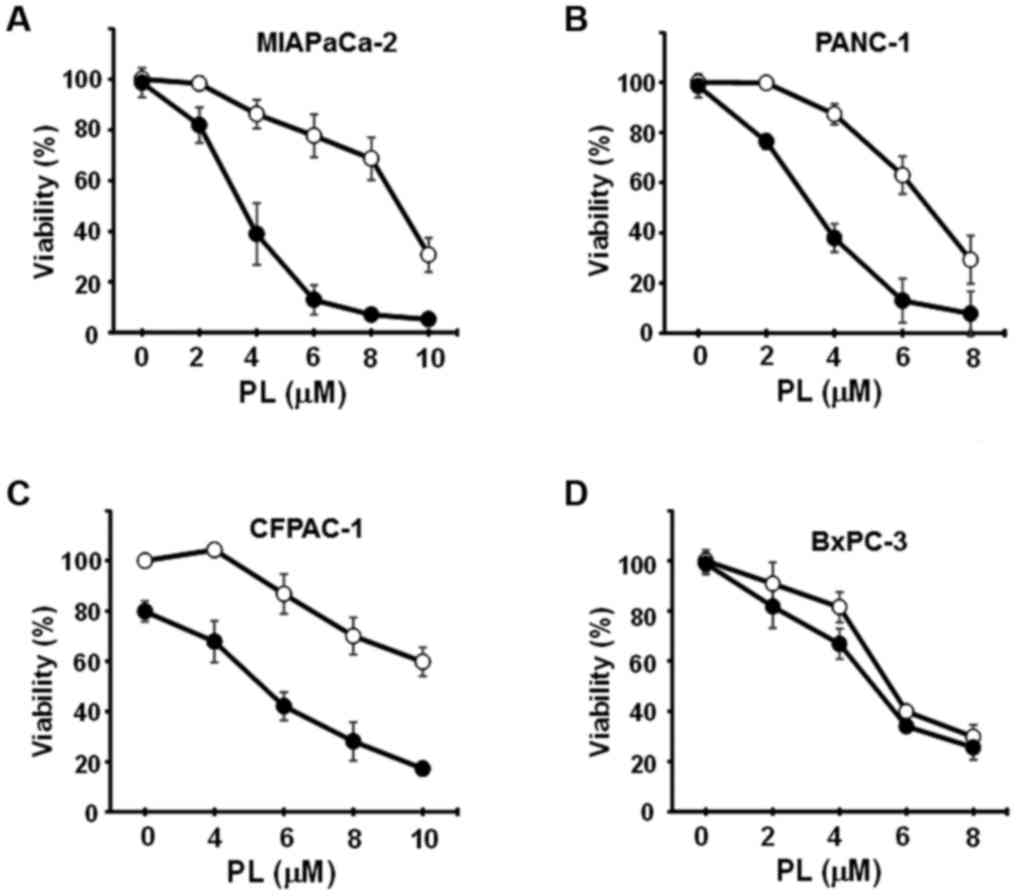
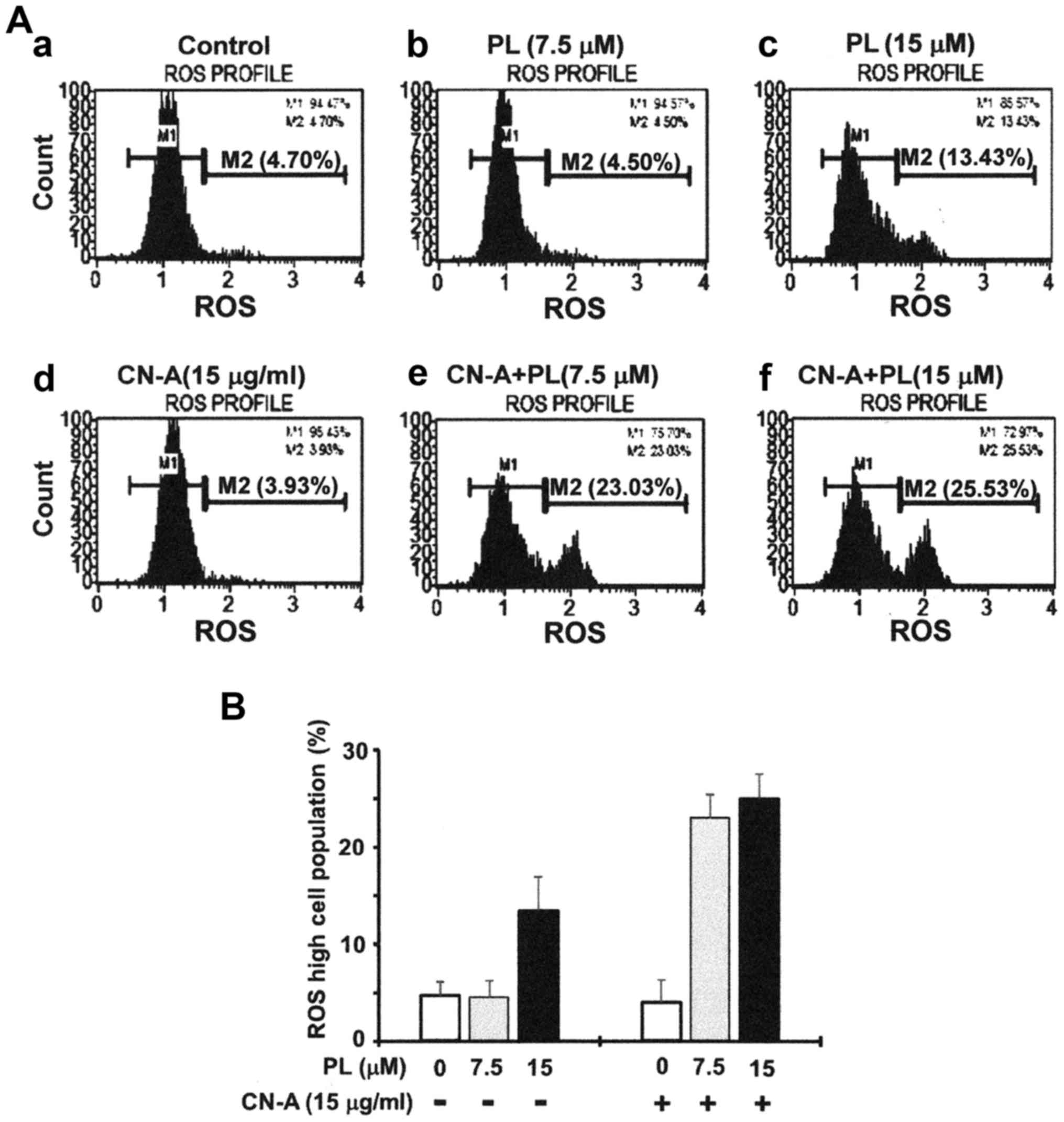
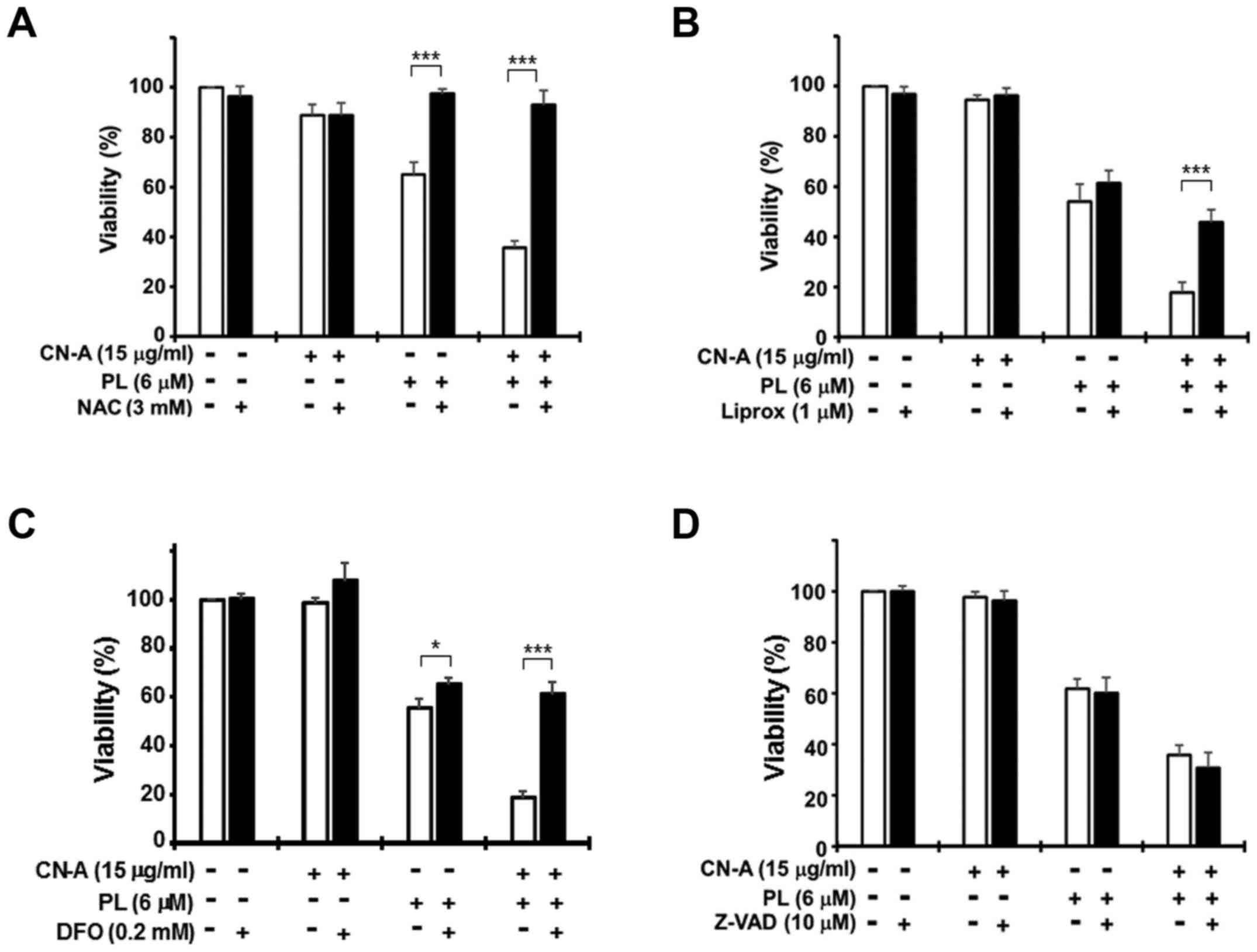
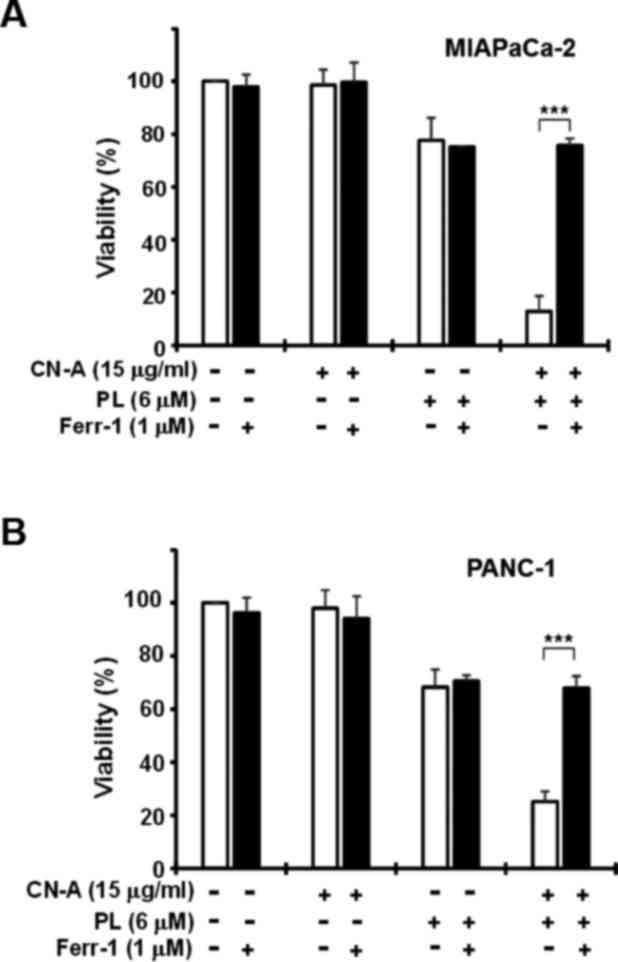
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Han X, Saiyin H, Zhao J, Fang Y, Rong Y,
Shi C, Lou W and Kuang T: Overexpression of miR-135b-5p promotes
unfavorable clinical characteristics and poor prognosis via the
repression of SFRP4 in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget.
8:62195–62207. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burris HA III, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green
MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo
AM, Tarassoff P, et al: Improvements in survival and clinical
benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with
advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J Clin Oncol.
15:2403–2413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O,
Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de
la Fouchardière C, et al Groupe Tumeurs Digestives of Unicancer;
PRODIGE Intergroup: FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic
pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 364:1817–1825. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kroep JR, Pinedo HM, van Groeningen CJ and
Peters GJ: Experimental drugs and drug combinations in pancreatic
cancer. Ann Oncol. 10(Suppl 4): 234–238. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jakstaite A, Maziukiene A, Silkuniene G,
Kmieliute K, Gulbinas A and Dambrauskas Z: HuR mediated
post-transcriptional regulation as a new potential adjuvant
therapeutic target in chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:13004–13019. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhong S, Qie S, Yang L, Yan Q, Ge L and
Wang Z: S-1 mono-therapy versus S-1 combination therapy in
gemcitabine-refractory advanced pancreatic cancer. A meta-analysis
(PRISMA) of randomized control trial Medicine (Baltimore).
96:e76112017.
|
|
9
|
Shaw AT, Winslow MM, Magendantz M, Ouyang
C, Dowdle J, Subramanian A, Lewis TA, Maglathin RL, Tolliday N and
Jacks T: Selective killing of K-ras mutant cancer cells by small
molecule inducers of oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:8773–8778. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hezel AF, Kimmelman AC, Stanger BZ,
Bardeesy N and Depinho RA: Genetics and biology of pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev. 20:1218–1249. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Honma Y, Ishii Y, Yamamoto-Yamaguchi Y,
Sassa T and Asahi K: Cotylenin A, a differentiation-inducing agent,
and IFN-alpha cooperatively induce apoptosis and have an antitumor
effect on human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells in nude mice.
Cancer Res. 63:3659–3666. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kasukabe T, Okabe-Kado J, Kato N, Sassa T
and Honma Y: Effects of combined treatment with rapamycin and
cotylenin A, a novel differentiation-inducing agent, on human
breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells and xenografts. Breast Cancer Res.
7:R1097–R1110. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kasukabe T, Okabe-Kado J, Kato N, Honma Y
and Kumakura S: Cotylenin A and arsenic trioxide cooperatively
suppress cell proliferation and cell invasion activity in human
breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 46:841–848. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang WS and Stockwell BR: Synthetic lethal
screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent,
nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells.
Chem Biol. 15:234–245. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang WS and Stockwell BR: Ferroptosis:
Death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 26:165–176. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Latunde-Dada GO: Ferroptosis: Role of
lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1861:1893–1900. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiao D, Powolny AA, Moura MB, Kelley EE,
Bommareddy A, Kim SH, Hahm ER, Normolle D, Van Houten B and Singh
SV: Phenethyl isothiocyanate inhibits oxidative phosphorylation to
trigger reactive oxygen species-mediated death of human prostate
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 285:26558–26569. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hong Y-H, Uddin MH, Jo U, Kim B, Song J,
Suh DH, Kim HS and Song YS: ROS accumulation by PEITC selectively
kills ovarian cancer cells via UPR-mediated apoptosis. Front Oncol.
5:1672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kasukabe T, Honma Y, Okabe-Kado J, Higuchi
Y, Kato N and Kumakura S: Combined treatment with cotylenin A and
phenethyl isothiocyanate induces strong antitumor activity mainly
through the induction of ferroptotic cell death in human pancreatic
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 36:968–976. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Raj L, Ide T, Gurkar AU, Foley M, Schenone
M, Li X, Tolliday NJ, Golub TR, Carr SA, Shamji AF, et al:
Selective killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targeting the
stress response to ROS. Nature. 475:231–234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dhillon H, Mamidi S, McClean P and Reindl
KM: Transcriptome analysis of piperlongumine-treated human
pancreatic cancer cells reveals involvement of oxidative stress and
endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways. J Med Food. 19:578–585.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jin HO, Park JA, Kim HA, Chang YH, Hong
YJ, Park IC and Lee JK: Piperlongumine downregulates the expression
of HER family in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
486:1083–1089. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Alpay M, Yurdakok-Dikmen B, Kismali G and
Sel T: Antileukemic effects of piperlongumine and alpha lipoic acid
combination on Jurkat, MEC1 and NB4 cells in vitro. J Cancer Res
Ther. 12:556–560. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Harshbarger W, Gondi S, Ficarro SB, Hunter
J, Udayakumar D, Gurbani D, Singer WD, Liu Y, Li L, Marto JA, et
al: Structural and biochemical analyses reveal the mechanism of
glutathione S-transferase pi 1 inhibition by the anti-cancer
compound piperlongumine. J Biol Chem. 292:112–120. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Chen SY, Liu GH, Chao WY, Shi CS, Lin CY,
Lim YP, Lu CH, Lai PY, Chen HR and Lee YR: Piperlongumine
suppresses proliferation of human oral squamous cell carcinoma
through cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and senescence. Int J Mol Sci.
17:6162016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Wang JW, Xiao X, Shan Y, Xue B,
Jiang G, He Q, Chen J, Xu HG, Zhao RX, et al: Piperlongumine
induces autophagy by targeting p38 signaling. Cell Death Dis.
4:e8242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu QR, Liu JM, Chen Y, Xie XQ, Xiong XX,
Qiu XY, Pan F, Liu D, Yu SB and Chen XQ: Piperlongumine inhibits
migration of glioblastoma cells via activation of ROS-dependent p38
and JNK signaling pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:6537322014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Y, Liu JM, Xiong XX, Qiu XY, Pan F,
Liu D, Lan SJ, Jin S, Yu SB and Chen XQ: Piperlongumine selectively
kills hepatocellular carcinoma cells and preferentially inhibits
their invasion via ROS-ER-MAPKs-CHOP. Oncotarget. 6:6406–6421.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun
X, Kang R and Tang D: Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death
Differ. 23:369–379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sassa T, Tojyo T and Munakata K: Isolation
of a new plant growth substance with cytokinin-like activity.
Nature. 227:3791970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, Wang S-J, Su T,
Hibshoosh H, Baer R and Gu W: Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated
activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 520:57–62. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hangauer MJ, Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Bole
D, Eaton JK, Matov A, Galeas J, Dhruv HD, Berens ME, Schreiber SL,
et al: Drug-tolerant persister cancer cells are vulnerable to GPX4
inhibition. Nature. 551:247–250. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ma S, Henson ES, Chen Y and Gibson SB:
Ferroptosis is induced following siramesine and lapatinib treatment
of breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 7:e23072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zou P, Xia Y, Ji J, Chen W, Zhang J, Chen
X, Rajamanickam V, Chen G, Wang Z, Chen L, et al: Piperlongumine as
a direct TrxR1 inhibitor with suppressive activity against gastric
cancer. Cancer Lett. 375:114–126. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Y, Wu X, Zhou Y, Jiang H, Pan S and
Sun B: Piperlongumine suppresses growth and sensitizes pancreatic
tumors to gemcitabine in a xenograft mouse model by modulating the
NF-kappa B pathway. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 9:234–244. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kwon MY, Park E, Lee SJ and Chung SW: Heme
oxygenase-1 accelerates erastin-induced ferroptotic cell death.
Oncotarget. 6:24393–24403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee HN, Jin HO, Park JA, Kim JH, Kim JY,
Kim B, Kim W, Hong SE, Lee YH, Chang YH, et al: Heme oxygenase-1
determines the differential response of breast cancer and normal
cells to piperlongumine. Mol Cells. 38:327–335. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kawakami K, Hattori M, Inoue T, Maruyama
Y, Ohkanda J, Kato N, Tongu M, Yamada T, Akimoto M, Takenaga K, et
al: A novel fusicoccin derivative preferentially targets hypoxic
tumor cells and inhibits tumor growth in xenografts. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 12:791–800. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kasukabe T, Okabe-Kado J, Haranosono Y,
Kato N and Honma Y: Inhibition of rapamycin-induced Akt
phosphorylation by cotylenin A correlates with their synergistic
growth inhibition of cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 42:767–775. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Miyake T, Honma Y, Urano T, Kato N and
Suzumiya J: Combined treatment with tamoxifen and a fusicoccin
derivative (ISIR-042) to overcome resistance to therapy and to
enhance the antitumor activity of 5-fluorouracil and gemcitabine in
pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 47:315–324. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Dhruv HD, Gill S,
Eichhoff OM, Seashore-Ludlow B, Kaffenberger SD, Eaton JK, Shimada
K, Aguirre AJ, et al: Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of
cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway. Nature. 547:453–457.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|