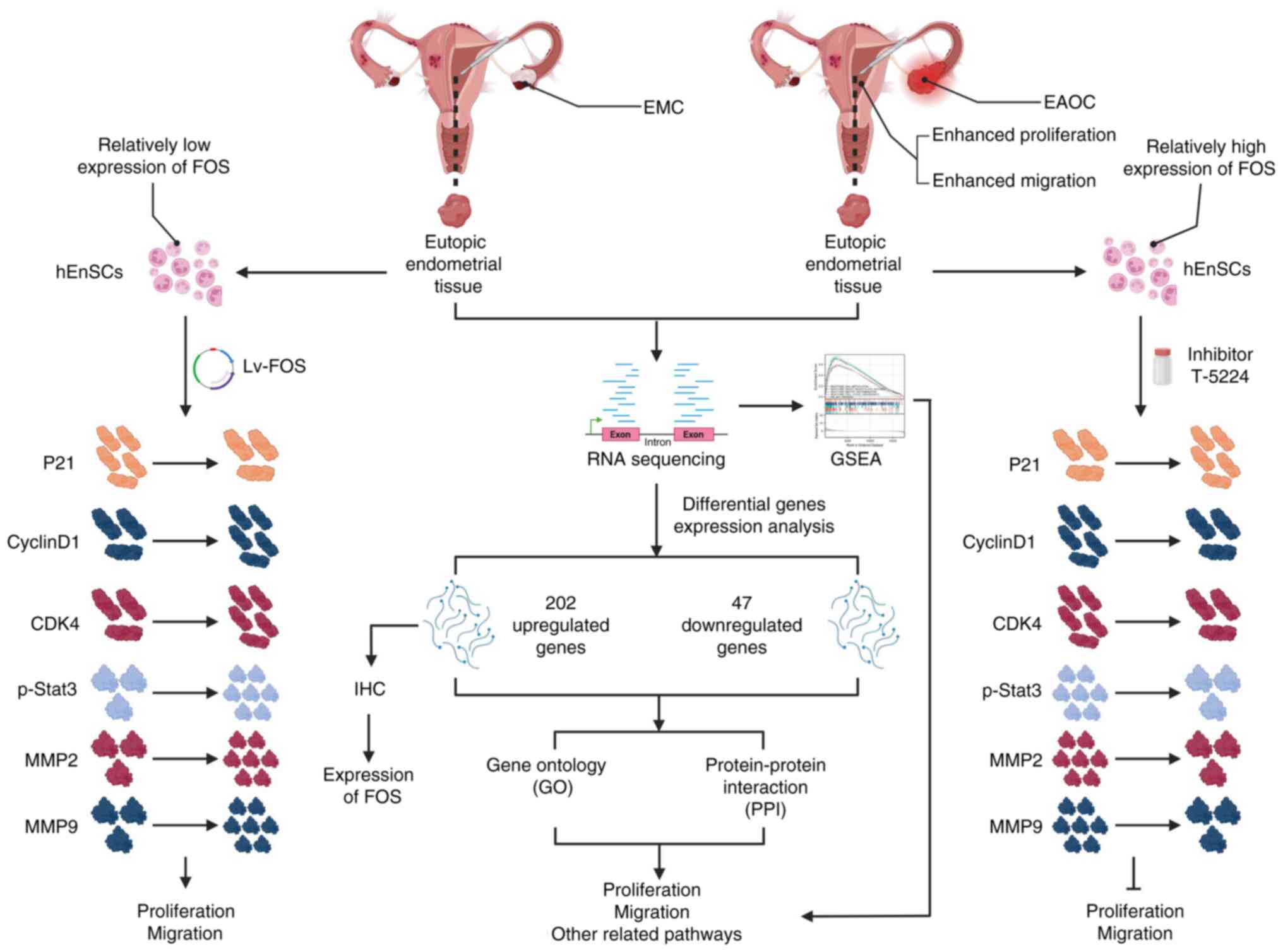
Introduction
Endometriosis (EM) is defined as the presence of
endometrium-like tissue outside the endometrium and myometrium and
is often detected in ovaries as an endometrial cyst of the ovary
(EMC) (1). Long-term development of
EMC may lead not only to chronic pelvic pain and infertility but
also to malignant transformation, which is considered EM-associated
ovarian cancer (EAOC) (2). The
incidence of malignant transformation has been reported to be
0.7–2.5% (3). The main pathological
types of EAOC are clear cell carcinoma and endometrioid carcinoma,
which are characterized by co-occurrence within the same lesion of
EM and cancerous tissue (4).
However, the pathogenesis of EAOC remains unclear.
For several decades, a wide range of mechanisms,
including oxidative stress, inflammation and estrogen stimulation,
involved in the malignant transformation of ovarian EM to EAOC,
have been studied (5–7). However, most of these studies focused
only on the effects of the external microenvironment on the
malignant transformation of ovarian lesions and ignored the changes
that had already occurred while the lesion was in the eutopic
endometrium, which might be the origin of EAOC. Previous studies
have indicated that EAOC can be caused by implantation of eutopic
endometrial epithelium and mesenchymal cells containing oncogenic
changes in ovaries via retrograde menstruation (8). These changes in the eutopic
endometrium include DNA methylation aberrance, oncogene activation
and antioncogene inactivation (7,8).
Interestingly, several researchers have indicated that compared
with eutopic endometrium in normal patients, abnormal eutopic
endometrium in EM patients is characterized by gene mutations and
increased adhesion, metastasis and angiopoiesis (8,9).
In this regard, it was hypothesized that the eutopic
endometrium of EAOC patients may exhibit more profound and diverse
oncogenic mutations than those of EM patients. These mutations
could encompass a range of genetic and epigenetic alterations,
including but not limited to changes in cytoskeletal and
chromatin-remodeling proteins, activation of oncogenes such as
KRAS, and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes.
Additionally, the eutopic endometrium in EAOC might be
characterized by increased expression of genes such as RRM2,
which are implicated in abnormal cell proliferation and potential
malignant transformation. These complex genetic and molecular
changes suggest a multifactorial pathogenesis of EAOC, diverging
significantly from the pathogenesis observed in EM (10–13),
which provided new insight into the detection of EAOC. Based on the
differences in mRNA or protein expression in the eutopic
endometrium between EAOC patients and EMC patients, endometrial
biopsy followed by specific biomarker detection might be employed
for distinguishing EAOC from EM.
The aim of the present study was to elucidate the
potential eutopic endometrium-related pathogenesis of EAOC and to
identify a feasible biomarker of EAOC in the eutopic endometrium
via RNA sequencing. Subsequently, the protein expression of the
biomarker was tested by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in eutopic
endometrial tissue. Finally, the molecular function of the
biomarker was explored in eutopic endometrial cells from EAOC and
EM patients.
Materials and methods
Specimens
The present study was approved (approval no.
2021202) by the Jilin University Second Hospital's Ethics Committee
(Changchun, China). Informed consent was provided by all patients
for participation in the study.
Between January 2022 and September 2022, five
eutopic endometrial samples and four eutopic endometrial samples
were taken from EAOC and EMC patients at the Second Hospital of
Jilin University. Within 30 min of excision, the samples were
collected in liquid nitrogen and utilized for RNA sequencing.
At the Second Hospital of Jilin University,
paraffin-embedded eutopic endometrial samples were collected from
63 patients with EAOC, 95 patients with EMC, and 16 healthy
controls who were diagnosed between January 2012 and September
2022. The baseline clinical characteristics of the EAOC and EMC
patients are displayed in Table I.
The detailed clinical information of the normal patients included
in the present study is presented in Table SI.
 | Table I.Clinical characteristics of the
patients with EMC or EAOC. |
Table I.
Clinical characteristics of the
patients with EMC or EAOC.
|
Characteristics | EMC (n=95) | EAOC (n=63) | P-value |
|---|
| Agea | 43 (39, 47) | 49 (44, 54) |
P<0.001b |
|
Menopauseb |
|
|
P<0.001b |
|
Yes | 3 (3.2%) | 25 (39.7%) |
|
| No | 92 (96.8%) | 38 (60.3%) |
|
| Body mass
indexa | 23.63 (21.09,
25.79) | 23.81 (21.64,
26.50) | 0.794 |
| Endometrium
phase |
|
|
P<0.001b |
|
Proliferation phase | 57 (60%) | 55 (87.3%) |
|
|
Secretory phase | 38 (40%) | 8 (12.7%) |
|
| MOD of FOS
expression | 0.026 (0.014,
0.041) | 0.035 (0.024,
0.057) |
P=0.006c |
The inclusion criteria for EAOC patients were as
follows: In accordance with Sampson's diagnostic criteria (SAMPSON
1925) (14), the lesions were
histologically identified as EAOC, and eutopic endometrium
specimens were obtained.
The following criteria were applied to the included
EMC patients: i) Eutopic endometrial specimens could be obtained;
and ii) the lesions were histologically identified as EMC.
The following criteria were applied to the included
normal controls: i) An EM diagnosis was ruled out through
laparoscopic hysterectomy or hysteromyomectomy; ii) Specimens of
the eutopic endometrium were obtained.
The exclusion criteria for patients were as follows:
The use of hormone medications prior to surgery, diabetes or other
endocrine illnesses, abnormal uterine hemorrhage, or major systemic
diseases.
All the samples gathered, including those preserved
in liquid nitrogen and those embedded in paraffin, fulfilled the
aforementioned criteria.
RNA extraction and sequencing
Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co., Ltd., handled
the RNA extraction and sequencing. Briefly, the whole RNA was
extracted from the aforementioned samples. After that, oligo (DT)
magnetic beads were used to select for mRNAs with polyA structures
in total RNA. The enriched mRNA was then cut into pieces of ~300 bp
in length by ion interruption, which were subsequently used as the
template for reverse transcription into cDNA and PCR amplification.
The cDNA library was subsequently sequenced using Illumina HiSeq
and paired-end sequencing via next-generation sequencing (NGS).
RNA-seq data analysis
FPKM was used to normalize the raw counts. In
Bayesian analysis, the R package ‘limma’ was utilized to identify
the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) across eutopic
endometrial samples from EAOC and EMC patients. The threshold for
DEGs was defined as a |log2 Fold Change (logFC)|>1 and an
adjusted P-value of 0.05. The STRING database (https://string-db.org/) was used to visualize the DEGs
(15), and protein-protein
interaction (PPI) analysis of the DEGs was performed using
Cytoscape software (https://cytoscape.org/) network analysis. Gene
functional enrichment analysis was based on Gene Ontology (GO) and
gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) using the R packages
‘clusterProfiler’ and ‘org.Hs.eg.db’, respectively (16). An adjusted P-value <0.05 or a
false discovery rate (FDR) <0.25 were considered to indicate
significant enrichment. c2.cp.v7.2. symbols. gmt was used as the
reference gene set for GSEA. This gene set is part of the Molecular
Signatures Database [MSigDB(https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/msigdb)] and is
extensively utilized in GSEA for identifying biologically
meaningful patterns within gene expression data. The choice of this
particular gene set was influenced by its extensive coverage of
known biological pathways and processes. This comprehensive scope
is invaluable for accurately interpreting our RNA-seq data,
especially in the context of eutopic endometrium-related
pathogenesis in EAOC.
IHC
IHC staining was carried out as previously described
(17). The paraffin-embedded
materials were divided into 3-µm thick sections. The sections were
heated in a microwave after being deparaffinized with xylol and
then rehydrated with a succession of decreasing alcohol
concentrations, starting with 100% ethanol, followed by 95, 85,
70%, and finally 50% ethanol for gradual rehydration. After
incubation at room temperature for 20 min, non-specific binding was
inhibited with 5% bovine serum albumin (cat. no. AR1006; Boster
Biological Technology). The histological sections were then
incubated at 4°C overnight with rabbit anti-FOS antibody
(Wuhan Servicebio Technology Co., Ltd.; cat. no. GB12069; 1:400).
The secondary antibody used was goat anti-rabbit IgG coupled with
horseradish peroxidase (Proteintech Group, Inc.; cat. no.
SA00001-2; 1:200), and the staining process was performed at 37°C
for 30 min. Sections were counterstained with 0.1% hematoxylin
(Boster Biological Technology) at room temperature for 2 min to
detect reactive reactions using the chromogen 3,3′-diaminobenzidine
(Boster). With an objective magnification of ×200 or ×400,
histological images were recorded using a light microscope (Motic
Incorporation, Ltd.; cat. no. AE2000). The program Image-Pro Plus
6.0 (Media Cybernetics, Inc.) was used to determine the positive
cell density, and the results are shown as the mean optical density
(MOD) values (17).
Isolation, identification and culture
conditions for human endometrial stromal cells (hEnSCs)
As previously mentioned, the hEnSCs were separated
from 3 EAOC patients and 3 EMC patients. Briefly, eutopic
endometrial samples were received and dissected from the scalpels.
Collagenase IV (MilliporeSigma) was then used to lyse the tissues
for 1 h at 37°C. Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM)/nutrient
combination F12 medium (DMEM/F12; Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.) was used to cultivate the hEnSCs after they had been filtered
via a 40-µm filter. A total of 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gibco;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin
(cat. no. P1400; Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co.,
Ltd.) were added as supplements. Using flow cytometry (BD
Biosciences), the homogeneity of the cultures was assessed based on
morphological traits and confirmed by surface-positive (CD73,
CD90 and CD105) and negative (HLA-II) markers.
Furthermore, as previously described,
immunofluorescence staining was performed to detect the stromal and
epithelial markers Vimentin and Src (18). The main antibodies utilized were
rabbit anti-Src (Wuhan Servicebio Technology Co., Ltd.; cat.
no. GB111035; 1:500) and mouse anti-vimentin (Wuhan
Servicebio Technology Co., Ltd.; cat. no. GB12192; 1:500). The
secondary antibodies used were goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L)
conjugated with Cy3 (Wuhan Servicebio Technology Co., Ltd.; cat.
no. GB21303; 1:300) and goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) conjugated
with FITC (Wuhan Servicebio Technology Co., Ltd.; cat. no. GB22301;
1:100). Slides were examined under a fluorescence microscope
(Olympus Corporation). In the resulting images, Src protein is
indicated by red fluorescence, Vimentin protein by green, and cell
nuclei were counterstained with DAPI, appearing blue.
Generation of stably transfected
hEnSCs
LV-FOS and LV-NC were purchased from Hunan
Fenghui Biological Co., Ltd. The lentivirus had titers of 1.8 and
1.5×108 TU/ml, respectively. To prevent frequent
freezing and thawing, the samples were often kept in a
low-temperature refrigerator at −80°C and put at 4°C before use.
The suspended initial cells were injected into six-well plates
(5×105 cells/well). After the cells had adhered to the
wall for 12 h, MOI=200 cell culture media containing LV-FOS
or LV-NC was added. Polybrene (5 g/ml) was added to the medium to
increase the rate of infection. After 12 h of incubation at 37°C,
5% CO2, and saturated humidity, the medium was replaced.
A total of 72 h after infection, the expression of FOS was
assessed using an inverted fluorescence microscope. Green luminous
cells with the FOS signature were positive cells. To
calculate the transfection efficiency, the number of fluorescent
positive cells was counted and this value was divided by the total
number of cells present in the field of view. This ratio was then
multiplied by 100 to express the efficiency as a percentage.
Specifically, fields were randomly selected, and both fluorescent
(indicating successful transfection) and non-fluorescent cells were
counted using a fluorescence microscope. Then, cells with the virus
that encodes the gene for puromycin resistance were chosen from 1.5
g/ml puromycin. Prior to cell collection and analysis, puromycin
(0.5 g/ml) screening was carried out for an additional week.
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay
hEnSCs were seeded onto 96-well plates at a density
of 3,000 cells/well along with FOS inhibitor (T-5224; cat.
no. HY-12270; MedChemExpress) at various concentrations (0, 5, 10
and 20 M). CCK-8 reagent (10 µl/well; cat. no. K009; Zeta Life
Inc.) was then added to each well 48 and 72 h later. Using a
microplate reader (cat. no. E0226; Nanjing DeTie Laboratory
Equipment Co., Ltd.), the absorbance of each well was assessed at
450 nm after 1.5 h of culture at 37°C.
Colony formation assay
A total of 100 cells per well of 6-well plates were
plated with the appropriate cells. A total of 10 days later, the
development of a typical cell clone was observed. The cells were
stained with 10% Giemsa (Biotopped; http://www.bjbiotopped.com/) at room temperature for
10 min after being fixed with methanol at room temperature for 30
min. To assess the colony production capacity of the cells, visible
colonies were counted. Traditionally, a dense conglomerate of cells
is regarded as a colony when the number of cells exceeds 50. The
software ImageJ [Fiji (https://imagej.net/software/fiji/downloads) (National
Institutes of Health)] was used to count the number of
colonies.
Cell scratch assay
The specified cells were seeded onto 6-well plates
(6×105 cells/well) for the cell scratch test. T-5224 was
introduced to hEnSCs at concentrations of 0, 5, 10 and 20 M after
the cells had been cultured at 37°C for 24 h. A plastic pipette tip
was used to scrape the cell layer. After 48 h, the rate of cell
migration near the scratch edge was examined. The cells were
serum-starved during the assay.
Western blot analysis
RIPA lysis buffer (cat. no. P0013B; Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology) was used to separate the soluble
proteins from the different concentrations (0, 5, 10 and 20 M) of
T-5224-treated or stably transfected hEnSCs. A Detergent Compatible
Bradford Protein Assay Kit (cat. no. P0006C; Beyotime Institute of
biotechnology) was used to quantify the protein concentrations.
Then, 15 µg of protein was run through each lane of a 4–20% Precast
Bis-Tris Gel (Absin; cat. no. abs9384;). Preserved standards, which
are molecular weight markers, (Beijing Transgen Biotech Co., Ltd.;
cat. no. DM141-01) were employed. The separated proteins were
electrophoretically transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride
membranes (iBlot system; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.). The membranes were then blocked with 5% skim milk for 1 h at
room temperature. Subsequently, membranes were incubated with
primary antibodies, including anti-FOS (Wuhan Servicebio
Technology Co., Ltd.; cat. no. GB12069; 1:1,000), anti-P21
(Proteintech Group, Inc.; cat. no. 10355-1-AP; 1:2,000),
anti-CDK4 (Proteintech Group, Inc.; cat. no. 11026-1-AP;
1:2,000), anti-CyclinD1 (Proteintech Group, Inc.; cat. no.
26939-1-AP; 1:5,000), anti-phosphorylated (p-)Stat3 (BIOSS;
cat. no. bs-1658R; 1:1,000), anti-Stat3 (BIOSS; cat. no.
bsm-52235R; 1:750), anti-MMP2 (BIOSS; cat. no. bs-0412R;
1:500), anti-MMP9 (BIOSS; cat. no. bs-4593R; 1:500) and
anti-GAPDH (Bioworld Technology, Inc.; cat. no. BS65656;
1:20,000), at room temperature for 1.5 h. After 1 h of room
temperature incubation with secondary-HRP antibodies
(Bioworld Technology, Inc.; cat. nos. BS13278 and BS12478;
1:20,000), the protein levels were assessed using an image
densitometer (Clinx Science Instruments Co., Ltd.) and an ECL kit
(cat. no. KF8005; Affinity Biosciences).
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis utilized the mean of three
independent tests together with the standard deviation (SD). When
performing the statistical analyses with SPSS 23.0 IBM Corp._ or R
version 3.6.3 (https://www.r-project.org/), one-way analysis of
variance (ANOVA) was used to examine group differences, followed by
Dunnett's post hoc test, the Kruskal-Wallis test, or unpaired
Student's t-test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
Identification of DEGs via RNA
sequencing
The RNA-seq data were used to analyze the
significant (|logFC|>1, adjusted P-value <0.05) differences
between the eutopic endometrium of EAOC patients and those of EMC
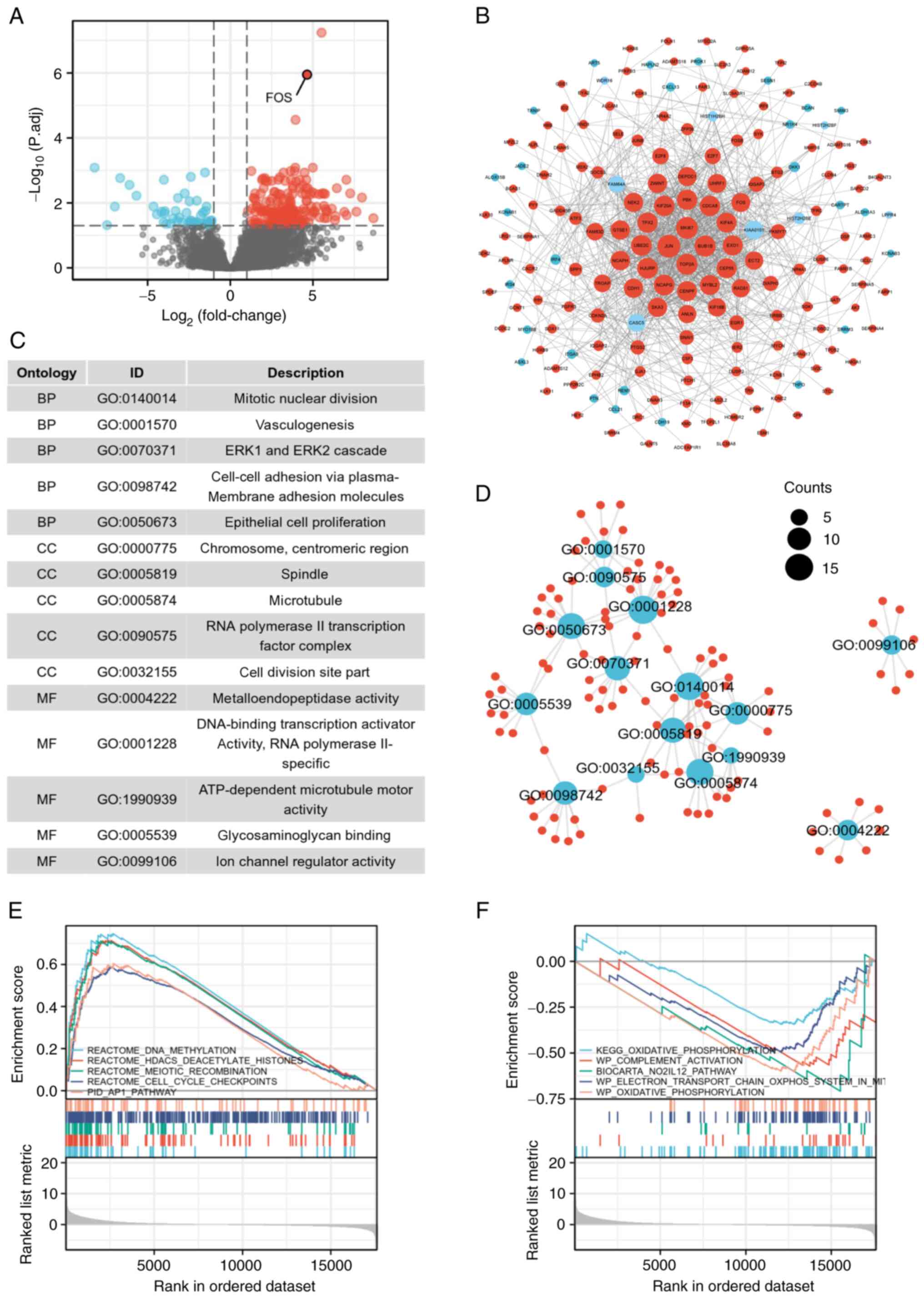
patients, and 249 DEGs were identified, including 202 significantly
upregulated and 47 downregulated genes (Fig. 1A). The data of eutopic endometrium
samples from EMC patients were considered controls. FOS mRNAs with
significant differences are indicated in the volcano plot. The
interactions among the DEGs are demonstrated in the PPI network
(Fig. 1B). PPI network analysis
revealed that genes such as JUN, MKI67, BUB1B, TOP2A, EXO1,
UBE2C, KIF4A and CENPF occupied central positions in the
network, indicating a greater functional correlation with the FOS
gene. Investigating the roles of these genes could be instrumental
in elucidating the potential pathways and functional mechanisms
through which the FOS gene may contribute to the progression from
EMC to EAOC.
Pathway enrichment of DEGs
A total of 15 signaling pathways related to the 249
DEGs were enriched according to GO analysis. Notably, it was found
that the enrichment pathways were associated mainly with mitotic
nuclear division, vasculogenesis, the ERK1 and ERK2
cascades, cell-cell adhesion and epithelial cell proliferation
(Fig. 1C). The interactions among
these pathways are revealed in Fig.
1D.
Moreover, to explore the relevant pathways more
comprehensively, the data of all genes were further subjected to
GSEA. The GSEA results indicated that DNA methylation, HDACS
deacetylase histones, meiotic recombination, cell cycle checkpoints
and the AP1 pathway were enhanced in the samples from EAOC
patients (Fig. 1E), whereas some
pathways were inhibited, including oxidative phosphorylation
(OXPHOS), complement activation, the No2-IL12 pathway, and
the electron transport chain OXPHOS system (Fig. 1F).
IHC verification of FOS expression in
endometrial clinical samples
The endometrium exhibits notable differences between
the proliferative and secretory phases. Specifically, the
proliferative phase typically spans from the 5th to the 14th day of
the menstrual cycle and is predominantly regulated by estrogen. The
pathological characteristics of this phase include: i) Progressive
thickening of the endometrium; ii) glandular structures appearing
as straight, elongated tubes, uniformly distributed; iii) glandular
cells exhibiting a columnar shape with evident signs of mitosis;
iv) proliferation of stromal cells, presenting a loose arrangement;
and v) vascular proliferation without notable coiling.
Conversely, the secretory phase generally occurs
from the 15th to the 28th day of the menstrual cycle and is
influenced primarily by progesterone. The pathological hallmarks of
this phase include the following: i) continued thickening of the
endometrium, reaching its peak; ii) glands acquiring a ‘serrated’
or spiral configuration, becoming more convoluted and dilated; iii)
enlargement of glandular cells, with the presence of secretory
granules in the cytoplasm and nuclei migrating basally (indicative
of subnuclear vacuolation); iv) densification of stromal cells and
the matrix, possibly involving pre-decidual cells; and v) increased
coiling of blood vessels, forming a distinctive spiral pattern.
To validate the expression of FOS, samples from 57
patients with EMC and 55 patients with EAOC during the
proliferative phase and 38 EMC and 8 EAOC patient samples during
the secretory phase were utilized. The control group comprised 16
patients, including 3 in the secretory phase and 13 in the
proliferative phase. FOS expression in proliferative
endometrial tissues was assessed via IHC staining. The results
indicated that FOS expression was upregulated in the
endometrial tissues of patients with EAOC compared with that in
patients with EMC (Fig. 2A and B).
FOS expression levels in secretory endometrial tissues were
measured by the same method. As demonstrated in Fig. 2C and D, FOS expression was
upregulated in the endometrial tissues of patients in the EAOC
group compared with that of patients in the EMC group.
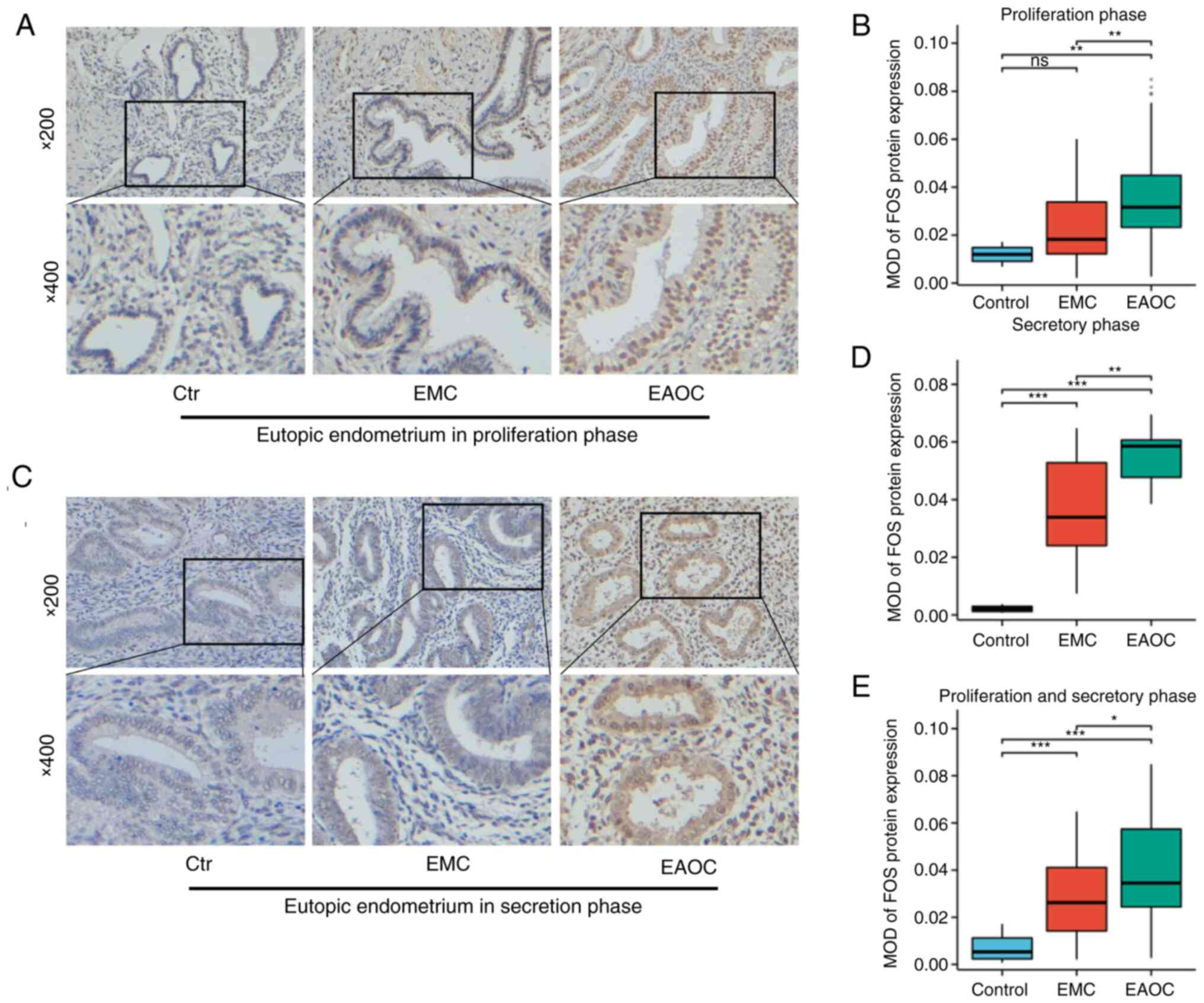 | Figure 2.IHC results of FOS expression
in different types of tissues. (A and B) IHC results of FOS
expression in the proliferative eutopic endometrium (n=57 for EMC,
n=55 for EAOC, n=13 for control). (C and D) Immunohistochemical
results of FOS expression in the secretory eutopic endometrium
(n=38 for EMC, n=8 for EAOC, n=3 for control). (E) FOS expression
in all samples including EAOC patients (n=95 for EMC, n=63 for
EAOC) and the Control group (n=16). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and
***P<0.001. IHC, immunohistochemical; EMC, endometrial cyst of
ovary; EAOC, endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer; ns,
non-significant (P≥0.05). |
The expression of FOS in all endometria is
shown in Fig. 2E. These results
were consistent with previous results. FOS expression was
higher in EAOC than in EMC, suggesting that FOS might be
closely related to the conversion from EMC to EAOC.
Identification of human endometrial
stromal cells
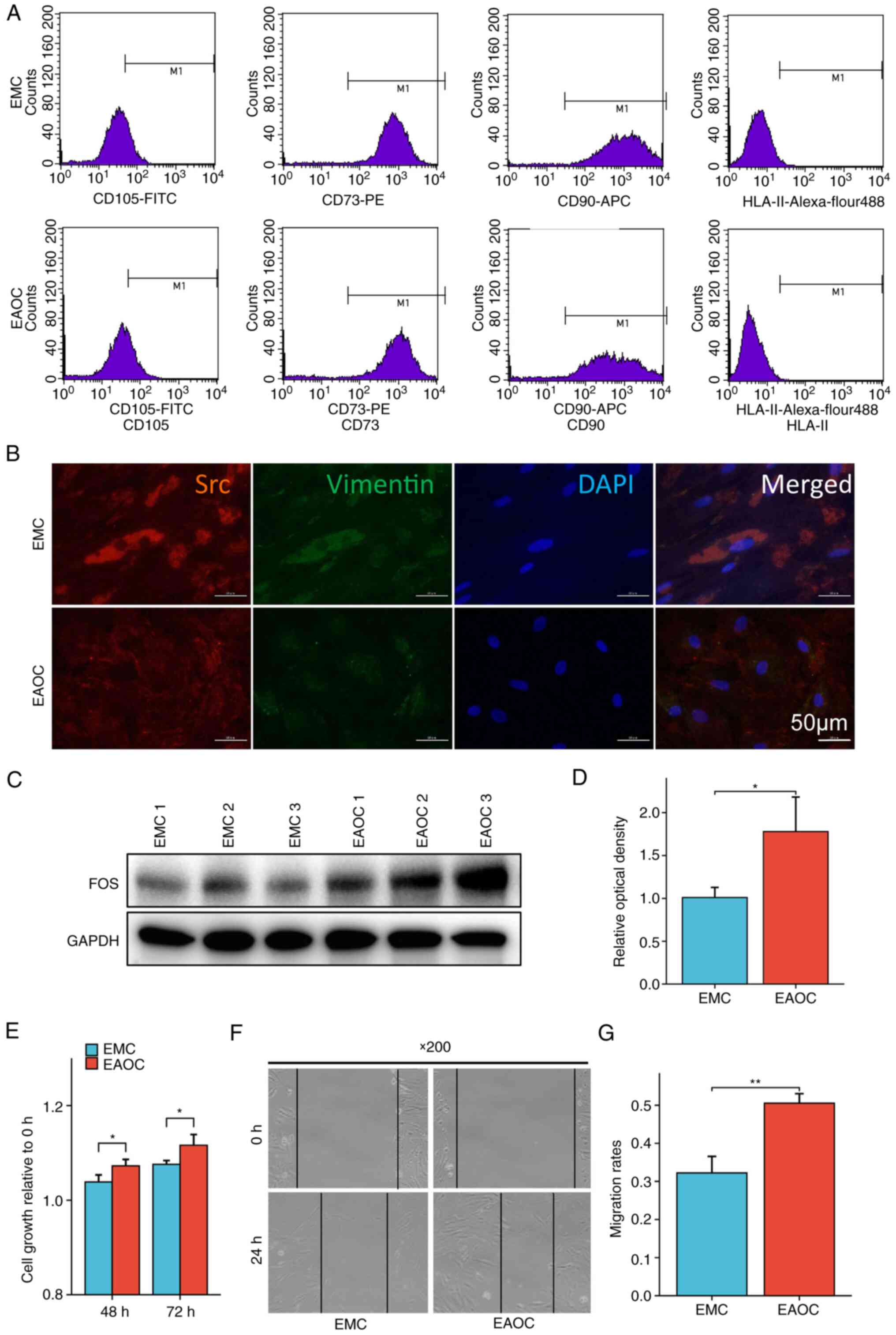
hEnSCs were cultured from fresh endometrial tissues
from EMC and EAOC patients, and flow cytometry and
immunofluorescence staining were used to identify the endometrial
cells cultured in vitro. The cell surface markers CD105,
CD73, CD90 and HLA-II were detected via flow
cytometry. The results showed that the expression of CD105,
CD73 and CD90 on the surface of the endometrial membrane
was positive in primary culture, while the expression of
HLA-II was negative (Fig.
3A).
The immunofluorescence staining results are
displayed in Fig. 3B. The
endometrial cell markers Src and Vimentin could be
detected in the cytoplasm. These results confirmed that the
extracted cells were endometrial cells.
Detection of differences in FOS
expression levels and proliferation and migration abilities of EMC-
and EAOC-derived hEnSCs
Western blot assays were performed using hEnSCs from
EMC and EAOC, respectively, to measure the expression levels of FOS
protein in the cells, and it was found that the expression of
FOS in EAOC was significantly higher than that in EMC
(Fig. 3C and D). Subsequently,
CCK-8 was performed to detect the cell viability and proliferation
ability of hEnSCs from different tissues, and it was found that the
proliferation ability of hEnSCs from EAOC was significantly
stronger than that of hEnSCs from EMC (Fig. 3E). Finally, the migration ability of
hEnSCs was examined using a scratch assay. The migration ability of
hEnSCs from EAOC was still significantly higher than that of hEnSCs
from EMC (Fig. 3F and G).
The effect of inhibiting FOS on the
proliferation of hEnSCs
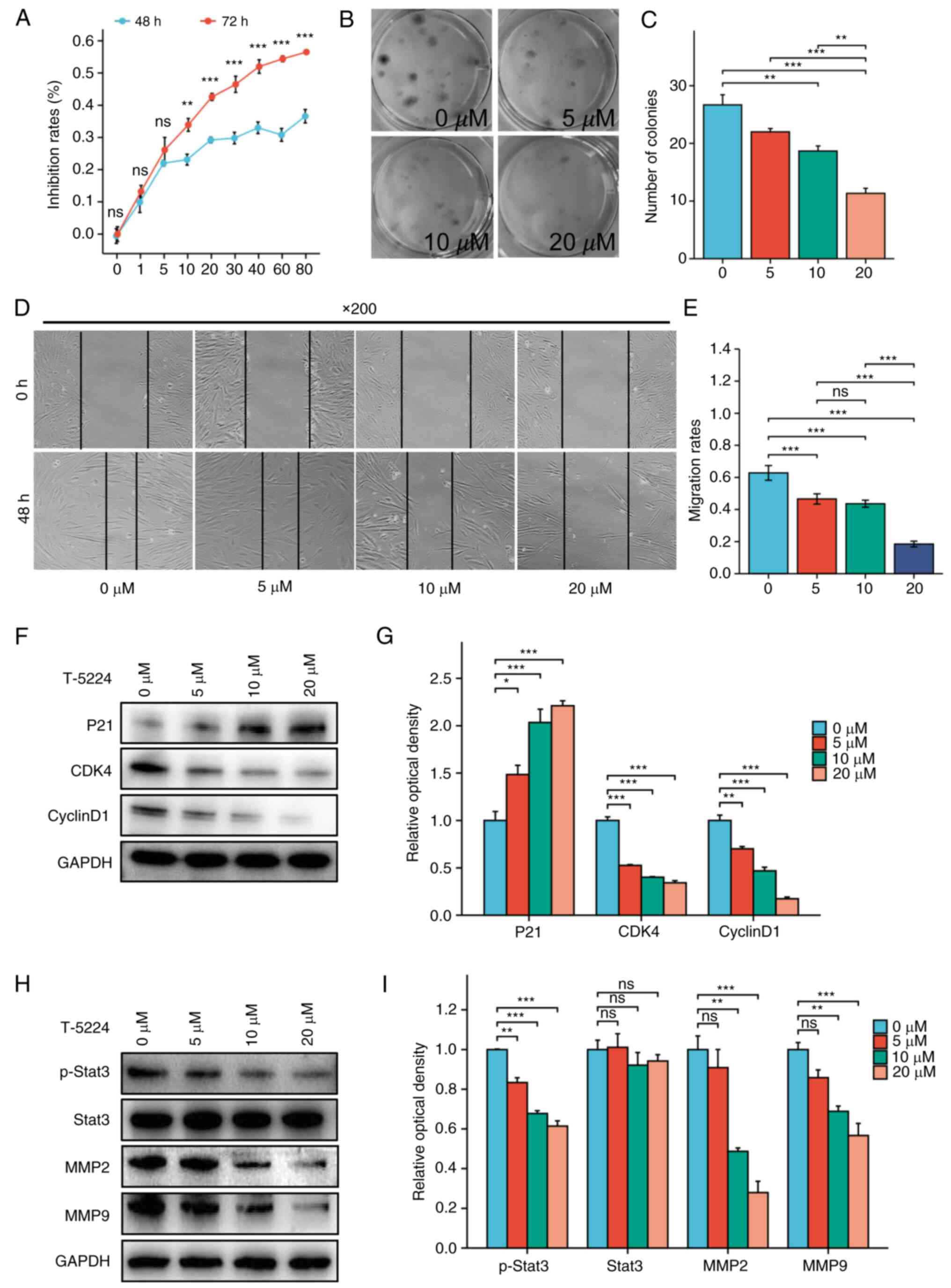
hEnSCs derived from EAOC were treated with different
concentrations of the FOS inhibitor T-5224, and cell
viability was determined via a CCK-8 assay. After treatment with
T-5224 ≥10 µM, the viability of hEnSCs significantly decreased with
increasing FOS inhibitor concentration for 48 or 72 h
(P<0.01), and the effect was dose-dependent (Fig. 4A).
The effect of the FOS inhibitor T-5224 on the
proliferation of hEnSCs derived from EAOC was further detected by a
colony formation assay (Fig. 4B and
C). The colony formation ability of hEnSCs was significantly
reduced after treatment with 10 or 20 µM T-5224 (P<0.01).
The effect of inhibiting FOS on the
migration of hEnSCs
A cell scratch assay was performed to determine the
effect of the FOS inhibitor T-5224 on the migration of
hEnSCs derived from EAOC. As demonstrated in Fig. 4D and E, 5, 10 and 20 µM T-5224 inhibited the
migration of hEnSCs in a dose-dependent manner.
Effect of FOS inhibition on the
expression of cell cycle-related proteins in hEnSCs
Western blotting was used to detect the expression
of cell cycle-related proteins in hEnSCs derived from EAOC after
treatment with the FOS inhibitor T-5224. As the T-5224
concentration increased, the expression of P21 gradually
increased, and the expression of CDK4 and Cyclin D1
gradually decreased (Fig. 4F and
G).
Effect of FOS inhibition on the
expression of proteins associated with endometrial cell
invasion
Western blotting was used to detect the expression
of invasion-related proteins in EAOC-derived hEnSCs treated with
the FOS inhibitor T-5224. As the FOS inhibitor
concentration increased, the expression of p-Stat3, MMP2 and
MMP9 gradually decreased (Fig.
4H and I).
Effect of the upregulation of FOS on
the proliferation of hEnSCs
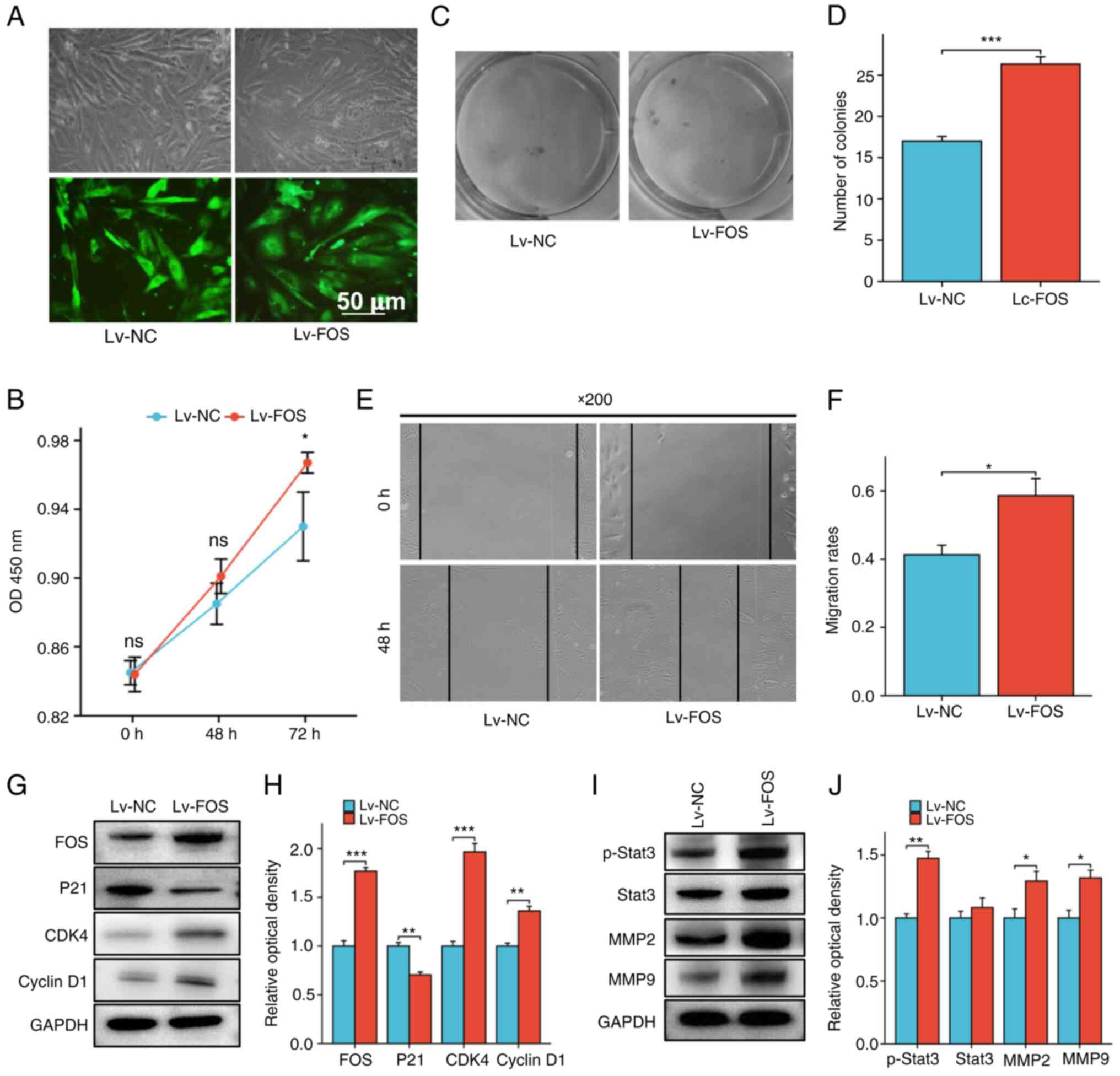
The pLKO1-FOS plasmid was transfected into
EMC hEnSCs using a lentiviral vector, after which the stably
transfected cell lines were screened. As revealed in Fig. 5A, the transfection efficiency was
~80–90%. Further western blot detection of FOS expression in
stably transfected cell lines identified that FOS expression
was significantly upregulated in stably transfected cell lines
compared with that in the parent strains (Fig. 5G and H).
CCK-8 and colony formation assays were subsequently
used to evaluate the effect of upregulated FOS expression on
cell proliferation. The results demonstrated that, compared with
that of the control group, the viability of hEnSCs from EMC was
significantly increased after the upregulation of FOS
expression (Fig. 5B). The results
of the colony formation assay also suggested that upregulated
FOS expression could promote the proliferation of hEnSCs
(Fig. 5C and D).
Effect of upregulated FOS on the
migration of hEnSCs
Cell scratch assays were used to detect the effect
of stable transfection of FOS on the migration of
EMC-derived hEnSCs. As indicated in Fig. 5E and F, stable transfection of
FOS promoted the migration of endometrial cells.
Effect of upregulated FOS on the
expression of proliferation-related proteins in hEnSCs
Western blotting was used to detect the expression
of cell cycle-related proteins in hEnSCs from EMC after stable
transfection with FOS. It was identified that with the
upregulation of FOS expression, P21 expression was
downregulated, while CDK4 and Cyclin D1 expression
was upregulated (Fig. 5G and
H).
Effect of upregulated FOS on the
expression of migration-related proteins in hEnSCs
The expression of invasion-related proteins in
hEnSCs derived from EMC was detected by western blotting. The
results demonstrated that p-Stat3, MMP2 and MMP9
expression was upregulated along with the upregulation of
FOS expression (Fig. 5I and
J). The mechanism through which the FOS protein
regulates the proliferation and migration ability of hEnSCs is
shown in Fig. 6.
Discussion
In the present study, RNA sequencing technology was
utilized to identify 249 DEGs between the eutopic endometrium of
patients with EMC and those with EAOC. Notably, a core group of
genes, FOS, JUN, MKI67, TOP2A, BUB1B, EXO1, KIF4A, KIF20A,
CENPF, NEK2 and KIF18B, was highlighted as central to
the present PPI analysis, which indicated that the functions of
these genes are strongly related to each other.
Further analysis revealed that these genes are
notably involved in critical cellular processes. Specifically, FOS
and JUN are key components of the MAPK signaling pathway and are
known for their roles in cell proliferation, differentiation and
apoptosis, and for their link to tumor development (19,20).
MKI67 is implicated in cell proliferation and maintaining
the organization of chromosomes during cell division (21). TOP2A plays a crucial role in
cell division and growth, particularly in ovarian cancer (22). Along with CENPE and NEK2,
BUB1B ensures accurate chromosome separation during cell
division (23–26). In previous years, EXO1 has
been shown to be overexpressed in various cancers, contributing to
the survival of cancer cells through its DNA repair function
(27–29). Additionally, the KIF family
of proteins is known for its involvement in cell cycle regulation
and cell division (30,31).
Notably, FOS was found to be overexpressed in
the eutopic endometrium of EAOC patients compared with that in the
eutopic endometrium of EMC patients. The overexpression of
FOS suggested its potential role in modulating the behavior
of human endometrial stromal cells (hEnSCs), specifically by
influencing their proliferation and migration abilities.
These findings provide a detailed picture of the
molecular interactions and processes involved in the transformation
of EMC to EAOC. Understanding these dynamics provides valuable
insights into the biological pathways involved in this transition,
setting the stage for further discussion on the results of gene
functional enrichment analysis, where the broader implications of
these gene expression changes on cellular functions will be we
explored.
To further reveal the potential changes in signaling
pathways caused by differences in gene expression between eutopic
endometria from EMC patients and those from EAOC patients,
differential GO analysis and GSEA was performed in the present
study. Notably, GO analysis revealed that the following signaling
pathways were significantly enriched: Angiogenesis, the ERK1
and ERK2 cascades, and cell-cell adhesion. Angiogenesis is
an important factor that supports malignant tumor transformation,
development and metastasis (32,33).
ERKs ensure cell proliferation, differentiation, survival
and metastasis by receiving a large number of growth factors
(EGF, NGF and PDGF) and acting on nuclear
transcription factors such as AP-1 and NF-κB
(34,35). In addition, dysfunction of cell
adhesion molecules also plays an important role in tumor metastasis
(36). Interestingly, GSEA revealed
that DNA methylation, HDACS-mediated deacetylation of
histones, the cell cycle checkpoint, and the AP1 pathway
were enhanced in the eutopic endometrium of EAOC patients, while
complement activation was inhibited (37–39).
AP-1, an intracellular transcriptional activator, is a dimer
composed of c-FOS and c-JUN. Previous studies have
shown that the AP-1 pathway mediates tumor cell
proliferation and metastasis (40,41).
These results showed that the proliferation and metastasis
abilities of eutopic endometrium in patients with EAOC were
enhanced, which was consistent with the PPI prediction, implying
that the endometrium has more potential for malignant
transformation in patients with EAOC than in patients with EMC. The
malignant transformation caused by dysfunction of these pathways
might increase the likelihood of developing EAOC in the eutopic
endometrium. However, further experiments are needed to confirm
these predictions.
Considering the important role of the AP1
pathway in cell proliferation and metastasis and the high
expression of FOS mRNA in eutopic endometrium of EAOC
patients, FOS protein expression in eutopic endometria of
patients with EAOC and EMC was further analyzed using IHC staining.
The current results revealed that the FOS protein was
overexpressed in the eutopic endometrium of EAOC patients compared
with that in the endometrium of EMC patients. Notably, previous
studies have reported that FOS, a nuclear protein
transcription factor, plays an important role in cervical cancer,
prostate cancer and other tumors by regulating cell growth,
proliferation and metastasis (42–45).
Hence, it was suggested that the FOS protein might be
involved in enhancing the malignant potential of the eutopic
endometrium.
To test this hypothesis, primary hEnSCs were
extracted from the eutopic endometrial tissues of EMC and EAOC
patients to further verify the regulatory mechanism of FOS protein
on the eutopic endometrium in EAOC. According to previous studies,
primary hEnSCs cultured to the 3rd generation exhibit a
fibroblast-like morphology, with positive expression of the cell
surface markers CD105, CD73 and CD90 and negative
expression of HLA-II (46,47).
Moreover, Src and Vimentin proteins were positively
expressed in hEnSCs (48,49). The present identification results
for hEnSCs were consistent with previous studies, indicating that
the extraction of primary hEnSCs was successful and could be used
for subsequent experimental studies.
Subsequently, in the present study, using hEnSCs
extracted from endometrial tissues of EMC and EAOC patients,
western blot experiments revealed differential expression of
FOS protein. The results of CCK-8 and scratch assays also
suggested that the proliferation and migration ability of hEnSCs
from endometrial tissues of EAOC patients were significantly
stronger than that of hEnSCs from endometrial tissues of EMC
patients. The potential mechanism of the proliferation and
migration ability of hEnSCs needs to be further investigated.
In the present study, the authors delved deeper
into the multifaceted role of the FOS protein in modulating
the cellular dynamics of hEnSCs derived from EAOC patients. The
inhibition of FOS protein activity by T-5224 revealed a
dose-dependent decrease in the proliferation and migration of
hEnSCs from EAOC patients, highlighting the central role of FOS in
these processes. Moreover, the overexpression of FOS in
hEnSCs from EMC patients significantly augmented their
proliferative and migratory capabilities, corroborating the
findings from the inhibition experiments and underscoring the dual
regulatory nature of FOS.
The decision to use inhibitors instead of
interfering plasmids to suppress FOS was informed by several
considerations. Primarily, the focus on the short-term functions
and mechanisms of FOS necessitated a methodology that provided
swift action and easy control over effects, attributes aptly met by
the inhibitors. Their rapid onset and the ability to fine-tune the
dosage offered a precise way to study FOS's immediate impact. By
contrast, for experiments involving FOS overexpression, interfering
plasmids were used due to the lack of suitable FOS activators.
Furthermore, the use of inhibitors aligns with previous research
(50), where FOS inhibitors
effectively blocked human chorionic gonadotropin-induced increases
in PGE2 and the expression of prostaglandin synthases and
transporters in human granulosa cells. This approach, supported by
literature, allowed for a more straightforward and controllable
operation, avoiding the variables potentially introduced by the
varying transfection efficiencies of interfering plasmids. Thus,
the authors' methodology harnessing the specificity and
controllability of inhibitors significantly contributed to the
understanding of FOS's role in the pathogenesis of EAOC.
At the molecular level, FOS has been
implicated in the transition from the G1 phase to the S phase of
the cell cycle, a critical juncture for cell division and
proliferation. This regulation is orchestrated through the
suppression of P21, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, and
the concurrent upregulation of CDK4 and CyclinD1,
proteins that are pivotal in driving cell cycle progression
(51–53). The modulation of these molecular
players by FOS underscores its integral role in the
proliferation of not only tumor cells but also hEnSCs, as evidenced
by the present findings.
Furthermore, FOS has been demonstrated to bolster
cell migration, an attribute pivotal for tissue remodeling and
potentially metastasis. This migration facilitation is mediated
through the upregulation of MMP2 and MMP9, which are
matrix metalloproteinases that modulate the extracellular matrix
and facilitate cellular movement (53). The present observations resonate
with this mechanism, as the FOS protein in the current study was
shown to regulate the Stat3/MMP2/MMP9 signaling pathway,
aligning with its established role in promoting cell migration.
Notably, the interplay between P21,
CDK4/CyclinD1 and FOS orchestrates a delicate balance
between cell cycle arrest and progression. P21 acts as a
brake, halting the cell cycle in response to various stimuli,
including DNA damage. FOS, by inhibiting P21,
effectively releases this brake, allowing CDK4/CyclinD1 to
drive the cell cycle forward. This mechanism is central not only to
normal cellular functions but also to the pathology of cancer,
where dysregulated cell cycle progression is a hallmark.
In the context of cell migration, the
Stat3/MMP2/MMP9 pathway regulated by FOS is indicative of
its role in cellular architecture remodeling. In particular,
MMP2 and MMP9 are crucial for degrading the
extracellular matrix, a process essential for cell movement and
invasion. This capability, while vital for normal processes such as
wound healing, can be coopted by cancer cells to facilitate
metastasis.
Thus, the present study elucidated the pivotal role
of FOS in regulating the proliferation and migration of
hEnSCs through the P21/CyclinD1/CDK4 and
Stat3/MMP2/MMP9 signaling pathways. These findings not only
shed light on the molecular underpinnings of FOS function
but also highlight its potential as a therapeutic target in
conditions characterized by aberrant cellular proliferation and
migration.
In conclusion, the DEGs-enriched signal pathways
regulating proliferation and migration were promoted in eutopic
endometrium of EAOC patients compared with those in the eutopic
endometrium of EMC patients, indicating that the malignant
potential of the eutopic endometrium of EAOC patients was enhanced.
FOS protein was overexpressed in the eutopic endometrium of
EAOC patients and could enhance the malignant potential of hEnSCs
by regulating the P21/CyclinD1/CDK4 and
Stat3/MMP2/MMP9 signaling pathways.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Department of Science and
Technology of Jilin (grant no. 3D5214067433) and the project of
Jilin Provincial Development and Reform Commission (grant no.
3J1196620433).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the
current study are available in the Gene Expression Omnibus
Repository (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE226575).
Authors' contributions
MC and LZ conceived and designed the study. KH, JC
and MW acquired the data and performed the statistical analysis.
XL, KW, WJ, ZY and ZW performed the experiments and analyzed the
data. KH and JC drafted the manuscript. JC, KH and ZY contributed
to revising the manuscript for intellectual content and language
editing. All authors read and approved the final version of the
manuscript. MC and JC confirm the authenticity of all the raw
data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Ethics
Committee of Jilin University Second Hospital (approval no.
2021202; Changchun, China). Informed consents were obtained from
patients for participation in the EAOC-relative study.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
EM
|
endometriosis
|
|
EMC
|
endometrial cyst of ovary
|
|
EAOC
|
endometriosis-associated ovarian
cancer
|
|
DEGs
|
differential expressed genes
|
|
PPI
|
protein-protein interaction
|
|
GO
|
Gene Ontology
|
|
GSEA
|
Gene set enrichment analysis
|
|
IHC
|
immunohistochemical
|
|
CCK-8
|
Cell Counting Kit-8
|
|
hEnSCs
|
human endometrial stromal cells
|
References
|
1
|
Becker CM, Bokor A, Heikinheimo O, Horne
A, Jansen F, Kiesel L, King K, Kvaskoff M, Nap A, Petersen K, et
al: ESHRE guideline: Endometriosis. Hum Reprod Open.
2022:hoac0092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kawahara N, Miyake R, Yamanaka S and
Kobayashi H: A novel predictive tool for discriminating
endometriosis associated ovarian cancer from ovarian endometrioma:
The R2 predictive index. Cancers (Basel). 13:38292021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mikhaleva LM, Davydov AI, Patsap OI,
Mikhaylenko EV, Nikolenko VN, Neganova ME, Klochkov SG,
Somasundaram SG, Kirkland CE and Aliev G: Malignant transformation
and associated biomarkers of ovarian endometriosis: A narrative
review. Adv Ther. 37:2580–2603. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sampson JA: Endometrial carcinoma of the
ovary, arising in endometrial tissue in that organ. Arch Surg.
10:1–72. 1925. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yamaguchi K, Kitamura S, Furutake Y,
Murakami R, Yamanoi K, Taki M, Ukita M, Hamanishi J and Mandai M:
Acquired evolution of mitochondrial metabolism regulated by HNF1B
in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 13:24132021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Leenen S, Hermens M, de Vos van Steenwijk
PJ, Bekkers RLM and van Esch EMG: Immunologic factors involved in
the malignant transformation of endometriosis to
endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 70:1821–1829. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang D, Guo C, Li Y, Zhou M, Wang H, Liu J
and Chen P: Oestrogen up-regulates DNMT1 and leads to the
hypermethylation of RUNX3 in the malignant transformation of
ovarian endometriosis. Reprod Biomed Online. 44:27–37. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Murakami K, Kotani Y, Nakai H and
Matsumura N: Endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer: The origin
and targeted therapy. Cancers (Basel). 12:16762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu H and Lang JH: Is abnormal eutopic
endometrium the cause of endometriosis? The role of eutopic
endometrium in pathogenesis of endometriosis. Med Sci Monit.
17:RA92–RA99. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Murakami K, Kanto A, Sakai K, Miyagawa C,
Takaya H, Nakai H, Kotani Y, Nishio K and Matsumura N: Frequent
PIK3CA mutations in eutopic endometrium of patients with ovarian
clear cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 34:2071–2079. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Veronika V, Prisyazhnaya T, Zhamoydik VI,
Berlev IV and Malek A: Molecular-genetic background of
endometriosis: Diagnostic potential of heritable and expressed
factors. J Obstet Women's Dis. 67:64–73. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Wang L, Wu Z, Mei
Q, Nie J, Li X, Li Y, Fu X, et al: Whole-exome sequencing of
endometriosis identifies frequent alterations in genes involved in
cell adhesion and chromatin-remodeling complexes. Hum Mol Genet.
23:6008–6021. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang B, Wang T, Li N, Zhang W and Hu Y:
The high expression of RRM2 can predict the malignant
transformation of endometriosis. Adv Ther. 38:5178–5190. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sampson JA: Perforating hemorrhagic
(chocolate) cysts of the ovary: Their importance and especially
their relation to pelvic adenomas of endometrial type (‘adenomyoma’
of the uterus, rectovaginal septum, sigmoid, etc.). Arch Surg.
3:245–323. 1921. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jensen LJ, Kuhn M, Stark M, Chaffron S,
Creevey C, Muller J, Doerks T, Julien P, Roth A, Simonovic M, et
al: STRING 8-a global view on proteins and their functional
interactions in 630 organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 37((Database
Issue)): D412–D416. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen J, Xu D, Wang T, Yang Z, Yang Y, He K
and Zhao L: HMGB1 promotes the development of castration-resistant
prostate cancer by regulating androgen receptor activation. Oncol
Rep. 48:1972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Teng B, Zhao L, Gao J, He P, Li H, Chen J,
Feng Q and Yi C: 20(s)-Protopanaxadiol (PPD) increases the
radiotherapy sensitivity of laryngeal carcinoma. Food Funct.
8:4469–4477. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O and Kolch W:
MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 26:3279–3290.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mishra A, Bharti AC, Saluja D and Das BC:
Transactivation and expression patterns of Jun and Fos/AP-1
super-family proteins in human oral cancer. Int J Cancer.
126:819–829. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cuylen S, Blaukopf C, Politi AZ,
Müller-Reichert T, Neumann B, Poser I, Ellenberg J, Hyman AA and
Gerlich DW: Ki-67 acts as a biological surfactant to disperse
mitotic chromosomes. Nature. 535:308–312. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou Y, Li J, Yang X, Song Y and Li H:
Rhophilin rho GTPase binding protein 1-antisense RNA 1 (RHPN1-AS1)
promotes ovarian carcinogenesis by sponging microRNA-485-5p and
releasing DNA topoisomerase II alpha (TOP2A). Bioengineered.
12:12003–12022. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matsuura S, Matsumoto Y, Morishima KI,
Izumi H, Matsumoto H, Ito E, Tsutsui K, Kobayashi J, Tauchi H,
Kajiwara Y, et al: Monoallelic BUB1B mutations and defective
mitotic-spindle checkpoint in seven families with premature
chromatid separation (PCS) syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 140:358–367.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chan GK, Schaar BT and Yen TJ:
Characterization of the kinetochore binding domain of CENP-E
reveals interactions with the kinetochore proteins CENP-F and
hBUBR1. J Cell Biol. 143:49–63. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Paizula X, Mutailipu D, Xu W, Wang H and
Yi L: Identification of biomarkers related to tumorigenesis and
prognosis in breast cancer. Gland Surg. 11:1472–1488. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fu G, Ding X, Yuan K, Aikhionbare F, Yao
J, Cai X, Jiang K and Yao X: Phosphorylation of human Sgo1 by NEK2A
is essential for chromosome congression in mitosis. Cell Res.
17:608–618. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
He D, Li T, Sheng M and Yang B:
Exonuclease 1 (Exo1) participates in mammalian non-homologous end
joining and contributes to drug resistance in ovarian cancer. Med
Sci Monit. 26:e9187512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang S, Cai W, Li J, An W, Zheng H and
Liao M: Bioinformatics analysis and experimental study of
exonuclease 1 gene in lung adenocarcinoma. Biochem Genet.
60:1934–1945. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dracea A, Angelescu C, Danciulescu M,
Ciurea M, Ioana M and Burada F: Mismatch repair gene expression in
gastroesophageal cancers. Turk J Gastroenterol. 26:373–377. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Geng A, Qiu R, Murai K, Liu J, Wu X, Zhang
H, Farhoodi H, Duong N, Jiang M, Yee JK, et al: KIF20A/MKLP2
regulates the division modes of neural progenitor cells during
cortical development. Nat Commun. 9:27072018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Louw JJ, Nunes Bastos R, Chen X, Verdood
C, Corveleyn A, Jia Y, Breckpot J, Gewillig M, Peeters H, Santoro
MM, et al: Compound heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in
KIF20A are associated with a novel lethal congenital cardiomyopathy
in two siblings. PLoS Genet. 14:e10071382018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tian L, Goldstein A, Wang H, Ching Lo H,
Sun Kim I, Welte T, Sheng K, Dobrolecki LE, Zhang X, Putluri N, et
al: Mutual regulation of tumour vessel normalization and
immunostimulatory reprogramming. Nature. 544:250–254. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis: An organizing
principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:273–286. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao J, Klausen C, Yi Y, Cheng JC, Chang
HM and Leung PCK: Betacellulin enhances ovarian cancer cell
migration by up-regulating Connexin43 via MEK-ERK signaling. Cell
Signal. 65:1094392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gao Y, Li H, Han Q, Li Y, Wang T, Huang C,
Mao Y, Wang X, Zhang Q, Tian J, et al: Overexpression of DUSP6
enhances chemotherapy-resistance of ovarian epithelial cancer by
regulating the ERK signaling pathway. J Cancer. 11:3151–3164. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang S, Xie B, Wang L, Yang H, Zhang H,
Chen Y, Wang F, Liu C and He H: Macrophage-mediated vascular
permeability via VLA4/VCAM1 pathway dictates ascites development in
ovarian cancer. J Clin Invest. 131:e1403152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Koch A, Joosten SC, Feng Z, de Ruijter TC,
Draht MX, Melotte V, Smits KM, Veeck J, Herman JG, Van Neste L, et
al: Analysis of DNA methylation in cancer: Location revisited. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 15:459–466. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hu XT, Xing W, Zhao RS, Tan Y, Wu XF, Ao
LQ, Li Z, Yao MW, Yuan M, Guo W, et al: HDAC2 inhibits EMT-mediated
cancer metastasis by downregulating the long noncoding RNA H19 in
colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:2702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kastan MB and Bartek J: Cell-cycle
checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 432:316–323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Koo JH, Plouffe SW, Meng Z, Lee DH, Yang
D, Lim DS, Wang CY and Guan KL: Induction of AP-1 by YAP/TAZ
contributes to cell proliferation and organ growth. Genes Dev.
34:72–86. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shaulian E and Karin M: AP-1 as a
regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol. 4:E131–E136. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li P, Lin Z, Liu Q, Chen S, Gao X, Guo W,
Gong F, Wei J and Lin H: Enhancer RNA SLIT2 inhibits bone
metastasis of breast cancer through regulating P38 MAPK/c-Fos
signaling pathway. Front Oncol. 11:7438402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Riedel M, Berthelsen MF, Cai H, Haldrup J,
Borre M, Paludan SR, Hager H, Vendelbo MH, Wagner EF, Bakiri L and
Thomsen MK: In vivo CRISPR inactivation of Fos promotes prostate
cancer progression by altering the associated AP-1 subunit Jun.
Oncogene. 40:2437–2447. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gupte R, Lin KY, Nandu T, Lea JS and Kraus
WL: Combinatorial treatment with PARP-1 inhibitors and cisplatin
attenuates cervical cancer growth through Fos-driven changes in
gene expression. Mol Cancer Res. 20:1183–1192. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Matsuoka K, Bakiri L, Wolff LI, Linder M,
Mikels-Vigdal A, Patiño-García A, Lecanda F, Hartmann C, Sibilia M
and Wagner EF: Wnt signaling and Loxl2 promote aggressive
osteosarcoma. Cell Res. 30:885–901. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sohn JO, Seong SY, Kim HJ, Jo YM, Lee KH,
Chung MK, Song HJ, Park KS and Lim JM: Alterations in intracellular
Ca2+ levels in human endometrial stromal cells after
decidualization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 515:318–324. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zlatska AV, Rodnichenko AE, Gubar OS,
Zubov DO, Novikova SN and Vasyliev RG: Endometrial stromal cells:
Isolation, expansion, morphological and functional properties. Exp
Oncol. 39:197–202. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chiappini F, Bastón JI, Vaccarezza A,
Singla JJ, Pontillo C, Miret N, Farina M, Meresman G and Randi A:
Enhanced cyclooxygenase-2 expression levels and metalloproteinase 2
and 9 activation by Hexachlorobenzene in human endometrial stromal
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 109:912016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu L, Chen G, Chen T, Shi W, Hu H, Song
K, Huang R, Cai H and He Y: si-SNHG5-FOXF2 inhibits TGF-β1-induced
fibrosis in human primary endometrial stromal cells by the
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:4792020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Choi Y, Rosewell KL, Brännström M, Akin
JW, Curry TE Jr and Jo M: FOS, a critical downstream mediator of
PGR and EGF signaling necessary for ovulatory prostaglandins in the
human ovary. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 103:4241–4252. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pandey K, An HJ, Kim SK, Lee SA, Kim S,
Lim SM, Kim GM, Sohn J and Moon YW: Molecular mechanisms of
resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: A review. Int J
Cancer. 145:1179–1188. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu TZ, Chen CY, Yiin SJ, Chen CH, Cheng
JT, Shih MK, Wang YS and Chern CL: Molecular mechanism of cell
cycle blockage of hepatoma SK-Hep-1 cells by Epimedin C through
suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and
increased expression of CDK inhibitors p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1).
Food Chem Toxicol. 44:227–235. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wu S, Wu Z, Xu H, Zhang J, Gu W, Tan X,
Pan Z, Cao D, Li D, Yang L, et al: miR-34a-5p inhibits the
malignant progression of KSHV-infected SH-SY5Y cells by targeting
c-fos. PeerJ. 10:e132332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|