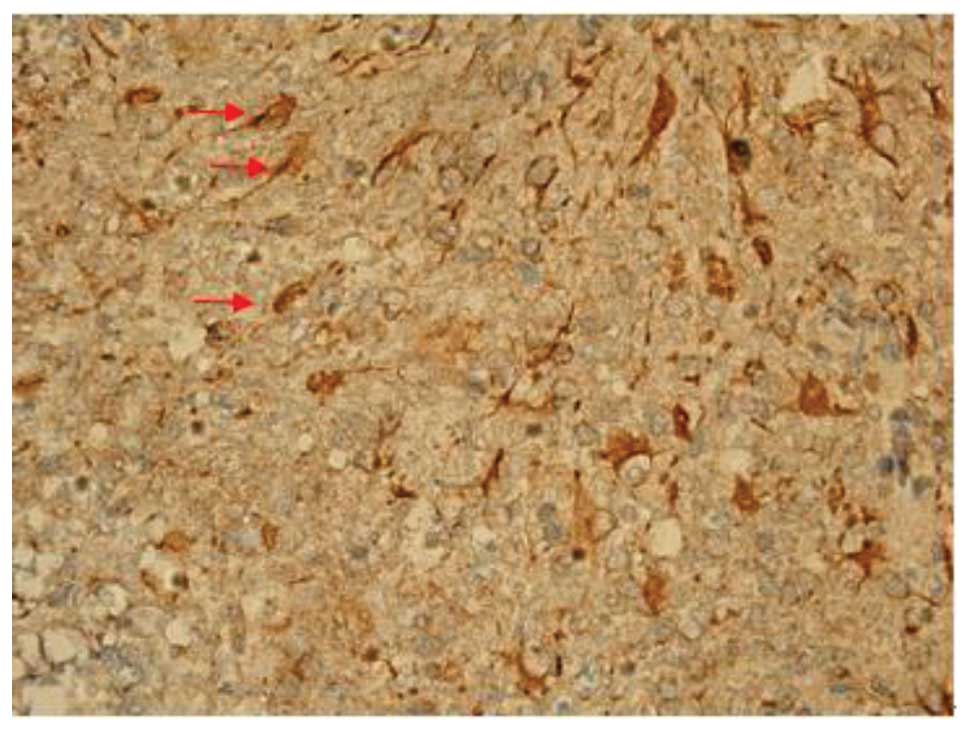
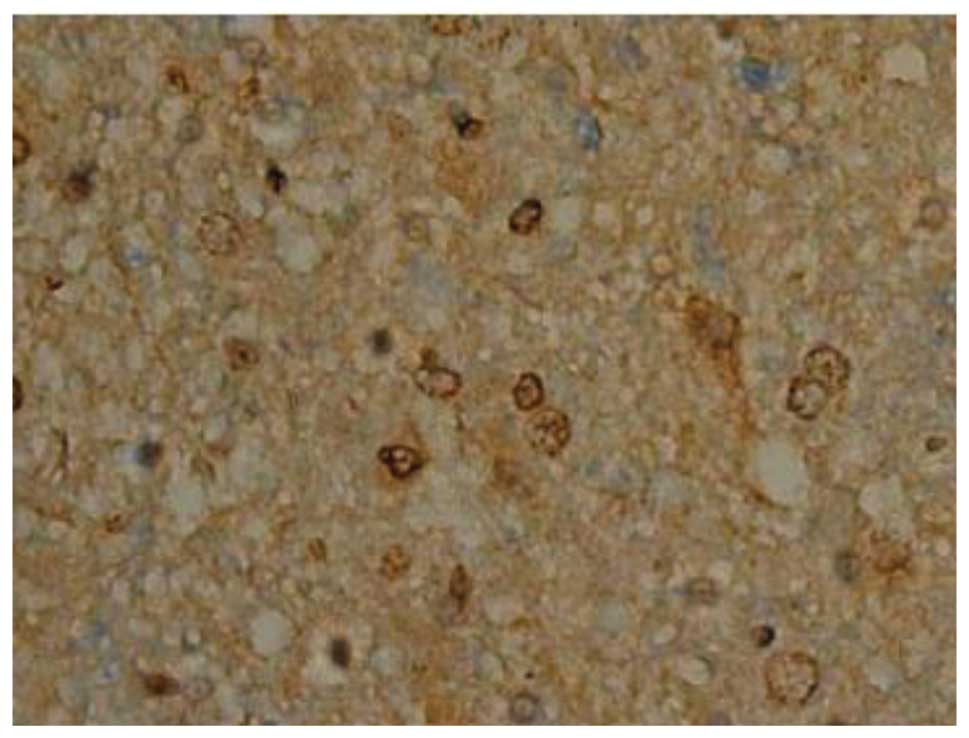
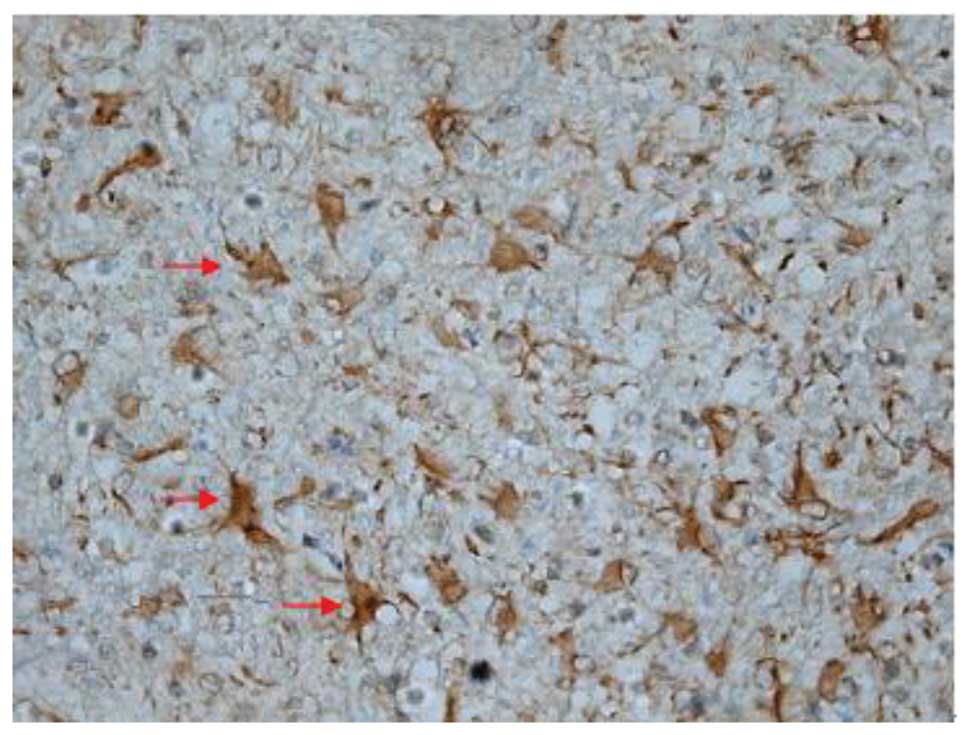
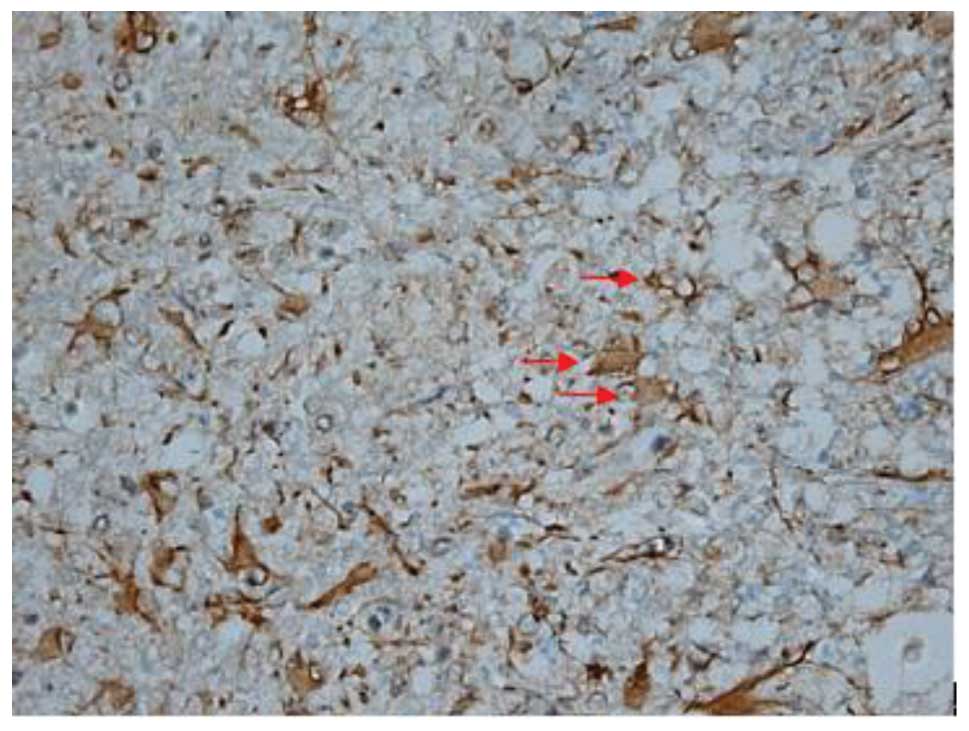
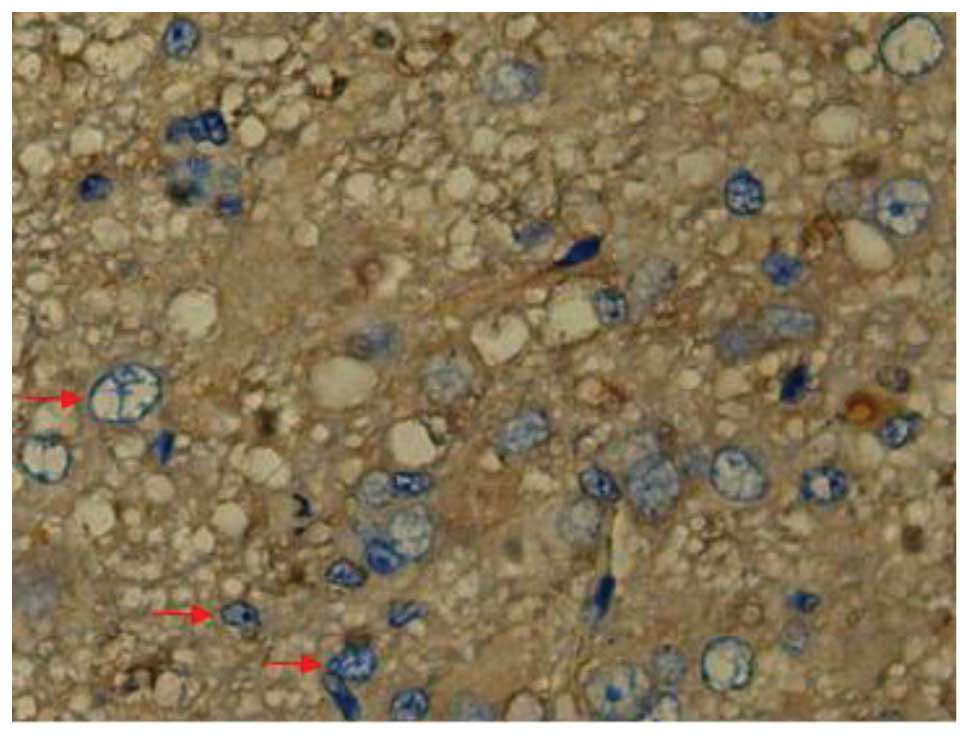
|
1
|
Cao HQ and Dong ED: An update on spinal
cord injury research. Neurosci Bull. 29:94–102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McEwen ML, Sullivan PG, Rabchevsky AG and
Springer JE: Targeting mitochondrial function for the treatment of
acute spinal cord injury. Neurotherapeutics. 8:168–179. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Inman DM and Steward O: Physical size does
not determine the unique histopathological response seen in the
injured mouse spinal cord. J Neurotrauma. 20:33–42. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mautes AE, Weinzierl MR, Donovan F and
Noble LJ: Vascular events after spinal cord injury: Contribution to
secondary pathogenesis. Phys Ther. 80:673–687. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kwon BK, Tetzlaff W, Grauer JN, Beiner J
and Vaccaro AR: Pathophysiology and pharmacologic treatment of
acute spinal cord injury. Spine J. 4:451–464. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Byrnes KR, Stoica BA, Fricke S, Di
Giovanni S and Faden AI: Cell cycle activation contributes to
post-mitotic cell death and secondary damage after spinal cord
injury. Brain. 130:2977–2992. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mattson MP: Apoptosis in neurodegenerative
disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 1:120–129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mizuno Y, Mochizuki H, Sugita Y and Goto
K: Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Intern Med.
37:192–193. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lewis KM, Turner RJ and Vink R: Blocking
neurogenic inflammation for the treatment of acute disorders of the
central nervous system. Int J Inflamm. 2013:5784802013.
|
|
10
|
Sondell M, Lundborg G and Kanje M:
Vascular endothelial growth factor has neurotrophic activity and
stimulates axonal outgrowth, enhancing cell survival and Schwann
cell proliferation in the peripheral nervous system. J Neurosci.
19:5731–5740. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schoch HJ, Fischer S and Marti HH:
Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression
causes vascular leakage in the brain. Brain. 125:2549–2557. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pereira Lopes FR, Lisboa BC, Frattini F,
et al: Enhancement of sciatic nerve regeneration after vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene therapy. Neuropathol Appl
Neurobiol. 37:600–612. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jin K, Zhu Y, Sun Y, Mao XO, Xie L and
Greenberg DA: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) stimulates
neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:11946–11950. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Herrera JJ, Nesic O and Narayana PA:
Reduced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in contusive
spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 26:995–1003. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sakowski SA, Heavener SB, Lunn JS, Fung K,
Oh SS, Spratt SK, Hogikyan ND and Feldman EL: Neuroprotection using
gene therapy to induce vascular endothelial growth factor-A
expression. Gene Ther. 16:1292–1299. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma Y, Liu W, Wang Y, Chao X, Qu Y, Wang K
and Fei Z: VEGF protects rat cortical neurons from mechanical
trauma injury induced apoptosis via the MEK/ERK pathway. Brain Res
Bull. 86:441–446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Storkebaum E, Lambrechts D and Carmeliet
P: VEGF: Once regarded as a specific angiogenic factor, now
implicated in neuroprotection. BioEssays. 26:943–954. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
You WK, Choi WS, Koh YS, Shin HC, Jang Y
and Chung KH: Functional characterization of recombinant
batroxobin, a snake venom thrombin-like enzyme, expressed from
Pichia pastoris. FEBS Lett. 571:67–73. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bell WR Jr: Defibrinogenating enzymes.
Drugs. 54:(Suppl 3). 18–31. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gusev EI, Skvortsova VI, Suslina ZA,
Avakian GN, Martynov MIu, Temirbaeva SL, Tanashian MA, Kamchtnov
PR, Stakhovskaia LV and Efremova NM: Batroxobin in patients with
ischemic stroke in the carotid system (the multicenter study). Zh
Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 106:31–34. 2006.[(In Russian)].
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shiraishi T, Kubo T and Matsunaga T:
Chronological study of recovery of sudden deafness treated with
defibrinogenation and steroid therapies. Acta Otolaryngol.
111:867–871. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Black P, Markowitz RS, Damjanov I,
Finkelstein SD, Kushner H, Gillespie J and Feldman M: Models of
spinal cord injury: Part 3. Dynamic load technique. Neurosurgery.
22:51–60. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC:
Graded histological and locomotor outcomes after spinal cord
contusion using the NYU weight-drop device versus transection. Exp
Neurol. 139:244–256. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goldsmith HS: The evolution of omentum
transposition: From lymphedema to spinal cord, stroke and
Alzheimer's disease. Neurol Res. 26:586–593. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yiu G and He Z: Glial inhibition of CNS
axon regeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 7:617–627. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Gu J, Feng X, Wang H, Tao Y and
Wang J: Effects of Nogo-A receptor antagonist on the regulation of
the Wnt signaling pathway and neural cell proliferation in newborn
rats with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Mol Med Rep. 8:883–886.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Beattie MS, Hermann GE, Rogers RC and
Bresnahan JC: Cell death in models of spinal cord injury. Prog
Brain Res. 137:37–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Gu J, Wang J, et al: BDNF and NT-3
expression by using glucocorticoid-induced bicistronic expression
vector pGC-BDNF-IRES-NT3 protects apoptotic cells in a cellular
injury model. Brain Res. 1448:137–143. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jia LY, Yao AH, Kuang F, Zhang YK, Shen XF
and Ju G: Beneficial effect of the traditional chinese drug
shu-xue-tong on recovery of spinal cord injury in the rat. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011:8621972011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ennett AB, Kaigler D and Mooney DJ:
Temporally regulated delivery of VEGF in vitro and in vivo. J
Biomed Mater Res A. 79:176–184. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peters MC, Polverini PJ and Mooney DJ:
Engineering vascular networks in porous polymer matrices. J Biomed
Mater Res. 60:668–678. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO,
Logvinova A and Greenberg DA: VEGF-induced neuroprotection,
neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J
Clin Invest. 111:1843–1851. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sondell M, Sundler F and Kanje M: Vascular
endothelial growth factor is a neurotrophic factor which stimulates
axonal outgrowth through the flk-1 receptor. Eur J Neurosci.
12:4243–4254. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Silverman WF, Krum JM, Mani N and
Rosenstein JM: Vascular, glial and neuronal effects of vascular
endothelial growth factor in mesencephalic explant cultures.
Neuroscience. 90:1529–1541. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Facchiano F, Fernandez E, Mancarella S,
Maira G, Miscusi M, D'Arcangelo D, Cimino-Reale G, Falchetti ML,
Capogrossi MC and Pallini R: Promotion of regeneration of
corticospinal tract axons in rats with recombinant vascular
endothelial growth factor alone and combined with adenovirus coding
for this factor. J Neurosurg. 97:161–168. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Widenfalk J, Lipson A, Jubran M,
Hofstetter C, Ebendal T, Cao Y and Olson L: Vascular endothelial
growth factor improves functional outcome and decreases secondary
degeneration in experimental spinal cord contusion injury.
Neuroscience. 120:951–960. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Narayana PA, Grill RJ, Chacko T and Vang
R: Endogenous recovery of injured spinal cord: Longitudinal in vivo
magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosci Res. 78:749–759. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Maikos JT and Shreiber DI: Immediate
damage to the blood-spinal cord barrier due to mechanical trauma. J
Neurotrauma. 24:492–507. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Patel CB, Cohen DM, Ahobila-Vajjula P,
Sundberg LM, Chacko T and Narayana PA: Effect of VEGF treatment on
the blood-spinal cord barrier permeability in experimental spinal
cord injury: Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.
J Neurotrauma. 26:1005–1016. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sundberg LM, Herrera JJ and Narayana PA:
In vivo longitudinal MRI and behavioral studies in experimental
spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 27:1753–1767. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Adams RA, Passino M, Sachs BD, Nuriel T
and Akassoglou K: Fibrin mechanisms and functions in nervous system
pathology. Mol Interv. 4:163–176. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|