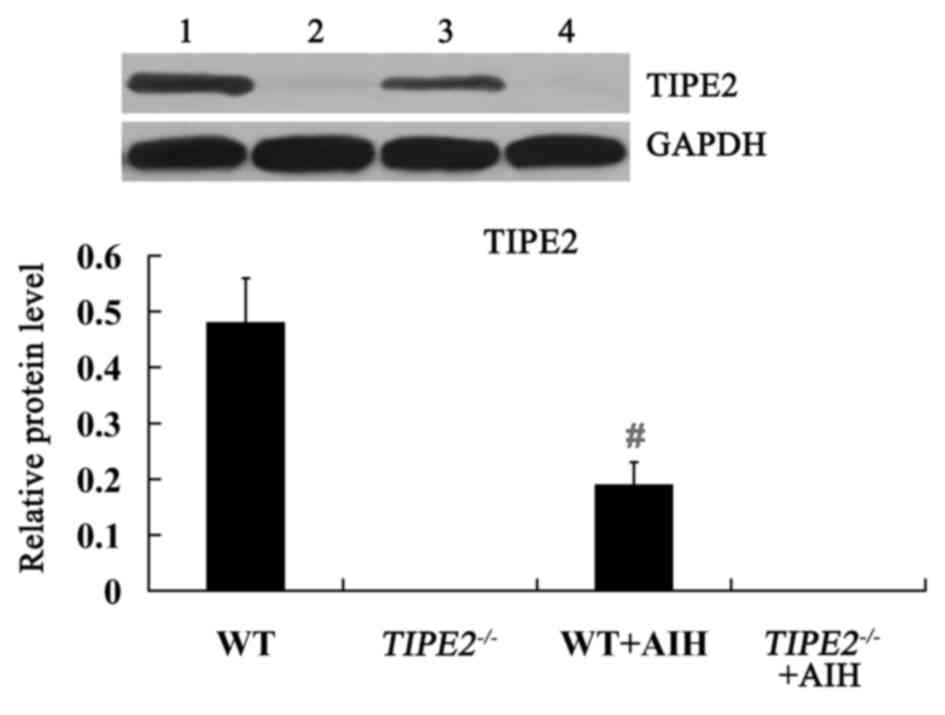
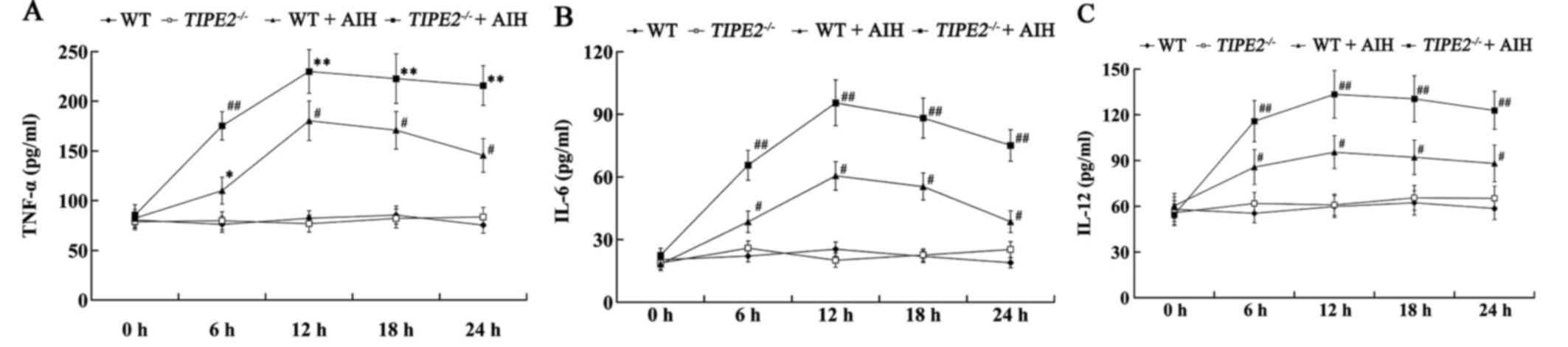
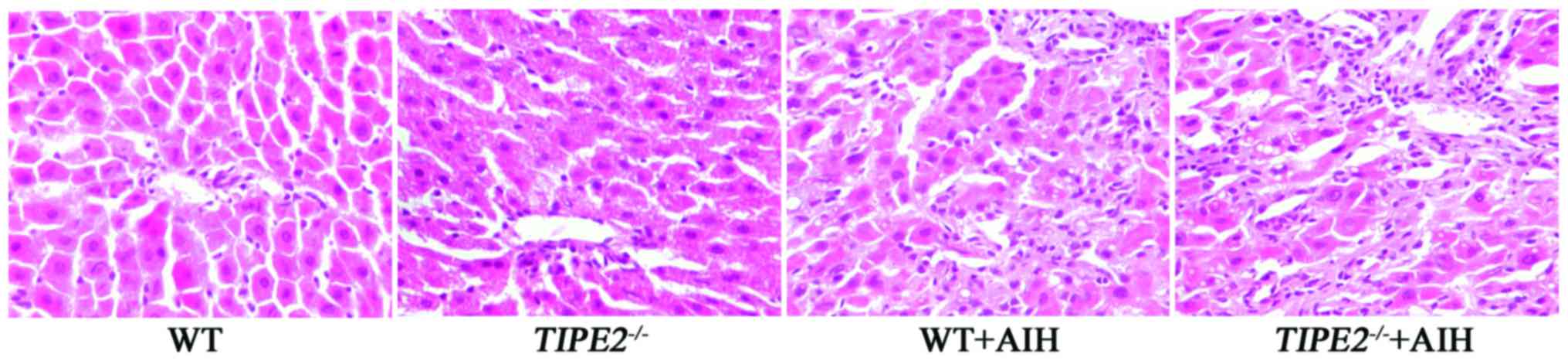
|
1
|
Vergani D and Mieli-Vergani G:
Aetiopathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol.
14:3306–3312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Verma S, Maheshwari A and Thuluvath P:
Liver failure as initial presentation of autoimmune hepatitis:
Clinical characteristics, predictors of response to steroid
therapy, and outcomes. Hepatology. 49:1396–1397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Strassburg CP: Autoimmune hepatitis. Dig
Dis. 31:155–163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lapierre P, Béland K, Yang R and Alvarez
F: Adoptive transfer of ex vivo expanded regulatory T cells in an
autoimmune hepatitis murine model restores peripheral tolerance.
Hepatology. 57:217–227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wong RJ, Gish R, Frederick T, Bzowej N and
Frenette C: The impact of race/ethnicity on the clinical
epidemiology of autoimmune hepatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol.
46:155–161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schramm C, Kanzler S, zum Büschenfelde KH,
Galle PR and Lohse AW: Autoimmune hepatitis in the elderly. Am J
Gastroenterol. 96:1587–1591. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Abe M, Mashiba T, Zeniya M, Yamamoto K,
Onji M and Tsubouchi H: Autoimmune Hepatitis Study Group-Subgroup
of the Intractable Hepato-Biliary Disease Study Group in Japan:
Present status of autoimmune hepatitis in Japan: A nationwide
survey. J Gastroenterol. 46:1136–1141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peng M, Li Y, Zhang M, Jiang Y, Xu Y, Tian
Y, Peng F and Gong G: Clinical features in different age groups of
patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Exp Ther Med. 7:145–148.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Muratori P, Granito A, Quarneti C, Ferri
S, Menichella R, Cassani F, Pappas G, Bianchi FB, Lenzi M and
Muratori L: Autoimmune hepatitis in Italy: The Bologna experience.
J Hepatol. 50:1210–1218. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen J, Eslick GD and Weltman M:
Systematic review with meta-analysis: Clinical manifestations and
management of autoimmune hepatitis in the elderly. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 39:117–124. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun H, Gong S, Carmody RJ, Hilliard A, Li
L, Sun J, Kong L, Xu L, Hilliard B, Hu S, et al: TIPE2, a negative
regulator of innate and adaptive immunity that maintains immune
homeostasis. Cell. 133:415–426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lou Y and Liu S: The TIPE (TNFAIP8) family
in inflammation, immunity, and cancer. Mol Immunol. 49:4–7. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang G, Hao C, Lou Y, Xi W, Wang X, Wang
Y, Qu Z, Guo C, Chen Y, Zhang Y and Liu S: Tissue-specific
expression of TIPE2 provides insights into its function. Mol
Immunol. 47:2435–2442. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang L, Shi Y, Wang Y, Zhu F, Wang Q, Ma
C, Chen YH and Zhang L: The unique expression profile of human
TIPE2 suggests new functions beyond its role in immune regulation.
Mol Immunol. 48:1209–1215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang X, Wang J, Fan C, Li H, Sun H, Gong
S, Chen YH and Shi Y: Crystal structure of TIPE2 provides insights
into immune homeostasis. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 16:89–90. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun H, Zhuang G, Chai L, Wang Z, Johnson
D, Ma Y and Chen YH: TIPE2 controls innate immunity to RNA by
targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Rac pathway. J Immunol.
189:2768–2773. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Z, Fayngerts S, Wang P, Sun H,
Johnson DS, Ruan Q, Guo W and Chen YH: TIPE2 protein serves as a
negative regulator of phagocytosis and oxidative burst during
infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:15413–15418. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lou Y, Liu S, Zhang C, Zhang G, Li J, Ni
M, An G, Dong M, Liu X, Zhu F, et al: Enhanced atherosclerosis in
TIPE2-deficient mice is associated with increased macrophage
responses to oxidized low-density lipoprotein. J Immunol.
191:4849–4857. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cao X, Zhang L, Shi Y, Sun Y, Dai S, Guo
C, Zhu F, Wang Q, Wang J, Wang X, et al: Human tumor necrosis
factor (TNF)-alpha-induced protein 8-like 2 suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through inhibiting Rac1. Mol
Cancer. 12:1492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang YH, Yan HQ, Wang F, Wang YY, Jiang
YN, Wang YN and Gao FG: TIPE2 inhibits TNF-α-induced hepatocellular
carcinoma cell metastasis via Erk1/2 downregulation and NF-κB
activation. Int J Oncol. 46:254–264. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang W, Zhang J, Zhao L, Shao J, Cui J,
Guo C, Zhu F, Chen YH and Liu S: TIPE2 protein negatively regulates
HBV-specific CD8+ T lymphocyte functions in humans. Mol
Immunol. 64:204–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xi W, Hu Y, Liu Y, Zhang J, Wang L, Lou Y,
Qu Z, Cui J, Zhang G, Liang X, et al: Roles of TIPE2 in hepatitis B
virus-induced hepatic inflammation in humans and mice. Mol Immunol.
48:1203–1208. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kong L, Liu K, Zhang YZ, Jin M, Wu BR,
Wang WZ, Li W, Nan YM and Chen YH: Downregulation of TIPE2 mRNA
expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with
chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol Int. 7:844–849. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang LY, Fan YC, Zhao J, Gao S, Sun FK,
Han J, Yang Y and Wang K: Elevated expression of tumour necrosis
factor-α-induced protein 8 (TNFAIP8)-like 2 mRNA in peripheral
blood mononuclear cells is associated with disease progression of
acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure. J Viral Hepat.
21:64–73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gus-Brautbar Y, Johnson D, Zhang L, Sun H,
Wang P, Zhang S, Zhang L and Chen YH: The anti-inflammatory TIPE2
is an inhibitor of the oncogenic Ras. Mol Cell. 45:610–618. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Z, Liang X, Gao L, Ma H, Liu X, Pan
Y, Yan W, Shan H, Wang Z, Chen YH and Ma C: TIPE1 induces apoptosis
by negatively regulating Rac1 activation in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 34:2566–2574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fayngerts SA, Wu J, Oxley CL, Liu X,
Vourekas A, Cathopoulis T, Wang Z, Cui J, Liu S, Sun H, et al:
TIPE3 is the transfer protein of lipid second messengers that
promote cancer. Cancer Cell. 26:465–478. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tiegs G, Hentschel J and Wendel A: A T
cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by
concanavalin A. J Clin Invest. 90:196–203. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shao X, Qian Y, Xu C, Hong B, Xu W, Shen
L, Jin C, Wu Z, Tong X and Yao H: The protective effect of
intrasplenic transplantation of Ad-IL-18BP/IL-4 gene-modified fetal
hepatocytes on ConA-induced hepatitis in mice. PLoS One.
8:e588362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ichiki Y, Aoki CA, Bowlus CL, Shimoda S,
Ishibashi H and Gershwin ME: T cell immunity in autoimmune
hepatitis. Autoimmun Rev. 4:315–321. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|