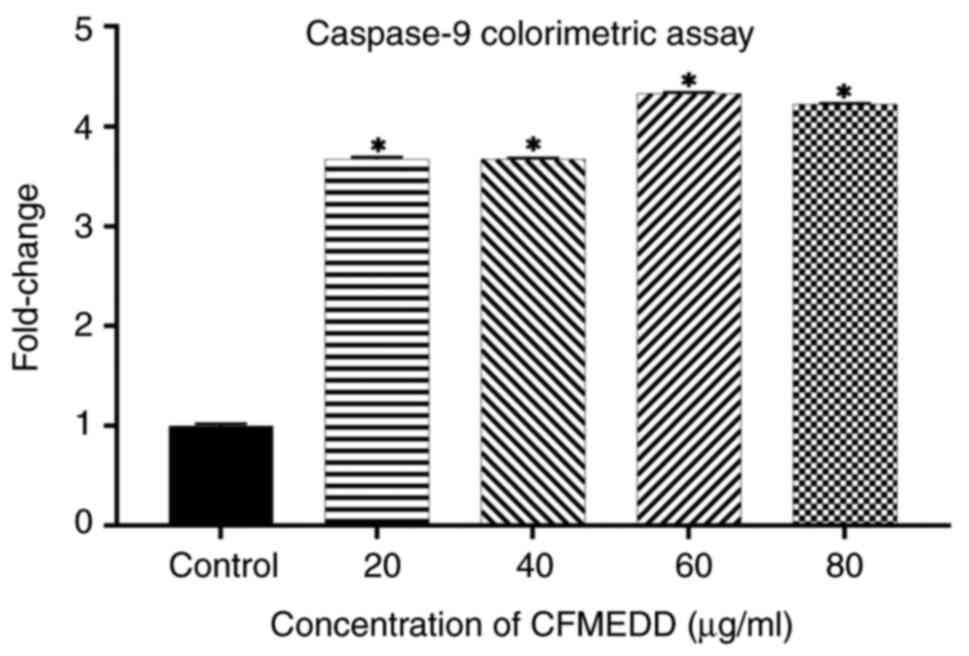
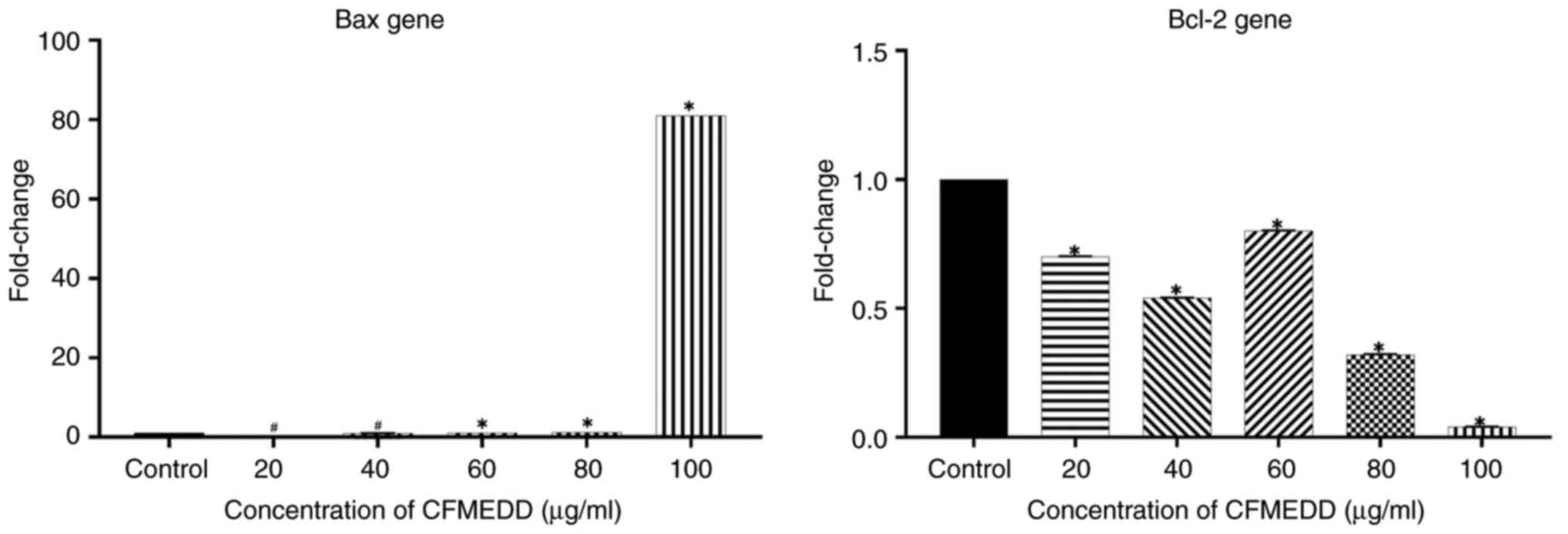
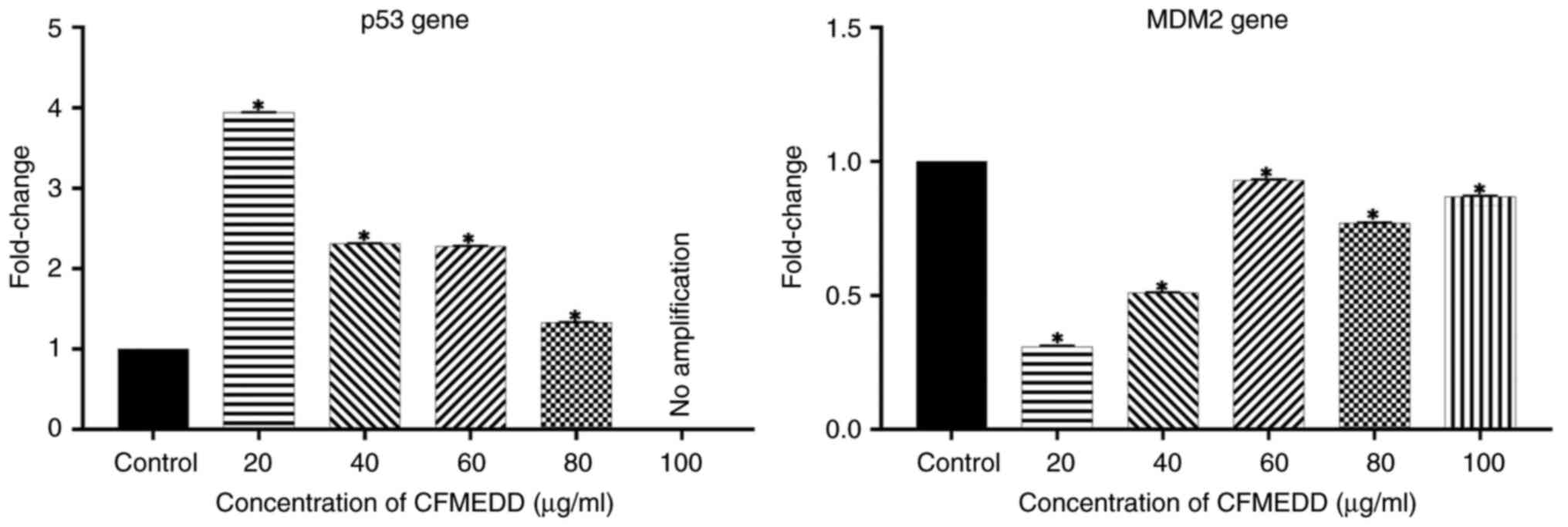
|
1
|
World Health Organization: Cancer: Key
facts. WHO, Geneva, 2018. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer.
Accessed February 7, 2019.
|
|
2
|
Tariq A, Sadia S, Pan K, Ullah I, Mussarat
S, Sun F, Abiodun OO, Batbaatar A, Li Z, Song D, et al: A
systematic review on ethnomedicines of anti-cancer plants.
Phytother Res. 31:202–264. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Aliyu-Amoo H, Isa HI, Njoya EM and McGaw
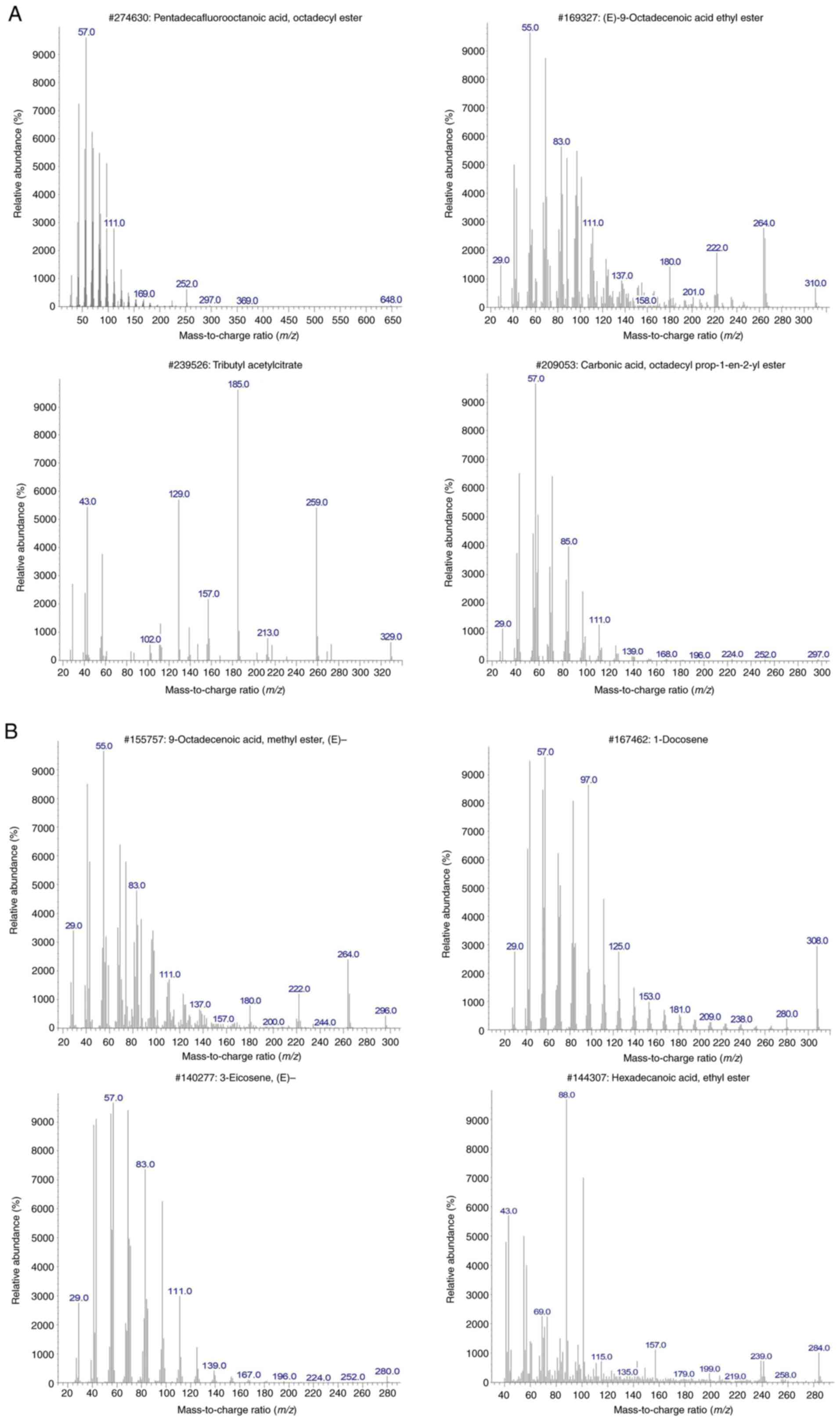
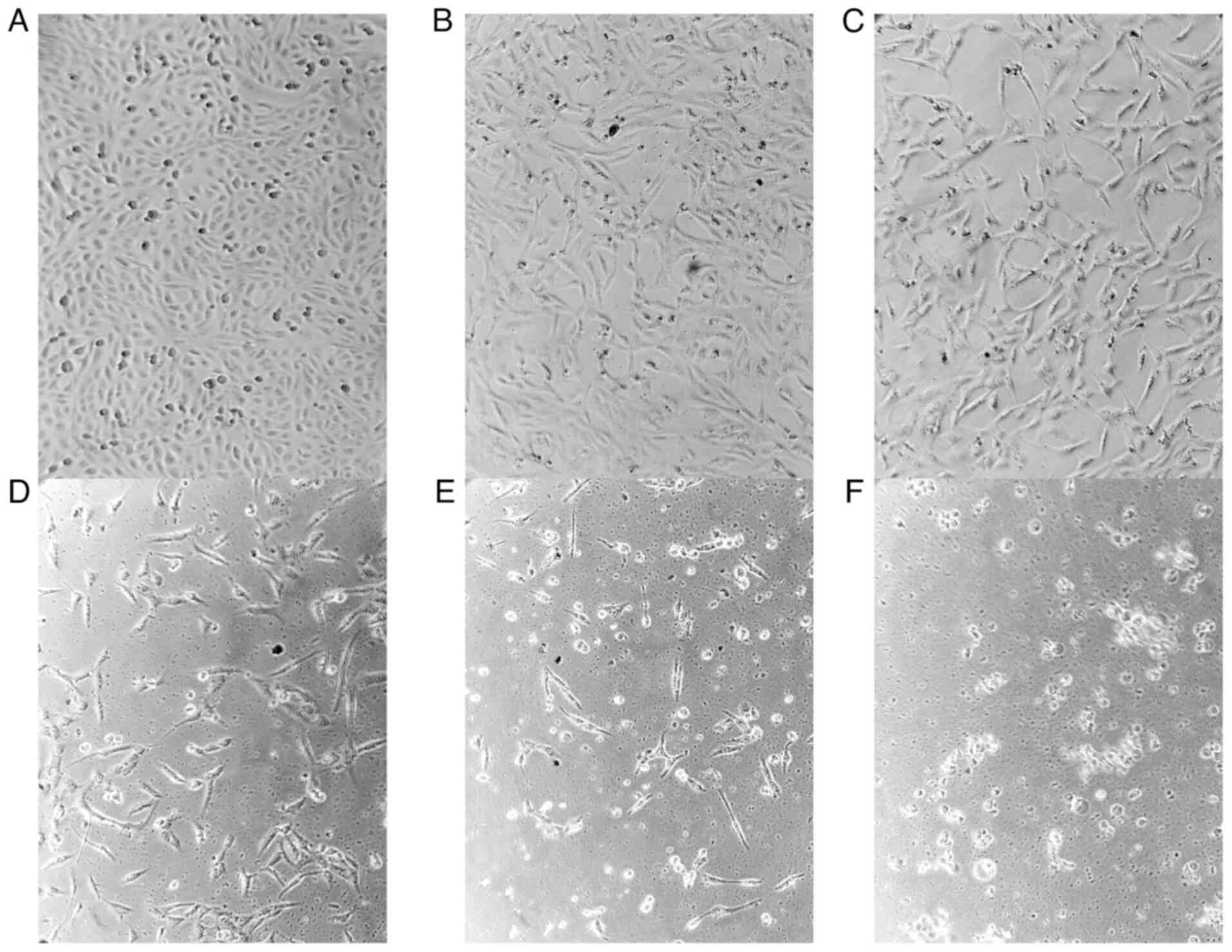
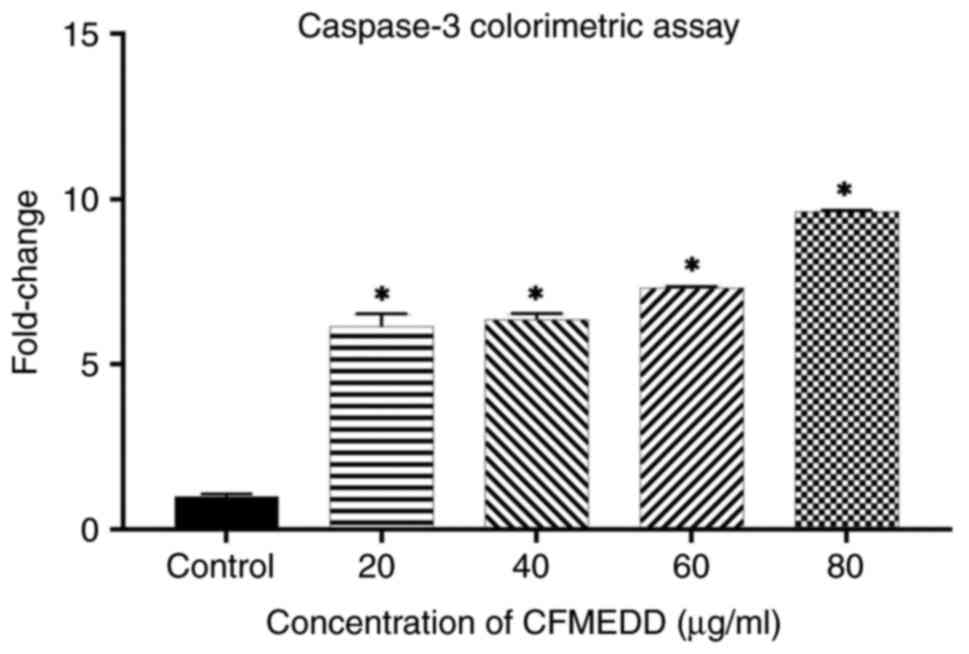
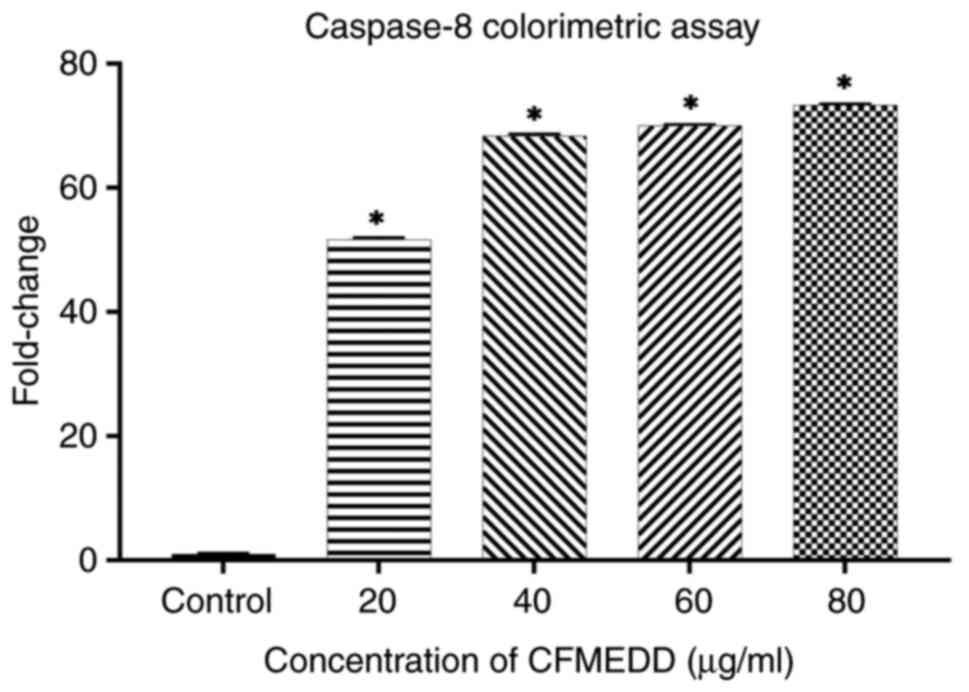
LJ: Antiproliferative effect of extracts and fractions of the root
of Terminalia avicennioides (Combretaceae) Guill and Perr.
On HepG2 and Vero Cell Lines. Int J Phytomed Phytother.
7(71)2021.
|
|
4
|
Kadan S, Rayan M and Rayan A: Anticancer
activity of anise (Pimpinella anisum L.) seed extract. Open
Nutraceuticals J. 6:1–5. 2013.
|
|
5
|
Wang Z, Li Z, Ye Y, Xie L and Li W:
Oxidative stress and liver cancer: Etiology and therapeutic
targets. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016(7891574)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Maluccio M and Covey A: Recent progress in
understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma.
CA Cancer J Clin. 62:394–399. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sun Y, Ma W, Yang Y, He M, Li A, Bai L, Yu
B and Yu Z: Cancer nanotechnology: Enhancing tumor cell response to
chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Asian J Pharm
Sci. 14:581–594. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nekvindova J, Mrkvicova A, Zubanova V,
Hyrslova Vaculova A, Anzenbacher P, Soucek P, Radova L, Slaby O,
Kiss I, Vondracek J, et al: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Gene
expression profiling and regulation of xenobiotic-metabolizing
cytochromes P450. Biochem Pharmacol. 177(113912)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Florio AA, Campbell PT, Zhang X,
Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Wactawski-Wende J, Smith-Warner SA, Sinha R,
Simon TG, Sesso HD, Schairer C, et al: Abdominal and gluteofemoral
size and risk of liver cancer: The liver cancer pooling project.
Int J Cancer. 147:675–685. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Manosroi A, Akazawa H, Kitdamrongtham W,
Akihisa T, Manosroi W and Manosroi J: Potent antiproliferative
effect on liver cancer of medicinal plants selected from the
Thai/Lanna medicinal plant recipe database ‘MANOSROI III’. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015(397181)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Khalil R, Ali Q, Hafeez M and Malik A:
Phytochemical activities of Conocarpus erectus: An overview.
Biol Clin Sci Res J. 2020:1–6. 2020.
|
|
13
|
Kaur R, Kapoor K and Kaur H: Plants as a
source of anticancer agents. J Nat Prod Plant Resour. 1:19–124.
2011.
|
|
14
|
Jesus M, Martins AP, Gallardo E and
Silvestre S: Diosgenin: Recent highlights on pharmacology and
analytical methodology. J Anal Methods Chem.
2016(4156293)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Salehi B, Sener B, Kilic M, Sharifi-Rad J,
Naz R, Yousaf Z, Mudau FN, Fokou PVT, Ezzat SM, El Bishbishy MH, et
al: Dioscorea plants: A genus rich in vital
nutra-pharmaceuticals-A review. Iran J Pharm Res. 18(Suppl):68–89.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Keshava R, Muniyappa N and Gope R:
Bioactivity guided fractionation and elucidation of anti-cancer
properties of Imperata cylindrica leaf extracts. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 21:707–714. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Waziri PM, Abdullah R, Yeap SK, Omar AR,
Kassim NK, Malami I, How CW, Etti IC and Abu ML: Clausenidin
induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in colon cancer. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 16(256)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Win DT: Oleic acid-The anti-breast cancer
component in olive oil. AU J.T. 9:75–78. 2005.
|
|
20
|
Yu F, Lu S, Yu F, Shi J, McGuire PM and
Wang R: Cytotoxic activity of an octadecenoic acid extract from
Euphorbia kansui (Euphorbiaceae) on human tumour cell
strains. J Pharm Pharmacol. 60:253–259. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sangpairoj K, Settacomkul R, Siangcham T,
Meemon K, Niamnont N, Sornkaew N, Tamtin M, Sobhon P and
Vivithanaporn P: Hexadecanoic acid-enriched extract of Halymenia
durvillei induces apoptotic and autophagic death of human
triple-negative breast cancer cells by upregulating ER stress.
Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 12:132–140. 2022.
|
|
22
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Häcker G: The morphology of apoptosis.
Cell Tissue Res. 301:5–17. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Pfeffer CM and Singh ATK: Apoptosis: A
target for anticancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
19(448)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Obeng E: Apoptosis (programmed cell death)
and its signals-A review. Braz J Biol. 81:1133–1143.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lossi L: The concept of intrinsic versus
extrinsic apoptosis. Biochem J. 479:357–384. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Olsson M and Zhivotovsky B: Caspases and
cancer. Cell Death Differ. 18:1441–1449. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nagata S: Apoptotic DNA fragmentation. Exp
Cell Res. 256:12–18. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cheng EH, Wei MC, Weiler S, Flavell RA,
Mak TW, Lindsten T and Korsmeyer SJ: BCL-2, BCL-XL sequester BH3
domain-only molecules preventing BAX-and BAK-mediated mitochondrial
apoptosis. Mol Cell. 8:705–711. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T,
Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB and
Korsmeyer SJ: Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: A requisite gateway to
mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science. 292:727–730.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Weinberg RA: How cancer arises. Sci Am.
275:62–70. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Eischen CM: Role of Mdm2 and Mdmx in DNA
repair. J Mol Cell Biol. 9:69–73. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chène P: Inhibiting the p53-MDM2
interaction: An important target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:102–109. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Campbell KJ and Tait SWG: Targeting BCL-2
regulated apoptosis in cancer. Open Biol. 8(180002)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jain AK and Barton MC: p53: Emerging roles
in stem cells, development and beyond. Development.
145(dev158360)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|