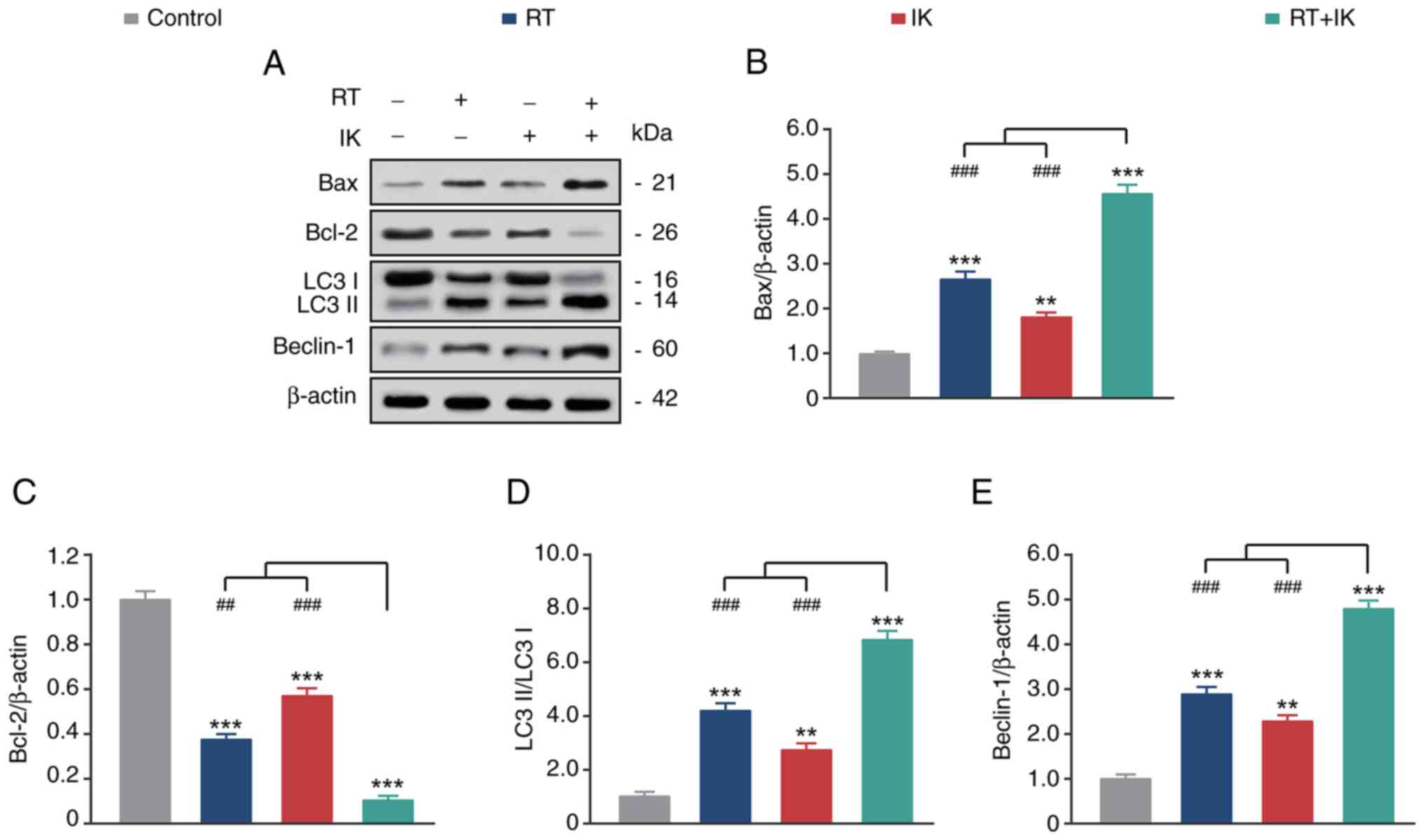
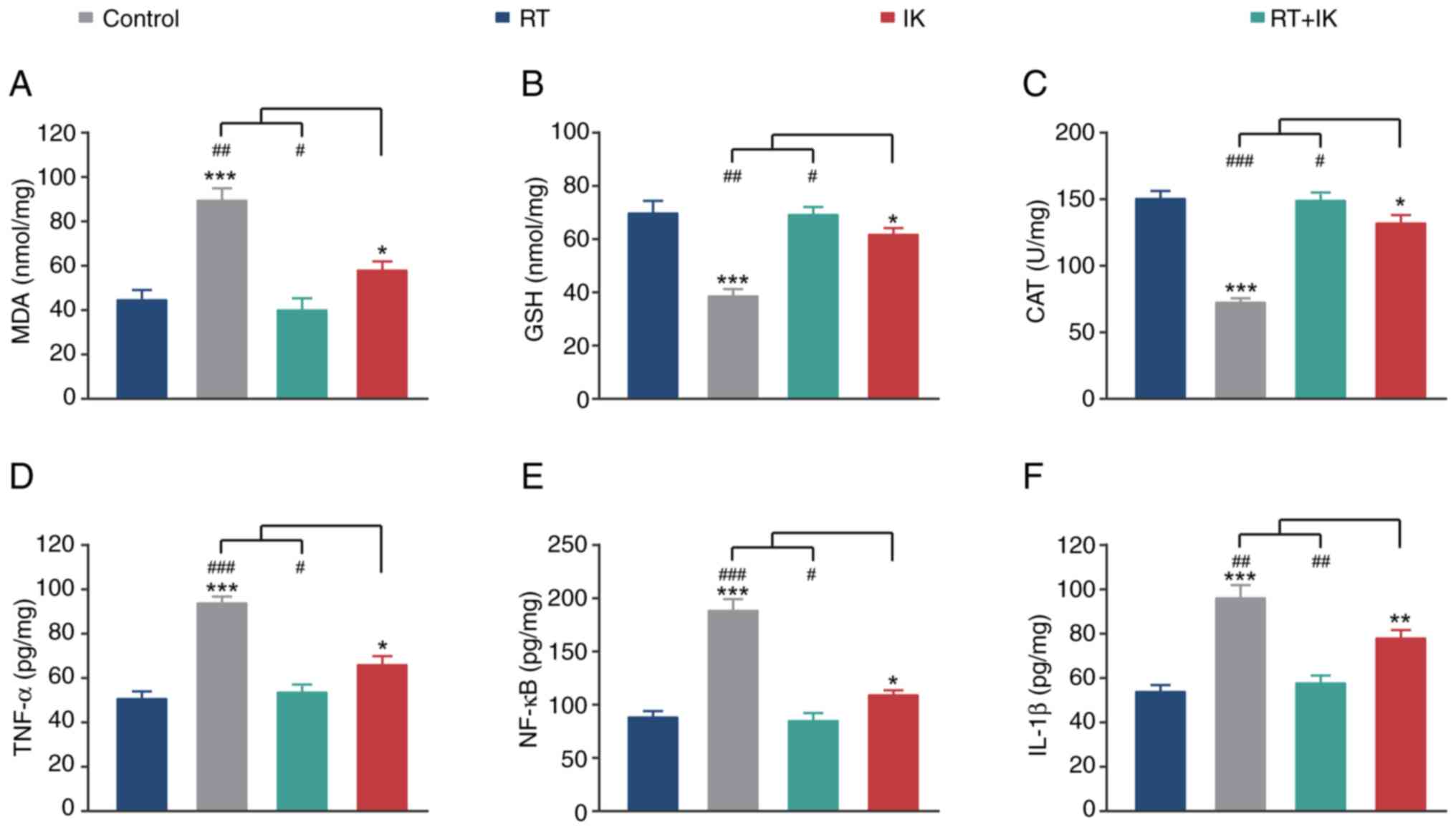
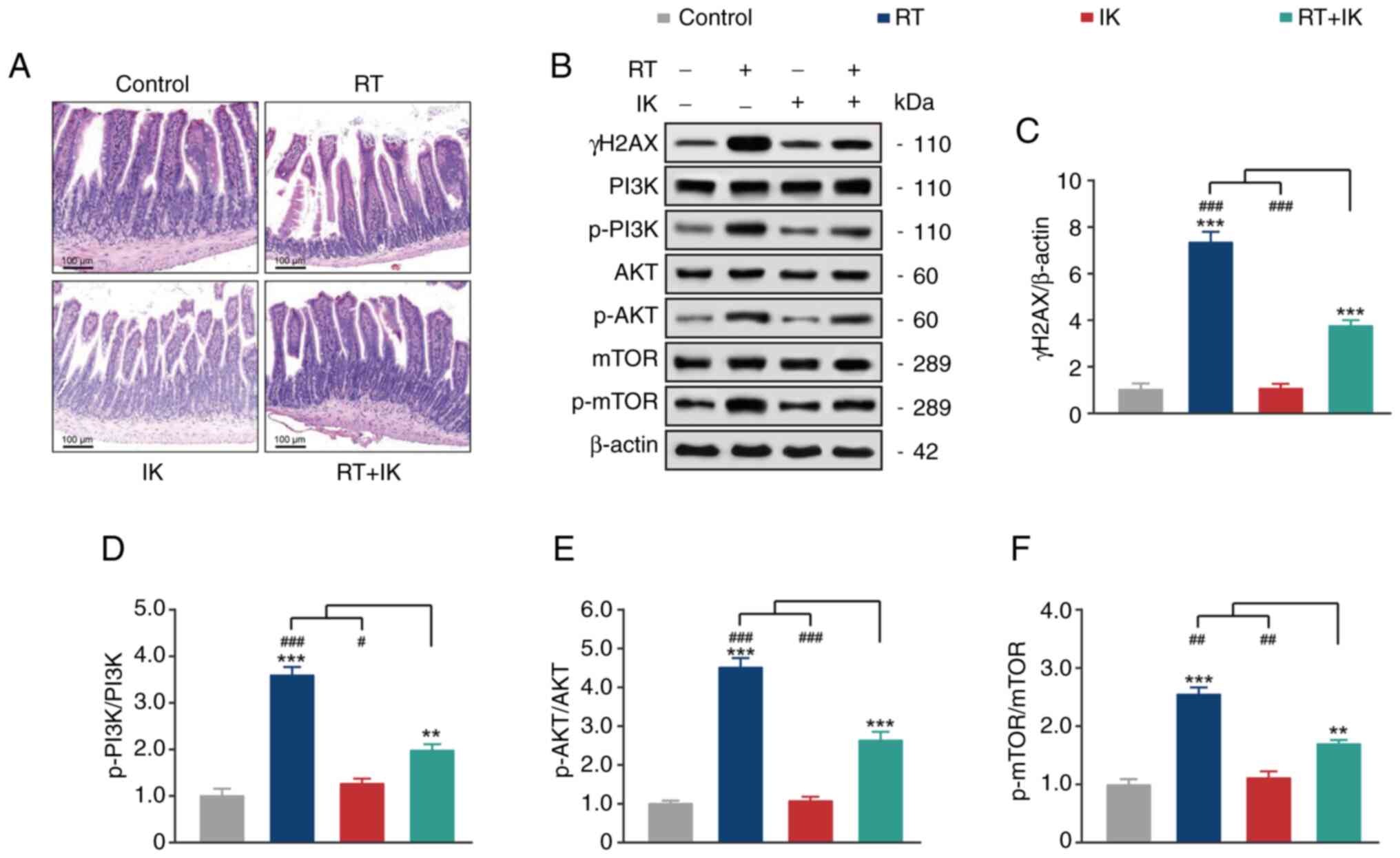
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Morgan E, Arnold M, Gini A, Lorenzoni V,
Cabasag CJ, Laversanne M, Vignat J, Ferlay J, Murphy N and Bray F:
Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and
mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut. 72:338–344. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global patterns and trends in
colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 66:683–691. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA
and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin.
73:233–254. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sung H, Siegel RL, Rosenberg PS and Jemal
A: Emerging cancer trends among young adults in the USA: Analysis
of a population-based cancer registry. Lancet Public Health.
4:e137–e147. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Araghi M, Soerjomataram I, Bardot A,
Ferlay J, Cabasag CJ, Morrison DS, De P, Tervonen H, Walsh PM,
Bucher O, et al: Changes in colorectal cancer incidence in seven
high-income countries: A population-based study. Lancet
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 4:511–518. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Biller LH and Schrag D: Diagnosis and
treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: A review. JAMA.
325:669–685. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Buccafusca G, Proserpio I, Tralongo AC,
Rametta Giuliano S and Tralongo P: Early colorectal cancer:
Diagnosis, treatment and survivorship care. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
136:20–30. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dariya B, Aliya S, Merchant N, Alam A and
Nagaraju GP: Colorectal cancer biology, diagnosis, and therapeutic
approaches. Crit Rev Oncog. 25:71–94. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kusano M, Aoyama T, Okabayashi K, Hirata
K, Tsuji Y, Nakamori S, Asahara T, Ohashi Y, Yoshikawa T, Sakamoto
J, et al: A randomized phase III study of hepatic arterial infusion
chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil and subsequent systemic
chemotherapy versus systemic chemotherapy alone for colorectal
cancer patients with curatively resected liver metastases (Japanese
foundation for multidisciplinary treatment of cancer 32). J Cancer
Res Ther. 14 (Suppl):S761–S766. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zielińska A, Włodarczyk M, Makaro A,
Sałaga M and Fichna J: Management of pain in colorectal cancer
patients. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 157:1031222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang H, Li X, Peng R, Wang Y and Wang J:
Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for colorectal cancer liver
metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 71:21–32. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu J, Li N, Tang Y, Wang X, Tang Y, Wang
SL, Song YW, Liu YP, Li YX and Jin J: Outcomes after
hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for colorectal cancer
oligometastases. J Surg Oncol. 119:532–538. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang X, Qiu H, Li C, Cai P and Qi F: The
positive role of traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive
therapy for cancer. Biosci Trends. 15:283–298. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cho BO, Jin CH, Park YD, Ryu HW, Byun MW,
Seo KI and Jeong IY: Isoegomaketone induces apoptosis through
caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways in human DLD1
cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 75:1306–1311. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang R, Zhang Q, Feng C, Zhang J, Qin Y
and Meng L: Advances in the pharmacological activities and effects
of perilla ketone and isoegomaketone. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2022:88097922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jin CH, Park HC, So Y, Nam B, Han SN and
Kim JB: Comparison of the anti-inflammatory activities of
supercritical carbon dioxide versus ethanol extracts from leaves of
perilla frutescens Britt. radiation mutant. Molecules. 22:3112017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chi HC, Tsai CY, Tsai MM and Lin KH:
Impact of DNA and RNA methylation on radiobiology and cancer
progression. Int J Mol Sci. 19:5552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lapierre A, Gourgou S, Brengues M, Quéro
L, Deutsch É, Milliat F, Riou O and Azria D: Tumour and normal
tissue radiosensitivity. Cancer Radiother. 26:96–103. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kwak SY, Jang WI, Lee SB, Kim MJ, Park S,
Cho SS, Kim H, Lee SJ, Shim S and Jang H: Centella asiatica-derived
endothelial paracrine restores epithelial barrier dysfunction in
radiation-induced enteritis. Cells. 11:25442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang J, Wang R, Qin Y and Feng C:
Defining the potential targets for biological activity of
isoegomaketone based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
methods. Life (Basel). 12:21152022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jin CH, So Y, Nam B, Han SN and Kim JB:
Isoegomaketone alleviates the development of collagen
antibody-induced arthritis in male balb/c mice. Molecules.
22:12092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jing X, Yang F, Shao C, Wei K, Xie M, Shen
H and Shu Y: Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the
tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. 18:1572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan CS, Deng ZW, Qin D, Mu YZ, Chen XG
and Liu Y: Hypoxia-modulatory nanomaterials to relieve tumor
hypoxic microenvironment and enhance immunotherapy: Where do we
stand? Acta Biomater. 125:1–28. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brown JM: Tumor hypoxia in cancer therapy.
Methods Enzymol. 435:297–321. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kilic M, Kasperczyk H, Fulda S and Debatin
KM: Role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha in modulation of
apoptosis resistance. Oncogene. 26:2027–2038. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Freudlsperger C, Horn D, Weißfuß S,
Weichert W, Weber KJ, Saure D, Sharma S, Dyckhoff G, Grabe N,
Plinkert P, et al: Phosphorylation of AKT(Ser473) serves as an
independent prognostic marker for radiosensitivity in advanced head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 136:2775–2785.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miyasaka A, Oda K, Ikeda Y, Sone K, Fukuda
T, Inaba K, Makii C, Enomoto A, Hosoya N, Tanikawa M, et al:
PI3K/mTOR pathway inhibition overcomes radioresistance via
suppression of the HIF1-α/VEGF pathway in endometrial cancer.
Gynecol Oncol. 138:174–180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
D'Arcy MS: Cell death: A review of the
major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol Int.
43:582–592. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Edlich F: BCL-2 proteins and apoptosis:
Recent insights and unknowns. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
500:26–34. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li X, He S and Ma B: Autophagy and
autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer. 19:122020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kimmelman AC and White E: Autophagy and
tumor metabolism. Cell Metab. 25:1037–1043. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ding GB, Sun J, Wu G, Li B, Yang P, Li Z
and Nie G: Robust anticancer efficacy of a biologically synthesized
tumor acidity-responsive and autophagy-inducing functional beclin
1. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 10:5227–5239. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cao Y, Luo Y, Zou J, Ouyang J, Cai Z, Zeng
X, Ling H and Zeng T: Autophagy and its role in gastric cancer.
Clin Chim Acta. 489:10–20. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lu L, Sun C, Su Q, Wang Y, Li J, Guo Z,
Chen L and Zhang H: Radiation-induced lung injury: Latest molecular
developments, therapeutic approaches, and clinical guidance. Clin
Exp Med. 19:417–426. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Barker CA, Kim SK, Budhu S, Matsoukas K,
Daniyan AF and D'Angelo SP: Cytokine release syndrome after
radiation therapy: Case report and review of the literature. J
Immunother Cancer. 6:12018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ran Z, Zhang Y, Wen X and Ma J: Curcumin
inhibits high glucose-induced inflammatory injury in human retinal
pigment epithelial cells through the ROS-PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 19:1024–1031. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hawkins PT and Stephens LR: PI3K
signalling in inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1851:882–897.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang JT, Xie WQ, Liu FQ, Bi Y, Zhu XJ,
Wang QE and Zheng YF: NADH protect against radiation enteritis by
enhancing autophagy and inhibiting inflammation through PI3K/AKT
pathway. Am J Transl Res. 10:1713–1721. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang CY, Deng JS, Huang WC, Jiang WP and
Huang GJ: Attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury by hispolon in mice, through regulating the
TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways, and suppressing
oxidative stress-mediated er stress-induced apoptosis and
autophagy. Nutrients. 12:17422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|