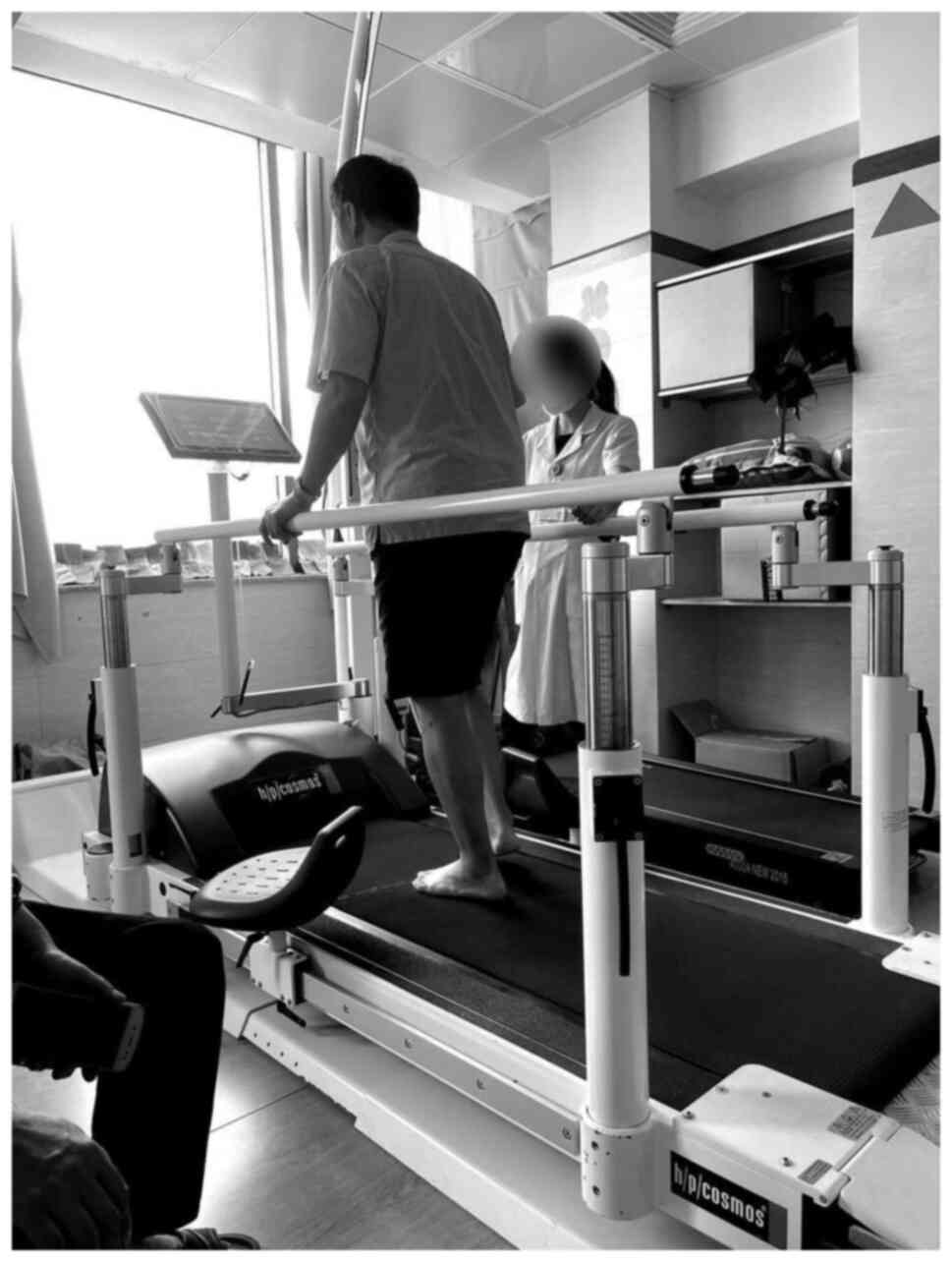
|
1
|
Seshadri S and Wolf PA: Lifetime risk of
stroke and dementia: Current concepts, and estimates from the
Framingham Study. Lancet Neurol. 6:1106–1114. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Skolarus LE, Burke JF, Brown DL and
Freedman VA: Understanding stroke survivorship: Expanding the
concept of poststroke disability. Stroke. 45:224–230.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mellon L, Brewer L, Hall P, Horgan F,
Williams D and Hickey A: ASPIRE-S study group. Cognitive impairment
six months after ischaemic stroke: A profile from the ASPIRE-S
study. BMC Neurol. 15(31)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jokinen H, Melkas S, Ylikoski R,
Pohjasvaara T, Kaste M, Erkinjuntti T and Hietanen M: Post-stroke
cognitive impairment was common even after successful clinical
recovery. Eur J Neurol. 22:1288–1294. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Winstein CJ, Stein J, Warena R, Bates B,
Cherney LR, Cramer SC, Deruyter F, Eng JJ, Fisher B, Harvey RL, et
al: Guidelines for adult stroke rehabilitation and recovery: A
guideline for healthcare professionals from the American heart
Association/American stroke association. Stroke. 47:e98–e169.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cappa SF, Benke T, Clarke S, Rossi B,
Stemmer B and Van Heugten CM: Cognitive rehabilitation. Gilhus NE,
Barnes MP and Brainin M (eds). In: European Handbook of
Neurological Management. 2nd edition. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford,
pp545-568, 2011.
|
|
7
|
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines
Network (SIGN). Management of Patients with Stroke: Rehabilitation,
Prevention and Management of Complications, and Discharge Planning,
SIGN Publication 118, 2010.
|
|
8
|
Gillespie DC, Bowen A, Chung CS, Cockburn
J, Knapp P and Pollock A: Rehabilitation for post-stroke cognitive
impairment: An overview of recommendations arising from systematic
reviews of current evidence. Clin Rehabil. 29:120–128.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Starovasnik Žagavec B, Mlinaric Lešnik V
and Goljar N: Training of selective attention in work-active stroke
patients. Int J Rehabil Res. 38(370)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lin ZC, Tao J, Gao YL, Yin DZ, Chen AZ and
Chen LD: Analysis of central mechanism of cognitive training on
cognitive impairment after stroke: Resting-state functional
magnetic resonance imaging study. J Int Med Res. 42:659–668.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Cumming TB, Tyedin K, Churilov L, Morris
ME and Bernhardt J: The effect of physical activity on cognitive
function after stroke: A systematic review. Int Psychogeriatr.
24:557–567. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Laurin D, Verreault R, Lindsay J,
MacPherson K and Rockwood K: Physical activity and risk of
cognitive impairment and dementia in elderly persons. Arch Neurol.
58:498–504. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zheng G, Zhou W, Xia R, Tao J and Chen L:
Aerobic exercises for cognition rehabilitation following stroke: A
systematic review. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 25:2780–2789.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Barber SE, Clegg AP and Young JB: Was
there a role for physical activity in preventing cognitive decline
in people with mild cognitive impairment? Age Ageing. 41:5–8.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Langdon KD and Corbett D: Improved working
memory following novel combinations of physical and cognitive
activity. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 26:523–532. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Oswald WD, Gunzelmann T, Rupprecht R and
Hagen B: Differential effects of single versus combined cognitive
and physical training with older adults: The SimA study in a 5-year
perspective. Eur J Ageing. 3:179–1792. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Law LLF, Barnett F, Yau MK and Gray MA:
Effects of combined cognitive and exercise interventions on
cognition in older adults with and without cognitive impairment: A
systematic review. Ageing Res Rev. 15:61–75. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bo W, Lei M, Tao S, Jie LT, Qian L, Lin FQ
and Ping WX: Effects of combined intervention of physical exercise
and cognitive training on cognitive function in stroke survivors
with vascular cognitive impairment: A randomized controlled trial.
Clin Rehabil. 33:54–63. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Additive effects of physical exercise and
environmental enrichment on adult hippocampal neurogenesis in
mice-PubMed. Accessed September 23, 2022.
|
|
20
|
Labban JD and Etnier JL: Effects of acute
exercise on long-term memory. Res Q Exerc Sport. 82:712–721.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yeh TT, Chang KC, Wu CY, Chen CJ and
Chuang IC: Clinical efficacy of aerobic exercise combined with
computer-based cognitive training in stroke: A multicenter
randomized controlled trial. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation.
29:255–264. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yeh TT, Chang KC and Wu CY: The active
ingredient of cognitive restoration: A multicenter randomized
controlled trial of sequential combination of aerobic exercise and
Computer-based cognitive training in stroke survivors with
cognitive decline. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 100:821–827.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Marzolini S, Oh P, McIlroy W and Brooks D:
The effects of an aerobic and resistance exercise training program
on cognition following stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair.
27:392–402. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu CY, Hung SJ, Lin K, Chen KH, Chen P and
Tsay PK: Responsiveness, minimal clinically important difference,
and validity of the MoCA in stroke rehabilitation. Occup Ther Int.
2019(2517658)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lauenroth A, Ioannidis AE and Teichmann B:
Influence of combined physical and cognitive training on cognition:
A systematic review. BMC Geriatr. 16(141)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|