adjunctive therapy in treatment of
malignancies, including brain tumours. Med Oncol. 33:1012016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kim SW, Kim IK, Ha JH, Yeo CD, Kang HH,
Kim JW and Lee SH: Normobaric hyperoxia inhibits the progression of
lung cancer by inducing apoptosis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
243:739–748. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Thews O and Vaupel P: Spatial oxygenation
profiles in tumors during normo- and hyperbaric hyperoxia.
Strahlenther Onkol. 191:875–882. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Heyboer M III, Sharma D, Santiago W and
McCulloch N: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Side effects defined and
quantified. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 6:210–224. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Jones LW, Viglianti BL, Tashjian JA,
Kothadia SM, Keir ST, Freedland SJ, Potter MQ, Moon EJ, Schroeder
T, Herndon JE II and Dewhirst MW: Effect of aerobic exercise on
tumor physiology in an animal model of human breast cancer. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 108:343–348. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Jo S, Jeon J, Park G, Do HK, Kang J, Ahn
KJ, Ma SY, Choi YM, Kim D, Youn B and Ki Y: Aerobic exercise
improves radiation therapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer:
Preclinical study using a xenograft mouse model. Int J Mol Sci.
25:27572024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ghosh P, Vidal C, Dey S and Zhang L:
Mitochondria targeting as an effective strategy for cancer therapy.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:33632020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Ashton TM, McKenna WG, Kunz-Schughart LA
and Higgins GS: Oxidative phosphorylation as an emerging target in
cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 24:2482–2490. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Kalyanaraman B, Cheng G, Hardy M and You
M: OXPHOS-targeting drugs in oncology: New perspectives. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 27:939–952. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Shameem M, Bagherpoor AJ, Nakhi A, Dosa P,
Georg G and Kassie F: Mitochondria-targeted metformin (mitomet)
inhibits lung cancer in cellular models and in mice by enhancing
the generation of reactive oxygen species. Mol Carcinog.
62:1619–1629. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Skwarski M, McGowan DR, Belcher E, Di
Chiara F, Stavroulias D, McCole M, Derham JL, Chu KY, Teoh E,
Chauhan J, et al: Mitochondrial inhibitor atovaquone increases
tumor oxygenation and inhibits hypoxic gene expression in patients
with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 27:2459–2469.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Benej M, Hong X, Vibhute S, Scott S, Wu J,
Graves E, Le QT, Koong AC, Giaccia AJ, Yu B, et al: Papaverine and
its derivatives radiosensitize solid tumors by inhibiting
mitochondrial metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:10756–10761.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Sohoni S, Ghosh P, Wang T, Kalainayakan
SP, Vidal C, Dey S, Konduri PC and Zhang L: Elevated heme synthesis
and uptake underpin intensified oxidative metabolism and
tumorigenic functions in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 79:2511–2525. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Wang T, Ashrafi A, Konduri PC, Ghosh P,
Dey S, Modareszadeh P, Salamat N, Alemi PS, Berisha E and Zhang L:
Heme sequestration as an effective strategy for the suppression of
tumor growth and progression. Mol Cancer Ther. 20:2506–2518. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Dewhirst MW and Secomb TW: Transport of
drugs from blood vessels to tumour tissue. Nat Rev Cancer.
17:738–750. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Sukhatme V, Bouche G, Meheus L, Sukhatme
VP and Pantziarka P: Repurposing drugs in oncology
(ReDO)-nitroglycerin as an anti-cancer agent.
Ecancermedicalscience. 9:5682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Reymen BJT, van Gisbergen MW, Even AJG,
Zegers CML, Das M, Vegt E, Wildberger JE, Mottaghy FM, Yaromina A,
Dubois LJ, et al: Nitroglycerin as a radiosensitizer in non-small
cell lung cancer: Results of a prospective imaging-based phase II
trial. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 21:49–55. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Wong PP, Bodrug N and Hodivala-Dilke KM:
Exploring novel methods for modulating tumor blood vessels in
cancer treatment. Curr Biol. 26:R1161–R1166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Guelfi S, Hodivala-Dilke K and Bergers G:
Targeting the tumour vasculature: From vessel destruction to
promotion. Nat Rev Cancer. 24:655–675. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Wigerup C, Påhlman S and Bexell D:
Therapeutic targeting of hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in
cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 164:152–169. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Xia Y, Choi HK and Lee K: Recent advances
in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem.
49:24–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Iommarini L, Porcelli AM, Gasparre G and
Kurelac I: Non-canonical mechanisms regulating hypoxia-inducible
factor 1 alpha in cancer. Front Oncol. 7:2862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Albadari N, Deng S and Li W: The
transcriptional factors HIF-1 and HIF-2 and their novel inhibitors
in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 14:667–682. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ma J, Cao K, Ling X, Zhang P and Zhu J:
LncRNA HAR1A suppresses the development of non-small cell lung
cancer by inactivating the STAT3 pathway. Cancers (Basel).
14:28452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Deng H, Chen Y, Li P, Hang Q, Zhang P, Jin
Y and Chen M: PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, hypoxia, and glucose
metabolism: Potential targets to overcome radioresistance in small
cell lung cancer. Cancer Pathog Ther. 1:56–66. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Lara MS, Blakely CM and Riess JW:
Targeting MEK in non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Probl Cancer.
49:1010652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhu H and Zhang S: Hypoxia inducible
factor-1α/vascular endothelial growth factor signaling activation
correlates with response to radiotherapy and its inhibition reduces
hypoxia-induced angiogenesis in lung cancer. J Cell Biochem.
119:7707–7718. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Tian W, Cao C, Shu L and Wu F:
Anti-angiogenic therapy in the treatment of non-small cell lung
cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 13:12113–12129. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Mahdi A, Darvishi B, Majidzadeh-A K,
Salehi M and Farahmand L: Challenges facing antiangiogenesis
therapy: The significant role of hypoxia-inducible factor and MET
in development of resistance to anti-vascular endothelial growth
factor-targeted therapies. J Cell Physiol. 234:5655–5663. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Yuan X, Xie Z and Zou T: Recent advances
in hypoxia-activated compounds for cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Bioorg Chem. 144:1071612024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Bryant JL, Meredith SL, Williams KJ and
White A: Targeting hypoxia in the treatment of small cell lung
cancer. Lung Cancer. 86:126–132. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Wilson WR and Hay MP: Targeting hypoxia in
cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:393–410. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Chen SX, Zhang J, Xue F, Liu W, Kuang Y,
Gu B, Song S and Chen H: In situ forming oxygen/ROS-responsive
niche-like hydrogel enabling gelation-triggered chemotherapy and
inhibition of metastasis. Bioact Mater. 21:86–96. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Shepherd F, Koschel G, Von Pawel J,
Gatzmeier U, Van Zandwiyk N, Woll P, Van Klavren R, Krasko P,
Desimone P, Nicolson M, et al: Comparison of Tirazone
(Tirapazamine) and cisplatin vs. etoposide and cisplatin in
advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Final results of the
International phase III CATAPULT II trial. Lung Cancer. 29:282000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Marcu L and Olver I: Tirapazamine: From
bench to clinical trials. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 1:71–79. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Graham K and Unger E: Overcoming tumor
hypoxia as a barrier to radiotherapy, chemotherapy and
immunotherapy in cancer treatment. Int J Nanomedicine.
13:6049–6058. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Lindsay D, Garvey CM, Mumenthaler SM and
Foo J: Leveraging hypoxia-activated prodrugs to prevent drug
resistance in solid tumors. PLoS Comput Biol. 12:e10050772016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Meaney C, Powathil GG, Yaromina A, Dubois
LJ, Lambin P and Kohandel M: Role of hypoxia-activated prodrugs in
combination with radiation therapy: An in silico approach. Math
Biosci Eng. 16:6257–6273. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Oronsky BT, Knox SJ and Scicinski JJ: Is
nitric oxide (NO) the last word in radiosensitization? A review.
Transl Oncol. 5:66–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Oronsky B, Scicinski J, Ning S, Peehl D,
Oronsky A, Cabrales P, Bednarski M and Knox S: RRx-001, A novel
dinitroazetidine radiosensitizer. Invest New Drugs. 34:371–377.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Zhao L, Li M, Shen C and Luo Y, Hou X, Qi
Y, Huang Z, Li W, Gao L, Wu M and Luo Y: Nano-assisted radiotherapy
strategies: New opportunities for treatment of non-small cell lung
cancer. Research (Wash D C). 7:04292024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Chen Y, Zhou Y, Feng X, Wu Z, Yang Y, Rao
X, Zhou R, Meng R, Dong X, Xu S, et al: Targeting FBXO22 enhances
radiosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting the
FOXM1/Rad51 axis. Cell Death Dis. 15:1042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Dey P, Das R, Chatterjee S, Paul R and
Ghosh U: Combined effects of carbon ion radiation and PARP
inhibitor on non-small cell lung carcinoma cells: Insights into DNA
repair pathways and cell death mechanisms. DNA Repair (Amst).
144:1037782024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Demizu Y, Fujii O, Iwata H and Fuwa N:
Carbon ion therapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:7279622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Bentzen SM and Gregoire V:
Molecular-imaging-based dose painting: A novel paradigm for
radiation therapy prescription. Semin Radiat Oncol. 21:101–110.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Meijer G, Steenhuijsen J, Bal M, De Jaeger
K, Schuring D and Theuws J: Dose painting by contours versus dose
painting by numbers for stage II/III lung cancer: Practical
implications of using a broad or sharp brush. Radiother Oncol.
100:396–401. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|