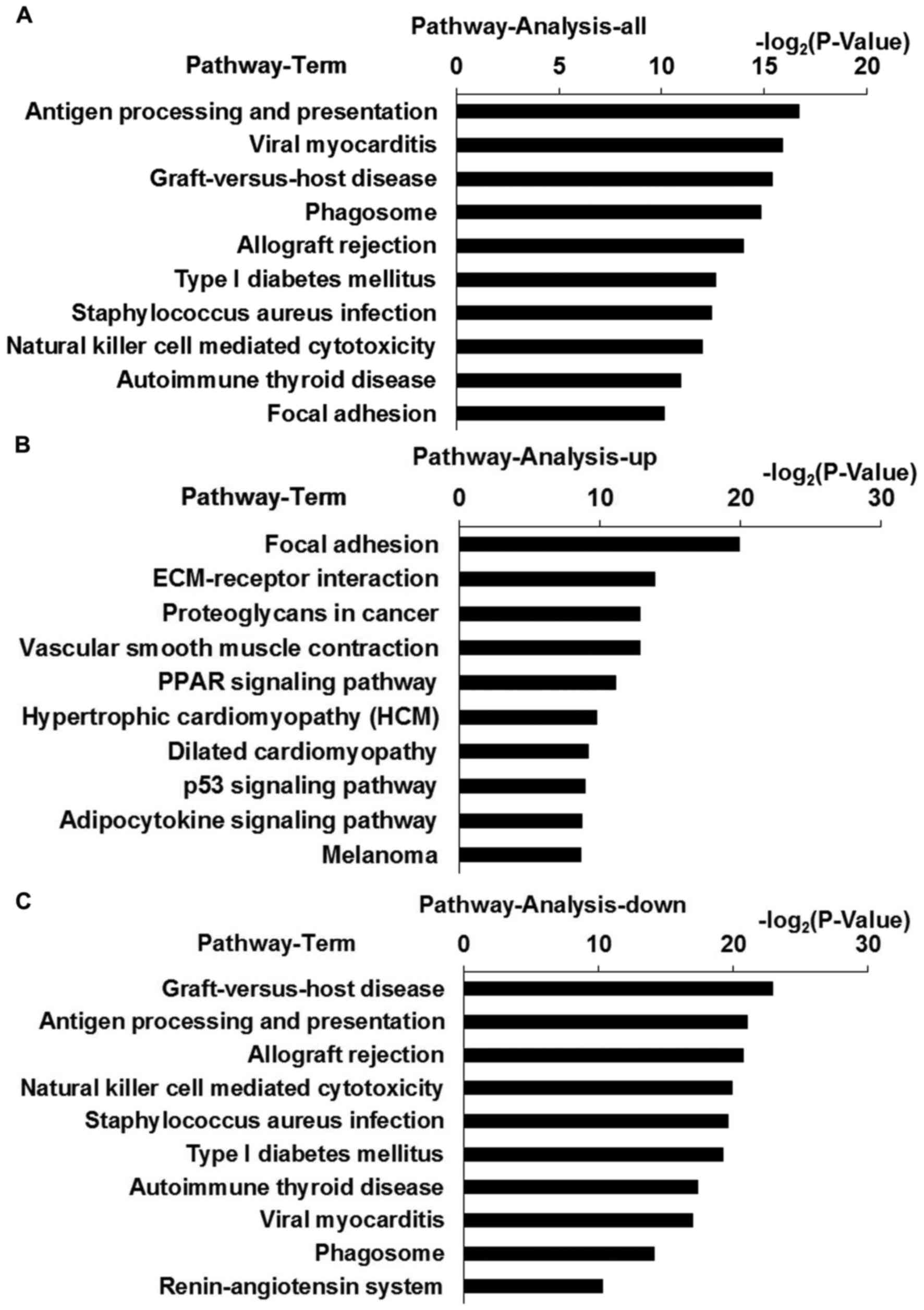
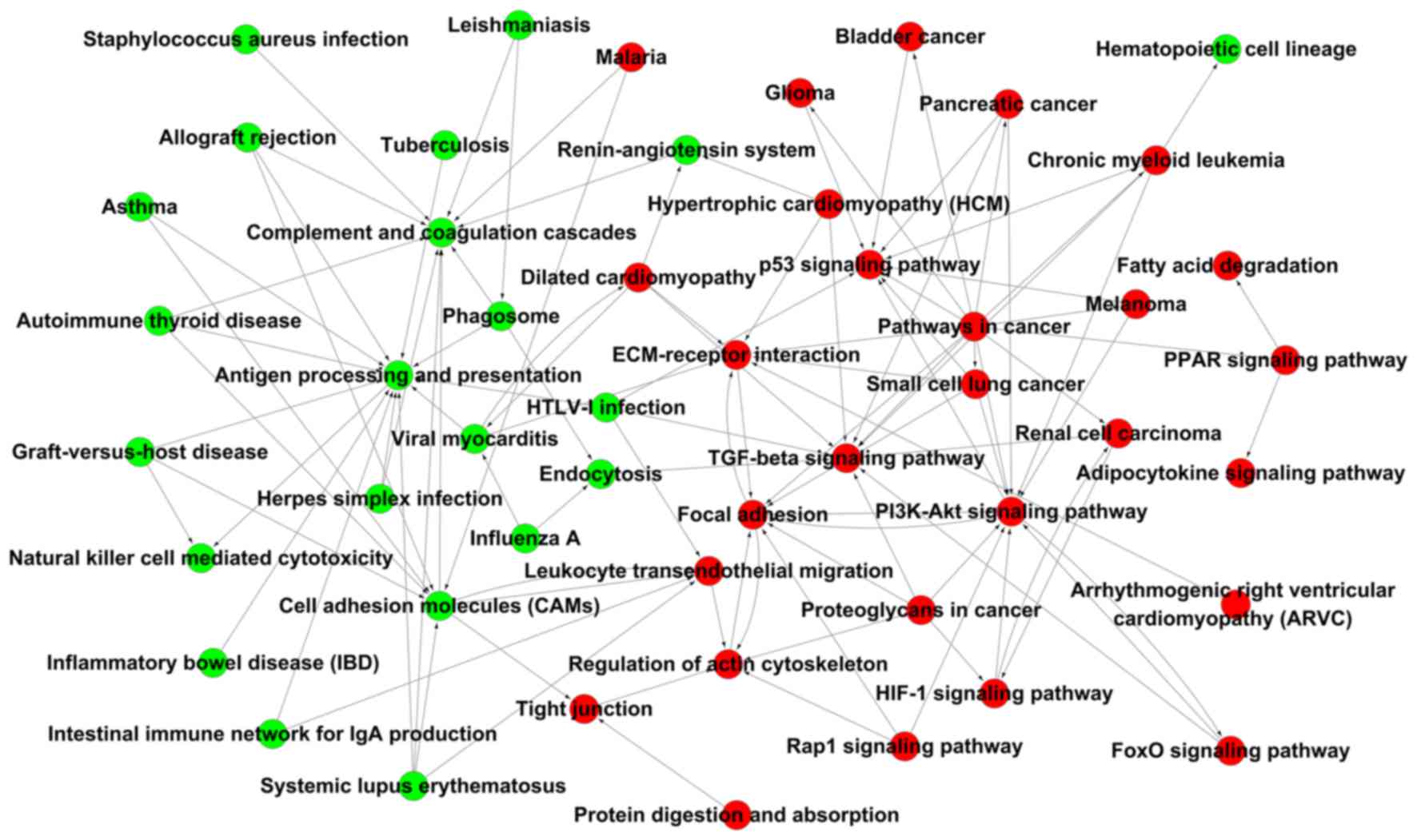
|
1
|
Kjos SL and Buchanan TA: Gestational
diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 341:1749–1756. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kasuga M: Insulin resistance and
pancreatic beta cell failure. J Clin Invest. 116:1756–1760. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
White MF: Insulin signaling in health and
disease. Science. 302:1710–1711. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wójcik M, Chmielewska-Kassassir M,
Grzywnowicz K, Woźniak L and Cypryk K: The relationship between
adipose tissue-derived hormones and gestational diabetes mellitus
(GDM). Endokrynol Pol. 65:134–142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fasshauer M, Blüher M and Stumvoll M:
Adipokines in gestational diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.
2:488–499. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ibrahim MM: Subcutaneous and visceral
adipose tissue: Structural and functional differences. Obes Rev.
11:11–18. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Insenser M, Montes-Nieto R, Vilarrasa N,
Lecube A, Simó R, Vendrell J and Escobar-Morreale HF: A nontargeted
proteomic approach to the study of visceral and subcutaneous
adipose tissue in human obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 363:10–19.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun G: Application of DNA microarrays in
the study of human obesity and type 2 diabetes. OMICS. 11:25–40.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Draghici S, Khatri P, Eklund AC and
Szallasi Z: Reliability and reproducibility issues in DNA
microarray measurements. Trends Genet. 22:101–109. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Allison DB, Cui X, Page GP and Sabripour
M: Microarray data analysis: From disarray to consolidation and
consensus. Nat Rev Genet. 7:55–65. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V and
Czech MP: Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin
resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:367–377.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maassen JA, Romijn JA and Heine RJ: Fatty
acid-induced mitochondrial uncoupling in adipocytes as a key
protective factor against insulin resistance and beta cell
dysfunction: A new concept in the pathogenesis of
obesity-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia.
50:2036–2041. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma Y, Gao J, Yin J, Gu L, Liu X, Chen S,
Huang Q, Lu H, Yang Y, Zhou H, et al: Identification of a Novel
Function of Adipocyte Plasma Membrane-Associated Protein (APMAP) in
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus by Proteomic Analysis of Omental
Adipose Tissue. J Proteome Res. 15:628–637. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Oliva K, Barker G, Rice GE, Bailey MJ and
Lappas M: 2D-DIGE to identify proteins associated with gestational
diabetes in omental adipose tissue. J Endocrinol. 218:165–178.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Evangelou M, Smyth DJ, Fortune MD, Burren
OS, Walker NM, Guo H, Onengut-Gumuscu S, Chen WM, Concannon P, Rich
SS, et al: A method for gene-based pathway analysis using
genomewide association study summary statistics reveals nine new
type 1 diabetes associations. Genet Epidemiol. 38:661–670. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou F, Huang X, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Liu X,
Xing J and He X: Functional polymorphisms of ITGB1 are associated
with clinical outcome of Chinese patients with resected colorectal
cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 75:1207–1215. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang L, Zhang Y, Lv W, Lu J, Mu J, Liu Y
and Dong P: Long non-coding RNA Linc-ITGB1 knockdown inhibits cell
migration and invasion in GBC-SD/M and GBC-SD gallbladder cancer
cell lines. Chem Biol Drug Des. 86:1064–1071. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fabbri C, Crisafulli C, Gurwitz D, Stingl
J, Calati R, Albani D, Forloni G, Calabrò M, Martines R, Kasper S,
et al: Neuronal cell adhesion genes and antidepressant response in
three independent samples. Pharmacogenomics J. 15:538–548. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eves R, Oldham R, Jia L and Mak AS: The
roles of akt isoforms in the regulation of podosome formation in
fibroblasts and extracellular matrix invasion. Cancers (Basel).
7:96–111. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Phung TL, Du W, Xue Q, Ayyaswamy S, Gerald
D, Antonello Z, Nhek S, Perruzzi CA, Acevedo I, Ramanna-Valmiki R,
et al: Akt1 and akt3 exert opposing roles in the regulation of
vascular tumor growth. Cancer Res. 75:40–50. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Waisberg J, De Souza Viana L, Affonso
Junior RJ, Silva SR, Denadai MV, Margeotto FB, De Souza CS and
Matos D: Overexpression of the ITGAV gene is associated with
progression and spread of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res.
34:5599–5607. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Denadai MV, Viana LS, Affonso RJ Jr, Silva
SR, Oliveira ID, Toledo SR and Matos D: Expression of integrin
genes and proteins in progression and dissemination of colorectal
adenocarcinoma. BMC Clin Pathol. 13:162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hosen I, Rachakonda PS, Heidenreich B, de
Verdier PJ, Ryk C, Steineck G, Hemminki K and Kumar R: Mutations in
TERT promoter and FGFR3 and telomere length in bladder cancer. Int
J Cancer. 137:1621–1629. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guancial EA, Werner L, Bellmunt J, Bamias
A, Choueiri TK, Ross R, Schutz FA, Park RS, O'Brien RJ, Hirsch MS,
et al: FGFR3 expression in primary and metastatic urothelial
carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Med. 3:835–844. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Noctor E, Crowe C, Carmody LA, Kirwan B,
O'Dea A, Glynn LG, McGuire BE, O'Shea PM and Dunne FP:
ATLANTIC-DIP: Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and insulin
resistance in women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus by
International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Groups
criteria. Acta Diabetol. 52:153–160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Koning SH, Hoogenberg K, Scheuneman KA,
Baas MG, Korteweg FJ, Sollie KM, Schering BJ, van Loon AJ,
Wolffenbuttel BH, van den Berg PP, et al: Neonatal and obstetric
outcomes in diet- and insulin-treated women with gestational
diabetes mellitus: A retrospective study. BMC Endocr Disord.
16:522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao YH, Wang DP, Zhang LL, Zhang F, Wang
DM and Zhang WY: Genomic expression profiles of blood and placenta
reveal significant immune-related pathways and categories in
Chinese women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med.
28:237–246. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang L, Roh YS, Song J, Zhang B, Liu C,
Loomba R and Seki E: Transforming growth factor beta signaling in
hepatocytes participates in steatohepatitis through regulation of
cell death and lipid metabolism in mice. Hepatology. 59:483–495.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mauricio D and de Leiva A: Autoimmune
gestational diabetes mellitus: A distinct clinical entity? Diabetes
Metab Res Rev. 17:422–428. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Evangelista AF, Collares CV, Xavier DJ,
Macedo C, Manoel-Caetano FS, Rassi DM, Foss-Freitas MC, Foss MC,
Sakamoto-Hojo ET, Nguyen C, et al: Integrative analysis of the
transcriptome profiles observed in type 1, type 2 and gestational
diabetes mellitus reveals the role of inflammation. BMC Med
Genomics. 7:282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Binder AM, LaRocca J, Lesseur C, Marsit CJ
and Michels KB: Epigenome-wide and transcriptome-wide analyses
reveal gestational diabetes is associated with alterations in the
human leukocyte antigen complex. Clin Epigenetics. 7:792015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Steinborn A, Saran G, Schneider A, Fersis
N, Sohn C and Schmitt E: The presence of gestational diabetes is
associated with increased detection of anti-HLA-class II antibodies
in the maternal circulation. Am J Reprod Immunol. 56:124–134. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oben JA, Mouralidarane A, Samuelsson AM,
Matthews PJ, Morgan ML, McKee C, Soeda J, Fernandez-Twinn DS,
Martin-Gronert MS, Ozanne SE, et al: Maternal obesity during
pregnancy and lactation programs the development of offspring
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. J Hepatol. 52:913–920.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dotta F, Fondelli C and Falorni A: Can NK
cells be a therapeutic target in human type 1 diabetes? Eur J
Immunol. 38:2961–2963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hauguel-de Mouzon S and Guerre-Millo M:
The placenta cytokine network and inflammatory signals. Placenta.
27:794–798. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee BC and Lee J: Cellular and molecular
players in adipose tissue inflammation in the development of
obesity-induced insulin resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1842:446–462. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lumeng CN and Saltiel AR: Inflammatory
links between obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest.
121:2111–2117. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hursting SD and Dunlap SM: Obesity,
metabolic dysregulation, and cancer: A growing concern and an
inflammatory (and microenvironmental) issue. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1271:82–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Balsan GA, Vieira JL, Oliveira AM and
Portal VL: Relationship between adiponectin, obesity and insulin
resistance. Rev Assoc Med Bras 1992. 61:72–80. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lebrun P, Baron V, Hauck CR, Schlaepfer DD
and Van Obberghen E: Cell adhesion and focal adhesion kinase
regulate insulin receptor substrate-1 expression. J Biol Chem.
275:38371–38377. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gupta A and Dey CS: PTEN, a widely known
negative regulator of insulin/PI3K signaling, positively regulates
neuronal insulin resistance. Mol Biol Cell. 23:3882–3898. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gupta A, Bisht B and Dey CS: Focal
adhesion kinase negatively regulates neuronal insulin resistance.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1822:1030–1037. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bisht B and Dey CS: Focal Adhesion Kinase
contributes to insulin-induced actin reorganization into a mesh
harboring Glucose transporter-4 in insulin resistant skeletal
muscle cells. BMC Cell Biol. 9:482008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang L, Cui Y, Fu F, Li Z, Pan X, Li H
and Li L: An insight into the key genes and biological functions
associated with insulin resistance in adipose tissue with
microarray technology. Mol Med Rep. 11:1963–1967. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|