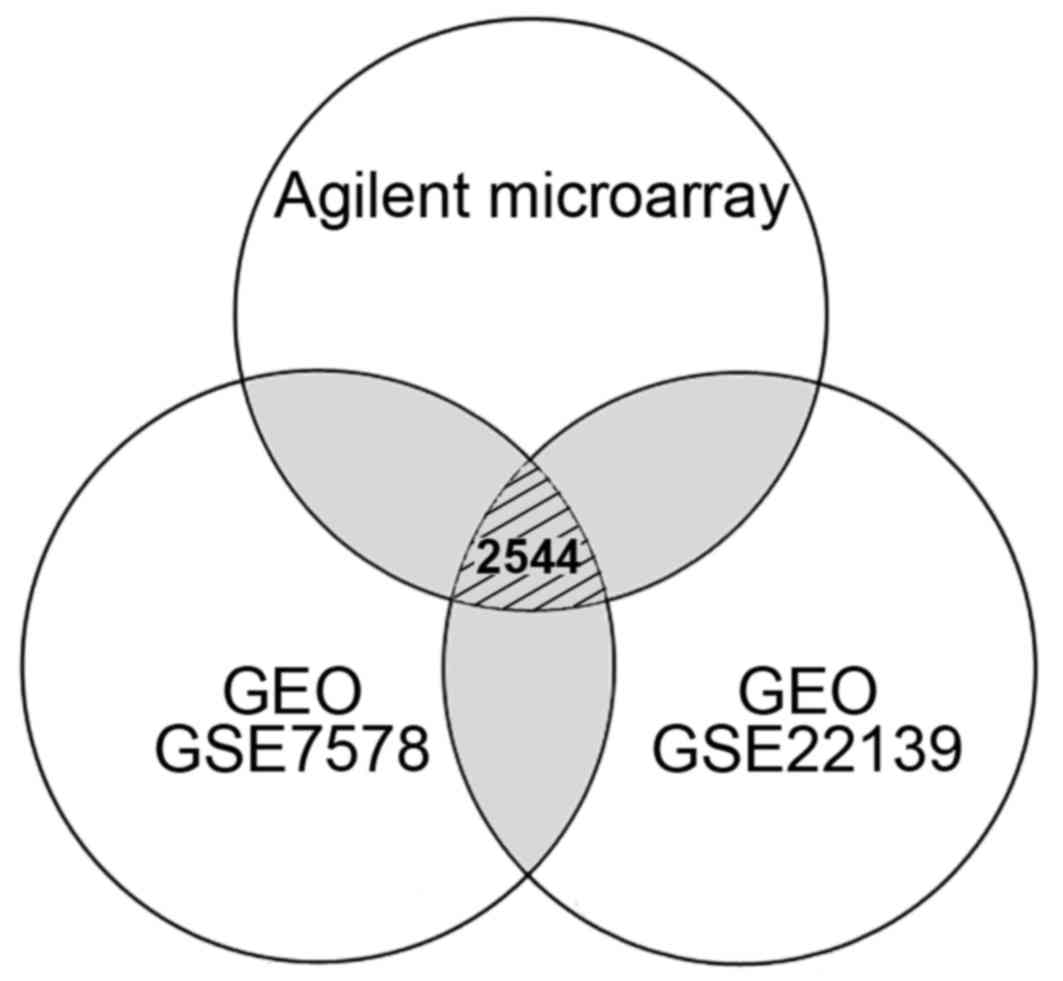
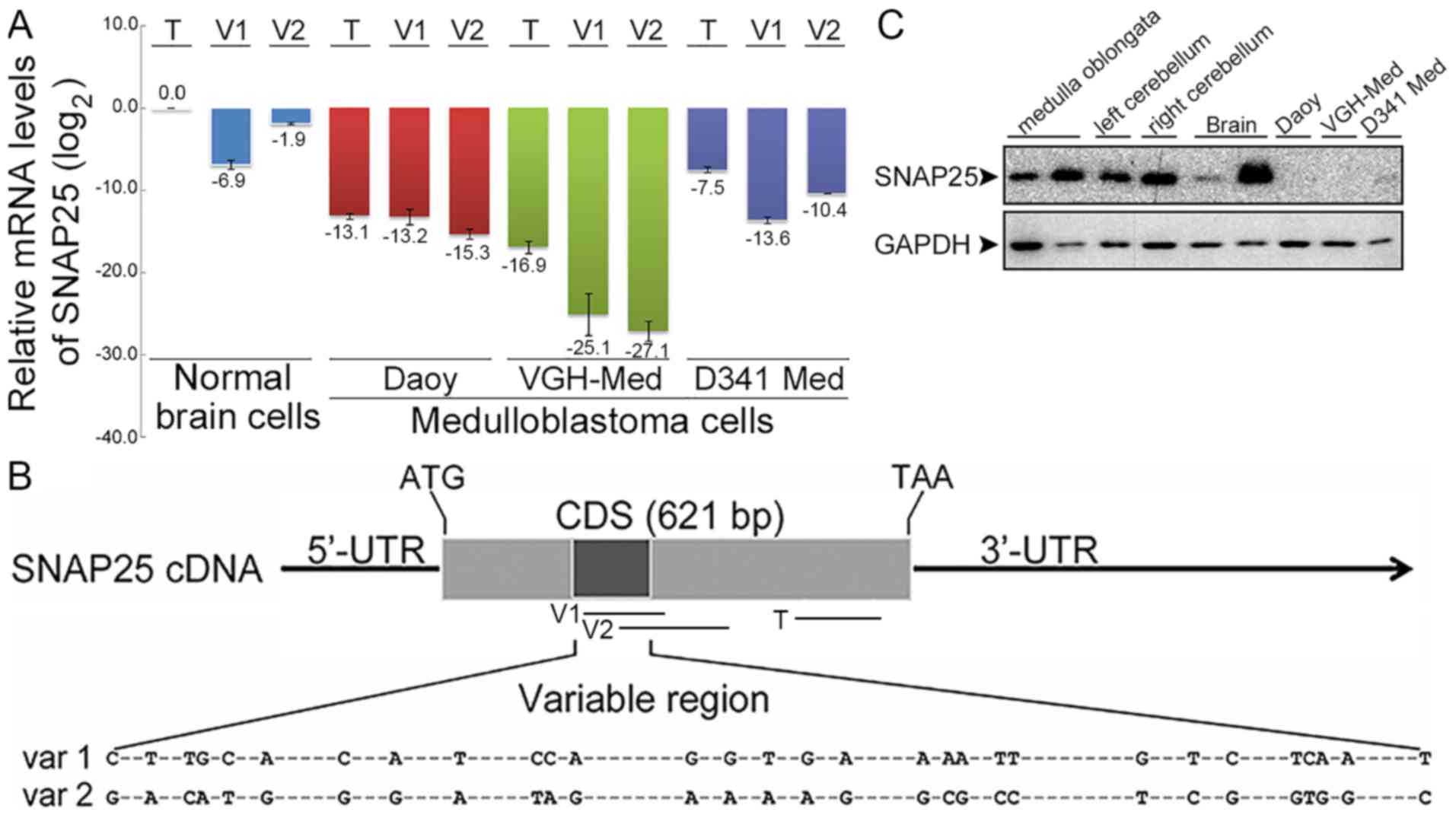
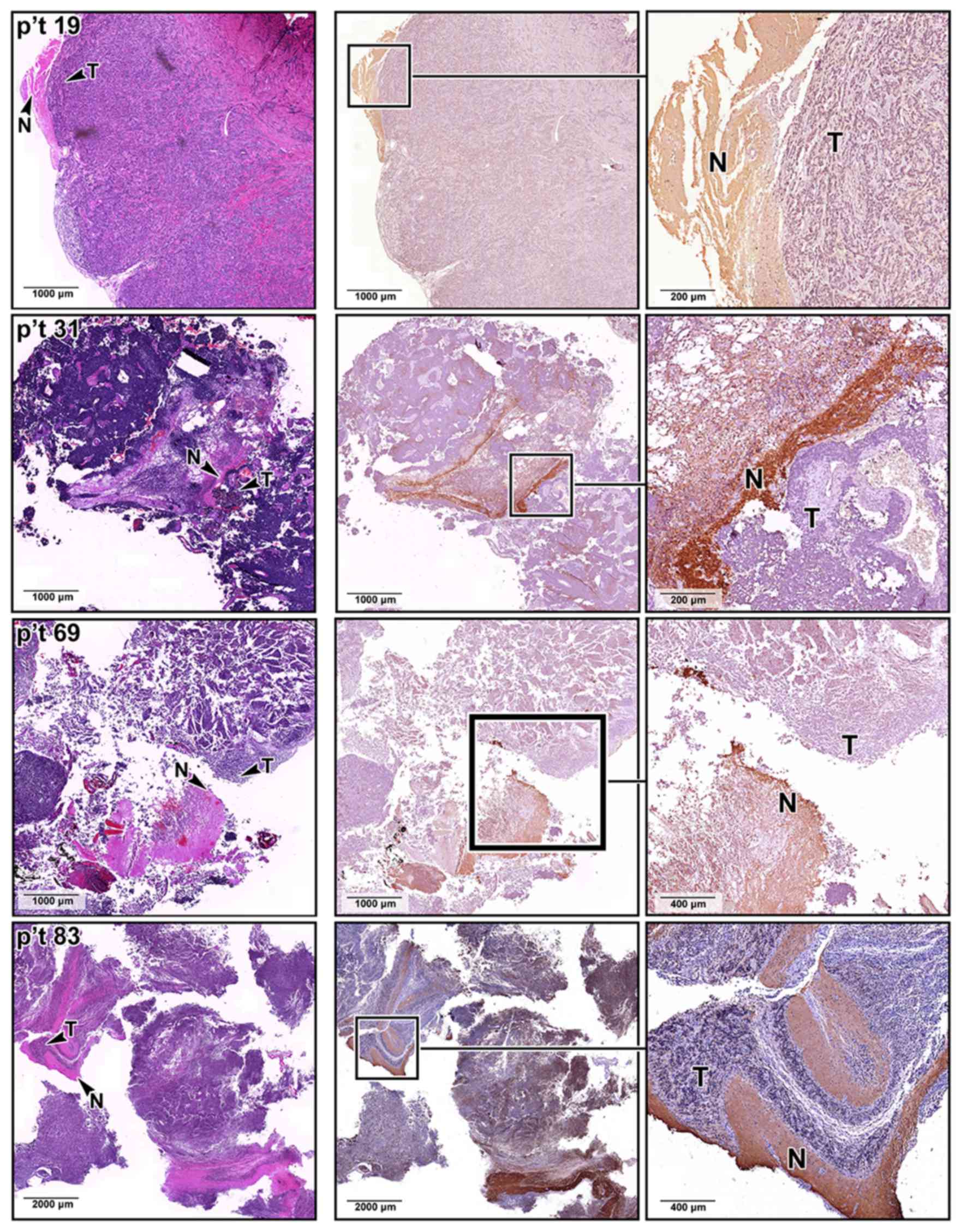
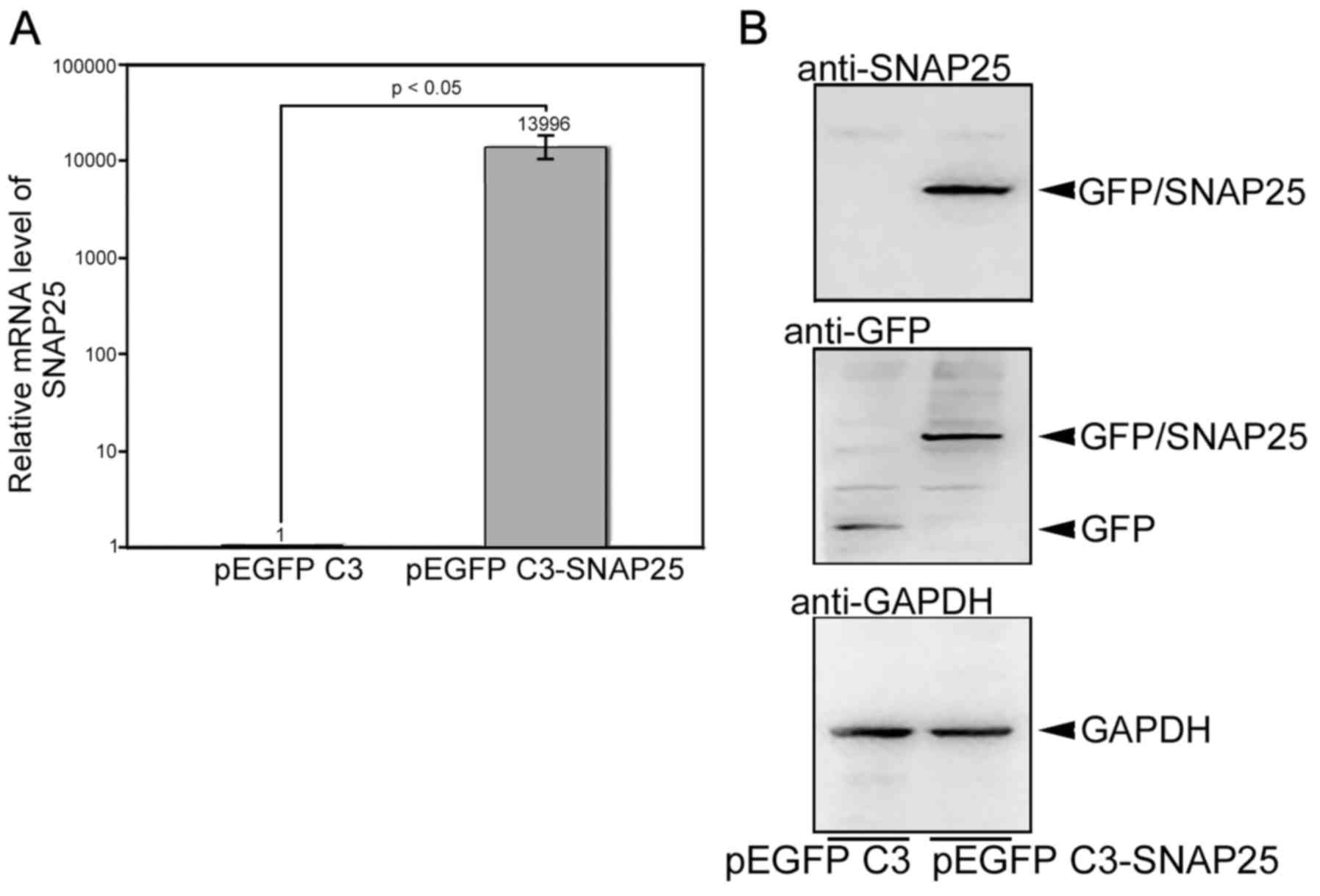
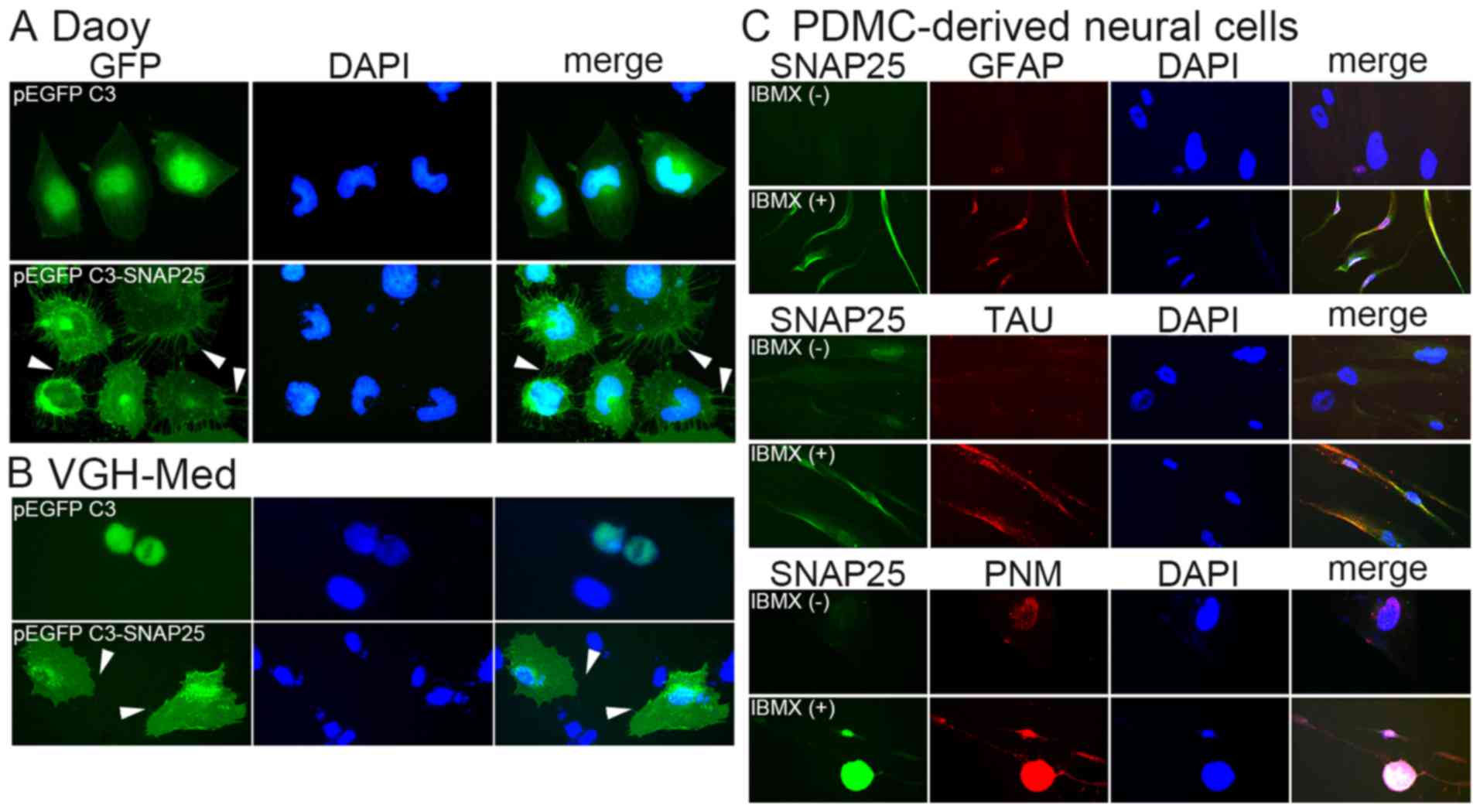
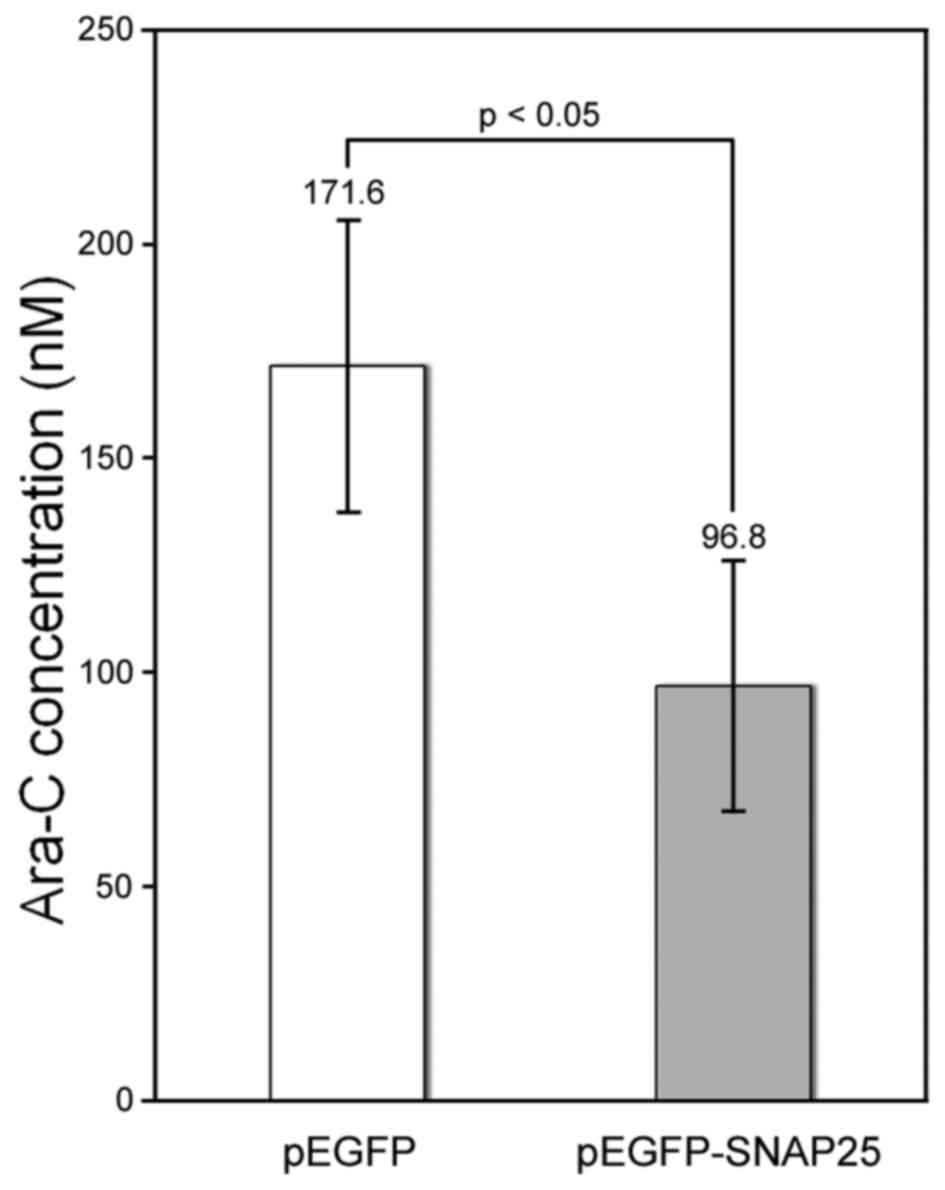
|
1
|
Shih DJ, Northcott PA, Remke M, Korshunov
A, Ramaswamy V, Kool M, Luu B, Yao Y, Wang X, Dubuc AM, et al:
Cytogenetic prognostication within medulloblastoma subgroups. J
Clin Oncol. 32:886–896. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Anne SL, Govek EE, Ayrault O, Kim JH, Zhu
X, Murphy DA, Van Aelst L, Roussel MF and Hatten ME: WNT3 inhibits
cerebellar granule neuron progenitor proliferation and
medulloblastoma formation via MAPK activation. PLoS One.
8:e817692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lastowska M, Al-Afghani H, Al-Balool HH,
Sheth H, Mercer E, Coxhead JM, Redfern CP, Peters H, Burt AD,
Santibanez-Koref M, et al: Identification of a neuronal
transcription factor network involved in medulloblastoma
development. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 1:352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rajurkar M, Huang H, Cotton JL, Brooks JK,
Sicklick J, McMahon AP and Mao J: Distinct cellular origin and
genetic requirement of Hedgehog-Gli in postnatal rhabdomyosarcoma
genesis. Oncogene. 33:5370–5378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Unland R, Kerl K, Schlosser S, Farwick N,
Plagemann T, Lechtape B, Clifford SC, Kreth JH, Gerss J, Mühlisch
J, et al: Epigenetic repression of the dopamine receptor D4 in
pediatric tumors of the central nervous system. J Neurooncol.
116:237–249. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
MacDonald TJ, Aguilera D and Castellino
RC: The rationale for targeted therapies in medulloblastoma. Neuro
Oncol. 16:9–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Robinson G, Parker M, Kranenburg TA, Lu C,
Chen X, Ding L, Phoenix TN, Hedlund E, Wei L, Zhu X, et al: Novel
mutations target distinct subgroups of medulloblastoma. Nature.
488:43–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gerber NU, Mynarek M, von Hoff K,
Friedrich C, Resch A and Rutkowski S: Recent developments and
current concepts in medulloblastoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:356–365.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jahn R and Fasshauer D: Molecular machines
governing exocytosis of synaptic vesicles. Nature. 490:201–207.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma HI, Kao CL, Lee YY, Chiou GY, Tai LK,
Lu KH, Huang CS, Chen YW, Chiou SH, Cheng IC, et al: Differential
expression profiling between atypical teratoid/rhab and
medulloblastoma tumor in vitro and in vivo using microarray
analysis. Childs Nerv Syst. 26:293–303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wybranska I, Polus A, Mikolajczyk M, Knapp
A, Sliwa A, Zapala B, Staszel T and Dembinska-Kiec A:
Apoptosis-related gene expression in glioblastoma (LN-18) and
medulloblastoma (Daoy) cell lines. Hum Cell. 26:137–148. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fiaschetti G, Castelletti D, Zoller S,
Schramm A, Schroeder C, Nagaishi M, Stearns D, Mittelbronn M,
Eggert A, Westermann F, et al: Bone morphogenetic protein-7 is a
MYC target with prosurvival functions in childhood medulloblastoma.
Oncogene. 30:2823–2835. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wiederschain D, Chen L, Johnson B, Bettano
K, Jackson D, Taraszka J, Wang YK, Jones MD, Morrissey M, Deeds J,
et al: Contribution of polycomb homologues Bmi-1 and Mel-18 to
medulloblastoma pathogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 27:4968–4979. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kong B, Yang T, Chen L, Kuang YQ, Gu JW,
Xia X, Cheng L and Zhang JH: Protein-protein interaction network
analysis and gene set enrichment analysis in epilepsy patients with
brain cancer. J Clin Neurosci. 21:316–319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Russell MD, Young AM and Karri SK:
Biomarkers of pediatric brain tumors. Front Pediatr. 1:72013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rustici G, Kolesnikov N, Brandizi M,
Burdett T, Dylag M, Emam I, Farne A, Hastings E, Ison J, Keays M,
et al: ArrayExpress update - trends in database growth and links to
data analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:D987–D990. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Glatt SJ, Everall IP, Kremen WS, Corbeil
J, Sásik R, Khanlou N, Han M, Liew CC and Tsuang MT: Comparative
gene expression analysis of blood and brain provides concurrent
validation of SELENBP1 up-regulation in schizophrenia. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:15533–15538. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tarnopolsky M, Phillips S, Parise G,
Varbanov A, Demuth J, Stevens P, Qu A, Wang F and Isfort R: Gene
expression, fiber type, and strength are similar between left and
right legs in older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
62:1088–1095. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Adler P, Kolde R, Kull M, Tkachenko A,
Peterson H, Reimand J and Vilo J: Mining for coexpression across
hundreds of datasets using novel rank aggregation and visualization
methods. Genome Biol. 10:R1392009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alvo M, Liu Z, Williams A and Yauk C:
Testing for mean and correlation changes in microarray experiments:
An application for pathway analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 11:602010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES, et al: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bauer S, Grossmann S, Vingron M and
Robinson PN: Ontologizer 20. - a multifunctional tool for GO term
enrichment analysis and data exploration. Bioinformatics.
24:1650–1651. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yen BL, Chien CC, Chen YC, Chen JT, Huang
JS, Lee FK and Huang HI: Placenta-derived multipotent cells
differentiate into neuronal and glial cells in vitro. Tissue Eng
Part A. 14:9–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Northcott PA, Dubuc AM, Pfister S and
Taylor MD: Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma. Expert Rev
Neurother. 12:871–884. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ramakrishnan NA, Drescher MJ and Drescher
DG: The SNARE complex in neuronal and sensory cells. Mol Cell
Neurosci. 50:58–69. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dubuc AM, Morrissy AS, Kloosterhof NK,
Northcott PA, Yu EP, Shih D, Peacock J, Grajkowska W, van Meter T,
Eberhart CG, et al: Subgroup-specific alternative splicing in
medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 123:485–499. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cefalo MG, De Ioris MA, Cacchione A, Longo
D, Staccioli S, Arcioni F, Bernardi B and Mastronuzzi A: Wernicke
encephalopathy in pediatric neuro-oncology: Presentation of 2 cases
and review of literature. J Child Neurol. 29:NP181–NP185. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Nygaard R and Kivivuori SM: Treatment for
recurrent medulloblastoma with intrathecal liposomal cytarabine and
systemic metronomic combination therapy. Anticancer Drugs.
23:342–346. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chen P, Fan Y, Man TK, Hung YS, Lau CC and
Wong ST: A gene signature based method for identifying subtypes and
subtype-specific drivers in cancer with an application to
medulloblastoma. BMC Bioinformatics. 14(Suppl 18): S12013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
He XM, Wikstrand CJ, Friedman HS, Bigner
SH, Pleasure S, Trojanowski JQ and Bigner DD: Differentiation
characteristics of newly established medulloblastoma cell lines
(D384 Med, D425 Med, and D458 Med) and their transplantable
xenografts. Lab Invest. 64:833–843. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schroeder K and Gururangan S: Molecular
variants and mutations in medulloblastoma. Pharmgenomics Pers Med.
7:43–51. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gudrunardottir T, Lannering B, Remke M,
Taylor MD, Wells EM, Keating RF and Packer RJ: Treatment
developments and the unfolding of the quality of life discussion in
childhood medulloblastoma: A review. Childs Nerv Syst. 30:979–990.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Duman JG and Forte JG: What is the role of
SNARE proteins in membrane fusion? Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
285:C237–C249. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hiersemenzel K, Brown ER and Duncan RR:
Imaging large cohorts of single ion channels and their activity.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 4:1142013.
|
|
35
|
Jiménez-Garduño AM, Mitkovski M,
Alexopoulos IK, Sánchez A, Stühmer W, Pardo LA and Ortega A: KV10.1
K(+)-channel plasma membrane discrete domain partitioning and its
functional correlation in neurons. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1838:921–931. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mohrmann R, de Wit H, Connell E, Pinheiro
PS, Leese C, Bruns D, Davletov B, Verhage M and Sørensen JB:
Synaptotagmin interaction with SNAP-25 governs vesicle docking,
priming, and fusion triggering. J Neurosci. 33:14417–14430. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Manca P, Mameli O, Caria MA,
Torrejón-Escribano B and Blasi J: Distribution of SNAP25, VAMP1 and
VAMP2 in mature and developing deep cerebellar nuclei after
estrogen administration. Neuroscience. 266:102–115. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ramakrishnan NA, Drescher MJ and Drescher
DG: Direct interaction of otoferlin with syntaxin 1A, SNAP-25, and
the L-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.3. J Biol Chem.
284:1364–1372. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Xu J, Luo F, Zhang Z, Xue L, Wu XS, Chiang
HC, Shin W and Wu LG: SNARE proteins synaptobrevin, SNAP-25, and
syntaxin are involved in rapid and slow endocytosis at synapses.
Cell Reports. 3:1414–1421. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Woodbury DJ and Rognlien K: The t-SNARE
syntaxin is sufficient for spontaneous fusion of synaptic vesicles
to planar membranes. Cell Biol Int. 24:809–818. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bühren J, Christoph AH, Buslei R, Albrecht
S, Wiestler OD and Pietsch T: Expression of the neurotrophin
receptor p75NTR in medulloblastomas is correlated with distinct
histological and clinical features: Evidence for a medulloblastoma
subtype derived from the external granule cell layer. J Neuropathol
Exp Neurol. 59:229–240. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Südhof TC and Rizo J: Synaptic vesicle
exocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 3:a0056372011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fatemi SH, Earle JA, Stary JM, Lee S and
Sedgewick J: Altered levels of the synaptosomal associated protein
SNAP-25 in hippocampus of subjects with mood disorders and
schizophrenia. Neuroreport. 12:3257–3262. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Thompson PM, Egbufoama S and Vawter MP:
SNAP-25 reduction in the hippocampus of patients with
schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry.
27:411–417. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
DeSouza RM, Jones BR, Lowis SP and Kurian
KM: Pediatric medulloblastoma - update on molecular classification
driving targeted therapies. Front Oncol. 4:1762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Selak S, Paternain AV, Aller MI, Picó E,
Rivera R and Lerma J: A role for SNAP25 in internalization of
kainate receptors and synaptic plasticity. Neuron. 63:357–371.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lesch KP and Schmitt A: Antidepressants
and gene expression profiling: How to SNARE novel drug targets.
Pharmacogenomics J. 2:346–348. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Hamdan FF, Piton A, Gauthier J, Lortie A,
Dubeau F, Dobrzeniecka S, Spiegelman D, Noreau A, Pellerin S, Côté
M, et al: De novo STXBP1 mutations in mental retardation and
nonsyndromic epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 65:748–753. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hussain S: Developing a PPI
inhibitor-based therapy for STXBP1 haploinsufficiency-associated
epileptic disorders. Front Mol Neurosci. 7:62014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Murmu RP, Li W, Holtmaat A and Li JY:
Dendritic spine instability leads to progressive neocortical spine
loss in a mouse model of Huntington's disease. J Neurosci.
33:12997–13009. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Northcott PA, Jones DT, Kool M, Robinson
GW, Gilbertson RJ, Cho YJ, Pomeroy SL, Korshunov A, Lichter P,
Taylor MD, et al: Medulloblastomics: The end of the beginning. Nat
Rev Cancer. 12:818–834. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Perreault S, Ramaswamy V, Achrol AS, Chao
K, Liu TT, Shih D, Remke M, Schubert S, Bouffet E, Fisher PG, et
al: MRI surrogates for molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma. AJNR
Am J Neuroradiol. 35:1263–1269. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sengupta R, Dubuc A, Ward S, Yang L,
Northcott P, Woerner BM, Kroll K, Luo J, Taylor MD, Wechsler-Reya
RJ, et al: CXCR4 activation defines a new subgroup of Sonic
hedgehog-driven medulloblastoma. Cancer Res. 72:122–132. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhang X, Cruz FD, Terry M, Remotti F and
Matushansky I: Terminal differentiation and loss of tumorigenicity
of human cancers via pluripotency-based reprogramming. Oncogene.
32:2249–2260. e1–21. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Snuderl M, Batista A, Kirkpatrick ND, Ruiz
de Almodovar C, Riedemann L, Walsh EC, Anolik R, Huang Y, Martin
JD, Kamoun W, et al: Targeting placental growth factor/neuropilin 1
pathway inhibits growth and spread of medulloblastoma. Cell.
152:1065–1076. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hodel A: Snap-25. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
30:1069–1073. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu J, Guo L, Jun-Wei L, Liu N and Li H:
All-trans retinoic acid modulates fas expression and enhances
chemosensitivity of human medulloblastoma cells. Int J Mol Med.
5:145–149. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ruggiero A, Conter V, Milani M, Biagi E,
Lazzareschi I, Sparano P and Riccardi R: Intrathecal chemotherapy
with antineoplastic agents in children. Paediatr Drugs. 3:237–246.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hudson TJ: Genome variation and
personalized cancer medicine. J Intern Med. 274:440–450. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sreenivasan Y, Sarkar A and Manna SK:
Mechanism of cytosine arabinoside-mediated apoptosis: Role of Rel A
(65) dephosphorylation. Oncogene. 22:4356–4369. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|