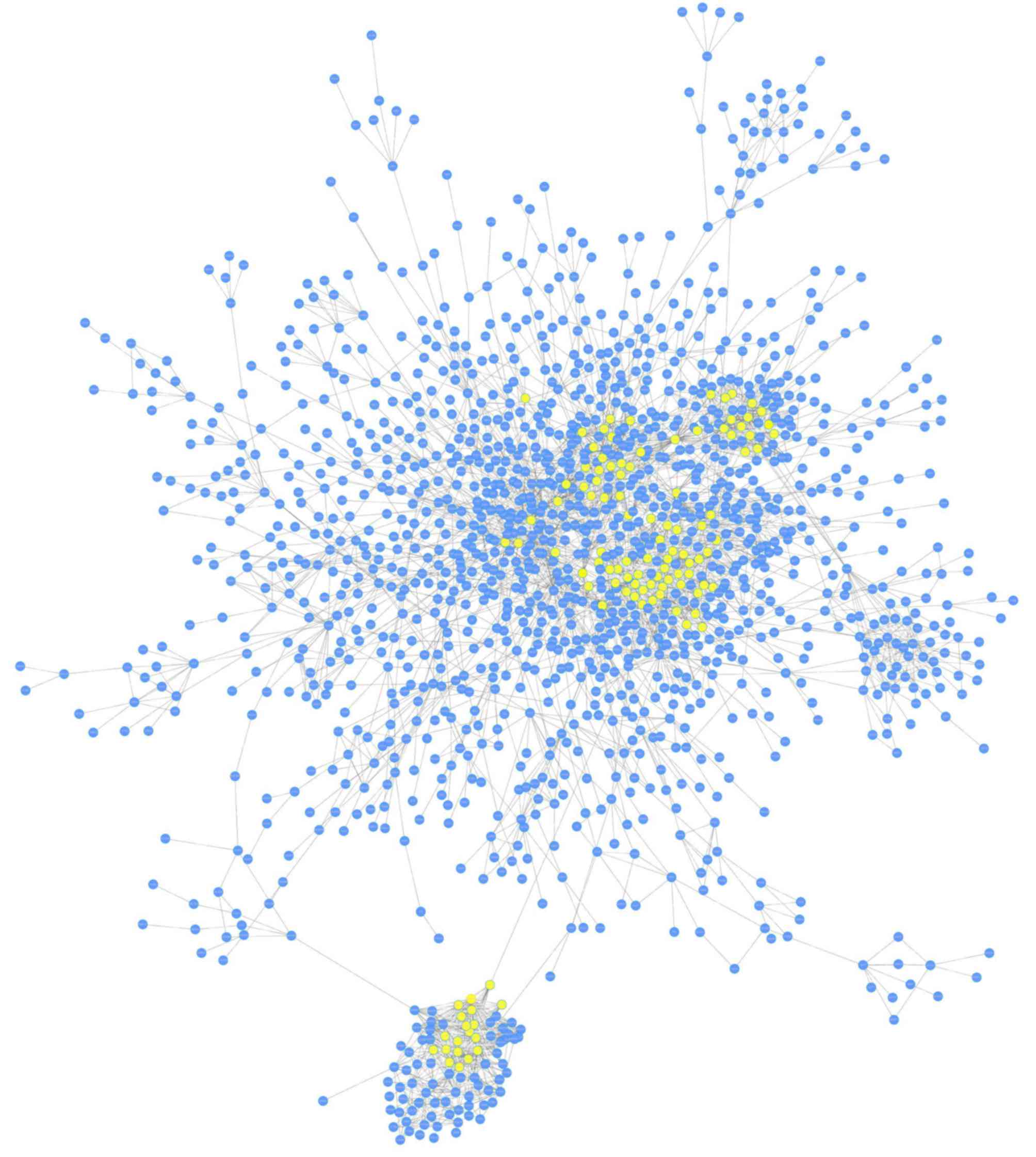
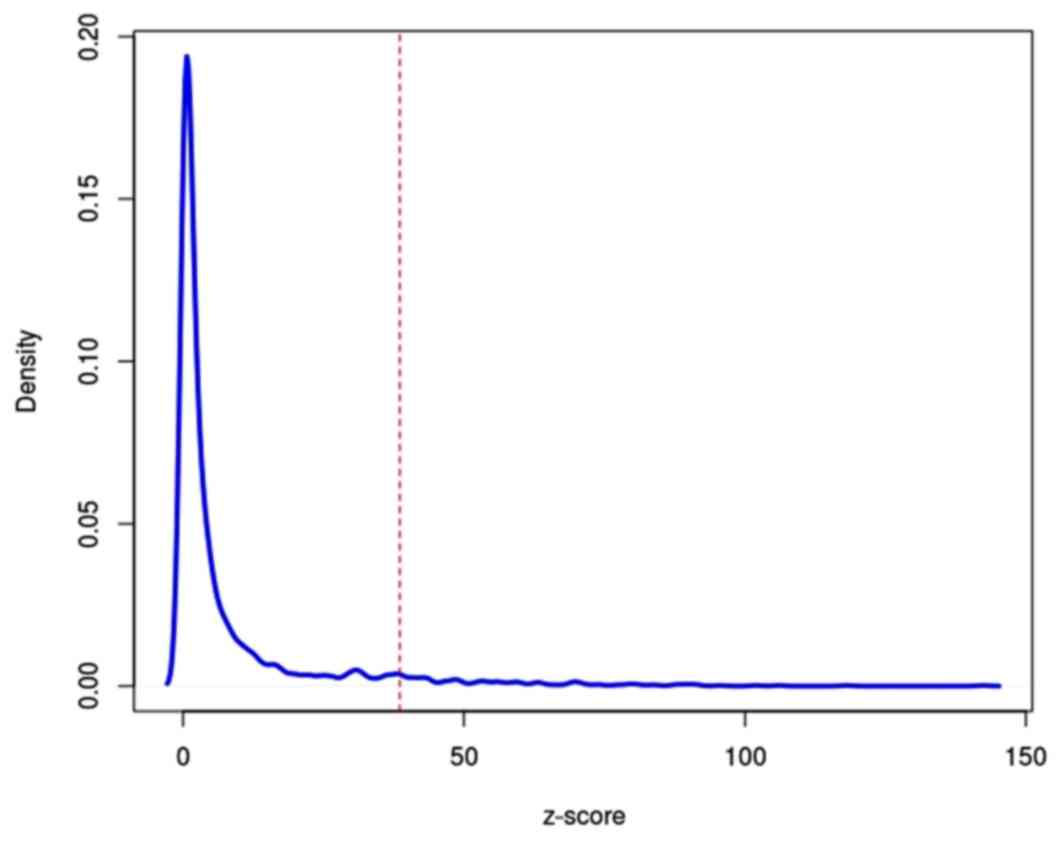
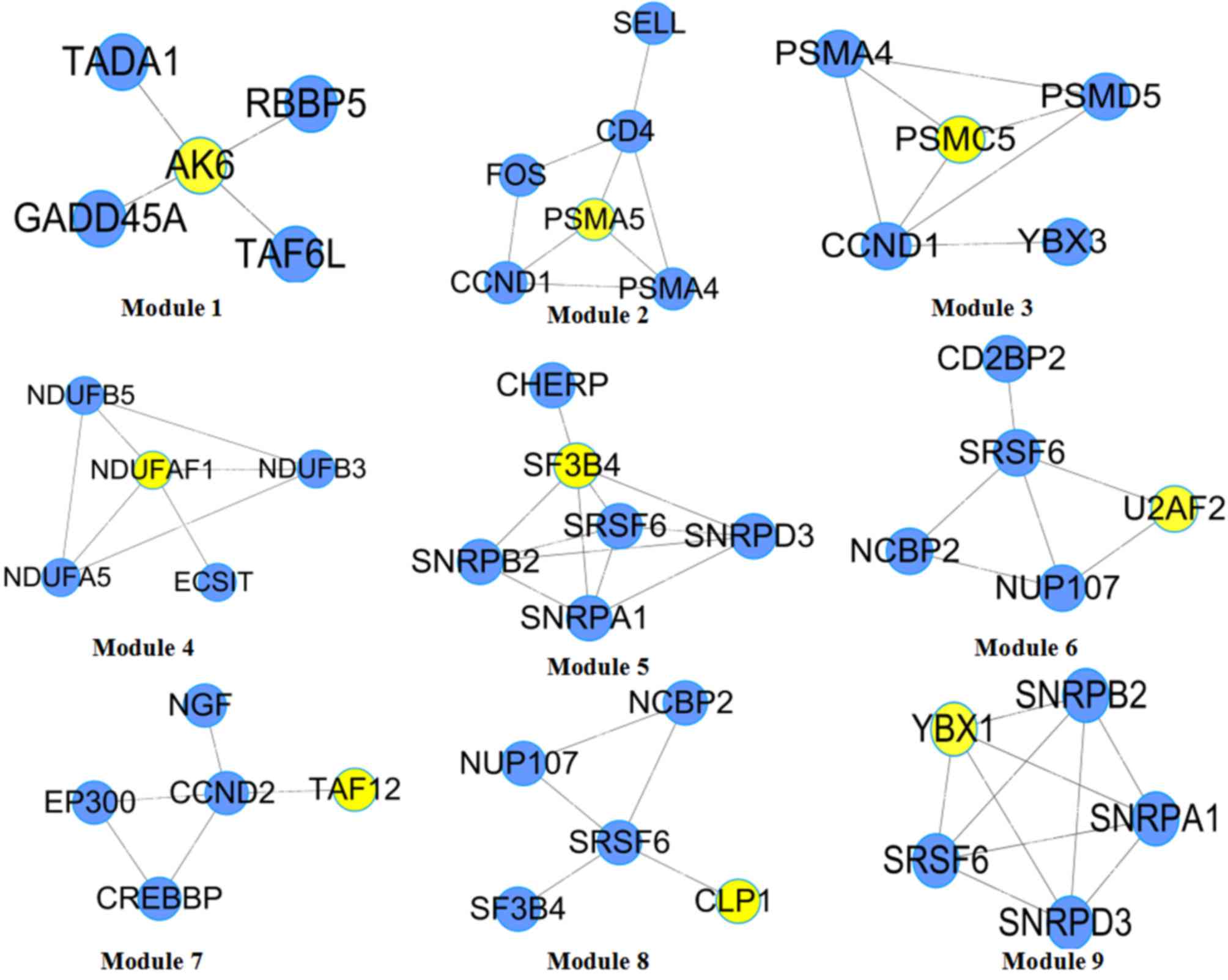
|
1
|
Cosman F, de Beur SJ, LeBoff MS, Lewiecki
EM, Tanner B, Randall S and Lindsay R; National Osteoporosis
Foundation, : Clinician's guide to prevention and treatment of
osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 25:2359–2381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Black DM and Rosen CJ: Postmenopausal
osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 374:2096–2097. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kanis J, McCloskey E, Johansson H, Cooper
C, Rizzoli R and Reginster J-Y: European guidance for the diagnosis
and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos
Int. 24:23–57. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haaland DA, Cohen DR, Kennedy CC, Khalidi
NA, Adachi JD and Papaioannou A: Closing the osteoporosis care
gap-increased osteoporosis awareness among geriatrics and
rehabilitation teams. BMC Geriatrics. 9:282009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cho DY, Kim YA and Przytycka TM: Chapter
5: Network biology approach to complex diseases. PLoS Comput Biol.
8:e10028202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen L, Xuan J, Riggins RB, Wang Y and
Clarke R: Identifying protein interaction subnetworks by a bagging
Markov random field-based method. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:e42. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nie Y and Yu J: Mining breast cancer genes
with a network based noise-tolerant approach. BMC Syst Biol.
7:492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dutkowski J and Ideker T: Protein networks
as logic functions in development and cancer. PLoS Comput Biol.
7:e10021802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu Y, Shen X and Pan W: Network-based
support vector machine for classification of microarray samples.
BMC Bioinformatics. 10:S212009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang R, Bai Y, Qin Z and Yu T: EgoNet:
Identification of human disease ego-network modules. BMC Genomics.
15:3142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ayati M, Erten S, Chance MR and Koyutürk
M: MOBAS: Identification of disease-associated protein subnetworks
using modularity-based scoring. EURASIP J Bioinform Syst Biol.
2015:72015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jordán F, Nguyen T-P and Liu W-c: Studying
protein-protein interaction networks: A systems view on diseases.
Brief Funct Genomics. 11:497–504. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xie LH, Zhao YP, Chen K and Lai YL:
Bioinformatics analysis of genes expression profiles of
postmenopausal osteoporosis with Kidney Yin deficiency. J Clin
Rehab Tissue Engi Res. 15:2833–2837. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Ma L, Robinson LN and Towle HC: ChREBP•
Mlx is the principal mediator of glucose-induced gene expression in
the liver. J Biol Chem. 281:28721–28730. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rifai N and Ridker PM: Proposed
cardiovascular risk assessment algorithm using high-sensitivity
C-reactive protein and lipid screening. Clin Chem. 47:28–30.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pepper SD, Saunders EK, Edwards LE, Wilson
CL and Miller CJ: The utility of MAS5 expression summary and
detection call algorithms. BMC Bioinformatics. 8:2732007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Benesty J, Chen J, Huang Y and Cohen I:
Pearson correlation coefficientNoise reduction in speech
processing. Springer; New York, NY: pp. 1–4. 2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
EdgeR: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J Royal Stat Soc. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
20
|
Goodman LA: Snowball sampling. Ann Math
Statist. 32:148–170. 1961. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ahn T, Lee E, Huh N and Park T:
Personalized identification of altered pathways in cancer using
accumulated normal tissue data. Bioinformatics. 30:i422–i429. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ralston SH: Genetic control of
susceptibility to osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
87:2460–2466. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kumar S, Mahendra G, Nagy TR and
Ponnazhagan S: Osteogenic differentiation of recombinant
adeno-associated virus 2-transduced murine mesenchymal stem cells
and development of an immunocompetent mouse model for ex vivo
osteoporosis gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 15:1197–1206. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kotrych D, Dziedziejko V, Safranow K,
Sroczynski T, Staniszewska M, Juzyszyn Z and Pawlik A: TNF-alpha
and IL10 gene polymorphisms in women with postmenopausal
osteoporosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 199:92–95. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rivadeneira F, van Meurs JB, Kant J,
Zillikens MC, Stolk L, Beck TJ, Arp P, Schuit SC, Hofman A,
Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, et al: Estrogen receptor beta (ESR2)
polymorphisms in interaction with estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1)
and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1) variants influence the risk
of fracture in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res.
21:1443–1456. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alami S, Hervouet L, Poiraudeau S, Briot K
and Roux C: Barriers to effective postmenopausal osteoporosis
treatment: A qualitative study of patients' and practitioners'
views. PLoS One. 11:e01583652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Stratford JK, Bentrem DJ, Anderson JM, Fan
C, Volmar KA, Marron JS, Routh ED, Caskey LS, Samuel JC, Der CJ, et
al: A six-gene signature predicts survival of patients with
localized pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. PLoS Med.
7:e10003072010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boutros PC, Lau SK, Pintilie M, Liu N,
Shepherd FA, Der SD, Tsao MS, Penn LZ and Jurisica I: Prognostic
gene signatures for non-small-cell lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci.
106:pp. 2824–2828. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Furumichi M, Tanabe M
and Hirakawa M: KEGG for representation and analysis of molecular
networks involving diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:D355–D360. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Venet D, Dumont JE and Detours V: Most
random gene expression signatures are significantly associated with
breast cancer outcome. PLoS Comput Biol. 7:e10022402011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Barabási A-L, Gulbahce N and Loscalzo J:
Network medicine: A network-based approach to human disease. Nat
RevGenet. 12:56–68. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang YX, Sun HL, Liang H, Li K, Fan QM
and Zhao QH: Dynamic and distinct histone modifications of
osteogenic genes during osteogenic differentiation. J Biochem.
158:445–457. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Deng P, Chen QM, Hong C and Wang CY:
Histone methyltransferases and demethylases: Regulators in
balancing osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal
stem cells. Int J Oral Sci. 7:197–204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang P, Liu Y, Jin C, Zhang M, Lv L,
Zhang X, Liu H and Zhou Y: Histone H3K9 acetyltransferase PCAF is
essential for osteogenic differentiation through bone morphogenetic
protein signaling and may be involved in osteoporosis. Stem Cells.
34:2332–2341. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang P, Liu Y, Jin C, Zhang M, Tang F and
Zhou Y: Histone acetyltransferase GCN5 regulates osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting NF-κB. J
Bone Miner Res. 31:391–402. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schroeder TM and Westendorf JJ: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors promote osteoblast maturation. J Bone Miner
Res. 20:2254–2263. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dudakovic A, Evans JM, Li Y, Middha S,
McGee-Lawrence ME, van Wijnen AJ and Westendorf JJ: Histone
deacetylase inhibition promotes osteoblast maturation by altering
the histone H4 epigenome and reduces Akt phosphorylation. J Biol
Chem. 288:28783–28791. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Alao JP, Stavropoulou AV, Lam EW, Coombes
RC and Vigushin DM: Histone deacetylase inhibitor, trichostatin A
induces ubiquitin-dependent cyclin D1 degradation in MCF-7 breast
cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 5:82006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Alao JP, Lam EW, Ali S, Buluwela L,
Bordogna W, Lockey P, Varshochi R, Stavropoulou AV, Coombes RC and
Vigushin DM: Histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A represses
estrogen receptor alpha-dependent transcription and promotes
proteasomal degradation of cyclin D1 in human breast carcinoma cell
lines. Clin Cancer Res. 10:8094–8104. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fujita M, Urano T, Horie K, Ikeda K,
Tsukui T, Fukuoka H, Tsutsumi O, Ouchi Y and Inoue S: Estrogen
activates cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 through induction of
cyclin D in rat primary osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
299:222–228. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tian J, Xu XJ, Shen L, Yang YP, Zhu R,
Shuai B, Zhu XW, Li CG, Ma C and Lv L: Association of serum Dkk-1
levels with β-catenin in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis.
J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci. 35:212–218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Urano T and Inoue S: Recent genetic
discoveries in osteoporosis, sarcopenia and obesity. Endocr J.
62:475–484. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wolski H, Drweska-Matelska N,
Seremak-Mrozikiewicz A, Lowicki Z and Czerny B: The role of
Wnt/β-catenin pathway and LRP5 protein in metabolism of bone tissue
and osteoporosis etiology. Ginekol Pol. 86:311–314. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ma C, Shuai B, Shen L, Yang YP, Xu XJ and
Li CG: Serum carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion
molecule 1 level in postmenopausal women: Correlation with
β-catenin and bone mineral density. Osteoporos Int. 27:1529–1535.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|