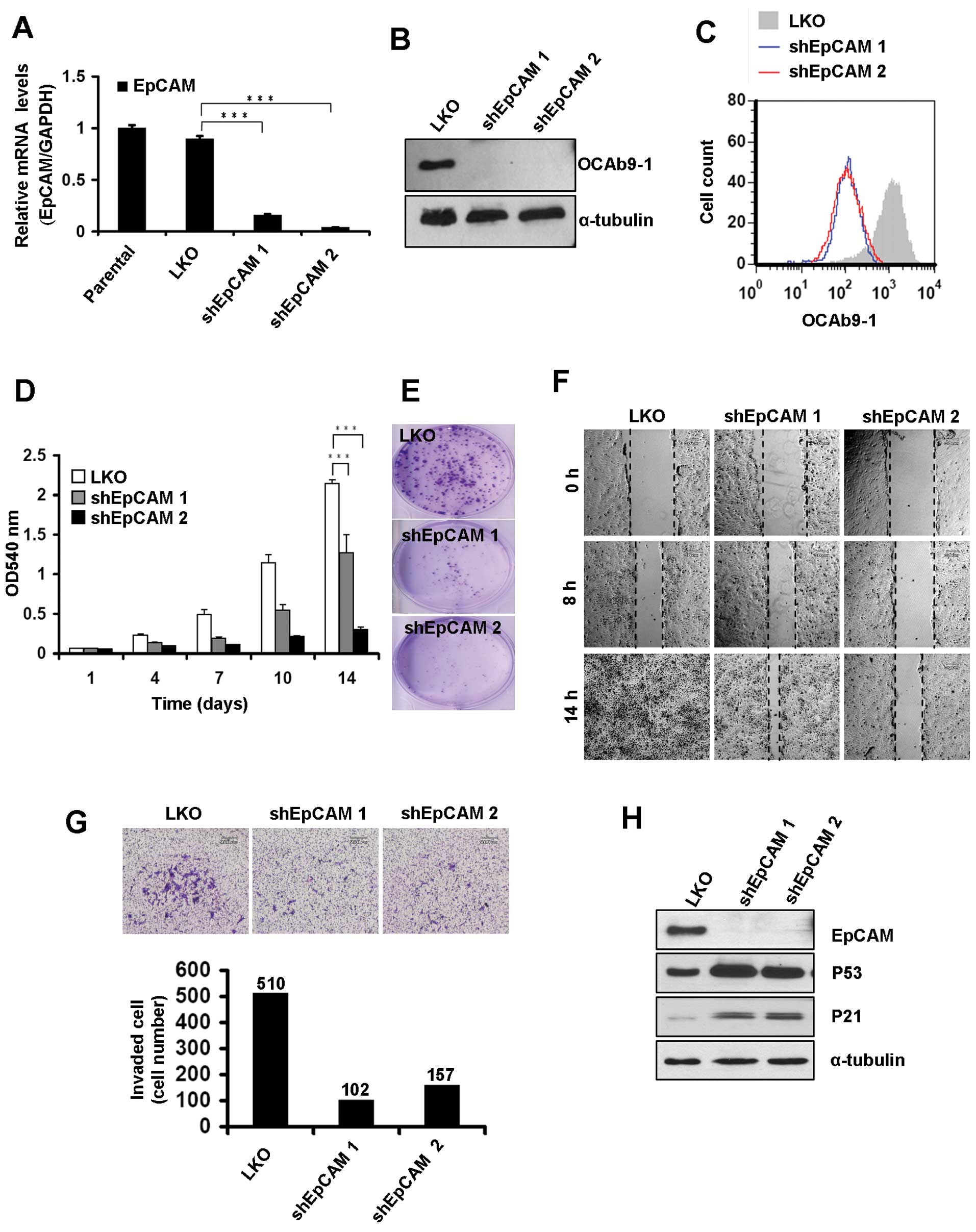
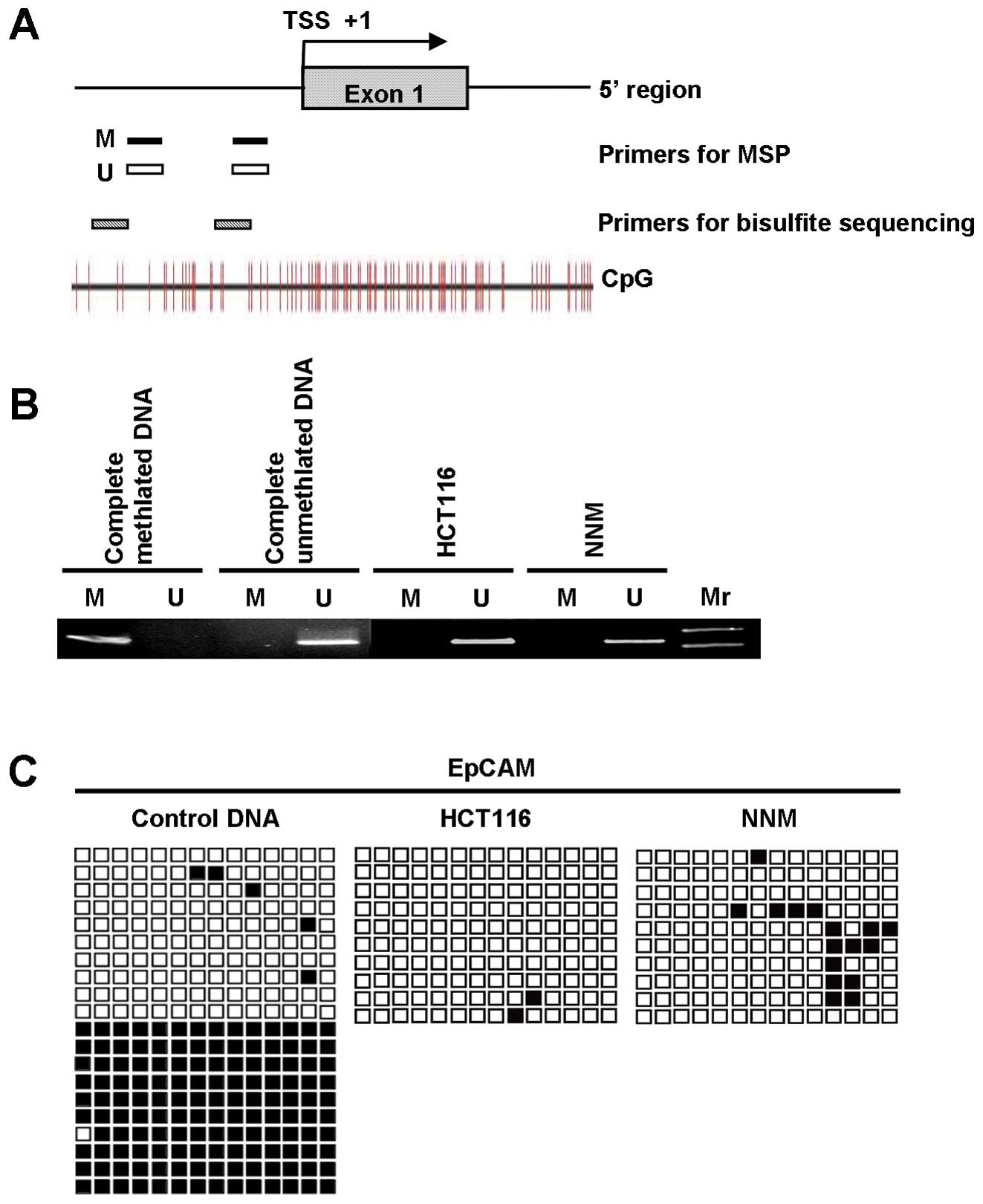
|
1
|
Peto J: Cancer epidemiology in the last
century and the next decade. Nature. 411:390–395. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van der Gun BT, Melchers LJ, Ruiters MH,
et al: EpCAM in carcinogenesis: the good, the bad or the ugly.
Carcinogenesis. 31:1913–1921. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved
questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:755–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Litvinov SV, Velders MP, Bakker HA, et al:
a human epithelial antigen is a homophilic cell-cell adhesion
molecule. J Cell Biol. 125:437–446. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Litvinov SV, Balzar M, Winter MJ, et al:
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (Ep-CAM) modulates cell-cell
interactions mediated by classic cadherins. J Cell Biol.
139:1337–1348. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Balzar M, Prins FA, Bakker HA, et al: The
structural analysis of adhesions mediated by Ep-CAM. Exp Cell Res.
246:108–121. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
de Boer CJ, van Krieken JH, Janssen-van
Rhijn CM, et al: Expression of Ep-CAM in normal, regenerating,
metaplastic, and neoplastic liver. J Pathol. 188:201–206. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Litvinov SV, van Driel W, van Rhijn CM, et
al: Expression of Ep-CAM in cervical squamous epithelia correlates
with an increased proliferation and the disappearance of markers
for terminal differentiation. Am J Pathol. 148:865–875.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maetzel D, Denzel S, Mack B, et al:
Nuclear signalling by tumour-associated antigen EpCAM. Nat Cell
Biol. 11:162–171. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
et al: Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dalerba P, Dylla SJ, Park IK, et al:
Phenotypic characterization of human colorectal cancer stem cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:10158–10163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schmelzer E, Wauthier E and Reid LM: The
phenotypes of pluripotent human hepatic progenitors. Stem Cells.
24:1852–1858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dan YY, Riehle KJ, Lazaro C, et al:
Isolation of multipotent progenitor cells from human fetal liver
capable of differentiating into liver and mesenchymal lineages.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:9912–9917. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schmelzer E, Zhang L, Bruce A, et al:
Human hepatic stem cells from fetal and postnatal donors. J Exp
Med. 204:1973–1987. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Anderson R, Schaible K, Heasman J, et al:
Expression of the homophilic adhesion molecule, Ep-CAM, in the
mammalian germ line. J Reprod Fertil. 116:379–384. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Stingl J, Raouf A, Emerman JT, et al:
Epithelial progenitors in the normal human mammary gland. J Mammary
Gland Biol Neoplasia. 10:49–59. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moldenhauer G, Salnikov AV, Luttgau S, et
al: Therapeutic potential of amanitin-conjugated anti-epithelial
cell adhesion molecule monoclonal antibody against pancreatic
carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 104:622–634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Simon M, Stefan N, Pluckthun A, et al:
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule-targeted drug delivery for cancer
therapy. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 10:451–468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Punt CJ, Nagy A, Douillard JY, et al:
Edrecolomab alone or in combination with fluorouracil and folinic
acid in the adjuvant treatment of stage III colon cancer: a
randomised study. Lancet. 360:671–677. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schmidt M, Scheulen ME, Dittrich C, et al:
An open-label, randomized phase II study of adecatumumab, a fully
human anti-EpCAM antibody, as monotherapy in patients with
metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 21:275–282. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Went P, Vasei M, Bubendorf L, et al:
Frequent high-level expression of the immunotherapeutic target
Ep-CAM in colon, stomach, prostate and lung cancers. Br J Cancer.
94:128–135. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
MacDonald GC, Rasamoelisolo M, Entwistle
J, et al: A phase I clinical study of VB4-845: weekly intratumoral
administration of an anti-EpCAM recombinant fusion protein in
patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Drug
Des Devel Ther. 2:105–114. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Migliore L, Migheli F, Spisni R, et al:
Genetics, cytogenetics, and epigenetics of colorectal cancer. J
Biomed Biotechnol. 2011:7923622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Coppede F: Epigenetic biomarkers of
colorectal cancer: focus on DNA methylation. Cancer Lett.
342:238–247. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tai KY, Shiah SG, Shieh YS, et al: DNA
methylation and histone modification regulate silencing of
epithelial cell adhesion molecule for tumor invasion and
progression. Oncogene. 26:3989–3997. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Spizzo G, Gastl G, Obrist P, et al:
Methylation status of the Ep-CAM promoter region in human breast
cancer cell lines and breast cancer tissue. Cancer Lett.
246:253–261. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yu G, Zhang X, Wang H, et al: CpG island
methylation status in the EpCAM promoter region and gene
expression. Oncol Rep. 20:1061–1067. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shiah SG, Chang LC, Tai KY, et al: The
involvement of promoter methylation and DNA methyltransferase-1 in
the regulation of EpCAM expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Oral Oncol. 45:e1–8. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
van der Gun BT, Wasserkort R, Monami A, et
al: Persistent downregulation of the pancarcinoma-associated
epithelial cell adhesion molecule via active intranuclear
methylation. Int J Cancer. 123:484–489. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Heyn H and Esteller M: DNA methylation
profiling in the clinic: applications and challenges. Nat Rev
Genet. 13:679–692. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lin CT, Chan WY, Chen W, et al:
Characterization of seven newly established nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cell lines. Lab Invest. 68:716–727. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oefinger PE, Bronson DL and Dreesman GR:
Induction of hepatitis B surface antigen in human hepatoma-derived
cell lines. J Gen Virol. 53:105–113. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lo A, Lin CT and Wu HC: Hepatocellular
carcinoma cell-specific peptide ligand for targeted drug delivery.
Mol Cancer Ther. 7:579–589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee TY, Wu HC, Tseng YL, et al: A novel
peptide specifically binding to nasopharyngeal carcinoma for
targeted drug delivery. Cancer Res. 64:8002–8008. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kohler G and Milstein C: Continuous
cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined
specificity. Nature. 256:495–497. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu IJ, Chiu CY, Chen YC, et al: Molecular
mimicry of human endothelial cell antigen by autoantibodies to
nonstructural protein 1 of dengue virus. J Biol Chem.
286:9726–9736. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tung KH, Lin CW, Kuo CC, et al: CHC
promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis through regulation of
HIF-1alpha and VEGF signaling. Cancer Lett. 331:58–67. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Spizzo G, Went P, Dirnhofer S, et al: High
Ep-CAM expression is associated with poor prognosis in
node-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 86:207–213.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lu TY, Kao CF, Lin CT, et al: DNA
methylation and histone modification regulate silencing of OPG
during tumor progression. J Cell Biochem. 108:315–325. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Huang HP, Chen PH, Yu CY, et al:
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) complex proteins promote
transcription factor-mediated pluripotency reprogramming. J Biol
Chem. 286:33520–33532. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Esteller M: Epigenetics in cancer. N Engl
J Med. 358:1148–1159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bernstein BE, Kamal M, Lindblad-Toh K, et
al: Genomic maps and comparative analysis of histone modifications
in human and mouse. Cell. 120:169–181. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, et al:
High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human
genome. Cell. 129:823–837. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mutskov V and Felsenfeld G: Silencing of
transgene transcription precedes methylation of promoter DNA and
histone H3 lysine 9. EMBO J. 23:138–149. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Munz M, Baeuerle PA and Gires O: The
emerging role of EpCAM in cancer and stem cell signaling. Cancer
Res. 69:5627–5629. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gires O, Klein CA and Baeuerle PA: On the
abundance of EpCAM on cancer stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:143author reply 143. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Saltz LB, Cox JV, Blanke C, et al:
Irinotecan plus fluorouracil and leucovorin for metastatic
colorectal cancer. Irinotecan Study Group. N Engl J Med.
343:905–914. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fields AL, Keller A, Schwartzberg L, et
al: Adjuvant therapy with the monoclonal antibody Edrecolomab plus
fluorouracil-based therapy does not improve overall survival of
patients with stage III colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:1941–1947.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
de Bono JS, Tolcher AW, Forero A, et al:
ING-1, a monoclonal antibody targeting Ep-CAM in patients with
advanced adenocarcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 10:7555–7565. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Goel S, Bauer RJ, Desai K, et al:
Pharmacokinetic and safety study of subcutaneously administered
weekly ING-1, a human engineere monoclonal antibody targeting human
EpCAM, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Ann Oncol.
18:1704–1707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lin CW, Liao MY, Lin WW, et al: Epithelial
cell adhesion molecule regulates tumor initiation and tumorigenesis
via activating reprogramming factors and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition gene expression in colon cancer. J Biol Chem.
287:39449–39459. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Schuettengruber B, Chourrout D, Vervoort
M, et al: Genome regulation by polycomb and trithorax proteins.
Cell. 128:735–745. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Schwartz YB and Pirrotta V: Polycomb
silencing mechanisms and the management of genomic programmes. Nat
Rev Genet. 8:9–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Cao R and Zhang Y: SUZ12 is required for
both the histone methyltransferase activity and the silencing
function of the EED-EZH2 complex. Mol Cell. 15:57–67. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Pasini D, Bracken AP, Jensen MR, et al:
Suz12 is essential for mouse development and for EZH2 histone
methyltransferase activity. EMBO J. 23:4061–4071. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Swigut T and Wysocka J: H3K27
demethylases, at long last. Cell. 131:29–32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Agger K, Cloos PA, Christensen J, et al:
UTX and JMJD3 are histone H3K27 demethylases involved in HOX gene
regulation and development. Nature. 449:731–734. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Boyer LA, Plath K, Zeitlinger J, et al:
Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine
embryonic stem cells. Nature. 441:349–353. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|