|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xia C, Dong X, Li H, Cao M, Sun D, He S,
Yang F, Yan X, Zhang S, Li N and Chen W: Cancer statistics in China
and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin
Med J (Engl). 135:584–590. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Simmons JK, Hildreth BE III, Supsavhad W,
Elshafae SM, Hassan BB, Dirksen WP, Toribio RE and Rosol TJ: Animal
models of bone metastasis. Vet Pathol. 52:827–841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang SH, Kao YH, Muller CJF, Joubert E
and Chuu CP: Aspalathin-rich green Aspalathus linearis extract
suppresses migration and invasion of human castration-resistant
prostate cancer cells via inhibition of YAP signaling.
Phytomedicine. 69:1532102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gebrael G, Fortuna GG, Sayegh N, Swami U
and Agarwal N: Advances in the treatment of metastatic prostate
cancer. Trends Cancer. 9:840–854. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Skotheim RI, Bogaard M, Carm KT, Axcrona U
and Axcrona K: Prostate cancer: Molecular aspects, consequences,
and opportunities of the multifocal nature. Biochim Biophys Acta
Rev Cancer. 1879:1890802024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu Z, Zou H, Wang H, Li Q and Yu D:
Identification of key gene signatures associated with bone
metastasis in castration-resistant prostate cancer using
co-expression analysis. Front Oncol. 10:5715242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qu L, Li S, Zhuo Y, Chen J, Qin X and Guo
G: Anticancer effect of triterpenes from Ganoderma lucidum in human
prostate cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 14:7467–7472. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Morale MG, Tamura RE and Rubio IGS:
Metformin and cancer hallmarks: Molecular mechanisms in thyroid,
prostate and head and neck cancer models. Biomolecules. 12:3572022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chi JT, Lin PH, Tolstikov V, Oyekunle T,
Chen EY, Bussberg V, Greenwood B, Sarangarajan R, Narain NR,
Kiebish MA and Freedland SJ: Metabolomic effects of androgen
deprivation therapy treatment for prostate cancer. Cancer Med.
9:3691–3702. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Salji M, Hendry J, Patel A, Ahmad I, Nixon
C and Leung HY: Peri-prostatic fat volume measurement as a
predictive tool for castration resistance in advanced prostate
cancer. Eur Urol Focus. 4:858–866. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang L, Jin M, Park SJ, Seo SY and Jeong
KW: SETD1A promotes proliferation of castration-resistant prostate
cancer cells via FOXM1 transcription. Cancers (Basel). 12:17362020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Boopathi E, Birbe R, Shoyele SA, Den RB
and Thangavel C: Bone health management in the continuum of
prostate cancer disease. Cancers (Basel). 14:43052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Talreja DB: Importance of antiresorptive
therapies for patients with bone metastases from solid tumors.
Cancer Manag Res. 4:287–297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Clézardin P, Coleman R, Puppo M, Ottewell
P, Bonnelye E, Paycha F, Confavreux CB and Holen I: Bone
metastasis: Mechanisms, therapies, and biomarkers. Physiol Rev.
101:797–855. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sgouros G, Bodei L, McDevitt MR and Nedrow
JR: Radiopharmaceutical therapy in cancer: Clinical advances and
challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 19:589–608. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lawal IO, Ndlovu H, Kgatle M, Mokoala KMG
and Sathekge MM: Prognostic value of PSMA PET/CT in prostate
cancer. Semin Nucl Med. 54:46–59. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Houshmand S, Lawhn-Heath C and Behr S:
PSMA PET imaging in the diagnosis and management of prostate
cancer. Abdom Radiol (NY). 48:3610–3623. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pyka T, Okamoto S, Dahlbender M, Tauber R,
Retz M, Heck M, Tamaki N, Schwaiger M, Maurer T and Eiber M:
Comparison of bone scintigraphy and (68)Ga-PSMA PET for skeletal
staging in prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
43:2114–2121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Harmon SA, Bergvall E, Mena E, Shih JH,
Adler S, McKinney Y, Mehralivand S, Citrin DE, Couvillon A, Madan
RA, et al: A prospective comparison of 18F-sodium
fluoride PET/CT and PSMA-Targeted 18F-DCFBC PET/CT in
metastatic prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 59:1665–1671. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Luna A, Vilanova JC and Alcalá Mata L:
Total body MRI in early detection of bone metastasis and its
indication in comparison to bone scan and other imaging techniques.
Arch Esp Urol. 68:371–390. 2015.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kang J, La Manna F, Bonollo F, Sampson N,
Alberts IL, Mingels C, Afshar-Oromieh A, Thalmann GN and
Karkampouna S: Tumor microenvironment mechanisms and bone
metastatic disease progression of prostate cancer. Cancer Lett.
530:156–169. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
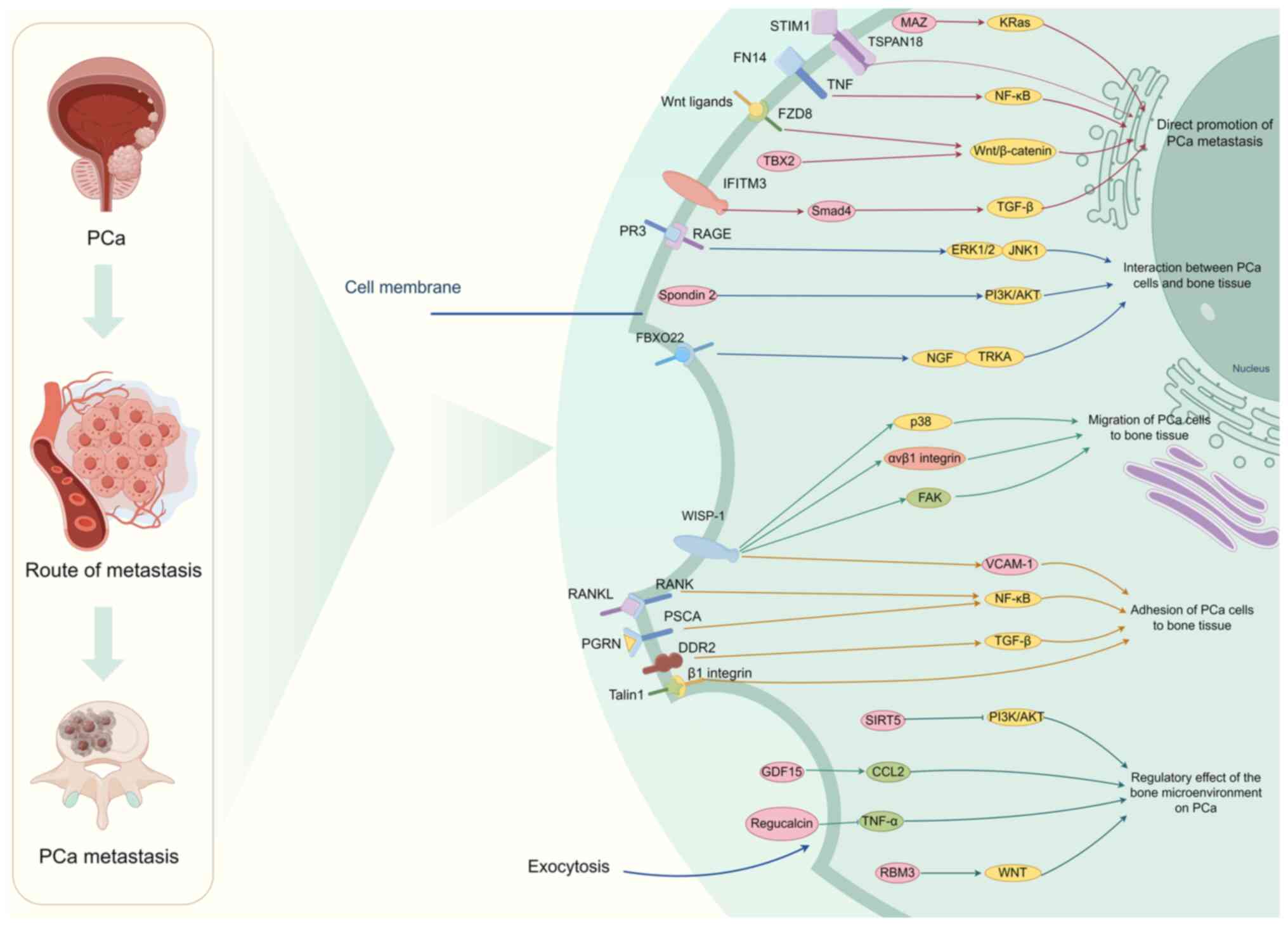
|
|
23
|
Zhou Q, Chen X, Yao K, Zhang Y, He H,
Huang H, Chen H, Peng S, Huang M, Cheng L, et al: TSPAN18
facilitates bone metastasis of prostate cancer by protecting STIM1
from TRIM32-mediated ubiquitination. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
42:1952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Chen L, Fan Y, Hong Y, Yang X, Li
Y, Lu J, Lv J, Pan X, Qu F, et al: IFITM3 promotes bone metastasis
of prostate cancer cells by mediating activation of the TGF-β
signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 10:5172019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Abramovic I, Ulamec M, Katusic Bojanac A,
Bulic-Jakus F, Jezek D and Sincic N: miRNA in prostate cancer:
Challenges toward translation. Epigenomics. 12:543–558. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lang C, Yin C, Lin K, Li Y, Yang Q, Wu Z,
Du H, Ren D, Dai Y and Peng X: m6A modification of
lncRNA PCAT6 promotes bone metastasis in prostate cancer through
IGF2BP2-mediated IGF1R mRNA stabilization. Clin Transl Med.
11:e4262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li FX, Liu JJ, Xu F, Lin X, Zhong JY, Wu F
and Yuan LQ: Role of tumor-derived exosomes in bone metastasis.
Oncol Lett. 18:3935–3945. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yin J, Liu YN, Tillman H, Barrett B,
Hewitt S, Ylaya K, Fang L, Lake R, Corey E, Morrissey C, et al:
AR-regulated TWEAK-FN14 pathway promotes prostate cancer bone
metastasis. Cancer Res. 74:4306–4317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang H, Weng H and Chen J: m6A
modification in coding and non-coding RNAs: Roles and therapeutic
implications in cancer. Cancer Cell. 37:270–288. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kolonin MG, Sergeeva A, Staquicini DI,
Smith TL, Tarleton CA, Molldrem JJ, Sidman RL, Marchiò S,
Pasqualini R and Arap W: Interaction between tumor cell surface
receptor RAGE and proteinase 3 mediates prostate cancer metastasis
to bone. Cancer Res. 77:3144–3150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park M, Cho YJ, Kim B, Ko YJ, Jang Y, Moon
YH, Hyun H and Lim W: RANKL immunisation inhibits prostate cancer
metastasis by modulating EMT through a RANKL-dependent pathway. Sci
Rep. 11:121862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Q, Ye L, Zhang X, Wang M, Lin C, Huang
S, Guo W, Lai Y, Du H, Li J, et al: FZD8, a target of p53, promotes
bone metastasis in prostate cancer by activating canonical
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cancer Lett. 402:166–176. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nandana S, Tripathi M, Duan P, Chu CY,
Mishra R, Liu C, Jin R, Yamashita H, Zayzafoon M, Bhowmick NA, et
al: Bone metastasis of prostate cancer can be therapeutically
targeted at the TBX2-WNT signaling axis. Cancer Res. 77:1331–1344.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang Q, Lang C, Wu Z, Dai Y, He S, Guo W,
Huang S, Du H, Ren D and Peng X: MAZ promotes prostate cancer bone
metastasis through transcriptionally activating the KRas-dependent
RalGEFs pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3912019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang S, Lv C, Niu Y, Li C, Li X, Shang Y,
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y and Zeng Y: RBM3 suppresses stemness
remodeling of prostate cancer in bone microenvironment by
modulating N6-methyladenosine on CTNNB1 mRNA. Cell Death Dis.
14:912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yamaguchi M, Murata T and Ramos JW:
Extracellular regucalcin suppresses the growth, migration,
invasion, and adhesion of metastatic human prostate cancer cells.
Oncology. 100:399–412. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yamaguchi M, Murata T and Ramos JW:
Overexpression of regucalcin blocks the migration, invasion, and
bone metastatic activity of human prostate cancer cells: Crosstalk
between cancer cells and bone cells. Prostate. 82:1025–1039. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lagunas-Rangel FA: Role of SIRT5 in
cancer. Friend or Foe? Biochimie. 209:131–141. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang X, Li Z and Sun Y: T-box
transcription factor 2 mediates antitumor immune response in
cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the expression of
programmed death ligand 1. Skin Res Technol. 29:e132542023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Trivedi T, Pagnotti GM, Guise TA and
Mohammad KS: The role of TGF-β in bone metastases. Biomolecules.
11:16432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gerratana L, Davis AA, Polano M, Zhang Q,
Shah AN, Lin C, Basile D, Toffoli G, Wehbe F, Puglisi F, et al:
Understanding the organ tropism of metastatic breast cancer through
the combination of liquid biopsy tools. Eur J Cancer. 143:147–157.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yonezawa I, Waki M, Tamura Y, Onoda R,
Narushima M, Ishizuka T and Tajima S: Gemcitabine-based regimen for
primary ovarian angiosarcoma with MYC amplification. Curr Oncol.
21:e782–e789. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Stopsack KH, Nandakumar S, Wibmer AG,
Haywood S, Weg ES, Barnett ES, Kim CJ, Carbone EA, Vasselman SE,
Nguyen B, et al: Oncogenic genomic alterations, clinical
phenotypes, and outcomes in metastatic castration-sensitive
prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 26:3230–3238. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Archer Goode E, Wang N and Munkley J:
Prostate cancer bone metastases biology and clinical management
(Review). Oncol Lett. 25:1632023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang H, Zhang M, Lu W and Yuan C: Prostate
cancer cell-derived spondin 2 boosts osteogenic factor levels in
osteoblasts via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Oncol Rep. 49:232023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang Y, Li W, Guo S, Wu Z, Zhang L, Liu
Y, Li X, Guo X, Cao J, Yang C and Wang Z: FBXO22 mediates the
NGF/TRKA signaling pathway in bone metastases in prostate cancer.
Am J Pathol. 193:1248–1266. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ziaee S and Chung LWK: Induction of
integrin α2 in a highly bone metastatic human prostate cancer cell
line: Roles of RANKL and AR under three-dimensional suspension
culture. Mol Cancer. 13:2082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ye XC, Choueiri M, Tu SM and Lin SH:
Biology and clinical management of prostate cancer bone metastasis.
Front Biosci. 12:3273–3286. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nayerpour Dizaj T, Doustmihan A,
Sadeghzadeh Oskouei B, Akbari M, Jaymand M, Mazloomi M and
Jahanban-Esfahlan R: Significance of PSCA as a novel prognostic
marker and therapeutic target for cancer. Cancer Cell Int.
24:1352024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhao Z, Li E, Luo L, Zhao S, Liu L, Wang
J, Kang R and Luo J: A PSCA/PGRN-NF-κB-integrin-α4 axis promotes
prostate cancer cell adhesion to bone marrow endothelium and
enhances metastatic potential. Mol Cancer Res. 18:501–513. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Azemikhah M, Ashtiani HA, Aghaei M and
Rastegar H: Evaluation of discoidin domain receptor-2 (DDR2)
expression level in normal, benign, and malignant human prostate
tissues. Res Pharm Sci. 10:356–363. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yan Z, Jin S, Wei Z, Huilian H, Zhanhai Y,
Yue T, Juan L, Jing L, Libo Y and Xu L: Discoidin domain receptor 2
facilitates prostate cancer bone metastasis via regulating
parathyroid hormone-related protein. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1842:1350–1363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Calderwood DA, Campbell ID and Critchley
DR: Talins and kindlins: Partners in integrin-mediated adhesion.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:503–517. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jin JK, Tien PC, Cheng CJ, Song JH, Huang
C, Lin SH and Gallick GE: Talin1 phosphorylation activates β1
integrins: A novel mechanism to promote prostate cancer bone
metastasis. Oncogene. 34:1811–1821. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Holbourn KP, Acharya KR and Perbal B: The
CCN family of proteins: Structure-function relationships. Trends
Biochem Sci. 33:461–473. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tai HC, Chang AC, Yu HJ, Huang CY, Tsai
YC, Lai YW, Sun HL, Tang CH and Wang SW: Osteoblast-derived
WNT-induced secreted protein 1 increases VCAM-1 expression and
enhances prostate cancer metastasis by down-regulating miR-126.
Oncotarget. 5:7589–7598. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chang AC, Chen PC, Lin YF, Su CM, Liu JF,
Lin TH, Chuang SM and Tang CH: Osteoblast-secreted WISP-1 promotes
adherence of prostate cancer cells to bone via the VCAM-1/integrin
α4β1 system. Cancer Lett. 426:47–56. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yao L and Zhang X: Interaction between
prostate cancer stem cells and bone microenvironment regulates
prostate cancer bone metastasis and treatment resistance. J Cancer.
13:2757–2767. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Choi SY, Jeon JM, Na AY, Kwon OK, Bang IH,
Ha YS, Bae EJ, Park BH, Lee EH, Kwon TG, et al: SIRT5 directly
inhibits the PI3K/AKT pathway in prostate cancer cell lines. Cancer
Genomics Proteomics. 19:50–59. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Siddiqui JA, Seshacharyulu P, Muniyan S,
Pothuraju R, Khan P, Vengoji R, Chaudhary S, Maurya SK, Lele SM,
Jain M, et al: GDF15 promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis and
colonization through osteoblastic CCL2 and RANKL activation. Bone
Res. 10:62022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Toden S, Zumwalt TJ and Goel A: Non-coding
RNAs and potential therapeutic targeting in cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta Rev Cancer. 1875:1884912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Loganathan T and Doss CGP: Non-coding RNAs
in human health and disease: Potential function as biomarkers and
therapeutic targets. Funct Integr Genomics. 23:332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ma L, Bajic VB and Zhang Z: On the
classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 10:925–933. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bhan A, Soleimani M and Mandal SS: Long
noncoding RNA and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. 77:3965–3981.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wang J, Yue BL, Huang YZ, Lan XY, Liu WJ
and Chen H: Exosomal RNAs: Novel potential biomarkers for
diseases-a review. Int J Mol Sci. 23:24612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Prigol AN, Rode MP, da Luz Efe F, Saleh NA
and Creczynski-Pasa TB: The bone microenvironment soil in prostate
cancer metastasis: An miRNA approach. Cancers (Basel). 15:40272023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
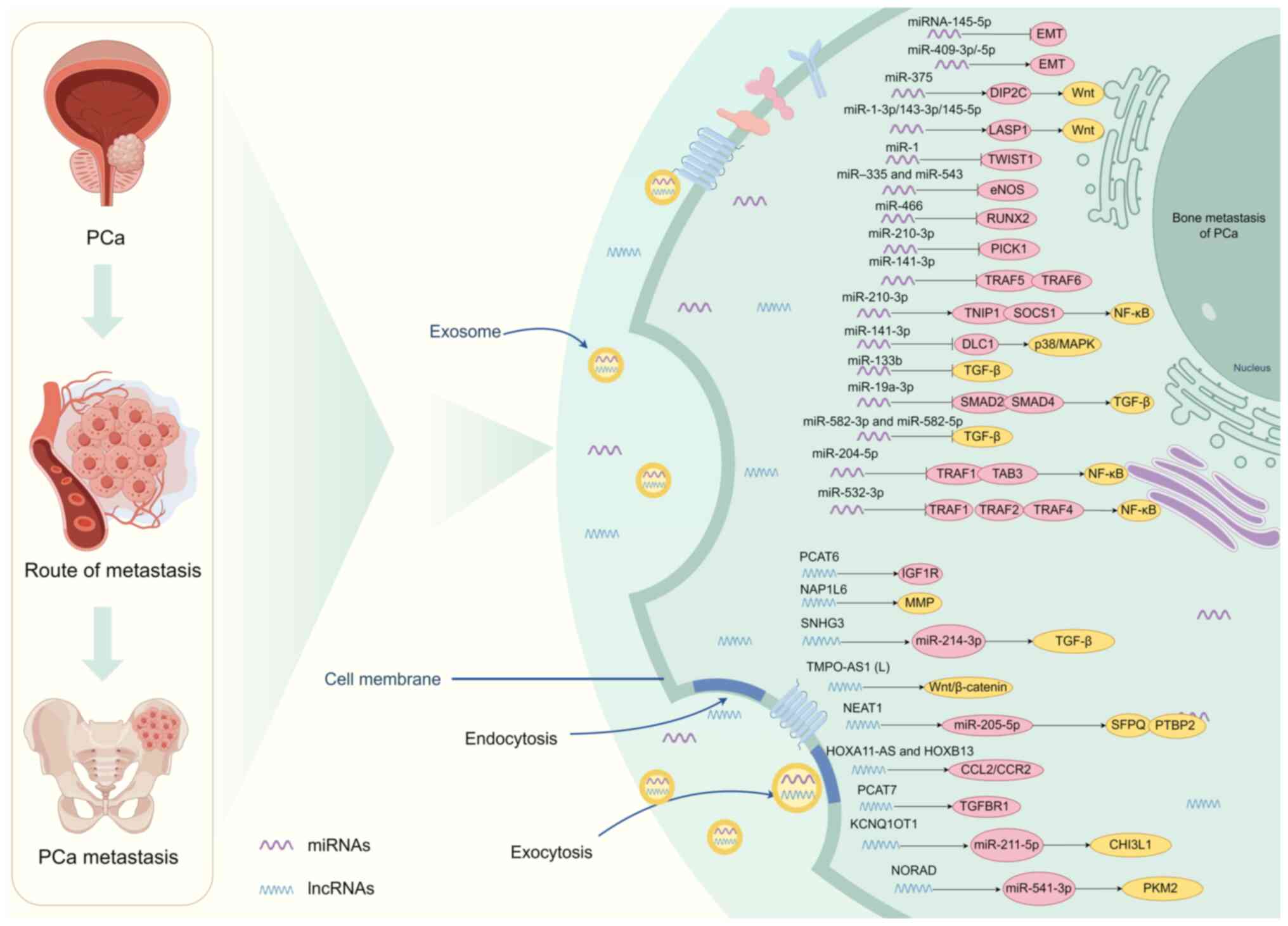
|
67
|
Liu Y, Yang C, Chen S, Liu W, Liang J, He
S and Hui J: Cancer-derived exosomal miR-375 targets DIP2C and
promotes osteoblastic metastasis and prostate cancer progression by
regulating the Wnt signaling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 30:437–449.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zheng Y, Qi F, Li L, Yu B, Cheng Y, Ge M,
Qin C and Li X: LncNAP1L6 activates MMP pathway by stabilizing the
m6A-modified NAP1L2 to promote malignant progression in prostate
cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 30:209–218. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Guo H, Zhao J, Li X, Sun F, Qin Y, Yang X,
Xiong X, Yin Q, Wang X, Gao L, et al: Identification of miR-1-3p,
miR-143-3p and miR-145-5p association with bone metastasis of
Gleason 3+4 prostate cancer and involvement of LASP1 regulation.
Mol Cell Probes. 68:1019012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Josson S, Gururajan M, Hu P, Shao C, Chu
GY, Zhau HE, Liu C, Lao K, Lu CL, Lu YT, et al: miR-409-3p/-5p
promotes tumorigenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and
bone metastasis of human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:4636–4646. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Dai Y, Ren D, Yang Q, Cui Y, Guo W, Lai Y,
Du H, Lin C, Li J, Song L and Peng X: The TGF-β signalling negative
regulator PICK1 represses prostate cancer metastasis to bone. Br J
Cancer. 117:685–694. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ye Y, Li SL, Ma YY, Diao YJ, Yang L, Su
MQ, Li Z, Ji Y, Wang J, Lei L, et al: Exosomal miR-141-3p regulates
osteoblast activity to promote the osteoblastic metastasis of
prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 8:94834–94849. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wa Q, Zou C, Lin Z, Huang S, Peng X, Yang
C, Ren D, Xu D, Guo Y, Liao Z, et al: Ectopic expression of
miR-532-3p suppresses bone metastasis of prostate cancer cells via
inactivating NF-κB signaling. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 17:267–277.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ren D, Yang Q, Dai Y, Guo W, Du H, Song L
and Peng X: Oncogenic miR-210-3p promotes prostate cancer cell EMT
and bone metastasis via NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Cancer.
16:1172017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chen Q, Zhang H, Zhang J, Shen L, Yang J,
Wang Y, Ma J and Zhuan B: miR-210-3p promotes lung cancer
development and progression by modulating USF1 and PCGF3. Onco
Targets Ther. 14:3687–3700. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Tuo X, Zhou Y, Yang X, Ma S, Liu D, Zhang
X, Hou H, Wang R, Li X and Zhao L: miR-532-3p suppresses
proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells via
GPNMB/HIF-1α/HK2 axis. Pathol Res Pract. 237:1540322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Luo B, Yuan Y, Zhu Y, Liang S, Dong R, Hou
J, Li P, Xing Y, Lu Z, Lo R and Kuang GM: microRNA-145-5p inhibits
prostate cancer bone metastatic by modulating the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Front Oncol. 12:9887942022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Chang YS, Chen WY, Yin JJ,
Sheppard-Tillman H, Huang J and Liu YN: EGF receptor promotes
prostate cancer bone metastasis by downregulating miR-1 and
activating TWIST1. Cancer Res. 75:3077–3086. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Fu Q, Liu X, Liu Y, Yang J, Lv G and Dong
S: MicroRNA-335 and −543 suppress bone metastasis in prostate
cancer via targeting endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Int J Mol
Med. 36:1417–1425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Colden M, Dar AA, Saini S, Dahiya PV,
Shahryari V, Yamamura S, Tanaka Y, Stein G, Dahiya R and Majid S:
MicroRNA-466 inhibits tumor growth and bone metastasis in prostate
cancer by direct regulation of osteogenic transcription factor
RUNX2. Cell Death Dis. 8:e25722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Huang S, Wa Q, Pan J, Peng X, Ren D, Huang
Y, Chen X and Tang Y: Downregulation of miR-141-3p promotes bone
metastasis via activating NF-κB signaling in prostate cancer. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 36:1732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Huang S, Wa Q, Pan J, Peng X, Ren D, Li Q,
Dai Y, Yang Q, Huang Y, Zhang X, et al: Transcriptional
downregulation of miR-133b by REST promotes prostate cancer
metastasis to bone via activating TGF-β signaling. Cell Death Dis.
9:7792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Huang S, Zou C, Tang Y, Wa Q, Peng X, Chen
X, Yang C, Ren D, Huang Y, Liao Z, et al: miR-582-3p and miR-582-5p
suppress prostate cancer metastasis to bone by repressing TGF-β
signaling. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 16:91–104. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Wa Q, Huang S, Pan J, Tang Y, He S, Fu X,
Peng X, Chen X, Yang C, Ren D, et al: miR-204-5p represses bone
metastasis via inactivating NF-κB signaling in prostate cancer. Mol
Ther Nucleic Acids. 18:567–579. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Wa Q, Li L, Lin H, Peng X, Ren D, Huang Y,
He P and Huang S: Downregulation of miR-19a-3p promotes invasion,
migration and bone metastasis via activating TGF-β signaling in
prostate cancer. Oncol Rep. 39:81–90. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Qu L, Li Z and Liu P: mir-204-5p Acts as a
tumor suppressor by targeting DNM2 in osteosarcoma cells. J Healthc
Eng. 2022:89445882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Sun R, Wei T, Ding D, Zhang J, Chen S, He
HH, Wang L and Huang H: CYCLIN K down-regulation induces androgen
receptor gene intronic polyadenylation, variant expression and PARP
inhibitor vulnerability in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 119:e22055091192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Yang S, Chen B, Zhang B, Li C, Qiu Y, Yang
H and Huang Z: miR-204-5p promotes apoptosis and inhibits migration
of gastric cancer cells by targeting HER-2. Mol Med Rep.
22:2645–2654. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Peng L, Li P and Peng Z: miR-141-3p
enhanced radiosensitivity of CRC cells. Comb Chem High Throughput
Screen. 27:118–126. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Liu Y, Fu W, Yin F, Xia L, Zhang Y, Wang
B, Li T, Zhang T, Cheng L, Wei Y and Gao B: miR-141-3p suppresses
development of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by regulating NEK6.
Anticancer Drugs. 33:e125–e133. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ferraz RS, Cavalcante JVF, Magalhães L,
Ribeiro-Dos-Santos  and Dalmolin RJS: Revealing metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer master regulator through
lncRNAs-centered regulatory network. Cancer Med. 12:19279–19290.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang M, Yin C, Wu Z, Wang X, Lin Q, Jiang
X, Du H, Lang C, Peng X and Dai Y: The long transcript of lncRNA
TMPO-AS1 promotes bone metastases of prostate cancer by regulating
the CSNK2A1/DDX3X complex in Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cell Death
Discov. 9:2872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Xi X, Hu Z, Wu Q, Hu K, Cao Z, Zhou J,
Liao J, Zhang Z, Hu Y, Zhong X and Bao Y: High expression of small
nucleolar RNA host gene 3 predicts poor prognosis and promotes bone
metastasis in prostate cancer by activating transforming growth
factor-beta signaling. Bioengineered. 13:1895–1907. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Misawa A, Kondo Y, Takei H and Takizawa T:
Long noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS and transcription factor HOXB13
modulate the expression of bone metastasis-related genes in
prostate cancer. Genes (Basel). 12:1822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Lang C, Dai Y, Wu Z, Yang Q, He S, Zhang
X, Guo W, Lai Y, Du H, Wang H, et al: SMAD3/SP1 complex-mediated
constitutive active loop between lncRNA PCAT7 and TGF-β signaling
promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis. Mol Oncol. 14:808–828.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hao H, Chen H, Xie L, Liu H and Wang D:
LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes proliferation, invasion and metastasis of
prostate cancer by regulating miR-211-5p/CHI3L1 pathway. Onco
Targets Ther. 14:1659–1671. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Hu CY, Chen J, Qin XH, You P, Ma J, Zhang
J, Zhang H and Xu JD: Long non-coding RNA NORAD promotes the
prostate cancer cell extracellular vesicle release via
microRNA-541-3p-regulated PKM2 to induce bone metastasis of
prostate cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:982021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Mo C, Huang B, Zhuang J, Jiang S, Guo S
and Mao X: LncRNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 shuttled
by prostate cancer cells-secreted exosomes initiates osteoblastic
phenotypes in the bone metastatic microenvironment via
miR-205-5p/runt-related transcription factor 2/splicing factor
proline- and glutamine-rich/polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 2
axis. Clin Transl Med. 11:e4932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Ma Q, Qi X, Lin X, Li L, Chen L and Hu W:
LncRNA SNHG3 promotes cell proliferation and invasion through the
miR-384/hepatoma-derived growth factor axis in breast cancer. Hum
Cell. 33:232–242. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Zheng S, Jiang F, Ge D, Tang J, Chen H,
Yang J, Yao Y, Yan J, Qiu J, Yin Z, et al: LncRNA
SNHG3/miRNA-151a-3p/RAB22A axis regulates invasion and migration of
osteosarcoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 112:1086952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Xuan Y and Wang Y: Long non-coding RNA
SNHG3 promotes progression of gastric cancer by regulating
neighboring MED18 gene methylation. Cell Death Dis. 10:6942019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Fendler WP, Eiber M, Beheshti M, Bomanji
J, Calais J, Ceci F, Cho SY, Fanti S, Giesel FL, Goffin K, et al:
PSMA PET/CT: Joint EANM procedure guideline/SNMMI procedure
standard for prostate cancer imaging 2.0. Eur J Nucl Med Mol
Imaging. 50:1466–1486. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Eiber M, Herrmann K, Calais J, Hadaschik
B, Giesel FL, Hartenbach M, Hope T, Reiter R, Maurer T, Weber WA
and Fendler WP: Prostate cancer molecular imaging standardized
evaluation (PROMISE): Proposed miTNM classification for the
interpretation of PSMA-ligand PET/CT. J Nucl Med. 59:469–478. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Regula N, Kostaras V, Johansson S, Trampal
C, Lindström E, Lubberink M, Iyer V, Velikyan I and Sörensen J:
Comparison of 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT with fluoride PET/CT for
detection of bone metastatic disease in prostate cancer. Eur J
Hybrid Imaging. 6:52022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Brenner AI, Koshy J, Morey J, Lin C and
DiPoce J: The bone scan. Semin Nucl Med. 42:11–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Even-Sapir E, Metser U, Mishani E,
Lievshitz G, Lerman H and Leibovitch I: The detection of bone
metastases in patients with high-risk prostate cancer: 99mTc-MDP
Planar bone scintigraphy, single- and multi-field-of-view SPECT,
18F-fluoride PET, and 18F-fluoride PET/CT. J Nucl Med. 47:287–297.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Calais J, Ceci F, Eiber M, Hope TA, Hofman
MS, Rischpler C, Bach-Gansmo T, Nanni C, Savir-Baruch B, Elashoff
D, et al: 18F-fluciclovine PET-CT and
68Ga-PSMA-11 PET-CT in patients with early biochemical
recurrence after prostatectomy: A prospective, single-centre,
single-arm, comparative imaging trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:1286–1294.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
van Boxtel W, Lütje S, van Engen-van
Grunsven ICH, Verhaegh GW, Schalken JA, Jonker MA, Nagarajah J,
Gotthardt M and van Herpen CML: 68Ga-PSMA-HBED-CC PET/CT
imaging for adenoid cystic carcinoma and salivary duct carcinoma: A
phase 2 imaging study. Theranostics. 10:2273–2283. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Sonni I, Felker ER, Lenis AT, Sisk AE,
Bahri S, Allen-Auerbach M, Armstrong WR, Suvannarerg V, Tubtawee T,
Grogan T, et al: Head-to-head comparison of 68Ga-PSMA-11
PET/CT and mpMRI with a histopathology gold standard in the
detection, intraprostatic localization, and determination of local
extension of primary prostate cancer: Results from a prospective
single-center imaging trial. J Nucl Med. 63:847–854. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Zhou J, Gou Z, Wu R, Yuan Y, Yu G and Zhao
Y: Comparison of PSMA-PET/CT, choline-PET/CT, NaF-PET/CT, MRI, and
bone scintigraphy in the diagnosis of bone metastases in patients
with prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Skeletal Radiol. 48:1915–1924. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Zhou J, Wu R, Wang W, Zhao Y and Liu X:
68Ga-PSMA PET/CT for the detection of bone metastases in
prostate cancer: A systematic review of the published literature.
Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. Oct 29–2017.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
112
|
Coleman RE, Croucher PI, Padhani AR,
Clézardin P, Chow E, Fallon M, Guise T, Colangeli S, Capanna R and
Costa L: Bone metastases. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 6:832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Urabe F, Kosaka N, Yamamoto Y, Ito K,
Otsuka K, Soekmadji C, Egawa S, Kimura T and Ochiya T: Metastatic
prostate cancer-derived extracellular vesicles facilitate
osteoclastogenesis by transferring the CDCP1 protein. J Extracell
Vesicles. 12:e123122023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Hu C, Chen Q, Wu T, Du X, Dong Y, Peng Z,
Xue W, Sunkara V, Cho YK and Dong L: The role of extracellular
vesicles in the treatment of prostate cancer. Small.
20:e23110712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Wang Y, Fang YX, Dong B, Du X, Wang J,
Wang X, Gao WQ and Xue W: Discovery of extracellular vesicles
derived miR-181a-5p in patient's serum as an indicator for
bone-metastatic prostate cancer. Theranostics. 11:878–892. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Yu L, Sui B, Fan W, Lei L, Zhou L, Yang L,
Diao Y, Zhang Y, Li Z, Liu J and Hao X: Exosomes derived from
osteogenic tumor activate osteoclast differentiation and
concurrently inhibit osteogenesis by transferring COL1A1-targeting
miRNA-92a-1-5p. J Extracell Vesicles. 10:e120562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Wang J, Du X, Wang X, Xiao H, Jing N, Xue
W, Dong B, Gao WQ and Fang YX: Tumor-derived miR-378a-3p-containing
extracellular vesicles promote osteolysis by activating the
Dyrk1a/Nfatc1/Angptl2 axis for bone metastasis. Cancer Lett.
526:76–90. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Zeng F, Zhao C, Wang R, Ren L, Qiu H, Zou
Z, Ding H, Sun Z, Li J and Dong S: Antagonizing exosomal miR-18a-5p
derived from prostate cancer cells ameliorates metastasis-induced
osteoblastic lesions by targeting Hist1h2bc and activating
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Genes Dis. 10:1626–1640. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Baldessari C, Pipitone S, Molinaro E,
Cerma K, Fanelli M, Nasso C, Oltrecolli M, Pirola M, D'Agostino E,
Pugliese G, et al: Bone metastases and health in prostate cancer:
From pathophysiology to clinical implications. Cancers (Basel).
15:15182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Schwartz GG: Prostate cancer, serum
parathyroid hormone, and the progression of skeletal metastases.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:478–483. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Yuan S, Hoggard NK, Kantake N, Hildreth BE
III and Rosol TJ: Effects of dickkopf-1 (DKK-1) on prostate cancer
growth and bone metastasis. Cells. 12:26952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhang B, Li Y, Wu Q, Xie L, Barwick B, Fu
C, Li X, Wu D, Xia S, Chen J, et al: Acetylation of KLF5 maintains
EMT and tumorigenicity to cause chemoresistant bone metastasis in
prostate cancer. Nat Commun. 12:17142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Gomez-Veiga F, Ponce-Reixa J,
Martinez-Breijo S, Planas J and Morote J: Advances in prevention
and treatment of bone metastases in prostate cancer. Role of
RANK/RANKL inhibition. Actas Urol Esp. 37:292–304. 2013.(In
English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Mizuta K, Oshiro H, Katsuki R, Tsuha Y,
Aoki Y, Tome Y and Nishida K: Denosumab administration for bone
metastases from solid tumors: A retrospective cross-sectional
study. BMC Cancer. 23:9992023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Agarwal N, McGregor B, Maughan BL, Dorff
TB, Kelly W, Fang B, McKay RR, Singh P, Pagliaro L, Dreicer R, et
al: Cabozantinib in combination with atezolizumab in patients with
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Results from an
expansion cohort of a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b trial
(COSMIC-021). Lancet Oncol. 23:899–909. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Yu EY, Wilding G, Posadas E, Gross M,
Culine S, Massard C, Morris MJ, Hudes G, Calabrò F, Cheng S, et al:
Phase II study of dasatinib in patients with metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:7421–7428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Qiao L, Liang Y, Li N, Hu X, Luo D, Gu J,
Lu Y and Zheng Q: Endothelin-A receptor antagonists in prostate
cancer treatment-a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:3465–3473.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Lee YT, Tan YJ and Oon CE: Molecular
targeted therapy: Treating cancer with specificity. Eur J
Pharmacol. 834:188–196. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Reichert ZR, Urrutia J and Alumkal JJ:
Microsatellite Instability as an emerging biomarker for checkpoint
inhibitor response in advanced prostate cancer. JAMA Oncology.
5:478–479. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Mitsogiannis I, Tzelves L, Dellis A, Issa
H, Papatsoris A and Moussa M: Prostate cancer immunotherapy. Expert
Opin Biol Ther. 22:577–590. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Wu YM, Cieślik M, Lonigro RJ, Vats P,
Reimers MA, Cao X, Ning Y, Wang L, Kunju LP, de Sarkar N, et al:
Inactivation of CDK12 delineates a distinct immunogenic class of
advanced prostate cancer. Cell. 173:1770–1782.e14. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Bochum S, Berger S and Martens UM:
Olaparib. Recent Results Cancer Res. 211:217–233. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Risdon EN, Chau CH, Price DK, Sartor O and
Figg WD: PARP inhibitors and prostate cancer: To infinity and
beyond BRCA. Oncologist. 26:e115–e129. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Chen A: PARP inhibitors: Its role in
treatment of cancer. Chin J Cancer. 30:463–471. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Stamatakos PV, Fragkoulis C, Leventi A,
Gklinos K, Kontolatis N, Papatsoris A and Dellis A: PSMA-based
therapeutics for prostate cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother.
25:1405–1419. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Combes AD, Palma CA, Calopedos R, Wen L,
Woo H, Fulham M and Leslie S: PSMA PET-CT in the diagnosis and
staging of prostate cancer. Diagnostics (Basel). 12:25942022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Sun M, Niaz MO, Nelson A, Skafida M and
Niaz MJ: Review of 177Lu-PSMA-617 in patients with metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cureus.
12:e89212020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Narayan V, Barber-Rotenberg JS, Jung IY,
Lacey SF, Rech AJ, Davis MM, Hwang WT, Lal P, Carpenter EL, Maude
SL, et al: PSMA-targeting TGFβ-insensitive armored CAR T cells in
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A phase 1 trial.
Nat Med. 28:724–734. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Almuradova E, Seyyar M, Arak H, Tamer F,
Kefeli U, Koca S, Sen E, Telli TA, Karatas F, Gokmen I, et al: The
real-world outcomes of Lutetium-177 PSMA-617 radioligand therapy in
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Turkish oncology
group multicenter study. Int J Cancer. 154:692–700. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Maharaj M, Heslop L, Govender T, Korowlay
N, Singh A, Choudhary P and Sathekge M: The outcome and safety of
re-challenge Lutetium-177 PSMA (177Lu-PSMA) therapy with
low-dose docetaxel as a radiosensitizer-a promising combination in
metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC): A case
report. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 55:136–140. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Flegar L, Thoduka SG, Librizzi D, Luster
M, Zacharis A, Heers H, Eisenmenger N, Ahmadzadehfar H, Eiber M,
Weber W, et al: Adoption of Lutetium-177 PSMA
radioligand therapy for metastatic castration resistant prostate
cancer: A total population analysis in Germany from 2016 to 2020.
Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 50:2188–2195. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Khreish F, Ghazal Z, Marlowe RJ, Rosar F,
Sabet A, Maus S, Linxweiler J, Bartholomä M and Ezziddin S: 177
Lu-PSMA-617 radioligand therapy of metastatic castration-resistant
prostate cancer: Initial 254-patient results from a prospective
registry (REALITY study). Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 49:1075–1085.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Zarrabi KK, Narayan V, Mille PJ, Zibelman
MR, Miron B, Bashir B and Kelly WK: Bispecific PSMA antibodies and
CAR-T in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Ther Adv
Urol. 15:175628722311822192023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Lund ME, Howard CB, Thurecht KJ, Campbell
DH, Mahler SM and Walsh BJ: A bispecific T cell engager targeting
Glypican-1 redirects T cell cytolytic activity to kill prostate
cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 20:12142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Yamamoto K, Trad A, Baumgart A, Hüske L,
Lorenzen I, Chalaris A, Grötzinger J, Dechow T, Scheller J and
Rose-John S: A novel bispecific single-chain antibody for ADAM17
and CD3 induces T-cell-mediated lysis of prostate cancer cells.
Biochem J. 445:135–144. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Nyquist MD, Corella A, Coleman I, De
Sarkar N, Kaipainen A, Ha G, Gulati R, Ang L, Chatterjee P, Lucas
J, et al: Combined TP53 and RB1 loss promotes prostate cancer
resistance to a spectrum of therapeutics and confers vulnerability
to replication stress. Cell Rep. 31:1076692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Patel SA: Managing the unmanageable:
Evidence-driven approaches to real-world patient prototypes of
TP53-mutant myelodysplastic neoplasms and acute myeloid leukemia.
Leukemia. Sep 30–2024.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Lee YC, Lee YL and Li CY: BRCA genes and
related cancers: A meta-analysis from epidemiological cohort
studies. Medicina (Kaunas). 57:9052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Sweeney C, Bracarda S, Sternberg CN, Chi
KN, Olmos D, Sandhu S, Massard C, Matsubara N, Alekseev B, Parnis
F, et al: Ipatasertib plus abiraterone and prednisolone in
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (IPATential150): A
multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet.
398:131–142. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Fizazi K, Carducci M, Smith M, Damião R,
Brown J, Karsh L, Milecki P, Shore N, Rader M, Wang H, et al:
Denosumab versus zoledronic acid for treatment of bone metastases
in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer: A randomised,
double-blind study. Lancet. 377:813–822. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Shenderov E, Boudadi K, Fu W, Wang H,
Sullivan R, Jordan A, Dowling D, Harb R, Schonhoft J, Jendrisak A,
et al: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab, with or without enzalutamide, in
AR-V7-expressing metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A
phase-2 nonrandomized clinical trial. Prostate. 81:326–338. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Graff JN, Beer TM, Alumkal JJ, Slottke RE,
Redmond WL, Thomas GV, Thompson RF, Wood MA, Koguchi Y, Chen Y, et
al: A phase II single-arm study of pembrolizumab with enzalutamide
in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
progressing on enzalutamide alone. J Immunother Cancer.
8:e0006422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
McNeel DG, Eickhoff JC, Wargowski E,
Johnson LE, Kyriakopoulos CE, Emamekhoo H, Lang JM, Brennan MJ and
Liu G: Phase 2 trial of T-cell activation using MVI-816 and
pembrolizumab in patients with metastatic, castration-resistant
prostate cancer (mCRPC). J Immunother Cancer. 10:e0041982022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Xia QD, Zhang SH, Zeng N, Lu YC, Qin BL
and Wang SG: Novel androgen receptor inhibitors for metastatic
hormone-sensitive prostate cancer: Current application and future
perspectives. Biomed Pharmacother. 168:1158062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Shah H and Vaishampayan U: Therapy of
advanced prostate cancer: Targeting the androgen receptor axis in
earlier lines of treatment. Target Oncol. 13:679–689. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Zhang Y, Ming A, Wang J, Chen W and Fang
Z: PROTACs targeting androgen receptor signaling: Potential
therapeutic agents for castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Pharmacol Res. 205:1072342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Petrylak DP, Vaishampayan UN, Patel KR,
Higano CS, Albany C, Dawson NA, Mehlhaff BA, Quinn DI, Nordquist
LT, Wagner VJ, et al: A randomized phase IIa study of quantified
bone scan response in patients with metastatic castration-resistant
prostate cancer (mCRPC) treated with radium-223 dichloride alone or
in combination with abiraterone acetate/prednisone or enzalutamide.
ESMO Open. 6:1000822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Manna F, Karkampouna S, Zoni E, De Menna
M, Hensel J, Thalmann GN and Kruithof-de Julio M: Metastases in
prostate cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 9:a0336882019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Zhang X: Interactions between cancer cells
and bone microenvironment promote bone metastasis in prostate
cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond). 39:762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Lu J, Hu D, Zhang Y, Ma C, Shen L and
Shuai B: Current comprehensive understanding of denosumab (the
RANKL neutralizing antibody) in the treatment of bone metastasis of
malignant tumors, including pharmacological mechanism and clinical
trials. Front Oncol. 13:11338282023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Shiota M, Akamatsu S, Tsukahara S,
Nagakawa S, Matsumoto T and Eto M: Androgen receptor mutations for
precision medicine in prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer.
29:R143–R155. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Farahzadi R, Valipour B, Montazersaheb S
and Fathi E: Targeting the stem cell niche micro-environment as
therapeutic strategies in aging. Front Cell Dev Biol.
11:11621362023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Fathi E, Farahzadi R, Sheervalilou R,
Sanaat Z and Vietor I: A general view of CD33+ leukemic
stem cells and CAR-T cells as interesting targets in acute
myeloblatsic leukemia therapy. Blood Res. 55:10–16. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Fathi E, Valipour B, Vietor I and
Farahzadi R: An overview of the myocardial regeneration potential
of cardiac c-Kit+ progenitor cells via PI3K and MAPK
signaling pathways. Future Cardiol. 16:199–209. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|