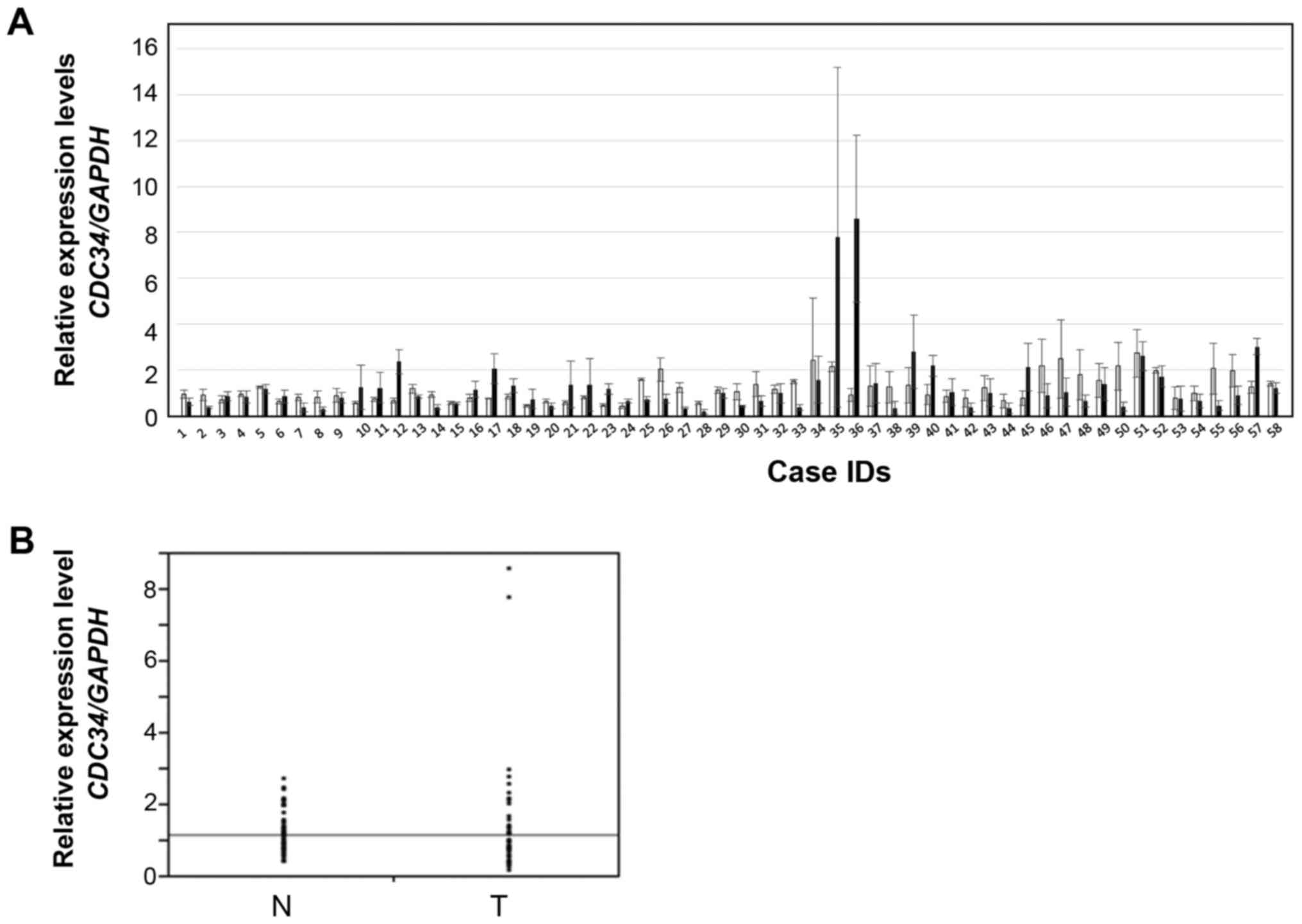
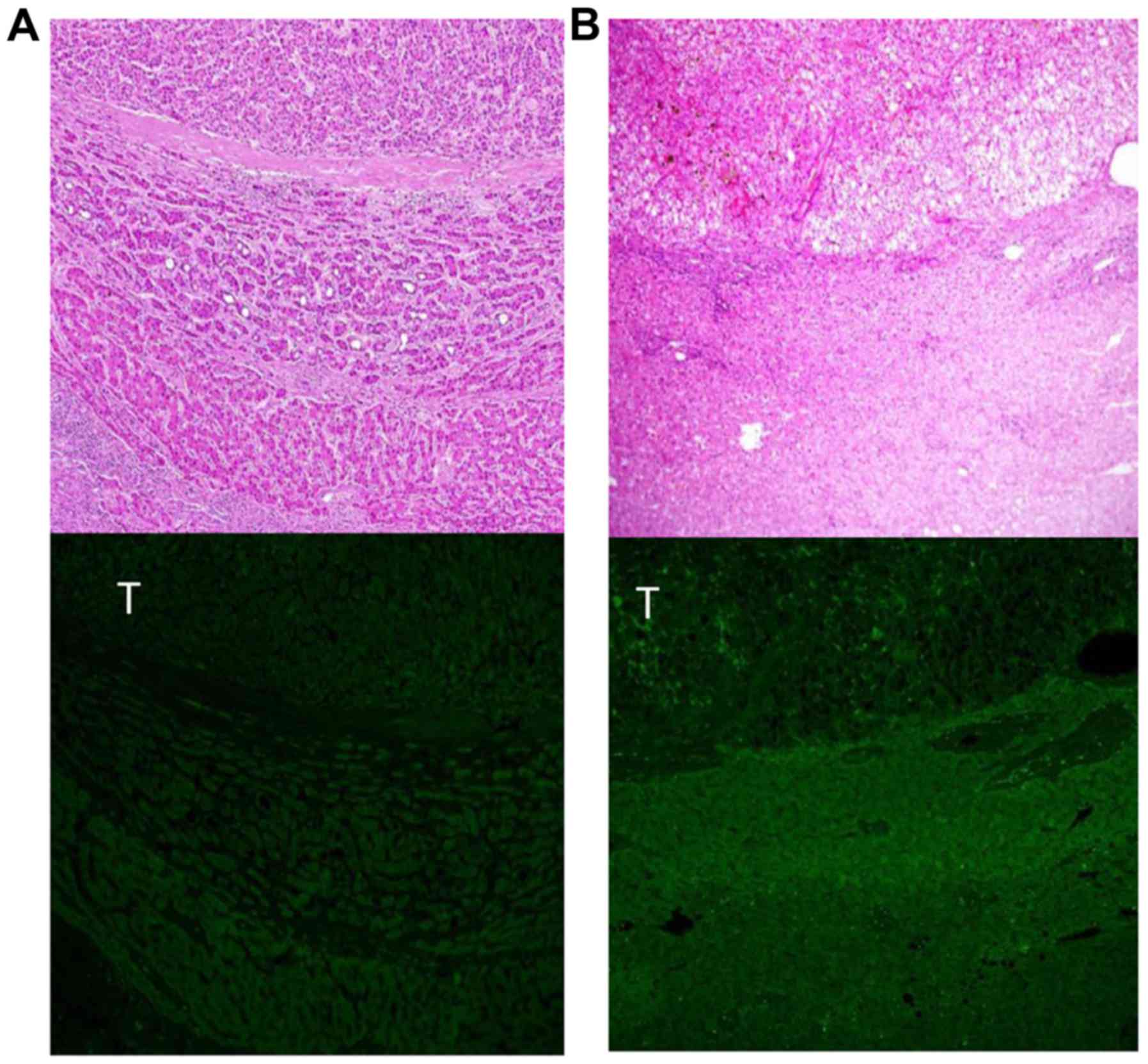
|
1
|
Globocan 2012: Estimated Cancer Incidence,
Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide in 2012. Lyon, France: 2012,
http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_cancer.aspx
|
|
2
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van Malenstein H, van Pelt J and Verslype
C: Molecular classification of hepatocellular carcinoma anno 2011.
Eur J Cancer. 47:1789–1797. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lavanchy D: The global burden of hepatitis
C. Liver Int. 29 Suppl 1:74–81. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grazi GL, Ercolani G, Pierangeli F, Del
Gaudio M, Cescon M, Cavallari A and Mazziotti A: Improved results
of liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma on cirrhosis give
the procedure added value. Ann Surg. 234:71–78. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo
T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S, Sugawara Y, Minagawa M, Takayama T,
Kawasaki S and Makuuchi M: Risk factors contributing to early and
late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma
after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 38:200–207. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, De Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al SHARP Investigators Study Group, : Sorafenib in advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 359:378–390. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheng AL, Guan Z, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S,
Kim JS, Yang TS, Tak WY, Pan H, Yu S, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
according to baseline status: Subset analyses of the phase III
Sorafenib Asia-Pacific trial. Eur J Cancer. 48:1452–1465. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ivanov AV, Bartosch B, Smirnova OA,
Isaguliants MG and Kochetkov SN: HCV and oxidative stress in the
liver. Viruses. 5:439–469. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Korenaga M, Wang T, Li Y, Showalter LA,
Chan T, Sun J and Weinman SA: Hepatitis C virus core protein
inhibits mitochondrial electron transport and increases reactive
oxygen species (ROS) production. J Biol Chem. 280:37481–37488.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Minouchi K, Kaneko S and Kobayashi K:
Mutation of p53 gene in regenerative nodules in cirrhotic liver. J
Hepatol. 37:231–239. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Laurent-Puig P and Zucman-Rossi J:
Genetics of hepatocellular tumors. Oncogene. 25:3778–3786. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li CW, Chang PY and Chen BS: Investigating
the mechanism of hepatocellular carcinoma progression by
constructing genetic and epigenetic networks using NGS data
identification and big database mining method. Oncotarget.
7:79453–79473. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lemon SM and McGivern DR: Is hepatitis C
virus carcinogenic? Gastroenterology. 142:1274–1278. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Higgs MR, Lerat H and Pawlotsky JM:
Hepatitis C virus-induced activation of β-catenin promotes c-Myc
expression and a cascade of pro-carcinogenetic events. Oncogene.
32:4683–4693. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Takagi K, Fujiwara K, Takayama T, Mamiya
T, Soma M and Nagase H: DNA hypermethylation of zygote arrest 1
(ZAR1) in hepatitis C virus positive related hepatocellular
carcinoma. Springerplus. 2:1502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fujiwara K, Ghosh S, Liang P, Morien E,
Soma M and Nagase H: Genome-wide screening of aberrant DNA
methylation which associated with gene expression in mouse skin
cancers. Mol Carcinog. 54:178–188. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ceccarelli DF, Tang X, Pelletier B,
Orlicky S, Xie W, Plantevin V, Neculai D, Chou YC, Ogunjimi A,
Al-Hakim A, et al: An allosteric inhibitor of the human Cdc34
ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Cell. 145:1075–1087. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Micel LN, Tentler JJ, Smith PG and
Eckhardt GS: Role of ubiquitin ligases and the proteasome in
oncogenesis: Novel targets for anticancer therapies. J Clin Oncol.
31:1231–1238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morrow JK, Lin HK, Sun SC and Zhang S:
Targeting ubiquitination for cancer therapies. Future Med Chem.
7:2333–2350. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wittekind C, Compton CC, Greene FL and
Sobin LH: TNM residual tumor classification revisited. Cancer.
94:2511–2516. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schwob E, Böhm T, Mendenhall MD and
Nasmyth K: The B-type cyclin kinase inhibitor p40SIC1 controls the
G1 to S transition in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 79:233–244. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tyers M and Jorgensen P: Proteolysis and
the cell cycle: With this RING I do thee destroy. Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 10:54–64. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Legesse-Miller A, Elemento O, Pfau SJ,
Forman JJ and Tavazoie S: Coller HA let-7 Overexpression leads to
an increased fraction of cells in G2/M, direct down-regulation of
Cdc34, and stabilization of Wee1 kinase in primary fibroblasts. J
Biol Chem. 284:6605–6609. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Eliseeva E, Pati D, Diccinanni MB, Yu AL,
Mohsin SK, Margolin JF and Plon SE: Expression and localization of
the CDC34 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in pediatric acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Cell Growth Differ. 12:427–433.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tanaka K, Kondoh N, Shuda M, Matsubara O,
Imazeki N, Ryo A, Wakatsuki T, Hada A, Goseki N, Igari T, et al:
Enhanced expression of mRNAs of antisecretory factor-1, gp96, DAD1
and CDC34 in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1536:1–12. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Butterfield LH, Ribas A, Meng WS, Dissette
VB, Amarnani S, Vu HT, Seja E, Todd K, Glaspy JA, McBride WH, et
al: T-cell responses to HLA-A*0201 immunodominant peptides derived
from α-fetoprotein in patients with hepatocellular cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:5902–5908. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|