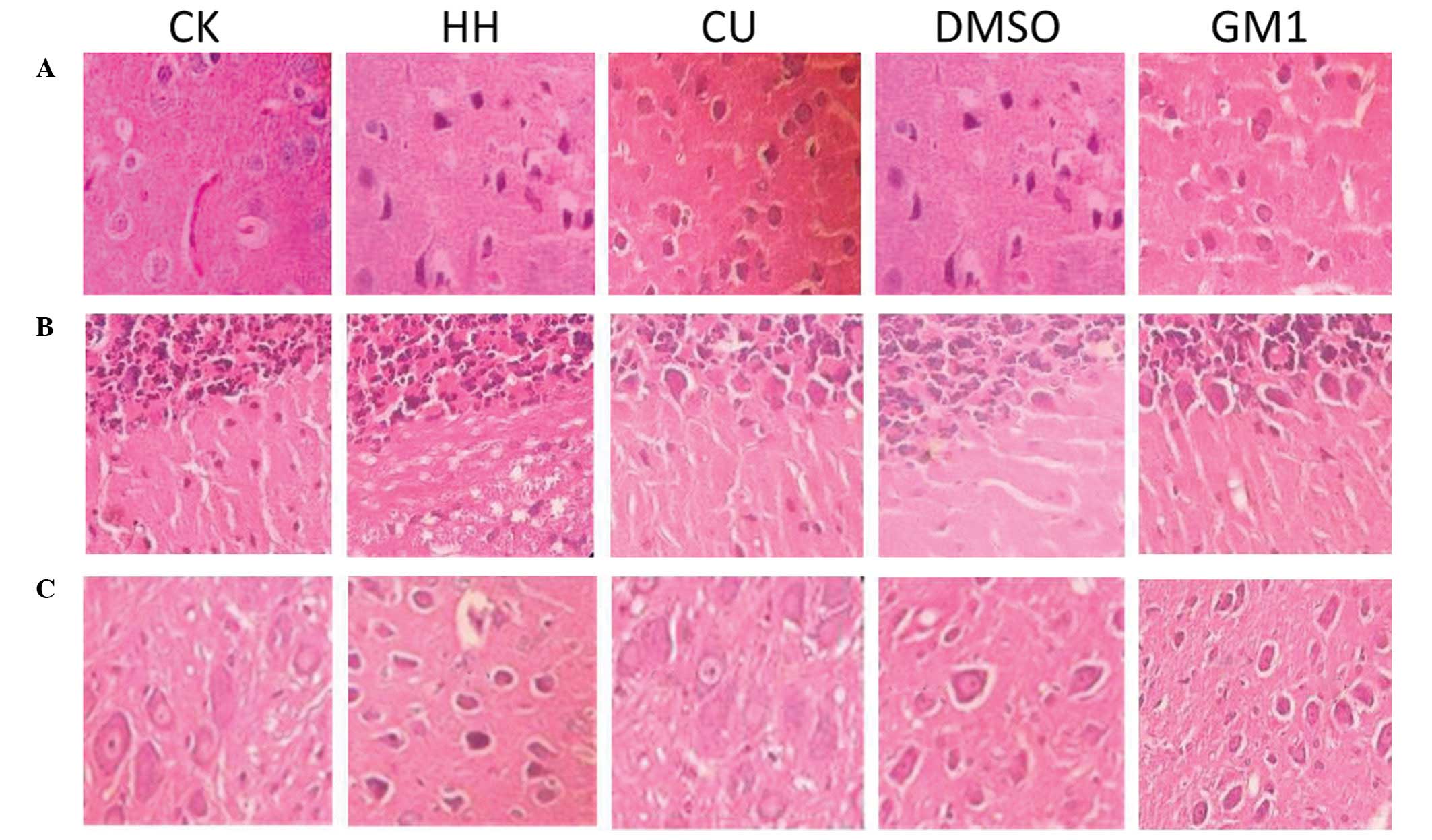
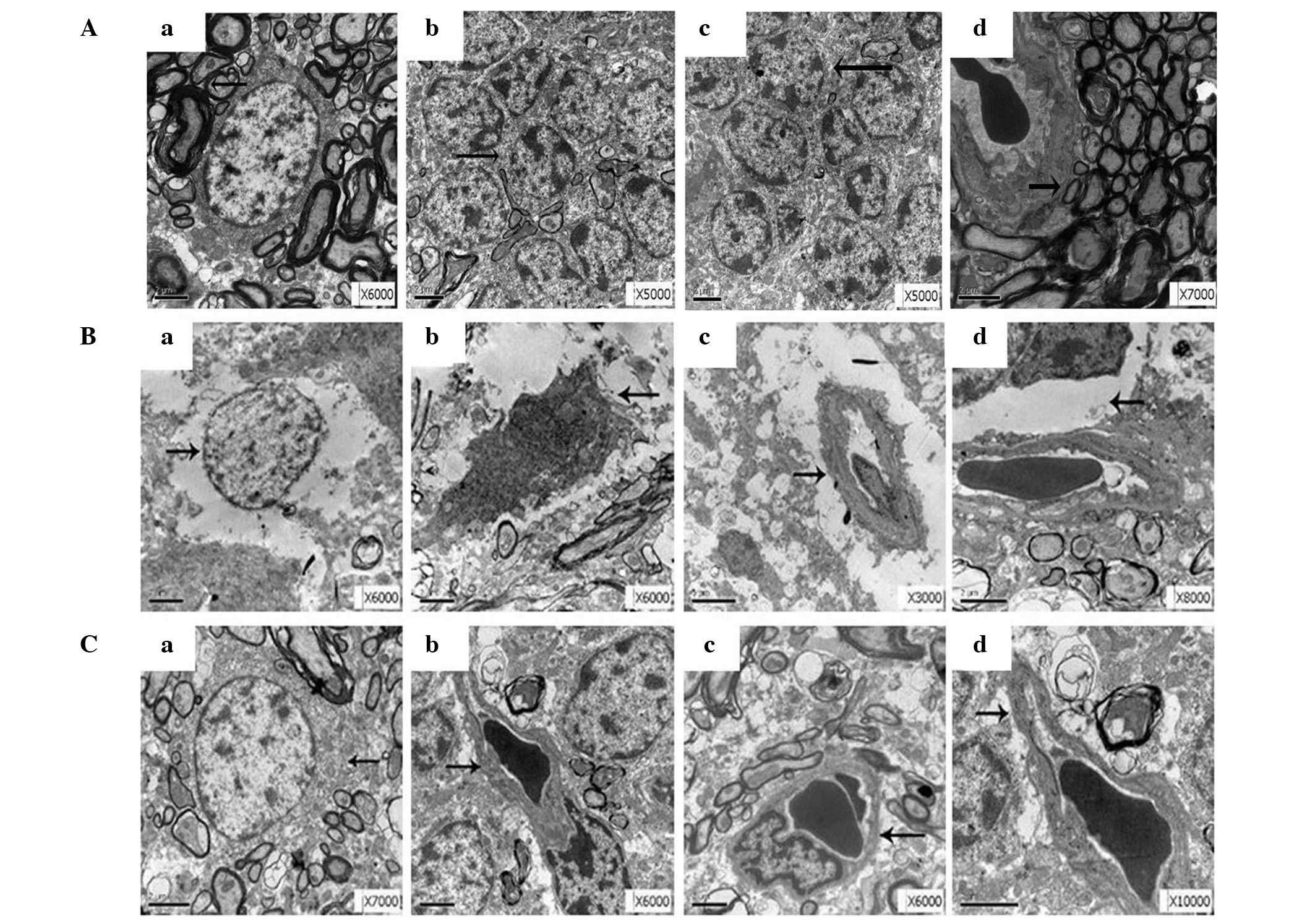
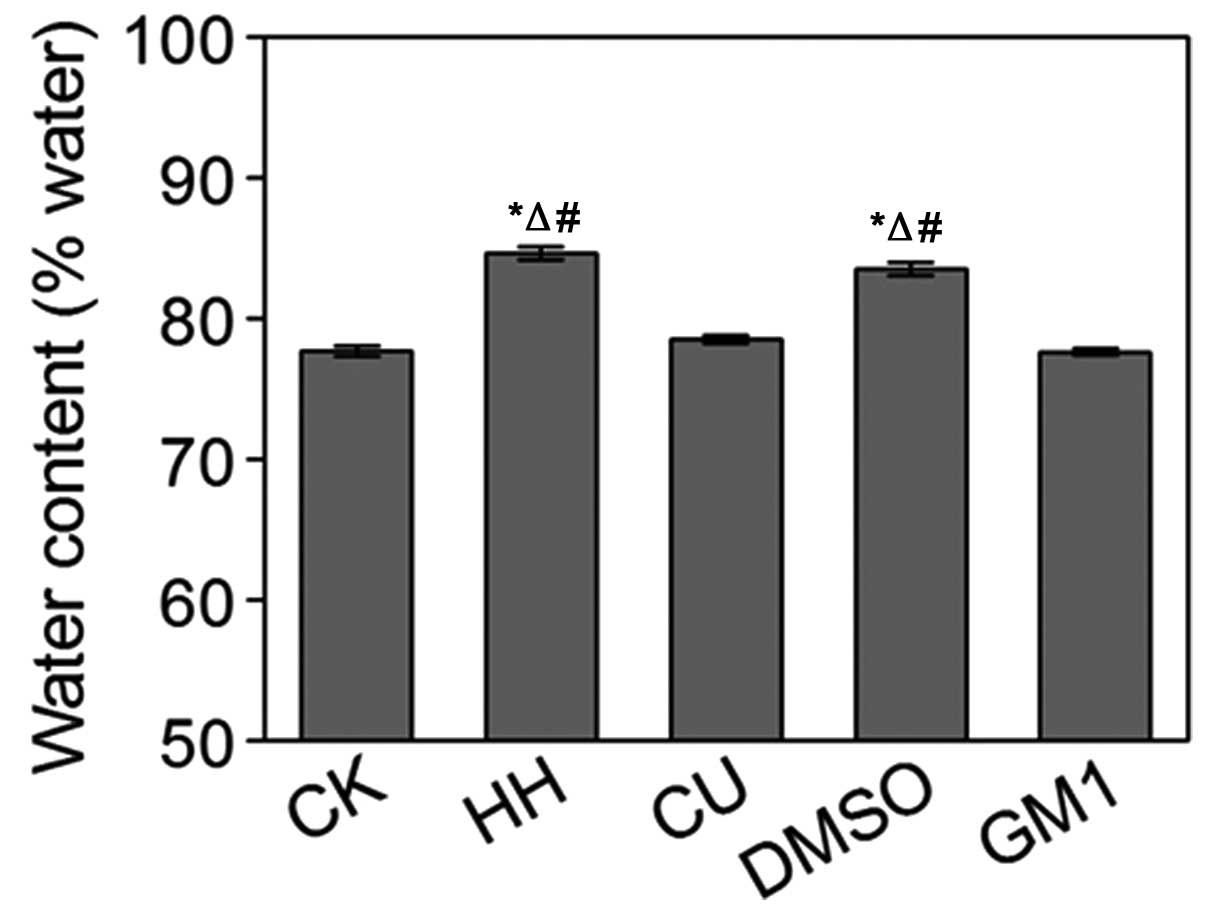
|
1
|
Bakay L and Lee JC: The effect of acute
hypoxia and hypercapnia on the ultrastructure of the central
nervous system. Brain. 91:697–706. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yu L, Yi J, Ye G, Zheng Y, Song Z, Yang Y,
Song Y, Wang Z and Bao Q: Effects of curcumin on levels of nitric
oxide synthase and AQP-4 in a rat model of hypoxia-ischemic brain
damage. Brain Res. 1475:88–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ainslie PN and Ogoh S: Regulation of
cerebral blood flow in mammals during chronic hypoxia: A matter of
balance. Exp Physiol. 95:251–262. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Donkin JJ and Vink R: Mechanisms of
cerebral edema in traumatic brain injury: Therapeutic developments.
Curr Opin Neurol. 23:293–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Von Sarnowski B, Guerra Kleist-Welch W,
Kohlmann T, Moock J, Khaw AV, Kessler C, Schminke U and Schroeder
HW: Long-term health-related quality of life after decompressive
hemicraniectomy in stroke patients with life-threatening
space-occupying brain edema. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 114:627–633.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rite I, Machado A, Cano J and Venero JL:
Intracerebral VEGF injection highly upregulates AQP4 mRNA and
protein in the perivascular space and glia limitans externa.
Neurochem Int. 52:897–903. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yoshida H, Yanai H, Namiki Y,
Fukatsu-Sasaki K, Furutani N and Tada N: Neuroprotective effects of
edaravone: A novel free radical scavenger in cerebrovascular
injury. CNS Drug Rev. 12:9–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mcconeghy KW, Hatton J, Hughes L and Cook
AM: A review of neuroprotection pharmacology and therapies in
patients with acute traumatic brain injury. CNS Drugs. 26:613–636.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gaire BP and Kim H: Neuroprotective
effects of Fructus Chebulae extracts on experimental models
of cerebral ischemia. J Tradit Chin Med. 34:69–75. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu QS, Chen XY, Zhuang SJ and Li KQ:
Research on effect of Baimai powder effective compounds group
promotes neurogenesis and maintains of neural stem cells after
cerebral infarction. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 38:3776–3781.
2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gupta YK, Briyal S and Gulati A:
Therapeutic potential of herbal drugs in cerebral ischemia. Indian
J Physiol Pharmacol. 54:99–122. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bu Y, Lee K, Jung HS and Moon SK:
Therapeutic effects of traditional herbal medicine on cerebral
ischemia: A perspective of vascular protection. Chin J Integr Med.
19:804–814. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou H, Beevers CS and Huang S: Targets of
curcumin. Current drug targets. 12:332–347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wilken R, Veena MS, Wang MB and Srivatsan
ES: Curcumin: A review of anti-cancer properties and therapeutic
activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
10:122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen SY, Chen Y, Li YP, Chen SH, Tan JH,
Ou TM, Gu LQ and Huang ZS: Design, synthesis and biological
evaluation of curcumin analogues as multifunctional agents for the
treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Bioorg Med Chem. 19:5596–5604.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tu XK, Yang WZ, Chen JP, Chen Y, Ouyang
LQ, Xu YC and Shi SS: Curcumin inhibits TLR2/4-NF-κB signaling
pathway and attenuates brain damage in permanent focal cerebral
ischemia in rats. Inflammation. 37:1544–1551. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuo CP, Lu CH, Wen LL, Cherng CH, Wong CS,
Borel CO, Ju DT, Chen CM and Wu CT: Neuroprotective effect of
curcumin in an experimental rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Anesthesiology. 115:1229–1238. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu L, Yi J, Ye G, Zheng Y, Song Z, Yang Y,
Song Y, Wang Z and Bao Q: Effects of curcumin on levels of nitric
oxide synthase and AQP-4 in a rat model of hypoxia-ischemic brain
damage. Brain Res. 1475:88–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu L, Yi J, Ye G, Zheng Y, Song Z, Yang Y,
Song Y, Wang Z and Bao Q: Effects of curcumin on levels of nitric
oxide synthase and AQP-4 in a rat model of hypoxia-ischemic brain
damage. Brain Res. 1475:88–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Hua LH: Preservation of animal tissue
within the RNA method to improve. Sheng Wu Ji Shu Tong Bao.
4:2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Chen FH, Wang L and Hu LH: Real time
fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR reference genes selection. Zhong
Guo Lin Chuang Jian Yan Za Zhi. 23:393–395. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Shibata M, Yamawaki T, Sasaki T, Hattori
H, Hamada J, Fukuuchi Y, Okano H and Miura M: Upregulation of Akt
phosphorylation at the early stage of middle cerebral artery
occlusion in mice. Brain Res. 942:1–10. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Beziaud T, Chen XR, El Shafey N, Fréchou
M, Teng F, Palmier B, Beray-Berthat V, Soustrat M, Margaill I,
Plotkine M, et al: Simvastatin in traumatic brain injury: Effect on
brain edema mechanisms. Crit Care Med. 39:2300–2307. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun L, Yang L, Xu YW, Liang H, Han J, Zhao
RJ and Cheng Y: Neuroprotection of hydroxysafflor yellow A in the
transient focal ischemia: Inhibition of protein
oxidation/nitration, 12/15-lipoxygenase and blood-brain barrier
disruption. Brain Res. 1473:227–235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tang Y, Cai D and Chen Y: Thrombin
inhibits aquaporin 4 expression through protein kinase C-dependent
pathway in cultured astrocytes. J Mol Neurosci. 31:83–93. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zheng GQ, Wang Y and Wang XT: Chronic
hypoxia-hypercapnia influences cognitive function: A possible new
model of cognitive dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease. Med Hypotheses. 71:111–113. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oechmichen M and Meissner C: Cerebral
hypoxia and ischemia: The forensic point of view: A review. J
Forensic Sci. 51:880–887. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen YF: Traditional Chinese herbal
medicine and cerebral ischemia. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 4:809–817.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeremitsky E, Omert L, Dunham CM, Protetch
J and Rodriguez A: Harbingers of poor outcome the day after severe
brain injury: Hypothermia, hypoxia and hypoperfusion. J Trauma.
54:312–319. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dohare P, Garg P, Jain V, Nath C and Ray
M: Dose dependence and therapeutic window for the neuroprotective
effects of curcumin in thromboembolic model of rat. Behav Brain
Res. 193:289–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ghoneim AI, Abdel-Naim AB, Khalifa AE and
El-Denshary ES: Protective effects of curcumin against
ischaemia/reperfusion insult in rat forebrain. Pharmacol Res.
46:273–279. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
King MD, Mccracken DJ, Wade FM, Meiler SE,
Alleyne CH Jr and Dhandapani KM: Attenuation of hematoma size and
neurological injury with curcumin following intracerebral
hemorrhage in mice. J Neurosurg. 115:116–123. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Papadopoulos MC and Verkman AS:
Aquaporin-4 and brain edema. Pediatr Nephrol. 22:778–784. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Loreto C and Reggio E: Aquaporin and
vascular diseases. Curr Neuropharmacol. 8:105–111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Laird MD, Sukumari-Ramesh S, Swift AE,
Meiler SE, Vender JR and Dhandapani KM: Curcumin attenuates
cerebral edema following traumatic brain injury in mice: A possible
role for aquaporin-4? J Neurochem. 113:637–648. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ji FT, Cao MH, Liang JJ, Liu L, Li F and
Bu XZ: Effects of chemical synthesized curcumin preconditioning on
the expression of AQP 4 and cerebral edema after focal cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion damage in rats. Zhong Guo Yao Li Xue Tong Bao.
4:0192011.(In Chinese).
|
|
38
|
Zu J, Wang Y, Xu G, Zhuang J, Gong H and
Yan J: Curcumin improves the recovery of motor function and reduces
spinal cord edema in a rat acute spinal cord injury model by
inhibiting the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Acta Histochem.
116:1331–1336. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Moftakhar P, Lynch MD, Pomakian JL and
Vinters HV: Aquaporin expression in the brains of patients with or
without cerebral amyloid angiopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
69:1201–1209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang B, Zador Z and Verkman A: Glial cell
aquaporin-4 overexpression in transgenic mice accelerates cytotoxic
brain swelling. J Biol Chem. 283:15280–15286. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vieira KP, De Almeida E, Silva Lima,
Zollner AR, Malaguti C, Vilella CA and De Lima Zollner R:
Ganglioside GM1 effects on the expression of nerve growth factor
(NGF), Trk-A receptor, proinflammatory cytokines and on autoimmune
diabetes onset in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice. Cytokine.
42:92–104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen ZG, Lu YC, Zhu C, Zhang GJ, Ding XH
and Jiang JY: Effects of ganglioside GM1 on reduction of brain
edema and amelioration of cerebral metabolism after traumatic brain
injury. Chin J Traumatol. 6:23–27. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|