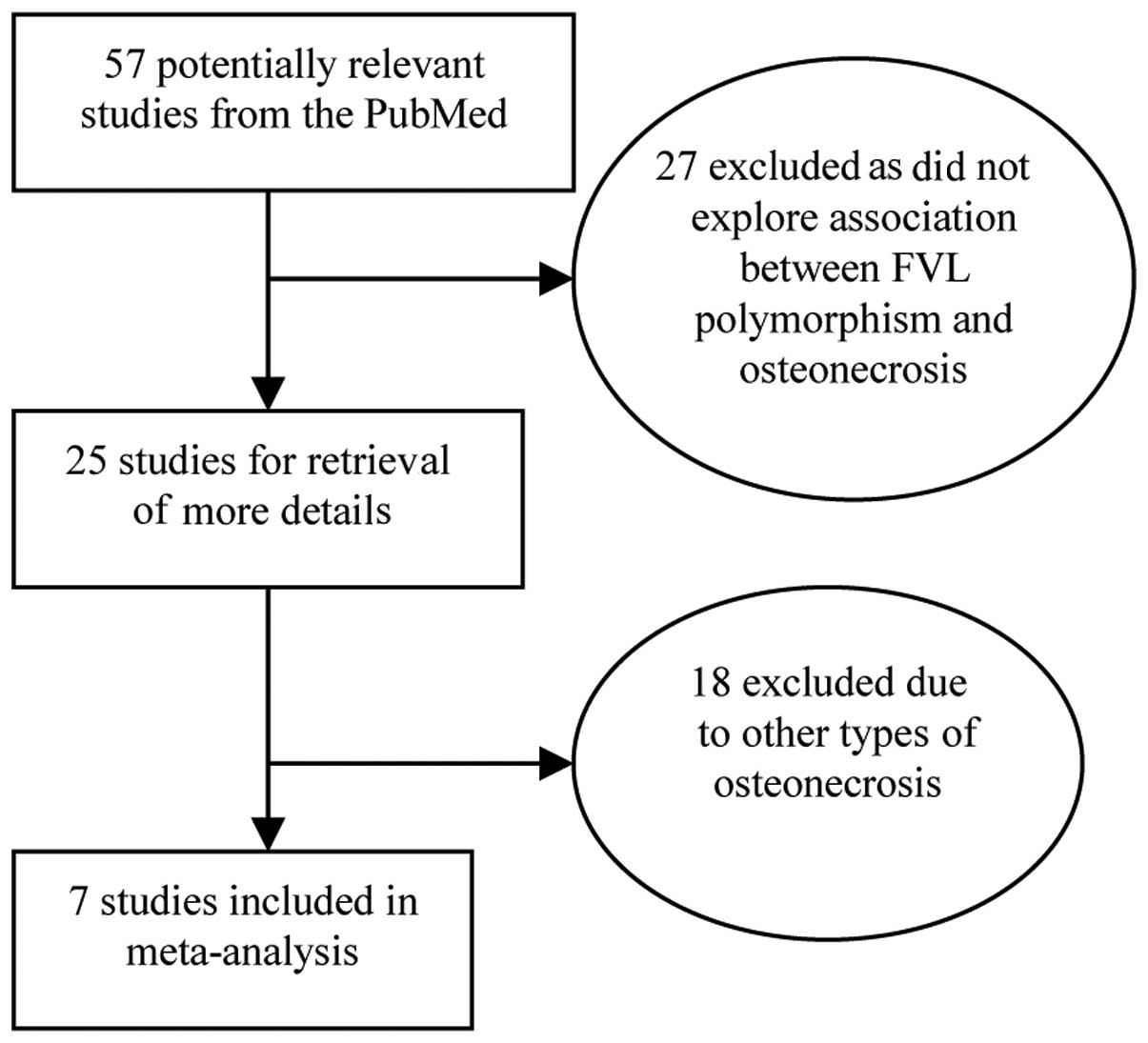
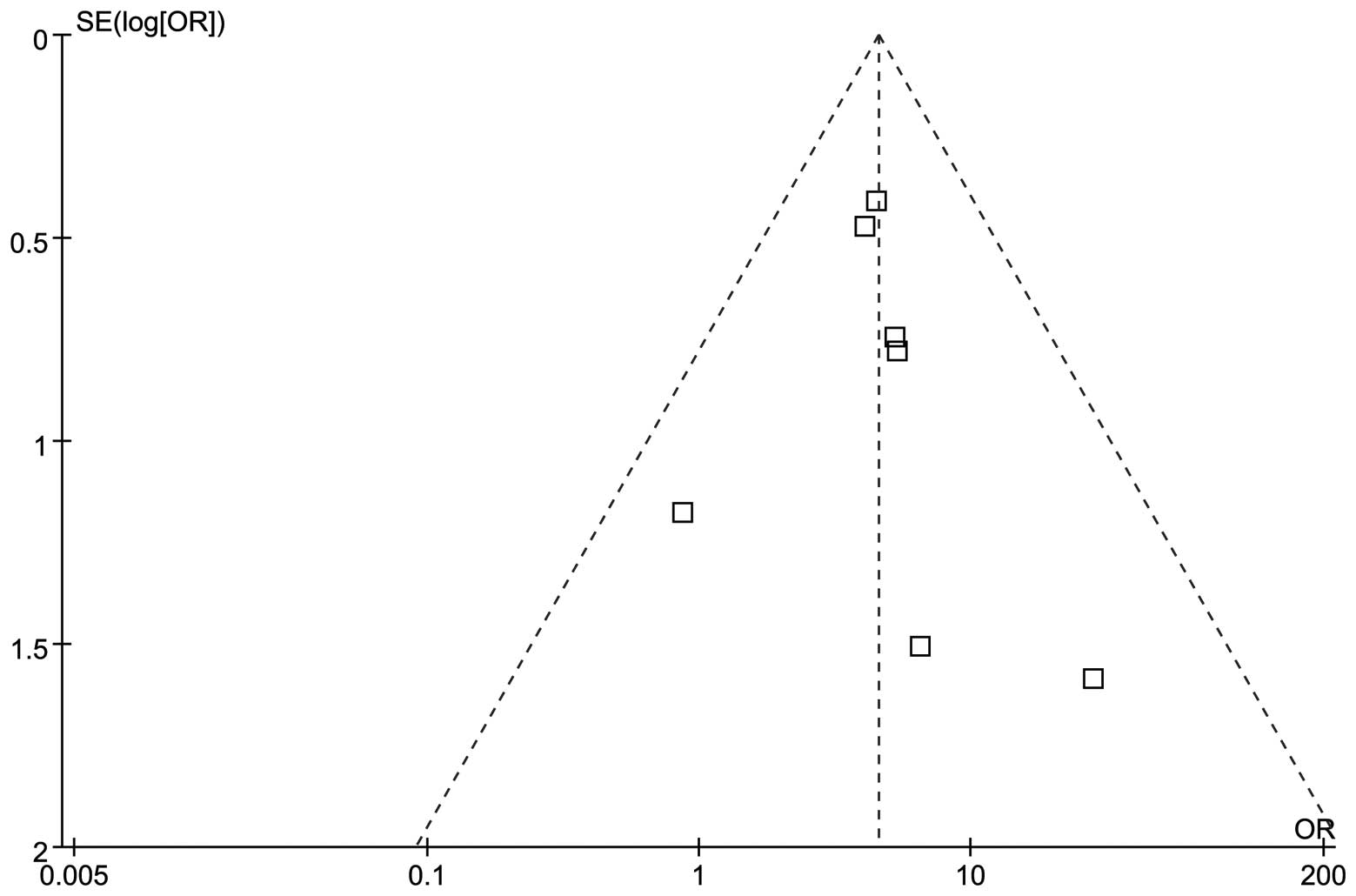
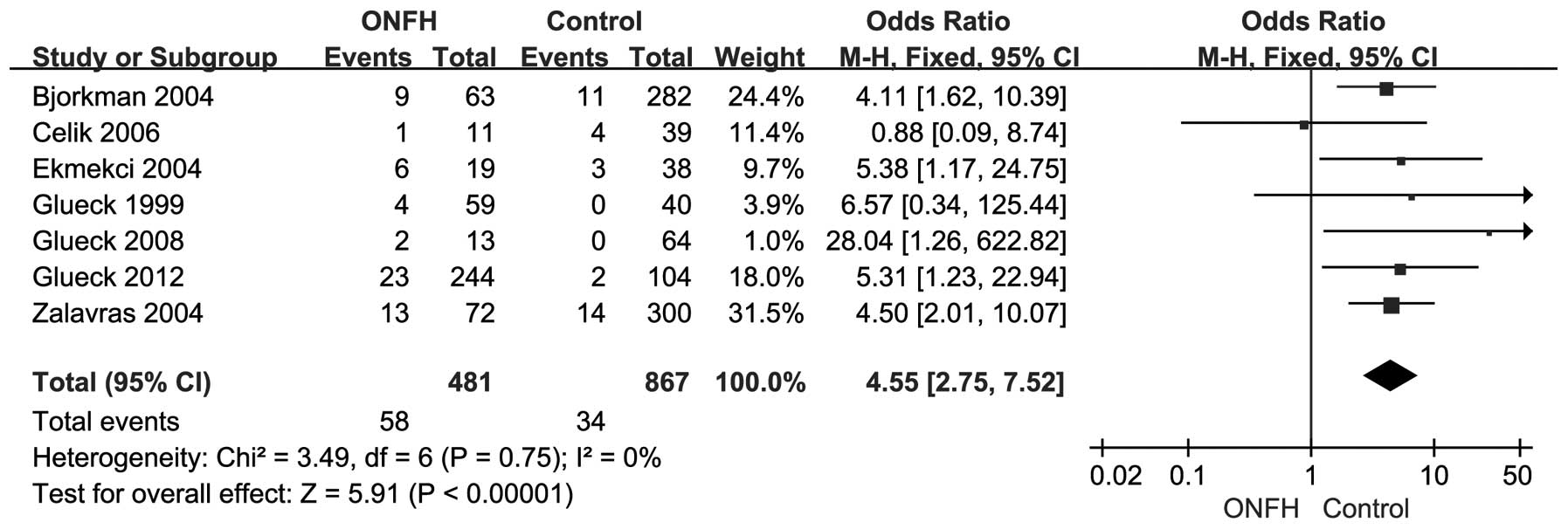
|
1
|
Malizos KN, Karantanas AH, Varitimidis SE,
Dailiana ZH, Bargiotas K and Maris T: Osteonecrosis of the femoral
head: etiology, imaging and treatment. Eur J Radiol. 63:16–28.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jones LC and Hungerford DS: Osteonecrosis:
etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
16:443–449. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lafforgue P: Pathophysiology and natural
history of avascular necrosis of bone. Joint Bone Spine.
73:500–507. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rosing J and Tans G: Coagulation factor V:
an old star shines again. Thromb Haemost. 78:427–433.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bertina RM, Koeleman BPC, Koster T, et al:
Mutation in blood coagulation factor V associated with resistance
to activated protein C. Nature. 369:64–67. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dentali F, Ageno W, Bozzato S, et al: Role
of factor V Leiden or G20210A prothrombin mutation in patients with
symptomatic pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis: a
meta-analysis of the literature. J Thromb Haemost. 10:732–737.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dowaidar M and Settin A: Risk of
myocardial infarction related to factor V Leiden mutation: a
meta-analysis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 14:493–498. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bjorkman A, Svensson PJ, Hillarp A,
Burtscher IM, Runow A and Benoni G: Factor V leiden and prothrombin
gene mutation: risk factors for osteonecrosis of the femoral head
in adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 452:168–172. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Celik A, Tekis D, Saglam F, et al:
Association of corticosteroids and factor V, prothrombin, and MTHFR
gene mutations with avascular osteonecrosis in renal allograft
recipients. Transplant Proc. 38:512–516. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ekmekci Y, Keven K, Akar N, et al:
Thrombophilia and avascular necrosis of femoral head in kidney
allograft recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 21:3555–3558. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Glueck CJ, Fontaine RN, Gruppo R, et al:
The plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene, hypofibrinolysis, and
osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 366:133–146. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Glueck CJ, Freiberg RA, Boppana S and Wang
P: Thrombophilia, hypofibrinolysis, the eNOS T-786C polymorphism,
and multifocal osteonecrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 90:2220–2229.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Glueck CJ, Freiberg RA, Boriel G, et al:
The role of the factor V Leiden mutation in osteonecrosis of the
hip. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. June 12–2012.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
14
|
Zalavras CG, Vartholomatos G, Dokou E and
Malizos KN: Genetic background of osteonecrosis: associated with
thrombophilic mutations? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 251–255.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cochran WG: The combination of estimates
from different experiments. Biometrics. 10:101–129. 1954.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jones JP Jr: Intravascular coagulation and
osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 277:41–53. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jones JP Jr: Coagulopathies and
osteonecrosis. Acta Orthop Belg. 65(Suppl 1): 5–8. 1999.
|
|
21
|
Lowe GD, Rumley A, Woodward M, Reid E and
Rumley J: Activated protein C resistance and the FV: R506Q mutation
in a random population sample-associations with cardiovascular risk
factors and coagulation variables. Thromb Haemost. 81:918–924.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang JD, Hur M, Lee SS, Yoo JH and Lee
KM: Genetic background of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral
head in the Korean population. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
466:1041–1046. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kechli AM, Wilimas JA, Pui CH, Park VM,
Tonkel S and Deitcher SR: Factor V Leiden and other hypercoagulable
state mutations are not associated with osteonecrosis during or
after treatment for pediatric malignancy. J Pediatr. 134:310–314.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sun W, Li ZR, Shi ZC, et al: Hematological
changes and related gene mutation of post-severe acute respiratory
syndrome patients with osteonecrosis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
86:442–445. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Jun ZJ, Ping T, Lei Y, Li L, Ming SY and
Jing W: Prevalence of factor V Leiden and prothrombin G20210A
mutations in Chinese patients with deep venous thrombosis and
pulmonary embolism. Clin Lab Haematol. 28:111–116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim YW, Yoon KY, Park S, Shim YS, Cho HI
and Park SS: Absence of factor V Leiden mutation in Koreans. Thromb
Res. 86:181–182. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
De Stefano V, Chiusolo P, Paciaroni K and
Leone G: Epidemiology of factor V Leiden: clinical implications.
Semin Thromb Hemost. 24:367–379. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rosendorff A and Dorfman DM: Activated
protein C resistance and factor V Leiden: a review. Arch Pathol Lab
Med. 131:866–871. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Frosst P, Blom HJ, Milos R, et al: A
candidate genetic risk factor for vascular disease: a common
mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Nat Genet.
10:111–113. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Eldibany MM and Caprini JA:
Hyperhomocysteinemia and thrombosis: an overview. Arch Pathol Lab
Med. 131:872–884. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rosendaal FR, Doggen CJ, Zivelin A, et al:
Geographic distribution of the 20210 G to A prothrombin variant.
Thromb Haemost. 79:706–708. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|