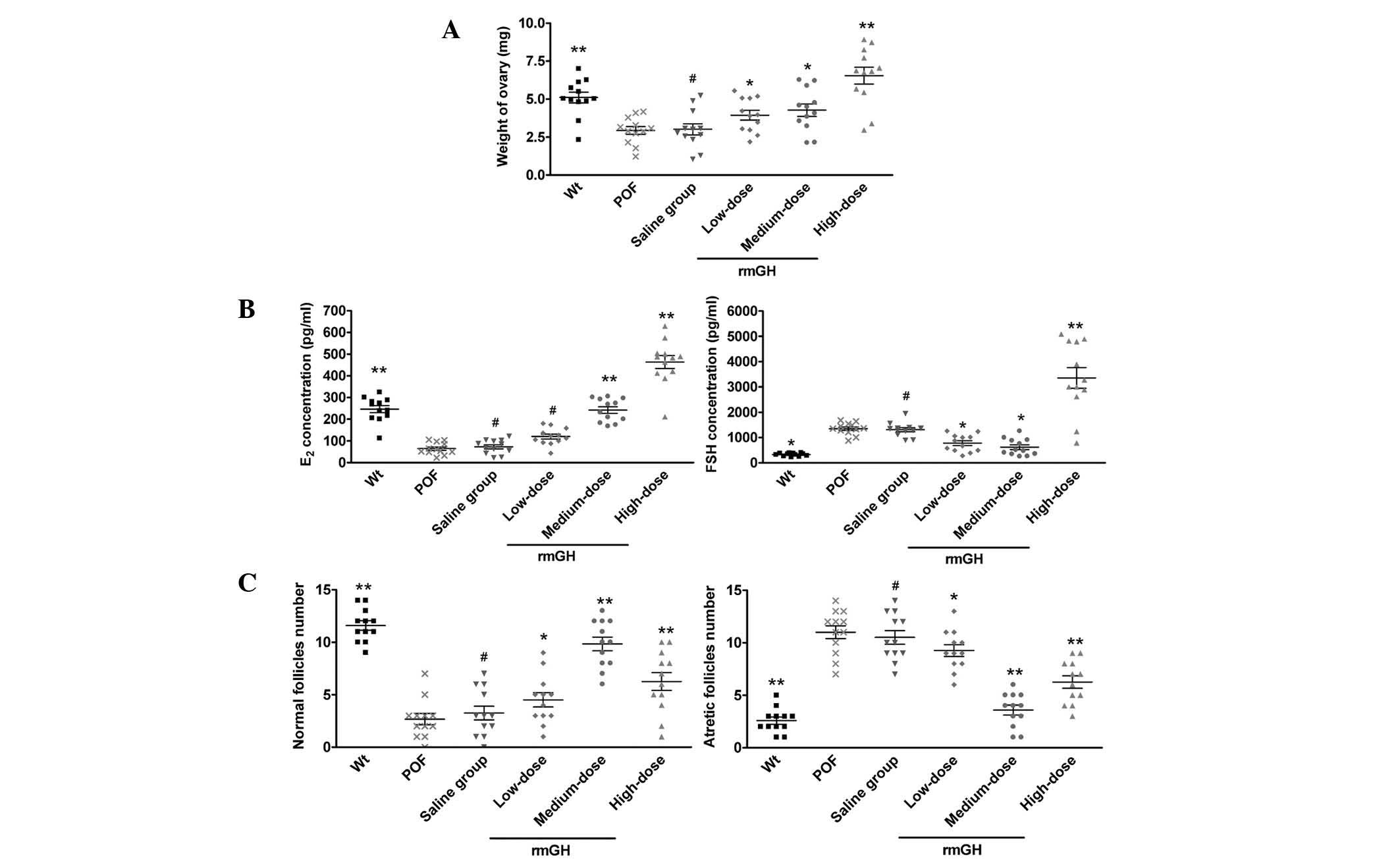
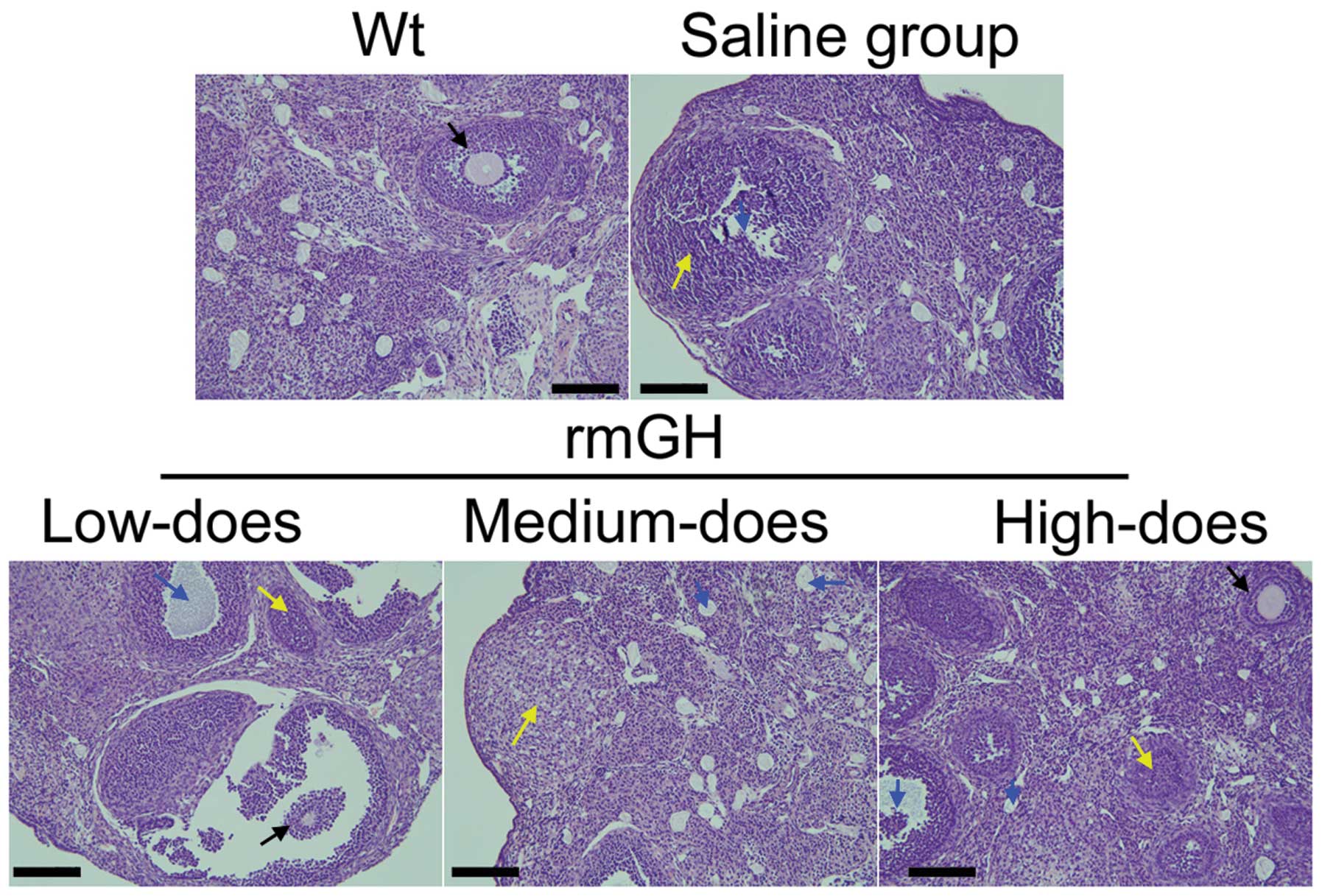
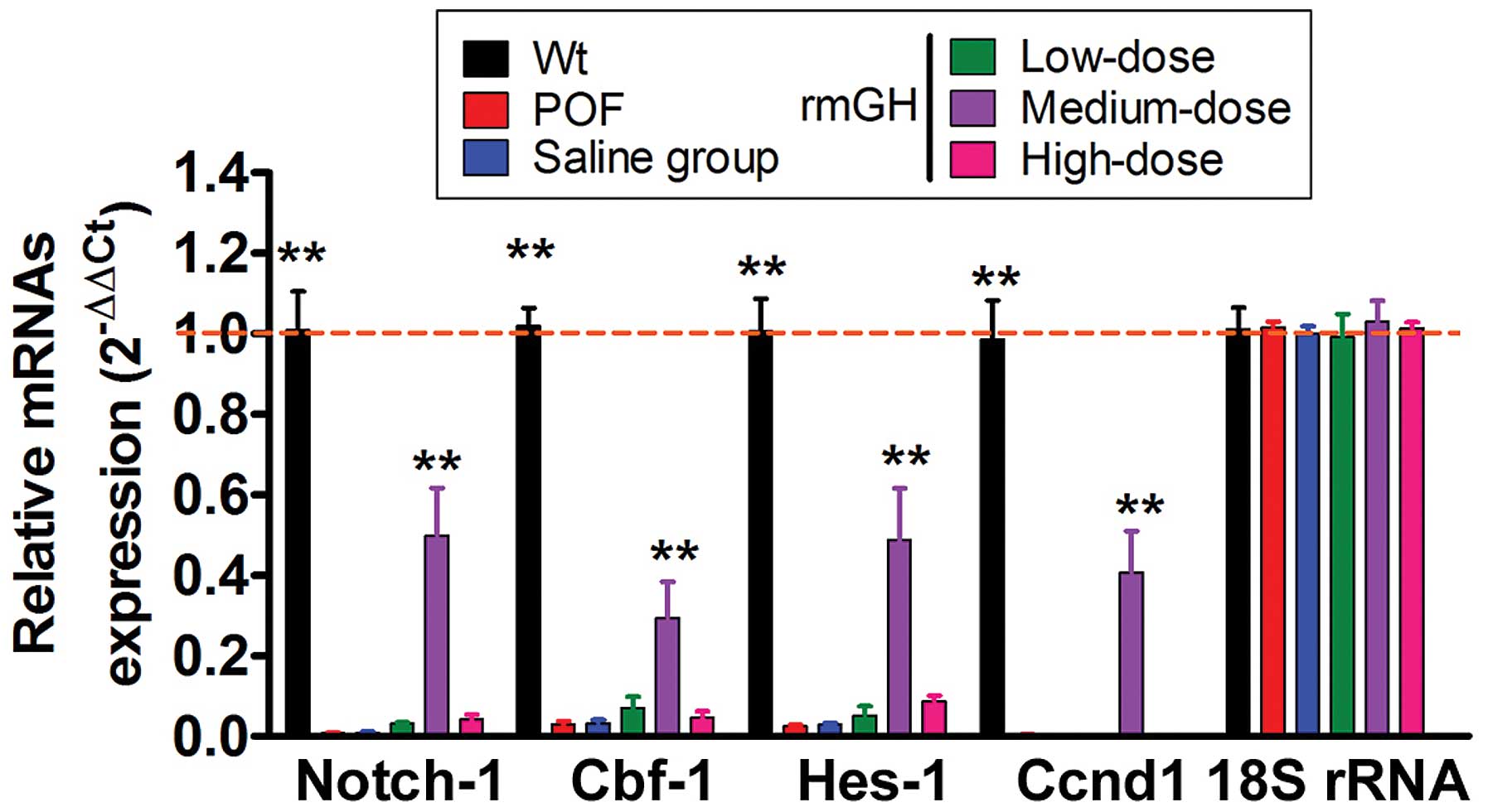
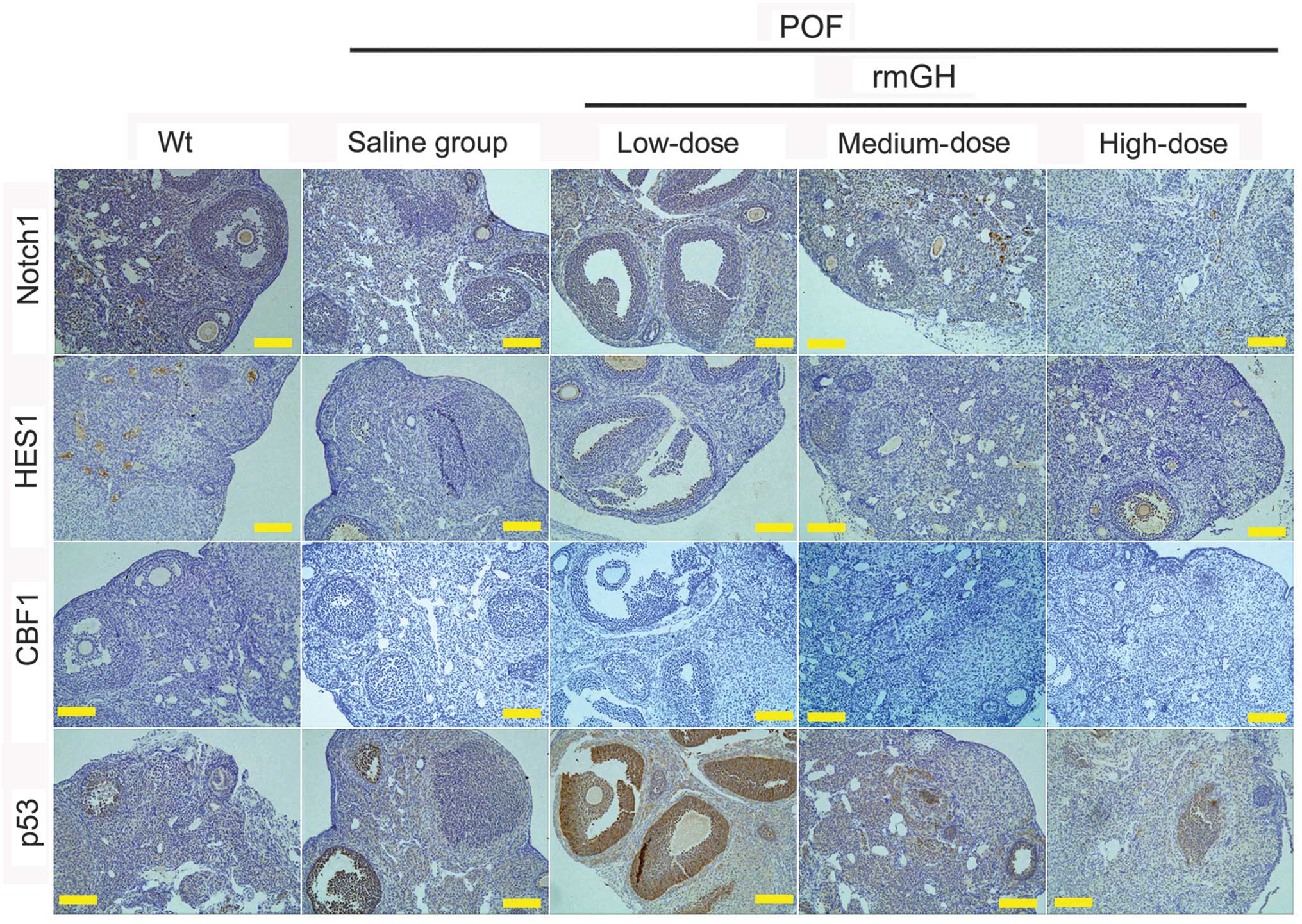
|
1
|
Bandyopadhyay S, Chakrabarti J, Banerjee
S, Pal AK, Goswami SK, Chakravarty BN and Kabir SN: Galactose
toxicity in the rat as a model for premature ovarian failure: An
experimental approach readdressed. Hum Reprod. 18:2031–2038. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Beck-Peccoz P and Persani L: Premature
ovarian failure. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 1:92006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Persani L, Rossetti R and Cacciatore C:
Genes involved in human premature ovarian failure. J Mol
Endocrinol. 45:257–279. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McGuire MM, Bowden W, Engel NJ, Ahn HW,
Kovanci E and Rajkovic A: Genomic analysis using high-resolution
single-nucleotide polymorphism arrays reveals novel microdeletions
associated with premature ovarian failure. Fertil Steril.
95:1595–1600. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vujović S, Ivović M, Tancić-Gajić M,
Marina L, Barać M, Arizanorić Z, Nenezić A, Ivaniserić M, Micić J,
Sajić S and Micić D: Premature ovarian failure. Srp Arh Celok Lek.
140:806–811. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qin Y, Sun M, You L, Wei D, Sun J, Liang
X, Zhang B, Jiang H, Xu J and Chen ZJ: ESR1, HK3 and BRSK1 gene
variants are associated with both age at natural menopause and
premature ovarian failure. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 7:52012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rebar RW: Premature ovarian 'failure' in
the adolescent. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1135:138–145. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kalantari H, Madani T, Zari Moradi S,
Mansouri Z, Almadani N, Gourabi H and Mohseni Meybodi A:
Cytogenetic analysis of 179 Iranian women with premature ovarian
failure. Gynecol Endocrinol. 29:588–591. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Duncan M, Cummings L and Chada K: Germ
cell deficient (gcd) mouse as a model of premature ovarian failure.
Biol Reprod. 49:221–227. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cecchi CR, Higuti E, Oliveira NA, Lima ER,
Jakobsen M, Dagnaes-Hansen F, Gissel H, Aagaard L, Jensen TG, Jorge
AA, et al: A novel homologous model for gene therapy of dwarfism by
non-viral transfer of the mouse growth hormone gene into
immunocompetent dwarf mice. Curr Gene Ther. 14:44–51. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Visser JA, Hokken-Koelega AC, Zandwijken
GR, Limacher A, Ranke MB and Flück CE: Anti-Müllerian hormone
levels in girls and adolescents with Turner syndrome are related to
karyotype, pubertal development and growth hormone treatment. Hum
Reprod. 28:1899–1907. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hartmann BW, Kirchengast S, Albrecht A,
Huber JC and Söregi G: Effect of hormone replacement therapy on
growth hormone stimulation in women with premature ovarian failure.
Fertil Steril. 68:103–107. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kopchick JJ, List EO, Kelder B, Gosney ES
and Berryman DE: Evaluation of growth hormone (GH) action in mice:
Discovery of GH receptor antagonists and clinical indications. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 386:34–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rojanathammanee L, Rakoczy S and
Brown-Borg HM: Growth hormone alters the glutathione S-transferase
and mitochondrial thioredoxin systems in long-living Ames dwarf
mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 69:1199–1211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chesnokova V, Zhou C, Ben-Shlomo A, Zonis
S, Tani Y, Ren SG and Melmed S: Growth hormone is a cellular
senescence target in pituitary and nonpituitary cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:E3331–E3339. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Villares R, Kakabadse D, Juarranz Y,
Gomariz RP, Martínez AC and Mellado M: Growth hormone prevents the
development of autoimmune diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:E4619–E4627. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Subramaniam D, Ponnurangam S, Ramamoorthy
P, Standing D, Battafarano RJ, Anant S and Sharma P: Curcumin
induces cell death in esophageal cancer cells through modulating
Notch signaling. PLoS One. 7:e305902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yao L, Kan EM, Kaur C, Dheen ST, Hao A, Lu
J and Ling EA: Notch-1 signaling regulates microglia activation via
NF-κB pathway after hypoxic exposure in vivo and in vitro. PLoS
One. 8:e784392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ji X, Wang Z, Geamanu A, Goja A, Sarkar FH
and Gupta SV: Delta-tocotrienol suppresses notch-1 pathway by
upregulating miR-34a in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 131:2668–2677. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang H, Hilton MJ, Anolik JH, Welle SL,
Zhao C, Yao Z, Li X, Wang Z, Boyce BF and Xing L: NOTCH inhibits
osteoblast formation in inflammatory arthritis via noncanonical
NF-κB. J Clin Invest. 124:3200–3214. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen G, Qiu Y, Sun L, Yu M, Wang W, Xiao
W, Yang Y, Liu Y, Yang S, Teitelbaum DH, et al: The
Jagged-2/Notch-1/Hes-1 pathway is involved in intestinal epithelium
regeneration after intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS
One. 8:e762742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Z, Azmi AS, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Wang
S, Sarkar FH and Mohammad RM: TW-37, a small-molecule inhibitor of
Bcl-2, inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in pancreatic
cancer: Involvement of Notch-1 signaling pathway. Cancer Res.
69:2757–2765. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu T, Huang Y, Zhang J, Qin W, Chi H,
Chen J, Yu Z and Chen C: Transplantation of human menstrual blood
stem cells to treat premature ovarian failure in mouse model. Stem
Cells Dev. 23:1548–1557. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shen DZ, Xin SL, Chen C and Liu T: Effect
of atorvastatin on expression of TLR4 and NF-κB p65 in
atherosclerotic rabbits. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 6:493–496. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|