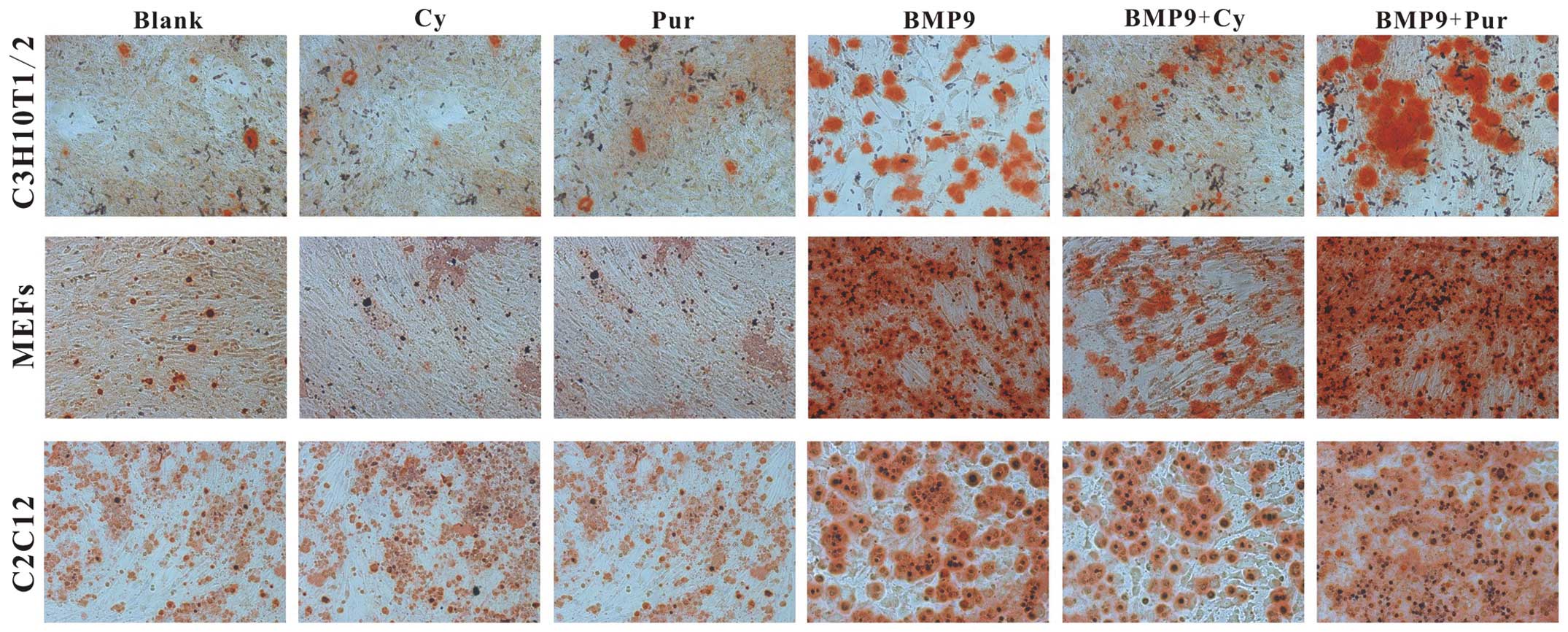
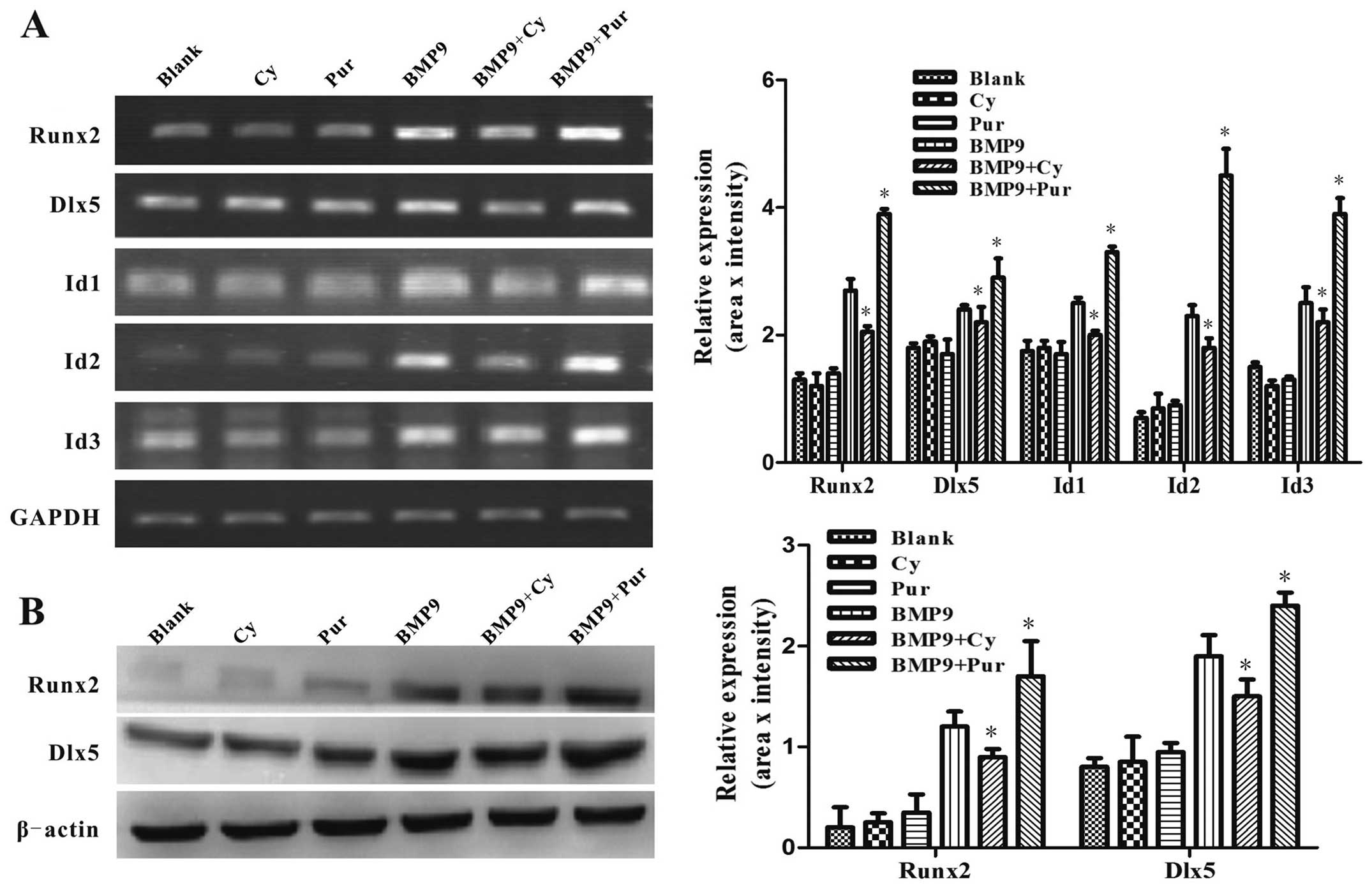
|
1
|
Caplan AI and Bruder SP: Mesenchymal stem
cells: Building blocks for molecular medicine in the 21st century.
Trends Mol Med. 7:259–264. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Prockop DJ: Marrow stromal cells as stem
cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 276:71–74. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Prockop DJ: Marrow stromal cells as stem
cells for continual renewal of nonhematopoietic tissues and as
potential vectors for gene therapy. J Cell Biochem Suppl.
30–31:284–285. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Deng ZL, Sharff KA, Tang N, Song WX, Luo
J, Luo X, Chen J, Bennett E, Reid R, Manning D, et al: Regulation
of osteogenic differentiation during skeletal development. Front
Biosci. 13:2001–2021. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shi Y and Massagué J: Mechanisms of TGF-β
signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell. 113:685–700.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Luu HH, Song WX, Luo X, Manning D, Luo J,
Deng ZL, Sharff KA, Montag AG, Haydon RC and He TC: Distinct roles
of bone morphogenetic proteins in osteogenic differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 25:665–677. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Varga AC and Wrana JL: The disparate role
of BMP in stem cell biology. Oncogene. 24:5713–5721. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hogan BL: Bone morphogenetic proteins:
Multifunctional regulators of vertebrate development. Genes Dev.
10:1580–1594. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang RN, Green J, Wang Z, Deng Y, Qiao M,
Peabody M, Zhang Q, Ye J, Yan Z, Denduluri S, et al: Bone
Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling in development and human
diseases. Genes Dis. 1:87–105. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Boraiah S, Paul O, Hawkes D, Wickham M and
Lorich DG: Complications of recombinant human BMP-2 for treating
complex tibial plateau fractures: A preliminary report. Clin Orthop
Relat Res. 467:3257–3262. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rutherford RB, Nussenbaum B and Krebsbach
PH: Bone morphogenetic protein 7 ex vivo gene therapy. Drug News
Perspect. 16:5–10. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Varady P, Li JZ, Alden TD, Kallmes DF,
Williams MB and Helm GA: CT and radionuclide study of BMP-2 gene
therapy-induced bone formation. Acad Radiol. 9:632–637. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kang Q, Sun MH, Cheng H, Peng Y, Montag
AG, Deyrup AT, Jiang W, Luu HH, Luo J, Szatkowski JP, et al:
Characterization of the distinct orthotopic bone-forming activity
of 14 BMPs using recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene delivery.
Gene Ther. 11:1312–1320. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen L, Jiang W, Huang J, He BC, Zuo GW,
Zhang W, Luo Q, Shi Q, Zhang BQ, Wagner ER, et al: Insulin-like
growth factor-2 (IGF-2) potentiates BMP-9-induced osteogenic
differentiation and bone formation. J Bone Miner Res. 25:2447–2459.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song T, Wang W, Xu J, Zhao D, Dong Q, Li
L, Yang X, Duan X, Liang Y, Xiao Y, et al: Fibroblast growth factor
2 inhibits bone morphogenetic protein 9-induced osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by repressing Smads
signaling and subsequently reducing Smads dependent up-regulation
of ALK1 and ALK2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:1639–1646. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao Y, Song T, Wang W, Wang J, He J, Wu
N, Tang M, He B and Luo J: P38 and ERK1/2 MAPKs act in opposition
to regulate BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal
progenitor cells. PLoS One. 7:e433832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu X, Qin J, Luo Q, Bi Y, Zhu G, Jiang W,
Kim SH, Li M, Su Y, Nan G, et al: Cross-talk between EGF and BMP9
signalling pathways regulates the osteogenic differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 17:1160–1172.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao YF, Xu J, Wang WJ, Wang J, He JW, Li
L, Dong Q, Xiao Y, Duan XL, Yang X, et al: Activation of JNKs is
essential for BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. BMB Rep. 46:422–427. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fietz MJ, Concordet J-P, Barbosa R,
Johnson R, Krauss S, McMahon AP, Tabin C and Ingham PW: The
hedgehog gene family in Drosophila and vertebrate development. Dev
Suppl. 1994:43–51. 1994.
|
|
20
|
Oldak M, Grzela T, Lazarczyk M, Malejczyk
J and Skopinski P: Clinical aspects of disrupted Hedgehog signaling
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 8:445–452. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Varjosalo M and Taipale J: Hedgehog:
Functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev. 22:2454–2472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mundy GR and Yang X: Hedgehog coordination
of postnatal osteoclast and osteoblast activities. Dev Cell.
14:637–638. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu X, Walker J, Zhang J, Ding S and
Schultz PG: Purmorphamine induces osteogenesis by activation of the
hedgehog signaling pathway. Chem Biol. 11:1229–1238. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mak KK, Bi Y, Wan C, Chuang PT, Clemens T,
Young M and Yang Y: Hedgehog signaling in mature osteoblasts
regulates bone formation and resorption by controlling PTHrP and
RANKL expression. Dev Cell. 14:674–688. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ohba S, Kawaguchi H, Kugimiya F, Ogasawara
T, Kawamura N, Saito T, Ikeda T, Fujii K, Miyajima T, Kuramochi A,
et al: Patched1 haploinsufficiency increases adult bone mass and
modulates Gli3 repressor activity. Dev Cell. 14:689–699. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yuasa T, Kataoka H, Kinto N, Iwamoto M,
Enomoto-Iwamoto M, Iemura S, Ueno N, Shibata Y, Kurosawa H and
Yamaguchi A: Sonic hedgehog is involved in osteoblast
differentiation by cooperating with BMP-2. J Cell Physiol.
193:225–232. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhao X, Yu X, Hu Y,
Geronimo B, Fromm SH and Chen YP: A new function of BMP4: Dual role
for BMP4 in regulation of Sonic hedgehog expression in the mouse
tooth germ. Development. 127:1431–1443. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu N, Zhao Y, Yin Y, Zhang Y and Luo J:
Identification and analysis of type II TGF-β receptors in
BMP-9-induced osteogenic differentiation of C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal
stem cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 42:699–708. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Luo J, Tang M, Huang J, He BC, Gao JL,
Chen L, Zuo GW, Zhang W, Luo Q, Shi Q, et al: TGFbeta/BMP type I
receptors ALK1 and ALK2 are essential for BMP9-induced osteogenic
signaling in mesenchymal stem cells. J Biol Chem. 285:29588–29598.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW,
Nielsen CM, Roberts DJ, Lauwers GY, Qi YP, Gysin S, Fernández-del
Castillo C, Yajnik V, et al: Hedgehog is an early and late mediator
of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature. 425:851–856. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Warzecha J, Dinges D, Kaszap B, Henrich D,
Marzi I and Seebach C: Effect of the Hedgehog-inhibitor cyclopamine
on mice with osteosarcoma pulmonary metastases. Int J Mol Med.
29:423–427. 2012.
|
|
32
|
Sinha S and Chen JK: Purmorphamine
activates the Hedgehog pathway by targeting Smoothened. Nat Chem
Biol. 2:29–30. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lopez-Coviella I, Mellott TM, Kovacheva
VP, Berse B, Slack BE, Zemelko V, Schnitzler A and Blusztajn JK:
Developmental pattern of expression of BMP receptors and Smads and
activation of Smad1 and Smad5 by BMP9 in mouse basal forebrain.
Brain Res. 1088:49–56. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu C, Weng Y, Yuan T, Zhang H, Bai H, Li
B, Yang D, Zhang R, He F, Yan S, et al: CXCL12/CXCR4 signal axis
plays an important role in mediating bone morphogenetic protein
9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Int
J Med Sci. 10:1181–1192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kondo A, Otsuka T, Kuroyanagi G, Yamamoto
N, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Mizutani J, Kozawa O and Tokuda H:
Resveratrol inhibits BMP-4-stimulated VEGF synthesis in
osteoblasts: Suppression of S6 kinase. Int J Mol Med. 33:1013–1018.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liang W, Lin M, Li X, Li C, Gao B, Gan H,
Yang Z, Lin X, Liao L and Yang M: Icariin promotes bone formation
via the BMP-2/Smad4 signal transduction pathway in the hFOB 1.19
human osteoblastic cell line. Int J Mol Med. 30:889–895.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song JJ, Celeste AJ, Kong FM, Jirtle RL,
Rosen V and Thies RS: Bone morphogenetic protein-9 binds to liver
cells and stimulates proliferation. Endocrinology. 136:4293–4297.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
López-Coviella I, Berse B, Krauss R, Thies
RS and Blusztajn JK: Induction and maintenance of the neuronal
cholinergic phenotype in the central nervous system by BMP-9.
Science. 289:313–316. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen C, Grzegorzewski KJ, Barash S, Zhao
Q, Schneider H, Wang Q, Singh M, Pukac L, Bell AC, Duan R, et al:
An integrated functional genomics screening program reveals a role
for BMP-9 in glucose homeostasis. Nat Biotechnol. 21:294–301. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Spinella-Jaegle S, Rawadi G, Kawai S,
Gallea S, Faucheu C, Mollat P, Courtois B, Bergaud B, Ramez V,
Blanchet AM, et al: Sonic hedgehog increases the commitment of
pluripotent mesenchymal cells into the osteoblastic lineage and
abolishes adipocytic differentiation. J Cell Sci. 114:2085–2094.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Harris MP, Simandl
BK, Li Y, Beachy PA and Fallon JF: Manifestation of the limb
prepattern: Limb development in the absence of sonic hedgehog
function. Dev Biol. 236:421–435. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Levi B, James AW, Nelson ER, Brugmann SA,
Sorkin M, Manu A and Longaker MT: Role of Indian hedgehog signaling
in palatal osteogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 127:1182–1190. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Reichert JC, Schmalzl J, Prager P, Gilbert
F, Quent VM, Steinert AF, Rudert M and Nöth U: Synergistic effect
of Indian hedgehog and bone morphogenetic protein-2 gene transfer
to increase the osteogenic potential of human mesenchymal stem
cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 4:1052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jiang Q, Du J, Yin X, Shan Z, Ma Y, Ma P,
Du J and Fan Z: Shh signaling, negatively regulated by BMP
signaling, inhibits the osteo/dentinogenic differentiation
potentials of mesenchymal stem cells from apical papilla. Mol Cell
Biochem. 383:85–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shimoyama A, Wada M, Ikeda F, Hata K,
Matsubara T, Nifuji A, Noda M, Amano K, Yamaguchi A, Nishimura R
and Yoneda T: Ihh/Gli2 signaling promotes osteoblast
differentiation by regulating Runx2 expression and function. Mol
Biol Cell. 18:2411–2418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Oliveira FS, Bellesini LS, Defino HL, da
Silva Herrero CF, Beloti MM and Rosa AL: Hedgehog signaling and
osteoblast gene expression are regulated by purmorphamine in human
mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 113:204–208. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|